#Coastal preservation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Title: International Coastal Cleanup Day: Protecting Our Shores, One Beach at a Time
Celebrate International Coastal Cleanup Day on September 21 by joining efforts to clean our shores and protect marine life. Participate in local cleanups, reduce plastic use, and raise awareness for a healthier coastline.
Introduction International Coastal Cleanup Day, observed annually on September 21, is dedicated to preserving the health and beauty of our coastlines. This global event encourages individuals and communities to come together to clean up beaches, shores, and waterways, removing debris and raising awareness about the impact of pollution. Join in the efforts to protect our oceans and coasts, making…
#Beach Cleanup#Coastal Preservation#community involvement#environmental protection#International Coastal Cleanup Day#Marine Conservation#Ocean Health#Pollution Awareness#September 21#Shoreline Cleanup
0 notes
Text
Malibu Sand Dunes
Nestled along the picturesque coastline of Malibu, the Malibu Sand Dunes stand as a captivating natural wonder, offering a unique blend of rugged beauty and coastal tranquility. These magnificent dunes, sculpted over time by the gentle caress of the Pacific winds, create a mesmerizing landscape that tells tales of nature’s artistic prowess. Rising in undulating patterns, the dunes present a study…
View On WordPress
#Beach conservation#Beach habitats#California beaches#Coastal conservation#Coastal ecosystems#Coastal geography#Coastal landscapes#Coastal management#Coastal preservation#Coastal tourism#Dune ecology#Dune plants#Dune restoration#Dune stabilization#Environmental preservation#Erosion control#Malibu#Malibu attractions#Malibu coastline#Natural beauty#Nature reserves#Public recreation#Sand dunes#Sand formation#Sandy landscapes
0 notes
Text

Coastal Drama LaVerna Preserve, Bristol, Maine
Yashica Yashinon-DX 35mm f/2.8 Sony A7
#maine coast#seacoast#original photographers#photographers on tumblr#original photography#rocky coast#LaVerna#coastal preserve#ocean#atlantic#atlantic ocean#sky#clouds#waves#rocks#rocky shore#drama#clearing sky#seascape#maine photograph#vintage lens#yashica#yashinon#sony alpha#maine#new england
374 notes
·
View notes
Video
Photography is the story that you can’t quite put into words by Shelly Lynn Hachey O Via Flickr: Coastal brown bear in Alaska fishing for his meal as the tide comes in. The skies were not the best when we first landed on the beach but cleared up later in the afternoon. A chartered sea plane took us to this remote area to watch the bears - it was an amazing experience.
#outside#perspective#view#photography#camera#natural#light#canon#water#bear#wild#Alaska#animal#landscape#explore#look#mammal#nature#outdoors#sky#watch#wildlife#The 49th State#Lake Clark National Park and Preserve#coastal brown bear#brown bear#brown#predator#The Last Frontier#North America
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
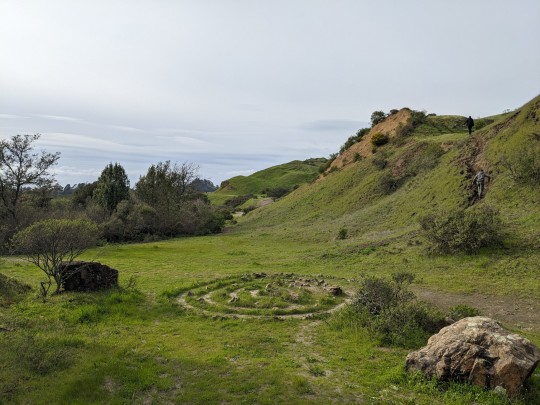

#san francisco bay area#east bay#clouds#coastal#labyrinth#walking labyrinth#Oakland hills#green#gray#a springtime hike#sibley volcanic preserve
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unveiling the Secrets of Life Below Water: Goal 14 for a Sustainable Future

In our journey towards achieving a sustainable future, Goal 14 of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) plays a pivotal role. Life Below Water, as it is commonly referred to, focuses on the preservation and sustainable use of oceans, seas, and marine resources. With this goal, the international community aims to safeguard marine ecosystems, mitigate the impacts of human activities, and promote sustainable livelihoods for coastal communities. This article delves into the significance of Goal 14, explores the challenges faced, and highlights the initiatives that can help us ensure a healthier and more vibrant life below water.
