#Curiosity Mars panorama
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

Mars Panorama from Curiosity
Credits: NASA, JPL-Caltech, MSSS
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Curiosity Rover postcard from Mars' Marker Band Valley

NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover used its navigation cameras to capture panoramas at two times of day on April 8, 2023, at 9:20 AM and 3:40 PM local Mars time, then merged the two images together. Blue represents the morning panorama and yellow the afternoon.
Each of these new panoramas took about 7-1/2 minutes to capture and include five individual images stitched together. By capturing the panoramas at two different times of day, the scene shows dramatic shadows similar to stage lighting coming in from the left and right of center stage. Because it was winter (when dust is at its lowest in the Martian atmosphere) at the time, shadows are sharper and deeper.
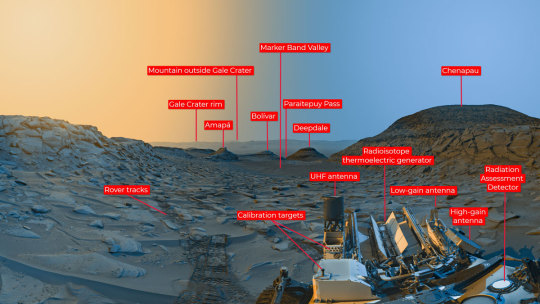
(Some annotated details from the scene.)
Curiosity is ascending the foothills of Mount Sharp, a 3-mile-tall (5km) mountain found within Gale Crater. The crater rim is visible roughly 25 miles (40 km) away. And because skies were so clear, you can see a mountain beyond the crater rim, even though it’s 54 miles (87 kilometers) outside of Gale.
NASA source page: X
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
NASA’s Curiosity Mars Rover Takes a Last Look at Mysterious Sulfur
NASA’s Curiosity rover is preparing for the next leg of its journey, a monthslong trek to a formation called the boxwork, a set of weblike patterns on Mars’ surface that stretches for miles. It will soon leave behind Gediz Vallis channel, an area wrapped in mystery. How the channel formed so late during a transition to a drier climate is one big question for the science team. Another mystery is the field of white sulfur stones the rover discovered over the summer.
Curiosity imaged the stones, along with features from inside the channel, in a 360-degree panorama before driving up to the western edge of the channel at the end of September.
The rover is searching for evidence that ancient Mars had the right ingredients to support microbial life, if any formed billions of years ago, when the Red Planet held lakes and rivers. Located in the foothills of Mount Sharp, a 3-mile-tall (5-kilometer-tall) mountain, Gediz Vallis channel may help tell a related story: what the area was like as water was disappearing on Mars. Although older layers on the mountain had already formed in a dry climate, the channel suggests that water occasionally coursed through the area as the climate was changing.
Scientists are still piecing together the processes that formed various features within the channel, including the debris mound nicknamed “Pinnacle Ridge,” visible in the new 360-degree panorama. It appears that rivers, wet debris flows, and dry avalanches all left their mark. The science team is now constructing a timeline of events from Curiosity’s observations.
The science team is also trying to answer some big questions about the sprawling field of sulfur stones. Images of the area from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) showed what looked like an unremarkable patch of light-colored terrain. It turns out that the sulfur stones were too small for MRO’s High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) to see, and Curiosity’s team was intrigued to find them when the rover reached the patch. They were even more surprised after Curiosity rolled over one of the stones, crushing it to reveal yellow crystals inside.
Science instruments on the rover confirmed the stone was pure sulfur — something no mission has seen before on Mars. The team doesn’t have a ready explanation for why the sulfur formed there; on Earth, it’s associated with volcanoes and hot springs, and no evidence exists on Mount Sharp pointing to either of those causes.
“We looked at the sulfur field from every angle — from the top and the side — and looked for anything mixed with the sulfur that might give us clues as to how it formed. We’ve gathered a ton of data, and now we have a fun puzzle to solve,” said Curiosity’s project scientist Ashwin Vasavada at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
Spiderwebs on Mars
Curiosity, which has traveled about 20 miles (33 kilometers) since landing in 2012, is now driving along the western edge of Gediz Vallis channel, gathering a few more panoramas to document the region before making tracks to the boxwork.
Viewed by MRO, the boxwork looks like spiderwebs stretching across the surface. It’s believed to have formed when minerals carried by Mount Sharp’s last pulses of water settled into fractures in surface rock and then hardened. As portions of the rock eroded away, what remained were the minerals that had cemented themselves in the fractures, leaving the weblike boxwork.
On Earth, boxwork formations have been seen on cliffsides and in caves. But Mount Sharp’s boxwork structures stand apart from those both because they formed as water was disappearing from Mars and because they’re so extensive, spanning an area of 6 to 12 miles (10 to 20 kilometers).
“These ridges will include minerals that crystallized underground, where it would have been warmer, with salty liquid water flowing through,” said Kirsten Siebach of Rice University in Houston, a Curiosity scientist studying the region. “Early Earth microbes could have survived in a similar environment. That makes this an exciting place to explore.”

