#Chinese Construction company
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
BEIJING — China’s struggling real estate developers won’t be getting a major bailout, Chinese authorities have indicated, warning that those who “harm the interests of the masses” will be punished.
“For real estate companies that are seriously insolvent and have lost the ability to operate, those that must go bankrupt should go bankrupt, or be restructured, in accordance with the law and market principles,” Ni Hong, Minister of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, said at a press conference Saturday.
“Those who commit acts that harm the interests of the masses will be resolutely investigated and punished in accordance with the law,” he said. “They will be made to pay the due price.”
That’s according to a CNBC translation of his Mandarin-language remarks published in an official transcript of the press conference, held alongside China’s annual parliamentary meetings.
Ni’s comments come as major real estate developers from Evergrande to Country Garden have defaulted on their debt, while plunging new home sales have put future business into question.
In 2020, Beijing cracked down on developers’ high reliance on debt for growth in an attempt to clamp down on property market speculation. But many developers soon ran out of money to finish building apartments, which are typically sold to homebuyers in China ahead of completion. Some buyers stopped paying their mortgages in a boycott.
Authorities have since announced measures to provide some developers with financing. But the national stance on reducing the role of real estate in the economy hasn’t changed.
This year’s annual government gathering has emphasized the country’s focus on investing in and building up high-end manufacturing capabilities. In contrast, the leadership has not mentioned the massive real estate sector as much.
Real estate barely came up during a press conference focused on the economy last week, while Ni was speaking during a meeting that focused on “people’s livelihoods.”
Ni said authorities would promote housing sales and the development of affordable housing, while emphasizing the need to consider the longer term.
Near-term changes in the property sector have a significant impact on China’s overall economy.
Real estate was once about 25% of China’s GDP, when including related sectors such as construction. UBS analysts estimated late last year that property now accounts for about 22% of the economy.
Last week, Premier Li Qiang said in his government work report that in the year ahead, China would “move faster to foster a new development model for real estate.”
“We will scale up the building and supply of government-subsidized housing and improve the basic systems for commodity housing to meet people’s essential need for a home to live in and their different demands for better housing,” an English-language version of the report said.
next time you complain about how things are in America, consider that if you lived in some kind of scary communist country like China, you wouldn't even get to fund a bailout for the real estate company owners who ruined the economy like you can (whether you like it or not) in the good old US of A! 🇺🇲
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Time to message Hoyo about the colorism...
This is the text I prepared to send to Hoyo, to their emails ([email protected] | [email protected]), feedback, eventual surveys...
Feel free to copy paste and send this exact thing as well. Feedback is appreciated before I send anything.
Shorter version below, and imo it's better.
-----------
Subject: [Constructive Feedback] You can and should darken the skin tone of Natlan characters
Regarding the skin color discussion started by the reveal of Natlan characters:
We fans understand that the world of Teyvat is fictional, and that the Nations and characters are informed by different real cultures that end up being mixed to create a fictional setting. But it's also undeniable that some Nations in the world of Genshin are primarily inspired by some cultures more than others, and that character traits tend to reflect the main countries the Nation they inhabit is based on.
There are no consensus amongst fans regarding how accurate outfits are, and we know very little about the Nation itself, but it's undeniable that Hoyoverse researched and put a lot of effort into designing Natlan. Which is why it's a shame that all that effort is being drowned by the obvious racism and colorism reflected in the designs.
After Sumeru, Natlan was the only chance Hoyoverse would have to prove they were not afraid of designing characters with darker skin tones. Many people had hope, and the people of some of the cultures Natlan were based on hoped to see themselves represented. Even if you do not care about representation and respecting your fans, you should care about not bastardizing all of the good things that the new nation has to offer, and having at least some characters with a darker skin tone was the bare minimum that made sense.
YOU STILL HAVE TIME TO FIX THIS. Darken their skin tones. Significantly. Even Chinese fans are mocking you over your decisions, you're running out of excuses.
Hoyoverse has proven capable of change and adjusting their values over time - for example, your early depiction of female characters in Honkai Impact 3rd paled in comparison with the great writing of current female characters being put out, to not call it sexist. So me and many still want to believe you can recognize your mistake and fix it. You are a company that heavily supports fan and fan works, and who constantly invests in things that have a positive impact in society, which is why many people like to support you, and why this is so disapointing to see.
Do not let this taint your legacy. Tech otakus were supposed to change the world, remember? And perpetuating colorism is not how you should do it.
-----------
Shorter version:
Regarding the skin color discussion started by the reveal of Natlan characters:
We fans understand that the world of Teyvat is fictional, and that the Nations and characters are informed by different real cultures that are mixed to create a fictional setting.
But it's undeniable that different Nations are inspired by different cultures, and that character traits tend to reflect the main countries the Nation they inhabit is based on.
With so much clear research put into the characterization of each nation, Natlan included, it's a shame to let those efforts be drowned by designs that reflect colorist and racist views.
It would make sense to have characters with significantly darker skin tons in Natlan, and many fans hoped for that.
Hoyoverse has proven capable of change for the better - for example, your early depiction of female characters in HI3 leaned on sexism and paled in comparison with the great writing of current female characters.
There are other things that the company does right, and you can do it again. Tech otakus were supposed to change the world, remember? And perpetuating colorism is not how you should do it.
So don't let this taint your legacy. Even Chinese fans are mocking your decisions.
Darken the skin color of the Natlan characters. You still have time.
#genshin#genshin impact#genshinimpact#natlan#natlan trailer#genshin designs#genshin feedback#colorism#racism#representation#social issues#poc representation#poc#black people#natlan discourse
268 notes
·
View notes
Text
Love in the Big City Timeline in the Series
Here are the facts I've put together about the timeline in the series (which feels, unlike the book, a little more linear and so actually possible to do this with):
[indeterminate, elementary school, est. early 2000s] Yeong's mom finds out about Yeong's father's second family and divorces him
[indeterminate, high school, est. late 2000s] Yeong is caught kissing another boy on the playground and institutionalized by his mother
2012: The year that T-ara's song Sexy Love comes out (at this point I've just kept this on here for reference)
2014: As per his own narration in ep5, this is the year Yeong contracts HIV (in Feb) and is diagnosed by the military (and he only spends 1 month in the military before getting a medical discharge). He meets with the T-aras a few months later and says they're next for the military (shoutout to @impala124); he meets Nam Gyu and Mi Ae in late 2014, and Mi Ae tries to bum a cigarette from him in Dec 2014 (shout-out to @my-rose-tinted-glasses); Yeong moves in with Mi Ae in either late 2014 or early 2015, and soon after that is the T-ara karaoke sendoff after which he breaks up with Nam Gyu.
2015: Mi Ae's application to her job had 2015 on it; Mi Ae goes to the job retreat for a month, meets Jun Ho, and then several months after that, Yeong stops talking to Mi Ae for 10 months after she outs him. Some time in late 2015/early 2016, Yeong breaks things off with Nam Gyu again.
2016: We know Yeong won the contest in 2016 as per the book we see on Yeong Su's nightstand, and since Yeong called Mi Ae after that, we know they reconciled in 2016. Also, as per the last text message from him, Nam Gyu dies in 2016. After his funeral, Yeong takes over Mi Ae's apartment and Mi Ae gets married. Also, Yeong's mother gets diagnosed with cancer 3 years before she dies, which would be 3 years before Yeong tells Gyu Ho about Kylie, so that means her cancer diagnosis was also in 2016.
2017: Yeong Su tells Yeong he's moving to America [guessing based on how much time seemed to pass in their relationship]; Yeong attempts suicide
2018: Yeong Su sends Yeong the manuscript (which he throws out) [we know this was a year after Yeong Su leaves, but before Yeong's mother dies]
2019: Yeong's mother dies [I'm inferring because we know Yeong tells Gyu-Ho about Kylie in Jan 2020 after his mother's death and after they'd been seeing each other for a little while, so that puts Yeong's mother's death in 2019]
2020: We see Yeong's phone date the day he tells Gyu-Ho about Kylie as Saturday, Jan 25, which was a date in 2020 (but not 2019) [shoutout to @my-rose-tinted-glasses for pointing this out]; Yeong also has an article in his office with 2020 on it, so he was definitely dating Gyu-Ho and had moved from his job at the musical theatre to the company by 2020.
2021: [This is a guess, but we know Yeong's been together with Gyu-Ho for a year when he complains to the T-aras about their relationship and they suggest a trip, so I'm guessing the trip to Bangkok took place in Feb 2021 (around Chinese new year)--my best attempt to date this was the reference to the construction of the Pearl Building in Bangkok but that was constructed 2015-2017]
2022: Shoutout to @my-rose-tinted-glasses for catching the label on the package of his suitcase that Gyu-Ho buys for Shanghai, which says Jan 2022. We know Gyu-Ho leaves for Shanghai soon after that because in Feb 2023 the T-aras check in with Yeong saying it's 'that time of year'.
2023: In Feb 2023 we see Yeong quits his company to be a full-time writer; he writes the date on the book he signs for his former colleague and on his phone screen we can see Feb 2023 as well. We also got some confirmations of the timeline above, since he says in his voiceovers in eps 7&8 that it's been a year since Gyu-Ho left and he's been living with Kylie 9 years. [Note: there were subs in ep7 that said 2022, but they don't align with what's actually on screen]. In March, Yeong goes to Bangkok with Q/Habibi (Habibi's phone screen says it's March 8 when Yeong looks at it in the shower).
Feel free to correct me or add any concrete dates that I missed! I've now updated this with details from the last 2 episodes on Nov 12.
#love in the big city#typed so that i can stop thinking it#updating this made me realize that the anniversary of Gyu-Ho leaving is around the anniversary of Yeong contracting HIV (both in Feb)#also did anyone else notice that in ep 5 Yeong has Gyu-Ho stored in his phone as Q~❤[hearto]?#there are so many tiny details in this show that just wreck me
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
They’ve built a “Great Wheel” on the Seattle waterfront [...].
The small timber village became a military outpost in the Puget Sound War [...], [and] soon evolved into a trade gateway, with timber tailings and other industrial trash from Henry Yesler’s mill used to fill in the marshlands [...], atop which migrant laborers raised tents and shanties [...] now working to feed raw materials into the furnaces of the Second Industrial Revolution burning in the East. [...] The first nationwide strike ripped across the country’s railways in 1877, but in Seattle the unrest took on a grim character, as thousands of unemployed white workers rioted against their Chinese counterparts [...]. Meanwhile, [...] local elites rebuilt [...] downtown [...] from scratch, hosting the tallest building on the West Coast alongside other new constructs [fueled] with money gleaned from the supply chains linking eastern capital to Alaskan gold. [...] Today the city - again rebuilt [...] - is seen as one of the primary beneficiaries of the “Fifth” Industrial Revolution in information technology, outshone only by California’s Silicon Valley. [...] The digital was increasingly thought of as somehow "immaterial," sustained by intellectual labor more than physical toil [...].
Silicon Valley myths of [...] "immaterial" labor disguise a more gruesome dynamic in which growing segments of the global labor force are being deprived even of the basic brutality of the wage, instead forced out into growing rings of slums, prisons, and global wastelands. [...]
---
Perched alongside a downtown business corridor [...], Seattle's Great Wheel seems to peer out over [...] [the] prophesied “cooperative commons,” an infotech metropolis abutting the beauty of an evergreen arcadia. But travel below Seattle’s cluster of infotech industries and the image appears much the same as that of a hundred years prior - a trade gateway, squeezing value from supply chains by selling transport and logistical support. The southern stretch of the metropolis bears little resemblance to the revitalized urban core of the city proper. Instead of the “cognitive labor” of Microsoft, it is defined instead by the cold calculation of companies like UPS, founded in Seattle when the city was one link in a colonial supply chain built first for timber, then Alaskan gold, then World War. [...]
In south Seattle, this logistics empire takes the form of faceless warehouses, food processing facilities, container trucks, rail yards, and industrial parks concentrated between two seaports, an international airport, three major interstates, and railroads traveling in all directions. Meanwhile, the poor have been priced out of the old inner city, moving southward [...]. [T]hey can be found staffing the airport and the rail yards, hauling cargo in and out of two the major seaports, loading boxes in warehouses [...]. And, beyond them, the shadow stretches out to Washington’s rural hinterlands where migrant laborers staff a new boom in agriculture and raw materials [...] - and further still into America’s long-depressed interior, where the Great Wheel meets its opposite: Memphis, the FedEx logistics city, watched over by a great black pyramid [the infamous Bass Pro Shop pyramid]. [...]
Every Seattle is capable of creating an eco-friendly, “cooperative commonwealth” tended by apps and algorithms only insofar as there is a Memphis that can provide human workers to sort the packages, a Shanghai to build the containers that carry them, and a Shenzhen to solder together the circuits of the machines that govern it all.
---
All text above by: Phil A. Neel. "The Great Wheel". Brooklyn Rail. April 2015. Published online at: brooklynrail.org/2015/04/field-notes/the-great-wheel. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Text within brackets added by me for clarity. Presented here for commentary, teaching, personal use, criticism purposes.]
#ecology#multispecies#abolition#imperial#colonial#edwardian#temporality#hinterlands#tidalectics#archipelagic thinking#intimacies of four continents#caribbean#carceral geography
124 notes
·
View notes
Text
Robe à la Française
French, ca. 1770
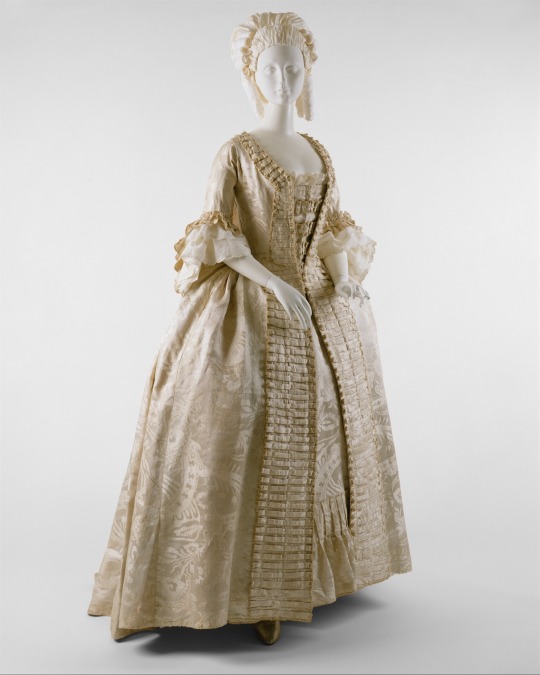

