#Contemporary English Version
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Fear Not
When I saw him, I fell at his feet like a dead person. But he put his right hand on me and said: Don't be afraid! I am the first, the last — Revelation 1:17 | Contemporary English Version (CEV) Contemporary English Version Copyright © 1995 by American Bible Society. Cross References: Exodus 3:6; Isaiah 51:4; Isaiah 44:6; Isaiah 48:12; Ezekiel 1:28; Daniel 8:17-18
Read full chapter
Revelation 1:17 - Verse-by-Verse Bible Commentary
#terror#submission#do not fear#the First and the Last#Revelation 1:17#Book of Revelation#New Testament#CEV#Contemporary English Version#American Bible Society
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
happy week of tests day 2 today they're gonna make us read and analyse a text from the puritan movement in 17th century unadulterated english fingers crossed i can understand it
#test lasts 6 hours too god..... yesterday was 7h and i actually used 6h55 of that time#i dont understand why they wouldn't give us the contemporary english version of that text so that we may understand something#NOOOOO#pure unadulterated transcription of old manuscripts with missing letters and everything#p
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reading Tolkien’s annotated translation of Beowulf, and learning all kinds of things about LOTR and the Silm from it!
First:
Leave here your warlike shields [from Beowulf]
[Tolkien’s commentary; bold mine:] Note the prohibition of weapons or accoutrements of battle in the hall. To walk in with spear and shield was like walking in nowadays with your hat on. The basis of these rules was of course fear and prudence among the ever-present dangers of a heroic age, but they were made part of the ritual, of good manners. Compare the prohibition against drawing a sword in the officers’ mess. Swords of course also were dangerous; but they were evidently regarded as part of a knight’s attire, and he would not in any case be willing to lay aside his sword, a thing of great cost and often an heirloom.
This gives me some perspective around Tolkien’s probable intended tone for the moment in Meduseld in The Two Towers where Aragon strongly protests against being told to leave Andúril (a sword of very great value and ancientry, and very much an heirloom) with the door-warden. From a contemporary perspective it’s easy to read it as Aragorn being unnecessarily prideful and combative, but this passage strongly indicates that Tolkien intends it to be Théoden who is being unreasonable in that event, an indication - along with many others in the scene, prior to Gandalf dislodging Saruman’s influence - that Théoden is being discourteous and behaving in a manner unworthy of a king who is recieving heroes offering aid. (The fact of Meduseld being a ‘golden hall’ like famous Heorot in Beowulf may be deliberate to strengthen the parallel.)
Second (immediately following the above commentary):
But against this danger [from swords] very severe laws existed protecting the ‘peace’ of a king’s hall. It was death in Scandanavia to cause a brawl in the king’s hall. Among the laws of the West Saxon king Ine is found: ‘If any man fight in the king’s house, he shall forfeit all his estate, and it shall be for the king to judge whether he be put to death or not.’
This adds context to the incident in the story of Túrin in The Silmarillion where Saeros taunts Túrin in Menegroth and Túrin responds by throwing a heavy drinking-vessel at him and injuring him (it’s indicated the injury is serious, so I’d take it along the lines of him giving him a broken nose and knocking out some teeth.) It is stated in at least some versions of the story that death is the punishment for drawing weapons in the king’s hall, in line with the historical customs mentioned here. This gives a further emphasis that what actually happens - Túrin is not punished at all and Mablung strongly reprimands Saeros for provoking him - illustrates that Túrin is, Saeros’ behaviour notwithstanding, in very high favour in Menegroth. (Saeros as the king’s counsellor is also in roughly the same position as Unferth in Beowulf, who taunts the titular character - Beowulf responds heatedly but without violence. Tolkien may be setting up a deliberate contrast here.)
Third:
The word hádor is an adjective meaning ‘clear, bright’…it is almost always found in reference to the sky (or the sun or stars). But that association is in description of brightness…
This was one a lightbulb moment: oh, in the name of Hador Goldenhead (the ancestor of Húrin, Túrin, and Tuor in The Silmarillion), ‘Goldenhead’ isn’t an additional name/epessë so much as it’s a glossed translation of ‘Hador’! The guy with bright, golden hair.
Fourth: Going back to the Rohirrim - Edoras, the name of their capital city/royal court, is basically just the Old English for ‘courts’:
under was very frequently used in describing position within, or movement to within, a confined space, especially of enclosures or prisons, ‘within four walls’. Cf. in under eoderas (eoderas being the outer fences of the courts), ‘in amid the courts’….‘eoder’ means both ‘fence (protection)’ and ‘fenced enclosure, a court’.
I’m also learning a lot about Beowulf - Tolkien’s notes are clarifying a lot of tone and nuances, not to mention the political/diplomatic relationships between the different kingdoms, which were confusing me - but it’s amazing how much it reveals about ways that Tolkien’s knowledge informed his legendarium!
#tolkien#the silmarillion#the lord of the rings#rohan#aragorn#theoden#turin#hador#edain#beowulf#translation
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
At the outset of H. G. Wells’s The War of the Worlds (1898), Wells asks his English readers to compare the Martian invasion of Earth with the Europeans’ genocidal invasion of the Tasmanians, thus demanding that the colonizers imagine themselves as the colonized, or the about-to-be-colonized. But in Wells this reversal of perspective entails something more, because the analogy rests on the logic prevalent in contemporary anthropology that the indigenous, primitive other’s present is the colonizer’s own past. Wells’s Martians invading England are like Europeans in Tasmania not just because they are arrogant colonialists invading a technologically inferior civilization, but also because, with their hypertrophied brains and prosthetic machines, they are a version of the human race’s own future.
The confrontation of humans and Martians is thus a kind of anachronism, an incongruous co-habitation of the same moment by people and artifacts from different times. But this anachronism is the mark of anthropological difference, that is, the way late-nineteenth-century anthropology conceptualized the play of identity and difference between the scientific observer and the anthropological subject-both human, but inhabiting different moments in the history of civilization. As George Stocking puts it in his intellectual history of Victorian anthropology, Victorian anthropologists, while expressing shock at the devastating effects of European contact on the Tasmanians, were able to adopt an apologetic tone about it because they understood the Tasmanians as “living representatives of the early Stone Age,” and thus their “extinction was simply a matter of … placing the Tasmanians back into the dead prehistoric world where they belonged” (282-83). The trope of the savage as a remnant of the past unites such authoritative and influential works as Lewis Henry Morgan’s Ancient Society (1877), where the kinship structures of contemporaneous American Indians and Polynesian islanders are read as evidence of “our” past, with Sigmund Freud’s Totem and Taboo (1913), where the sexual practices of “primitive” societies are interpreted as developmental stages leading to the mature sexuality of the West. Johannes Fabian has argued that the repression or denial of the real contemporaneity of so-called savage cultures with that of Western explorers, colonizers, and settlers is one of the pervasive, foundational assumptions of modern anthropology in general. The way colonialism made space into time gave the globe a geography not just of climates and cultures but of stages of human development that could confront and evaluate one another.
The anachronistic structure of anthropological difference is one of the key features that links emergent science fiction to colonialism. The crucial point is the way it sets into motion a vacillation between fantastic desires and critical estrangement that corresponds to the double-edged effects of the exotic. Robert Stafford, in an excellent essay on “Scientific Exploration and Empire” in the Oxford History of the British Empire, writes that, by the last decades of the century, “absorption in overseas wilderness represented a form of time travel” for the British explorer and, more to the point, for the reading public who seized upon the primitive, abundant, unzoned spaces described in the narratives of exploration as a veritable “fiefdom, calling new worlds into being to redress the balance of the old” (313, 315). Thus when Verne, Wells, and others wrote of voyages underground, under the sea, and into the heavens for the readers of the age of imperialism, the otherworldliness of the colonies provided a new kind of legibility and significance to an ancient plot. Colonial commerce and imperial politics often turned the marvelous voyage into a fantasy of appropriation alluding to real objects and real effects that pervaded and transformed life in the homelands. At the same time, the strange destinations of such voyages now also referred to a centuries-old project of cognitive appropriation, a reading of the exotic other that made possible, and perhaps even necessary, a rereading of oneself.
John Rieder, Colonialism and the Emergence of Science Fiction
#words#hg wells#fiction#science fiction#colonialism and the emergence of science fiction#john rieder
471 notes
·
View notes
Text
L's Apple Computers
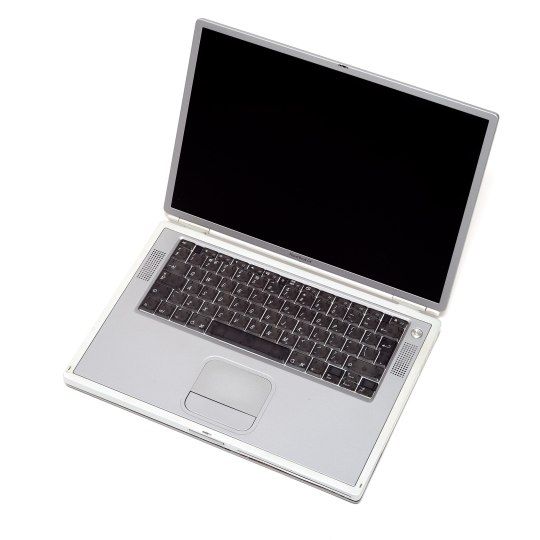
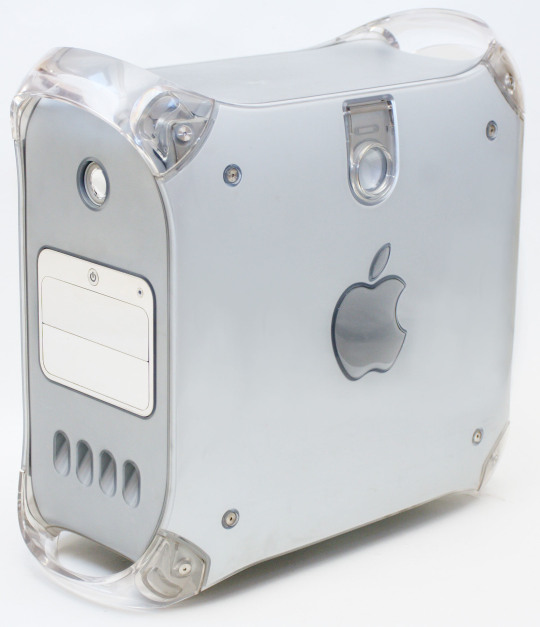
death note is now twenty years old & the anime replaced the logos with generic knockoffs so it's no longer visually obvious that L's computers are macs but he is canonically an apple user. i've decided to gather up all this incredibly vital information about which specific devices he uses. his computers his laptop is a powerbook g4 titanium. his desktop is the powermac g4 mirrored drive doors version.
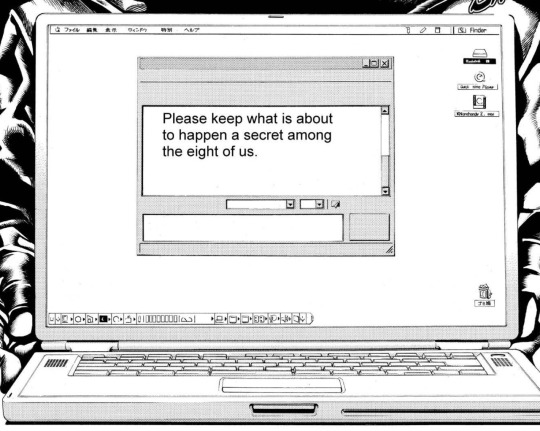



