#Century 21 Productions
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
TPAC announces 45th Anniversary Broadway season featuring six Nashville premieres and two-week engagements of HAMILTON and Disney’s BEAUTY AND THE BEAST
A storybook season awaits as the nonprofit Tennessee Performing Arts Center® announces its 2025-26 HCA Healthcare/TriStar Health Broadway at TPAC season, presented in partnership with Nissan and Farm Bureau Health Plans, as part of its 45th Anniversary. The upcoming season features six Nashville premieres, plus the return of a classic fairy tale and the revolutionary re-telling of American…
#2025 beautyandthebeastthemusical.com Be Our Guest at Disney’s 30th Anniversary production of BEAUTY AND THE BEAST#2025 Disney’s BEAUTY AND THE BEAST – Nov. 4-16#2025 outsidersmusical.com The winner of the 2024 Tony Award® for Best Musical is THE OUTSIDERS. This classic coming-of-age story takes you t#2025 SUFFS – March 3-8#2025 THE OUTSIDERS – Oct. 14-19#2025 wizmusical.com The Tony® Award-winning Best Musical that took the world by storm is back. THE WIZ comes to Nashville in an all-new Broa#2026 Additional Broadway at TPAC presentations LES MISÉRABLES – Jan. 20-25#2026 BACK TO THE FUTURE – March 17-22#2026 backtothefuturemusical.com Great Scott! BACK TO THE FUTURE#2026 Below is additional information on the season lineup provided by each production. THE WIZ Sept. 23-28#2026 bookofmormonbroadway.com The New York Times calls it “the best musical of this century and Jimmy Fallon of The Tonight Show calls it &q#2026 HAMILTON – June 17-28#2026 hamiltonmusical.com A revolutionary story of passion#2026 SIX – Feb. 3-8#2026 sixonbroadway.com From Tudor Queens to Pop Icons#2026 SOME LIKE IT HOT – April 21-26#2026 somelikeithotmusical.com Winner of 4 Tony Awards®#2026 suffsmusical.com Direct from Broadway#2026 THE BOOK OF MORMON – June 2-7#2026 us-tour.lesmis.com Cameron Mackintosh presents the acclaimed production of Boublil and Schönberg’s Tony Award-winning musical phenomeno#2026 WATER FOR ELEPHANTS – May 12-17#2026 waterforelephantsthemusical.com The critically acclaimed bestselling novel comes to “thrilling#a young man jumps a moving train unsure of where the road will take him and finds a new home with the crew of a traveling circus#All-Out Song-And-Dance Spectacular!” (The New York Times). Set in Chicago when Prohibition has everyone thirsty for a little excitement#and a legacy that would shape the course of a nation. Based on Ron Chernow’s acclaimed biography and set to a score that blends hip-hop#and a life—and love—beyond his wildest dreams. Seen through the eyes of his older self#and a soaring score by the acclaimed PigPen Theatre Co. HAMILTON June 17-28#and across North America#and funny American women who fought tirelessly for the right to vote. From the singular mind of history-making artist Shaina Taub#and much more. To purchase season tickets and review the full benefits
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
01.02.25
#Marco-Marathon | Night at the Museum
Film Name: Night at the Museum: Battle of the Smithsonian (2009); Production Studios: Twentieth Century Fox, Moving Picture Company (MPC), 21 Laps Entertainment, Janimation, Dune Entertainment, 1492 Pictures, Museum Canada Productions; Director by: Shawn Levy; Screenwriter: Robert Ben Garant, Thomas Lennon; Starring: Ben Stiller, Amy Adams, Owen Wilson, Hank Azaria, Robin Williams; Genres: Fantasy, Comedy, Action, Family; Running Time: 1 hour 45 minutes;
"Night at the Museum: Battle of the Smithsonian" (2009) is a less successful sequel, suffering from an overabundance of special effects and a predictable plot. Despite the charismatic Amy Adams and Hank Azaria, the film does not reach the level of the first part.
Two stars - a disappointing, although sometimes funny sequel.
My rating:
⭐⭐

#marco marathon#night at the museum#film#night at the museum battle of the smithsonian#battle of the smithsonian#2009#twentieth century fox#mpc#21 laps entertainment#janimation#dune entertainment#1492 pictures#museum canada productions#shawn levy#thomas lennon#robert ben garant#amy adams#owen wilson#ben stiller#robin williams#hank azaria#fantasy#action#comedy#family#1 hour#⭐⭐
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bossware is unfair (in the legal sense, too)

You can get into a lot of trouble by assuming that rich people know what they're doing. For example, might assume that ad-tech works – bypassing peoples' critical faculties, reaching inside their minds and brainwashing them with Big Data insights, because if that's not what's happening, then why would rich people pour billions into those ads?
https://pluralistic.net/2020/12/06/surveillance-tulip-bulbs/#adtech-bubble
You might assume that private equity looters make their investors rich, because otherwise, why would rich people hand over trillions for them to play with?
https://thenextrecession.wordpress.com/2024/11/19/private-equity-vampire-capital/
The truth is, rich people are suckers like the rest of us. If anything, succeeding once or twice makes you an even bigger mark, with a sense of your own infallibility that inflates to fill the bubble your yes-men seal you inside of.
Rich people fall for scams just like you and me. Anyone can be a mark. I was:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/05/cyber-dunning-kruger/#swiss-cheese-security
But though rich people can fall for scams the same way you and I do, the way those scams play out is very different when the marks are wealthy. As Keynes had it, "The market can remain irrational longer than you can remain solvent." When the marks are rich (or worse, super-rich), they can be played for much longer before they go bust, creating the appearance of solidity.
Noted Keynesian John Kenneth Galbraith had his own thoughts on this. Galbraith coined the term "bezzle" to describe "the magic interval when a confidence trickster knows he has the money he has appropriated but the victim does not yet understand that he has lost it." In that magic interval, everyone feels better off: the mark thinks he's up, and the con artist knows he's up.
Rich marks have looong bezzles. Empirically incorrect ideas grounded in the most outrageous superstition and junk science can take over whole sections of your life, simply because a rich person – or rich people – are convinced that they're good for you.
Take "scientific management." In the early 20th century, the con artist Frederick Taylor convinced rich industrialists that he could increase their workers' productivity through a kind of caliper-and-stopwatch driven choreographry:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/08/21/great-taylors-ghost/#solidarity-or-bust
Taylor and his army of labcoated sadists perched at the elbows of factory workers (whom Taylor referred to as "stupid," "mentally sluggish," and as "an ox") and scripted their motions to a fare-the-well, transforming their work into a kind of kabuki of obedience. They weren't more efficient, but they looked smart, like obedient robots, and this made their bosses happy. The bosses shelled out fortunes for Taylor's services, even though the workers who followed his prescriptions were less efficient and generated fewer profits. Bosses were so dazzled by the spectacle of a factory floor of crisply moving people interfacing with crisply working machines that they failed to understand that they were losing money on the whole business.
To the extent they noticed that their revenues were declining after implementing Taylorism, they assumed that this was because they needed more scientific management. Taylor had a sweet con: the worse his advice performed, the more reasons their were to pay him for more advice.
Taylorism is a perfect con to run on the wealthy and powerful. It feeds into their prejudice and mistrust of their workers, and into their misplaced confidence in their own ability to understand their workers' jobs better than their workers do. There's always a long dollar to be made playing the "scientific management" con.
Today, there's an app for that. "Bossware" is a class of technology that monitors and disciplines workers, and it was supercharged by the pandemic and the rise of work-from-home. Combine bossware with work-from-home and your boss gets to control your life even when in your own place – "work from home" becomes "live at work":
https://pluralistic.net/2021/02/24/gwb-rumsfeld-monsters/#bossware
Gig workers are at the white-hot center of bossware. Gig work promises "be your own boss," but bossware puts a Taylorist caliper wielder into your phone, monitoring and disciplining you as you drive your wn car around delivering parcels or picking up passengers.
In automation terms, a worker hitched to an app this way is a "reverse centaur." Automation theorists call a human augmented by a machine a "centaur" – a human head supported by a machine's tireless and strong body. A "reverse centaur" is a machine augmented by a human – like the Amazon delivery driver whose app goads them to make inhuman delivery quotas while punishing them for looking in the "wrong" direction or even singing along with the radio:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/08/02/despotism-on-demand/#virtual-whips
Bossware pre-dates the current AI bubble, but AI mania has supercharged it. AI pumpers insist that AI can do things it positively cannot do – rolling out an "autonomous robot" that turns out to be a guy in a robot suit, say – and rich people are groomed to buy the services of "AI-powered" bossware:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/29/pay-no-attention/#to-the-little-man-behind-the-curtain
For an AI scammer like Elon Musk or Sam Altman, the fact that an AI can't do your job is irrelevant. From a business perspective, the only thing that matters is whether a salesperson can convince your boss that an AI can do your job – whether or not that's true:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/07/25/accountability-sinks/#work-harder-not-smarter
The fact that AI can't do your job, but that your boss can be convinced to fire you and replace you with the AI that can't do your job, is the central fact of the 21st century labor market. AI has created a world of "algorithmic management" where humans are demoted to reverse centaurs, monitored and bossed about by an app.
The techbro's overwhelming conceit is that nothing is a crime, so long as you do it with an app. Just as fintech is designed to be a bank that's exempt from banking regulations, the gig economy is meant to be a workplace that's exempt from labor law. But this wheeze is transparent, and easily pierced by enforcers, so long as those enforcers want to do their jobs. One such enforcer is Alvaro Bedoya, an FTC commissioner with a keen interest in antitrust's relationship to labor protection.
Bedoya understands that antitrust has a checkered history when it comes to labor. As he's written, the history of antitrust is a series of incidents in which Congress revised the law to make it clear that forming a union was not the same thing as forming a cartel, only to be ignored by boss-friendly judges:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/14/aiming-at-dollars/#not-men
Bedoya is no mere historian. He's an FTC Commissioner, one of the most powerful regulators in the world, and he's profoundly interested in using that power to help workers, especially gig workers, whose misery starts with systemic, wide-scale misclassification as contractors:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/02/upward-redistribution/
In a new speech to NYU's Wagner School of Public Service, Bedoya argues that the FTC's existing authority allows it to crack down on algorithmic management – that is, algorithmic management is illegal, even if you break the law with an app:
https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/bedoya-remarks-unfairness-in-workplace-surveillance-and-automated-management.pdf
Bedoya starts with a delightful analogy to The Hawtch-Hawtch, a mythical town from a Dr Seuss poem. The Hawtch-Hawtch economy is based on beekeeping, and the Hawtchers develop an overwhelming obsession with their bee's laziness, and determine to wring more work (and more honey) out of him. So they appoint a "bee-watcher." But the bee doesn't produce any more honey, which leads the Hawtchers to suspect their bee-watcher might be sleeping on the job, so they hire a bee-watcher-watcher. When that doesn't work, they hire a bee-watcher-watcher-watcher, and so on and on.
For gig workers, it's bee-watchers all the way down. Call center workers are subjected to "AI" video monitoring, and "AI" voice monitoring that purports to measure their empathy. Another AI times their calls. Two more AIs analyze the "sentiment" of the calls and the success of workers in meeting arbitrary metrics. On average, a call-center worker is subjected to five forms of bossware, which stand at their shoulders, marking them down and brooking no debate.
For example, when an experienced call center operator fielded a call from a customer with a flooded house who wanted to know why no one from her boss's repair plan system had come out to address the flooding, the operator was punished by the AI for failing to try to sell the customer a repair plan. There was no way for the operator to protest that the customer had a repair plan already, and had called to complain about it.
Workers report being sickened by this kind of surveillance, literally – stressed to the point of nausea and insomnia. Ironically, one of the most pervasive sources of automation-driven sickness are the "AI wellness" apps that bosses are sold by AI hucksters:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/15/wellness-taylorism/#sick-of-spying
The FTC has broad authority to block "unfair trade practices," and Bedoya builds the case that this is an unfair trade practice. Proving an unfair trade practice is a three-part test: a practice is unfair if it causes "substantial injury," can't be "reasonably avoided," and isn't outweighed by a "countervailing benefit." In his speech, Bedoya makes the case that algorithmic management satisfies all three steps and is thus illegal.
On the question of "substantial injury," Bedoya describes the workday of warehouse workers working for ecommerce sites. He describes one worker who is monitored by an AI that requires him to pick and drop an object off a moving belt every 10 seconds, for ten hours per day. The worker's performance is tracked by a leaderboard, and supervisors punish and scold workers who don't make quota, and the algorithm auto-fires if you fail to meet it.
Under those conditions, it was only a matter of time until the worker experienced injuries to two of his discs and was permanently disabled, with the company being found 100% responsible for this injury. OSHA found a "direct connection" between the algorithm and the injury. No wonder warehouses sport vending machines that sell painkillers rather than sodas. It's clear that algorithmic management leads to "substantial injury."
What about "reasonably avoidable?" Can workers avoid the harms of algorithmic management? Bedoya describes the experience of NYC rideshare drivers who attended a round-table with him. The drivers describe logging tens of thousands of successful rides for the apps they work for, on promise of "being their own boss." But then the apps start randomly suspending them, telling them they aren't eligible to book a ride for hours at a time, sending them across town to serve an underserved area and still suspending them. Drivers who stop for coffee or a pee are locked out of the apps for hours as punishment, and so drive 12-hour shifts without a single break, in hopes of pleasing the inscrutable, high-handed app.
All this, as drivers' pay is falling and their credit card debts are mounting. No one will explain to drivers how their pay is determined, though the legal scholar Veena Dubal's work on "algorithmic wage discrimination" reveals that rideshare apps temporarily increase the pay of drivers who refuse rides, only to lower it again once they're back behind the wheel:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/12/algorithmic-wage-discrimination/#fishers-of-men
This is like the pit boss who gives a losing gambler some freebies to lure them back to the table, over and over, until they're broke. No wonder they call this a "casino mechanic." There's only two major rideshare apps, and they both use the same high-handed tactics. For Bedoya, this satisfies the second test for an "unfair practice" – it can't be reasonably avoided. If you drive rideshare, you're trapped by the harmful conduct.
The final prong of the "unfair practice" test is whether the conduct has "countervailing value" that makes up for this harm.
To address this, Bedoya goes back to the call center, where operators' performance is assessed by "Speech Emotion Recognition" algorithms, a psuedoscientific hoax that purports to be able to determine your emotions from your voice. These SERs don't work – for example, they might interpret a customer's laughter as anger. But they fail differently for different kinds of workers: workers with accents – from the American south, or the Philippines – attract more disapprobation from the AI. Half of all call center workers are monitored by SERs, and a quarter of workers have SERs scoring them "constantly."
Bossware AIs also produce transcripts of these workers' calls, but workers with accents find them "riddled with errors." These are consequential errors, since their bosses assess their performance based on the transcripts, and yet another AI produces automated work scores based on them.
In other words, algorithmic management is a procession of bee-watchers, bee-watcher-watchers, and bee-watcher-watcher-watchers, stretching to infinity. It's junk science. It's not producing better call center workers. It's producing arbitrary punishments, often against the best workers in the call center.
There is no "countervailing benefit" to offset the unavoidable substantial injury of life under algorithmic management. In other words, algorithmic management fails all three prongs of the "unfair practice" test, and it's illegal.
What should we do about it? Bedoya builds the case for the FTC acting on workers' behalf under its "unfair practice" authority, but he also points out that the lack of worker privacy is at the root of this hellscape of algorithmic management.
He's right. The last major update Congress made to US privacy law was in 1988, when they banned video-store clerks from telling the newspapers which VHS cassettes you rented. The US is long overdue for a new privacy regime, and workers under algorithmic management are part of a broad coalition that's closer than ever to making that happen:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/12/06/privacy-first/#but-not-just-privacy
Workers should have the right to know which of their data is being collected, who it's being shared by, and how it's being used. We all should have that right. That's what the actors' strike was partly motivated by: actors who were being ordered to wear mocap suits to produce data that could be used to produce a digital double of them, "training their replacement," but the replacement was a deepfake.
With a Trump administration on the horizon, the future of the FTC is in doubt. But the coalition for a new privacy law includes many of Trumpland's most powerful blocs – like Jan 6 rioters whose location was swept up by Google and handed over to the FBI. A strong privacy law would protect their Fourth Amendment rights – but also the rights of BLM protesters who experienced this far more often, and with far worse consequences, than the insurrectionists.
The "we do it with an app, so it's not illegal" ruse is wearing thinner by the day. When you have a boss for an app, your real boss gets an accountability sink, a convenient scapegoat that can be blamed for your misery.
The fact that this makes you worse at your job, that it loses your boss money, is no guarantee that you will be spared. Rich people make great marks, and they can remain irrational longer than you can remain solvent. Markets won't solve this one – but worker power can.