The robe à la française, with open robe and petticoat, was the quintessential dress of the eighteenth century. Characteristic of 1770s costume are the piece's low neckline, fitted bodice, narrow sleeves with double layered cuffs, as well as the sack back and fullness at the hips supported by panniers. This exquisite example is constructed from a rare Chinese export silk dating from the first quarter of the eighteenth century. The textile is an ivory "bizarre" patterned damask (created by reversing the weave structure so that both the warp-float and weft-float faces of the satin are on the same surface).
As early as the late sixteenth century, Chinese craftsmen created silks for the European market, which were exported by the East India companies of England, France, and Holland. Due to the exchange of design motifs by both Eastern and Western artisans, Chinese export silks often bore little relation to traditional Chinese aesthetics. While this patterned damask closely resembles the European "bizarre" silks popular during the first quarter of the eighteenth century, the selvedge-to-selvedge width, fabric weight, and selvedge markings all indicate Chinese manufacture. To fully appreciate the sumptuousness of this dress, one might imagine the sense of movement candlelight would have created across its surface.
The MET Museum
208 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fascinating how when a Taiwanese game dev company develops a game with complex worldbuilding, a specific and beautiful aesthetic, an entire constructed language, people are immediately chomping at the fucking bit to show their ass about how it's ACTUALLY about covid or criticism of the chinese government and it cannot possibly be about telling a story.
Like damn, people sure love the ~asian aesthetic~ but when actual devs from those countries try to make their own stories you can't resist being fucking racist! I'm fucking ashamed of everyone who mindlessly agrees with those posts and says WHOAAAAA I DIDNT REALIZE IT COULD BE COMMENTING ON CURRENT EVENTS. Like god, go fuck yourselves.
45 notes
·
View notes
Note
Oooooh… Cowgirl AU got me feeling things…
Clorinde as the sheriff who cuffs you and tosses you in a dark little cell in the town jail so she breed you in private…
Lynette and/or Arlecchino as wild bandits, bringing you back to their camp in the middle of the desert to fuck you by the campfire… the town thinks you’re an innocent maiden who’s been kidnapped just as she was due to be happily (unwillingly) wedded to a good (horrible) man, but you were actually seduced by their roguish charm…
Maybe Beidou is one of the Chinese workers the rail company imported as cheap labor to work on the new rail line coming though*, and she sneaks into your fancy house at night so she can fuck you nice and good before you shoo her out at dawn so your father doesn’t learn you’ve fallen in love with one of those ‘damn [insert slur typical of the 19th Century here]’…
*per the Smithsonian, 1/6 of Chinese immigrants in the 1860s ended up working on railroad construction, and the Guardian puts a more specific number of Chinese working on railroad construction at roughly 15,000.
Ohmygod this is all really cool! Sheriff Clorinde and Arlecchino + Lynette as bandits?? That’s so hot jaidjsjdn 💕
I will say though, despite how cool it is that you know so much about the historical accuracy of the cowboy times, I’m going to leave out any racial/discriminatory topics since it can be really sensitive/triggering for my readers.
If I choose to write an AU based on historic times (Ex. Empress AU, Pirate AU, Cowboy AU, etc.) there will be little to no mention of discrimination even if it’s historically accurate. This blog is safe space for all sapphics 💘
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
Daily update post:
Two independent terrorist attacks against Israelis took place over the last 24 hours. Yesterday, a Hamas terrorist stabbed in the back a 49 years old Israeli reserves soldier, who stopped to buy something at a shop in a gas station, on his way home. The soldier turned around and, despite being injured, pursued the terrorist, shot and wounded him. The terrorist was later arrested, he had a permit to work in Israel. In the second one, a terrorist started shooting at civilian vehicles passing by, and ended up injuring a 27 years old woman. Thankfully, a baby who is 1.5 months old, who was in the car with her, was not injured, despite at least 10 bullets being retrieved from her vehicle. The IDF is searching for the terrorist.
Israeli soldiers have found and confiscated suitcases with 5 million shekels in cash from the home of a senior Hamas terrorist in Gaza. I want everyone to understand that this sum is currently 1,369,507 $ (yes, I checked with professor Google), and that most Israelis will never see that kind of money. I imagine a majority of "privileged" westerners never will, either. And this kind of money was just lying around in this terrorist's home...

