#Capital Expenditure
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Malcolm H. Smith - Capital Expenditure
(Fantasy Fiction - November 1954)
#malcolm h. smith#capital expenditure#fantasy fiction magazine#pulp a#horror art#witch#witchcraft#black magic#art#illustration
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tata Steel Reports Strong Q1 Financial Results for FY 2024-25
Tata Steel’s consolidated revenues for Q1 FY 2024-25 reached Rs 54,771 crores, with an EBITDA of Rs 6,822 crores, reflecting a robust 12.5% EBITDA margin. Tata Steel today announced its financial results for the first quarter of the Financial Year 2024-25, showcasing a significant 75% year-over-year increase in consolidated net profit, which stood at Rs 919 crore. JAMSHEDPUR – Tata Steel reported…
#फोकस#बिजनेस#business#Capital Expenditure#consolidated revenues#EBITDA#financial results#focus#India operations#Kalinganagar expansion#Net Profit#Netherlands operations#Q1 FY 2024-25#Tata Steel#UK operations
0 notes
Text
India to spend $75 billion on its military, the largest among PM Modi's ministries
By A Correspondent In the regular Union Budget of Financial Year (FY) 2024-25, the Ministry of Defence (MoD) has been allocated Rs 6,21,940.85 crore (approx. US$75 billion), the highest allocation among Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s ministries in his third term in government. While maintaining the allocation made to MoD during the interim budget, the Modi government has made an additional…
#Armed Forces#Arming India#Budget#Capital Expenditure#Defence#Defence Minister#Defence R&D#Defence Research and Development Organisation#Defense#DRDO#Finance Minister#India#Indian Air Force#Indian Army#Indian Coast Guard#Indian Navy#Industry#Military#Minister of Defence#Minister of Finance#Modi#Narendra Modi#Nirmala Sitharaman#Prime Minister#Procurement#Rajnath Singh#Revenue Expenditure
0 notes
Text
Getting a Grip on Cost for Automation
Tracking the costs of automation in a business, especially in sectors like manufacturing or metal fabricating, involves a comprehensive approach that considers various factors. Here are key areas to focus on and methods to track these costs effectively:
Initial Investment Costs:
Capital Expenditure: Record the purchase price of automated equipment, rigging, installation costs, any modifications needed to the facility, and the cost of integrating new systems with existing ones.
Software and Licensing Fees: Include the cost of software required to run and manage the automated systems, along with any ongoing licensing or subscription fees.
Tooling and Setup Costs: Account for any specialized tooling or additional equipment needed to support the automation.
Operational Costs:
Maintenance and Repairs: Regular maintenance and any repairs needed to keep automated systems running efficiently.
Utilities: Increased costs in electricity or other utilities due to the operation of automated machinery.
Supplies and Materials: Additional materials or supplies needed for the operation of automated systems.
Labor Costs:
Training and Development: Costs associated with training staff to operate and maintain the new systems.
Salaries for Technical Staff: Salaries for employees who manage, maintain, or program the automated systems.
Indirect Costs:
Downtime Costs: Costs incurred during the implementation phase when machines are not operational, or during any downtime for maintenance or breakdowns.
Depreciation: The depreciation of equipment over time, affecting the overall financial valuation of the assets.
Financial Management Tools:
Accounting Software: Utilize accounting software to track and categorize expenses related to automation. This software can help allocate costs appropriately and generate reports for analysis.
Budgeting and Forecasting Tools: Use these tools to plan for future costs and assess the financial impact of automation over time.
Cost Centers: Create specific cost centers or codes in your financial system to track automation-related expenses distinctly from other operational costs.
Performance Metrics:
ROI Analysis: Calculate the return on investment by comparing the costs of automation against the savings and increased revenue it generates.
Productivity Metrics: Monitor changes in productivity and efficiency to evaluate the performance of automated systems relative to cost.
Regular Reviews and Audits:
Conduct periodic reviews and audits of automation costs to ensure they are tracked accurately and to identify areas for cost optimization.
By systematically tracking these costs, a business can gain a clear understanding of the financial impact of automation and make informed decisions about future investments and operational strategies.
#Automation#business#manufacturing#metal fabricating#costs effectively#Initial Investment Costs#Capital Expenditure#Software and Licensing Fees#Tooling and Setup Costs#Operational Costs#Maintenance and Repairs#Supplies and Materials#Training an
0 notes
Text
Capital Expenditure (CapEx) vs. Operational Expenditure (OpEx)
Do you have a hard time understanding what CaPex or OpEx is? CapEx CapEx, or capital expenditure, is a financial term that describes the cost of acquiring, maintaining, or improving fixed assets such as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). In simple terms, CapEx refers to the money that a company invests in its infrastructure or long-term assets to generate future benefits. These expenses can…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
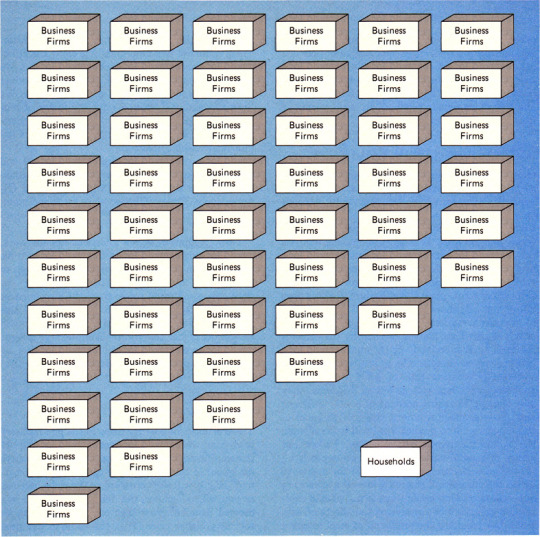
page 566 - it was a nice town until everyone started turning their households into business firms.
Everyone thought the same thing: my household is inefficient. It provides shelter for myself and my family but I cannot quantify that using my late-capitalism vocabulary. Also, I am not generating income from the pull-out couch in the basement.
So, instead of uniting with neighbours to build a new vocabulary that spoke of secure households for all people, they washed towels for strangers and fretted over star numbers. Hopefully, their business firm would earn enough that their household could join the wealthy hegemony actively destroying the public good. A new vocabulary was never created.
#economics#economists#economy#simplified general equilibrium model guns and butter#guns#butter#business#business firms#firm#firms#households#goods and services#consumer#expenditure#markets#payment#airbnb#hotels#travel#vacation#tourism#marxism#union#unite#hegemon#late capitalism
21 notes
·
View notes
Text

Never forget what the barrons stole from us.
#Never forget what the barrons stole from us.#ausgov#politas#australia#life expectancy#health#humans#society#health expenditure#expenditure#auspol#tasgov#taspol#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
the efficiency trap will stop you living
#daemon.md#capitalism makes us play its game of maximising our time and productivity and minimising expenditure#and sometimes you have no choice#but the trap is when that mindset takes you over
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Importance of Capital Expenditures in SMEs

Why Are Capital Expenditures Important for SMEs?