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#alvaro bedoya#ftc#workers#algorithmic management#veena dubal#bossware#taylorism#neotaylorism#snake oil#dr seuss#ai#sentiment analysis#digital phrenology#speech emotion recognition#shitty technology adoption curve
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Year - 2024 Edition
Welcome to our special edition newsletter recapping the best news from the past year. I've picked one highlight from each month to give you a snapshot of 2024. No frills, just straightforward news that mattered. Let's relive the good stuff that made our year shine.
1. January - South Korea passes law banning dog meat trade

The slaughter and sale of dogs for their meat is to become illegal in South Korea after MPs backed a new law. The legislation, set to come into force by 2027, aims to end the centuries-old practice of humans eating dog meat.
2. February - Greece legalises same-sex marriage

Greece has become the first Christian Orthodox-majority country to legalise same-sex marriage. Same-sex couples will now also be legally allowed to adopt children after Thursday's 176-76 vote in parliament. Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis said the new law would "boldly abolish a serious inequality".
3. March - Global child deaths reach historic low in 2022 – UN report

The number of children who died before their fifth birthday has reached a historic low, dropping to 4.9 million in 2022. The report reveals that more children are surviving today than ever before, with the global under-5 mortality rate declining by 51 per cent since 2000.
4. April - Restoring sight is possible now with optogenetics

Max Hodak's startup, Science, is developing gene therapy solutions to restore vision for individuals with macular degeneration and similar conditions. The Science Eye utilizes optogenetics, injecting opsins into the eye to enhance light sensitivity in retinal cells. Clinical trials and advancements in optogenetics are showing promising results, with the potential to significantly improve vision for those affected by retinal diseases.
5. May - Vaccine breakthrough means no more chasing strains
Scientists at UC Riverside have demonstrated a new, RNA-based vaccine strategy that is effective against any strain of a virus and can be used safely even by babies or the immunocompromised.
6. June - Bill Gates-backed startup creates Lego-like brick that can store air pollution for centuries

The Washington Post detailed a "deceptively simple" procedure by Graphyte to store a ton of CO2 for around $100 a ton, a number long considered a milestone for affordably removing carbon dioxide from the air. Direct air capture technologies used in the United States and Iceland cost $600 to $1,200 per ton, per the Post.
7. July - Stem cell therapy cures man with type 2 diabetes
A 59-year-old man had been suffering from diabetes for 25 years, needing more and more insulin every day to avoid slipping into a diabetic coma and was at risk of death. But then Chinese researchers cured his disease for the first time in the world. The patient received a cell transplant in 2021 and has not taken any medication since 2022.
8. August - Chinese drones will fly trash out of Everest slopes

Come autumn, Nepal will deploy heavy lifter drones to transport garbage from the 6,812-metre tall Ama Dablam, south of Everest. This will be the first commercial work an unmanned aerial vehicle does in Nepal’s high-altitude zone.
9. November - Tokyo to make day care free to boost birth rate

Tokyo plans to make day care free for all preschool children starting in September, the city governor has announced as part of efforts to boost Japan's low birth rate.
10. October - FTC Rule Banning Fake Product Reviews Takes Effect With Stiff Penalties

Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Chair Lina Khan announced on Oct. 21 that the agency’s prohibition on fake online reviews was taking effect, imposing fines as high as $50,000 for violations. Khan encouraged followers to report the proscribed practices at reportfraud.ftc.gov.
11. November - Bumblebee population increases 116 times over in 'remarkable' Scotland rewilding project

The bumblebee population has made an impressive comeback in a developed area by increasing to 116 times what it was two years ago thanks to a nature restoration group.
12. December - Spain to enshrine gay marriage and abortion rights into its constitution so 'they cannot be undone in the future'

