#Dataset Creation Company
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Haivo.AI: Your Premier Dataset Creation Company for Machine Learning and AI
At Haivo.AI, we specialize in crafting high-quality datasets tailored for machine learning and artificial intelligence. Our expert team excels in data collection, data validation, and curation, ensuring your AI projects thrive. Partner with us for precise and reliable dataset creation services. Transform your data into insights with Haivo. AI.

0 notes
Text
How LLM Unlearning Is Shaping the Future of AI Privacy
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/how-llm-unlearning-is-shaping-the-future-of-ai-privacy/
How LLM Unlearning Is Shaping the Future of AI Privacy
The rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs) has brought about significant advancements in artificial intelligence (AI). From automating content creation to providing support in healthcare, law, and finance, LLMs are reshaping industries with their capacity to understand and generate human-like text. However, as these models expand in use, so do concerns over privacy and data security. LLMs are trained on large datasets that contain personal and sensitive information. They can reproduce this data if prompted in the right way. This possibility of misuse raises important questions about how these models handle privacy. One emerging solution to address these concerns is LLM unlearning—a process that allows models to forget specific pieces of information without compromising their overall performance. This approach is gaining popularity as a vital step in protecting the privacy of LLMs while promoting their ongoing development. In this article, we examine how unlearning could reshape LLMs’ privacy and facilitate their broader adoption.
Understanding LLM Unlearning
LLM unlearning is essentially the reverse of training. When an LLM is trained on vast datasets, it learns patterns, facts, and linguistic nuances from the information it is exposed to. While the training enhances its capabilities, the model may inadvertently memorize sensitive or personal data, such as names, addresses, or financial details, especially when training on publicly available datasets. When queried in the right context, LLMs can unknowingly regenerate or expose this private information.
Unlearning refers to the process where a model forgets specific information, ensuring that it no longer retains knowledge of such information. While it may seem like a simple concept, its implementation presents significant challenges. Unlike human brains, which can naturally forget information over time, LLMs don’t have a built-in mechanism for selective forgetting. The knowledge in an LLM is distributed across millions or billions of parameters, making it challenging to identify and remove specific pieces of information without affecting the model’s broader capabilities. Some of the key challenges of LLM unlearning are as follows:
Identifying Specific Data to Forget: One of the primary difficulties lies in identifying exactly what needs to be forgotten. LLMs are not explicitly aware of where a piece of data comes from or how it influences model’s understanding. For example, when a model memorizes someone’s personal information, pinpointing where and how that information is embedded within its complex structure becomes challenging.
Ensuring Accuracy Post-Unlearning: Another major concern is that the unlearning process should not degrade the model’s overall performance. Removing specific pieces of knowledge could lead to a degradation in the model’s linguistic capabilities or even create blind spots in certain areas of understanding. Finding the right balance between effective unlearning and maintaining performance is a challenging task.
Efficient Processing: Retraining a model from scratch every time a piece of data needs to be forgotten would be inefficient and costly. LLM unlearning requires incremental methods that allow the model to update itself without undergoing a full retraining cycle. This necessitates the development of more advanced algorithms that can handle targeted forgetting without significant resource consumption.
Techniques for LLM Unlearning
Several strategies are emerging to address the technical complexities of unlearning. Some of the prominent techniques are as follows:
Data Sharding and Isolation: This technique involves breaking data down into smaller chunks or sections. By isolating sensitive information within these separate pieces, developers can more easily remove specific data without affecting the rest of the model. This approach enables targeted modifications or deletions of relevant portions, enhancing the efficiency of the unlearning process.
Gradient Reversal Techniques: In certain instances, gradient reversal algorithms are employed to alter the learned patterns linked to specific data. This method effectively reverses the learning process for the targeted information, allowing the model to forget it while preserving its general knowledge.
Knowledge Distillation: This technique involves training a smaller model to replicate the knowledge of a larger model while excluding any sensitive data. The distilled model can then replace the original LLM, ensuring that privacy is maintained without the necessity for full model retraining.
Continual Learning Systems: These techniques are employed to continuously update and unlearn information as new data is introduced or old data is eliminated. By applying techniques like regularization and parameter pruning, continual learning systems can help make unlearning more scalable and manageable in real-time AI applications.
Why LLM Unlearning Matters for Privacy
As LLMs are increasingly deployed in sensitive fields such as healthcare, legal services, and customer support, the risk of exposing private information becomes a significant concern. While traditional data protection methods like encryption and anonymization provide some level of security, they are not always foolproof for large-scale AI models. This is where unlearning becomes essential.
LLM unlearning addresses privacy issues by ensuring that personal or confidential data can be removed from a model’s memory. Once sensitive information is identified, it can be erased without the need to retrain the entire model from scratch. This capability is especially pertinent in light of regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which grants individuals the right to have their data deleted upon request, often referred to as the “right to be forgotten.”
For LLMs, complying with such regulations presents both a technical and ethical challenge. Without effective unlearning mechanisms, it would be impossible to eliminate specific data that an AI model has memorized during its training. In this context, LLM unlearning offers a pathway to meet privacy standards in a dynamic environment where data must be both utilized and protected.
The Ethical Implications of LLM Unlearning
As unlearning becomes more technically viable, it also brings forth important ethical considerations. One key question is: who determines which data should be unlearned? In some instances, individuals may request the removal of their data, while in others, organizations might seek to unlearn certain information to prevent bias or ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
Additionally, there is a risk of unlearning being misused. For example, if companies selectively forget inconvenient truths or crucial facts to evade legal responsibilities, this could significantly undermine trust in AI systems. Ensuring that unlearning is applied ethically and transparently is just as critical as addressing the associated technical challenges.
Accountability is another pressing concern. If a model forgets specific information, who bears responsibility if it fails to meet regulatory requirements or makes decisions based on incomplete data? These issues underscore the necessity for robust frameworks surrounding AI governance and data management as unlearning technologies continue to advance.
The Future of AI Privacy and Unlearning
LLM unlearning is still an emerging field, but it holds enormous potential for shaping the future of AI privacy. As regulations around data protection become stricter and AI applications become more widespread, the ability to forget will be just as important as the ability to learn.
In the future, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of unlearning technologies, especially in industries dealing with sensitive information like healthcare, finance, and law. Moreover, advancements in unlearning will likely drive the development of new privacy-preserving AI models that are both powerful and compliant with global privacy standards.
At the heart of this evolution is the recognition that AI’s promise must be balanced with ethical and responsible practices. LLM unlearning is a critical step toward ensuring that AI systems respect individual privacy while continuing to drive innovation in an increasingly interconnected world.
The Bottom Line
LLM unlearning represents a critical shift in how we think about AI privacy. By enabling models to forget sensitive information, we can address growing concerns over data security and privacy in AI systems. While the technical and ethical challenges are significant, the advancements in this area are paving the way for more responsible AI deployments that can safeguard personal data without compromising the power and utility of large language models.