his operating systems for some reason, he is using a different OS on his laptop and desktop. both his computer models came pre-installed with Mac OS and macOS (then called OS X) in a dual-boot configuration. Mac OS is the classic line of operating systems; macOS is the current one. on his laptop, he's running one of the the classic Mac OS systems. this would most likely have been OS 9, as that was the version installed on the g4 laptops. macOS/OS X was the default option, so this was an active choice he made. he has his language set to japanese.
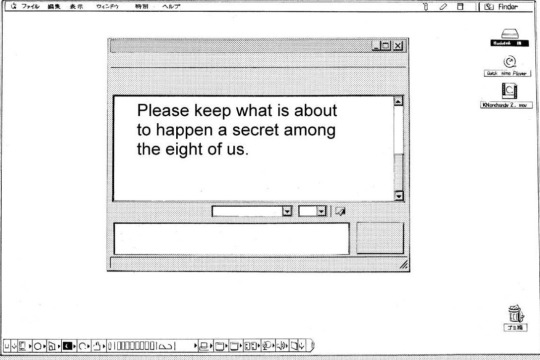

on his desktop, however, he's using the more contemporary macOS/OS X in english. (this also suggests english is the language he's more comfortable in, since the desktop is the one no one else sees.) these are a bit more difficult to visually distinguish, but it's probably panther, which would have been the contemporary one, since previous versions didn't have borders around their windows. he's got the dock collapsed, which was a built-in option.

398 notes
·
View notes
Text
Limahl - The NeverEnding Story 1984
"The NeverEnding Story" is the title song from the English version of the 1984 film The NeverEnding Story. It was produced and composed by Italian musician Giorgio Moroder and performed by English pop singer Limahl. He released two versions of the song, one in English and one in French. The English version featured vocals by Beth Andersen, and the French version, "L'Histoire Sans Fin", featured vocals by Ann Calvert. It was a success in many countries, reaching #1 in both Norway and Sweden, #2 in Austria, West Germany and Italy, #4 in the UK, #6 in Australia and on the US Billboard Adult Contemporary chart. The song was composed by Giorgio Moroder with lyrics by Keith Forsey, though it (and other electronic pop elements of the soundtrack) is not present in the German version of the film, which features Klaus Doldinger's orchestral score exclusively. In the final episode of the third season of Stranger Things, set in 1985, "The NeverEnding Story" is sung by Dustin and his long-distance girlfriend Suzie as a way to reconnect after not seeing each other for some time. Following the season's release on July 4, 2019, interest in "The NeverEnding Story" surged; viewership of the original music video had increased by 800% within a few days according to YouTube (not linked to here), while Spotify reported an 825% increase in stream requests for the song. It recieved a total of 68,2% yes votes!
youtube
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Liberals say a lot of dumb shit, but if you're going to bother critiquing it then you need to understand what they're trying to say in the first place. Like "Late Stage Capitalism" isn't an especially useful or coherent term, but you can't dismiss it with "just say Imperialism" because that is very obviously not what people are talking about when they use it. Even just by contemporary usage, you should notice how it's nearly always employed by people complaining about declining quality of life (i.e. cuts to social safety nets, reduced domestic regulations, growing mismatch between costs of living and wages) within the Imperial Core. You never hear left liberals use it to discuss even the most obviously evil manifestations of Imperialism (i.e. coups and election subversion, "unjust" invasions, dropping napalm on children etc.) that even they are willing to criticise sometimes. In the contemporary discourse, it's functionally just a way to critique Neoliberalism by comparing it to Social Democracy- both are still equally Imperialist systems. Like "The Highest Stage of Capitalism" is consistently used by ML to mean imperialism, while "Late Stage Capitalism" is mostly used by Liberals to complain about getting an insufficient share of the loot.
There's also a need to consider that the idea of "Late Stage Capitalism" wasn't even popularised by left liberals; they merely adopted it and became its most enthusiastic users/abusers. The original use of the term "Late Capitalism" was in the early 20th century by reactionary (but Marxist influenced) German sociologist Werner Sombart to describe the state of capitalism in his time. However, by the 1960s it was most popular among members of the Frankfurt school of Marxism when discussing the features of the Post WW2 era. Its first popular use in English was in the 1975 translation of the thesis Late Capitalism by Belgian Trotskyist Ernest Mandel, but the person who popularised it the most was probably USamerican Marxist Frederic Jameson. He used it in his 1991 essay "Postmodernism or the Cultural Logic of Late Capitalism, which effectively engaged in the sort of "society has become soooo superficial and consumerist" critique that liberals are happy to eat up. This implanted the phrase firmly in the heads of Anglophone Imperial-Core Left Liberals and adjacent revisionists, and by the 2010s as more and more people were drawn into that whole milieu ("became radicalised" as they like to put it) the phrase spread and spread and now you see it everywhere in any vaguely "leftist" space.
Now this whole summary isn't an attempt to defend the phrase by discussing its pedigree; I don't think it was ever a very good or useful phrase and that developments in global capitalism can be discussed without declaring the dawn of a new epoch based on a disconnected jumble of often superficial changes. My point is that the phrase has a whole history of its own; it's not something that got thoughtlessly made up one day and any meaningful critique of the phrase has to consider this. You need to meet people where they are at, based on what they're actually saying and not what it roughly sounds like they're saying. When you treat "Late Stage Capitalism" as just the Liberal version of "Highest Stage of Capitalism" because the two phrases sound kinda similar, it's criticism of the most superficial and idealist type. In your attempt to "pwn the liberals", you've ended up talking like one
#stella speaks#I've linked to essays about the works rather than the works in question because#A. I haven't personally read them I'm just tracing the way they use a particular phrase and#B. I'm not especially concerned with the works themselves but rather their context and impact#I don't especially care for any of them so track them down yourself if you want but I'm not inclined to help lmao
189 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think it's so fucking clever that Hozier put Jackie & Wilson and Someone New back to back in his self-titled album. I mean, they're two ends of the same situationship and depict so well the current dating culture in general. Jackie & Wilson is that needy, hopeless, lonesome state where u just really long for companionship, connection, and stability. It doesn't matter with whom, it doesn't matter where, it doesn't matter how. Every person who crosses your path seems the one because you craft an idealized version of them in your mind. On the other hand, Someone New, besides keeping partially the idealizing strangers theme, goes for a more hedonistic route. It rejects the prospect of a stable relationship that leads to the traditional path of marriage and family in favor of exploration, the pleasures of the flesh (not necessarily only sex), adventure, and excitement. Yet it gets even more interesting if you consider that the persona is the same in both songs, but in different moments of their life (we all have been in both positions at least once). It beautifully captures how the experience of being a young adult is so much different than it once was. It brings up the contemporary developmental psychology that rejects that view of adulthood as the absolute end of development.
I particularly like to think about these songs through the concept of emerging adulthood and how, due to the cultural and economic changes of our times, the self-exploration, construction of identity, and the "not really knowing what you wanna do with your life", that is usually expected only in adolescence, stays with us for longer nowadays. We're always changing, we'll be always developing till the day we die, and developing doesn't necessarily mean going forward.
Sometimes we take a few steps back, and that's completely okay. We can be Jackie & Wilson one day, Someone New the next one and then Jackie & Wilson all over again. So in this essay, I will discuss Hozier's discography through the views of contemporary developmental psychology and the common themes with 20th century Latin American poetry…
(My grammar in English is not the best, but I swear I'm not that illiterate in my first language)
#the hoziest#andrew hozier byrne#hozier#psychology#wasteland baby#unreal unearth#in this essay i will#can i make a thesis on hozier's discography alone?#literature
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cross-posting an essay I wrote for my Patreon since the post is free and open to the public.

Hello everyone! I hope you're relaxing as best you can this holiday season. I recently went to see Miyazaki's latest Ghibli movie, The Boy and the Heron, and I had some thoughts about it. If you're into art historical allusions and gently cranky opinions, please enjoy. I've attached a downloadable PDF in the Patreon post if you'd prefer to read it that way. Apologies for the formatting of the endnotes! Patreon's text posting does not allow for superscripts, which means all my notations are in awkward parentheses. Please note that this writing contains some mild spoilers for The Boy and the Heron.