Understanding the Importance of Goal 14
The Earth's oceans are vast and cover more than 70% of the planet's surface. They are teeming with life and harbor a remarkable diversity of species and ecosystems. From the mesmerizing coral reefs to the mysterious depths of the abyss, the oceans are a treasure trove of biodiversity, supporting millions of species, including plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Beyond their ecological significance, the oceans play a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. They act as a massive heat sink, absorbing a significant amount of the sun's energy and distributing it across the planet. Additionally, oceans play a vital role in the water cycle, facilitating the evaporation of water, which then falls as precipitation and sustains terrestrial ecosystems.
The oceans are not only important for the environment but also for human societies. They provide sustenance to millions of people around the world. Fishing, both for subsistence and commercial purposes, is a primary source of livelihood for coastal communities. The oceans also support economic activities such as tourism, shipping, and offshore industries, contributing significantly to global economies.
However, the delicate balance of marine ecosystems is under threat due to various human activities. Overfishing, driven by unsustainable practices and the demand for seafood, has led to the depletion of fish stocks worldwide. Large-scale industrial fishing, with destructive methods such as bottom trawling, threatens not only the targeted species but also the entire marine food web.
Marine pollution is another significant challenge faced by the oceans. Pollution from land-based sources, including plastic waste, chemicals, oil spills, and agricultural runoff, finds its way into the marine environment, causing severe harm to marine life and ecosystems. The accumulation of plastic debris in the oceans has reached alarming levels, forming giant garbage patches and causing entanglement and ingestion by marine organisms.
Habitat destruction and degradation are also taking a toll on marine ecosystems. Destructive practices such as coral reef destruction, coastal development, and the destruction of mangroves and seagrass beds result in the loss of critical habitats and the disruption of delicate ecological relationships. These habitats serve as nurseries and breeding grounds for many species, and their loss has far-reaching consequences for marine biodiversity.
Furthermore, climate change poses one of the most significant threats to life below water. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and sea-level rise are already impacting marine ecosystems. Corals, which are vital for the survival of countless marine species, are particularly vulnerable to rising temperatures and increased ocean acidity, leading to coral bleaching events and the degradation of coral reefs.
In recognition of the urgent need to protect and sustainably manage marine resources, Goal 14 of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) was established. Also known as Life Below Water, this goal aims to ensure the conservation and sustainable use of the oceans, seas, and marine resources for present and future generations.
Goal 14 encompasses various targets and indicators to guide efforts towards sustainable ocean management. One of the key focuses is the protection and restoration of coral reefs, which are among the most diverse and valuable ecosystems on Earth. Coral reefs provide habitat for numerous species, protect coastlines from erosion, and support vibrant tourism industries. By implementing measures to reduce coral bleaching, enhance reef resilience, and combat destructive practices, Goal 14 seeks to safeguard these vital ecosystems.
Another critical aspect of Goal 14 is the reduction of marine pollution. It calls for the prevention and significant reduction of marine debris, particularly plastic waste. Efforts are being made to promote better waste management systems, recycling and reusing plastics, and raising awareness about the detrimental effects of single-use plastics. Innovative technologies for ocean cleanup are also being developed to tackle existing pollution.
To address the issue of overfishing, Goal 14 emphasizes the need to restore fish stocks to sustainable levels. This involves implementing science-based management plans, combating illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing, and promoting responsible fishing practices. Creating marine protected areas and adopting ecosystem-based management approaches can help protect critical habitats and ensure the long-term viability of fisheries.