#adoption#ai#AI compliance with GDPR#ai model#AI models#ai privacy#AI systems#Algorithms#applications#approach#Article#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#bears#Bias#brains#challenge#Companies#compliance#content#content creation#cybersecurity#data#Data Management#data protection#data security#Data security in AI#datasets#details#developers
0 notes
Note
How exactly do you advance AI ethically? Considering how much of the data sets that these tools use was sourced, wouldnt you have to start from scratch?
a: i don't agree with the assertion that "using someone else's images to train an ai" is inherently unethical - ai art is demonstrably "less copy-paste-y" for lack of a better word than collage, and nobody would argue that collage is illegal or ethically shady. i mean some people might but i don't think they're correct.
b: several people have done this alraedy - see, mitsua diffusion, et al.
c: this whole argument is a red herring. it is not long-term relevant adobe firefly is already built exclusively off images they have legal rights to. the dataset question is irrelevant to ethical ai use, because companies already have huge vaults full of media they can train on and do so effectively.
you can cheer all you want that the artist-job-eating-machine made by adobe or disney is ethically sourced, thank god! but it'll still eat everyone's jobs. that's what you need to be caring about.
the solution here obviously is unionization, fighting for increased labor rights for people who stand to be affected by ai (as the writer's guild demonstrated! they did it exactly right!), and fighting for UBI so that we can eventually decouple the act of creation from the act of survival at a fundamental level (so i can stop getting these sorts of dms).
if you're interested in actually advancing ai as a field and not devils advocating me you can also participate in the FOSS (free-and-open-source) ecosystem so that adobe and disney and openai can't develop a monopoly on black-box proprietary technology, and we can have a future where anyone can create any images they want, on their computer, for free, anywhere, instead of behind a paywall they can't control.
fun fact related to that last bit: remember when getty images sued stable diffusion and everybody cheered? yeah anyway they're releasing their own ai generator now. crazy how literally no large company has your interests in mind.
cheers
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Some thoughts on Cara
So some of you may have heard about Cara, the new platform that a lot of artists are trying out. It's been around for a while, but there's been a recent huge surge of new users, myself among them. Thought I'd type up a lil thing on my initial thoughts.
First, what is Cara?
From their About Cara page:
Cara is a social media and portfolio platform for artists. With the widespread use of generative AI, we decided to build a place that filters out generative AI images so that people who want to find authentic creatives and artwork can do so easily. Many platforms currently accept AI art when it’s not ethical, while others have promised “no AI forever” policies without consideration for the scenario where adoption of such technologies may happen at the workplace in the coming years. The future of creative industries requires nuanced understanding and support to help artists and companies connect and work together. We want to bridge the gap and build a platform that we would enjoy using as creatives ourselves. Our stance on AI: ・We do not agree with generative AI tools in their current unethical form, and we won’t host AI-generated portfolios unless the rampant ethical and data privacy issues around datasets are resolved via regulation. ・In the event that legislation is passed to clearly protect artists, we believe that AI-generated content should always be clearly labeled, because the public should always be able to search for human-made art and media easily.
Should note that Cara is independently funded, and is made by a core group of artists and engineers and is even collaborating with the Glaze project. It's very much a platform by artists, for artists!
Should also mention that in being a platform for artists, it's more a gallery first, with social media functionalities on the side. The info below will hopefully explain how that works.
Next, my actual initial thoughts using it, and things that set it apart from other platforms I've used:
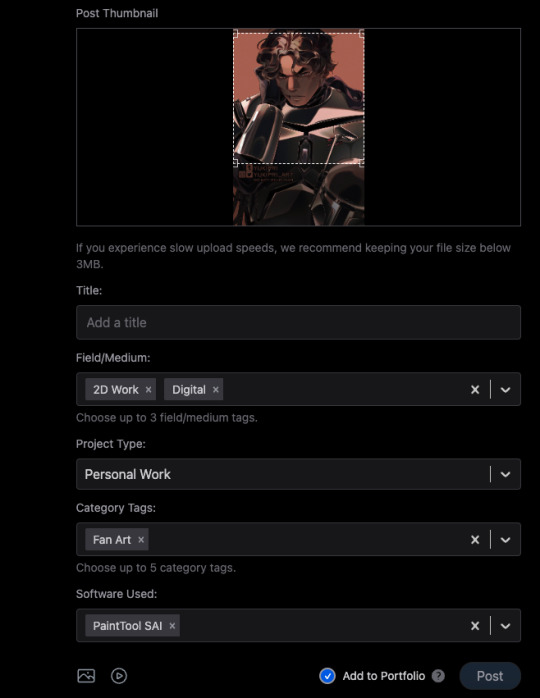
1) When you post, you can choose to check the portfolio option, or to NOT check it. This is fantastic because it means I can have just my art organized in my gallery, but I can still post random stuff like photos of my cats and it won't clutter things. You can also just ramble/text post and it won't affect the gallery view!
2) You can adjust your crop preview for your images. Such a simple thing, yet so darn nice.
3) When you check that "Add to portfolio," you get a bunch of additional optional fields: Title, Field/Medium, Project Type, Category Tags, and Software Used. It's nice that you can put all this info into organized fields that don't take up text space.
4) Speaking of text, 5000 character limit is niiiiice. If you want to talk, you can.
5) Two separate feeds, a "For You" algorithmic one, and "Following." The "Following" actually appears to be full chronological timeline of just folks you follow (like Tumblr). Amazing.
6) Now usually, "For You" being set to home/default kinda pisses me off because generally I like curating my own experience, but not here, for this handy reason: if you tap the gear symbol, you can ADJUST your algorithm feed!
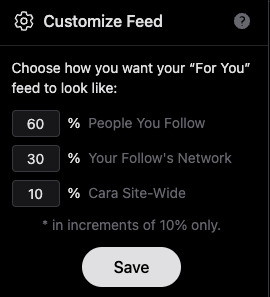
So you can choose what you see still!!! AMAZING. And, again, you still have your Following timeline too.
7) To repeat the stuff at the top of this post, its creation and intent as a place by artists, for artists. Hopefully you can also see from the points above that it's been designed with artists in mind.
8) No GenAI images!!!! There's a pop up that says it's not allowed, and apparently there's some sort of detector thing too. Not sure how reliable the latter is, but so far, it's just been a breath of fresh air, being able to scroll and see human art art and art!
To be clear, Cara's not perfect and is currently pretty laggy, and you can get errors while posting (so far, I've had more success on desktop than the mobile app), but that's understandable, given the small team. They'll need time to scale. For me though, it's a fair tradeoff for a platform that actually cares about artists.
Currently it also doesn't allow NSFW, not sure if that'll change given app store rules.
As mentioned above, they're independently funded, which means the team is currently paying for Cara itself. They have a kofi set up for folks who want to chip in, but it's optional. Here's the link to the tweet from one of the founders:
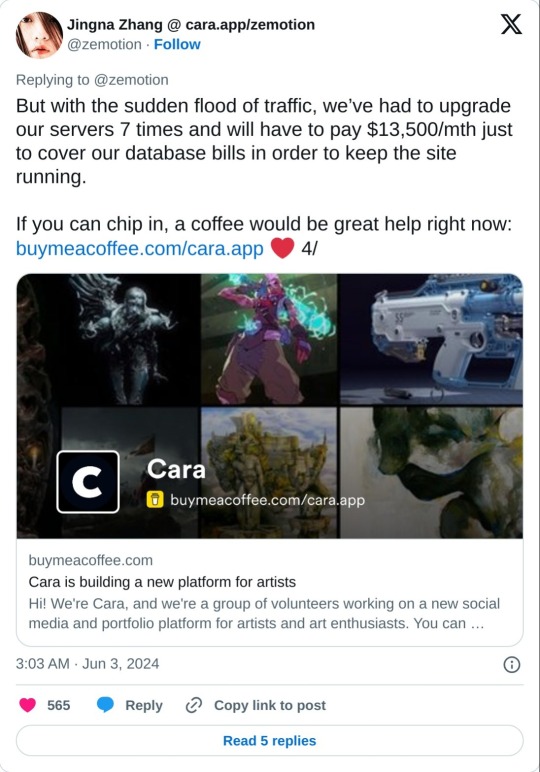
And a reminder that no matter that the platform itself isn't selling our data to GenAI, it can still be scraped by third parties. Protect your work with Glaze and Nightshade!
Anyway, I'm still figuring stuff out and have only been on Cara a few days, but I feel hopeful, and I think they're off to a good start.
I hope this post has been informative!
Lastly, here's my own Cara if you want to come say hi! Not sure at all if I'll be active on there, but if you're an artist like me who is keeping an eye out for hopefully nice communities, check it out!