Hayao Miyazaki’s 2023 feature animated film The Boy and the Heron reads as an extended meditation on grief and legacy. The Master of a grand tower seeks a descendant to carry on his maddening duty, balancing toy blocks of magical stone upon which the entire fabric of his little pocket of reality rests. The world’s foundations are frail and fleeting, and can pass away into the cold void of space should he neglect to maintain this task. The Master’s desire to pass the torch undergirds much of the film’s narrative.

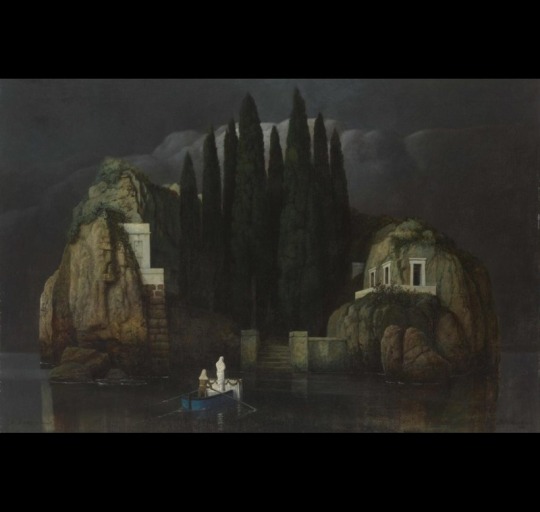
(Isle of the Dead. Arnold Böcklin. 1880. Oil on Canvas. Kunstmuseum. Basel, Switzerland.)
Arnold Böcklin, a Swiss Symbolist(1) painter, was born on October 16 in 1827, the same year the Swiss Evangelical Reformed Church bought a plot of land in Florence from the Grand Duke of Tuscany, Leopold II, that had long been used for the burials of Protestants around Florence. It is colloquially known as The English Cemetery, so called because it was the resting place of many Anglophones and Protestants around Tuscany, and Böcklin frequented this cemetery—his workshop was adjacent and his infant daughter Maria was buried there. In 1880, he drew inspiration from the cemetery, a lone plot of Protestant land among a sea of Catholic graveyards, and began to paint what would be the first of six images entitled Isle of the Dead. An oil on canvas piece, it depicts a moody little island mausoleum crowned with a gently swaying grove of cypresses, a type of tree common in European cemeteries and some of which are referred to as arborvitae. A figure on a boat, presumably Charon, ferries a soul toward the island and away from the viewer.
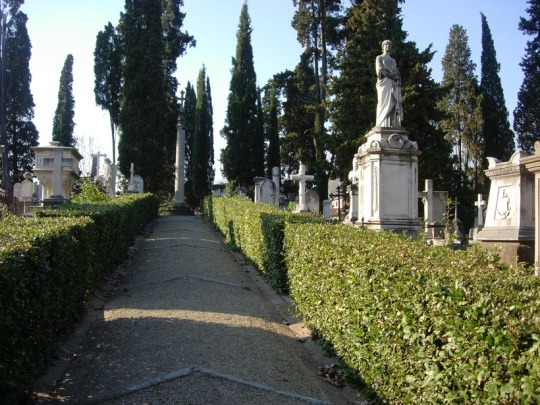

(Photo of The English Cemetery in Florence. Samuli Lintula. 2006.)
The Isle of the Dead paintings varied slightly from version to version, with figures and names added and removed to suit the needs of the time or the commissioner. The painting was glowingly referenced and remained fairly popular throughout the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The painting used to be inescapable in much of European popular culture. Professor Okulicz-Kozaryn, a philologist (someone with a deep interest in the ways language and cultural canons evolve)(2) observed that the painting, like many other works in its time, was itself iterative and became widely reiterated and referenced among its contemporaries. It became something like Romantic kitsch in the eyes of modern art critics, overwrought and excessively Byronic. I imagine Miyazaki might also resent a work of that level of manufactured ubiquity, as Miyazaki famously held Disney animated films in contempt (3). Miyazaki’s films are popularly aspirational to young animators and cartoonists, but gestures at imitation typically fall well short, often reducing Miyazaki’s weighty films to kitschy images of saccharine vibes and a lazy indulgence in a sort of empty magical domestic coziness. Being trapped in a realm of rote sentiment by an uncritical, unthoughtful viewership is its own Isle of Death.

(Still from The Boy and the Heron, 2023. Studio Ghibli.)
The Boy and the Heron follows a familiar narrative arc to many of Miyazaki’s other films: a child must journey through a magical and quietly menacing world in order to rescue their loved ones. This arc is an echo of Satsuki’s journey to find Mei in My Neighbor Totoro (1988) and Chihiro’s journey to rescue her parents Spirited Away (2001). To better understand Miyazaki’s fixation with this particular character journey, it can be instructive to watch Lev Atamanov’s 1957 animated film, The Snow Queen (4)(5), a beautifully realized take on Hans Christian Andersen’s 1844 children’s story (6)(7). Mahito’s journey continues in this tradition, as the boy travels into a painted world to rescue his new stepmother from a mysterious tower.
Throughout the film, Miyazaki visually references Isle of the Dead. Transported to a surreal world, Mahito initially awakens on a little green island with a gated mausoleum crowned with cypress trees. He is accosted by hungry pelicans before being rescued by a fisherwoman named Kiriko. After a day of catching and gutting fish, Mahito wakes up under the fisherwoman’s dining table, surrounded by kokeshi—little wooden dolls—in the shapes of the old women who run Mahito’s family’s rural household. Mahito is told they must not be touched, as the kokeshi are wards set up for his protection. There is a popular urban legend associated with the kokeshi wherein they act as stand-ins for victims of infanticide, though there seems to be very little available writing to support this legend. Still, it’s a neat little trick that Miyazaki pulls, placing a stray reference to a local legend of unverifiable provenance that persists in the popular imagination, like the effect of fairy stories passed on through oral retellings, continually remolded each new iteration.

(Still from The Boy and the Heron, 2023. Studio Ghibli.)
Kiriko’s job in this strange landscape is to catch fish to nourish unborn spirits, the adorable floating warawara, before they can attempt to ascend on a journey into the world of the living. Their journey is thwarted by flocks of supernatural pelicans, who swarm the warawara and devour them. This seems to nod to the association of pelicans with death in mythologies around the world, especially in relationship to children (8). Miyazaki’s pelicans contemplate the passing of their generations as each successive generation seems to regress, their capacity to fulfill their roles steadily diminishing.

(Still from The Boy and the Heron, 2023. Studio Ghibli.)
As Mahito’s adventure continues, we find the landscapes changing away from Böcklin’s Isle of the Dead into more familiar Ghibli territories as we start to see spaces inspired by one of Studio Ghibli’s aesthetic mainstays, Naohisa Inoue and his explorations of the fantasy realms of Iblard. He might be most familiar to Ghibli enthusiasts as the background artists for the more fantastical elements of Whisper of the Heart (1995).

(Naohisa Inoue, for Iblard Jikan, 2007. Studio Ghibli.)
By the time we arrive at the climax of The Boy and the Heron, the fantasy island environment starts to resemble English takes on Italian gardens, the likes of which captivated illustrators and commercial artists of the early 20th century such as Maxfield Parrish. This appears to be a return to one of Böcklin’s later paintings, The Island of Life (1888), a somewhat tongue-in-cheek reaction to the overwhelming presence of Isle of the Dead in his life and career. The Island of Life depicts a little spot of land amid an ocean very like the one on which Isle of the Dead’s somber mausoleum is depicted, except this time the figures are lively and engaged with each other, the vegetation lush and colorful, replete with pink flowers and palm fronds.

(Island of Life. Arnold Böcklin. Oil on canvas. 1888. Kunstmuseum. Basel, Switzerland.)
In 2022, Russia’s State Hermitage Museum in Saint Petersburg acquired the sixth and final Isle of the Dead painting. In the last year of his life, Arnold Böcklin would paint this image in collaboration with his son Carlo Böcklin, himself an artist and an architect. Arnold Böcklin spent three years painting the same image three times over at the site of his infant daughter’s grave, trapped on the Isle of the Dead. By the time of his death in 1901 at age 74, Böcklin would be survived by only five of his fourteen children. That the final Isle of the Dead painting would be a collaboration between father and son seemed a little ironic considering Hayao Miyazaki’s reticence in passing on his own legacy. Like the old Master in The Boy and the Heron, Miyazaki finds himself with no true successors.
The Master of the Tower's beautiful islands of painted glass fade into nothing as Mahito, his only worthy descendant, departs to live his own life, fulfilling the thesis of Genzaburo Yoshino’s 1937 book How Do You Live?, published three years after Carlo Böcklin’s death. In evoking Yoshino and Böcklin’s works, Hayao Miyazaki’s The Boy and the Heron suggests that, like his character the Master, Miyazaki himself must make peace with the notion that he has no heirs to his legacy, and that those whom he wished to follow in his footsteps might be best served by finding their own paths.