The left-wing PSOE leader made the announcement at an event marking the 46th anniversary of the Spanish Magna Carta.
“We believe that these are rights that we must protect in the Constitution so that no one can touch them in the future,” Sanchez said in a statement in parliament on Friday.
----------
That's it for last year :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation here:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Also don’t forget to share this post with your friends.
462 notes
·
View notes
Text
Adele - Rolling in the Deep 2010
"Rolling in the Deep" is a song by English singer-songwriter Adele from her second studio album, 21 (2011). It is the lead single and opening track on the album. The song was composed by Paul Epworth and Adele in a single afternoon following Adele's breakup with her boyfriend. It was her reaction to, "being told that my life was going to be boring and lonely and rubbish, and that I was a weak person if I didn't stay in the relationship. I was very insulted, and wrote that as a sort of 'fuck you'."
"Rolling in the Deep" received widespread critical acclaim with praise drawn towards the song's production, its lyrics, and Adele's vocal performance. It represented a commercial breakthrough for Adele, propelling her to global superstardom. The song topped the charts in twelve countries and reached the top 10 in over twenty territories. It was Adele's first number-one song in the US, reaching the top spot on many Billboard charts, including the Billboard Hot 100 where it was number one for seven weeks. By February 2012, "Rolling in the Deep" had sold over 8.7 million copies in the US, making it the best-selling digital song by a female artist in the US, the second-best-selling digital song in the US and Adele's best-selling single outside her native country, topping her previous best-selling "Chasing Pavements". Worldwide, it was the fifth-best-selling digital single of 2011 with sales of 8.2 million copies. As of 2019, with sales of over 20.6 million copies worldwide, "Rolling in the Deep" is one of the best-selling digital singles of all time.
Its music video received a leading seven nominations at the 2011 MTV Video Music Awards, including for Video of the Year, and won three other awards: Best Editing, Best Cinematography and Best Art Direction. "Rolling in the Deep" was also the Billboard Year End Hot 100 Number One Single of 2011. At the 54th Annual Grammy Awards, it won awards for Record of the Year, Song of the Year, and Best Short Form Music Video, making it just the second song in Grammy history to win all three awards after "We Are the World" in 1986. Various critics and music publications ranked it as the best song of the year on their end-of-year lists with Rolling Stone ranking it at number 8 spot on its list of "The 100 Greatest Songs of the 21st Century". In 2021, the song was ranked at number 82 on the list of Rolling Stone's 500 Greatest Songs of All Time.
"Rolling in the Deep" received a total of 87,7% yes votes!
youtube
#finished#high votes#high yes#low no#low reblog#10s#o1#o1 sweep#o1 ultrasweep#lo24#lo24 tie#lo2#lo4#popular#adele#english
645 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - March 22-28
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles! This month’s doodles, like every third month, will be free to the public, so take a look!
1. Crucial and heartwarming: see world’s first-ever wild jaguar translocation in Argentina

“Miní[, an offspring of rewilded jaguars,] is the first-ever release of a wild-born jaguar that’s been translocated for conservation purposes. […] Miní has joined two previously captive female jaguars [in a park] where a small, all-male wild population had been dwindling.”
2. Illinois Gov. Pritzker stands up for LGBTQ+ community in fiery HRC speech

“The governor particularly spoke out for transgender youth, saying we must not sacrifice the most persecuted for the most popular. [… “]Bullies respond to one thing, and one thing only, a punch in the face.”
3. The UK’s First ‘Stork Village’ Takes Flight

“For the first time in more than six centuries, white storks are calling Britain home again thanks to a dedicated conservation initiative to save the species. […] At the end of 2024, breeding numbers saw egg-straordinary results with 27 nests and 53 baby storks, doubling the previous year’s numbers.”
4. A quiet shift: The grid is being redefined by household consumers who no longer need it full time

“With rising adoption of rooftop solar, batteries, and electric vehicles, households are gradually altering their relationship with the grid. […] This redefined relationship doesn’t signal rejection — it reflects the growing capacity of households to meet part of their own needs.”
5. Europe’s Wolf Population On The Rise

““The recovery of wolves across human-dominated landscapes of Europe has been continuing during the past decade, with their population growing to over 21,500 individuals by 2022—a 58% increase in a decade,” the authors wrote. [… O]n average wolves killed 0.02% of livestock each year.”
6. Hospitals awarded funding for solar power work

“The investment of £8.5m by state-owned Great British Energy will enable rooftop panels and solar car ports to be installed at [several hospitals]. […] "Together, these panels will generate estimated savings of more than £635,000 a year."”
7. Nebraska Boards Sponsor Grain Bin Rescue Equipment, Training for Fire Departments

“[Nebraska Corn and Soybean boards are] donating two grain rescue tubes and two training sessions to fire and rescue departments in Nebraska. [… T]he initiative aims to equip rural fire and rescue teams with the knowledge and tools to respond to grain bin entrapments effectively.“
8. Sugar beet pulp fibers show potential for nutritional supplements and sustainable plastic alternatives

“New technology can separate the fibers in the sugar beet pulp left over after sugar production. Part of the fiber can be used as a nutritional supplement due to its anti-inflammatory properties[… and a]nother part of the fiber, the cellulose, can be made into components to replace, for example, plastic.”
9. Osmotic Power: The Next Wave of Renewable Energy

“Sweetch Energy’s technology could [produce] around 20 or 25 W/m2, a significant leap compared to the 1 W/m2 achieved by previous membrane devices. Moreover, by utilizing a biosourced material readily available within the industry for their membranes, the company anticipates the cost of materials would be reduced to one-tenth of the current price[….]”
10. Renegade Colorado Farmer Pushes Deeper into Unconventional Agriculture