#YukiPri rambles#cara#cara app#social media#artists on tumblr#review#longpost#long post#mostly i'd already typed this up on twitter so i figured why not share it here too#also since tumblr too is selling our data to GenAI
176 notes
·
View notes
Note
ok so i do think the "ai art isnt real art" argument sucks but what about "stealing" art? in the sense of ai being trained on other peoples work and then profiting off of it. for both visual art and written work.
(i know the bigger problem here are the abused workers doing the filtering etc but im interested in this particular problem too)
so first of all i think this argument is kind of silly (im not aiming this at you but at a certain genre of ai critic) because there's no way to distinguish, ontologically or legally, between a generative language model being trained on a certain dataset and a human having artistic influences. that's sort of just how creative production works. it would be really hellish if "having stylistic influences" was like, ethically or legally forbidden lmao. i mean certain forms of art (blackout poetry, collage) can even work explicitly by taking some already existing piece and altering it---but even when that's not happening, human creation and inspiration don't happen in a vacuum or in some kind of transcendent artistic revelation from god above lol.
anyway i do actually think it's fucked for companies to be profiting on the creations of their generative language models, but only in the same way and to the same extent that capitalist production generally is fucked. i do not think the solution here is to further reinforce copyright or monetary ownership of art. and as many people have pointed out, you actually can see a kind of trial run of how this would shake out in the music industry, where laws about sampling have gotten more and more restrictive to protect copyright/ip. it's very easy for massive labels to sue whoever they want, it's hard-to-impossible for smaller artists to fight back even if it's genuinely a case of accidental resemblance, it's legally absurd because like half of rock n roll uses the same few chord progressions anyway, and meanwhile the actual art form has basically been shrunken and restricted because sampling is so threatened and expensive.
591 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello and happy endless January! Despite how long this month may have seemed, it is almost over - and that means it's soon time for another art party hosted by my guild, Verdant Shield [VS]! We're taking a little tour of the cozy size of the jungle this time, over at Mabon Market in Caledon!
For those who aren’t familiar with art parties, they’re a concept carried over from Final Fantasy XIV - in-game get-togethers for artists/writers/creatives of all types to hang out, chat, and create together! Get your favorite character/look together, head to the location, find someone that catches your eye, and create! Afterwards, everyone posts their creations in a shared tag (ours is #VSArtParty) so others can see, interact, and share! Tl;dr: the ‘goal’ of an art party isn’t to be drawn, but to draw others, and share with the community!
Time and /squadjoin information is under the cut, but will also be posted again via reblogs as the squads go up on the day of the party!
Location Information:
Caledon Forest is a nice easily-accessible map for everyone, and Mabon Market even has its own dedicated waypoint (that is, Mabon Waypoint)! I imagine we'll kind of scatter out across the market and beach, so don't take my exact location in this screenshot too seriously!
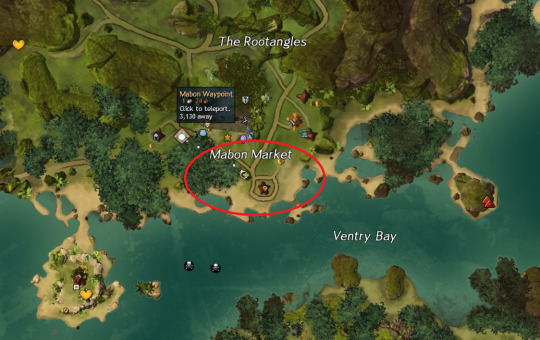
Time & Squad Details:
As we always do, we'll be having two parties - one on EU servers and one on NA ones - with an hour break in between. People tend to arrive early and/or jump between accounts as soon as the break comes up, so don't be surprised to see tags and announcements going up ahead of schedule!
The first party will be on EU servers and begin at 9pm Central European Time (aka 3pm Eastern Standard Time or 4 hours before in-game reset). I’ll be hosting on my EU alt account, so to join either /squadjoin or whisper Aemryn of Dusk for an invite.
The second party will be on NA servers and begin at 7pm Eastern Standard Time (aka 1am Central European Time or at in-game reset). I’ll be hosting this one on my main account, so to join either /squadjoin or whisper Kirslyn for an invite.
Closing Words:
A few days ago some nasty info came to the surface about various GW2 sources being scraped for AI purposes, with tumblr tags specifically being mentioned. Though I certainly wouldn't blame anyone for being discouraged and not wanting to draw at all (even this post was delayed because of it), I think at the end of the day, even if you don't post anything publicly, you still shouldn't deny yourself the company and community of your fellow creatives! If you'd like to make this art party have more of a focus on screenshots, or even just hang out and not draw at all, please feel free - your presence is what makes these parties...well, parties, after all!
If you are still interested in posting your artwork though, please check out Glaze and Nightshade as potential ways to protect yourself (and hurt AI datasets) if you haven't already! And even if you don't do that, make sure to slap signatures/watermarks/etc wherever you can. This may be a disheartening time for us, but it doesn't mean we have to stop doing what we love.
So, whether you're coming to create or just to hang out, I look forward to seeing you all this Saturday. Take care, stay safe, and see you soon! ♥
#please check the closing words this time too btw#i don't usually draw attention to them but it's about all the ai bullshittery that came up a few days ago#gw2#guild wars 2#vsartparty#obnoxious tourist simulator#📢🎨
143 notes
·
View notes
Note
Not defending ai art, genuinely asking: does the "If you don't make it with your own hands it doesn't count" argument equally apply to photography, in your opinion? The exact same criticism was leveled against it when cameras started to become widespread, which made me start to think more closely about where I draw the line and why.
(From a Baltimore Sun article:
As early as 1842, a magazine writer was complaining that “the artist cannot compete with the minute accuracy of the Daguerreotype.” By 1859, essayist Charles Baudelaire was denouncing photography as “the mortal enemy of art.”
“If photography is allowed to stand in for art in some of its functions,” Baudelaire fumed, “it will soon supplant or corrupt it completely.”
And a few years later, the writer Hippolyte Fandrin lamented: “I greatly fear that photography has dealt a death blow to art.”)
Again, this is a genuine question. I'm not an AI fan I'm just trying to figure out why people (including myself) treat it differently from other image generation or manipulation methods.
Oh! Thanks for the ask! It prompted a lot of thoughts, actually. This got kinda long, but as a philosophy nerd I like this stuff so buckle up! (I'm purely freestyling this btw, consider it more of a philosophical discussion rather than something based on empirical evidence - nearly impossible to do while discussing what defines "art"):
Yeah photography is real art as much as any other kind of art. I should not have limited it to art only being art if it's produced using hands, but rather mainly involving the creative process of a human consciousness somehow. I think my comment in the tags was more of a way to express the opinion that "AI art will never be human in the same intrinsically valuable way that human-made art is". In my opinion, humanity is intrinsically valuable and therefore the human creative component is integral to art. This creative component can of course look very different depending on the medium.
One could however argue that AI art does involve human intention. It is the human that picks the prompts and evaluates the finished image, after all. As with photography, the human picks an object, frames it, clicks the button and then evaluates and perhaps edits/develops the image. The absolute greatest problem I have with AI art however, which the original post focuses a lot on, is the art theft and the fact that many companies are actually using AI art as a direct replacement for human art.
And AI art can imitate a wide range of styles taken from huge datasets of existing images and create something that looks like an oil painting, a photo, watercolour, digital art, graphite, or written works like poems, articles, etc! So AI art can be everything, with much the same creation process behind it. Photography might have replaced a lot of demand for portrait art and photo-realistic art in society, but that is only one single quite small branch of the overall ocean of genres within art (it perhaps rather expanded on it!) and eventually became a whole branch of its own with many different subgenres.
Some questions that popped up in my head while writing this that I realize might actually be quite difficult to answer (these are for thinking about & discussing only, don't read these questions as me trying to justify anything):
Is the process of writing in prompts for an AI work art? Why/why not?