Capital expenditures (CapEx) are essential investments for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), enabling them to purchase, maintain, and upgrade physical assets such as buildings, machinery, and technology. These expenditures are crucial for several reasons. Firstly, they drive business growth by expanding operational capacity and enhancing productivity. Without CapEx, SMEs would struggle to scale their operations, innovate, and compete effectively in the market. Secondly, CapEx investments are often necessary to comply with regulatory requirements and industry standards, ensuring that the business remains viable and sustainable. Additionally, CapEx can significantly impact the financial health of SMEs by affecting depreciation, tax liabilities, and overall profitability. Understanding the role and importance of CapEx is vital for any SME aiming to achieve long-term success and stability.
How Do Capital Expenditures Differ from Operating Expenditures?
To fully appreciate the importance of CapEx, it is essential to distinguish it from operating expenditures (OpEx). While CapEx involves investments in long-term assets that provide benefits over several years, OpEx refers to the ongoing costs required for the daily functioning of the business. These include expenses such as salaries, rent, utilities, and office supplies. The primary difference lies in the duration and impact of the expenditures. CapEx typically involves significant upfront costs that contribute to the long-term growth and capability of the business, whereas OpEx represents the recurring costs necessary to maintain current operations.
Another key distinction is in financial reporting and tax treatment. CapEx is capitalized on the balance sheet and depreciated over the asset's useful life, spreading the expense over several years. This approach aligns the cost of the asset with the revenue it generates. In contrast, OpEx is fully deducted in the year it is incurred, directly reducing taxable income for that period. Understanding these differences helps SMEs plan and manage their financial resources more effectively, ensuring that both types of expenditures are optimized to support business objectives.
Strategic Importance of CapEx for SME Growth
Capital expenditures play a strategic role in driving the growth and development of SMEs. One of the primary benefits of CapEx is the enhancement of operational efficiency. By investing in modern equipment, technology, and infrastructure, SMEs can streamline processes, reduce waste, and increase productivity. For example, upgrading to advanced manufacturing machinery can significantly boost production speed and quality, leading to higher output and reduced operational costs. Similarly, investing in information technology systems can improve data management, customer service, and overall business agility.
CapEx also enables SMEs to expand their market presence and competitiveness. Investments in new facilities, distribution networks, and marketing initiatives can open up new markets and customer segments, driving revenue growth. For instance, a small retail business might invest in a new store location or an e-commerce platform to reach a broader audience. Such strategic investments not only increase sales but also enhance the brand's visibility and reputation.
Moreover, CapEx is crucial for fostering innovation and staying ahead of industry trends. By allocating funds to research and development (R&D), SMEs can create new products, improve existing ones, and adopt cutting-edge technologies. This continuous innovation is vital for maintaining a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market. For example, a tech startup might invest in developing a new software application or integrating artificial intelligence into its services, setting it apart from competitors.
Challenges SMEs Face with Capital Expenditures
Despite the strategic benefits of CapEx, SMEs often face significant challenges in planning and executing these investments. One of the most common challenges is securing adequate financing. SMEs typically have limited access to capital compared to larger enterprises, making it difficult to fund substantial CapEx projects. Traditional financing options, such as bank loans, often require a strong credit history and collateral, which many SMEs may lack. Additionally, high-interest rates and strict repayment terms can strain cash flow and financial stability.
Another challenge is the inherent risk and uncertainty associated with CapEx. Large investments in assets like machinery or technology involve significant upfront costs and long payback periods. If the anticipated returns do not materialize, the business could face financial difficulties. Market conditions, regulatory changes, and technological advancements can also impact the viability and profitability of CapEx projects. For instance, an SME investing in new technology might find that it becomes obsolete faster than expected, requiring further investment to stay competitive.
Furthermore, SMEs often struggle with the complexity of managing CapEx projects. Effective planning, budgeting, and execution require specialized knowledge and skills, which may be scarce in smaller organizations. Inadequate project management can lead to cost overruns, delays, and suboptimal outcomes. SMEs must also navigate regulatory requirements and compliance issues related to CapEx, which can add to the complexity and cost of these projects.
Future Trends in CapEx for SMEs
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape the future of CapEx for SMEs. One significant trend is the increasing importance of digital transformation. As technology continues to evolve rapidly, SMEs will need to invest in digital infrastructure, cybersecurity, and innovative tech solutions to remain competitive. This shift towards digitalization will drive CapEx in areas such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. SMEs that embrace digital transformation can expect improved efficiency, new revenue streams, and enhanced customer experiences.
Sustainability and green investments are also emerging trends in CapEx. As environmental concerns gain prominence, SMEs are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices and eco-friendly technologies. Investments in renewable energy, energy-efficient equipment, and sustainable production processes not only reduce environmental impact but also offer cost savings and enhance brand reputation. SMEs that prioritize sustainability can attract environmentally conscious customers and meet regulatory requirements more effectively.
Another trend is the rise of alternative financing options. Traditional bank loans are no longer the sole source of CapEx funding. SMEs can now explore a range of financing solutions, including crowdfunding, peer-to-peer lending, and fintech platforms. These options offer greater flexibility, faster approval processes, and access to a broader pool of investors. By leveraging alternative financing, SMEs can overcome capital constraints and execute their CapEx plans more efficiently.In conclusion, capital expenditures are a critical component of SME growth and success. By understanding the importance of CapEx, navigating the associated challenges, and staying abreast of emerging trends, SMEs can make informed investment decisions that drive innovation, operational efficiency, and long-term sustainability.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Challenges and Opportunities in the Methanol Capacity And Capital Expenditure Market: A SWOT Analysis

For more insights into the Methanol capacity and capex market forecast, download a free report sample
Strengths:
Versatility as a Feedstock:
Methanol serves as a versatile feedstock for various industries, including chemicals, plastics, and fuels, providing a stable and diverse demand base.
Growing Global Demand:
The increasing demand for methanol, driven by industrial growth, alternative energy applications, and the desire for cleaner fuel sources, presents a positive outlook for the market.
Technological Advancements:
Ongoing advancements in methanol production technologies enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and contribute to the overall competitiveness of the industry.
Strategic Regional Presence:
Major players have strategically positioned their operations in key regions, allowing them to tap into local markets and leverage regional strengths and resources.
Weaknesses:
Volatile Feedstock Prices:
The market is susceptible to fluctuations in feedstock prices, especially natural gas. Volatility in raw material costs can impact profit margins and long-term planning for manufacturers.
Environmental Concerns:
Methanol production processes may raise environmental concerns, particularly in terms of carbon emissions. Addressing these concerns is crucial as environmental regulations become more stringent.
Dependency on Downstream Industries:
The market's reliance on downstream industries exposes it to fluctuations in demand from sectors such as chemicals, plastics, and transportation, making it sensitive to broader economic conditions.
Opportunities:
Rising Interest in Renewable Methanol:
Growing interest in renewable methanol production presents an opportunity for the industry to align with sustainability goals and cater to environmentally conscious markets.
Methanol-to-Olefins (MTO) Growth:
The expanding Methanol-to-Olefins (MTO) segment offers new revenue streams and opportunities for market players to diversify their product portfolios.
Bio-based Methanol Production:
Investments in bio-based methanol production technologies offer the potential to create a more sustainable and eco-friendly product, tapping into the increasing demand for green chemicals.
Integration Across the Value Chain:
Companies can explore opportunities for vertical integration by combining methanol production with downstream activities, ensuring greater control over the supply chain and potentially improving cost efficiency.
Threats:
Economic Downturns:
The industry is vulnerable to global economic downturns, impacting construction, manufacturing, and transportation sectors that are key consumers of methanol.