The IDF has exposed and is now in control of what is likely the biggest Hamas terror tunnel. It is about 4 kilometers long (roughly 2.5 miles), and it is wide enough for vehicles to comfortably drive through it. Israeli soldiers have also found footage showing Muhammad Sinwar, the brother of Hamas leader in Gaza Yahya Sinwar, doing exactly that, in addition to footage showing the construction of this terror tunnel...
youtube
I don't post every single day about the Israeli soldiers injured and killed in Gaza, because the truth is that it has become technically difficult and emotionally painful to keep track. Yesterday, five more soldiers were confirmed as killed, one of them having been injured last week, and he has now succumbed to his wounds. So far, 128 soldiers were killed in Gaza.
Last month, there was a cyber attack on Israeli hospital Ziv, trying to derail its medical activity. Israel has confirmed today that it has traced Iran and Hezbollah as responsible for the attack. If we count the cyber war (and in terms of requiring manpower and resources, as well as in terms of the potential loss in human life, there is no reason not to count it), then Israel has been defending its citizens on no less than six fronts.
The Iran-funded terrorist Houthis in Yemen have been attacking ships unconnected to Israel, for simply passing through territory close to Yemen. A lot of shipment companies from around the world have announced they will not be sailing through this area for at least a time, which means they would have to sail all around Africa, to pass goods between the far east and the western world. This will hurt the entire world's economy, as shipment prices are expected to rise (think of the Evergreen ship blockade of the Suez Canal... these ships will not be trying to get anywhere near the canal. Symbolically, Evergreen is one of the companies announcing they will no longer sail through the Red Sea due to the threat of the Houthis). This will financially hurt so many countries, including Egypt (which operates the Suez Canal), the US and China (this means Iran's move has created a rare moment when American and Chinese financial interests align). The biggest question is, when will the world fully take in the fact that the biggest threat to world peace is the Islamist regime in Iran, and start acting accordingly?
This is Haj Amin al-Husseini.
Out of all of the people who helped shape the Israeli-Arab conflict, he's probably the most influential one, an antisemite, a Nazi collaborator, and a believer in pan-Arab nationalism (he didn't want to fight Jews to establish a Palestinian state, he wanted to exterminate the Jews and establish a greater Arab Islamic state, a new chaliphate, if you will. There is a FASCINATING docu series in Israel, dedicated to the Arab and Muslim leaders who have fought Jews and Israel, interviewing intelligence agents from many countries. The ep dedicated to al-Husseini is unbelievable, and I wish everyone could watch it. It's available online, but sadly, only in Hebrew. The truth is, I don't think anyone can understand the Israeli-Arab conflict without understanding the role of al-Husseini in it, and how different things could have been, if only the more moderate Arab leaders in the Land of Israel at the time had managed to squash his influence, or if the British hadn't tried to "tame" him by appointing him to the position of Jerusalem's grand mufti.
This is the Belchassan family, 31 years old Yuval and Ofir, and their two years old son Tai.
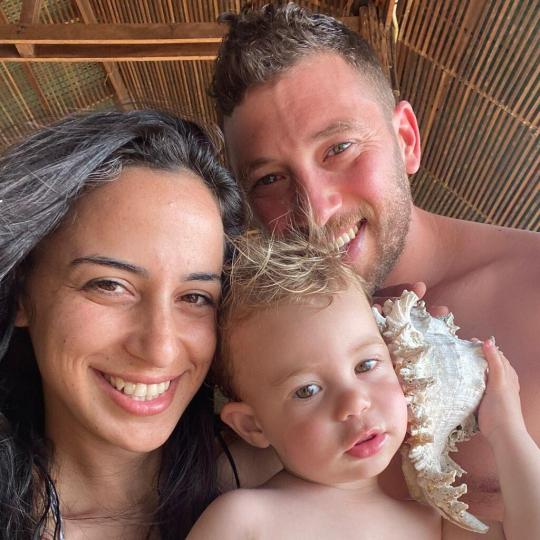

On Oct 7, Yuval left Ofir and Tai to hide in the bomb shelter, and went out to fight off the Hamas terrorists. He and his friends saved their kibbutz, but now, as Ofir is due to give birth to a daughter, they have no home to bring her back to.
(for all of my updates and ask replies regarding Israel, click here)
#israel#antisemitism#israeli#israel news#israel under attack#israel under fire#israelunderattack#terrorism#anti terrorism#hamas#antisemitic#antisemites#jews#jew#judaism#jumblr#frumblr#jewish#Youtube
106 notes
·
View notes
Text

LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
November 26, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Nov 27, 2024
Today presented a good example of the difference between governance by social media and governance by policy.
Although incoming presidents traditionally stay out of the way of the administration currently in office, last night, Trump announced on his social media site that he intends to impose a 25% tariff on all products coming into the U.S. from Mexico and Canada “until such time as Drugs, in particular Fentanyl, and all Illegal Aliens stop this Invasion of our Country!” Trump claimed that they could solve the problem “easily” and that until they do, “it is time for them to pay a very big price!”
In a separate post, he held China to account for fentanyl and said he would impose a 10% tariff on all Chinese products on top of the tariffs already levied on those goods. “Thank you for your attention to this matter,” he added.
In fact, since 2023 there has been a drop of 14.5% in deaths from drug overdose, the first such decrease since the epidemic began, and border patrol apprehensions of people crossing the southern border illegally have fallen to the lowest number since August 2020, in the midst of the pandemic. In any case, a study by the libertarian Cato Institute shows that from 2019 to 2024, more than 80% of the people caught with fentanyl at ports of entry—where the vast majority of fentanyl is seized—were U.S. citizens.
Very few undocumented immigrants and very little illegal fentanyl come into the U.S. from Canada.
Washington Post economics reporter Catherine Rampell noted that Mexico and Canada are the biggest trading partners of the United States. Mexico sends cars, machinery, electrical equipment, and beer to the U.S., along with about $19 billion worth of fruits and vegetables. About half of U.S. fresh fruit imports come from Mexico, including about two thirds of our fresh tomatoes and about 90% of our avocados.
Transferring that production to the U.S. would be difficult, especially since about half of the 2 million agricultural workers in the U.S. are undocumented and Trump has vowed to deport them all. Rampell points out as well that Project 2025 calls for getting rid of the visa system that gives legal status to agricultural workers. U.S. farm industry groups have asked Trump to spare the agricultural sector, which contributed about $1.5 trillion to the U.S. gross domestic product in 2023, from his mass deportations.
Canada exports a wide range of products to the U.S., including significant amounts of oil. Rampell quotes GasBuddy’s head of petroleum analysis, Patrick De Haan, as saying that a 25% tax on Canadian crude oil would increase gas prices in the Midwest and the Rockies by 25 cents to 75 cents a gallon, costing U.S. consumers about $6 billion to $10 billion more per year.
Canada is also the source of about a quarter of the lumber builders use in the U.S., as well as other home building materials. Tariffs would raise prices there, too, while construction is another industry that will be crushed by Trump’s threatened deportations. According to NPR’s Julian Aguilar, in 2022, nearly 60% of the more than half a million construction workers in Texas were undocumented.
Construction company officials are begging Trump to leave their workers alone. Deporting them “would devastate our industry, we wouldn’t finish our highways, we wouldn’t finish our schools,” the chief executive officer of a major Houston-based construction company told Aguilar. “Housing would disappear. I think they’d lose half their labor.”
Former trade negotiator under George W. Bush John Veroneau said Trump’s plans would violate U.S. trade agreements, including the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA) that replaced the 1994 North American Free Trade Agreement that Trump killed. The USMCA was negotiated during Trump’s own first term, and although it was based on NAFTA, he praised it as “the fairest, most balanced, and beneficial trade agreement we have ever signed into law. It’s the best agreement we’ve ever made.”
Trump apologists immediately began to assure investors that he really didn’t mean it. Hedge fund manager Bill Ackman posted that Trump wouldn’t impose the tariffs if “Mexico and Canada stop the flow of illegal immigrants and fentanyl into the U.S.” Trump’s threat simply meant that Trump “is going to use tariffs as a weapon to achieve economic and political outcomes which are in the best interest of America,” Ackman wrote.
Iowa Republican lawmaker Senator Chuck Grassley, who represents a farm state that was badly burned by Trump’s tariffs in his first term, told reporters that he sees the tariff threats as a “negotiating tool.”
Foreign leaders had no choice but to respond. Mexican president Claudia Sheinbaum issued an open letter to Trump pointing out that Mexico has developed a comprehensive immigration system that has reduced border encounters by 75% since December 2023, and that the U.S. CBP One program has ended the “caravans” he talks about. She noted that it is imperative for the U.S. and Mexico jointly to “arrive at another model of labor mobility that is necessary for your country and to address the causes that lead families to leave their places of origin out of necessity.”
She noted that the fentanyl problem in the U.S. is a public health problem and that Mexican authorities have this year “seized tons of different types of drugs, 10,340 weapons, and arrested 15,640 people for violence related to drug trafficking,” and added that “70% of the illegal weapons seized from criminals in Mexico come from your country.” She also suggested that Mexico would retaliate with tariffs of its own if the U.S. imposed tariffs on Mexico.
Canadian prime minister Justin Trudeau did not go that far but talked to Trump shortly after the social media post. The U.S. is Canada’s biggest trading partner, and a 25% tariff would devastate its economy. The premier of Alberta, Danielle Smith, seemed to try to keep her province’s oil out of the line of fire by agreeing with Trump that the Canadian government should work with him and adding, “The vast majority of Alberta’s energy exports to the US are delivered through secure and safe pipelines which do not in any way contribute to these illegal activities at the border.”
Trudeau has called an emergency meeting with Canada’s provincial premiers tomorrow to discuss the threat.
Spokesperson for the Chinese embassy in Washington Liu Pengyu simply said: “No one will win a trade war or a tariff war” and “the idea of China knowingly allowing fentanyl precursors to flow into the United States runs completely counter to facts and reality.”
In contrast to Trump’s sudden social media posts that threaten global trade and caused a frenzy today, President Joe Biden this evening announced that, after months of negotiations, Israel and Lebanon have agreed to a ceasefire brokered by the U.S. and France, to take effect at 4:00 a.m. local time on Wednesday. “This is designed to be a permanent cessation of hostilities,” Biden said.
Lebanon’s Iran-backed Hezbollah attacked Israel shortly after Hamas’s attack of October 7, 2023. Fighting on the border between Israel and Lebanon has turned 300,000 Lebanese people and 70,000 Israelis into refugees, with Israel bombing southern Lebanon to destroy Hezbollah’s tunnel system and killing its leaders. According to the Lebanese Ministry of Public Health, Israeli attacks have killed more than 3,000 people and injured more than 13,000, while CBS News reports that about 90 Israeli soldiers and nearly 50 Israeli civilians have been killed in the fighting. Under the agreement, Israel’s forces currently occupying southern Lebanon will withdraw over the next 60 days as Lebanon’s army moves in. Hezbollah will be kept from rebuilding.
According to Laura Rozen in her newsletter Diplomatic, before the agreement went into effect, Israel increased its airstrikes in Beirut and Tyre.
When he announced the deal, Biden pushed again for a ceasefire in Gaza, whose people, he said, “have been through hell. Their…world is absolutely shattered.” Biden called again for Hamas to release the more than 100 hostages it still holds and to negotiate a ceasefire. Biden said the U.S. will “make another push with Turkey, Egypt, Qatar, Israel, and others to achieve a ceasefire in Gaza with the hostages released and the end to the war without Hamas in power.”
Today’s announcement, Biden said, brings closer the realization of his vision for a peaceful Middle East where both Israel and a Palestinian state are established and recognized, a plan he tried to push before October 7 by linking Saudi Arabia’s normalization of relations with Israel to a Palestinian state. Biden has argued that such a deal is key to Israel’s long-term security, and today he pressed Israel to “be bold in turning tactical gains against Iran and its proxies into a coherent strategy that secures Israel’s long-term…safety and advances a broader peace and prosperity in the region.”
“I believe this agenda remains possible,” Biden said. “And in my remaining time in office, I will work tirelessly to advance this vision of—for an integrated, secure, and prosperous region, all of which…strengthens America’s national security.”
“Today’s announcement is a critical step in advancing that vision,” Biden said. “It reminds us that peace is possible.”
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Heather Cox Richardson#Letters From An American#American History#justice#bribes#billionaires#rule of law#plunder#economic madness#tariffs#deportation
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
While I was pondering whether Mrs. Douglas had a "freeze" reaction to trauma in chapter V of The Valley of Fear, chapter VI appeared with the answer, and I fear Letters from Watson will soon provide chapter VII, so let's get cracking.
There are three things top of mind for me today:
The Panic of 1873
Yews
Dumbbells
The Panic of 1873
When I worked out the timeline for Cecil Barker's recounting of "we did this for five years and this for one year," etc., etc., assuming that the story takes place in late 1888 or early 1889, the year I got for Barker's likely arrival in the U.S. was 1873.
That's significant: he set off to make his fortune, ending up in the gold fields of California, about the time that a global depression was starting.
The short version of the Panic of 1873 is that after the Civil War, U.S. railroad bonds (that is, the debt used to finance railroad construction) were the hot investment, not just in the US, but in Europe, especially Germany. Nineteenth-century investing was mostly in bonds -- this is why people talk in Victorian novels about having investments in 3-percents that pay 10,000 pounds a year, or similar. When you invested your money, the company was literally in debt to you, and it paid you a safe "coupon" of interest on that debt.
Not all bonds were the same. People were "ruined" by investing in companies that did not have stable cash flow or were outright fraudulent.
The initial problem in 1873 was not with the railroads, though, but with trading in the bonds. When German investors moved on to other investments, there were too many railroad bonds running loose, causing their value to plummet. That took out a US bank that had a hefty investment in those bonds, as their asset value dropped. The bank failure caused a panic, which cascaded through the system. This article and this one explain some of the specifics.
Anyway, Cecil Barker seeks his fortune abroad at a time loosely equivalent to the Great Recession of 2008.
In 1873, California was wrapping up efforts to exterminate native peoples -- no, I'm not exaggerating. This was not covered in 4th grade state history, 5th grade U.S. history, nor 8th or 11th grade U.S. history when I was in school!
By 1873, Gold Rush hysteria was over and some of the original sites in the Sierra Nevada foothills had been largely mined-out and abandoned, though mining still continued where it could. San Francisco was establishing itself as "the Paris of the West." The Central Valley, where I live, was getting rail built down its length, with towns established at various points for taking on fuel and water, as well as for picking up wheat and other crops that didn't require intensive irrigation (which wouldn't arrive for ~40 years).
It's not me, it's YEW
After decades of reading British novels, I have finally looked up what a yew is. I'd always envisioned something like the Chinese juniper that's planted everywhere around here: a low, dense hedge with soft packets of needles and a pungent, dusty scent.
Nope. I far underestimated the yew. It is a tree that makes Tolkien's Ents look small and non-threatening. Visit this yew-focused page to see the most terrifying trees. The existence of the yew also explains folktales of the British Isles where fair folk live in hollow trees. Yikes.
The yew traditionally symbolizes death, so the yew hedge is an excellent place to hang out after one's husband is mysteriously murdered.
(While you're there, the Ancient Tree Inventory is great for hours of exploration and arboreal terror.)
Where is the missing dumbbell?
The fact that Douglas has dumbbells at all is interesting, as the physical culture movement only really took off in the US in the 1880s, and it was slower to arise in England due to a greater cultural emphasis on "games."
He may have been influenced by his German first wife, as it was German immigrants in the 1850s who popularized the "Turner" movement of liberal political philosophy and physical fitness, the latter through vigorous gymnastics. Turnverein had a significant role in bringing PE into American schools.
Depending how one interprets the dumbbells, Douglas could be:
Forward-thinking
Eccentric
Worried about physical attacks or about aging
Very into German culture
We can't ask Mrs. Douglas, as, per Cecil Barker, Douglas' "perfect" trust in her did not include telling her... oh, anything actually important about his life.
I really want to know who was using whom in this household.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dean Obeidallah at The Dean's Report:
“The one big thing nobody is talking about: Did Elon want to shut the government down because of his business deals with China?” That was the first line of Rep. Jim McGovern (D-Mass) multi-part statement Saturday posted on Elon Musk’s platform, X--ironically enough. A similar point was also made Friday by Rep. Rosa DeLauro (D-CT)—the ranking minority member of the House Appropriations Committee-in a detailed letter to leaders of the House and the Senate. What was the issue the two were flagging? As Rep. McGovern wrote: “The original funding bill (that he [Musk] killed) included what’s called an “outbound investment” provision—which would limit & screen U.S. money flowing to China. That would have made it easier to keep cutting-edge AI and quantum computing tech—as well as jobs—in America. But Elon had a problem.” DeLauro gave even more context to this provision vetting investments in China: “This outbound investment provision was agreed to after months of bipartisan, bicameral negotiations and years of advocacy from Members of Congress. It would have kept innovation and manufacturing in semiconductors, artificial intelligence (AI), quantum computing, and other cutting-edge technologies in the United States and prevented wealthy investors from continuing to offshore production and U.S. intellectual property into China – benefiting only their bottom lines and the Chinese Communist Party.” But Musk—per these two members of Congress—led the charge to block this proposed legislation because as McGovern accurately noted, Musk’s “second-largest market is China. He’s building huge factories there. His bottom line depends on staying in China’s good graces.” The result was that when the new budget deal was agreed upon Friday, guess what was missing? Yep, the provision that would’ve been bad for Musk’s business deals with the Chinese Communist Party—which is in essence Musk’s business partner as the NY Times detailed earlier this year in an article titled, “How Elon Musk Became ‘Kind of Pro-China.’” (Musk’s exact words.)
Rep. DeLauro explained in more detail the financial incentive behind Musk’s action to block this provision: “Musk’s car company, Tesla has poured billions of dollars into investments in China, particularly its “gigafactory” in Shanghai. The Shanghai plant is Tesla’s largest car manufacturing facility – the Chinese gigafactory produced about 50 percent of Tesla’s global automobile output over the last year.” DeLauro continued, “And in May of this year, Tesla broke ground on a new $200 million factory to manufacture large batteries critical to its electric vehicle supply chain…Notably, proponents of regulating U.S. investment in China have advocated for the inclusion of large battery manufacturing in the list of technologies subject to outbound investment screening.” Yep, these new law could’ve impacted Musk’s new business venture per DeLauro.
Rep. McGovern also raised concerns about Musk’s future business plans involving China, explaining Musk “wants to build an AI data center there too—which could endanger U.S. security.” Importantly, DeLauro detailed for all to see Musk’s documented personal relations with the Chinese Communist Party, noting, “Musk has ingratiated himself with Chinese Communist Party leadership.” For example, she cited Musk’s close ties with “Chinese premier Li Qiang, who helped rush the construction of Tesla’s Shanghai gigafactory.” DeLauro concluded her letter by writing, “It is extremely alarming that House Republican leadership, at the urging of an unelected billionaire, scrapped…this critical provision to protect American jobs and critical capabilities.” Adding, “This is particularly concerning given Elon Musk’s extensive investments in China in key sectors and his personal ties with Chinese Communist Party leadership, and calls into question the real reason for Musk’s opposition to the original funding deal.”
[...] In fact, even a well-known Republican raised alarm bells about Musk’s loyalty to Beijing. Vivek Ramaswamy--who Trump tapped with Musk to co-head the newly created Department of Government Efficiency--was publicly warning in 2023 that Musk was a puppet for the Chinese Communist Party. As CNN recently reported, Ramaswamy was concerned that “Tesla is increasingly beholden to China,” adding damningly, “I have no reason to think Elon won’t jump like a circus monkey when [China’s leader] Xi Jinping calls in the hour of need.” The GOP silence on Musk’s extensive ties to the Chinese Communist Party is beyond hypocritical given that for years Republicans have slammed China as a threat. For example, in January 2023, the House GOP created “The Select Committee on the Chinese Communist Party” designed to address the “threat posed by the Chinese Communist Party and develop a plan of action to defend the American people, our economy, and our values.” Earlier this year, the House GOP led the charge to ban Tik Tok from having access to the United States--which was signed into law and goes into effect Jan. 19, 2025 unless the Chinese company that owns the social media platform sells it to a non-Chinese company. But when it comes to Musk, the GOP doesn’t care that he has documented ties to top Chinese Communist Party officials.
CCP puppet and de facto “President” Elon Musk helped block the original CR to protect his business deals with the Chinese government, because it had an “outbound investment” provision that would screen any US money sent to China.
#Elon Musk#China#Vivek Ramaswamy#GOP Hypocrisy#Tesla#President Musk#Rosa DeLauro#Jim McGovern#CCP#US/China Relations#TikTok Ban#TikTok#DOGE#Department of Government Efficiency
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