(Isle of the Dead. Arnold and Carlo Böcklin. Oil on canvas. 1901. The State Hermitage Museum. Saint Petersburg, Russia.)
INFORMAL ENDNOTES
1 - Symbolists are sort of tough to nail down. They were started as a literary movement to 1 distinguish themselves from the Decadents, but their manifesto was so vague that critics and academics fight about it to this day. The long and the short of it is that the Symbolists made generous use of a lot of metaphorical imagery in their work. They borrow a lot of icons from antiquity, echo the moody aesthetics from the Romantics, maintained an emphasis on figurative imagery more so than the Surrealists, and were only slightly more technically married to the trappings of traditionalist academic painters than Modernists and Impressionists. They're extremely vibes-forward.
2 - Okulicz-Kozaryn, Radosław. Predilection of Modernism for Variations. Ciulionis' Serenity among Different Developments of the Theme of Toteninsel. ACTA Academiae Artium Vilnensis 59. 2010. The article is incredibly cranky and very funny to read in parts. Contains a lot of observations I found to be helpful in placing Isle of the Dead within its context.
3 - "From my perspective, even if they are lightweight in nature, the more popular and common films still must be filled with a purity of emotion. There are few barriers to entry into these films-they will invite anyone in but the barriers to exit must be high and purifying. Films must also not be produced out of idle nervousness or boredom, or be used to recognise, emphasise, or amplify vulgarity. And in that context, I must say that I hate Disney's works. The barrier to both the entry and exit of Disney films is too low and too wide. To me, they show nothing but contempt for the audience." from Miyazaki's own writing in his collection of essays, Starting Point, published in 2014 from VIZ Media.
4 - You can watch the movie here in its original Russian with English closed captions here.
5 If you want to learn more about the making of Atamanoy's The Snow Queen, Animation Obsessive wrote a neat little article about it. It's a good overview, though I have to gently disagree with some of its conclusions about the irony of Miyazaki hating Disney and loving Snow Queen, which draws inspiration from Bambi. Feature film animation as we know it hadonly been around a few decades by 1957, and I find it specious, particularly as a comic artistand author, to see someone conflating an entire form with the character of its content, especially in the relative infancy of the form. But that's just one hot take. The rest of the essay is lovely.
6 - Miyazaki loves this movie. He blurbed it in a Japanese re-release of it in 2007.
7 - Julia Alekseyeva interprets Princess Mononoke as an iteration of Atamanov's The Snow Queen, arguing that San, the wolf princess, is Miyazaki's homage to Atamanoy's little robber girl character.
8 - Hart, George. The Routledge Dictionary of Egyptian Gods And Goddesses. Routledge Dictionaries. Abingdon, United Kingdom: Routledge. 2005.
#hayao miyazaki#the boy and the heron#how do you live#arnold böcklin#carlo böcklin#symbolists#symbolism#animation#the snow queen#lev atamanov#naohisa inoue#the endnotes are very very informal aksjlsksakjd#sorry to actual essayists
525 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Soul who Sins will Die
Just as we will die because of Adam, we will be raised to life because of Christ.
Because I do not have pleasure in the death of a dead person, says THE LORD OF LORDS, but return and live. — 1 Corinthians 15:21 and Ezekiel 18:32 | Contemporary English Version (CEV) and Aramaic Bible in Plain English (ABPE) The Holy Bible, Contemporary English Version Copyright © 1995 by American Bible Society and The Aramaic Bible in Plain English 8th edition; Copyright © 2013 All rights reserved. Cross References: Job 37:23; Isaiah 31:6; Ezekiel 18:23; Ezekiel 33:11; Romans 5:12; Romans 5:17; 1 Timothy 2:4
#Adam#sin#death#Jesus Christ#resurrection#eternal life#God#repent#repentance#return#Lord of Lords#1 Corinthians 15:21#Ezekiel 18:32#Old Testament#New Testament#CEV#Contemporary English Version#Aramaic Bible in Plain English#ABPE#American Bible Society#Holy Bible
9 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi,
I am very much not american so I must admit that my first impulse when seeing all the rap/racism discourse was something like "do I really need to consume more american culture, it's fucking everywhere already". Idk but to me it feels like american/english-speaking culture absolutely dominates a lot of the world, sometimes at the cost of out own cultures and languages, if something is in English it is "good", if it is in own own languages it is "bad". Musicians often start singing in English and more american-like after a while to get bigger. We value American culture and music, they mock our accents (and languages sometimes) and best case scenario see us as funny and silly.
Then I started thinking. Do you think that americans kind of see rap kind of like foreign music still? Like low-brow unexotic foreign music.
I don't know this is a really fresh thought and I'm not sure if I am explaining it very well.
hey first off I just want to say -
you are entirely correct in your reaction that people outside of America/the English-speaking world do not need more American culture thrust upon them! this discussion is extremely centered on Americans, the reception and reaction to rap within America, and excuses that white American use to avoid interacting meaningfully with Black culture, art, and ideas. while anti-Blackness as an issue obviously extends far outside of America, this particular conversation is deeply tied to American culture. I appreciate you pointing that out!
I also think you're point about rap, and by extension other Black artforms, being Othered in American pop culture. certainly in terms of language, African American Vernacular English (AAVE), which is utilized by many rappers, is still heavily disputed in its validity as a "real" language, with many dismissing it as a bastardized version of "proper" English and associating it heavily with those who are lower-class and uneducated. in a similar way to many international artists having to work in English to gain wider recognition and validation, many Black Americans are proficient in "code switching," the practice of switching between AAVE that they likely grew up speaking and an English dialect that is considered more "professional."
similarly, I think your use of the term "low-brow" is very apt. Black music has always been met with distrust and disdain by white audiences. there's a reason that so many people feel the need to bring up sex, drugs, and violence when they talk about rap; to many white cultural gatekeepers that was all rap was. (and, like, we should very much talk about why that is in and of itself a bad thing, when white crime is so often glorified in pop culture. why is the Godfather a classic masterpiece but Black men making art about their own experiences with racism, violence, poverty, and survival don't deserve serious consideration?) and that didn't start with rap! in the early 20th century jazz, also a Black creation, was seen as dangerous for promoting promiscuity among nice white teens. no matter what Black people make, white cultural gatekeepers will find a way to start a moral panic about it.
the reverse also happens as well, with Black people being treated as foreigners even in music genres that they helped pioneer. Black Americans were hugely formative in the early days of country, but are met with hostility in the contemporary country scene. Lil Nas X's Old Town Road was one of the biggest songs of the year it was released and undeniably country but was largely snubbed by country music community, and Beyoncé's new country album, Cowboy Carter, is a direct response to her hostile reception at the Country Music Awards in 2016.
the point being, yes, I don't think it's off-base to say that, to many Americans, rap and Black music and art generally are like... very optional and avoidable parts of pop culture in the way that more white-dominated genres are not, similarly to a lot of international and especially non-English art.
194 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hamlet’s Age
Not to bring up an age-old debate that doesn’t even matter, but I have been thinking recently how interesting Hamlet’s age is both in-text and as meta-text.
To summarize a whole lot of discussion, we basically only have the following clues as to Hamlet’s age:
Hamlet and Horatio are both college students at Wittenberg. In Early Modern/Late Renaissance Europe, noble boys typically began their university education at 14 and usually completed at their Bachelor’s degree by 18 or 19. However, they may have been studying for their Master’s degrees, which was typically awarded by age 25 at the latest. For reference, contemporary Kit Marlowe was a pretty late bloomer who received a bachelor’s degree at 20 and a master’s degree at 23.
Hamlet is AGGRESSIVELY described as a “youth” by many different characters - I believe more than any other male shakespeare character (other than 16yo Romeo). While usage could vary, Shakespeare tended to use “youth” to mean a man in his late teens/very early 20s (actually, he mostly uses it to describe beardless ‘men’ who are actually crossdressing women - likely literally played by young men in their late teens)
King Hamlet is old enough to be grey-haired, but Queen Gertrude is young enough to have additional children (or so Hamlet strongly implies)
Hamlet talks about plucking out the hairs of his beard, so he is old enough to at least theoretically have a beard
In the folio version, the gravedigger says he became a gravedigger the day of Hamlet’s birth, and that he’s be “sixteene here, man and boy, thirty years.” However, it’s unclear if “sixteene” means “sixteen” or “sexton” (ie has he worked here for 16 years but is 30 years old, or has he been sexton there for thirty years?)
Hamlet knew Yorick as a young child, and the gravedigger says Yorick was buried 23 years ago. However, the first quarto version version of Hamlet says “dozen years” instead of “three and twenty.” This suggests the line changed over time. (Or that the bad quarto sucks - I really need to make that post about it, huh…)
Yorick is a skull, and according to the gravedigger’s expertise, he has thus been dead for at least 7-8 years - implying Hamlet is at least ~15yo if he remembers Yorick from his childhood
One important thing sometimes overlooked - Claudius takes the throne at King Hamlet’s death, not Prince Hamlet. That is mostly a commentary on English and French monarchist politics at the time, but it is strange within the internal text. A thirty year old Hamlet presumably would have become the new monarch, not the married-in uncle (unless Gertrude is the vehicle through which the crown passes a la Mary I/Phillip II - certainly food for thought)
Honestly, Hamlet is SO aggressively described as being very young that I’m fairly confident the in-text intention is to have him be around 18-23yo. Placing his age at 30yo simply does not make much sense in the context of his descriptors, his narrative role, and his status as a university student.
However, it doesn’t really matter what the “right” answer is, because the confusion itself is what makes the gravedigger scene so interesting and metatextual. We can basically assume one of the following, given the folio text:
Hamlet really is meant to be 30yo, and that was supposed to surprise or imply something to the contemporary audience that is now lost to us
Older actors were playing Hamlet by the time the folio was written down, and the gravedigger’s description was an in-text justification of the seeming disconnect between age of actor and description of “youth”
Older actors were playing Hamlet by the time the folio was set down, and the gravedigger’s description was an in-text JOKE making fun of the fact that a 30-something year old is playing a high-school aged boy. This makes sense, as the gravedigger is a clown and Hamlet is a play that constantly pokes fun at its own tropes and breaks the fourth wall for its audience
The gravedigger cannot count or remember how old he is, and that’s the joke (this is the most common modern interpretation whenever the line isn’t otherwise played straight). If the clown was, for example, particularly old, those lines would be very funny
Any way you look at it, I believe something is echoing there. It seems like this is one of the many moments in Hamlet where you catch a glimpse of some contemporary in-joke about theater and theater culture* that we can only try to parse out from limited context 430 years later. And honestly, that’s so interesting and cool.
*(My other favorite example of this is when Hamlet asks Polonius about what it was like to play Julius Caesar in an exchange that pokes fun of Polonius’ actor a little. This is clearly an inside-joke directed at Globe regulars - the actor who played Polonius must have also played Julius Caesar in Shakespeare’s play, and been very well reviewed. Hamlet’s joke about Brutus also implies the actor who played Brutus is one of the main cast in Hamlet - possibly even the prince himself, depending on how the line is read).
#hamlet#hamlet meta#hamlet’s age#this obviously does NOT imply anything about being 30yo btw#any age is a good age to be driven to madness by guilt and grief#It’s just very usual for shakespeare to describe somebody well past their apprentice age as a ‘youth’ SO MUCH#and that makes those lines very interesting#shut up e#willy shakes#posting this while EXHAUSTED going to see a million errors and tone problems tomorrow sorry in advance yall#**very unusual#long post#posting Hamlet meta like it’s 2014 hell yeah
905 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm in a dodgy hotel with bad wifi and somewhat bored, so I thought I'd come up with a list of things that I wish I could get from GMMTV but I know I won't.
A reveal towards the end of a series that two friends of the main couple have been dating the whole time (think Warm/Cop from Perfect 10 Liners or Mick/Beer from We Are).
Fourth and Gemini in something more serious like Moonlight Chicken.
POLY. DAMMIT.
Lift and Papang playing father and son. (Look at their beautiful faces!). And let them both have romances.

