#Capita region
Text

Desperate Annie’s Saratoga March 20th Monday 21+ Free Live Show
#Saratoga#saratoga springs#saratoga ny#518#518 music#Upstate new york music#Live music northeast#Northeast live music#New england live music#Capita region#Capital region live music
5 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
ARGÉLIA vs MARROCOS | PIB PER CAPITA (US$)
0 notes
Text
Rántí, confused: but you're dead!
Ming Ho: I didn't die.
Ming Ho, revealing a bulletproof vest: see? Chinese juju.
#this would be a comedy if this town hadn't shot (badum tss) to the top of the regional murder rate per capita ranking#real life ming ho is the only one smiling at the end of the film#ìjọ̀gbọ̀n#ijogbon
0 notes
Text
People often react to the phrase "carbon footprint" with something about how it's coined by the fossil fuel industry to direct blame from producers to consumers, but I think there's still something extremely valuable about looking at emissions per capita -
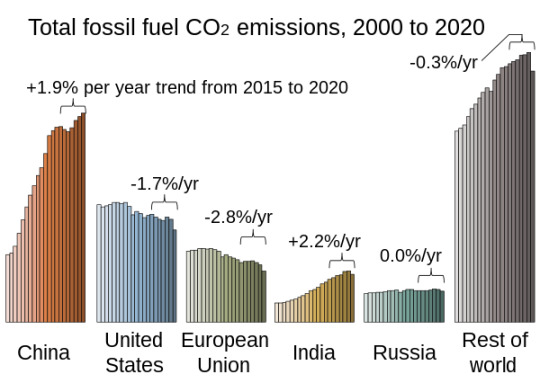
graph one: total CO2 emissions, NOT per capita, by region. By 2020, China, the US, the EU, India, and Russia are the largest players, with the entire rest of the world barely surpassing China's emissions.
Graph two: The same regions but weighted per capita.
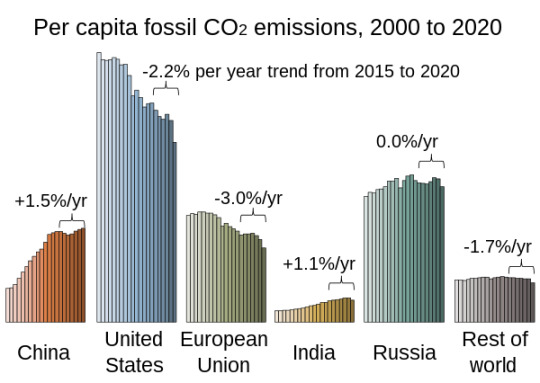
The US is unique in being extremely emissions-intense per capita while also being large and wealthy. This graph doesn't count emissions generated in China to produce goods shipped to America - it counts those under China's emissions.
485 notes
·
View notes
Note
could you explain why, if china is communist/trying to become communists, it still has a lot of sweat shops and relies on that kind of exploitative production? I'm just curious because this never made much sense to me
China at the time of revolution was one of the poorest countries on the Earth, only ten countries had a lower GDP per capita. A century of humiliation, colonial occupation, and genocide had destroyed the nation.
Until the recent eradication of absolute poverty, many Chinese people still lived in sparse mountainous regions with little access to infrastructure, healthcare, or education, and subsisted off absolutely brutal dependence on local resources. Much of the countryside is still under the process of modernisation. China's current GDP per capita is equivalent to that of Mexico. China is not a rich country. In as much as China interacts with the global economy, it does so as a global south nation, a target of exploitation by the imperial powers.
The benefits of interacting with the global economy - technology transfer, trade, outside capital - have been significant, and worth the negatives. Don't be confused, China's worker protections are strict, and its defense of its people absolute - but it is true that foreign corporations operating in China absolutely exploited Chinese workers and subjected them to bad conditions. To a large degree, straightforwardly *because this strategy has worked*, China has developed significantly, and now relies significantly less on foreign capital, and has a much greater focus on its own domestic market.