Regulatory and Policy Risks:
Evolving environmental regulations and policy changes can pose risks to traditional methanol production processes, requiring companies to adapt to new standards and invest in cleaner technologies.
Global Energy Market Dynamics:
The methanol market is influenced by global energy market dynamics, including shifts in oil prices, geopolitical tensions, and changes in energy policies, which can affect both supply and demand.
Competition and Pricing Pressures:
Intense competition in the global market can lead to pricing pressures, impacting profit margins for companies. This is particularly true in regions with multiple players vying for market share.
In conclusion, the methanol capacity and capital expenditure market exhibit a mix of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Strategic positioning, technological innovation, and adaptation to changing market dynamics will be key factors determining the success of companies in this dynamic and evolving industry.
0 notes
Text
"Amsterdam’s roofs have just been converted into a giant sponge that will make the city more climate resilient.
The Dutch have always been famous for their ability to control water, born out of the necessity of their homeland, much of which is below sea level.
Now, their expert water management skills are transforming the city skyline in the capital city of Amsterdam from one of terracotta tile, concrete, and shingles into green grass and brown earth.
It’s part of a new climate-resiliency trend in architecture and civic planning known as the ‘sponge city concept,’ in which a garden of water-loving plants, mosses, and soil absorbs excess rainwater before feeding it into the building for use in flushing toilets or watering plants on the ground.
If heavy rains are predicted, a smart valve system empties the stored rainwater into the municipal storm drains and sewers in advance of the weather, allowing the roof to soak up water and reduce flooding in the city.
In this way, the rooftops of buildings can be wrung out and filled up just like a sponge.
In Amsterdam, 45,000 square meters, or 11 acres of flat metropolitan rooftops have already been fitted with these systems, and the contracting firms behind the technology say they make sense in dry climates like Spain just as much as in wet climates like Amsterdam...
A 4-year project of different firms and organizations called Resilio, the resilient network for smart climate adaptive rooftops, rolled out thousands of square meters of sponge city technology into new buildings. As with many climate technologies, the costs are high upfront but tend to result in savings from several expenditures like water utilities and water damage, over a long-enough time horizon...
All together, Amsterdam’s sponge capacity is over 120,000 gallons.
“We think the concept is applicable to many urban areas around the world,” Kasper Spaan from Waternet, Amsterdam’s public water management organization, told Wired Magazine. “In the south of Europe–Italy and Spain–where there are really drought-stressed areas, there’s new attention for rainwater catchment.”
Indeed the sponge city concept comes into a different shade when installed in drought-prone regions. Waters absorbed by rooftops during heavy rains can be used for municipal purposes to reduce pressure on underground aquifers or rivers, or be sweated out under the Sun’s rays which cools the interior of the building naturally.
Additionally, if solar panels were added on top of the rooftop garden, the evaporation would keep the panels cooler, which has been shown in other projects to improve their energy generation.
“Our philosophy in the end is not that on every roof, everything is possible,” says Spaan, “but that on every roof, something is possible.”
Matt Simon, reporting on the Resilio project for Wired, said succinctly that perhaps science fiction authors have missed the mark when it came to envisioning the city of the future, and that rather than being a glittering metropolis of glass, metal, and marble as smooth as a pannacotta, it will look an awful lot more like an enormous sculpture garden."
-via Good News Network, May 15, 2024
#amsterdam#netherlands#green roof#blue roof#city planning#urban#urban landscape#flood#climate change#climate action#climate emergency#climate hope#solarpunk#hope posting#go green#eco friendly#climate adaptation#sponge city#urban planning#good news#hope#rooftop garden
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Budget Boosts Infrastructure, Spending to Fuel Steel Demand: Tata Steel CEO TV Narendran
Tata Steel CEO lauds reforms, sees positive impact on manufacturing and employment Next Generation Reforms in Union Budget set to enhance ease of doing business, promote holistic development across rural and urban India. JAMSHEDPUR – Expressing his strong support for the recently announced Union Budget, T.V. Narendran, CEO and MD of Tata Steel, has emphasized its potential to drive economic…
#बिजनेस#business#capital expenditure boost#economic reforms#emission reduction roadmap#Employment Linked Incentives#Indian manufacturing growth#industrial skill development#infrastructure development impact#steel industry outlook#Tata Steel CEO comments#Union Budget analysis
0 notes
Video
youtube
Cabinet (Liverpool City Council) 6th June 2023 Part 2 of 2
#youtube#Cabinet#Liverpool City Council#Liverpool#Liverpool Town Hall#West Reception Room.#Cabinet Recommendations#Coroner Service Mortuary Expenditure#Biodiversity Net Gain Policy Advice Note#Award of contract for collection of household bulky waste#Procurement of technical and professional services to support the delivery of the schools capital programme#Award of Rope Handling and Stevedore Contract at Liverpool Cruise Terminal#Procurement of travel tickets from Merseytravel for the academic year 2023/2024#Approval of Executive Scheme of Delegation & Key Decision Threshold
0 notes
Text
⊹₊⟡⋆ The Bet ⊹₊⟡⋆
Ryomen Sukuna x Female Reader x Gojo Satoru

⊹₊⟡⋆Masterlist ⊹₊⟡⋆
Warnings: Suggestive content. +18

Chapter 04
Yuuji stood outside the library, squinting at the glowing neon sign above the entrance. The clock on his phone read 6:58 PM. He groaned, glancing around the nearly deserted campus. “Why am I even here?” he muttered. Most students were either partying or relaxing—not trudging into a library on a Friday night. He shoved his hands into his hoodie pocket and pushed open the heavy glass door.
Inside, the library was quiet, almost hauntingly so. The rows of shelves stretched into the dim corners, and only a few desk lamps glowed faintly. He wandered deeper in, looking for anyone who might resemble a tutor.
“Is this Sukuna’s idea of a joke?” Yuuji muttered under his breath.
But then he saw you.
You were tucked away in the farthest corner, sitting at a table near the shelves. Glasses perched on your nose, a sweater too big for your frame draped over your shoulders, and baggy jeans swallowed your legs. Your hair was tied into a messy bun, and you were scribbling into a notebook with a focus that suggested you’d rather be anywhere but here.
Yuuji hesitated.
She looks serious…this is definitely not a prank.
He approached cautiously, the sound of his sneakers on the polished floor breaking the silence.
You glanced up as his shadow fell over your table. And for a split second, your stomach sank. His pink hair, sharp jawline, and even his stance—everything about him screamed Sukuna. The resemblance was uncanny, except for one thing: his expression. Where Sukuna’s was always distant, cold, or annoyed, this boy looked… approachable. Warm. Even friendly.
“Uh, are you my tutor?” he asked, tilting his head.
You stood, offering your hand. “That depends. Are you Yuuji Itadori?”
He grinned, shaking your hand. “That’s me! You can just call me Yuuji, though. Thanks for helping me out.”
As he settled into the chair across from you, you adjusted your glasses and opened your notebook. “Alright, let’s get started. You’re here for Principles of Financial Management, right?”
Yuuji nodded enthusiastically. “Yeah, I really need help. Like…badly.”
You chuckled softly, and his grin widened.

For the next two hours, the library filled with the sound of flipping pages, pens scratching on paper, and your patient explanations.
“Okay,” you began, pointing to a chart in the textbook. “This is the cash flow statement. It’s basically a summary of how cash moves in and out of a company over a period of time.”