Older queer romance as the main storyline - and when I say older I mean actual 40+ and not a 'second chance at love because first love left/died' but just two people who never really found their person meeting later in life and clicking.
Dance themed but with actors/actresses who can actually dance - and preferably contemporary dance (I don't know if you realise how homoerotic that can be) but it could also be traditional Thai dancing (rather than tpop/idol style).
Short-haired/butch Sapphics.
Produce Jeab's swansong series.

A character/storyline which makes AMPLE use of Phuwin's Mandarin and English (or any other actor proficient in other languages) - shows include thai subtitles for northern dialects so why not more than the usual token foreign language.
In fact, I'll go further to say: Utilise the different languages of the foreign actors who play supporting roles rather than make them speak English and try to fob them off as American. If they're Italian, let them speak Italien. If they're Dutch let them speak Dutch. Etc.
MIX-UP BRANDED PAIRS. Book/Drake. Fluke Nattanon/Inn. Or Fluke Nattanon/Ohm Thipakorn. Jimmy/Mix. (You see my vision). Satang/Title. Victor/Great. JOONG/OHM PAWAT. (They might be TOO powerful). Etc, etc etc.
Take Max from Be My Favourite as a foundation for a lead character for Aou.
GIVE PEPPER A FAEN.
Nanon and Mark Pakin leading a bl. Look I'd even take a bromance if Nanon doesn't want to do bl. Better still if Nanon is in drag/cross-dresses/is a trans woman. This must be serious though. Not played for laughs. (I'm thinking an aged up version of the sides in About Youth).

MORE POSITIVE ASEXUAL REP.
DEAR GOD let AJ and JJ lead a show together. Maybe a comedy bl/het with either mistaken identity or deliberate confusion because they're pretending to be one person but fall in love with different people/genders.
Jus Justina in another show. Preferably leading. (She screenwrites and directs, so might not act again).

More Ployphach…maybe with Jan in a GL if she'll do one.
Peaceful Property Our Skyy 3 edition with their friends-to lovers story set 6 months after the end of the show.
An unhinged female ensemble show - I don't care if it's romance or not, I want badass women working together or in support of each other other. Maybe with JoJo directing.
POPPY.

Please and thank you 🙏🏽
#gmmtv#gmmtv 2025#gmmtv series#thai bl#thai drama#bl drama#these are things I know we won't get#so if we don't then I WIN#but also if we do!!!...then I ALSO WIN!#it's a win win type of bingo#look I KNOW poppy isn't even signed at gmmtv#but you never know when he's gonna *ahem* pop up#and this IS a list of things I know I won't get so...#oh and when I said 'I'm in a dodgy hotel' it was actually on tuesday evening#but I couldn't post it until now
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
At the outset of H. G. Wells's The War of the Worlds (1898), Wells asks his English readers to compare the Martian invasion of Earth with the Europeans' genocidal invasion of the Tasmanians, thus demanding that the colonizers imagine themselves as the colonized, or the about-to-be-colonized. But in Wells this reversal of perspective entails something more, because the analogy rests on the logic prevalent in contemporary anthropology that the indigenous, primitive other's present is the colonizer's own past. Wells's Martians invading England are like Europeans in Tasmania not just because they are arrogant colonialists invading a technologically inferior civilization, but also because, with their hypertrophied brains and prosthetic machines, they are a version of the human race's own future.
The confrontation of humans and Martians is thus a kind of anachronism, an incongruous co-habitation of the same moment by people and artifacts from different times. But this anachronism is the mark of anthropological difference, that is, the way late-nineteenth-century anthropology conceptualized the play of identity and difference between the scientific observer and the anthropological subject-both human, but inhabiting different moments in the history of civilization. As George Stocking puts it in his intellectual history of Victorian anthropology, Victorian anthropologists, while expressing shock at the devastating effects of European contact on the Tasmanians, were able to adopt an apologetic tone about it because they understood the Tasmanians as "living representatives of the early Stone Age," and thus their "extinction was simply a matter of … placing the Tasmanians back into the dead prehistoric world where they belonged" (282-83). The trope of the savage as a remnant of the past unites such authoritative and influential works as Lewis Henry Morgan's Ancient Society (1877), where the kinship structures of contemporaneous American Indians and Polynesian islanders are read as evidence of "our" past, with Sigmund Freud's Totem and Taboo (1913), where the sexual practices of "primitive" societies are interpreted as developmental stages leading to the mature sexuality of the West. Johannes Fabian has argued that the repression or denial of the real contemporaneity of so-called savage cultures with that of Western explorers, colonizers, and settlers is one of the pervasive, foundational assumptions of modern anthropology in general. The way colonialism made space into time gave the globe a geography not just of climates and cultures but of stages of human development that could confront and evaluate one another.
The anachronistic structure of anthropological difference is one of the key features that links emergent science fiction to colonialism. The crucial point is the way it sets into motion a vacillation between fantastic desires and critical estrangement that corresponds to the double-edged effects of the exotic. Robert Stafford, in an excellent essay on "Scientific Exploration and Empire" in the Oxford History of the British Empire, writes that, by the last decades of the century, "absorption in overseas wilderness represented a form of time travel" for the British explorer and, more to the point, for the reading public who seized upon the primitive, abundant, unzoned spaces described in the narratives of exploration as a veritable "fiefdom, calling new worlds into being to redress the balance of the old" (313, 315). Thus when Verne, Wells, and others wrote of voyages underground, under the sea, and into the heavens for the readers of the age of imperialism, the otherworldliness of the colonies provided a new kind of legibility and significance to an ancient plot. Colonial commerce and imperial politics often turned the marvelous voyage into a fantasy of appropriation alluding to real objects and real effects that pervaded and transformed life in the homelands. At the same time, the strange destinations of such voyages now also referred to a centuries-old project of cognitive appropriation, a reading of the exotic other that made possible, and perhaps even necessary, a rereading of oneself.
John Rieder, Colonialism and the Emergence of Science Fiction
682 notes
·
View notes
Note
https://www.tumblr.com/thebaconsandwichofregret/189924928150/comepraisetheinfanta-thebaconsandwichofregret
whenever i see people rbing the op without the additions i die a little inside so i thought you should have a go at debunking it 🫠
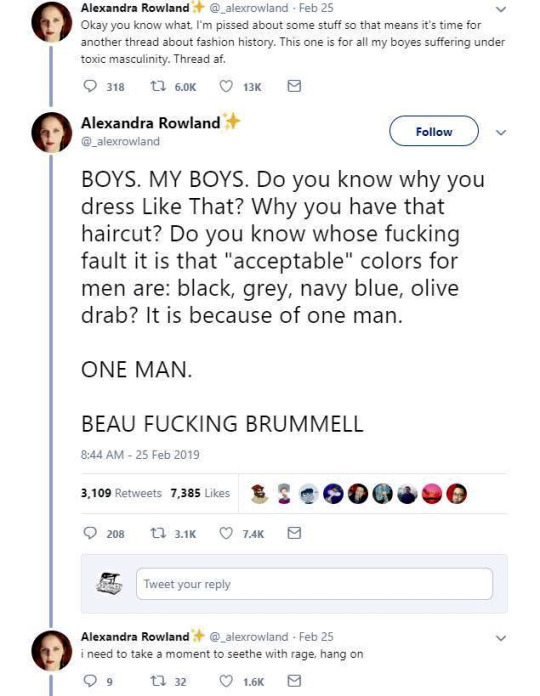