Foreign exploitation of Chinese workers is, really, a characteristic much more of the '90s-'00s period than modern China, which has developed, and now demands better wages and conditions from foreign prospects (who largely outsource their sweatshop work to, for example, Bangladesh, now).
240 notes
·
View notes
Note
Which country is the biggest exporter of video games?
Though China, Japan and the United States make great leaps and bounds in video game production each year, it is a small country in the Austrian/Bolivian borderlands that makes more tons of video game per capita than anywhere else in the world.
The small nation of San Sundertail was founded in 1981 by Mario von Wiisportz as a social experiment. Surviving at first on the quality of their mining craft and production of ceramic plastic, and mostly metal gears, their game industry grew quickly after. The government of the country was based on a tetrad of rulers who answered their nation's call of duty including the Prime Minister, the Prime Echoes Minister, and sadly another minister who was dismissed for Prime Corruption. Rumors of another arrest circulated but a 4th Prime still has yet to released. Hopefully a more straight-line tetrad will fall into place soon and clear the growing mess.
Sadly as a result, the nation is plagued by crimes such as grand theft auto, assassinations according to some kind of creed, and even the raiding of several tombs. Leaders insist that there is no inherent evil resident to their country, but the U.N. Squadron has declared this to be a fantasy, and the final one that they'd accept. Being a far cry from peaceful, they feel they now have just cause to enter the uncharted regions nearby and open a diplomatic portal, no matter what the fallout of such a commanding and conquering action may be.
This got depressing cuz all the franchises have negative or violent names. I'm gonna go take my mind off it with something else, something with serene rolling landscapes and lots of rest and quiet. Here we go, "Silent Hill" sounds nice, I'll try that.
210 notes
·
View notes
Text
"What is this force, these human beings, referred to in this word – resistance?
First, literally, we refer to the achievement of the poorest and most strategically disadvantaged people on the planet. Within the encircled and immiserated Gaza Strip, many of the Al-Qassam fighters are orphans. Amidst closure and de-development, the popular resistance has been able to consolidate an arsenal and bring 1.5% of its population into a guerrilla force of 30,000-40,000 men that can – man for man – outmatch nearly any in the world.
The resistance, secondly, has alloyed ideological commitment, willingness to sacrifice for their people, and technological ingenuity into armed capacity capable of going head-to-head with a nuclear power from underground tunnels, the ‘rear base’ and physical strategic depth needed for guerilla insurgency. The concrete is their mountains. From there they have imperiled an enemy with orders of magnitude higher GDP per capita – Israeli GDP is at $52,000 a year, with arsenals worth billions.
Third, the resistance, in launching its October 7 operation, is an example to the world that post-Soviet asphyxiation and extermination procedures, sanctions and terror lists and aid-based countermeasures, could not prevent the rise of a disciplined and new national movement from raising its head to the sky.
Fourth, the popular cradle brings the word resistance beyond armed men to doctors going to their deaths in lieu of abandoning their patients and women and men in the Gaza Strip’s North – facing white phosphorus rather than abandoning their homes. It is precisely the strength of the civilian commitment to the national project that provokes US-Israeli extermination: ‘the 'civilian' officials, including hospital administrators and school administrators, and also the entire Gaza population’ are, as a result, the targets – not out of cruelty but to break Hamas by breaking its cradle.
Fifth, through these achievements, the Palestinian resistance has been able to present an acute threat to the settler-capitalist property structures called Israel, to militarized accumulation, to the world’s workshop for counterinsurgency technology, and to the entire architecture of regional repression with its associated petrodollar flows, treasury and security purchases, and arms merchandising. For capitalism is not just the smooth clockwork of accumulation through generalized commodity exchange and labor exploitation, it is the machinery of violence – its technology – which ensures the smooth running of the clock, the thingification of its human elements, the political decisions to maintain and rework the machinery of monopoly accumulation, and the waste of human lives which is increasingly the core Arab input into global capitalism.