NASA’s Curiosity captured this panorama using its Mastcam while heading west away from Gediz Vallis channel on Nov. 2, 2024, the 4,352nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The Mars rover’s tracks across the rocky terrain are visible at right. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS

NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover captured this last look at a field of bright white sulfur stones on Oct. 11, before leaving Gediz Vallis channel. The field was where the rover made the first discovery of pure sulfur on Mars. Scientists are still unsure exactly why theses rocks formed here. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS

Scientists think that ancient groundwater formed this weblike pattern of ridges, called boxwork, that were captured by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on Dec. 10, 2006. The agency’s Curiosity rover will study ridges similar to these up close in 202… Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona

This weblike crystalline structure called boxwork is found in the ceiling of the Elk’s Room, part of Wind Cave National Park in South Dakota. NASA’s Curiosity rover is preparing for a journey to a boxwork formation that stretches for miles on Mars’ su… Credit: NPS Photo/Kim Acker
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Video panorama of Mars from Curiosity rover. NASA.com
Music https://lesfm.net/
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
NASAs Curiosity Mars Rover Takes a Last Look at Mysterious Sulfur
The rover captured a 360-degree panorama before leaving Gediz Vallis channel, a feature it’s been exploring for the past year. NASA’s Curiosity rover is preparing for the next leg of its journey, a monthslong trek to a formation called the boxwork, a set of weblike patterns on Mars’ surface that stretches for miles. It will […] from NASA https://ift.tt/wkOtYFB
0 notes
Text
Get this! Curiosity has been on mars for 11 years!!
NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover captured this 360-degree panorama using its black-and-white navigation cameras, or Navcams, at a location where it collected a sample from a rock nicknamed “Sequoia.” The panorama was captured on Oct. 21 and 26, 2023. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Does that make us invaders or explorers? 