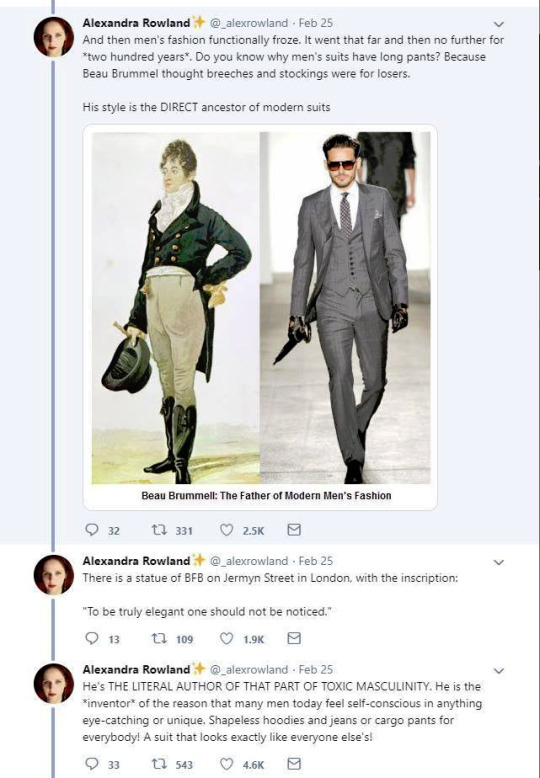
So these are the tweets from the post. I had blissfully not come across it before. This is one of the weirdest takes I have ever seen. It's amazing to see these fashion history takes that are so boldly and confidently wrong and inaccurate.
It's honestly hilariously ignorant to think that a massive cultural and societal shift that took couple of centuries was all because of one guy. It's so reductive and even goes to the great man territory to pick one person to blame for something like this that really had much more broad and complex reasons than "a guy did it". It's stressed in this tread that Beau Brummell was not noble or gentry and "just some guy", so how would he single-handedly change the fashions and concept of masculinity of the whole western world? He was a London socialite, it's not like most of his contemporaries in continental Europe knew about him. Like maybe the French, but does anyone really believe people in Eastern-Europe or Nordic countries or the Mediterranean knew about? Not to mention places like US. Yet everyone dressed like that in his lifetime, so how could his influence reach so far so quickly? Not even kings and queens could so directly and massively shift the fashions. So in the face of it the whole claim is ridiculous, but it's also full of inaccuracies.
The shift from Rococo fashion to regency fashion was extremely stark and quick in both men and women's fashion, but it happened during 1780s and 1790s, before Beau Brummell became a well known figure in the London society (he was born in 1778 and became well-known in the society after his military career, during which he befriended the Prince of Wales, around the end of 1790s). Here's first an example from 1780s and then from 1793-94 and 1797.
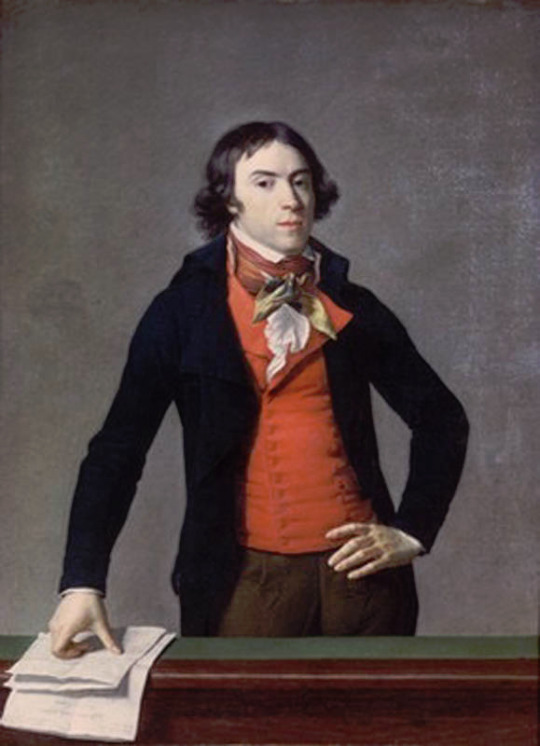



The one from 1780s still has some Rococo elements like the wig, but it's already much more toned down and the coat is already turning from frock coat to a tail coat. It's an example of the more casual men's countryside dress from the period. The court dress was still quite elaborate, though also toned down from the 1770s. But there's a big shift when it comes to the examples from 1790s. They are unmistakably Regency fashion. All of these example are French too. I'm sure these people had no idea and gained no influence from an unknown middle class English officer. So what did actually happen? Well, I'm pretty sure the French Revolution in 1789 had a little bigger impact on the European society and fashion than Beau Brummell.
I'm not going to go too deep into this, since I'm working on an in depth post about the masculinity and fashion in the modern era and I go into detail about how the French Revolution had a massive part in shaping them. But the short version is that the French revolutionaries rejected the elaborate fashions of the Rococo French nobility (in both men and women's fashion) as those over the top fashions stood as symbols of the excess wealth of the nobility and the extreme wealth gap. This is also why the high fashion was getting toned down thorough the 1780s before the Revolution. The anger towards the ruling class was mounting at the time and it encouraged the nobility to try to act a little more palatable in their aesthetics to maybe appease the angry people without doing any actual change to address the wealth gap and the centralization of power.
The revolutionaries looked for ideal masculinity and femininity elsewhere then. To contrast themselves against the ruling class, they looked to the antiquity and it's simplicity as well as the peasantry and the country gentleman fashion. Romanticism was the driving force behind the artistic expression of the Revolution. It weaved nationalism to the class struggle that was at the core of the revolutionary movement. So the Revolution was not just the working class and peasantry against the ruling class, but the French People against the nobility. That's how the bourgeois was able to align themselves with the working class and peasants. This is when physical labour, militarism, dominance and leadership really became intrinsically attached to masculinity, as the ideal man of the revolutionaries was a working peasant, who with military might took the the power back to the people from the nobility. The democracy would not last long, but it's not a mistake that only men could vote under the new democracy after the Revolution was won. It's also not a mistake that even when the post-Revolution France eventually abolished slavery (but not without some push-back first and a couple of slave revolts to force their hands) they didn't give most people of color rights to vote. Since colonialism whiteness had become intrinsic part of masculinity and femininity to dehumanize everyone else, and the new form of masculinity and femininity born out of the Revolution did not contest that. In fact the Enlightenment philosophy that had laid the ground work for the Revolution and the Romantic movement and it's nationalism that were driving force in it, in no way contested colonialism or it's white supremacy. In fact Enlightenment aimed to rationalize those things. Which is why the power in the new democracy went to the (mostly) white men.
These elements were in the new men's fashion too. Nationalism, the idealization of militarism, romanticization of peasantry and antiquity were basis of the fashion. Because antiquity was seen as the origins of democracy and the so called Western Civilization, that made it, and especially Antique Rome with it's militaristic connotations, perfect inspiration for the Revolutionary France. The short hairstyle was inspired from the Roman fashion seen in statues. The fashionable tail coat was influenced by military uniforms and the short jackets of the working class. The long trousers also came from working class dress. Here's examples of the revolutionary fashion of commoners, first from 1792 and then around 1790.
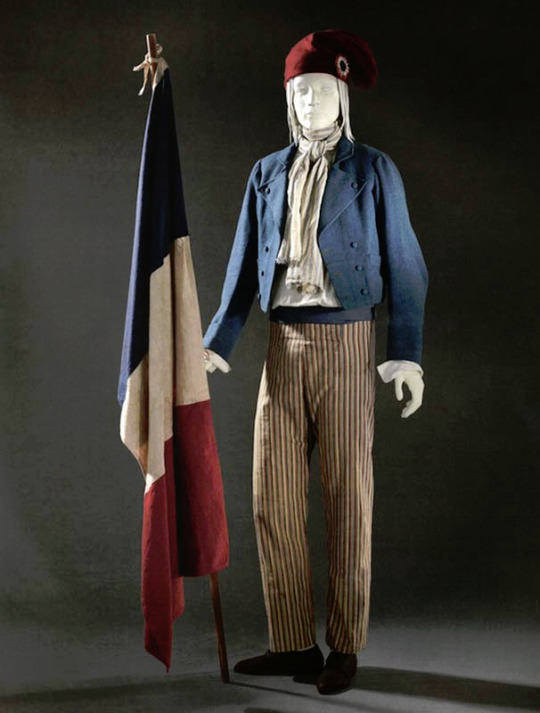


To be very clear, the revolutionaries were not a single entity with single ideology. They were collection of movements, who were united in their shared desire to overthrow the ruling class and establish some sort of democracy. But inside the movement were much more radical factions than what eventually ended in power after the French nobility. Socialists, abolitionists, feminists, slaves and others also fought for the Revolution and there was a lot of internal struggle too. Romantic movement was also very varied and contained extremely nationalistic elements as well as outright socialist elements.
It's important to note that the 18th century Rococo fashion was never as extreme elsewhere in the world as it was in France, so the change from Rococo to Regency style wasn't as stark elsewhere. If you put the most elaborate French court fashions of mid 1700s and Beau Brummell's style next to each other the difference is certainly massive, but fashion for men as well as women was through 18th century much more restrained and somber in England. Here's an English example from 1755-65 and for comparison a French example from 1755.
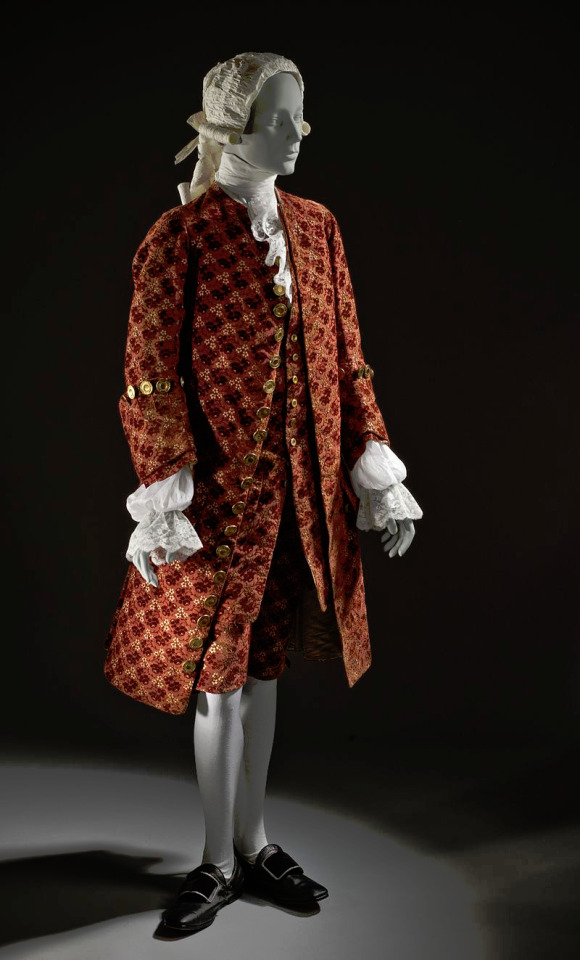