Furthermore, Goal 14 acknowledges the urgent need to address ocean acidification, which poses a grave risk to marine organisms. By reducing carbon dioxide emissions and taking steps to enhance the resilience of marine ecosystems, such as protecting mangroves and seagrass beds, this goal aims to mitigate the impacts of ocean acidification and ensure the survival of vulnerable species.
Achieving Goal 14 requires a collaborative effort from governments, businesses, civil society organizations, and individuals worldwide. International cooperation is crucial to strengthen governance frameworks, regulate resource exploitation, combat illegal fishing, and promote sustainable practices. By taking collective action and embracing sustainable approaches, we can secure a healthier and more vibrant future for life below water.
Challenges and Threats to Life Below Water
The life below water faces a multitude of challenges that require immediate attention and concerted efforts. Overfishing, driven by unsustainable practices and illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing, has led to a decline in fish stocks worldwide. The loss of biodiversity affects not only marine ecosystems but also the communities that depend on them for food security and economic opportunities.
Marine pollution poses another significant threat. Plastic waste, chemicals, oil spills, and other pollutants contaminate the oceans, harming marine life and ecosystems. The accumulation of plastic debris, in particular, has gained global attention due to its devastating impact on marine organisms and the potential consequences for human health through the food chain.
Ocean acidification, caused by the absorption of excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, poses a grave risk to marine organisms such as corals, shellfish, and plankton. Acidic waters can hinder the growth and survival of these organisms, disrupting the entire marine food web and impacting the livelihoods of coastal communities.
Initiatives and Solutions for a Sustainable Life Below Water
Achieving Goal 14 requires a comprehensive approach involving governments, businesses, civil society, and individuals. Several initiatives and solutions have emerged to address the challenges faced by life below water:
Sustainable Fisheries Management: Implementing science-based management plans, promoting responsible fishing practices, and combating illegal fishing are crucial steps towards replenishing fish stocks and ensuring the long-term sustainability of fisheries. Tools like marine protected areas and ecosystem-based management help preserve critical habitats and protect biodiversity.
Marine Pollution Prevention: Reducing plastic pollution and other sources of marine debris is vital. This can be achieved through improved waste management systems, recycling and reusing plastics, and raising awareness about the consequences of single-use plastics. Additionally, promoting the use of biodegradable alternatives and supporting innovative technologies for ocean cleanup can help mitigate the impact of existing pollution.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: Addressing climate change is fundamental to preserving life below water. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting sustainable coastal development are essential steps in mitigating the impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems. Additionally, enhancing the resilience of coastal communities through measures such as mangrove restoration, coastal protection, and sustainable tourism can aid adaptation efforts.
International Cooperation and Governance: Collaboration among nations is crucial for the effective implementation of Goal 14. Strengthening international frameworks, such as the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), and promoting regional cooperation can help combat illegal fishing, regulate resource exploitation, and ensure the sustainable use of marine resources.
Conclusion
Preserving life below water is not only crucial for the health of our oceans but also for the overall well-being of our planet. Goal 14 provides a roadmap for sustainable ocean management, aiming to conserve marine biodiversity, mitigate pollution, and promote the sustainable use of marine resources. By taking action at individual, local, and global levels, we can make a significant difference in ensuring a healthier and more vibrant future for life below water. Let us join hands and work together to safeguard the oceans for generations to come.
#Sustainable management of marine resources#Conserving marine biodiversity#Protecting coral reefs and marine ecosystems#Sustainable fishing practices for life below water#Reducing marine pollution for a healthier ocean#Restoring fish stocks for sustainable fisheries#Addressing the threats of overfishing#Combating illegal fishing activities#Preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems#Tackling plastic pollution in the oceans#Solutions for ocean acidification#Climate change impact on life below water#Sustainable tourism and the oceans#Promoting responsible coastal development#Achieving United Nations' Goal 14 for a sustainable future#Enhancing resilience of coastal communities#Sustainable livelihoods for coastal populations#Importance of ocean conservation and sustainability#Preserving marine habitats and species diversity#Ecosystem-based management for marine resources#Strengthening international cooperation for Goal 14#Achieving sustainable development through Goal 14#Role of marine protected areas in conservation#Long-term viability of marine ecosystems#Promoting sustainable shipping practices#Economic benefits of sustainable ocean management#Balancing human activities with marine conservation#The significance of Goal 14 in the SDGs#Ensuring a vibrant future for life below water#Global initiatives for the protection of marine environments
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Planet's Fucked: What Can You Do To Help? (Long Post)
Since nobody is talking about the existential threat to the climate and the environment a second Trump term/Republican government control will cause, which to me supersedes literally every other issue, I wanted to just say my two cents, and some things you can do to help. I am a conservation biologist, whose field was hit substantially by the first Trump presidency. I study wild bees, birds, and plants.