“The grasshoppers stayed in the [pollinator] strips, and that triggered praying mantis to come in and eat. […] An agrivoltaic system […] has reduced moisture consumption by significant levels[….] “Local food nationwide is how to counter the industrial scale food industry.””
March 15-21 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#conservation#jaguar#big cats#illinois#us politics#lgbt+#lgbtq#trans rights#stork#britain#birds#electricity#electric grid#solar panels#wolves#wolf#animals#solar energy#agriculture#grain#fire department#sustainability#plastic#renewableenergy#osmosis#clean energy#farming#research
133 notes
·
View notes
Text
Every Fallout 4 Companion’s Approximate Birth Year (Part 3/3)
CVRIE — 2076
I assume Miss Nannies went out of production when the world exploded.
Codsworth — 2077
His box is still in your house during the prologue.
He also mentions enjoying the “months” he’s spent with you, though he might mean since Shaun was born.
Nick — 2175
We know it was over a century ago, but it can’t have been too far prior to the Gen 3 rollout around 2227.
I think Nick is the older brother, because it makes sense to start by creating a synth with stored personalities before trying to make one that develops a personality autonomously.
Longfellow — 2223
This man is only in his SIXTIES, they are LYING TO YOU
The Children of Atom were full-fledged on the Island when Longfellow was young. Confessor Cromwell is the one who sent them to Maine.
But he couldn’t have become Confessor until the mid-2250s, because he’s only FORTY-FOUR in Fallout 3, and he had a background as a trader before that! AND there still had to be time for the Children to travel all the way to Maine.
So Longfellow was born in the twenties, had his sad backstory in the fifties, and is about 65 in Fallout 4.
Strong — 2230
Strong could have been anyone, but I think he was either a divorced dad who would’ve been an accountant in another life, or just Mayor McDonough.
Hancock — 2235
Is 53-year-old Hancock controversial? Let me cook.
There’s support for the theory that synth McDonough was created before the election in 2282. We can assume the human had full gray hair at that point, because synths don’t go gray. So he was probably in his fifties at least.
John was younger, but he can’t have been that much younger. So he was probably ghoulified in his late forties.
Deacon — 2245
If you accept the John D. theory, this does put him a little on the young side, but it fits.
Gage — 2251
There’s not much backstory from his teens up to 2286, and I’m tempted to believe it was a shorter period. But he has late-thirties eyes.
…Eye.
Cait — 2260
Her parents helpfully drew the line at child trafficking, so we have a good idea of her age. She was 18 when she went into slavery and about 23 when she left.
Some time later, she spent about three years at the Combat Zone. Assuming some buffer room between the two periods, I put her at 27 years.
Danse — 2261
He’d have lived in the Institute for awhile, then Rivet City, then the Brotherhood.
He was already a paladin in 2277, but Maxson says it took him “many years” to become one.
Preston — 2262
I don’t know what it is about him that screams 25-year-old to me.
He joined the Minutemen at 17, then had “a few good years” before 2282 when Becker died.
MacCready — 2264
He was twelve in August 2277, and at that point he’d been mayor for three years.
He became mayor at ten. So he’s got to be nearly thirteen at the start of Fallout 3, which would make him 23 in Fallout 4.
Piper — 2266
Nat seems 13 to me.
If Piper is old enough to have taken care of her as a baby, but not old enough to have significant memories of their mother, 21 sounds about wright.
Curie — 2277
Glory escaped the Institute in 2280, and she and G5 had known each other for some time before that.
Ada — 2281
Jackson seems to have created her reasonably recently.
Dogmeat IV — 2285
I think he is ouppy:)
X6-88 — 2287.
Yeah, I said it.
This man thinks he’s so evil but he’s an actual baby.
My reasoning is that he wishes he had been there to see the University Point massacre in 2286, but apparently wasn’t.
It makes the game so much funnier.
If he was born earlier in the year, he could have been trained in time for the Kellogg flashback.
Part 1
Part 2
#fo4 companions#fallout#fallout 4#fo4#rj maccready#paladin danse#codsworth#piper wright#preston garvey#hancock fallout#deacon fallout#cait fallout#old longfellow#porter gage#nick valentine#curie fallout#x6 88#deacon fallout 4#maccready#ada fo4
239 notes
·
View notes
Text
DAY 6274
Jalsa, Mumbai Aopr 20, 2025 Sun 11:17 pm
🪔 ,
April 21 .. birthday greetings and happiness to Ef Mousumi Biswas .. and Ef Arijit Bhattacharya from Kolkata .. 🙏🏽❤️🚩.. the wishes from the Ef family continue with warmth .. and love 🌺
The AI debate became the topic of discussion on the dining table ad there were many potent points raised - bith positive and a little indifferent ..
The young acknowledged it with reason and able argument .. some of the mid elders disagreed mildly .. and the end was kind of neutral ..
Blessed be they of the next GEN .. their minds are sorted out well in advance .. and why not .. we shall not be around till time in advance , but they and their progeny shall .. as has been the norm through generations ...
The IPL is now the greatest attraction throughout the day .. particularly on the Sunday, for the two on the day .. and there is never a debate on that ..
🤣
.. and I am most appreciative to read the comments from the Ef on the topic of the day - AI .. appreciative because some of the reactions and texts are valid and interesting to know .. the aspect expressed in all has a legitimate argument and that is most healthy ..
I am happy that we could all react to the Blog contents in the manner they have done .. my gratitude .. such a joy to get different views , valid and meaningful ..
And it is not the end of the day or the debate .. some impressions of the Gen X and some from the just passed Gen .. and some that were never ever the Gen are interesting as well :
The Printing Press (15th Century)
Fear: Scribes, monks, and elites thought it would destroy the value of knowledge, lead to mass misinformation, and eliminate jobs. Reality: It democratized knowledge, spurred the Renaissance and Reformation, and created entirely new industries—publishing, journalism, and education.
⸻
Industrial Revolution (18th–19th Century)
Fear: Machines would replace all human labor. The Luddites famously destroyed machinery in protest. Reality: Some manual labor jobs were displaced, but the economy exploded with new roles in manufacturing, logistics, engineering, and management. Overall employment and productivity soared.
⸻
Automobiles (Early 20th Century)
Fear: People feared job losses for carriage makers, stable hands, and horseshoe smiths. Cities worried about traffic, accidents, and social decay. Reality: The car industry became one of the largest employers in the world. It reshaped economies, enabled suburbia, and created new sectors like travel, road infrastructure, and auto repair.
⸻
Personal Computers (1980s)
Fear: Office workers would be replaced by machines; people worried about becoming obsolete. Reality: Computers made work faster and created entire industries: IT, software development, cybersecurity, and tech support. It transformed how we live and work.
⸻
The Internet (1990s)
Fear: It would destroy jobs in retail, publishing, and communication. Some thought it would unravel social order. Reality: E-commerce, digital marketing, remote work, and the creator economy now thrive. It connected the world and opened new opportunities.
⸻
ATMs (1970s–80s)
Fear: Bank tellers would lose their jobs en masse. Reality: ATMs handled routine tasks, but banks actually hired more tellers for customer service roles as they opened more branches thanks to reduced transaction costs.
⸻
Robotics & Automation (Factory work, 20th century–today)
Fear: Mass unemployment in factories. Reality: While some jobs shifted or ended, others evolved—robot maintenance, programming, design. Productivity gains created new jobs elsewhere.
The fear is not for losing jobs. It is the compromise of intellectual property and use without compensation. This case is slightly different.
I think AI will only make humans smarter. If we use it to our advantage.
That’s been happening for the last 10 years anyway
Not something new
You can’t control that in this day and age
YouTube & User-Generated Content (mid-2000s onward)
Initial Fear: When YouTube exploded, many in the entertainment industry panicked. The fear was that copyrighted material—music, TV clips, movies—would be shared freely without compensation. Creators and rights holders worried their content would be pirated, devalued, and that they’d lose control over distribution.
What Actually Happened: YouTube evolved to protect IP and monetize it through systems like Content ID, which allows rights holders to:
Automatically detect when their content is used
Choose to block, track, or monetize that usage
Earn revenue from ads run on videos using their IP (even when others post it)
Instead of wiping out creators or studios, it became a massive revenue stream—especially for musicians, media companies, and creators. Entire business models emerged around fair use, remixes, and reactions—with compensation built in.
Key Shift: The system went from “piracy risk” to “profit partner,” by embracing tech that recognized and enforced IP rights at scale.
This lead to higher profits and more money for owners and content btw
You just have to restructure the compensation laws and rewrite contracts
It’s only going to benefit artists in the long run
Yes
They can IP it
That is the hope
It’s the spread of your content and material without you putting a penny towards it
Cannot blindly sign off everything in contracts anymore. Has to be a lot more specific.
Yes that’s for sure
“Automation hasn’t erased jobs—it’s changed where human effort goes.”
Another good one is “hard work beats talent when talent stops working hard”
Which has absolutely nothing to with AI right now but 🤣
These ladies and Gentlemen of the Ef jury are various conversational opinions on AI .. I am merely pasting them for a view and an opinion ..
And among all the brouhaha about AI .. we simply forgot the Sunday well wishers .. and so ..
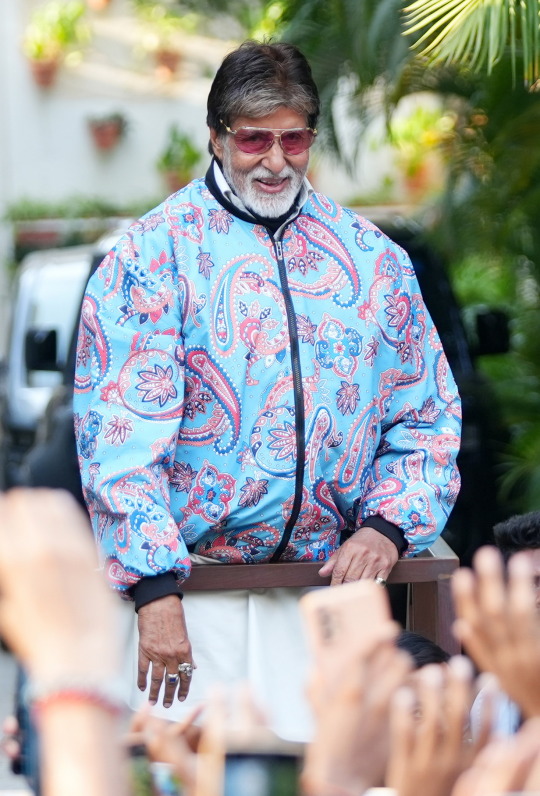
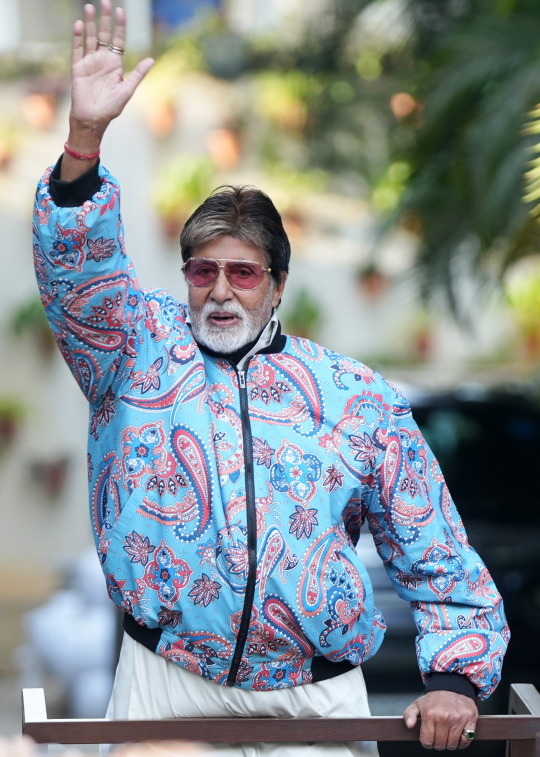
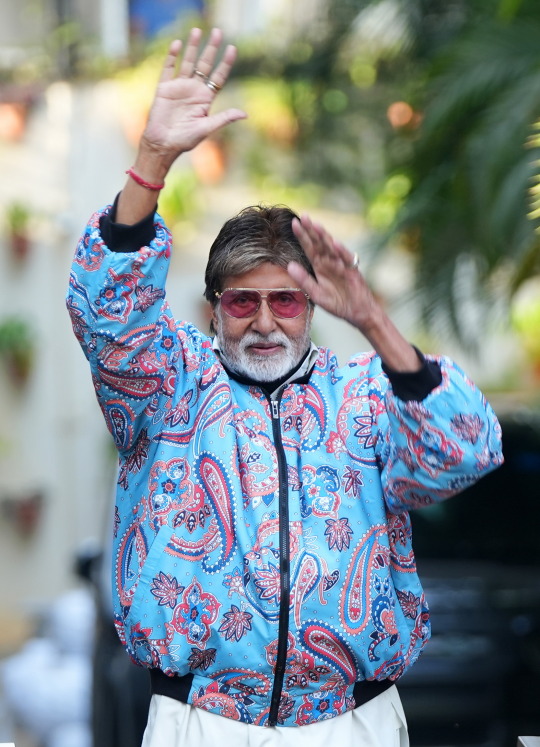














my love and the length be of immense .. pardon

Amitabh Bachchan
101 notes
·
View notes
Note
I would like to see a variety of historical cc for shoes, um modern kids mix match for kids, infants toddlers down the road if you can if not I understand. Thanks for all you do in the sims community!
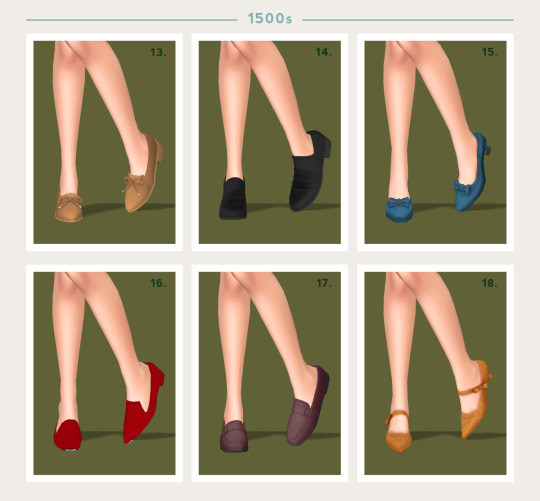
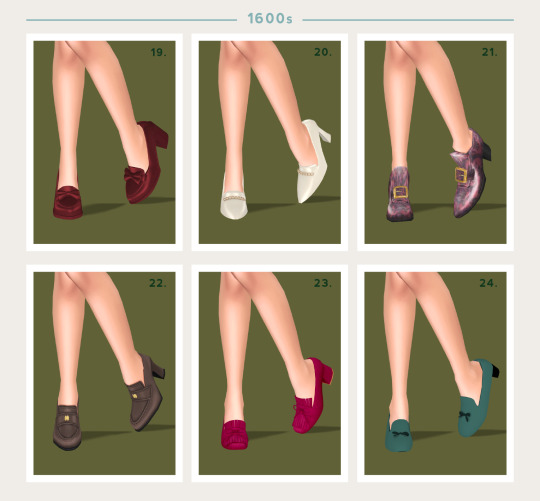
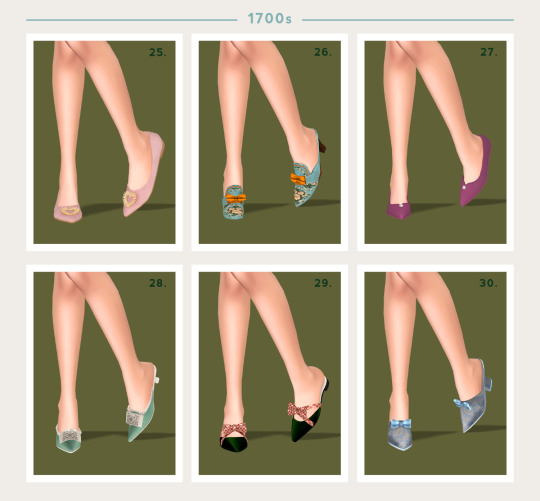







Unfortunately there's a pretty limited amount of dedicated historical footwear CC out there at the moment, but I've gathered up a bunch of options that could work for their respective century. I've only gone up to the 1700s as my Ultimate Decades Timeline series will soon be entering the 1800s, so I'll have plenty of shoe options for that century in the not-too-distant future. CC links and more information for each century under the cut.