In fact as the tensions were rising in France the upper class begun to adopt the more toned down English styles. After the Revolution the new Republican styles would spread to Britain too. In Britain though Romanticism had a more pronounced effect as it stayed firmly monarchist. Therefore the English fashion was especially influenced by the styles worn by country side gentlemen.
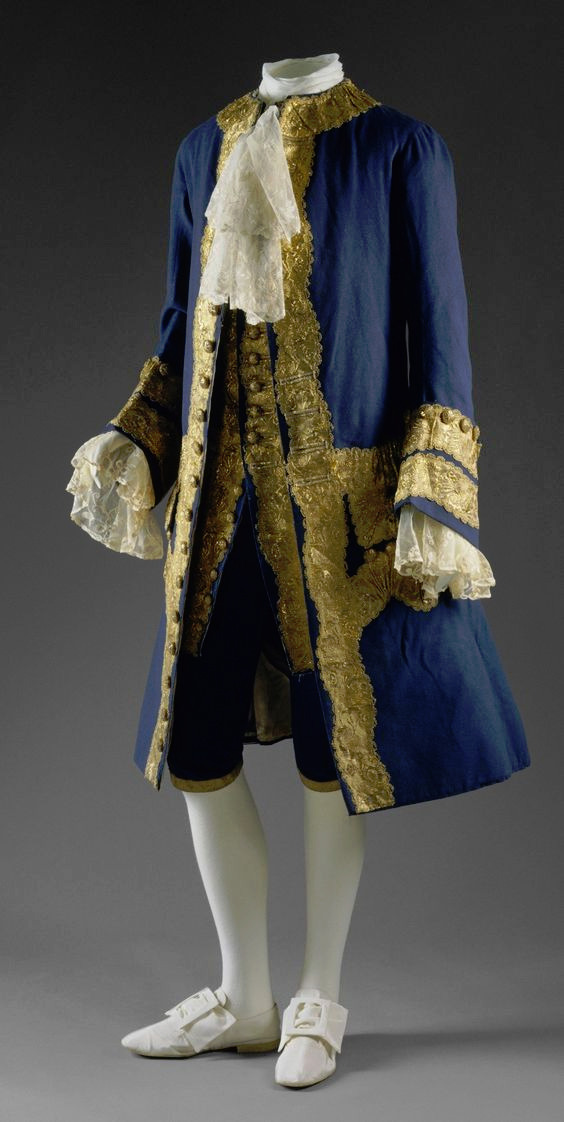
There's another claim in the thread that fully fails to understand the broad implications of fashion and societal gender and how these things change and evolve. It's the claim that Beau Brummell created the modern men's suit and he's the reason the suit has long trousers. We already went through how long trousers initially got into men's fashion and it was not him. But the writer is not wrong in saying that Beau Brummell's outfit in this picture is a direct ancestor of modern men's suit. It is.

But you know what else is a direct ancestor of men's suit? This.

The modern three piece suit has it roots as far as in late 17th century. Before suit men wore doublets, hose and jerkins, where the sleeveless piece, jerkin, was on top of doublet. Aside from hose, these were also items women used and the fashions for men and women resembled in style and construction each other much closer than after the suit took over (as seen in these examples from 1630s). However the distinction between men and women's fashion had started to grow much earlier. A big shift that happened during the 16th century was that men stopped wearing skirts. Men and women wore the same garments for centuries before that. The styles and silhouettes for men and women had some differences (the skirts were often shorter for men for example) but they were parallel to each other. I wrote a whole very long post about how skirts stopped being acceptable for men. In it I write about how the shift in men's fashion was part of the large shift from feudalism to colonialism and capitalism, that needed a new hierarchy to justify the new system after the previous divinely justified feudal hierarchy was no longer an option. The new hierarchy was white supremacist patriarchy and therefore needed a clearer distinction between white men and white woman, that would also help distinct white people from the racialized people.
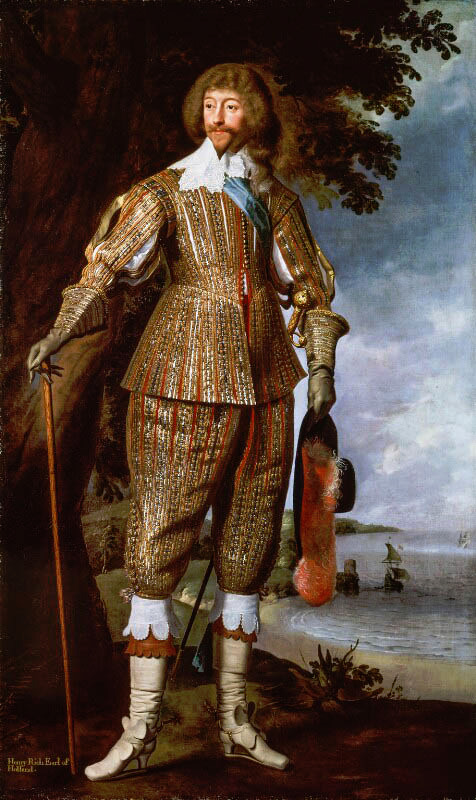


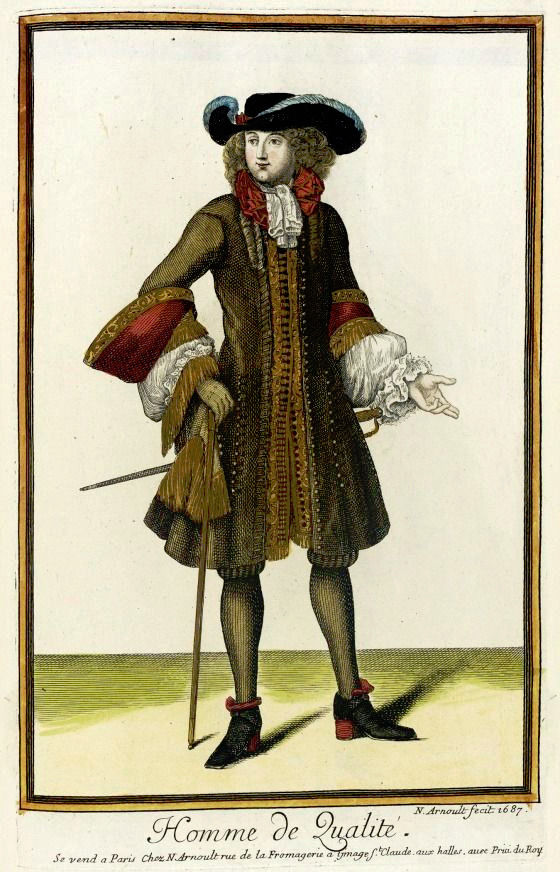
But such fundamental changes in the societal structure and culture are long processes. The process was continuing in the latter half of the 17th century, when Orientalism first became very popular. Orientalism is the dehumanization and fetishization of Asia and North-Africa, and it was born as the European colonial project was properly getting going in Asia. Colonialism in Asia and North-Africa took a little different form. I suspect it was because it was not that long ago, when Europeans had felt inferior to many of the peoples and empires in Asia and North-Africa, which they had always had much closer relationships with than the rest of Africa and certainly the Americas. I think that's why Orientalism is such a mix of coveting Asian and North-African cultures and bodies in a very fetishistic ways, while also demeaning and diminishing them. Nevertheless, Orientalism had a huge impact on European fashion in late 17th century. Both the way men and women's clothing was made after that to this day was strongly impacted by Orientalism. The coat and waistcoat combination was an adaptation of Turkish fashion. The three piece suit became popular in 1670s and fully took over men's fashion in 1680s (an example from 1687). The cravat was also adopted around the same time to men's wear from a light cavalry mercenary army in the Habsburgian Empire known as the Croats or Cravats. They were mainly Croatian, which to Western European was almost "Oriental" due to their proximity to Asia and Turkey in particular, and therefore the popularization of cravats as a fashion item was also influenced by Orientalism. Orientalist fashion encompasses the paradoxical nature of Orientalism itself; the Europeans coveted "the Orient" so they bastardized their fashions to construct a gender binary that left out the people who originated those fashions.