#mars#curiosity#nasa#panoramic#photography#space travel#space#outer space#landscape#alien#alien invasion#space exploration#space invaders#i
0 notes
Video
youtube
NASA’s Curiosity Mars Rover’s 1.8 Billion-Pixel Panorama
0 notes
Text
[ad_1] October tenth, 2023 – Los Angeles, California – Coinscribble by Coinbound What's Void 2122 // Within the ever-evolving panorama of Internet 3 gaming, a revolution was brewing. In February 2022, the founders of Void 2122 got here collectively, pushed by each frustration and a daring imaginative and prescient for the way forward for interactive leisure. The workforce noticed an trade marred by overly formidable initiatives, prolonged growth cycles, and a disconnection from the essence of enjoyable. Current video games appeared extra like speculative ventures, capitalizing on the NFT gaming hype, somewhat than delivering the fascinating experiences gamers craved. Void 2122 was the workforce’s reply, a testomony to ingenuity born from constraints. It was conceived as a card recreation, strategically tailor-made to embrace the NFT pattern whereas sustaining feasibility in growth, setting it other than grandiose 3D worlds and metaverses. On the coronary heart of Void 2122 beats what the workforce likes to name the “Three E’s”: Entertaining, Partaking, Evolving. Each side of the sport design needed to harmonize with these guiding ideas. But it surely wasn’t nearly creativity; it was about practicality. The founders knew they needed to navigate the treacherous nature of recreation growth, balancing guidelines, assets, and time to create a recreation that might endure in each gameplay and longevity. To make a recreation profitable, it primarily must be enjoyable. Hanging the fitting stability is a problem—too straightforward and gamers lose curiosity; too difficult, and solely dedicated gamers will keep. The goal was simple: create an exciting recreation the place technique is examined towards both laptop or human opponents. On this recreation, the “items” had been the celebrities. Drawing inspiration from the sport principle of famend franchises like Magic: The Gathering and Pokémon, each celebrated for his or her lasting affect on the gaming world, the founders took on a problem to refine and overhaul. Think about a world the place gamers couldn't solely select playing cards however craft them, the place the neighborhood’s creativity melded seamlessly with gameplay—a imaginative and prescient etched into the very DNA of Void 2122. In Void 2122, gamers don’t simply play the sport; they develop into part of it, shaping its evolution and sharing within the thrill of technique, wit, and camaraderie. This isn't only a recreation; it’s a testomony to the transformative energy of imaginative and prescient, innovation, and a profound love for the artwork of gaming. Welcome to Void 2122, the place the way forward for Internet 3 gaming is now. Gameplay // Void 2122 unveils a singular gameplay mechanic within the ever-changing world of Web3 gaming. Relatively than merely gathering highly effective playing cards and items, the system requires strategic planning and inventive decision-making. Gamers are invited to partake in a gaming expertise that challenges the norm and conjures up modern considering. Participant-Owned and Customized Items: Central to Void 2122 is the give attention to items that gamers personal and customise themselves. Breaking away from regular gaming limits, Void 2122 permits gamers to create and management their very own items. This added private contact makes every battle distinct and significant. Unit Upgrades and Modifications: Flexibility reigns supreme in Void 2122. Gamers possess the freedom to improve and modify their items, aligning them with their ever-evolving methods. Whether or not it’s honing skills or tailoring attributes, the scope for personalization is aware of no bounds. (coded however not activated) Unit Upgrades and Adjustments: Void 2122 presents lots of freedom. Gamers can simply replace and tweak their items to suit altering recreation plans. Whether or not it’s enhancing abilities or adjusting traits, customization choices are vast open. (coded however not activated) Create Your Personal
Items: Extra than simply tweaking, Void 2122 lets gamers and groups really make their very own items. This provides the neighborhood actual artistic energy and helps the sport develop together with its gamers. (coded however not activated) Participant-Led Story: In Void 2122, gamers aren’t simply enjoying; they’re a part of the continuing story. Lively involvement is inspired as every participant’s actions add to the general story of Void 2122. Each win and each transfer helps form the larger image. Play to Win, Not Pay to Win: The workforce stands firmly for a good and balanced gaming expertise in Void 2122. From the beginning, the sport was absolutely developed, underlining the dedication to player-centric gameplay. Right here, intelligent technique trumps pockets measurement—devoted and ingenious gamers can simply outsmart those that merely spend to amass highly effective items.Technique: With out making a gift of too many concepts and methods. Listed here are some examples. Cornering: Beginning with a unit in a nook requires defending solely two sides as an alternative of 4. Utilizing a low-level unit with two sturdy sides is a brilliant opening transfer, forcing the opponent to deploy a costlier unit to take that sector. Turtling: Turtling builds on the nook technique, aiming to ascertain sturdy defenses to dominate one aspect of the board. Brute Drive: The Brute Drive method entails utilizing items with excessive assault however low protection. This technique goals to grab a number of items every flip, tipping the stability in favor of the participant who goes second. Luck Issue: Moreover buying highly effective items and using strong methods, a component of luck provides unpredictability. With a typical deck of 26 items and a hand restrict of 5 playing cards, not each unit shall be in play. Drawing that essential card when wanted can tip the scales in a participant’s favor. NFT // Genesis NFTs: The preliminary Genesis launch of UNIT NFTs of Void 2122, shall be occurring on the Ethereum community. These NFTs are the keys to a universe of limitless potentialities. Uncommon and Outstanding Items: In these unique packs, gamers will discover not simply playing cards, however uncommon variations of the items themselves. These rarities boast the utmost beginning values for his or her particular items and are available geared up with the utmost modification slots obtainable. A Glimpse into the Previous and Future: What units these Genesis NFTs other than future releases is their age. Minted throughout the starting of Void 2122, these items will all the time have extra “expertise factors” than all future unit releases, permitting for earlier upgrades and enhancements. Pack Particulars: Every pack incorporates a meticulously curated choice of 6 playing cards, designed to raise a participant’s Void 2122 deck. Inside, gamers will uncover Two degree 1 items, Two degree 2 items, One degree 3 unit, and One Degree 4 unit, every of their rarest type, able to amplify methods. The Price of Immortality: To assert a stake in Void 2122’s historical past, every pack is priced at 0.1 ETH, offering entry to those distinctive NFTs. However act swiftly; there shall be a restricted provide of 2122 packs obtainable.Mark Your Calendar: Minting for these Genesis NFTs is about to begin on October 31, 2023. Keep tuned for the precise block quantity, which shall be introduced shortly. This is a chance to personal a bit of the longer term, the previous, and the current of Void 2122. [ad_2]