In case anyone forgot what he did last time, he gagged scientists' ability to talk about climate change, he tried zeroing budgets for agencies like the NOAA, he attempted to gut protections in the Endangered Species Act (mainly by redefining 'take' in a way that would allow corporations to destroy habitat of imperiled species with no ramifications), he tried to do the same for the Migratory Bird Treaty Act (the law that offers official protection for native non-game birds), he sought to expand oil and coal extraction from federal protected lands, he shrunk the size of multiple national preserves, HE PULLED US OUT OF THE PARIS CLIMATE AGREEMENT, and more.
We are at a crucial tipping point in being able to slow the pace of climate change, where we decide what emissions scenario we will operate at, with existential consequences for both the environment and people. We are also in the middle of the Sixth Mass Extinction, with the rate of species extinctions far surpassing background rates due completely to human actions. What we do now will determine the fate of the environment for hundreds or thousands of years - from our ability to grow key food crops (goodbye corn belt! I hated you anyway but), to the pressure on coastal communities that will face the brunt of sea level rise and intensifying extreme weather events, to desertification, ocean acidification, wildfires, melting permafrost (yay, outbreaks of deadly frozen viruses!), and a breaking down of ecosystems and ecosystem services due to continued habitat loss and species declines, especially insect declines. The fact that the environment is clearly a low priority issue despite the very real existential threat to so many people, is beyond my ability to understand. I do partly blame the public education system for offering no mandatory environmental science curriculum or any at all in most places. What it means is that it will take the support of everyone who does care to make any amount of difference in this steeply uphill battle.
There are not enough environmental scientists to solve these issues, not if public support is not on our side and the majority of the general public is either uninformed or actively hostile towards climate science (or any conservation science).
So what can you, my fellow Americans, do to help mitigate and minimize the inevitable damage that lay ahead?
I'm not going to tell you to recycle more or take shorter showers. I'll be honest, that stuff is a drop in the bucket. What does matter on the individual level is restoring and protecting habitat, reducing threats to at-risk species, reducing pesticide use, improving agricultural practices, and pushing for policy changes. Restoring CONNECTIVITY to our landscape - corridors of contiguous habitat - will make all the difference for wildlife to be able to survive a changing climate and continued human population expansion.
**Caveat that I work in the northeast with pollinators and birds so I cannot provide specific organizations for some topics, including climate change focused NGOs. Scientists on tumblr who specialize in other fields, please add your own recommended resources. **
We need two things: FUNDING and MANPOWER.
You may surprised to find that an insane amount of conservation work is carried out by volunteers. We don't ever have the funds to pay most of the people who want to help. If you really really care, consider going into a conservation-related field as a career. It's rewarding, passionate work.
At the national level, please support:
The Nature Conservancy
Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation
Cornell Lab of Ornithology (including eBird)
National Audubon Society
Federal Duck Stamps (you don't need to be a hunter to buy one!)