Yuuji squinted at the page. “So…it’s like tracking how much money I spend on snacks versus how much I make babysitting?”
You raised an eyebrow. “Sure, if you’re running a business of snack consumption and babysitting profits. But yes, conceptually, that’s correct.”
He grinned. “See? I’m already learning!”
“Don’t get too confident yet,” you teased. “What’s the formula for free cash flow?”
Yuuji frowned, tapping his chin. “Uh…Revenue minus…expenses?”
“Close. Revenue minus operating expenses and capital expenditures. Write that down.”
He scribbled furiously in his notebook. “Got it. You’re really good at this, you know.”
You blinked, caught off guard. “At what?”
“Explaining stuff. Making it…not boring.”
You smiled, brushing off the compliment. “Thanks, Yuuji. Now, let’s move on to break-even analysis.”

By the time you glanced at the clock, it was past 9 PM. You closed the textbook with a soft thud and stretched your arms. “Alright, I think that’s enough for today.”
Yuuji leaned back in his chair, letting out a dramatic sigh. “You just saved my life. Seriously. I actually understand this stuff now!”
You smiled. “That’s the point of tutoring.”
He paused, then asked, “Do you have space for another session this week?”
You pulled out your agenda. “Let’s see…yes, I can fit you in on Thursday at the same time.”
“Perfect!” he said, watching as you wrote his name neatly in your planner.
As you packed up, Yuuji hesitated before speaking again. “Hey, are you going to Hakari’s party tonight?”
You shook your head. “No, that’s not really my thing.”
“Aw, come on,” he said, leaning forward. “It’s a Friday night! You should enjoy college a little.”
You laughed softly. “I enjoy it just fine without parties, thanks.”
“Think of it as a thank-you for helping me out,” he insisted, pulling out his phone. Before you could protest, he sent you the address.
“You really don’t have to do that,” you said, slightly flustered.
“Just think about it, okay?” he said with a grin as he stood. “Even if you just stop by for a little while, it’d be fun to see you there.”
You watched him walk away, his energy and cheerfulness lingering like a faint echo in the quiet library. Alone again, you sat back down, staring at your phone with the address he’d sent.
Should you go?
You sighed, placing your chin in your hands. For someone as outgoing as Yuuji, this party was probably the highlight of his week. For you, though? It was a step outside of your comfort zone.

When you enter your dorm, the space feels unusually quiet. Shoko isn’t there, her usual music or chatter missing, which only adds to the unease bubbling in your chest. You drop your bag on the bed and walk toward your desk, where a small mirror leans against the wall.
You sit down and open your modest makeup bag, staring at the contents for a moment. It’s been a while since you’ve done anything other than a little mascara, but tonight, curiosity wins. You pick out a soft lipstick, something subtle but noticeable, and carefully apply it.
Leaning back, you undo your messy bun, letting your hair tumble down in waves around your shoulders. For a moment, you study your reflection, unsure.
“Do I look okay for a party?” you whisper to yourself, smoothing down a stray strand of hair.
Then your eyes drop to your clothes: the oversized sweatshirt that swallows your frame and the baggy jeans that are more comfort than style. A familiar wave of self-consciousness hits.
You sigh, standing. This is ridiculous. You’re not a party person. What are you even thinking?
Just as you’re about to give up and call it a night, the door swings open. Shoko strides in, the click of her heels echoing on the floor. Her outfit is as bold as ever—short, sleek, and paired with smoky eye makeup that makes her look effortlessly cool.
“I forgot my purse and my cigarettes,” she says, scanning the room. She freezes when her eyes land on you, her lips curling into a knowing smirk. “Wait a minute… Lipstick? What’s going on here?”
You feel your face flush. “Nothing. I was just…thinking about going to the party.”
Shoko arches a brow, tossing her purse onto her bed. “Thinking? Girl, you’re either in or out. And judging by that sweatshirt, I’m guessing you’re about to chicken out.”
You fidget, glancing at your reflection again. “I don’t know, Shoko. I feel like I’ll be so out of place. I don’t even know what to wear to something like this.”
She crosses the room in two strides, studying you with a critical eye. Then she shakes her head dramatically. “Honey, this isn’t grandma’s tea party. That outfit? No.”
Before you can protest, Shoko dives into her closet with purpose. Hangers rattle and clothes fly until she emerges, triumphant, holding a tight, short black dress. She thrusts it toward you like a sacred artifact.
You blink at it, wide-eyed. “Shoko…that’s way too short.”
She laughs, a deep, throaty sound that fills the room. “That’s the point. Trust me. Just try it on. You’ve been hiding under all that fabric for too long.”
When you hesitate, she grabs a pair of sleek black heels from her closet and sets them beside the dress. “These too. Go on, the bathroom’s right there. I want a fashion show.”
Reluctantly, you take the dress and heels, muttering something about peer pressure as you shut the bathroom door.
When you finally step out, your heart pounds. The dress hugs your curves in all the right places, and the heels add just enough height to make you feel confident—but also a little exposed.
Shoko’s jaw actually drops. She blinks a few times, then grins like the Cheshire Cat. “Holy… Where have you been hiding that body? Damn, Y/N, if I looked like you, I’d be breaking hearts left and right.”
You tug at the hem of the dress nervously. “I feel…exposed.”
Shoko waves you off, pulling a lightweight cardigan from her closet and tossing it at you. “Here, for when you get cold. But don’t even think about putting it on until the party is over.”
You smile softly, holding the cardigan to your chest. “Thanks, Shoko.”
She smirks, grabbing her purse. “What are roommates for? Now come on, you’re sticking with me tonight. I’ll make sure you survive.”
You laugh, feeling a little of the tension ease. Maybe tonight won’t be so bad after all.

Hakari’s parents’ house was a sprawling suburban mansion, the kind of place that screamed “old money” and had probably never seen this much chaos before. Tonight, it was packed to the brim with college students. The bass from the sound system reverberated through the walls, and every room was teeming with people. The living room had been converted into a makeshift dance floor, where bodies swayed and moved under the glow of string lights and a rotating disco ball that Hakari had apparently borrowed from somewhere.
The kitchen was a disaster zone—red solo cups piled high, bottles of vodka, tequila, and mixers scattered across the counters. Someone was attempting to make cocktails but clearly had no idea what they were doing, judging by the grimaces from those brave enough to drink them. The backyard was just as packed, with clusters of people gathered around the pool, some dipping their feet in, others reclining on lawn chairs with drinks in hand.
Hakari had bragged all week about how his parents were conveniently “away on business,” leaving him the house. Of course, they thought he was hosting a small study group. Judging by the dozens of cars parked haphazardly down the street, they were in for a rude awakening if a single neighbor decided to call the cops.
Sukuna stood near the wall in the living room, nursing his drink and watching the chaos with mild amusement. He wasn’t a big fan of these kinds of parties anymore—too predictable, too loud—but Hakari had insisted, and Sukuna figured there were worse ways to spend a Friday night. He leaned against the wall, one hand in his pocket, his sharp gaze scanning the room with the cool indifference of someone who always looked like he was above the noise.
Then he spotted Yuuji weaving through the crowd, his bright pink hair making him impossible to miss. Trailing behind him were his ever-present sidekicks, Nobara and Megumi. Yuuji’s usual energy was dialed up even higher tonight, his grin so wide it practically lit up the dimly lit room.