More worryingly from the perspective of monopoly power, the Palestinian resistance is not alone. It is part of a regional populist resistance enfolding the poorest people on Earth. ... It is unimaginable that the neocolonial authoritarian states nor their US benefactor would remotely tolerate massive working-class militia which speak a language of justice and republicanism and raise arms against those states’ sponsors. In turn, it is as natural as the sun rising in the East that the US, the UK, Germany, France, and their Gulf and Arab satraps would converge on support for Israel as the spear’s tip of the assault on the surrounding Arab popular militia.
And because Israel is the keystone of the regional imperialist order – maintained not by hegemonic consensus but the brutality of Apaches and Merkavas – it is as natural as water falling from clouds that what has developed in the Gaza Strip, as soon as it mobilized politically and militarily, would incite the Western reaction to wipe it from the face of the Earth and impose unimaginable horror to terrify the Palestinian, Arab, and Third World people to never again raise their heads.
The October 7 operation has perhaps overcome the central role of the Israeli state in accumulation on a world scale: ingraining a state of defeat amongst the Arab working classes, as part-and-parcel of the post-Soviet ideological defeat imposed by capital upon labor globally. Deterrence is the form that defeat takes when pushed to the military plane, and Israel openly admits that its deterrence has been shattered.
Seen from this perspective, the risks run by the western capitalist states – their imposition of fascist regulation against freedoms of speech and assembly, their backing for genocide, their desperation to see the Palestinian armed militia wiped from the face of the Earth – is logical, reasonable, and rational in its sociopathy. It is the logic of monopoly attempting to defend itself and the consciousness which bodyguards it with fire from the sky. It is a logic which fills graveyards, and a logic which makes orphans, and it is a logic which might yet meet its end in that crossroads of continents – that salient, and city and their camps and their people."
186 notes
·
View notes
Photo
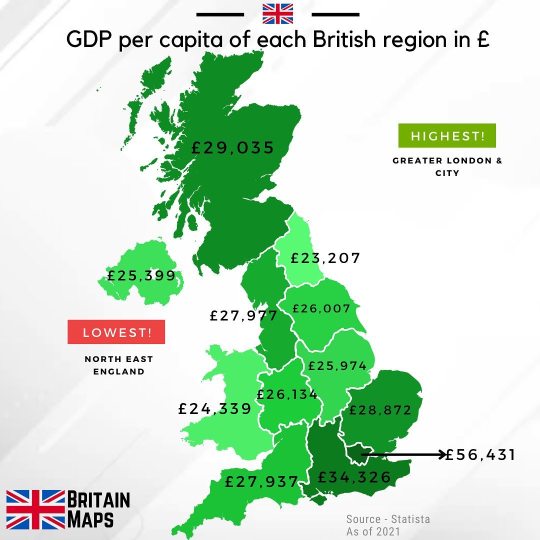
GDP per capita of each UK region as of 2021.
by britainmaps_
82 notes
·
View notes
Note
how... how did you find 190 different icecream flavors? Like you go for the signature name they are given(like one brand call vanilla vanilla but another one calls it cream paradise)? they're manufactured, home made? from those gourmet shops? those you find in supermarkets? You travel for them? or is all that around where you live and places you have passed by? you only consider milk based or also water based(tho those usually have another name)? does popsicles and things like icecream sandwich counts as flavors? have you ever gone on a trip specifically to try a region's typical ice cream? i'm sorry i am just honestly curious how you do your icecream flavors curatorship. and what is your top five out of 190 flavors.
I find ice-creams the following ways:
Cafes (we have many cafes selling their own gelato with unusual flavors, like cinnamonroll and avocado)
Traveling (Japan is a very good place for ice-creams! Although last time there I didn't find anything new.)
Finland consumes the most ice-cream per capita in the Europe. Because we're an ice-cream nation, every summer we get limited edition ice-cream flavors for all stores and kiosks. For example, this summer's new limited edition flavors are marshmallow-Biscotti cookie, and caramel-macadamia.