These first four work to acquire and restore critical habitat, change environmental policy, and educate the public. There is almost certainly a Nature Conservancy-owned property within driving distance of you. Xerces plays a very large role in pollinator conservation, including sustainable agriculture, native bee monitoring programs, and the Bee City/Bee Campus USA programs. The Lab of O is one of the world's leaders in bird research and conservation. Audubon focuses on bird conservation. You can get annual memberships to these organizations and receive cool swag and/or a subscription to their publications which are well worth it. You can also volunteer your time; we need thousands of volunteers to do everything from conducting wildlife surveys, invasive species removal, providing outreach programming, managing habitat/clearing trails, planting trees, you name it. Federal Duck Stamps are the major revenue for wetland conservation; hunters need to buy them to hunt waterfowl but anyone can get them to collect!
THERE ARE DEFINITELY MORE, but these are a start.
Additionally, any federal or local organizations that seek to provide support and relief to those affected by hurricanes, sea level rise, any form of coastal climate change...
At the regional level:
These are a list of topics that affect major regions of the United States. Since I do not work in most of these areas I don't feel confident recommending specific organizations, but please seek resources relating to these as they are likely major conservation issues near you.
PRAIRIE CONSERVATION & PRAIRIE POTHOLE WETLANDS
DRYING OF THE COLORADO RIVER (good overview video linked)
PROTECTION OF ESTUARIES AND SALTMARSH, ESPECIALLY IN THE DELAWARE BAY AND LONG ISLAND (and mangroves further south, everglades etc; this includes restoring LIVING SHORELINES instead of concrete storm walls; also check out the likely-soon extinction of saltmarsh sparrows)
UNDAMMING MAJOR RIVERS (not just the Colorado; restoring salmon runs, restoring historic floodplains)
NATIVE POLLINATOR DECLINES (NOT honeybees. for fuck's sake. honeybees are non-native domesticated animals. don't you DARE get honeybee hives to 'save the bees')
WILDLIFE ALONG THE SOUTHERN BORDER (support the Mission Butterfly Center!)
INVASIVE PLANT AND ANIMAL SPECIES (this is everywhere but the specifics will differ regionally, dear lord please help Hawaii)
LOSS OF WETLANDS NATIONWIDE (some states have lost over 90% of their wetlands, I'm looking at you California, Ohio, Illinois)
INDUSTRIAL AGRICULTURE, esp in the CORN BELT and CALIFORNIA - this is an issue much bigger than each of us, but we can work incrementally to promote sustainable practices and create habitat in farmland-dominated areas. Support small, local farms, especially those that use soil regenerative practices, no-till agriculture, no pesticides/Integrated Pest Management/no neonicotinoids/at least non-persistent pesticides. We need more farmers enrolling in NRCS programs to put farmland in temporary or permanent wetland easements, or to rent the land for a 30-year solar farm cycle. We've lost over 99% of our prairies to corn and soybeans. Let's not make it 100%.
INDIGENOUS LAND-BACK EFFORTS/INDIGENOUS LAND MANAGEMENT/TEK (adding this because there have been increasing efforts not just for reparations but to also allow indigenous communities to steward and manage lands either fully independently or alongside western science, and it would have great benefits for both people and the land; I know others on here could speak much more on this. Please platform indigenous voices)
HARMFUL ALGAL BLOOMS (get your neighbors to stop dumping fertilizers on their lawn next to lakes, reduce agricultural runoff)
OCEAN PLASTIC (it's not straws, it's mostly commercial fishing line/trawling equipment and microplastics)
A lot of these are interconnected. And of course not a complete list.
At the state and local level:
You probably have the most power to make change at the local level!
Support or volunteer at your local nature centers, local/state land conservancy non-profits (find out who owns&manages the preserves you like to hike at!), state fish & game dept/non-game program, local Audubon chapters (they do a LOT). Participate in a Christmas Bird Count!
Join local garden clubs, which install and maintain town plantings - encourage them to use NATIVE plants. Join a community garden!
Get your college campus or city/town certified in the Bee Campus USA/Bee City USA programs from the Xerces Society
Check out your state's official plant nursery, forest society, natural heritage program, anything that you could become a member of, get plants from, or volunteer at.