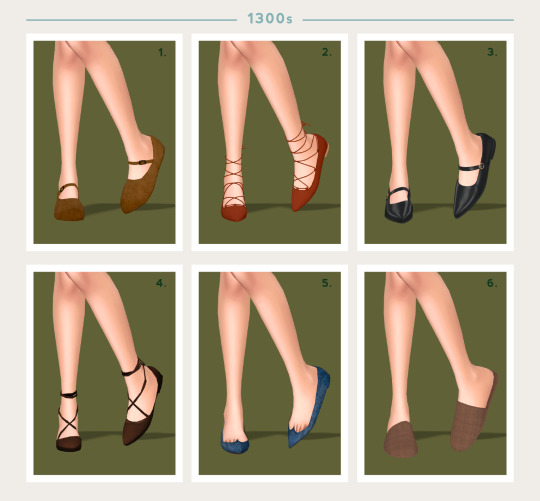
An extended, pointed toe was the quintessential shape for 14th century shoes, although shorter toes were worn by working class people due to their practicality. Footwear, much like the clothes of the period, was simple and non-fussy.
1 - Random Noble Shoe by Satterlly
2 - Suede Lace-Up Flats by Jius Sims
3 - Pointed Toe Flats by Arltos (TSR)
4 - Ballet Shoes by Dissia (TSR)
5 - Bahlam Flats by Madlen (TSR)
6 - Home Slipper by MMSIMS

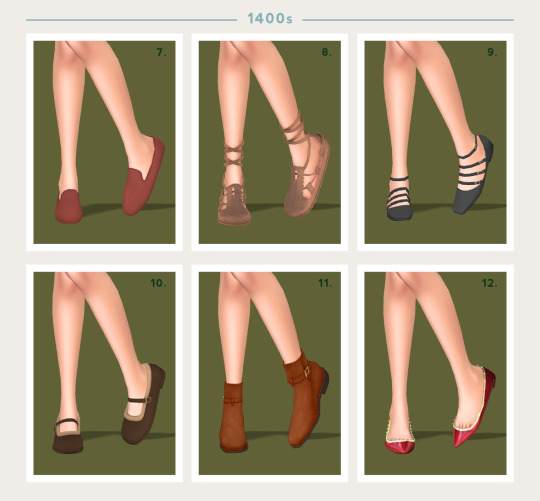
The 15th century saw a more rounded toe come into fashion beginning in Italy. Shoe styles started to become more ornate and decorated to coincide with burgeoning clothing trends.
7 - Lazy Loafers by Citrontart
8 - Ye Medieval Leather Shoes by Shake Productions (TSR)
9 - Ballet Flats by Luxy Sims
10 - Winter Mary Jane by Arltos (TSR)
11 - Suede Ankle Boots by Jius Sims
12 - Leandro Flats by Madlen (TSR)

Tudor-era shoes were quite basic in comparison to the clothing of the time and some even looked surprisingly modern in silhouette. Luxury fabrics such as silk and velvet were popular materials for the footwear of those with wealth.
13 - Loafer 51 by Arltos (TSR)
14 - Simple Loaf by Arltos (TSR)
15 - Satin Bow Pumps by Waxes Nostalgic
16 - Padova Shoes by Madlen (TSR)
17 - Loafer by Arltos (TSR)
18 - Lissa Shoes by Serenity

Come the 17th century heels really started to take off. In fact, all shoes and boots featured a heel that was at least an inch high, but more commonly two to three inches. Embellishments were all the rage - buckles, rosettes, pompoms and bows.
19 - Penny Loafers by Arltos (TSR)
20 - Pointed Toe Heels by Arltos (TSR)
21 - Rococo Shoes by Elfdor (TSR)
22 - Barbie Loafer Pumps by Serenity
23 - Suede Pumps by Jius Sims
24 - Olga Shoes by Isjao

As men's shoes reduced in height, women's grew higher and narrower. Slippers or mules become popular to wear around the home or for casual events. These were heeled slip-on shoes with no upper covering the heel.
25 - Pointed Pastel Flats with Rhines by MysteriousOo (TSR)
26 - Rococo Mules by Simulated Styles
27 - Shoes with Pearl by Arltos (TSR)
28 - Antoinette Buckle Shoe by Acanthus Sims
29 - Bow Flats by FYSims
30 - Rococo Shoe RC by Elfdor
With thanks to some amazing creators: @satterlly @citrontart @waxesnostalgic @serenity-cc @isjao @simulatedstyles
#friday finds#historical cc#1300s#1400s#1500s#1600s#1700s#1300s cc#1400s cc#1500s cc#1600s cc#1700s cc#medieval#renaissance#tudor#baroque#rococo#georgian#sims historical#ultimate decades challenge
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dylann's things
repost from my old acc + more info!!
his cameras
Cyber-shot DSC-W350 (the blue one)
14 megapixel Kodak Easyshare, model C1530 (on his neck)
lol, it's funny how they're all digital. To find the model of the one around his neck, I thought it was an analog camera, but I remembered he didn't have that much money to keep an analog camera, so I went after the digital ones.

his car
it's a hyundai elantra model 2000's
it was his father's car i guess. It's a sedan, one of the first models of elantra, cuz hyundai started to project them in 90's until i know


his gun
it's a glock 41 with a .45mm caliber, he bought it when he turned 21 and the money he used to buy it he got in his birthday, btw
well, the .45mm is a powerful caliber that has high impact force. glocks, in general, are a line of semi-automatic pistols used for tactical use or recreational shooting clubs or other activities. The Glock 41 specifically comes from a variation of the Glock 21, making it more susceptible to putting more cartridges inside. It has much greater accuracy (usually used by police officers)

his jacket
there are two flags on Dylann's jacket, one is from South Africa Apartheid flag, the other is from Rhodesia. These two countries are located on the African continent and, in the 20th century, they faced racial segregation. South Africa, for example, had specific areas for black people and specific areas for white people. Rhodesia did not have such direct segregation, but there were many laws that prevented interracial relationships or relationships between white people and black people in everyday life. These countries were under European rule, especially English.

his last.fm profile
in my opinion, this is the best curiosity of all!
The name "Derek Jeter 88" isn't a coincidence. Derek Jeter is a baseball player, he was elected fourteen times to the shortstop position in the Major League Baseball All-Star Game
these fourteen times plus the number 88 are a reference for "1488" used by himself in other accounts (aryanblood1488). Fourteen makes an allusion to the fourteen words "we must secure the existence of our people and the future of white children"

his gold's gym shirt
It's just research about "gold's gym shirt" and pick the black-golden option. It is a sports brand t-shirt exclusively for bodybuilding
his bunny
I still don't know for sure if it's his or not. But the bunny is wearing a full Confederate flag outfit, and the photo was apparently taken on top of Dylann's bed

his cat
The breed looks a lot like a Maine Coon, as the cat is larger compared to others, and its fur is quite long. It is a little difficult to identify from the photo

his skincare products
I was able to identify the orange one, and it is an Oil-Free Acne Wash, by Neutrogena. It is an anti-acne gel soap that prevents the appearance of pimples and contains vitamins to moisturize the skin.

92 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Young Person's Guide to 18th-Century Western Fashion
unabridged version at blogspot
General info Cox, Abby. "I Wore 18th-Century Clothing *Every Day for 5 YEARS & This Is What I Learned (Corsets Aren't Bad!)." YouTube. May 10, 2020. Cullen, Oriole. “Eighteenth-Century European Dress.” In Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2004. Glasscock, Jessica. "Eighteenth-Century Silhouette and Support." In Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2004. Accessories Banner, Bernadette. "Women's Pockets Weren't Always a Complete Disgrace | A Brief History: England, 15th c - 21st c." YouTube. April 10, 2021. Colonial Williamsburg. "#TradesTuesday: Men's Accessories." YouTube. June 13, 2021. Murden, Sarah. "The Georgian era fashion for straw hats." All Things Georgian. December 6, 2018. Cosmetics & hygiene Cox, Abby. "I Followed an 18th-Century Moisturizer & Sunscreen Recipe & it kinda worked??." YouTube. February 21, 2021. Cox, Abby. "We tried making *5* different 250 year old rouge (blush) recipes || [real] regencycore makeup." YouTube. August 29, 2021. JYF Museums. "Hygiene in the 18th Century | From the Farm to the Army." YouTube. August 21, 2021. Décor Heckscher, Morrison H. “American Rococo.” In Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2003. Munger, Jeffrey. “French Porcelain in the Eighteenth Century.” In Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2003. Formal wear SnappyDragon. "This dressing gown changed fashion forever : the feminist history of going out in loungewear." YouTube. April 15, 2022. Stowell, Lauren. "The Many Types of 18th Century Gowns." American Duchess. March 15, 2013. Zebrowska, Karolina. "Cottagecore Style Is Much Older Than You Think." YouTube. June 30, 2021. Hair care Cox, Abby. "I made 250-year-old Hair Products Using Original Recipes (and animal fat...)." YouTube. November 7, 2021. Cox, Abby. "I tried a 300-year-old hair care routine for a year & this is what I learned (it's awesome!)." YouTube. January 23, 2022. Cox, Abby. "What's the Deal with 18th Century Wigs? (and why Bridgerton really messed this up)." YouTube. June 1, 2023. Laundry Cox, Abby. "Making 300 Year Old SLIME for Laundry Day." YouTube. June 15, 2023. Townsends. "Historical Laundry Part 2: No Washing Machine, No Dryer, Hit It With A Stick?" YouTube. June 3, 2019. Outer- & working-wear JYF Museum. "Getting Dressed | Clothing for an 18th Century Middling Woman." YouTube. March 18, 2021. Major, Joanne. "The practicalities of wearing riding habits, and riding ‘en cavalier’." All Things Georgian. March 12, 2019. Rudolph, Nicole. "What did Pirates ACTUALLY Wear? Fashion at Sea in the 18th c & Our Flag Means Death Costumes." YouTube. May 8, 2022. Shoes Chin, Cynthia E. "Martha Washington's Shoes." George Washington's Mount Vernon. No date. Murden, Sarah. "18th-century shoes." All Things Georgian. December 15, 2015. Rudolph, Nicole. "Real 18th century Shoes? Historical Shoemaker Examines an Antique." YouTube. December 13, 2020. Textiles Cox, Abby. "18th Century Printed Cotton Do's & Don't's." American Duchess. December 23, 2019. Stowell, Lauren. "Fabrics for the 18th Century and Beyond." American Duchess. June 14, 2021. Townsends. "Oil Cloth - Waterproof Coverings for Your Campsite." YouTube. July 30, 2018. Undergarments Major, Joanne. "Quilted Petticoats: worn by all women and useful in more ways than one." All Things Georgian. November 20, 2018. Rudolph, Nicole. "Making 18th century Stays for the Ideal Body Shape : Historical Undergarments." YouTube. August 12, 2023. SnappyDragon. "RUMP ROAST : Ranking historical fashion's wildest fake butt pads." YouTube. October 27, 2023. Townsends. "Sewing Histories' Most Popular Garment - The Fabric Of History - Townsends." YouTube. September 3, 2022.
#reference#history#abby cox#bernadette banner#fashion#hair care#hairstyle#youtube#video#nicole rudolph#townsends#us history#american history#colonial williamsburg#jamestown#georgian era#rococo#1700s#american duchess#mount vernon#bridgerton#the metropolitan museum of art#our flag means death
204 notes
·
View notes
Text
02.06.24
#Mira-Marathon | Night at the Museum
Film Name: Night at the Museum (2006); Production Studios: Twentieth Century Fox, 21 Laps Entertainment, Ingenious Media, Dune Entertainment, 1492 Pictures, Sun Canada Productions; Director by: Shawn Levy; Screenwriters: Robert Ben Garant, Thomas Lennon; Starring: Ben Stiller, Jake Cherry, Carla Gugino, Robin Williams, Steve Coogan; Genres: Fantasy, Adventure, Comedy, Family; Running Time: 1 hour 48 minutes;
"Night at the Museum" (2006) is a comedy with Ben Stiller, where museum exhibits come alive at night. The film is distinguished by light humor, good acting and visual effects. Although the plot is predictable and the secondary characters are weakly developed, the film is ideal for family viewing.
My rating:
⭐⭐⭐

#mira marathon#night at the museum#natm#film#2006#twentieth century fox#21 laps entertainment#ingenious media#dune entertainment#1492 pictures#sun canada productions#shawn levy#robert ben garant#thomas lennon#ben stiller#jake cherry#carla gugino#robin williams#steve coogan#fantasy#adventure#comedy#family#1 hour#⭐⭐⭐
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Zuck’s gravity-defying metaverse money-pit

Tomorrow (Oct 31) at 10hPT, the Internet Archive is livestreaming my presentation on my recent book, The Internet Con.