Manufacturers are supposed to come up with new ice-creams and also import new flavors and brands.
International stores quite often have ice-creams and sometimes I discover new flavors from their selection.
I know how to make ice-cream but only 1 flavor from the list is self-made.
To other questions!
If it made out of milk or a milk substitute, it's an ice-cream. Popsicle, sherbet etc. are not counted as ice-creams but ice-cream sandwiches are.
We have no regional specialties that much, although I know in Porvoo city there's an ice-cream factory with really wonderful flavors. Some of their flavors are available in stores but to get to taste them all I should travel to Porvoo. Without a car it's a day's worth of trip and I'm too sick to travel just to get certain ice-creams.
Having said that, I've had some regional ice-creams in Berlin, Germany!
Someday when I'm rich and healthy, I can travel somewhere just to go to try out their ice-creams.
TOP 5 (really hard to choose, so many that I like!)
Matcha
Royal Milk Tea
Spruce
German Spekulatius Christmas Cookie
Milk
But honestly speaking? If I didn't live in the country which eats ice-cream like maniacs, I wouldn't be able to get new flavors on my list that easy. Just in the past week I gained 4 new flavors (Rom-Brittle;
Quark-strawberry; Marshmallow - Biscotti cookie; Vanilla-honey)
Just in these 7 months I've found 20 new flavors, all in Finland.
My ice-cream list, which updates as I find new flavors, is here.
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Changma River, in north-central China, was dammed in 2002 to provide a reservoir and irrigation to resource-poor areas of Gansu Province. The project aimed to increase production of food grains and commodity crops and to alleviate poverty for some 200,000 poor farmers living in the region. Though 159 households were involuntarily relocated to accommodate the dam, the per-capita net income of communities around it has risen since it was constructed.
39.940368°, 96.814933°
Source imagery: Google Timelapse
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
Girls are prized commodities in this part of the world, thanks to the one-child policy introduced in China in 1979. A Confucian preference for male children has resulted in many families opting for sex-selective abortions or performing female infanticide at home. Today, as a result, the nation has what its own officials term “the most serious and prolonged” gender imbalance in the world. By 2020, there will be an estimated 30 million more Chinese men than women of marrying age.
In particularly poor or remote areas, many Chinese men have countered this handicap by “buying” a bride from abroad, a practice billed as a cost-effective alternative to paying a dowry for a local one. The result has seen a surge of women and girls from neighbouring countries peddled into this lucrative bride industry, where “wives” can be purchased for as much as 80,000 yuan (£9,300). Some 1,281 women were rescued and repatriated by Chinese officials in 2012 alone, nearly all of them from neighbouring Laos, Myanmar and Vietnam. The practice sparked international fury at the end of last year, when a 12-year-old Vietnamese girl, who had been sold to a 35-year-old man in central China for 30,000 yuan (£3,400), presented at Xuzhou hospital for her first prenatal appointment.
Last year, Chinese authorities rescued 207 Vietnamese women, and one child, from a cross-border trafficking ring involving 61 gangs. Yet bride trafficking is a phenomenon that authorities struggle to contain. Lào Cai province, which sprawls from these fog-enveloped mountains and grassy valleys to border Yunnan in China, is one of the poorest and most ethnically diverse regions in Vietnam. Home to various hill tribes, including the H’mong, Dao and Tay, the province is popular with backpackers. But monthly per capita income here is just half of the national average, education levels remain frighteningly low and jobs are scarce. In Sapa, a slapdash town of touts and bars that serves as the main tourist base for the region, small children in traditional H’mong dress kneel at the edge of the dusty streets, selling trinkets, their newborn siblings in embroidered papooses on their backs.
#Andrea Dworkin#misandry#radical feminism#radblr#terfblr#all trans women are male rapists#anti sex industry#anti pornography#misandrist#pro abortion#feminism#proud misandrist#radical misandrist#anti male#radical feminist#female chauvinist#terfsafe
40 notes
·
View notes
Note
Now that you're back, I can toss some more asks your way! What sort of spices are common in which places? Is any region known for especially spicy food?