Volunteer to be part of your town's conservation commission, which makes decisions about land management and funding
Attend classes or volunteer with your land grant university's cooperative extension (including master gardener programs)
Literally any volunteer effort aimed at improving the local environment, whether that's picking up litter, pulling invasive plants, installing a local garden, planting trees in a city park, ANYTHING. make a positive change in your own sphere. learn the local issues affecting your nearby ecosystems. I guarantee some lake or river nearby is polluted
MAKE HABITAT IN YOUR COMMUNITY. Biggest thing you can do. Use plants native to your area in your yard or garden. Ditch your lawn. Don't use pesticides (including mosquito spraying, tick spraying, Roundup, etc). Don't use fertilizers that will run off into drinking water. Leave the leaves in your yard. Get your school/college to plant native gardens. Plant native trees (most trees planted in yards are not native). Remove invasive plants in your yard.
On this last point, HERE ARE EASY ONLINE RESOURCES TO FIND NATIVE PLANTS and LEARN ABOUT NATIVE GARDENING:
Xerces Society Pollinator Conservation Resource Center
Pollinator Pathway
Audubon Native Plant Finder
Homegrown National Park (and Doug Tallamy's other books)
National Wildlife Federation Native Plant Finder (clunky but somewhat helpful)
Heather Holm (for prairie/midwest/northeast)
MonarchGard w/ Benjamin Vogt (for prairie/midwest)
Native Plant Trust (northeast & mid-atlantic)
Grow Native Massachusetts (northeast)
Habitat Gardening in Central New York (northeast)
There are many more - I'm not familiar with resources for western states. Print books are your biggest friend. Happy to provide a list of those.
Lastly, you can help scientists monitor species using citizen science. Contribute to iNaturalist, eBird, Bumblebee Watch, or any number of more geographically or taxonomically targeted programs (for instance, our state has a butterfly census carried out by citizen volunteers).
In short? Get curious, get educated, get involved. Notice your local nature, find out how it's threatened, and find out who's working to protect it that you can help with. The health of the planet, including our resilience to climate change, is determined by small local efforts to maintain and restore habitat. That is how we survive this. When government funding won't come, when we're beat back at every turn trying to get policy changed, it comes down to each individual person creating a safe refuge for nature.
Thanks for reading this far. Please feel free to add your own credible resources and organizations.
#us election#climate change#united states election#resources#native plants#this took 3 hours to write so maybe don't let it flop? i know i write long posts. i know i follow scientists on here#that study birds and corals and other creatures#i realize i did not link sources/resources for everything. i encourage those more qualified to add things on. i need to go to work
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
Genocide experts warn that India is about to genocide the Shompen people
Who are the Shompen?
The Shompen are an indigenous culture that lives in the Great Nicobar Island, which is nowadays owned by India. The Shompen and their ancestors are believed to have been living in this island for around 10,000 years. Like other tribes in the nearby islands, the Shompen are isolated from the rest of the world, as they chose to be left alone, with the exception of a few members who occasionally take part in exchanges with foreigners and go on quarantine before returning to their tribe. There are between 100 and 400 Shompen people, who are hunter-gatherers and nomadic agricultors and rely on their island's rainforest for survival.
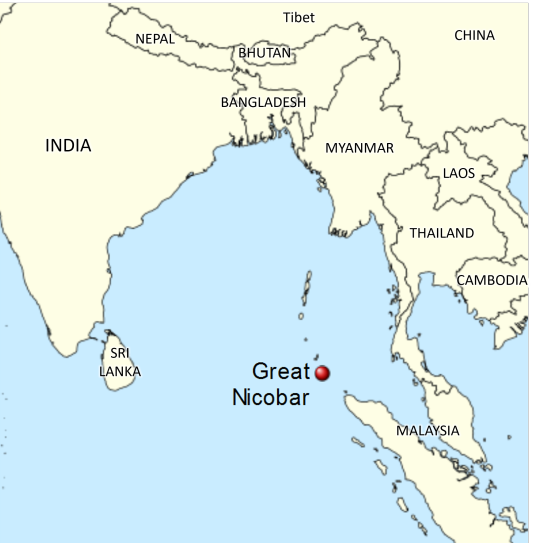
Why is there risk of genocide?