Is non-human art less valuable than human art? Why/why not?
If AI art is theft, does it disqualify it from being art? If so, what makes it different from human-made art that is directly plagiarizing another person's art?
Is the human process of programming an AI considered art?
How could AI art be produced and used ethically?
My own conclusion from this is that Art is a difficult concept to accurately assign one single universal definition to, and just as with everything in human society, it is constantly evolving. Whether or not it does qualify as art or not at the end of the day, however, it does not change the fact that AI art is currently being used in an unethical way that is having complex and direct real life repercussions on artists.
Again, thanks for the ask!! I love stuff like this and I try to think about it as critically as possible. My own opinion is probably still mostly "AI art bad" but mainly because of the negative effects and the unethical practice.
(Asking "why/why not" is so valuable btw, it allows one to continue asking and answering questions almost endlessly and eventually either arrive at some sort of "root" answer or go around in circles)
#anonymous#asks#ai art#philosophy#(generously applying that tag LOL i am not really a professional philosopher)
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Something I can't stand:
The proliferation of grift culture and "venture capitalist" techbros using AI as a way to steal and resell other people's art has completely ruined the awe and appreciation we had of early AI experiments that didn't hurt anyone, and had inevitably kneecapped those type of projects' continued existence
What am I talking about..? Stuff like background removers, upscalers, vocal removers, frame interpolators, tools to make art seamlessly tile, fucked up nightmare distortion images, AI based vocaloids (made from paid and consenting voice actors), comedic deepfakes, singing faces (think Dame da ne)
The fun stuff, that is either too poor quality to pass for a human creation, or is merely a free tool designed to fill a very specific niche in one step of art creation, or doesn't function in the way we currently think of AI and is made by a closed group of people all being paid for their contributions (eg vocaloid, of which the AI voicebanks are created and used almost the exact same way as they always have, with manual tuning and songwriting, employed voice actors, and the AI part being used to blend phonemes rather than create something from scratch)
Unfortunately I think it was kinda inevitable that AI turned into what it is, because for a lot of high profile people, the grift never ends. We are finding out more and more that those fun, mostly harmless tools they gave us at the beginning as our introduction to AI are being swiftly deprecated and paywalled, because they always intended to fuck us over once it became viable to do so.
And I think, based on the conversations I've had, at first a lot of people didn't really have opinions towards their art going into the AI mush machine, because what it generated was silly and unmarketable. It was deformed rooms with dog faces and scrungly trees. It was a sloppy mess most people considered harmless. And that's how they eased their way into turning theft from artists into something profitable for them, to be sold back to people who want to be artists without the effort. Or maybe not even that. Some don't give a shit about art, and just know that other people like art enough to give the lowest seller lots of money, and use AI as a grifting tool to undercut artists for Lamborghini money.
And now that we know that the people who made our background removers, our image upscalers, our wacky gray goo karl-marx-getting-slimed-at-the-kids-choice-awards generators, our funny singing face tech, etc have taken those data sets that many initially didn't even think twice about, and turned them on us for profit with other tools, there is no way in hell anyone will ever trust a movement like this again.
They played us, and are now crying and wiping their eyes with money about how we feel betrayed and stolen from. Capitalism and grift culture has ensured that the only way that AI could go is towards a point of automating out the emotion, work, quality, and ownership of art itself.
Have you noticed that while these techbro AI image generators have surged in quality, background removers and upscalers have stagnated in quality upgrades? Silly tools like making faces sing have been abandoned in the dust. The actual TOOLS that can be justified— those made from controlled datasets of a specific variety that are designed to help actual artists— have fallen completely out of favor in exchange for a focus on a low effort, generalized art-replacement that can be sold to anyone lazy or conniving enough to buy into it. And maybe the worst part is they're being made by the same companies, sometimes even using the same datasets they hid in the initially harmless tools that we once trusted to remain as such.
It's been so sad seeing the future of hyperspecific tools to help artists turn into this ratrace towards art replacement. I watched many of our opinions shift over time as the culture and tech did. I wrote this because I had a brief recall of "the fun early days" and how people were generally okay with things like that, and how a fair amount of people still are with low-level machine learning tools that aid specific processes rather than replacing them. I don't really have a point to make here. We were once again fucked over by the people who promised to make our work and lives easier, and then raged at for hating them for using that sentiment to abandon those projects in favor of stealing from us on a wide scale.
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
absolutely fucking insane to me that companies loathe any form of fan creation with every fiber of their being. fanfiction, fan art, any kind of unmonitized fan project like a YouTube abridged series, bc it's "infringing on intellectual property" but will spend thousands to millions of dollars on AI datasets trained on this content and actively scraping and stealing from these artists. like. make it make sense. they're legit buying up datasets trained on things that did not give their fucking consent to be trained on. it's all stolen material. it's insane. they seriously think they're not about to get hit with a class action lawsuit.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Optimizing Business Operations with Advanced Machine Learning Services
Machine learning has gained popularity in recent years thanks to the adoption of the technology. On the other hand, traditional machine learning necessitates managing data pipelines, robust server maintenance, and the creation of a model for machine learning from scratch, among other technical infrastructure management tasks. Many of these processes are automated by machine learning service which enables businesses to use a platform much more quickly.
What do you understand of Machine learning?
Deep learning and neural networks applied to data are examples of machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence focused on data-driven learning. It begins with a dataset and gains the ability to extract relevant data from it.
Machine learning technologies facilitate computer vision, speech recognition, face identification, predictive analytics, and more. They also make regression more accurate.
For what purpose is it used?
Many use cases, such as churn avoidance and support ticket categorization make use of MLaaS. The vital thing about MLaaS is it makes it possible to delegate machine learning's laborious tasks. This implies that you won't need to install software, configure servers, maintain infrastructure, and other related tasks. All you have to do is choose the column to be predicted, connect the pertinent training data, and let the software do its magic.
Natural Language Interpretation
By examining social media postings and the tone of consumer reviews, natural language processing aids businesses in better understanding their clientele. the ml services enable them to make more informed choices about selling their goods and services, including providing automated help or highlighting superior substitutes. Machine learning can categorize incoming customer inquiries into distinct groups, enabling businesses to allocate their resources and time.
Predicting
Another use of machine learning is forecasting, which allows businesses to project future occurrences based on existing data. For example, businesses that need to estimate the costs of their goods, services, or clients might utilize MLaaS for cost modelling.
Data Investigation
Investigating variables, examining correlations between variables, and displaying associations are all part of data exploration. Businesses may generate informed suggestions and contextualize vital data using machine learning.
Data Inconsistency
Another crucial component of machine learning is anomaly detection, which finds anomalous occurrences like fraud. This technology is especially helpful for businesses that lack the means or know-how to create their own systems for identifying anomalies.
Examining And Comprehending Datasets
Machine learning provides an alternative to manual dataset searching and comprehension by converting text searches into SQL queries using algorithms trained on millions of samples. Regression analysis use to determine the correlations between variables, such as those affecting sales and customer satisfaction from various product attributes or advertising channels.
Recognition Of Images
One area of machine learning that is very useful for mobile apps, security, and healthcare is image recognition. Businesses utilize recommendation engines to promote music or goods to consumers. While some companies have used picture recognition to create lucrative mobile applications.
Your understanding of AI will drastically shift. They used to believe that AI was only beyond the financial reach of large corporations. However, thanks to services anyone may now use this technology.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Synergy of Digital Marketing and AI: Transforming the Future
Digital marketing has become the backbone of modern business strategies, enabling brands to reach global audiences with precision and efficiency. As this field evolves, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing how companies engage with customers, analyze data, and optimize their campaigns. The integration of AI in digital marketing is not just a trend; it’s a transformative force reshaping the industry.