0 notes
Link
A recent study published in Nature examines how mud cracks observed on Mars by NASA’s Curiosity rover could provide insight into how life on the Red Planet could have formed in its ancient past. On Earth, mud cracks have traditionally been linked to cycles of wet and dry environments that assisted in developing the complex processes responsible for microbial life to take hold. This study was conducted by an international team of researchers and holds the potential to help scientists better understand the geological and chemical processes that might have existed in Mars’ ancient past, up to billions of years ago. “This is the first tangible evidence we’ve seen that the ancient climate of Mars had such regular, Earth-like wet-dry cycles,” said Dr. William Rapin, who is a CNRS Research Scientist at IRAP (Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie), and lead author of the study. “But even more important is that wet-dry cycles are helpful – maybe even required – for the molecular evolution that could lead to life.” For the study, the team analyzed images of mud cracks obtained from NASA’s Mars Curiosity rover, currently traversing Gale Crater on Mars, between sols 3154 to 3156 (June 20-22, 2021) when it was drilling in a rock nicknamed “Pontours”. The images reveal distinct T- and hexagonal-shaped cracks within the surface, which is indicative of many cycles of wet and dry conditions that once existed in this region. Wet conditions, such as flowing rivers or lakes, are responsible for producing the mud, but when that same mud dries out, it compresses and cracks, resulting in the broken surface we see today. For context on sols, one Martian sol equals one day on Mars, which is just under 40 minutes longer than one day on Earth. Zoomed in portion of the panorama image obtained by the Curiosity rover’s Mastcam at the rock target “Pontours” which unveils hexagonal patterns (red outlines in the same image, right) that propose these mud cracks were produced over a multitude of wet-dry cycles occurring over many years. (Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/IRAP) “These exciting observations of mature mud cracks are allowing us to fill in some of the missing history of water on Mars,” said Dr. Nina Lanza, who is principal investigator of the ChemCam instrument onboard NASA’s Curiosity rover, and a co-author on the study. “How did Mars go from a warm, wet planet to the cold, dry place we know today? These mud cracks show us that transitional time, when liquid water was less abundant but still active on the Martian surface.” The study’s findings indicate that these cracks are indicative of a transition of minerals, notably smectite clays to sulfate-bearing strata, which potentially indicates that Mars experienced an Earth-like environment during the Noachian-Hesperian transition, or 3.8 to 3.6 billion years ago. On Earth, smectite clays and sulfate-bearing strata are typically associated with aqueous environments. Also, like Earth, the Red Planet’s geologic history is divided into time periods from oldest to youngest, with those time periods being the Pre-Noachian, Noachian, Hesperian, and Amazonian and each lasting approximately from 4.5 to 4.1 billion years ago, 4.1 to 3.7 billion years ago, 3.7 to 2.9 billion years ago, and 2.9 billion years ago to the present, respectively. A panorama image taken by NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover shows a rock target nicknamed “Pontours” where researchers identified preserved, ancient mud cracks hypothesized to have shaped throughout lengthy cycles of wet and dry environments over many years. These cycles are hypothesized to support conditions where life could form. (Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/IRAP) While Mars is presently an extremely cold and dry planet that’s inhospitable for life as we know it, scientific evidence suggests things were much different billions of years ago when it first formed. This was when liquid water flowed into lakes, rivers, and oceans while volcanoes spewed gases to keep the atmosphere thick enough for this liquid water to keep cascading across the surface. Auroras danced across the sky from the solar wind interacting with the Red Planet’s magnetic field, much like we see on Earth today. But while these Earth-like conditions might have led to microbial life forming on Mars, these conditions weren’t meant to last. Artist illustration of an ancient ocean on Mars, which researchers have hypothesized contained more water than Earth’s Arctic Ocean and that the Red Planet has lost almost 90 percent of that water to space. (Credit: NASA/GSFC) Over millions of years, the interior of Mars began to cool due to its small size—half of Earth—resulting in the decreasing temperature of its molten liquid outer core which gradually reduced its geological and magnetic influence on the Red Planet. The volcanoes stopped spewing gases and the magnetic field dissipated, taking the auroras with it. Along with this, protection from the solar wind was also lost, resulting in the latter slowly stripping the planet’s atmosphere, leading to evaporation of all liquid water. In the end, Mars is the barren world we see today, without a drop of liquid water on its surface. What new discoveries will scientists make about Mars and its ancient past in the coming years and decades? Only time will tell, and this is why we science! As always, keep doing science & keep looking up! The post Ancient Cracked Mud Found on Mars appeared first on Universe Today.
0 notes
Text
NASA's Curiosity Captures Martian Morning and Evening in New 'Postcard'
El Curiosity de la NASA captura la mañana y la tarde marcianas en una nueva ‘postal’ Créditos: NASA/JPL-Caltech El rover Curiosity Mars de la NASA usó sus cámaras de navegación en blanco y negro para capturar panoramas de “Marker Band Valley” en dos momentos del día el 8 de abril. Se agregó color a una combinación de ambos panoramas para una interpretación artística de la escena. Se combinó la…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