“Hey, Sukuna!” Yuuji called out, raising a hand in greeting as he finally reached his older brother.
Sukuna barely shifted, taking another sip from his red cup. “What?” he asked, his tone as sharp as ever.
Yuuji wasn’t deterred in the slightest. “Just wanted to say thanks for hooking me up with that tutor. She’s great—really knows her stuff.”
“Good,” Sukuna said flatly. “You actually learning something, or are you just wasting her time?”
Yuuji groaned, rolling his eyes. “I’m learning, alright? Jeez. Why are you always so dramatic?”
Before Sukuna could fire back, Yuuji added casually, “Oh, by the way, I invited her to the party.”
Sukuna froze mid-sip, his eyes narrowing as he slowly lowered his cup. “You did what?”
“I invited her,” Yuuji repeated, grinning. “Thought it’d be a nice way to thank her, you know? Plus, she works too hard. She deserves to have some fun.”
Sukuna barked out a laugh, the sound sharp and humorless. “She’s not coming.”
Yuuji frowned. “How do you know?”
“Because she’s a nerd who lives in the library,” Sukuna said, his tone dripping with condescension. “This isn’t her scene. Trust me.”
Yuuji was about to argue when a new voice cut in.
“Yo, Sukuna!”
Gojo appeared out of nowhere, grinning ear to ear, holding a drink that looked suspiciously like it had more ice than actual liquid. He clapped Sukuna on the back with enough force to make him scowl.
“What do you want, Gojo?” Sukuna asked, clearly annoyed.
“Have you seen Geto?” Gojo asked, ignoring Sukuna’s tone entirely.
“No,” Sukuna replied, rolling his eyes. “And even if I did, I wouldn’t tell you.”
Gojo pouted dramatically. “You’ve really got to let this grudge go. It’s bad for your health, you know?”
Sukuna didn’t bother answering, taking another drink instead.
Meanwhile, Yuuji watched the exchange, grinning as he turned to Nobara and Megumi. “And you guys thought I had drama.”
The door opened wide, and Geto strolled in with his signature calm confidence, flanked by Shoko—whose outfit and energy screamed trouble—and…you.
Gojo, mid-laugh in a weak attempt to distract himself from his brewing nerves, froze. His grin slipped off his face like a melting snowman as his gaze landed on you. His heart skipped, then raced, and he quickly looked away, trying to play it cool. What were you doing here?
He had never seen you at a party before. Ever. This wasn’t your kind of scene—or so he thought. His mind raced. Were you dragged here by Shoko? Were you here because of someone? Was it him?
Gojo’s internal panic went unnoticed as he tried to inject himself into the conversation Yuuji was having with Sukuna, Nobara, and Megumi. His mouth moved, but his words were robotic, completely disconnected from his usual charm.
Meanwhile, Yuuji caught sight of you from across the room. His eyes widened in delight, and he immediately nudged Sukuna in the arm. “Told you she’d come! Man, I should’ve bet on it!”
Sukuna, who had been nursing his drink and half-listening to Yuuji, turned lazily in the direction his brother was pointing. And then he froze.
For a second, Sukuna genuinely thought his beer had been spiked. Was that…you?
It wasn’t like you looked unrecognizable. It was the same girl he’d seen in baggy jeans and oversized sweatshirts, usually with glasses sliding down your nose and a pen tucked behind your ear. But tonight? You were…different. The tight black dress hugged your body in ways Sukuna didn’t expect, and your legs seemed to go on forever under the dim, flashing lights.
The room felt like it shifted, the music blurring into static as Sukuna stood there, completely entranced. His usual sharp, cocky demeanor? Out the window. He didn’t even realize he was staring.
And he wasn’t the only one.
Gojo’s resolve to stay cool crumbled almost immediately. His eyes kept darting toward you despite his best efforts to focus elsewhere. Every time he caught sight of your dress, your hair, the way you looked slightly shy yet undeniably stunning, his face burned.
Across the room, Shoko—true to her energy—was having the time of her life, arm slung over your shoulder as she leaned in and whispered loudly enough for half the room to hear, “Everyone is staring at you!”
You winced, cheeks warming, and muttered back, “You don’t have to tell me. I can feel it.”
Shoko grinned devilishly, her confidence radiating. “That’s because you’re a total smoke show tonight, babe. Honestly, who knew all that was under those grandma sweaters?”
“Shoko!” you hissed, smacking her arm lightly.
She cackled, clearly enjoying your embarrassment, and leaned back to grab another drink from a passing tray. She started swaying to the music, trying to drag you into her rhythm. “Come on, let’s have fun!”
Meanwhile, Sukuna was still frozen. His eyes were glued to the way your dress hugged your curves, the way the lights hit your skin, the subtle confidence in your walk. He was so lost in thought that he didn’t even notice Gojo beside him, sneaking glances at you with the same dumbstruck expression.

Gojo wandered through the chaotic maze of Hakari’s house, dodging bodies dancing to the thumping bass and narrowly avoiding a girl who nearly spilled her drink on him. His sharp eyes scanned every corner until he spotted Geto leaning casually against a wall in the living room, his arm resting above a girl’s shoulder, his tone smooth as silk.
“Of course he’s flirting,” Gojo muttered to himself, sighing. Still, he made a beeline for him, determination fueling his long strides.
Geto glanced up mid-flirt, spotting Gojo’s disheveled and slightly panicked face approaching. He smirked, clearly amused. “Ah, Satoru. See what I brought you?”
Gojo ignored the girl completely, leaning in to whisper-yell, “Why didn’t you tell me you were bringing her?”
Geto raised a brow, his smirk widening. “What?” he chuckled. “I did stupid.”
Gojo rolled his eyes. “No, you did not.”
“First of all,” Geto said, holding up a finger, “I didn’t know she was Shoko’s roommate until I went to pick her up. Second—” He raised another finger, his smirk growing smug. “I texted you. Millions of times.”
“Bullshit,” Gojo snapped, immediately pulling out his phone. His thumb scrolled furiously through his notifications, his face dropping when he saw an embarrassing number of unread messages from Geto. He groaned, cursing under his breath. “Damn it.”
“Yeah, that’s what I thought,” Geto teased, taking a sip from his drink. “You really need to stop putting the none disturb mode.”
Gojo shot him a glare but quickly pivoted back to the issue at hand. “Okay, fine, you texted. But you could’ve called. You know how important this is!”
“Call you while she was in the car?” Geto raised an amused brow. “Let her know that you have liked her since middle school too?”
“Shut up,” Gojo snapped, feeling the tips of his ears heat up.
The girl Geto had been flirting with cleared her throat, clearly annoyed at being ignored. Geto glanced at her apologetically. “Sorry, babe. Give me a sec.”
She rolled her eyes and walked off, muttering something under her breath.
Geto turned back to Gojo, entirely unfazed. “She’s probably still somewhere around the party, you know. Why don’t you, oh, I don’t know…go talk to her?”
Gojo groaned, running a hand through his white hair. “It’s not that easy. I can’t just—”
“Oh, please,” Geto interrupted, grinning mischievously. “You’re Satoru Gojo, the guy who can charm anyone with just a wink. Don’t tell me you’re scared?”
“I’m not scared,” Gojo hissed, though his shifting gaze said otherwise.