Personalization at Scale
One of the most significant contributions of AI to digital marketing is the ability to deliver personalized experiences at scale. Traditional marketing approaches relied heavily on broad segmentation, often leading to generic messaging. AI, however, enables hyper-personalization by analyzing vast amounts of data, including browsing history, purchase behavior, and social media activity. This data allows marketers to create tailored content and product recommendations that resonate with individual consumers, enhancing engagement and boosting conversion rates.

For instance, AI-powered recommendation engines, like those used by Amazon and Netflix, analyze user behavior in real-time to suggest products or content that match the user’s preferences. This level of personalization was unimaginable just a few years ago, but today, it’s a key driver of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Enhanced Data Analysis and Decision-Making
AI has also revolutionized how marketers approach data analysis. In the past, analyzing large datasets was time-consuming and prone to human error. AI algorithms, however, can process and interpret data at unprecedented speeds, identifying patterns and insights that might be missed by human analysts. This capability allows marketers to make data-driven decisions with greater accuracy, optimizing their strategies for maximum impact.

For example, AI can analyze the performance of a digital marketing campaign in real-time, adjusting targeting and messaging based on the results. This agility not only improves the effectiveness of campaigns but also reduces costs by minimizing wasteful spending on ineffective tactics.
Automating Routine Tasks
Automation is another area where AI is making a significant impact. Tasks such as content creation, social media posting, and email marketing can be automated using AI tools. These tools can generate content, schedule posts, and even respond to customer inquiries with minimal human intervention. This frees up marketers to focus on more strategic activities, such as creative development and campaign planning.

Conclusion
The integration of AI in digital marketing is revolutionizing the industry, enabling unprecedented levels of personalization, efficiency, and effectiveness. As AI continues to advance, its role in digital marketing will only grow, offering new opportunities for brands to connect with their audiences in meaningful ways. Embracing this technology is no longer optional; it’s essential for staying competitive in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.

#digital marketing#marketing#seo services#seo#ai#artificial intelligence#digital work#learn digital marketing
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Empowering AI Innovation with Expert Dataset Creation | Haivo AI
Haivo AI specializes in dataset creation, offering comprehensive solutions for data collection, validation, and enhancement for AI applications. As a leading company in Lebanon, we drive AI innovation through high-quality datasets, ensuring your models receive the data they need to excel. For more information visit our website.

0 notes
Text
AI and The Coming Implosion of Media
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/ai-and-the-coming-implosion-of-media/
AI and The Coming Implosion of Media
It is popular among journalists these days to warn that AI might have catastrophic effects on humanity. These concerns are overblown with regards to humanity as a whole. But they are actually quite prescient with regards to journalists themselves.
To understand why, let’s take a closer look at the sub-disciplines that we collectively call AI. AI is the widest umbrella term, but we can generally break it down into rule-based systems and machine-learning systems. Machine-learning systems can be broken down by their application (video, images, natural language, etc). Among these, we’ve seen the greatest recent strides made in natural language processing. Specifically, we’ve seen the invention of the transformer model in 2017, followed by rapid growth in the size of transformers. Once the model exceeds 7 billion parameters, it is generally referred to as a large language model (LLM).
The core “skill” (if you might call it that) of an LLM is its ability to predict the most likely next word in an incomplete block of text. We can use this predictive mechanism to generate large blocks of text from scratch, by asking the LLM to predict one word at a time.
If you train the LLM on large datasets with variable quality, this predictive mechanism will often produce bad writing. This is the case with ChatGPT today. This is why, whenever I broach the topic with journalists, I encounter skepticism – journalists see how badly ChatGPT writes, and they assume AI poses no threat to them because it’s inept.
But ChatGPT is not the only LLM out there. If an LLM is trained on a carefully-selected dataset of text written by the best journalists – and no one else – then it will develop the ability to write like the best journalists.
Unlike journalists, however, this LLM will require no salary.
Writing vs. Knowing What to Write
Before we proceed, we need to distinguish between the mechanics of writing and the creativity required to know what is worth writing about. AI can’t interview whistleblowers or to badger a politician long-enough for the politician to accidentally tell the truth.
AI cannot gather information. But it can describe information gathered by humans in an eloquent way. This is a skill that journalists and writers used to have a monopoly over. They no longer do.
Given the current rate of progress, within a year, AI could write better than 99% of journalists and professional writers. It will do so for free, on demand, and with infinite throughput.
The Economics of Zero-Cost Writing
Anyone who has a list of facts to convey will be able to turn these facts into a well-written article. Anyone who finds an article on any subject will be able to produce another article, covering the same subject. This derivative article will be just as good as the first one, and won’t plagiarize it or violate its copyrights..
The marginal cost of written content will become zero.
Currently, the economics of written media are based on human labor. Well-written content is scarce, so it has value. Entire industries were built to capture this value.
When AI can produce high-quality content for free, the financial foundation of these industries will collapse.
The Abolition of Publications
Consider traditional publications. For decades, companies like The New York Times have employed skilled writers to produce a limited number of articles each day (typically around 300). This model is inherently constrained by the number of writers and the costs involved.
In a world where AI can generate an unlimited number of articles at no cost, why limit production to a fixed number? Why not create personalized content for every reader, tailored to their interests and generated on demand?
In this new paradigm, the traditional model of periodic issues and fixed article counts becomes obsolete. Publications can shift to a model where content is continuously created and personalized, catering to the specific needs of individual readers. One reader might need a single article each day. Another might need 5000.
Publications whose primary product is packing 300 articles into a single daily issue will go extinct.
Search Engines Becoming Answer Engines
Search engines act as distributors, connecting users to pre-existing content. To achieve this, they perform four steps.
First, they index vast amounts of pre-written content. Second, they receive a query from the user. Third, they search the pre-written content to find items that are relevant to the user’s query. And fourth, they rank the retrieved content and present a sorted list of results to the user.
So far so good. But if content can be created on demand, for free, then why would search engines return pre-existing content to the user? They could simply generate the answer instead. The user would certainly be happier with a single answer to her query, instead of a long list of results whose quality may vary.
Now let’s consider the logical next step. If search engines no longer lead users to any content written by others, what would happen to the “content” economy?
Most content on the internet was written to be monetized. People write articles, rank on Google, receive traffic, and turn it into income (using ads, affiliate links, or direct sales of products or services).
What will happen to this ecosystem when the traffic disappears?
Social Media: The Next Domino
Social media platforms were initially designed to facilitate interaction between users. I am old enough to remember the days when people logged into Facebook to write on a friend’s wall, poke, or throw a virtual sheep at someone.
Today’s social media is different. The most common number of followers users have on Instagram is zero. The second most common number of followers is one. The vast majority of views, shares, comments and followers is amassed by a small number of professional creators. Most users post nothing and are followed by no one.
Simply put – most users visit social media to find content they might enjoy. Social media companies act as distributors, just like search engines. The main difference between Facebook and Google is that Google uses a query to select content, whereas Facebook selects content without one.
If this is the case, then the next step becomes obvious. Why would social media promote user-generated content, when they can generate AI-based content on demand? Text-only at first, perhaps, but eventually images and videos too.
And once social media no longer leads users to content made by creators, what will happen to the “creator economy”?
The Star Trek Replicator Analogy
We are entering a new paradigm where AI functions as a Star Trek replicator for content.
In Star Trek, there is no need for farmers who grow food, stores who sell food, chefs who cook food or waiters who serve food. The replicator can create any food you like, on demand, by directly transforming raw materials into the final product.
Likewise, I see no place in our future for any company who creates written content, distributes written content, mixes written content in some special way, or serves pre-existing written content to the user. The only valuable functions will be obtaining raw materials and transforming them into the final product on demand.
We still need ways to create information that did not exist before and gather information that was not publicly available before. Everything else will be achieved by AI engines that convert the available information into personalized content.