Finally actually getting to this! As per usual I will not be answering this in any sort of concise or short manner, so get ready for a long read. Just so this isn't too long, I'm only going to focus on Kishetal and I will discuss the characteristics and some of the more popular ingredients, spices, and dishes in 8 different Kishite cities, each representing a different region of Kishetal.
A Brief Introduction to Kishite Cuisine

1. Shared Traits
Across the Seven (Technically 8, but I'm skipping the Makorian Colonies for now, I might return to them later if people are interested) Kishite regions there are a number of features which remain constant among Kishite culinary traditions. The most immediately recognizable of these features is how food itself is served. Kishite food is always served in bite-sized pieces, whether naturally or whether it is cut up before eating (soups and liquids are the exception to this). Food is eaten with the fingers or else with a spoon. There are no forks or chopsticks or similar utensils. Knives are a rarity as well, as typically it is expected that the food will already be served in pieces or that it can be broken into small pieces with the fingers.
Another shared trait is the "triad" which refers to three types of food which form the bulk of the average person's diet, these being Grain (Wheat, Barley, or Rye), Legumes (Lentils, Chickpeas, Peas, Vetch, Beans, Etc.), and Fat (Most typically olives/olive oil with sheep fat/lard and butter also appearing). The Makurian steppe is unique in that grain does not form the majority of the diet for commoners, with dairy and fats taking precedent.
The last similarity is a heavy reliance on condiments, whether these be seasonings or sauces or something else entirety. It is typical for a Kishite table to have several different kinds of toppings available at any time, what exactly these are will vary by region.
2. Regional Cuisines

(I honestly can't remember if I put a cut here, Tumblr isn't letting me put a cut, so I think I did....sorry if I didn't.)
1. The Red Cedar Mountains : Labisa

The Red Cedar Mountains stretch from the Shabalic Sea in the north nearly to the Sea of Agitu in the south. This region is home to cities like Labisa and Kepfis.
Labisian's are famed for the love of and skill in producing fried foods. The food of Labisa, and in the mountains in general, is viewed by other regions as hearty and heavy. Breads and cakes, sausages, and heavy sauces are well known from the region. Foods are often drizzled with fat. Olives are a popular snack.
Compared to other regions the people of Labisa eat relatively few vegetables. Per capita, the people of the mountains including the commoners, eat more meat than in any other region of Kishetal (typically in the form of sausages (Arashuki) and offal) while eating far less saltwater derived fish. Most meat comes from sheep, with horned-rabbits, goats, and pigs coming close behind. Cattle are largely reserved for the nobility. Game is common fare, though only for those with the time to hunt it or the money to buy it. Insects are very rarely consumed, particularly in the city. Rodents and other small animals, with the exception of the Cedar Squirrel, are rarely eaten.
Aside from a tendency towards rich textures and flavours, Labisan cuisine shows a strong preference for black pepper, which appears in almost all dishes, including desserts. Labisans, perhaps as a way to to counteract the fatty nature of their cuisine, are infamous for their love of vinegar, even more than other regions. It is not unusual for morsels to be dipped into first vinegar and then into various herbs most typically a mixture of parsely, mint, and salt. While herbs (mint, parsley, thyme, basil, coriander, rosemary, etc), aliums (onions and garlic) and acids (vinegar) are common aspects of Labisan seasoning, for the common person, spices are a relative rarity, with the exception of black pepper. Cumin is used at times, as is imported cardamom and cinnamon. Lisikip (Tickling seed), which is similar in nature and effect to the Szechuan peppercorn, is used on occasion. However on the whole Labisan food is not known for being "spicy" and while rich, has a reputation for being relatively bland.