The First Color Panorama from Mars by Curiosity
Credits: NASA, JPL-Caltech, MSSS
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text

Hello from Mars
Curiosity's 'Postcard' of 'Marker Band Valley': NASA's Curiosity Mars rover used its black-and-white navigation cameras to capture panoramas at two times of day on April 8, 2023. Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech.
1 note
·
View note
Text
NASA's Curiosity rover snaps extremely detailed 'postcard' of Martian landscape after waking up from a 'brain-boosting nap'
The new panorama snapped by NASA's Curiosity rover combines photos from two different times of day to create a highly detailed image of the Red Planet. from Livescience https://www.livescience.com/space/mars/nasas-curiosity-rover-snaps-extremely-detailed-postcard-of-martian-landscape-after-waking-up-from-a-brain-boosting-nap via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
Rover Curiosity da Nasa captura imagem impressionante da paisagem de Marte
O Rover Curiosity Mars da NASA capturou um impressionante novo mosaico que revela os tons dramáticos e coloridos da luz da manhã e da tarde na superfície de Marte. O explorador robótico usou suas câmeras de navegação em preto e branco para tirar fotos panorâmicas do Marker Band Valley em 8 de abril antes de deixar o local. Um panorama foi obtido às 9h20, enquanto o outro foi obtido às 15h40,…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
NASA Curiosity Rover Sends Home New Photo as it Climbs Martian Slope
[ad_1]

The ‘Martian selfie’ taken by NASA Curiosity rover, stitched together from 86 photos. (Photo: NASA/JPL)
After its epic 1.8-gigapixel panorama of the desolate Martian surface, Curiosity scaled a 31-degree slope of the Greenheugh Pediment before taking this photo.
News18.com
Last Updated: March 25, 2020, 12:42 PM IST
NASA’s Curiosity rover has sent us yet another…
View On WordPress
#Curiosity#Curiosity Mars panorama#Curiosity Mars rover#curiosity mars selfie#Curiosity Martian panorama#Curiosity rover#curiosity rover landing#curiosity rover selfie#curiosity selfie#curiosityselfie#handshake nasa mars#martian selfie#nasa#nasa curiosity#NASA Curiosity Rover#nasa mars#nasa mars 2020#NASA Mars 2020 Rover#nasa mars landing#NASA Mars Mission#NASA Mars photo#nasa mars rover
0 notes