Human arcane order AU!!
I finally present to you my human AU of the arcane order!! after so much time planning their designs and everything... I made this little graphic with information about them!!
I'll leave some bonuses for you to be curious about!! and maybe I'll do short stories on ao3.. but nothing so relevant just short stories hihi
information:
skrael:
• is 27 years old
•works as a stylist at a fashion agency and in his spare time works in a cafe.
•likes fighting games and stories (god of war, red dead redemption, dark deception, etc.)
•lives in the united states in las vegas with bellroc.
• loves cold foods, especially iced coffee and vanilla and mint ice cream
• married to bellroc for 3 years and has 10 years of friendship with nari and bellroc
bellroc:
• is 29 years old
•works as an architect in a very old construction company.
•likes boxing in his spare time and karate on the weekends
•lives in the United States in Las Vegas with Skrael (but has lived in China and Japan)
•fluent in English, Japanese, Chinese and knows a little Russian and Brazilian Portuguese (thanks to Nari is Skrael)
•likes hot and sweet foods (hot chocolate, cappuccino, cake, chicken and cheese snacks)
•He likes to sleep cuddled up in Skrael on hot nights and travels to Australia on summer holidays to see his country.
nari:
• is 25 years old
•works as a biologist for a TV show and takes care of a sanctuary in Canada.
•likes gardening in his spare time and hiking in the mountains for camping.
•lives in the united states in new york with douxie and archier.
•He likes to visit Bellroc and Skrael during the summer holidays and always prepares his famous feijoada (a typical Brazilian dish) with lots of pepper, because he knows that Bellroc likes it.
•fluent in English, Russian and a little Japanese.
•nari likes any type of food, but prefers less industrialized things as some can give her allergies.
•She goes to Brazil with Douxie and Archier almost every Christmas so she can be with her family.
Well!!! This was a little information about them!! I hope you like it and I'll see you later!! :3
#my art#arcane order#tales of arcadia#trollhunters#nari#bellroc#skrael#toa wizards#wizards tales of arcadia#skrael of the north wind#bellroc keeper of the flame#nari of the eternal forest#nari of the eternal#digital artist#artist on tumblr#brazilian artist#art#small artist#the arcane order#toa au#toanari#toa fanart#arcane order au
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cybernetics with Chinese Characteristics & why we suck at the real Grand Strategy Game
Part 2 - The Quickening
Back in 2023, I wrote this more blog-like post about the mid 20th century McCarthyite purges of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the knock on effects that had - Namely the inception of the Chinese nuclear program, one-child policy and Chinese computing scene.
Since nothing is new under the sun, we have recently witnessed yet another example of America shooting itself in the foot, yet again, due to it's McCarthyite style purge of Chinese technology.
The release of the Chinese created AI system DeepSeek R1 last week has lead to the largest US stock market loss in history with NVIDIA stock decimated.
A record $465 Billion was wiped off its valuation in a single day. In 2024, the government of Turkey spent this much in a year on it's responsibilities?
Why did this happen?

As always, a lot can be put down to US foreign policy, and the in-intended implications of seemingly positive actions.
Do you want to start a trade war?
Back in the relatively uncontroversial days of the first Trump Presidency (Yes it does feel odd saying that) there were scandals with hardware provided by Chinese company Huawei. This led to the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2019 which explicitly banned Huawei and ZTE's hardware from use in US Government institutions. It also meant the US had to authorise US component manufacturer purchases by these companies.
Crucially this had a 27 month window. This allowed both companies to switch suppliers, and production to domestic suppliers. This actually led to Chinese chip advances. Following on from this came the 2022 move by the US Department of Commerce: "Commerce Implements New Export Controls on Advanced Computing and Semiconductor Manufacturing Items to the People’s Republic of China (PRC) ". This further limited the supply of semiconductor, supercomputer, and similar hardware to the PRC and associated countries.
Ok, well so far this is fairly dry stuff. You might think it would hamper Chinese development and, to some extent, it did.
It also proved to be the main catalyst for one financial quant.
Meet the Quant

Meet Liang Wenfeng (梁文锋). Educated to masters level, Liang was keen to apply machine learning methods to various field, but couldn't get a break. Finally, in the mid 2000's, he settled on a career investigating quantitative trading using machine learning techniques.
He became successful, founding several trading firms based around using machine learning methods, but his interest in base AI never seemed to cease. It was in 2021 that he started purchasing multiple NVIDIA GPUs to create a side project, leading to the creation of DeepSeek in 2023.
Now, due to import limitations, there were limitations on computation. This, however, did not stop DeepSeek's programming team.
Instead they used it as their strength.
Constrains Breed Innovation