“Right. Sure.” Geto leaned in, his grin turning devilish. “You’re terrified. Look at you. Your hands are probably sweating.”
“They’re not!” Gojo exclaimed, holding his hands out defensively.
“Then why are you so anxious?” Geto countered, tilting his head. “Oh wait—don’t tell me…you’re scared she might actually like you back.”
Gojo groaned again, dragging a hand down his face. “You’re insufferable.”
“And yet, I’m right,” Geto replied smugly. “Listen, she’s here. She looks great. And if you don’t at least try to talk to her tonight, other than asking her for a book…you’re gonna regret it for the rest of your life. Or at least until your next existential crisis.”
Gojo opened his mouth to retort but closed it again when he realized he had no comeback. He exhaled sharply, shoving his phone back into his pocket.
“Fine,” he muttered.
“Atta boy.” Geto clapped him on the shoulder, his grin widening. “Now go sweep her off her feet, Romeo.”
Gojo rolled his eyes, but as he turned to walk away, Geto’s voice called after him, laced with teasing.
“And if you crash and burn, I’ll be right here to say ‘I told you so!’”
“Shut up, Suguru!” Gojo yelled over his shoulder, though the small smirk tugging at his lips betrayed his nerves.

The garden feels like a sanctuary compared to the chaos inside Hakari’s house. The muffled bass of the music and sporadic laughter barely touch this corner of the property. You sit stiffly on the stone bench, arms hugging your cardigan tight, watching the small lake ripple in the moonlight. The chill in the air bites, and you shift uncomfortably, wondering again why you came here.
From your spot, you can see Shoko by the patio, taking shot after shot, her cigarette glowing faintly in the dark as she laughs with a group of strangers. She’s magnetic, fearless, the complete opposite of how you feel in this moment.
The sound of gravel crunching underfoot pulls your attention, and you glance over your shoulder. Sukuna stands there, his tall figure silhouetted against the soft glow of the garden lights. He’s holding a red cup in his hand, his expression unreadable but calm.
Your breath catches, and you immediately look away, your cheeks burning as you focus intently on the lake.
“Didn’t think I’d see you here,” he says, his deep voice breaking the quiet. There’s no teasing edge, just a quiet observation.
You sneak another glance at him as he approaches and sits down on the bench, not too close, but close enough for you to feel the weight of his presence. He leans back casually, his arm draped along the back of the bench, his red cup hanging loosely from his fingers.
“Yuuji told me he invited you,” he continues, a faint smirk tugging at his lips, “but I told him there was no way. Guess I was wrong.”
You give a nervous chuckle, still looking anywhere but at him. “I just… wanted to try something different, I guess.”
“And now you regret it,” he says, more a statement than a question.
You nod, your fingers gripping the edge of your cardigan. “This isn’t really my thing.”
He chuckles, a low, rich sound that feels surprisingly warm. “Already figured that much.”
You glance at him, surprised by the lack of mockery in his tone. He’s just watching you, his sharp eyes softened slightly, as though he’s trying to understand you.
“Parties aren’t for everyone,” he adds after a moment, swirling the drink in his cup absentmindedly.
“Do you like them?” you ask, the question slipping out before you can stop yourself.
His brow lifts slightly, as though he didn’t expect you to ask. He leans forward, resting his elbows on his knees, staring out at the lake. “I used to,” he admits, his voice quieter now.
You tilt your head, studying his profile. There’s a hint of something deeper beneath his words, and it makes you ask, “And now?”
He turns his head, meeting your gaze, and for a moment, you feel like you’re under a microscope. His eyes are intense, searching, and it’s like he’s deciding whether to let you in. Finally, he exhales softly.
“Now, they’re just noise,” he says simply. “The same faces, the same meaningless conversations. I used to think they were fun. Freedom, I guess. But…” He trails off, shaking his head slightly.
You nod, your voice soft. “I guess it’s hard to enjoy something when it doesn’t mean the same thing anymore.”
He looks at you again, and this time, his gaze lingers. There’s something almost… gentle about it, like he’s surprised that you understand. “Yeah,” he murmurs.
The air between you feels heavy but not uncomfortable. It’s as if both of you are letting the conversation settle, the quiet of the garden wrapping around you.
“Have you had anything to drink?” he asks suddenly, breaking the silence.
You shake your head quickly. “No. I’ve never tried…alcohol before.”
His brow arches in genuine surprise. “Never?”
You shake your head again, your cheeks heating under his curious gaze. “Never…”
A small smirk tugs at his lips as he holds out his red cup. “Alright. Try this.”
You hesitate, staring at the cup as though it’s a loaded weapon. “What is it?”
“Vodka cranberry,” he says. “Not too strong. Sweet enough for a beginner.”
You hesitate, eyeing the drink with suspicion. “I don’t know…”
He chuckles, the sound soft but somehow coaxing. “Come on. One sip. It’s not gonna kill you.”
Reluctantly, you take the cup, bringing it to your lips. The liquid burns immediately, the sharpness overpowering whatever sweetness it’s supposed to have. You cough, your face contorting in disgust as you shove the cup back into his hand.
“That’s terrible,” you gasp, wiping your mouth.
Sukuna throws his head back with a laugh, the sound deep and genuine. It’s the first time you’ve heard him laugh like that, and despite yourself, you feel your lips twitch into a small smile.
“I should’ve warned you about the burn,” he says, still chuckling.
“You think?” you retort, your tone half-playful, half-annoyed.
He leans back again, his smirk lingering as he watches you recover. “Guess alcohol’s not for you.”
“Maybe not,” you mumble, still grimacing at the lingering taste.
The silence returns, but it’s softer now, more comfortable. You glance at him, catching him watching you, his expression unreadable but… softer than you expected.
In the distance, Mei Mei stands on the balcony, her sharp eyes locked on the two of you. Her fingers tap against the railing as jealousy flickers across her face.
Hakari’s arm slides around her waist, his fingers tracing lazy circles on her thigh. “What are you staring at?” he murmurs.
“Nothing,” she replies, though her gaze doesn’t waver.
Hakari leans in, brushing a kiss against her neck. “Come back inside. The party’s better when you’re in it.”
With one last glance at you and Sukuna, Mei Mei allows herself to be guided away, though her thoughts remain on the garden scene.

The moment feels strange as Sukuna, still leaning against the bench and lost in thought, suddenly notices Mahito and Jogo waving at him from across the garden. Their loud, obnoxious voices cut through the tranquility like nails on a chalkboard. Sukuna’s jaw tightens as he sighs, pulling himself up.
“I’ll be back,” he says, his voice low, as he glances at you.
You nod, your fingers tightening on your cardigan as you murmur, “Okay.”
Sukuna turns and heads toward his so-called friends, his expression immediately hardening. His patience is already thin, and the sight of Mahito’s wide, smug grin isn’t helping.
“Yo, Sukuna!” Mahito calls, throwing an arm around Sukuna’s shoulder like they’re old pals. “Who’s the hottie you’re sitting with?”
Sukuna stiffens, his brow furrowing. “Are you blind?” he snaps, shoving Mahito’s arm off him. “That’s Y/N.”
Mahito squints dramatically in your direction, then gasps, his expression exaggerated as always. “What?! That’s Y/N? The Y/N? The library nerd?”
Sukuna’s glare sharpens. “Yeah, and?”