Think of everything that makes you miserable as being caught between two opposing, irresistible, irrefutable truths:
"Anything that can't go on forever eventually stops" (Stein's Law)
"Markets can remain irrational longer than you can remain solvent" (Keynes)
Both of these are true, even though they seemingly contradict one another, and no one embodies that contradiction more perfectly than Mark Zuckerberg.
Take the metaverse.
Zuck's "pivot" to a virtual world he ripped off from a quarter-century old cyberpunk novel (reminder: cyberpunk is a warning, not a suggestion) was born of desperation.
Zuck fancies himself an avatar of the Emperor Augustus (that's why he has that haircut) (no, really). The emperors of antiquity are infamous for getting all weepy when they run out of lands to conquer.
But the lachrymosity of emperors has little causal relationship to the anxieties of tech monopolists! Alexander weeps because he just loves a good conquest and when he finishes conquering the world, he's terminally bored. That's not Zuck's problem at all. When Zuck attains monopoly status, his company develops an autoimmune disorder, as his vicious princelings run out of enemies to destroy and begin to knife one another.
Any monopoly faces these destructive microincentives, but tech is exceptional here because tech has the realtime flexibility and speed that brick-and-mortar businesses can never match:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/19/twiddler/
Sociopaths with tech monopolies are worse for the same reason that road-rage would be worse in a flying car: adding new capacity to indiscriminate self-destructive urges turns ordinary car crashes into low-level airburst warfare:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/28/microincentives-and-enshittification/
The flexibility of digital gives tech platforms so much latitude to break things in tiny increments. A tech platform is like a Jenga tower composed of infinitely divisible blocks. The Jenga players are the product managers and executives who have run out of the ability to grow by attracting new business thanks to their monopoly dominance. Now they compete with one another to increase the yield from their respective divisions by visiting pain upon the business customers and end users their platform connects. By tiny increments, they increase the product's cost, lower its reliability, and strip it of its utility and then charge rent to restore its functionality:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/24/cursed-bigness/#incentives-matter
This is the terminal stage of enshittification, the unstoppable autocannibalism of platforms as they seek to harvest all the value created by business customers and end users, leaving the absolute minimum of residual value needed to keep both stuck to the platform. This is a brittle equilibrium, because the difference between "I hate this service but I just can't stop using it," and "Get me the fuck out of here" is razor-thin.
All it takes is one tiny push – a whistleblower, a livestreamed mass-shooting, a Cambridge Analytica – and people bolt for the doors. This triggers the final stage: the "pivot," which is a tech euphemism for "panic."
For Zuck, the pivot got real after a disappointing earnings call triggered a mass sell-off of Facebook stock, history's worst one-day value incineration, which lopped a quarter of a trillion dollars off the company's market cap:
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-12-19/dramatic-stock-moves-of-2022-led-by-meta-dive-nordic-flash-crash
This was when the metaverse became the company's top priority.
Now, in my theory of enshittification, the step that follows the pivot is death: "Finally, they abuse those business customers to claw back all the value for themselves. Then, they die":
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/21/potemkin-ai/#hey-guys
Many people have asked me about the conspicuous non-death of Facebook! That's where I have to fall back on Stein's Law: "Anything that can't go on forever eventually stops." Facebook can't continue to annihilate value, alienate its workers, harm the public, hemorrhage money in support of a mediocrity's cherished folly forever. Can it?
Admittedly, it sure seems like it can. Facebook's metaverse pivot has thus far cost the company $46,500,000,000. That is: $46.5 billion. That's even more money than Uber torched, seeking to maintain the illusion that they will be able to create monopolies on both transport and the labor market for driving and recoup the billions the Saudi royal family let them use for the con:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/02/11/bezzlers-gonna-bezzle/#gryft
Don't worry: the Saudi royals are fine! They cashed out at the IPO, collecting a tidy profit at the expense of retail investors who assumed that a pile of shit as big as Uber must have a pony under it, somewhere:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/19/fake-it-till-you-make-it/#millennial-lifestyle-subsidy
Uber has doubled the cost of rides and halved drivers' wages, using illegal gimmicks like "algorithmic wage discrimination" to squeeze a little more juice out of the nearly exhausted husks of its workforce:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/12/algorithmic-wage-discrimination/#fishers-of-men
But Stein's Law hasn't been repealed. Drivers can't drive for sub-subsistence wages. Do that long enough and they'll literally starve: that's what "subsistence" means. We lost a decade of transit investment thanks to the Uber con, at the same time as traditional taxi drivers were forced out of the industry. Uber can't be profitable and still pay a living wage, and the fantasy of self-driving cars as a means of zeroing out the wage-bill altogether remains stubbornly, lethally unworkable:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/09/herbies-revenge/#100-billion-here-100-billion-there-pretty-soon-youre-talking-real-money
Which means we're at the point where you can get off a commuter train at a main station and find yourself stranded: no taxis at the taxi-queue, no busses due for an hour, and no Uber cars available unless you're willing to pay $95 for a ten-minute ride in a luxury SUV (why yes, this did happen to me recently, thanks for asking).
As more and more of us are exposed to these micro-crises, the political will to do something will increase. This can't go on forever. "Don't use commuter rail" isn't a viable option. "Walk three miles each way to the commuter rail station" isn't viable either. Neither is "Pay $95 for an Uber to get to the station." Something's gotta give…eventually.
"Eventually" is the key word here. Remember the corollary of Stein's Law: Keynes's maxim that "markets can remain irrational longer than you can remain solvent." Sure, anything that can't go on forever eventually stops, but that is no guarantee of a soft landing. You can't smoke two packs a day forever – but in the absence of smoking cessation, the eventual terminus of that habit is stage-four lung cancer. Keep hammering butts into your face and your last smoke will come out a crematorium chimney.
Zuckerberg hasn't merely blown a whole-ass Twitter on the metaverse with nothing to show for it – he's gotten richer while doing it! In the past year, his net worth increased by 130%, to $59 billion, thanks to an increase in Facebook's share-price, driven by investors who stubbornly remain irrational, keeping the Boy Emperor solvent long past any reasonable assessment of his performance.
What are these investors betting on? One possibility is that the rise and rise of Facebook's share-price represents a bet on technofeudalism. Since the Communist Manifesto, Marxists have been predicting the end of capitalism. That end seems to have come, but what followed capitalism wasn't socialism, it was the return of feudalism, an economic system where elites derive their wealth from rents, not profits:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/28/cloudalists/#cloud-capital
Profit is the income you get from investing in capital – machinery, systems, plant – and then harvesting the surplus value created by workers who mobilize this capital. Capitalism produces massive returns for its winners – in the Manifesto's first chapter, Marx and Engels just geek out about how productive and dynamic this system is.
But capitalism is also a Red Queen's Race, where the winners have to run faster and faster to stay in the same place. Capitalism drives competition, as other would-be winners pile into the sector, replicating the systems that the current winners are using and then improving on them. This is why the prophets of capitalist end-times like the FBI informant Peter Thiel say that "competition is for losers."
Capitalism's "profits" stand in contrast to the feudalist's "rents." Rents are income you get from owning something that other people need to produce things. The capitalist owns the coffee-shop, but the feudalist owns the building. When a rival capitalist opens a superior coffee-shop and drives the old shop out of business, the capitalist loses, but the rentier wins. Now they can rent out an empty storefront in the neighborhood everyone's coming to because of that hot new cafe.
Feudal and manorial lords also made their fortunes by extracting surplus value from workers, but these rentiers don't care about owning the means of production. The peasant in the field pays for their own agricultural equipment and livestock – control over the means of production is necessary for worker liberation, but it's not sufficient. The worker's co-op that owns its factory can still find the value it produces bled off by the landlord who owns the land the factory sits on.
The jury's still out on whether American workers really see themselves as "temporarily embarrassed millionaires," but America's capitalists have a palpable, undeniable loathing for capitalism. The dream of an American "entrepreneur" is *PassiveIncome: money you get from owning something capitalists and/or workers use to create value. Digital technology creates exciting new possibilities for rent-extraction: a taxi-operator had to buy and maintain a car that someone else drove. Uber can offload this hassle onto its drivers and rent out access to the chokepoint it created between drivers and riders, charging all the traffic can bear. This is feudalism in the cloud – or as Yannis Varoufakis calls it, cloudalism.
In Varoufakis's Technofeudalism, he describes Amazon as a feudal venture. From a distance, Amazon seems like a bustling marketplace of manic capitalism, with sellers avidly competing to offer more variety and lower costs in a million independently operated storefronts. But closer inspection reveals that Amazon is a planned economy, not a market.
Every one of those storefronts pays rent to the same landlord – Amazon – which determines which goods can be offered for sale. Amazon sets pricing for those goods, and extracts 45-51% of every dollar those sellers make. Amazon even controls which goods are shelved at eye-height when you enter the store, and which ones are banished to a dusty storeroom in a distant sub-basement you'll never find:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/06/14/flywheel-shyster-and-flywheel/#unfulfilled-by-amazon
Zuck's metaverse is pure-play technofeudalism, Amazon taken to the logical extreme. It's easy to get distracted by the part of Zuck's vision that will convert us all into legless, sexless, heavily surveilled low-resolution cartoon characters. But the real action isn't this digitization of our fleshy wants and needs. Zuck didn't spend $46.5B to torment us.
The cruelty isn't the point of the metaverse.
The point of the metaverse is to rent us out to capitalists.
Zuck doesn't know why we would use the metaverse, but he believes that if he can convince capitalists that we all want to live there, that they'll invest the capital to figure out how to serve us there, and then he can extract rent from those capitalists and start earning "passive income." It's an Uber for Cyberpunk Dystopias play.
Zuck's done this before. Remember the "pivot to video?" Zuckerberg wanted to compete with Youtube, but he didn't want to invest in paying for video production. Videos are really expensive to produce and the median video gets zero views. So Zuck used his captive audience to trick publishers into financing his move into video. He fraudulently told publishers that videos were blowing up on Facebook, outperforming boring old text by vast margins.
Publishers borrowed billions and raised billions more in the capital markets, financing the total conversion of newsrooms from text to video and precipitating a mass extinction event for print journalists. Zuck kept the con alive by giving away (fewer) billions to some of those publishers, falsely claiming that their videos were generating fortunes in advertising revenue. These lucky, credulous publishers became judas goats for their industry, luring others into the con, the same way that the "lucky" guy a carny lets win a giant teddy-bear at the start of the day lures others into putting down $5 to see if they can sink three balls in a rigged peach-basket.
But when we stubbornly refused to watch videos on Facebook, Zuck stopped spreading around these convincer payouts, and precipitated a second mass-extinction event in news media, as the new generation of video journalists joined their predecessors in Facebook-driven unemployment. Given this history, it's surreal to see publishers continue to insist that Facebook is stealing their content, when it is so clearly stealing their money:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2023/04/saving-news-big-tech
Metaverse is the new Pivot to Video. Zuckerberg is building a new world, which he will own, and he wants rent it to capitalists, who will compete with one another in just the way that Amazon's sellers compete. No matter who wins that competition, Zuckerberg will win. The prize for winning will be a rent increase, as Zuckerberg leverages the fact that your "successful" business relies on Facebook's metaverse to drain off all the value your workers have produced:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/18/metaverse-means-pivot-to-video/
This can't last forever, but how long until Zuck's reality distortion field runs out of battery? That's the $46.5B question.
The market can certainly remain irrational for a hell of a long time. But the market isn't the only force that regulates corporate outcomes. Regulators also regulate. Europe's GDPR is now seven years old, and it plainly outlaws Facebook's surveillance.
For nearly a decade, Facebook has pretended that this wasn't true, and they got away with it. Mostly, that's thanks to the fact that Ireland is a corporate crime-haven with a worse-than-useless Data Protection Commission:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/15/finnegans-snooze/#dirty-old-town
But anything that can't go on forever will eventually stop. Facebook has finally been dragged into EU federal jurisdiction, where it will face exterminatory fines if it continues to spy on Europeans:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/07/luck-of-the-irish/#schrems-revenge
In response, Facebook has rolled out a subscription version of its main service and its anticompetitive acquisition, Instagram:
https://about.fb.com/news/2023/10/facebook-and-instagram-to-offer-subscription-for-no-ads-in-europe/
For €10/month, Facebook will give you an ad-free experience across its service offerings (it's €13/month if you pay through an app, as Facebook recoups the 30% #AdTax rents that the feudal Google/Apple mobile duopoly extracts).
But this doesn't come close to satisfying Facebook's legal obligations under the GDPR. The GDPR doesn't ban ads, it bans spying. Facebook spies on every single internet user, all the time. The apps we use are built with "free" Facebook toolkits that extract rent from the capitalists who make them by harvesting our data as we use their apps. The web-pages we visit have embedded Facebook libraries that do the same thing for web publishers. Facebook buys our data from brokers. Facebook has so many ways of spying on us that there's almost certainly no way for Facebook to stop spying on you, without radically transforming it operation.
To comply with the GDPR, Facebook must halt surveillance advertising altogether. There's no way to square "spying on users" with "you can't surveil without explicit consent, and you can't punish people for refusing."
And of course, "not spying" isn't the same as "not advertising." "Contextual advertising" – where ads are placed based on the thing you're looking at, not who you are and what you do – is hundreds of years old. Context ads underperform surveillance ads by a slim margin – about 5% – but they're vastly more profitable for publishers. That's because surveillance ads are feudal, controlled by rentiers like Facebook, who own vast troves of the surveillance data needed to run these ads. Traditional ad intermediaries (agencies, brokers) took 10-15% out of the total advertising market. Ad-tech companies – the Google/Facebook duopoly – take 51% out of every ad dollar spent.
Eliminate surveillance ads and you torch their feudal estates. Facebook will always know more about someone reading a news article than the publisher – but the publisher will always know more about the article than Facebook does:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2023/05/save-news-we-must-ban-surveillance-advertising
There are rents under capitalism, just as there are profits under feudalism. The defining characteristic of a system is what happens when rents and profits come into conflict. If profits win – for example, if productive companies beat patent trolls, or if news publishers escape Facebook's rent-extraction – then the system is capitalist. If rents win – if investors continue to bet large on the metaverse as its losses pass $50 billion and head for the $100 billion mark – then the system is feudal.
Anything that can't go on forever will eventually stop. The question isn't whether the platforms will eventually become so enshittified that they die – the question is whether they will go down in an all-consuming fireball, or whether they'll go down in a controlled demolition that lets us evacuate the people they've trapped inside them first:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/09/let-the-platforms-burn/