Implications for Content Creators and Distributors
Traders often talk about “positive exposure” and “negative exposure”. The easiest way to understand these concepts is to ask yourself – if this thing goes up, will I benefit or suffer?
AI is going up. And it is going up especially fast in areas like natural language and other human-generated content. The question every professional needs to ask themselves is – do I have positive or negative exposure to AI right now?
If you are a content creator – let’s say a news publication – and your cost structure is non-zero, then you are likely in trouble. You will soon be competing with content creators whose cost is zero, and that is not a competition you can win. In all likelihood, you have exactly 3 choices: exit the market; reduce your costs to zero (by becoming an AI company); or go bankrupt.
If you are on the distribution side of things, you probably have more time before the full effects reach your bottom line. Network effects will help you stave off the disruption for a few years. But eventually, things that must happen, do happen. Search engines replaced web directories. Feeds replaced a large part of the function search engines served before. And soon, on-demand content creation will replace both.
The Role of Government and Regulation
As someone who was born in the Soviet Union, I am not a big fan of government regulating speech. The moral hazards are usually higher than any temporary benefit such regulation might bring.
Nevertheless, I think that governments might have an important role to play in determining how this unfolds.
We have good and bad examples of government regulations and the effects they’ve had on industry. The “26 words that created the internet” grew a nascent industry to trillions of dollars in value. The regulation of ISPs in the 90s, however, brought down the number of ISPs in the US from over 3000 to 6, and resulted in a situation where US consumers have the worst bandwidth access in the developed world.
When asked for my recommendations, I usually point out three ways in which government regulation can help, rather than hinder, the development of this new ecosystem:
1. Mandate interoperability, and make it easier for consumers to switch providers.
Capitalism works like natural selection – companies that do things better or more efficiently will grow faster than companies who don’t. “Lock in” mechanisms that make it harder to switch, like the inability to export one’s data out of a service and port it to a competitor, slow down this evolution and result in lower growth.
If governments can mandate interoperability throughout the tech industry, we will see more good features and good behaviors rewarded. We will create incentive for companies to innovate in things people want, rather than innovating in ways to squeeze more out of a captive audience.
2. Enforce antitrust by focusing on monopoly abuses, rather than monopoly risks.
We all know that when two companies merge, the resulting entity might become large and have outsized power relative to its customers. But the existence of outsized power does not always lead to bad service or predatory pricing.
Meanwhile, companies who already have outsized power are often engaging in anti-competitive behaviors right before our eyes. And yet the FTC focuses on blocking mergers and acquisitions.
If governments focus on banning and strict enforcement of anti-competitive practices like dumping and bundling, especially with regards to tech products that are used by the majority of the population, the entire system will become unclogged.
Some specific examples might help illustrate this point.
Providing a browser, which is a very complex piece of software that costs billions to develop, for free – is a clear case of dumping. New browser companies like Cliq or Brave find it hard to innovate in this space because their much larger competitors give this expensive product away for free. The result is that all browsers look the same these days, and there’s been no significant innovation in this space since 2016.
Providing a corporate messaging app as a part of a document editing suite that every business must buy – is a clear case of bundling. Even a very successful startup like Slack was essentially forced to sell itself to a larger company, just to be able to compete as a paid product in a space where their main competitor is bundled with something their customer must have anyway.
As AI develops into a new ecosystem that becomes larger than the internet, we’re bound to see even greater abuses in this nascent space – unless governments step in and ensure that dumping and bundling do not pay.
3. Consider ways to subsidize or protect original content creation.
Government funds basic research and science through grants and other subsidies. It also protects new ideas that people discover in their research through patents. The reason these two mechanisms are necessary is that copying an idea that works is much cheaper than coming up with a new idea that works. Without intervention, this might lead to a tragedy of the commons where everyone copies from their neighbor and no one creates anything new.
In journalism, and content creation in general, these mechanisms were unnecessary because copying without violating copyrights was a difficult process. But with the advent of AI, this is no longer true. As the price of paraphrasing others’ writing approaches zero, we will need mechanisms to incentivize something other than paraphrasing – and the best answers might look a lot like the ones we have in basic research today.
Making the Best of this Challenge
The transformation brought about by AI is one of the greatest challenges facing humanity today. Journalists and other content creators will be affected first. Distributors of content will follow soon thereafter. We will eventually enter a completely new paradigm, which I referred to as the “Star Trek Replicator” model for content creation and distribution.
We have an opportunity here to build something much better than what exists today. Just as the invention of the printing press led to the Enlightenment, the invention of AI could lead to a second Enlightenment. But unfortunately, not all the possible futures are benign.
It’s up to us to nudge this evolution in the right direction.
#acquisitions#affiliate#ai#AI engines#antitrust#app#Article#Articles#Best Of#billion#Born#browser#Business#Capture#chatGPT#Companies#competition#consumers#content#content creation#creativity#creators#data#datasets#development#Difference Between#direction#disruption#Economics#economy
1 note
·
View note
Text
How AI is Revolutionizing Digital Marketing Tools in 2024
wanna know How AI is Revolutionizing Digital Marketing Tools in 2024 look no futher . in this blog i have outlined the perfect way to help you know the insights of ai revolutionizing digital marketing tools in 2024

introduction
The digital marketing landscape is evolving at a breakneck pace, and artificial intelligence (AI) is at the forefront of this transformation. As we step into 2024, AI-powered tools are revolutionizing how businesses approach digital marketing, offering unprecedented levels of efficiency, personalization, and insight. In this article, we'll explore how AI is reshaping digital marketing tools and why incorporating these advanced technologies is essential for staying competitive.
The Rise of AI in Digital Marketing tools in 2024
AI has become an integral part of digital marketing strategies, with 80% of industry experts incorporating some form of AI technology in their marketing activities by the end of 2023. This trend is only expected to grow as AI tools become more sophisticated and accessible.
here's the top must have digital marketing tools in 2024
Stats & Facts:
Adoption Rate: By 2023, 80% of industry experts were using AI technology in their marketing activities (Source: Forbes).
Market Growth: The global AI in the marketing market is expected to grow from $12 billion in 2022 to $35 billion by 2025 (Source: MarketsandMarkets).
Enhancing Personalization
One of the most significant impacts of AI on digital marketing is its ability to deliver highly personalized experiences. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. This allows marketers to create tailored content, recommendations, and offers for individual users.
Example: E-commerce giants like Amazon and Netflix leverage AI to provide personalized product recommendations and content suggestions, resulting in higher engagement and conversion rates. According to a study by McKinsey, companies that excel in personalization generate 40% more revenue from those activities than average players.
Stats & Facts:
Revenue Increase: Companies that excel in personalization generate 40% more revenue than those that don't (Source: McKinsey).
Consumer Preference: 80% of consumers are more likely to make a purchase when brands offer personalized experiences (Source: Epsilon).
Improving Customer Insights
AI-powered analytics tools are transforming how businesses gather and interpret customer data. These tools can process and analyze large datasets in real-time, providing deep insights into customer behavior, sentiment, and preferences.
Example: Tools like Google Analytics 4 use AI to offer predictive metrics, such as potential revenue and churn probability. This helps businesses make informed decisions and refine their marketing strategies.
Stats & Facts:
Predictive Analytics: Companies that use predictive analytics are 2.9 times more likely to report revenue growth rates higher than the industry average
Data Processing: AI can analyze data up to 60 times faster than humans
Automating Routine Tasks
Automation is another area where AI is making a significant impact. AI-driven automation tools handle repetitive tasks, freeing up marketers to focus on more strategic activities.
Example: Email marketing platforms like Mailchimp use AI to automate email campaign scheduling, segmentation, and even content creation. This results in more efficient campaigns and improved ROI. In fact, automated email marketing can generate up to 320% more revenue than non-automated campaigns.