For many years, the Western model of AI releases have focussed on making ever larger and larger models.
Why?
Let's break this down from an evolutionary point of view. Modern Western technology companies are largely monopolistic and monolithic. Many of these companies have previously hired staff at higher salaries not to fill roles, but to deny their competitors, and middle market firms, high-flying staff.
They also closely guard trade secrets. What's the training data? What algorithms were used in construction? Guess you'd better chat up some Silicon Valley bros at parties to find out.
For these kinds of firms, having control over large models, housed in data centres makes perfect sense. Controlling model deployment on their own computing systems, and not using local machines, means that they can not only control their systems more carefully, it also means that they can gatekeep access.
If your business model is to allow people to access your models on your servers, and your employees are focussed on making the biggest, best, models, there is no impetus to innovate more efficient, smaller models.
Companies such as OpenAI therefore have the following traits:
Research/Model focus on size over efficiency
Profit driven culture, with emphasis on closed source code
OpenAI's initial focus was as a non-for-profit developing Artificial General Intelligence. This became a for-profit driven company over time. - “I personally chose the price and thought we would make some money.” - Sam Altman
Staff working within paradigm they set in the early 2020's with established code libraries and direct contact with hardware companies creating chips
Significant capital investment - Upwards of several $ billions
DeepSeek, in comparison, is slightly different
For DeepSeek, necessity made innovation necessary. In order to create similar, or better models, than their counterparts, they needed to significantly optimise their code. This requires significantly more work to create, and write, libraries compared to OpenAI.
DeepSeek was started by financial quants, with backgrounds in mainly mathematics and AI. With a focus on mathematics and research, the main drive of many in the company has been exploration of the research space over concerns about profitability.
DeepSeek has also done what OpenAI stopped years ago: actually releasing the code and data for their models. Not only can these models therefore be run via their own gated servers, anyone can replicate their work and make their own system.
For DeepSeek, their traits were:
Research/Model focus on both efficiency and accuracy
Research driven culture, with open nature - “Basic science research rarely offers high returns on investment” - Liang Wenfeng
Strong mathematical background of staff, with ability to work around software, and hardware, constraints
Low capital investment of around $5.5 million

From an evolutionary point of view, DeepSeek's traits have outcompeted those of OpenAI.
More efficient models cost less to run. They also more portable to local machines.
The strong ability of DeepSeek's research focussed staff allowed them to innovate around hardware constraints
Opening up the code to everyone allows anyone (still with the right hardware) to make their own version.
To top it off, the cost to make, and run, DeepSeek R1 is a fraction of the cost of OpenAI's model
House of Cards

Now we can return to today. NVIDIA has lost significant market value. It's not just limited to NVIDIA, but to the entire US technology sector with the most AI adjacent companies losing from 10% to 30% of their valuation in a single day.
The culture, and business model, of OpenAI isn't just limited to OpenAI, but to the entire US technology ecosystem. The US model has been to create rentier-style financial instruments at sky-high valuations.
US tech stocks have been one of the only success stories for America over the past few decades, ever since the offshoring of many manufacturing industries. Like a lost long-unemployed Detroit auto-worker the US has been mainlining technology like Fentanyl, ignoring the anti-trust doctors advice, injecting pure deregulated substances into its veins.
The new AI boom? A new stronger hit, ready for Wall Street, and Private Equity to tie the tourniquet around its arm and pump it right into the arteries.
Like Prometheus, DeepSeek has delved deep and retrieved fire from the algorithmic gods, and shown it's creation to the world. The stock market is on fire, as the traders are coming off of their high, realising they still live in the ruin of barren, decrepit, warehouses and manufactories. The corporate heads, and company leaders reigning over the wreckage like feudal lords, collecting tithes from the serfs working their domain.
A Tale of Two Cities

The rise of DeepSeek isn't just a one-off story of derring-do in the AI world: It's a symbolic representation of the changing world order. DeepSeek is but one company among many who are outcompeting the US, and the world, in innovation.
Where once US free-markets led the world in manufacturing, technology and military capability, now the US is a country devoid of coherent state regulated free-market principles - its place as the singular world power decimated by destroying the very systems which made it great.
"Our merchants and master-manufacturers complain much of the bad effects of high wages in raising the price, and thereby lessening the sale of their goods both at home and abroad. They say nothing concerning the bad effects of high profits. They are silent with regard to the pernicious effects of their own gains. They complain only of those of other people." - Adam Smith, The Wealth of Nations
By selling the jobs of working class communities to overseas businesses, destroying unions and creating rentier based business models without significant anti-trust measures, US business and political elites have sealed the present fate of the country.
The CCP led, but strongly anti-trust enforcing, China has been able to innovate, ironically, using the free-market principles of Adam Smith to rise up and create some of the world's best innovations. The factories, opened by Western business leaders to avoid union/worker labour costs in their own countries, have led Shenzhen, and similar cities, to become hubs of technological innovation - compounding their ability to determine the future of technologies across the world.

Will America be able to regain its position on top? It's too early to say, but the innovative, talented, people who made America in the 20th century can certainly do it again.
As Franklin D. Roosevelt once said: “The liberty of a democracy is not safe if the people tolerated the growth of private power to a point where it becomes stronger than the democratic state itself...
We know now that Government by organized money is just as dangerous as Government by organized mob.
Never before in all our history have these forces been so united against one candidate as they stand today. They are unanimous in their hate for me—and I welcome their hatred.”