Mahito whistles, nudging Jogo, who chuckles beside him. “Damn, she cleans up nice,” Mahito says, his tone turning sleazy. “She’s hot. Like, really hot. Who knew she had all that going on under those oversized sweaters?”
Jogo chimes in with a low laugh, adding, “Didn’t think she had it in her to show up here. Guess nerds can surprise you.”
“Shut up,” Sukuna growls, his voice low and dangerous. His fists clench, his irritation bubbling over in a way he doesn’t fully understand. “You two idiots have no idea what you’re talking about.”
Mahito smirks, leaning in closer to Sukuna like he’s sharing a secret. “Relax, man. If you’re not interested, I might just take a shot myself. Hell, I’d even do the bet—”
“Say one more thing,” Sukuna interrupts, his voice ice-cold as he steps closer to Mahito, towering over him. His crimson eyes burn with an intensity that makes even Mahito falter. “And I’ll shut you up permanently. Got it?”
Mahito raises his hands in mock surrender, though the smirk on his face remains. “Alright, alright, chill. No need to get all worked up.”
Sukuna’s glare shifts to Jogo, who’s still chuckling quietly. “And you—if you don’t want me to finish what I started earlier today, you’ll keep your mouth shut too.”
Jogo’s laughter dies instantly, and he looks away, muttering something under his breath.
Without another word, Sukuna turns and walks toward the drinks table, his jaw clenched and his mind racing. He grabs a bottle of something fruity he thinks you might like, pouring it into a fresh cup.
As he turns back toward the garden, his gaze catches someone moving through the crowd. It’s Gojo, his silver hair catching the dim party lights. Sukuna raises a hand, about to call out, but stops when he notices where Gojo is looking.
Gojo’s bright blue eyes are locked on you. His normally confident stride slows as he takes you in, and then, to Sukuna’s irritation, he starts walking toward you.
Sukuna’s grip on the cup tightens, his annoyance flaring into something more complicated. Was it irritation? Jealousy? Whatever it was, it was enough to make his blood boil.
He stays rooted for a moment, watching as Gojo closes the distance between himself and you. Sukuna’s lips curl into a scowl as he mutters under his breath, “What the hell is he doing?”
Gojo’s steps are slow as he maneuvers through the chaos of Hakari’s party. The pounding bass of the music, the loud laughter, and the constant chatter fade into the background as his sharp blue eyes focus on you sitting quietly on a bench near the lake.
He stops for a moment, watching you. The way the dim garden lights cast a soft glow on your face, how your cardigan is wrapped snugly around you, and the way you stare out at the water like the party doesn’t exist at all.
Gojo lets out a breath he didn’t know he was holding. He knew you wouldn’t blend into the noise of a place like this. It wasn’t your scene. And yet, here you were, sitting alone, so out of place but somehow fitting perfectly into this serene corner of the night.
As his nerves start to creep in, he runs a hand through his hair and takes a step forward. Okay, Satoru, he thinks to himself. Just be cool. Be yourself—okay, maybe not entirely yourself.
He finally reaches you, standing a few feet away before clearing his throat. “Hey,” he says, his voice softer than usual, almost hesitant.
You look up at him, your expression briefly surprised, but then you give him a soft smile. “Hi,” you reply, your voice gentle.
Gojo shifts awkwardly, his usual confidence faltering. There’s a quiet moment as he debates whether to sit down or not. After a beat, he lowers himself onto the bench beside you, leaving just enough space to not make it awkward but close enough to feel the tension of his presence.
The silence between you stretches, but it’s not uncomfortable. He glances at you from the corner of his eye, watching how your gaze remains fixed on the lake.
Finally, you break the stillness. “Did the book help?” you ask softly, turning to look at him. “For class, I mean.”
Gojo blinks, caught off guard for a moment, then smiles. “Oh, yeah,” he says, leaning back against the bench. “It helped a lot. No wonder it’s so hard to find—it’s a rare gem.”
Your lips curve into a small smile, and Gojo feels his chest tighten at the sight.
The conversation slows again, but this time, he feels the weight of the opportunity pressing on him. His palms are sweating, and for the first time in forever, he feels… nervous? Come on, Satoru, this is your shot.
“You know,” he starts, his voice uncharacteristically soft, “you look really pretty tonight.”
You blink, your cheeks instantly warming as you murmur, “Thank you.”
But Gojo doesn’t stop there. “Actually,” he continues, his tone playful yet sincere, “you’re even prettier when you’ve got that messy bun going. You know, the one you do with the pencil stuck in it.”
Your eyes widen slightly, and you let out a soft giggle. “How did you notice that?”
Gojo shrugs, flashing you a grin, though his gaze remains gentle. “How could I not? It’s kind of your signature look. Makes you… you.”
Your cheeks flush deeper as you glance away, trying to hide your smile. His words feel so genuine, so unlike the usual cocky, over-the-top persona he carries.
For a moment, neither of you speaks, but the atmosphere feels different now—warmer, softer. Gojo watches you, his heart pounding in a way he can’t explain.
“Thanks,” you finally say, your voice almost a whisper. “That’s… sweet of you.”
And for the first time that night, Gojo feels like he’s exactly where he’s supposed to be.

Sukuna leans against the wall, his red cup tilted idly in his hand, his sharp eyes focused on the bench where you and Gojo sit. His face is unreadable, but the way his jaw clenches and his fingers tighten around the cup is enough to reveal his mood.
Beside him, Mahito and Jogo are huddled together, whispering like schoolchildren. Mahito nudges Jogo with his elbow, his lips curling into a sly grin. “Look at that, Sukuna,” Mahito teases, his tone sing-song. “Gojo’s making his move. Looks like your little librarian has a new admirer.”
Sukuna doesn’t even glance at Mahito, his gaze fixed on you and Gojo. Mahito, emboldened by Sukuna’s silence, continues, “You know, maybe you should just let it go. Call it quits, hand me the $100, and admit you’re not getting anywhere with her.”
Jogo immediately stiffens and shakes his head at Mahito, trying to signal him to stop. “Mahito,” he mutters under his breath, “you’re going to get yourself killed.”
Mahito waves him off. “Come on, Jogo, we’re all friends here,” he says mockingly. “Sukuna can handle a little truth.”
Sukuna’s eyes finally tear away from you and Gojo, and he glares at Mahito with such intensity that Mahito’s grin falters slightly. His voice drops into a low, dangerous growl. “Mahito, if you don’t shut up right now, I’ll make sure you leave this party with more than just a bruised ego.”
Jogo quickly steps in, grabbing Mahito’s arm. “Alright, Mahito, that’s enough,” he says nervously.
But Mahito, never one to know when to quit, opens his mouth to push further—only to be interrupted.
“Yo, Sukuna!” Hakari’s loud, cheerful voice cuts through the tension as he saunters over, a drink in one hand and Mei Mei trailing behind him.
Hakari grins broadly as he approaches. “How’s the party? Everyone having fun?”
Mahito, eager to change the subject, raises his cup. “It’s great! Perfect chaos, as always,” he replies, though his grin is still a bit uneasy.
Mei Mei steps closer, her sharp eyes briefly flicking toward Sukuna. Her movements are smooth, calculated, almost predatory, as though she’s trying to draw his attention. But Sukuna doesn’t even spare her a glance, his focus now on Hakari.