Stats & Facts:
Revenue Boost: Automated email marketing can generate up to 320% more revenue than non-automated campaigns
Time Savings: AI can reduce the time spent on routine tasks by up to 50%
Enhancing Customer Service with Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots are revolutionizing customer service by providing instant, 24/7 support. These chatbots can handle a wide range of queries, from product information to troubleshooting, without human intervention.
Example: Companies like Sephora use AI chatbots to assist customers with product recommendations and booking appointments. According to a report by Gartner, by 2024, AI-driven chatbots will handle 85% of customer interactions without human agents.
Stats & Facts:
Interaction Handling: By 2024, AI-driven chatbots will handle 85% of customer interactions without human agents
Cost Savings: Businesses can save up to 30% in customer support costs by using chatbots
Boosting Content Creation and Optimization
AI is also transforming content creation and optimization. AI tools can generate high-quality content, suggest improvements, and even predict how content will perform.
“Aspiring to create top-notch content become a leader in the industry?
well here's the price drop alert for high quality content masterly course from digital scholar to enhance your branding viral on the social media, google better rankings
Example: Tools like Copy.ai and Writesonic use AI to create blog posts, social media content, and ad copy. Additionally, platforms like MarketMuse analyze content and provide optimization recommendations to improve search engine rankings. According to HubSpot, businesses that use AI for content marketing see a 50% increase in engagement.
Stats & Facts:
Engagement Increase: Businesses using AI for content marketing see a 50% increase in engagement
Content Generation: AI can generate content up to 10 times faster than humans
Enhancing Ad Targeting and Performance
AI-driven advertising platforms are changing the way businesses target and engage with their audiences. These tools use machine learning algorithms to analyze user data and optimize ad placements, ensuring that ads reach the right people at the right time.
Example: Facebook's AI-powered ad platform uses advanced algorithms to target users based on their behavior, interests, and demographics. This results in higher click-through rates (CTR) and lower cost-per-click (CPC). A study by WordStream found that AI-optimized ads can achieve up to 50% higher CTRs compared to non-optimized ads.
Stats & Facts:
CTR Increase: AI-optimized ads can achieve up to 50% higher click-through rates
Cost Efficiency: AI-driven ad platforms can reduce cost-per-click by up to 30%
Predictive Analytics for Better Decision-Making
Predictive analytics powered by AI enables marketers to forecast trends, customer behavior, and campaign outcomes. This allows for proactive decision-making and more effective strategy development.
Example: Platforms like IBM Watson Marketing use AI to predict customer behavior and provide actionable insights. This helps businesses tailor their marketing efforts to meet future demands. According to a report by Forrester, companies that use predictive analytics are 2.9 times more likely to report revenue growth rates higher than the industry average.
Stats & Facts:
Revenue Growth: Companies using predictive analytics are 2.9 times more likely to report higher revenue growth rates
Accuracy Improvement: AI can improve the accuracy of marketing forecasts by up to 70%
Enhancing Social Media Management
AI tools are revolutionizing social media management by automating content scheduling, analyzing engagement metrics, and even generating content ideas.
Example: Tools like Hootsuite and Sprout Social use AI to analyze social media trends and suggest optimal posting times. They also provide sentiment analysis to help businesses understand how their audience feels about their brand. According to Social Media Today, AI-powered social media tools can increase engagement by up to 20%.
Stats & Facts:
Engagement Boost: AI-powered social media tools can increase engagement by up to 20%
Efficiency Gains: AI can reduce the time spent on social media management by up to 30%
The Future of AI in Digital Marketing tools
here's the top must have digital marketing tools in 2024
As we look ahead, the role of AI in digital marketing will only continue to expand. Emerging technologies like natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and advanced machine learning models will further enhance AI's capabilities.
Example: AI-powered voice search optimization tools will become increasingly important as more consumers use voice assistants like Siri and Alexa for online searches. By 2024, voice searches are expected to account for 50% of all online searches.
Stats & Facts:
Voice Search Growth: By 2024, voice searches are expected to account for 50% of all online searches
NLP Advancements: The global NLP market is projected to reach $43 billion by 2025
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing digital marketing tools in 2024, offering businesses new ways to enhance personalization, improve customer insights, automate routine tasks, and optimize their marketing efforts. By leveraging AI-powered tools, businesses can stay competitive, drive higher engagement, and achieve better ROI. As AI technology continues to evolve, its impact on digital marketing will only grow, making it an essential component of any successful marketing strategy. Embrace the power of AI and transform your digital marketing efforts to stay ahead in the ever-changing digital landscape.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Overcoming Challenges in Data Integration: Insights from Consulting Experts
Data integration for enterprises can take longer due to technological, financial, and time constraints. As a result, modifying data strategies to mitigate risks like incompatibility between many tools or budget overruns is crucial. Companies must also prepare for new compliance requirements to ensure ethical data operations. This post will explore such challenges in data integration while listing valuable insights from consulting experts in this domain.
What is Data Integration?
Data integration merges data from disparate origins and presents it to maximize comprehension, consolidation, and summarization effectiveness. Integrated data views rely on data ingestion, preparation, and advanced insight extraction. It also streamlines the data operations services across regulatory report creation, helpdesks, and 360-degree client life cycle management.
All data integration strategies involve the extract, transform, and load (ETL) pipelines regardless of business units or target industries. At the same time, the scope of planning and quality assurance in each process varies due to domain-specific data classification factors.
For instance, the accounting departments must handle extensive numerical data while interpreting legal and organizational requirements for transparency. On the other hand, production engineering and design professionals will use visualizations to improve goods or service packages. Accordingly, accountants will use unique tools distinct from engineers’ software.
Later, the leaders might want a comprehensive overview of the synergy between these departments. Therefore, they must determine efficient data integration strategies. The data will move between several programs, carrying forward many updates throughout a project’s progression based on those roadmaps.
Overcoming the Challenges in Data Integration Using Insights from Consulting Experts
1| Data Quality Hurdles
Linking, consolidating, and updating data from several sources will exponentially increase the quality-related threats. For instance, consider multimedia assets from social networks or unreliable news outlets. They can help your secondary market research and social listening initiatives. However, you want to verify the authenticity of gathered intelligence to avoid inaccurate data ingestion.
Evaluating relevance, freshness, and consistency is essential to data quality assurance from creation to archival. So, corporations have started leveraging data lifecycle management to boost dataset integrity, helping make integration less of a hassle.
Insights:
Most consulting experts suggest developing ecosystems that check and recheck quality metrics at each stage of a data integration lifecycle. Moreover, they recommend maintaining periodic data backups with robust version control mechanisms. Doing so will help quality preservation efforts if errors arise after a feature update or a malicious third party is likely to break the system using malware.
2| Networking and Computing Infrastructure Problems
Legacy hardware and software often introduce bottlenecks, hurting data integration’s efficiency. Modern integration strategies demand more capable IT infrastructure due to the breakthroughs like the internet of things (IoT), 5G networks, big data, and large language models. If a company fails to procure the necessary resources, it must postpone data integration.
Technologies integral to capturing, storing, checking, sorting, transferring, and encrypting data imply significant electricity consumption. Besides, a stable networking environment with adequate governance implementations enables secure data transactions. The underlying computing infrastructure is not immune to physical damage or downtime risks due to maintenance mishaps.
What Consulting Experts Say:
Enterprises must invest in reliable, scalable, and efficient hardware-software infrastructure. This will benefit them by providing a stable working environment and allowing employees to witness productivity improvements. Upgrading IT systems will also enhance cybersecurity, lowering the risk of zero-day vulnerabilities.
3| Data Availability Delays
Governments, global firms, educational institutions, hospitals, and import-export organizations have a vast network of regional offices. These offices must also interact with suppliers, contractors, and customers. Due to the scale of stakeholder engagement, reports concerning office-level performance and inventory might arrive late.