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/30/markets-remaining-irrational/#steins-law

Image: Diego Delso (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Puente_de_las_cataratas_Victoria,_Zambia-Zimbabue,_2018-07-27,_DD_10.jpg
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
#pluralistic#mark zuckerberg#meta#enshittification#facebook#twitter#elon musk#billionaires#follies#failing up#metaverse#steins law#big tech#technofeudalism
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Pharmacist Lunsford Richardson made Vicks a household name throughout the nation, but his popular product did not do the same for him.
Even in his native North Carolina, where his most celebrated of chemical concoctions has been right under our stuffy noses and on our congested chests for generations, the mention of Richardson’s name elicits blank stares from all but those who study and cherish history.
Richardson’s salve, Vicks VapoRub, helped the world breathe easier during the devastating influenza pandemic of 1918 and during the countless colds and flus of our childhoods, yet most of us couldn’t pick Lunsford Richardson out of a one-man police lineup, much less a who’s who of medical pioneers.
Why didn’t Richardson — by all accounts a creative inventor and smart businessman — ever become as famous as those vapors packed into the familiar squat blue jar?
Because his name wouldn’t fit on the jar.
That’s one version of the story. According to company and family lore, Richardson initially dubbed his promising new product Richardson’s Croup and Pneumonia Cure Salve. Realizing that this name didn’t exactly roll off the tongue nor fit when printed on a small medicine jar, Richardson changed the name to honor his brother-in-law, Dr. Joshua Vick. Another account suggests the inventive druggist plucked the name from a seed catalog he’d been perusing that listed the Vick Seed Co.
The truth may never be known. What is known, though, is that Lunsford Richardson created a medicinal marvel for the ages, the likes of which may never be equaled.
Croupy beginnings
A Johnston County native born in 1854, Richardson loved chemistry and hoped to study it at Davidson College. The college’s chemistry program at the time wasn’t as strong as he’d hoped it would be, so he studied Latin instead, graduating with honors in three years. He returned to Johnston County and taught school, but it wasn’t long before the young man’s love of chemistry got the best of him. In 1880, he moved to Selma to work with his physician brother-in-law, Dr. Vick. It was not uncommon in those days for doctors to dispense drugs themselves, but Vick was so busy seeing patients that he teamed up with Richardson, allowing him to handle the pharmacy duties for him. Richardson relied on his knowledge of Latin to help him learn the chemical compounds required to become a pharmacist, and that’s when he began to experiment with recipes for the product that would become Vicks VapoRub.
It wasn’t until Richardson moved to his wife’s hometown of Greensboro in 1890 that his magical salve and other products he created began to take off.
“He was a man of great intellect and talent,” says Linda Evans, community historian for the Greensboro Historical Museum, which has an exhibit devoted to Richardson and Vicks.
“Druggists at the time fashioned their own remedies a lot, and he created a number of remedies, in addition to his magic salve, that he sold under the name of Vick’s Family Remedies. He was obviously a man of such creativity.”
In Greensboro, working out of a downtown drugstore he purchased (where he once employed a teenaged William Sydney Porter, the future short story writer O. Henry), Richardson patented some 21 medicines. The wide variety of pills, liquids, ointments, and assorted other medicinal concoctions included the likes of Vick’s Chill Tonic, Vick’s Turtle Oil Liniment, Vick’s Little Liver Pills and Little Laxative Pills, Vick’s Tar Heel Sarsaparilla, Vick’s Yellow Pine Tar Cough Syrup, and Vick’s Grippe Knockers (aimed at knocking out la grippe, an old-timey phrase for the flu).
These products sold with varying degrees of success, but the best seller in the lineup of Richardson’s remedies was Vick’s Magic Croup Salve, which he introduced in 1894. And by all accounts, necessity was the key to its success.
“He had what they referred to as a croupy baby — a baby with a lot of coughing and congestion,” explains Richardson’s great-grandson, Britt Preyer of Greensboro. “So as a pharmacist, he began experimenting with menthols from Japan and some other ingredients, and he came up with this salve that really worked. That’s how it all started.”
Another version of the story suggests that all three of the Richardson children caught bad colds at the same time, and Richardson, dissatisfied with the traditional treatment of the day, which included poultices and a vapor lamp, spent hours at his pharmacy developing his own treatment.
Richardson’s salve — a strong-smelling ointment combining menthol, camphor, oil of eucalyptus, and several other oils, blended in a base of petroleum jelly — was a chest-soothing, cough-suppressing, head-clearing sensation. When the salve was rubbed on the patient’s chest, his or her body heat vaporized the menthol, releasing a wave of soothing, medicated vapors that the patient breathed directly into the lungs.
Vicks in the mailbox
In 1911, Richardson’s son Smith, by now a successful salesman for his father’s company, recommended discontinuing all of the company’s products except for Vick’s Magic Croup Salve. He believed the salve could sell even better if the company stopped investing time and money in the other, less successful remedies. He also suggested renaming the salve Vicks VapoRub, according to the company’s history timeline, to “help dramatize the product’s performance.” Richardson agreed, and a century later, the name’s still the same.
Meanwhile, Richardson intensified his marketing efforts by providing free goods to druggists who placed large orders and publishing coupons for free samples in newspapers. He also advertised on billboards and sent promotional mailings to post office boxes, addressed to Boxholder rather than the individual’s name, thus earning him the distinction of being the father of junk mail.
In 1925, Vicks even published a children’s book to help promote the product. The book told the story of two elves, Blix and Blee, who rescued a frazzled mother whose sick child refused to take nasty-tasting medicines. Their solution, of course, was the salve known as Vicks VapoRub.
Expanding and experimenting
As successful as the marketing campaign was, nothing sold Vicks VapoRub like the deadly Spanish flu outbreak that ravaged the nation in 1918 and 1919, killing hundreds of thousands of Americans. Loyal Vicks customers and new customers stocked up on the medicine to stave off or fight the disease.
According to the company’s history timeline, VapoRub sales skyrocketed from $900,000 to $2.9 million in a single year because of the pandemic. The Vicks plant in Greensboro operated around the clock, and salesmen were pulled off the road to help at the manufacturing facility in an effort to keep up with demand.
As the flu spread across the nation, Richardson grew ill with pneumonia in 1919 and died. Smith took over the company. Vicks continued to grow, buying other companies until Procter & Gamble bought it in the 1980s. Through the years, Vicks continued adding new products to its arsenal of cold remedies: cough drops, nose drops, inhalers, cough syrup, nasal spray, Formula 44, NyQuil. And whatever success those products attained, they got there standing on the broad shoulders of Richardson.
Richardson will never be a household name, but his salve has held that status for more than a century — and may do so for the next hundred years. And for Richardson, were he still around, that ought to be enough to clear his head.
A cure-all salve
Vicks users have claimed the salve can cure and heal many maladies. Even though Vicks doesn’t say the salve works for these problems, people still believe.
Toenail fungus: Rub the salve on your toenails, cover with socks, and sleep your fungus problems away. Cough: For a similar fix to a nagging cough, some believe rubbing Vicks on the soles of your feet can fix the problem. Dandruff: Rub Vicks directly on the scalp, and your flakes may just disappear. Chapped lips: Petroleum jelly is one of the ingredients in Vicks, and some say the ointment can help heal cracked lips. Mosquito bites: If you smooth Vicks on the red bumps on your legs and arms, it can supposedly take the itch right out. Warts: Dab Vicks on the wart, cover with duct tape, and it may fall off in a few days.
Greensboro Historical Museum 130 Summit Avenue Greensboro, N.C. 27401 (336) 373-2043 greensborohistory.org
See historical Vicks VapoRub bottles and learn about Lunsford Richardson.
#VICKS#Vicks vapo rub#Lunsford Richardson#Vicks VapoRub#spanish american flu#Spanish flu outbreak#1918#1919#pneumonia#Black Inventors
557 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yule Lad