She tilts her head, her smirk faltering slightly. It’s clear she’s used to commanding attention, and Sukuna’s indifference irks her.
Hakari, oblivious to the tension or perhaps just unfazed, laughs loudly. “That’s what I like to hear!”
Suddenly there’s a loud crash, as if a vase had broken.
“Something just broke. I’m betting it was one of the glasses my mom keeps in the display cabinet.” Hakari explained unbothered.
Mahito snickers. “You’re not worried?”
Hakari waves dismissively. “Nah, I’ll just tell my parents a bird crashed into it or something. They’ll believe anything.”
Sukuna rolls his eyes, the annoyance in his expression growing. As Hakari rambles on about the potential excuses he could come up with, Sukuna’s gaze instinctively drifts back to the bench where you’re still sitting.
Gojo leans in slightly, his body language casual but attentive, his focus completely on you. Sukuna’s grip on his drink tightens again, and for a brief moment, he wonders why it’s bothering him so much.
Mahito notices Sukuna’s wandering attention and leans closer, whispering with a smirk, “Still thinking about that $100 bet?”
This time, Sukuna doesn’t answer. Instead, his lips curl into a faint smirk, one that doesn’t quite reach his eyes. “Shut up, Mahito,” he mutters, before downing the rest of his drink in one go.
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
If consumption promises satisfaction in substitution and then denies it because all objects are rest stops amid the process of remaining unsatisfied that counts for being alive under capitalism, in the impasse of desire, then hoarding seems like a solution to something. Hoarding controls the promise of value against expenditure, as it performs the enjoyment of an infinite present of holding pure potential.
Cruel Optimism - Lauren Berlant
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
By Tamino Dreisam
The World Socialist Web Site previously described Germany’s 2025 federal budget as a “war budget dictated by capital.” While billions are being spent on armaments and arms packages for Ukraine and Israel, vast cuts are being made to health and social services, including the planned cancellation of epidemic wastewater monitoring for COVID-19 and other pathogens.
The “Wastewater Monitoring for Epidemiological Situation Assessment” (Amelag) went into operation in 2022 and examines wastewater samples from up to 175 sewage treatment plants nationwide, searching for gene copies of coronaviruses on a weekly basis. Even if it is not possible to determine the exact incidence rate, Amelag provides information on whether the infection rate is growing or declining and where outbreaks are occurring. Waves of infection can also be recognised at an early stage.
Especially since the abolition of mandatory personal testing and all other coronavirus protection measures, wastewater monitoring is one of the most informative tools for determining the status of the pandemic. The planned abolition of this vital public health program illustrates the aggression and criminality with which the ruling class is enforcing the “forever COVID” policy. It not only spreads the lie that the pandemic is over, it also seeks to eliminate all data that proves the opposite.
Amelag’s federal funding expires at the end of the year and there are no plans to extend it. A spokesperson for Health Minister Karl Lauterbach (Social Democrat, SPD) confirmed: “Unfortunately, no funds for the continuation of wastewater surveillance could be included in the government’s draft federal budget for the time being.” Although attempts were being made “in the course of parliamentary deliberations to obtain funding for continuation,” it is quite clear that these are just empty phrases. In government questions in the Bundestag (parliament), Lauterbach attempted to shift the funding to the municipalities, which are already in debt as it stands. “The federal government is not responsible for every sensible expenditure,” he explained.
Last year, Lauterbach announced the cancellation of funding for research into Long Covid and the development of therapies and medicines to combat it. The cut from €100 million to €21 million was justified with claims of a “tight budget situation.” He thus made it clear where this cancelled money was going: into military armaments, the only area of the budget to be significantly increased. With regard to the continued operation of Amelag, the Robert Koch Institute (RKI) public health body explained that only €5 million per year would be necessary—that is, 0.8 percent of the sum of Germany’s most recent military support package for Ukraine.
A petition addressed to the Federal Ministry of Health on change.org under the title “Stop the end of AMELAG! Germany needs modern epidemiology” already has over 4,500 signatures. It explains: “Modern epidemiological surveillance is based on collecting data as quickly, comprehensively and unbureaucratically as possible. As the Sars-CoV-2 pandemic shows, modern surveillance systems are more necessary than ever in a globalised world affected by the overexploitation of natural resources.” The petition goes on to castigate the government’s abolition of all measures, noting, “Contrary to the experience of modern medicine, for the first time in human history we are relying on individual responsibility to overcome a pandemic.”
Many signatories of the petition write in their explanatory statement that the COVID-19 pandemic is not over and that they themselves have already fallen ill with Long Covid.
Just how drastic the situation is, is also shown by the figures for the rising autumn coronavirus wave. According to the RKI’s latest weekly report on acute respiratory illnesses (ARI), 7.4 million people are currently suffering from acute respiratory diseases—a particularly high level for this time of year. COVID-19 directly accounts for around 22 percent of these. However, it is quite clear that the unhindered spread of COVID in recent months and years has weakened the immune systems of millions of people. As a result, they also fall ill more easily with other forms of ARI.
COVID-19 currently accounts for 17 percent of the number of severe ARI cases, although there are clear age differences, with COVID-19 accounting for 30 percent of severe respiratory illnesses in the over-80 age group.
Wastewater levels of COVID have sharply increased since mid-September. Last week, 239,000 gene copies per litre of wastewater were measured, while in the previous week the figure was 185,000. The viral load has doubled in the last four weeks. According to GrippeWeb, which collects data on the incidence of infection based on information from a test group of volunteers, the estimated COVID incidence is currently around 1,100.
The number of hospitalisations is also rising slightly and now stands at a 7-day incidence of four hospitalisations per 100,000 inhabitants. The number of deaths rose to 129 last week, compared to around 80 per week in the previous weeks.
The dominant variant is currently KP.3.1.1, which accounts for 41 percent of infections. The recombinant sublines now account for 27 percent, with virologists estimating that XEC has around twice the growth advantage of KP.3.1.1 and will be the dominant variant in winter.
In the UK, British GP Helen Wall reported in a recent interview with the Manchester Evening News that she has observed a difference between XEC and previous infections in her practice. Anyone infected with this variant should be prepared to feel “knocked out.” She explained: “Previous symptoms were more like cough and cold symptoms, but at the moment Covid seems to be really knocking people out.”
The long-term effects of COVID-19 are also being increasingly discussed. Broadcaster SWR recently published a report on the first anniversary of the post-COVID outpatient clinic in Mainz. The internist interviewed, Christoph Lembens, reports that more than 1,000 patients had already been treated in these twelve months. The appointment diary was still fully booked well into next spring.
Lembens estimates that around a fifth of his patients have not recovered from their COVID infections. This not only affects older people with previous illnesses, but also many younger people. Those affected suffer from exhaustion and fatigue. Some of them also have severe circulatory fluctuations, for example an extreme drop in blood pressure as soon as they stand up, which can lead to their simply falling over.
For many, it gets even worse: they may also have major muscular problems, so that some sufferers are dependent on a wheelchair. Many have cognitive impairments, including “brain fog,” making it extremely difficult to concentrate or memorise things.
These reports illustrate the criminal nature of the ruling class “forever COVID” policy, which has condemned hundreds of millions globally to suffer long-term damage to their health so that profits continue to flow.
#mask up#covid#pandemic#public health#wear a mask#covid 19#wear a respirator#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#Germany#class war
44 notes
·
View notes