Until then, here's a farewell to the American Century 在那之前, 再见美国世纪
#cybernetics#cybernetic#ai#artificial intelligence#DeepSeek#OpenAI#ai technology#long reads#politics#us politics
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Soviet intervention in Hungary and the Khrushchev revelations produced in Europe a process that led – gradually – to the Eurocommunism of the Communist Party of Spain’s leader Santiago Carrillo, who said, in 1976, ‘once Moscow was our Rome, but no more. Now we acknowledge no guiding centre, no international discipline’. This was a communism that no longer believed in revolution but was quite satisfied with an evolutionary dynamic. The European parties, correct in their desire for the right to develop their own strategies and tactics, nonetheless, threw themselves onto a self-destructive path. Few remained standing after the USSR collapsed in 1991. They campaigned for polycentrism but, in the end, achieved only a return to social democracy.
Amongst the Third World communist parties, a different orientation became clear after 1956. While the Western European parties seemed eager to denigrate the USSR and its contributions, the parties in the Third World acknowledged the importance of the USSR but sought some distance from its political orientation. During their visits to Moscow in the 1960s, champions of ‘African socialism’ such as Modibo Keïta of Mali and Mamadou Dia of Senegal announced the necessity of non-alignment and the importance of nationally developed processes of socialist construction. Marshal Lin Biao spoke of the need for a ‘creative application’ of Marxism in the Chinese context. The young leader of the Indonesian Communist Party – Dipa Nusantara Aidit – moved his party towards a firm grounding in both Marxism-Leninism and the peculiarities of Indonesian history. [...]
In the Third World, where Communism was a dynamic movement, it was not treated as a religion that was incapable of error. ‘Socialism is young’, Che Guevara wrote in 1965, ‘and has its mistakes.’ Socialism required ceaseless criticism in order to strengthen it. Such an attitude was missing in Cold War Europe and North America [...] After 1956, Communism was penalized by the Cold Warriors for the Soviet intervention in Hungary. This played some role in the Third World, but it was not decisive. In India, in 1957 the Communists won an election in Kerala to become the ruling party in that state. In 1959, the Cuban revolution overthrew a dictatorship and adopted Marxism-Leninism as its general theory. In Vietnam, from 1954, the Communists took charge of the north of the country and valiantly fought to liberate the rest of their country. These were communist victories despite the intervention in Hungary.
[...]
Much the same history propelled the Indonesian Communist Party (PKI) forward from 1951, when it had merely 5,000 members, to 1964, when it had two million party members and an additional fifteen million members in its mass organizations (half of them in the Indonesian Peasants’ Front). The party had deep roots in the heavily populated sections of east and central Java but had – in the decade after 1951 – begun to make gains in the outer islands, such as Sumatra. A viciously anti-communist military was unable to stop the growth of the party. The new leadership from the 1953 Party Central Committee meeting were all in their thirties, with the new Secretary General – Aidit – merely thirty-one years old. These communists were committed to mass struggles and to mass campaigns, to building up the party base in rural Indonesia. The Indonesian Peasants’ Front and the Plantation Workers’ Union – both PKI mass organizations – fought against forced labour (romusha) and encouraged land seizures (aksi sepihak). These campaigns became more and more radical. In February 1965, the Plantation Workers’ Union occupied land held by the US Rubber Company in North Sumatra. US Rubber and Goodyear Tires saw this as a direct threat to their interests in Indonesia. Such audacity would not be tolerated. Three multinational oil companies (Caltex, Stanvac and Shell) watched this with alarm. US diplomat George Ball wrote to US National Security Advisor McGeorge Bundy that in ‘the long run’ events in Indonesia such as these land seizures ‘may be more important than South Vietnam’. Ball would know. He oversaw the 1963 coup in South Vietnam against the US ally Ngô Đình Diệm. The West felt it could not stand by as the PKI got more aggressive.
By 1965, the PKI had three million party members – adding a million members in the year. It had emerged as a serious political force in Indonesia, despite the anti-communist military’s attempts to squelch its growth. Membership in its mass organizations went up to 18 million. A strange incident – the killing of three generals in Jakarta – set off a massive campaign, helped along by the CIA and Australian intelligence, to excise the communists from Indonesia. Mass murder was the order of the day. The worst killings were in East Java and in Bali. Colonel Sarwo Edhie’s forces, for instance, trained militia squads to kill communists. ‘We gave them two or three days’ training,’ Sarwo Edhie told journalist John Hughes, ‘then sent them out to kill the communists.’ In East Java, one eyewitness recounted, the prisoners were forced to dig a grave, then ‘one by one, they were beaten with bamboo clubs, their throats slit, and they were pushed into the mass grave’. By the end of the massacre, a million Indonesian men and women of the left were sent to these graves. Many millions more were isolated, without work and friends. Aidit was arrested by Colonel Yasir Hadibroto, brought to Boyolali (in Central Java) and executed. He was 42.
There was no way for the world communist movement to protect their Indonesian comrades. The USSR’s reaction was tepid. The Chinese called it a ‘heinous and diabolical’ crime. But neither the USSR nor China could do anything. The United Nations stayed silent. The PKI had decided to take a path that was without the guns. Its cadre could not defend themselves. They were not able to fight the military and the anti-communist gangs. It was a bloodbath.
[...]
There was little mention in Havana of the Soviet Union. It had slowed down its support for national liberation movements, eager for detente and conciliation with the West by the mid-1960s. In 1963, Aidit had chastised the Soviets, saying, ‘Socialist states are not genuine if they fail to really give assistance to the national liberation struggle’. The reason why parties such as the PKI held fast to ‘Stalin’ was not because they defended the purges or collectivization in the USSR. It was because ‘Stalin’ in the debate around militancy had come to stand in for revolutionary idealism and for the anti-fascist struggle. Aidit had agreed that the Soviets could have any interpretation of Stalin in terms of domestic policy (‘criticize him, remove his remains from the mausoleum, rename Stalingrad’), but other Communist Parties had the right to assess his role on the international level. He was a ‘lighthouse’, Aidit said in 1961, whose work was ‘still useful to Eastern countries’. This was a statement against the conciliation towards imperialism of the Khrushchev era. It was a position shared across many of the Communist Parties of the Third World.
Many Communist parties, frustrated with the pace of change and with the brutality of the attacks on them, would take to the gun in this period – from Peru to the Philippines. The massacre in Indonesia hung heavily on the world communist movement. But this move to the gun had its limitations, for many of these parties would mistake the tactics of armed revolution for a strategy of violence. The violence worked most effectively the other way. The communists were massacred in Indonesia – as we have seen – and they were butchered in Iraq and Sudan, in Central Asia and South America. The image of communists being thrown from helicopters off the coast of Chile is far less known than any cliché about the USSR.
Red Star Over the Third World, Vijay Prashad, 2019
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
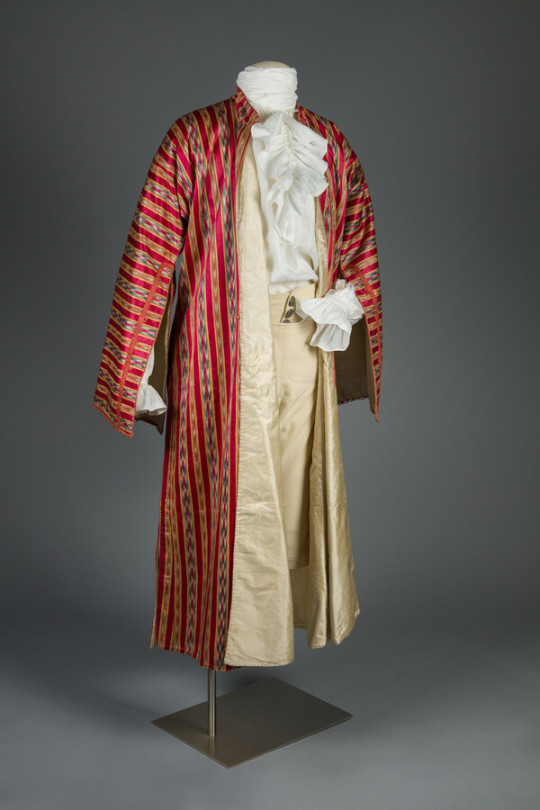

Banyan
1780s
The Maryland Center for History and Culture
"Red silk banyan owned and worn by Solomon Etting (1764-1847). Banyans, the loose robes or dressing gowns men wore informally in their homes, reveal the influences from the Middle East and Far East in the Western World. Constructed from luxurious imported fabrics, such as hand-painted India chintzes and Chinese silks, these robes symbolized a man’s worldliness and connections to foreign lands. Such a visual proclamation from Etting’s own banyan coincides with his career as a merchant involved in the Baltimore East India Trading Company."
108 notes
·
View notes
Text