India has announced a huge construction mega-project that will completely change the Great Nicobar Island to turn it into "the Hong Kong of India".
Nowadays, the island has 8,500 inhabitants, and over 95% of its surface is made up of national parks, protected forests and tribal reserve areas. Much of the island is covered by the Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve, described by UNESCO as covering “unique and threatened tropical evergreen forest ecosystems. It is home to very rich ecosystems, including 650 species of angiosperms, ferns, gymnosperms, and bryophytes, among others. In terms of fauna, there are over 1800 species, some of which are endemic to this area. It has one of the best-preserved tropical rain forests in the world.”
The Indian project aims to destroy this natural environment to create an international shipping terminal with the capacity to handle 14.2 million TEUs (unit of cargo capacity), an international airport that will handle a peak hour traffic of 4,000 passengers and that will be used as a joint civilian-military airport under the control of the Indian Navy, a gas and solar power plant, a military base, an industrial park, and townships aimed at bringing in tourism, including commercial, industrial and residential zones as well as other tourism-related activities.
This project means the destruction of the island's pristine rainforests, as it involves cutting down over 852,000 trees and endangers the local fauna such as leatherback turtles, saltwater crocodiles, Nicobar crab-eating macaque and migratory birds. The erosion resulting from deforestation will be huge in this highly-seismic area. Experts also warn about the effects that this project will have on local flora and fauna as a result of pollution from the terminal project, coastal surface runoff, ballasts from ships, physical collisions with ships, coastal construction, oil spills, etc.
The indigenous people are not only affected because their environment and food source will be destroyed. On top of this, the demographic change will be a catastrophe for them. After the creation of this project, the Great Nicobar Island -which now has 8,500 inhabitants- will receive a population of 650,000 settlers. Remember that the Shompen and Nicobarese people who live on this island are isolated, which means they do not have an immune system that can resist outsider illnesses. Academics believe they could die of disease if they come in contact with outsiders (think of the arrival of Europeans to the Americas after Christopher Columbus and the way that common European illnesses were lethal for indigenous Americans with no immunization against them).
And on top of all of this, the project might destroy the environment and the indigenous people just to turn out to be useless and sooner or later be abandoned. The naturalist Uday Mondal explains that “after all the destruction, the financial viability of the project remains questionable as all the construction material will have to be shipped to this remote island and it will have to compete with already well-established ports.” However, this project is important to India because they want to use the island as a military and commercial post to stop China's expansion in the region, since the Nicobar islands are located on one of the world's busiest sea routes.
Last year, 70 former government officials and ambassadors wrote to the Indian president saying the project would “virtually destroy the unique ecology of this island and the habitat of vulnerable tribal groups”. India's response has been to say that the indigenous tribes will be relocated "if needed", but that doesn't solve the problem. As a spokesperson for human rights group Survival International said: “The Shompen are nomadic and have clearly defined territories. Four of their semi-permanent settlements are set to be directly devastated by the project, along with their southern hunting and foraging territories. The Shompen will undoubtedly try to move away from the area destroyed, but there will be little space for them to go. To avoid a genocide, this deadly mega-project must be scrapped.”
On 7 February 2024, 39 scholars from 13 countries published an open letter to the Indian president warning that “If the project goes ahead, even in a limited form, we believe it will be a death sentence for the Shompen, tantamount to the international crime of genocide.”
How to help
The NGO Survival International has launched this campaign:
From this site, you just need to add your name and email and you will send an email to India's Tribal Affairs Minister and to the companies currently vying to build the first stage of the project.
Share it with your friends and acquittances and on social media.
Sources:
India’s plan for untouched Nicobar isles will be ‘death sentence’ for isolated tribe, 7 Feb 2024. The Guardian.
‘It will destroy them’: Indian mega-development could cause ‘genocide’ and ‘ecocide’, says charity, 8 Feb 2024. Geographical.
Genocide experts call on India's government to scrap the Great Nicobar mega-project, Feb 2024. Survival International.