The Regency three piece suit also has all the same elements as the suit 150 years earlier, the individual pieces had just evolved into different cuts and silhouettes. The construction and the basic elements have stayed pretty similar to this day.
My point is not to in any way deny Beau Brummell's influence on Regency fashion. He was the most influential fashion icon for men in his era after all. I hope this just made it very clear that these bigger changes are not about individual people but much larger shifts and movements in society and culture. His actual influence was popularizing some of the English countryside styles, that were already part of casual fashion, as more formal fashion in the London high society, making extremely elaborate cravats into the fashionable items of the day and becoming the image of the English dandy.
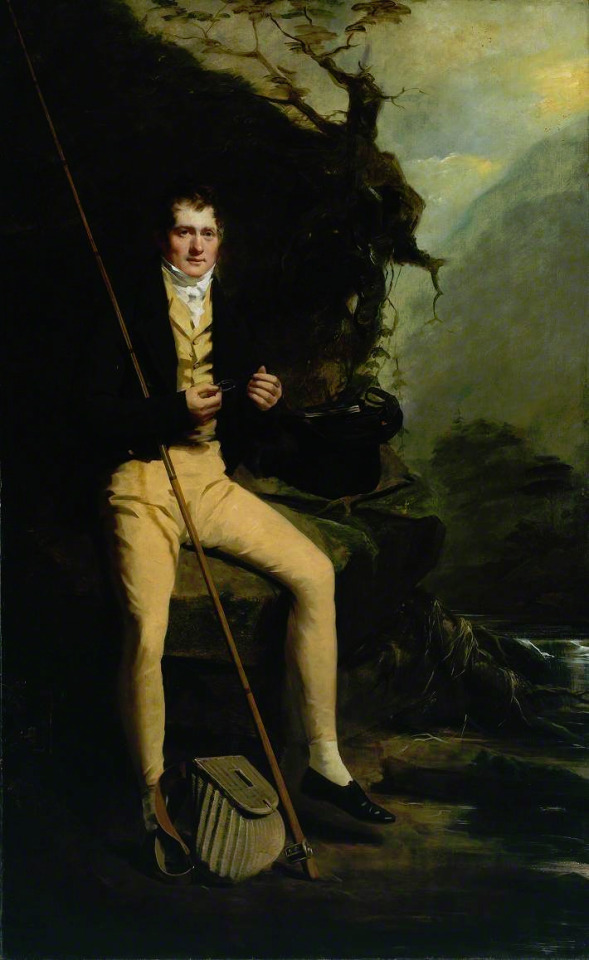
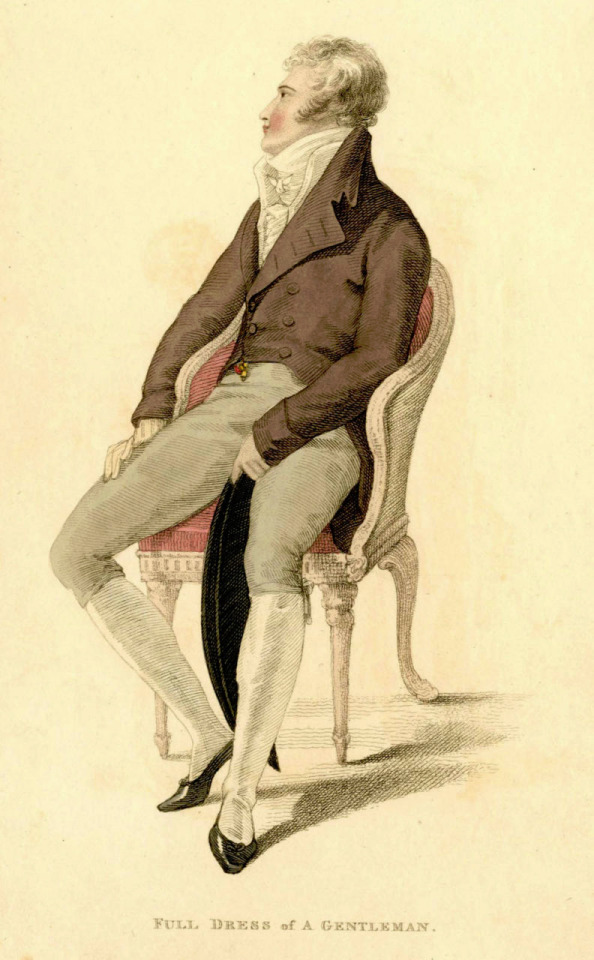
The picture of him above shows him the typical English countryside suit with dark blue tail coat, white cravat and light pantaloons with polished hessian boots. He helped to make the outfit and pantaloons in general fashionable. Breeches would stay as the formal leg wear for some a decade still, till young fashionable men would start to use black or gray pantaloons in formal events too. Pantaloons, which originated from military wear, were very fitted, basically similarly constructed as breaches but long. The trousers, which were looser than pantaloons, had their moment in France during the Revolution, but because of their Revolutionary and working class association, they didn't at first pick up in the high society, especially in Britain, until 1810s. They stayed as casual fashion through the Regency Era and only started gaining formal status in 1820s and 1830s. Beau Brummell is credited for inventing or at least popularizing trousers that have strap to go under the foot in order to keep them straight. Here's first a painting from of a gentleman in a very country style emphasized by the setting. Then a illustration from 1810 of a full formal dress with breeches and a fashion plate from 1817 of day wear with trousers.



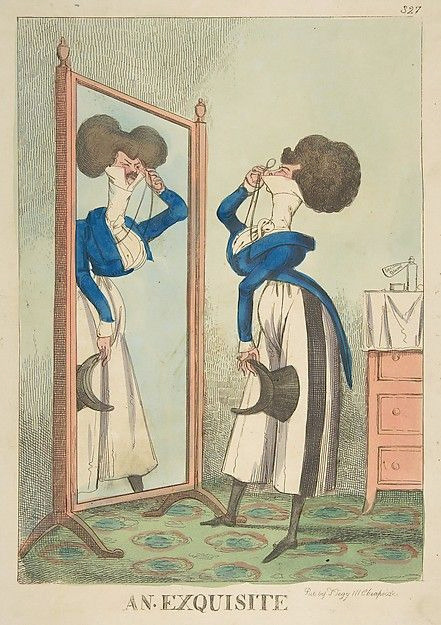
The thread also misses what dandy really was. Dandy was the embodiment of the middle class social mobility of the modern era. He was the "self-made man", the fashionable middle class and the new celebrity of a post-feudal era. He dressed in refined fashionable countryside middle class clothing and was celebrated for his style and refinement, not for his birth. Ironically though, there was a distinct reactionary quality to the Regency dandy. After all dandy did not embody social equality, but mobility. He was the ideal man of the capitalist hierarchy. A bit of dilemma for the dandy was that being extremely fashionable was central to the dandy, but after the French revolution being too fashionable and too concerned about looks had been associated with the aristocracy and was now therefore unmanly. Which is why dandy quickly came to be seen as effeminate. There is a lot of satiric cartoons from the time period that make fun of dandies and their preoccupation with fashion and looks. Here's couple from around 1810s.



In conclusion it's pretty ridiculous to say modern men's fashion was all created by one guy. The real reason why men's formal suit (and to be clear more colorful and elaborate styles have come and gone from men's informal fashion during that time) has been what it is for more than hundred years is because much bigger changes, like capitalism, colonialism, Orientalism and white supremacist patriarchy.
#fashion history#dress history#history#regency fashion#historical fashion#men's historical fashion#18th century fashion#answers#anon
613 notes
·
View notes
Text
julance week 1: broadsword
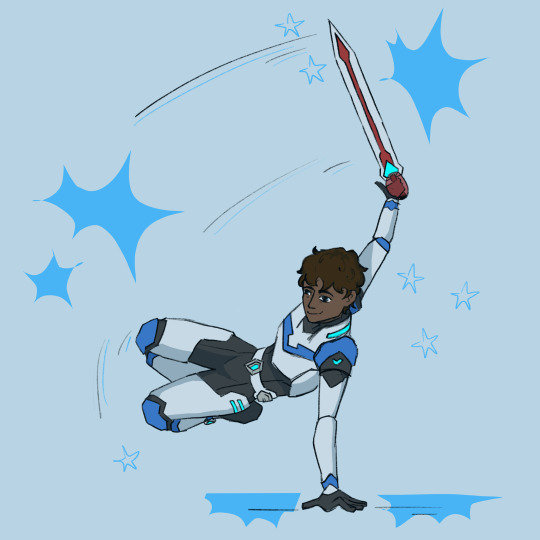

feel free to read whoever's interested is a small info dump about swords bc i went down a rabbit hole of sword classification when i looked up a broadsword LOL
disclaimer that if you are a sword expert and i got anything wrong i am sorry, i am a measly english major who dropped out of his history course and got all this information off of comparing appropriately 20 quora posts and two random sword classification websites
(also i may be an english major but english is not my first language so sorry if the x edged blade, y hilted sword is not the way it is grammatically correct)
okay so basically nowadays the most mainstream sword among fantasy media and D&D and stuff is the broadsword HOWEVER that is not actually what the broadsword is; what is used in games, tv, etc is most commonly the arming sword (a double edged blade, cross hilted sword, intended for single hand use)
the broadsword is generally a double edged blade, basket hilted sword which's blade is wider than that of a rapier, it is intended for single hand use (hence the guarding of the hand at the hilt), and more or less is a double edged version of a backsword; it can also be referred to as a claymore (which however has also been used for the longsword in the past)
however, in the broader historical context (haha funny pun), a broadsword is literally that, a broad sword, or in other words a sword broader than a contemporary one at a given time
then we have the longsword, generally a double edged blade, cross hilted sword intended for two hand use, but can be wielded with one hand if the situation is fitted
however, we also can use the term longsword as its semantical meaning, a long sword or in other words, a sword longer than a contemporary one at a given time
then we have for example the great sword which is similar in shape to the longsword however really long, like up to the size of the person wielding it and the hilt has space for three hands and it's also fairly heavy; i saw one person refer to it as a sword shaped polearm which i found quite funny
uhhh yea okay i think thats all i have to say
i would just like to add the little detail of the fact that sword classifications are a modern thing, people back in the day would just call any sword a sword, they might use long sword and broad sword in their semantic sense but other than that they were just swords
it was with the rise of fantasy media and their focus on the middle ages that swords became misclassified too with the arming sword becoming so popular under the wrong name
moral of the story: sword classification is really confusing :)
here is the quora post i found most interesting, and pretty much all of its information checked out with others i read, if anyone wants a (admittedly way) more comprehensive explanation than mine!
#art#digital art#fanart#vld#vld lance#julance#2024 julance#julance 2024#voltron#voltron lance#distardre art
61 notes
·
View notes