When Elon Musk took over Twitter and the platform began to tank, the stock value plummeted, and people were leaving in droves, many of us thought he was just an arrogant doofus, a parasitic man-child who became a billionaire by throwing around free money, more recently billions in government subsidies but originally, as a kid, his massive inheritance from South African diamond mines. And he is all those things, but there is also something more going on here.
The Twitter takeover, in fact, possesses an opaque but important similarity with—of all things—the Chinese government’s COVID policy. If we assume that Musk’s many fumbles with one of the world’s largest social media platforms is nothing but a blunder, nothing but stupidity, then we miss out on an illuminating question. Which, it turns out, is the same question we miss when we assume the Chinese government’s zero tolerance COVID policy is a mere example of totalitarian inclinations or a different public health culture (both of which are explanations infused with racist stereotypes).
So what on Earth connects Elon Musk to China’s COVID policy? For one thing, one of Musk’s other companies, Tesla, became the first foreign company to wholly own a car factory in China when they opened an assembly plant in Shanghai in 2019. The Shanghai Gigafactory is one of Tesla’s largest, though it ran into problems when the government temporarily closed it down in 2020, and again in March 2022, to enforce a COVID quarantine. As the threat of new quarantines pops up, Musk might consider sending new investments to countries with weaker regulations like India. Apple, for example, is increasingly relying on India over China for iPhone production, meaning China’s COVID policy is costing them foreign direct investment.
There’s the similarity. A government policy causing a loss in revenue. A new corporate policy causing a plummet in stock value. Are we to judge both of these policies failures, or at the least, ineffective, because they lost money?
And that gets us to our central question: do companies and governments in this capitalist world system exist to make money? Is money, capital accumulation, the fundamental driving force of our world?
If it is, then both the turbulence Elon Musk has caused at Twitter and the stagnation the Chinese government has inflicted on its own economy due to its zero tolerance COVID policies have to be viewed as blunders, as they have unarguably caused a loss of economic value. However, in both cases, we might at least entertain the possibility that such an argument is reductionist if it hides other factors and outcomes that cannot be so easily quantified.
And quantification is an angle we need to explore to be able to answer this question. Even though the vagaries of international finance make it an obscure field, economic loss is easy to measure relative to qualitative forms of evaluation. Did Twitter lose value? Did the growth rate of the Chinese economy contract? Since both of these questions can be reduced to a number and real numbers are arranged along a single dimension, meaning we can always say whether one number is more or less than another number, then yes, Twitter lost value, and yes, the Chinese economy began to grow at a slower rate. So if it’s all about money, both of these policies were mistakes.
Before considering the case closed, should we be thinking about any kinds of qualitative as opposed to quantitative analysis that might illuminate the topic? After all, the knowledge systems of all the dominant institutions of our society are heavily biased in favor of quantitative and objective frameworks of thought; in fact this epistemology is central to the rationalism of the modern state and of capitalism itself, given that they allow for reproducibility and thus industrialism as both an economic and a political or war-making mode, and they allow ethical and spiritual frameworks to be subsumed into the construction of society itself, therefore making them invisible and immune to being questioned. If you want me to explain this idea more, let me know and I’ll devote some time to it in the future, but for now, let’s get back to Twitter.
What did Musk accomplish at Twitter, aside from losing unimaginably vast sums of money and showing the entire world that he’s not as intelligent as he thinks he is? He has taken a huge step to create a more right-wing media environment in what might become the biggest change to the landscape since the emergence of Fox News. True, Twitter’s algorithms always favored the specific content and also the controversy-seeking, baiting tactics of the Right. It is also true that conversation on Twitter was more often than not superficial and demeaning. However, we should not deny that anarchists and other anticapitalists saw Twitter as an important space for organizing and outreach. I had never been on social media my entire life, until finally around the end of 2019, when other anarchists convinced me that it did not make sense for me to spend so much time writing if I was going to avoid the platforms where writing and political analysis were actually being distributed in the current day.
And there are other corners of Twitter where emotional supportiveness, care, and mutual aid are actually the norm, spaces important in many people’s lives for building safety and opportunities for healing and connection, in rejection of the ableist, trans- and homophobic, racist culture that predominates in public space.
So yes, Twitter is a hellsite, but if we so quickly forget about some of the things that brought us there, we risk missing the relevance of this moment. Musk’s takeover of Twitter has enabled a fierce campaign of censorship against anarchist and other anticapitalist accounts, frequently executed by Musk himself, to such an extent that we should seriously consider that this was one of his primary motivations, more than making money. We already know that restoring Trump’s account was a motivator for him.
Meanwhile, the centrist media has given massive coverage to the Right’s “free speech” anti-censorship alibi. They continue to portray Musk as an anti-censorship figure, restoring far-Right accounts that had been banned, and they refuse to mention the accounts that Musk has been banning.
What about the Chinese government’s zero-tolerance COVID policy? Obviously, shutting everything down in a neighborhood, a city, or an entire region as soon as a rise in COVID cases is detected is going to be disruptive to the economy, as when when authorities closed down Tesla’s Shanghai Gigafactory and so many other thousands of factories. For a while now, Chinese planners and economists internationally have figures detailing how the zero-tolerance and other regulatory policies are slowing the economy and causing unemployment to skyrocket.
It’s important to mention that GDP growth is not just a metric imposed by Western observers. The Chinese Communist Party under Xi Jinping has made GDP growth targets a central part of their ruling strategy and their conceptualization of development. And yet, midway through the year, when it became clear they would not even meet their already reduced target of 5.5% growth, they chose to prioritize their restrictive no COVID policies.
Most countries in the world chose to allow a massive number of deaths in exchange for better economic growth. In the US, that’s over 1 million deaths, a figure we don’t see the media mention very often. However, the Chinese government cannot accurately be accused of humanitarianism, given that their solutions have included locking workers into their factories. In fact, their zero-tolerance COVID policy bears a striking similarity to Mao’s Four Pests Campaign, which sought to drive animals like flies and sparrows to extinction as a part of the government’s ambitious agricultural program. The purpose is less to save lives and more to eliminate external, natural forces capable of disrupting a rational, quantitative planning process.
A couple notes here, for accuracy. Mao is frequently lambasted for trying to eliminate sparrows, and the disastrous ecological consequences that policy had. At the same time (late ‘50s) and for significantly longer, the US government was trying to exterminate the wolves. Also, Western hacks and mainstream media frequently refer to socialist states as “planned economies” and NATO states as “free market economies.” Though there are significant differences in the strategies of state intervention in the economy, these labels are bogus since all modern states exist on the same continuum. The US government, from the beginning but even more so since FDR, engages in substantive economic planning, deciding which sectors will get the most capital, deciding interest rates, setting targets for inflation; and the Chinese government allows and encourages a massive private sector that is more responsive to market forces.
The reason all states engage in planning, and a more accurate framework for understanding the nature of that planning, is social control.
What is social control? The Marxist I like the most told me it is a fetishistic, meaningless category. Actually, it’s a necessary concept for explaining some glaring holes in Marxism itself and in any framework that sees capital accumulation as the be-all and end-all for understanding our society.
Musk’s actions make sense, even though they lost him $9 billion dollars, because like any capitalist he is worried about fundamental questions of social control that allow him to be a capitalist in the first place. The Chinese government’s actions make sense because developing techniques that allow a state to neutralize and surpass epidemics would greatly increase that state’s planning powers, and even if they fail they are testing and amplifying their arsenal of social control techniques, and social control is the fundamental concern of any state and thus the fundamental concern of capitalism, being an economic system entirely dependent on state power.
In this context it is worth noting that the Chinese government decided to relax their COVID policy not in early July, when they were forced to choose that policy over their economic growth targets, but at the end of November, when mass protests bordering on insurrection against the policy broke out. The policy got in the way of economic accumulation: they stuck to it. The policy got in the way of social control: they abandoned it.
Academically trained Marxists are going to be biased in favor of a quantitative analysis, like seeing capital accumulation as the fundamental force in our society, for the same reasons that all our dominant institutions are biased in favor of quantitative analysis. A qualitative analysis is not reproducible, and the modern state needs access to reproducible sciences.
This seems like a contradiction to claim that the state is fundamentally motivated by a qualitative science, like social control, and yet constantly in need of a quantitative science like capital accumulation. In fact, this contradiction traces a tense balance, a relation, that has come to shape the entire planet in these last centuries. The fundamental truth of the State is social control, an existential war waged by centralized power against all life. And the most effective motor the State has ever developed to fuel its war is not a winning religion, it’s not a more streamlined process for the transfer of power, it’s economic accumulation. Before capitalism, states were exponentially weaker, frequently overthrown by the societies they tried to dominate, even when state and society shared the hierarchical culture produced by patriarchy and organized religion.
Capitalism, which requires the enclosure of the commons and the alienation of all life, cannot exist without the planning and war-making powers of the State. And once capitalism emerged, created in a continuum by the Italian city-states, the Castillian-Aragonese state, and finally in its modern form by the Dutch state, it bestowed the states that adopted it with such power that henceforth it became the duty of every government on the planet to embrace capitalism, lest they be overwhelmed by those that already had. This sheds light on one of the reasons that colonialism spread in such a rapid wave, especially where there were already states that could be instrumentalized in the conquered territories. And it helps explain why socialism, by not rejecting the state, was fully absorbed by capitalism in the early 20th century, and why all Marxist-inspired states are fully capitalist, fully colonial, and every bit as imperialist as their geopolitical circumstances allow them to be.
Capital accumulation is a necessary motor for the state; it is also a favored metric for a quantitative science of power. Given that accumulation is a result of oppressive, exploitative processes and it cannot happen without the domination of society and nature, high rates of accumulation are generally a good indicator that state power is firmly ensconced, that the State is winning its war against life. Still, the fundamental question is that of social control. Many capitalists, as specialists, will lose sight of this as they become obsessed with their numbers game, but in the end it’s just a game, a highly useful game, and when push comes to shove, questions of social war will always be more important for the institutions of power. The trick for them is to make sure that seeking capital accumulation and seeking social control always go hand in hand, rather than entering into contradiction.
As for anticapitalist movements, we lose sight of the social war at our own risk. The reasons for this are multiple. Marxism’s predictive power regarding the development of the revolution is nil, displaying a profound lack of understanding of what revolution actually means. Attempts to combine materialist with geopolitical analysis, as with Giovanni Arrighi’s development of world systems theory (on the whole an illuminating theoretical framework) also demonstrate their inaccuracy and disconnection from living history wherever they focus too heavily on quantitative questions of capital accumulation, a weakness explored in Alex Gorrion’s “Anarchy in World Systems.” These are not just obscure questions relating to debates from past centuries, given how academic, materialist-oriented journals and discussion groups continue to falsify the history of revolutionary struggle as we live it, claiming, for example, that the major uprisings of the past two decades have occurred as a result of the crisis of accumulation, when in fact the uprisings preceded the manifestation of that crisis and have occurred in countries experiencing polar opposite moments in the kinds of crises capitalism constantly produces.
(I shouldn’t have to provide this rebuttal, but alas, experience tells me I do: it is intellectually dishonest and a waste of everyone’s time to start off by claiming that rebellion is “produced” by a specific quantitative crisis in accumulation, to then be shown that in fact rebellions are occurring in completely different economic circumstances—the crises associated with growth, the crises associated with recession, the crises associated with inflation—and then to double back around and claim that one’s original argument was that crisis produces rebellion. Given that capitalism is a constant string of crises, this is a meaningless statement with nothing predictive or scientific about it, and it sets up the dishonest strawman that non-materialists believe that rebellions come out of thin air, in no way a response to their surroundings.)
Time and again, the first sign of crisis that materialists notice is the rebellion itself, meaning they are rarely on the front lines. Those who are more present tend to be those who decide to fight back even if objective conditions are supposedly unfavorable.
For our survival, we need to understand the ways the State is designing a constant war against us, and always has been, and always will be. For our liberation, we need to understand unquantifiable life, abundance without capital, and we need to develop an intelligence for a kind of struggle that also subverts the logic of warfare. A collective sight that can perceive the battlefield but destroy the opposing army by moving sideways, by burrowing, by climbing into the trees, by turning the battlefield back into a field, a forest, a community.
#elon musk#the muskrat#anarchism#revolution#climate crisis#ecology#climate change#resistance#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment
12 notes
·
View notes