The container terminal that could sink the Great Nicobar Island, 20 July 2022. Mongabay.
[Maps] Environmental path cleared for Great Nicobar mega project, 10 Oct 2022. Mongabay.
#shompen#genocide#stop genocide#india#indigenous#indigenous peoples#indigenous rights#human rights#anthropology#stateless nations#end occupation#andaman and nicobar islands#nicobar islands#great nicobar#💬#asia#geopolitics#ecocide#sustainability
23K notes
·
View notes
Text
How does one get a Golden-rumped Elephant Shrew to wear pants that show off its golden rump?
The golden-rumped elephant shrew (Rhynchocyon chrysopygus) is a fascinating and unique mammal native to the coastal forests of Kenya. Known for its striking golden-colored rump, this small, insectivorous mammal is not only a biological marvel but also a potential candidate for whimsical imaginings—such as getting it to wear pants that accentuate its distinctive golden rump. While this idea is…
#animal agility#animal anthropomorphism#animal behavior#animal enrichment#animal fashion#animal training#animal welfare#biodiversity#coastal forests#conservation awareness#costume design#creative conservation#endangered species#ethical animal treatment#exotic animals#golden rump#Golden-rumped elephant shrew#habitat preservation#humor in nature#imaginative projects#insectivorous mammals#Kenya wildlife#Miniature clothing#nature-inspired fashion#predator deterrent#sustainable practices#unique mammals#whimsical ideas#wildlife conservation#wildlife protection
0 notes
Text

The Tiny Historical Town In Florida That Survived Against All Odds
#florida#coastal#micanopy#inland#oldest town#king of spain#1817#historical#town#architectural#preservation#the sunshine state
0 notes
Text
watching broadchurch for the first time and alec hardy is truly offensive… like who tf gave you permission to make an autobiographical character of me??
#cares a lot but is too emotionally constipated to express it#so comes off as grouchy and standoffish#chronically ill and avoids doctors bc self preservation is overrated#reheats his tea in the microwave and eats like a rabbit#literally killing himself by overworking#like if I were a middle aged divorced detective#I would be on the phone to my lawyers right now#wait... he also lives in a small coastal town he hates WTF#CHIBNALL GET OUT OF MY WALLS#babblingsea#broadchurch
1 note
·
View note
Text
National Lighthouse Day: Celebrating the Beacons of Light and Hope
National Lighthouse Day on August 7th honors the iconic beacons that have guided sailors for centuries. Celebrate these symbols of hope and resilience by exploring their history and significance.
Every year on August 7th, we celebrate National Lighthouse Day, a day dedicated to honoring the iconic structures that have guided sailors safely to shore for centuries. Lighthouses are more than just navigational aids; they are symbols of hope, resilience, and the enduring human spirit. On this day, we take a moment to reflect on the history and significance of lighthouses, the stories they…
#Beacons of Light#Coastal Landmarks#Historic Preservation#Lighthouse Keepers#Lighthouse Tours#Lighthouses#Maritime History#National Lighthouse Day#Nautical Heritage#Navigational Aids
6 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Roof Extensions Deck in Providence Inspiration for a large timeless backyard deck remodel with a roof extension
0 notes
Photo

Home Bar - Single Wall Examples of large beach style single-wall wet bar designs with shaker cabinets, white cabinets, wood countertops, blue backsplashes, cement tile backsplashes, and brown countertops include a wet bar with a single wall, dark wood flooring, and a brown floor.
0 notes
Video
Gone fishing by Shelly Lynn Hachey O Via Flickr: Brown Coastal Bear wading in the rising tide in hopes of finding a fish.
#perspective#view#photography#camera#outside#natural#water#Awareness#bear#tide#fishing#Alaska#lake#summer#splash#mammal#brown bear#coastal brown bear#brown#hairy#four legged#Lake Clark National Park and Preserve#lakes#lakeside#United States of America#usa#The Last Frontier#vacation#memoirs#memories
26 notes
·
View notes