"Gryla and the Yule Lads" © Marc Potts, accessed on his Threads account here
[It's been a while since I made a new Christmas monster, hasn't it? I woke up this morning with an uncontrollable urge to stat up the Yule Lads. It's December 21st at the time of posting, so look out for Window Peeper!]
Yule Lad CR 4 CN Fey This odd little man has a red cap, a white beard and a look of disheveled mischief about him. His fingernails are claw-like, and the shadows around him cast eerie shapes.
The Yule Lads are a gang of gnomish pranksters, each of them specializing in a particular brand of theft or harassment. They are so named because their habit is to descend upon communities during the winter solstice in order to wreak their mischief. They are the sons of the wicked troll Grýla and the lazy ogre Leppalúði, but themselves are not evil. They once were, and happily abducted children for their mother to eat, but they have mellowed somewhat with the passing of the ages. A household that endures their thefts and torments with good humor may find themselves rewarded with small strange gifts (often those stolen from other households).
There are thirteen prominent Yule Lads who travel together, coming down from the mountains one by one to prey on the same community before leaving in turn after a few weeks of mischief. Each one is named after their preferred targets or habits. They are, in their typical order of operations:
Sheepcote Clod, who harasses sheep and drinks their milk straight from the udder
Gully Gawk, who peeps on milkmaids and steals milk once it has been collected
Stubby, who steals burnt food and dirty pans and has very short legs
Spoon Licker, who licks the stirring spoons between uses to contaminate them
Pot Scraper, who steals leftover food before it can be stored
Bowl Licker, who eats food left out for domestic animals
Door Slammer, who wakes families up in the night with loud banging noises
Skyr Gobbler, who is voracious for skyr, yogurt and other fermented dairy products
Sausage Swiper, who hides in the rafters of smokehouses to steal sausages
Window Peeper, who is a voyeur and general thief
Door Sniffer, who can smell fresh baked bread from miles away
Meat Hook, who uses an ogre hook to steal meat from butchers and pantries alike
Candle Beggar, who steals candles in order to eat them
The Yule Lads prefer not to fight if they can help it. They use their mastery over shadows to teleport in and out of houses to rob and to frighten off anyone who attempts to stop them. If they are met with lethal violence, they will fight back, but typically attempt to flee if they see an opportunity. If one of the Yule Lads is slain, however, his brothers will declare a vendetta against his killer and retaliate in turn. These feuds end with the death of the killer and their associates, or with the killer paying off the Lads with sufficient weregild. Rumors circulate that there have been as many as fifty Yule Lads over the centuries, some of whom were slain and others of whom have grown bored of vexing people and retreated into the wilderness for good.
Yule Lad CR 4 XP 1,200 Variant advanced ogrekin redkind CN Small fey (giant) Init +6; Senses low-light vision, Perception +7 Aura twisted shadows (30 ft., DC 14)
Defense AC 22, touch 17, flat-footed 16 (+1 size, +6 Dex, +5 natural) hp 28 (3d6+18) Fort +7, Ref +10, Will +5 Weakness giant-blood, situational blindness
Offense Speed 30 ft. Melee 2 claws +6 (1d4+5) Spell-like Abilities CL 3rd, concentration +6 At will—dancing lights, darkness, detect thoughts (DC 15), ghost sound (DC 13), lullaby (DC 13) 1/day—grease (DC 14), minor image (DC 15), snare
Statistics Str 20, Dex 22, Con 23, Int 12, Wis 13, Cha 17 Base Atk +1; CMB +5; CMD 21 Feats Alertness, Deft Hands Skills Climb +9, Disable Device +11, Escape Artist +12, Intimidate +10, Perception +9, Sense Motive +9, Sleight of Hand +14, Stealth +18; Racial Modifiers +4 Intimidate Languages Common, Giant, Sylvan SQ deformities (varies), shadow jump
Ecology Environment cold mountains and urban Organization solitary or family (2-13) Treasure standard (thieves tools, other gear)
Special Abilities Deformities (Ex) Each of the Yule Lads has two deformities, one beneficial and one disadvantageous. These are as follows:
Sheepcote Clod: gnarled hands (claws deal 1d6 damage); stiff back (-4 to grapple and trip combat maneuver checks; can only stand from prone as a full-round action)
Gully Gawk: bulging eye (darkvision 60 ft.); light sensitivity
Stubby: thick feet (+4 CMD vs. bull rush, overrun and trip, +2 AC vs. charge attacks); stunted legs (-10 ft. movement)
Spoon Licker: lanky (+5 ft. reach); fragile (-4 Con)
Pot Scraper: thick skin (+2 natural armor); distractible (when rolls a natural 1 on an ability check, attack roll, saving throw or skill check, confused for 1 round)
Bowl Licker: oversized maw (bite attack dealing 1d4 damage); brittle bones (creatures gain a +4 circumstance bonus to confirm critical hits against him)
Door Slammer: vice grip (+2 to CMB to disarm and grapple, +4 CMD vs. disarm and grapple); obese (-2 Dex)
Skyr Gobbler: quick metabolism (+2 to Fortitude saves), weak mind (-2 to Will saves)
Sausage Swiper: long fingers (Climb speed equal to ½ land speed); offensive odor (-2 Cha, detectable at double range with scent)
Window Peeper: enlarged skull (+2 Int, [3 ranks in Appraise]); deformed hand (only one claw attack, -2 to attack rolls with two-handed weapons)
Doorway Sniffer: snout (scent); trusting (-2 to Will saves vs. mind-influencing effects, -1 initiative)
Meat Hook: oversized limb (can wield Medium weapons without penalty); flaking skin (-1 natural armor, vulnerability to nonlethal damage)
Candle Beggar: grotesque ears (blindsense 10 ft., +4 Perception); massive girth (-4 to Stealth)
Giant-Blood (Ex) Although the Yule Lads are fey creatures, they are the children of giants, and as such are treated as having the giant subtype for the purposes of spells and abilities. Situational Blindness (Su) The Yule Lads have trouble targeting creatures who can’t see them. Any creature that can’t see a Yule Lad (such as by closing its own eyes) gains partial concealment from it. Any creature that covers itself entirely (such as by hiding under a blanket) gains full concealment, even if the creature would not otherwise be considered hidden. Shadow Jump (Su) A Yule Lad can travel between shadows as if using a dimension door spell. The Yule Lad must begin and end its transportation in an area of dim illumination. A Yule Lad can travel up to 40 feet a day in this fashion, and can split this distance up in 10 foot increments if he so chooses. Twisted Shadows (Su) In areas of dim illumination or darker, a Yule Lad’s presence animates the shadows within 30 feet of it into leering or wicked shapes. The first time a creature ends its turn within this aura, it must succeed at a DC 13 Will saving throw or become shaken for 10 minutes. If the creature succeeds at the saving throw, it cannot be affected again by the same Yule Lad’s twisted shadows for 24 hours. This is a fear effect, and the DC is Charisma-based.
#pathfinder 1e#fey#giant#yule lads#icelandic folklore#christmas folklore#christmas#merry christmas#merry shitscram#seasons greasons
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
Otto and Hua's pseudo-friendship is fascinating to me because they are two very different characters, yet are formed from similar circumstances. More than that, I feel like they are different reactions to those circumstances-two sides of a coin, in a sense.
Hua lost her whole world-her hometown, her family, her friends and comrades, and even her memories. Fundamentally, the only constant in her life has been the goal of protecting humanity from the Honkai. Hua's goal has been purely selfless, even costing her own happiness. But this has had consequences! Heck, one of those consequences was creating Otto! Senti points this out in Chapter 21, had Hua killed Otto and Kallen during the Crusade, none of the story events would have ever happened. Even more so, Hua was indirectly responsible for the events of Seven Swords, another Otto defining event, as her intention to kill one of her students has an attempt to preserve this mission got her literally murdered. And yet despite all these things...Hua was able to change. She was able to see her flaws and improve as a person, and find a path beyond her mission, save humanity, and build a new "world".
Otto's loss, on the other hand, is smaller in scale, yet carries equal consequence. Kallen Kaslana was his whole world, and everything that he believed that was good about the world. When she died, saying he lost it is the understatement of the last five centuries. Thus began his century-long goal of reviving her, committing multiple atrocities and harming many people, some of whom were his own family. His mission was a purely selfish one, something him and many other characters do not hesitate to admit. And yet...without his actions, humans wouldn't have been saved from the Honkai. It's a strange paradox. He did keep humanity from dying to the Honkai for his reign as Overseer, and he created Theresa, Bianka, and most importantly, Kiana, all important to the final battle, especially Kiana, who literally becomes the embodiment of Finality. Somehow, in a weird irony, Otto's actions do some good. More harm though. Lots of harm. Still, Otto was not able to change. He remained largely the same for 500 years. His goal remained unchanged for 500 years. And the Will of Honkai was right. He would die for it.
If Hua is a flower, waiting for a place to bloom and lay down her roots, Otto is a long dead tree, his roots stuck deep in the ground. Both are products of the flow of time. Yet, Hua's clock has just begun to turn, and Otto's has finally stopped.
#honkai impact 3rd#hi3#honkai impact#otto apolcalypse#fu hua#this has made cautiously optimistic for eventual luocha marshall hua interaction#morose talks
64 notes
·
View notes