Underproductive employees, tech troubleshooting, slow internet connectivity, and a poor data compression ratio will make data sourcing, updating, and analyzing inefficient. As a result, a data integration officer must address time-consuming activities through strategic resource allocation. If left unaddressed, delays in data delivery will adversely affect conflict resolution and customer service.
Expert Insights:
Train your employees to maximize their potential and reduce data acquisition, categorization, and transformation delays. Additionally, you will want to embrace automation through artificial intelligence (AI) applications. Find methods to increase the data compression ratio and accelerate encryption-decryption processing cycles. These measures will help accomplish near-real-time data integration objectives.
4| Vendor Lock-ins
A vendor lock-in results from inconvenience and restrictions when a client wants to switch to another service provider or toolkit. Although data integration platforms claim they celebrate the ease of migrating databases with competitors, they might covertly create vendor lock-ins.
For instance, some data sourcing and sorting ecosystems might limit the supported formats for bulk export commands. Others will use misleading methods to design the graphical user interface (GUI) of account deletion and data export features. They involve too many alerts or generate corrupt export files.
Practical Insights:
Combining multiple proprietary and open-source software tools offers the best cost optimization opportunities. When you select a data vendor, audit the tools the willing data integration providers use to deliver their assistance. Do they use a completely proprietary system based on an unknown file format unsupported by other platforms?
Finally, you must check all the data import, export, and bulk transfer options in vendors’ documentation. After you check a data firm’s current client base, track its online ratings and scan for red flags indicating potential vendor lock-ins.
5| Data-Related Ethical and Legal Liabilities
Confidentiality of investor communication and stakeholders’ privacy rights are two components of legal risk exposure due to enterprise data integration. Additionally, brands must interpret industry guidelines and regional directives for regulatory disclosures.
They must comply with laws concerning personally identifiable information (PII) about employees and customers. Otherwise, they will attract policymakers’ ire, and customers will lose faith in brands that do not comply with the laws of their countries.
Insights:
Consulting experts recommend collaborating with regional legal teams and global governance compliance specialists. After all, mitigating legal risks can help increase business resilience.
Improved compliance ratings have also benefited several brands wanting to be attractive to impact investors. Meanwhile, customers demanding ethical data operations at business establishments love supporting brands with an exceptional governance culture.
Conclusion
Most brands need specialists' help to develop consolidated data views during reporting because they have flawed data integration strategies. So, they require trustworthy insights from reputed consulting experts with a proven track record of overcoming challenges in data integration. The selected data partners must excel at ETL implementation, governance compliance, and data quality management (DQM).
The corporate world champions data-centric business development. Understandably, the need for scalable data integration reflects the increased stakeholder awareness regarding the importance of connecting disparate data sources. With transparent, fast, and accurate data, organizations will enhance their competitive edge amid this intense digital transformation race.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Marvel's Secret Invasion used AI-generated images to create its opening credits, which is why we're revisiting this blog from June 8th. Because, if a human didn't create the credits, does that mean Marvel can't claim copyright? Read the blog to learn about AI and the interesting legal questions it's raising 🤖
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the hot topic in every industry, as experts and commentators speculate how this rapidly evolving technology will change the future of work; and humanity.
However the water cooler exists at your job – maybe you’re playing it retro and still have an actual water cooler in your physical office – people are gathering around it to ask if you’ve tried ChatGPT yet, if AI will result in a shorter work week, or if the robots are coming for us Skynet-style. While there is nothing to suggest artificial intelligence has become sentient, the line between reality and science fiction is blurring.
Where does this leave people working in industries like video production? Will AI replace us, or will it become another tool in our utility belts?
This Just In
News headlines surrounding artificial intelligence are constantly fluctuating, and the biggest topics of conversation can be forgotten only a week later once something new eclipses it.
AI is progressing so rapidly, it’s hard for experts to say with any degree of certainty where it may take us, but that doesn’t stop everyone having an opinion on what will happen next. At the time of writing in June 2023, here is an overview of the leading artificial intelligence headlines:
Sam Altman, creator of ChatGPT, says AI poses an “existential risk” to humanity.
The United Kingdom will host the first global summit on artificial intelligence safety (date TBA).
The Beatles are back, as AI creates brand new songs from the Fab Four.
The European Union (EU) asks social media companies, including Google and Facebook, to label AI-generated content.
The latest AI trend is to expand famous paintings, creating more content but no art.
Read this article again in July and half of this will be old news. Or a reunited Beatles, half of whom are back from the grave, will become an acceptable reality. Really, it’s anyone’s guess.
Are You Sure That’s Legal?
Artificial intelligence is not entirely new in video production. AI has been used already for image manipulation and content editing. As the power of AI grows, however, it comes with the potential to create imagery from vast datasets. Seemingly making something from scratch, like a human would.

In May 2023, Adobe added an AI-powered image generator called Adobe Firefly to Photoshop. The software is promised to turn your wildest dream into an amazing image in seconds, but how is this image made? Rival software, such as Stability AI, have already faced legal action over the creation of their images. Groups like Getty Images claim Stability’s artificial intelligence generates content using existing images, or combining multiple images from the dataset its creator uploaded, which infringes their copyright.
Individuals using AI for personal use have a lot more legal freedoms than companies using AI to create images and videos for commercial use. Companies have to consider the copyright of the matter, and this is a huge ongoing debate that could take years to resolve.
As noted in the Berne Convention, an international treaty on copyright, copyright protection operates “for the benefit of the author and [their] successors in title” – the assumption being that there is a human creator. This has been affirmed in the US in the now famous “monkey selfie” dispute, during which both the Copyright Office and the courts found that animals could not hold copyright. The absence of a human creator in respect of AI-generated content therefore presents obstacles to the subsistence of copyright in the output that is generated. INFORMATION AGE, JUNE 2023
If a company uses AI to create a video, do they have ownership of it? Could the company face legal penalties if the AI is found to have used existing images and the artists’ sue, or is that a risk for the AI creator? Will users want to watch AI created content when there is such a big debate surrounding art and humanity; remember, the EU is campaigning for social media channels to put a label on AI content.
The simple answer is, we don’t know.
youtube
That’s a lot of potential legal issues and, because AI is evolving rapidly, there’s no clear answers. The earliest cases of these disputes are still ongoing, which means there’s little legal precedent to inform companies who are assessing how AI can help them with content creation.
Working with a video production company removes the uncertainty. Video production companies, like Squideo, give clients full ownership of the video once it’s created – meaning the video can be shared as widely as the company wants and, if it is replicated, the company can claim copyright.
Yet this doesn’t mean artificial intelligence has no place in the video production process whatsoever.
Judgement Day?
In 2023, 91% of businesses plan to use video as a marketing tool and 96% rate video as an ‘important part’ of their marketing strategy. There is growing demand for short videos, perfect for sharing to reels and stories on social media. Implementing AI in the video production process can speed things up and lower the cost.

ChatGPT can accelerate the scriptwriting process by providing a foundation to build upon – though it’s best not to rely entirely on AI writing generators just yet, as it’s still making a variety of mistakes. Voiceovers can be supplied by AI instead of recording artists too, as the technology has made artificial voices significantly more life-like. Although they’re less directable than voiceover artist, and not necessarily cheaper.
Video production companies like Squideo create your animated video from scratch, ensuring complete one-of-a-kindness. That doesn’t mean we can’t benefit from AI tools – but we’re not about to become obsolete either.
Ready to create a unique video of your own? Watch the video below to get a better understanding of how Squideo can help promote your business, then get in touch with us to find out more!
youtube
#marvel cinematic universe#marvel secret invasion#secret invasion#artificial intelligence#artificial intelligence artwork#ai#ai generated#ai image#ai art debate#ai artwork#ai legal#youtube#legal eagle#2d animation#animation#marketing strategy#small business#small business on tumblr#marketing#advertising#blog#Youtube
9 notes
·
View notes