You're unlikely to find much in the way of soups/broths in Labisa, though stews are relatively common. A common stew is Olibiha (aka Hot blood water) , which consists of boiled meat (this will vary but will regardless likely contain organ meat and other less expensive cuts), beets, onions, garlic, and fat of some sort. Traditionally this soup was sold by butchers and at markets at the end of the day as a way to use up unpurchased products. Though its name is typically in reference to the color imparted by the beets, it is not unheard of for blood to be added to the broth, though this form is less popular.
Similar to Olibiha, Chakun, are a popular butcher snack, typically made from pig or lamb skin, fried in its own fat and then seasoned. This is somewhat comparable to "cracklins" or chicharrons. Labisian cuisine in general holds an appreciation for crispy or crunchy textures that other regions do not tend to show.
Fried dough and fried cakes are a popular festival food somewhat similar to what we might associate with a doughnut. These doughnuts or Hasolikipun are typically fried in olive oil or sheep fat. Typically these are then split open and stuffed with a variety of fillings, including fish, offal, and nuts.
Another popular dish is Kipsha, a dense barley cake typically drizzled with honey and citrus and served with toppings like nuts and cheese. Kipsha is both sold on the street and made in houses, often for celebrations. Deserts, aside from fruit, are a relative rarity in Labisa, with Kipsha being perhaps the most well known kind.
Labisa's position on the shore of Lake Shebali, means that the city has access to lake fish, and thus freshwater species are consumed more here than in other regions. Trout and eels are particularly cherished by Kishite consumers, both are typically roasted. The most commonly consumed fish are various species of minnow and shad, which are caught in bulk and often served fried.
Labisan cuisine is strongly influenced by the cuisines of pre-Kishite tribes which existed in the mountains before the arrival of Tamel.
2. The Felic Plain : Seha

The Felic Plains primarily consist of grassland with occasional patches of deciduous forest. The plains are split by the Aratshin River, and most large settlements can be found on the edge of said river.
The region experiences hot summers and mild but wet winters, which makes the region ideal for farming. As such, the Felic Plains act as the bread-basket of Kishetal. In comparison to the mountains and other regions, the people of Seha eat far more vegetables, and considerably less meat and very little marine protein.
Compared to Labisian cuisine, Sehaic shows a far stronger affinity for spices, with cumin, garlic, lisjir, coriander, cardamom, cinnamon, fennel, and black pepper all appearing regularly in the diet. Felic cuisine in general is the "spiciest" variety, though it is in contention for that tightly with the Kipsian Desert. Mustard and mustard seeds are common ingredients as well, and in the rare instances where meat is eaten, mustard is almost always present.
In addition to their love of spices, Sehaic consumers are infamous for their general disdain for many textures. Sehaic foods have a reputation for being soft, often boiled or stir-fried or else pounded until quiet easy to chew. The cuisine shows an aversion to the crispy, crunchy, and chewy textures.
Sehaic cuisine is known for its heavy use of green vegetables such as lettuce and cabbage, as well as its preference for broths as opposed to thicker stews. Fried food is a relative rarity in Sehaic cuisine, with boiling or else "stir-frying" being far more common.
Cheese is a large part of the diet and is often the condiment of choice, with several different varieties of cheeses being used, all with their own distinct purposes. One variety of heavily salted cheese, is added on to savory dishes as a way of imparting salinity.
Sehaic's are known for drinking their wine and beer with cheese, that is to say they are known for crumbling a particular variety of sheep's cheese into their beverages. After the beverage has been consumed, the resultant cheesy sludge left at the bottom of the bowl is then mixed with honey and nuts and is eaten as a desert. This particular dish is called Birafepaha (Fepaha's Joy).
A common dish is Keriha or "hot green" a dish consisting of dark green leaves, typically spinach boiled with garlic, onion, coriander, and lisjir, in a broth or stock (typically made from fish bones). This may be mixed and cooked down until the liquid has all but evaporated, producing a thick substance which may then be used to dip bread, or if the liquid is not boiled out, it may be eaten as a soup.
While meat is rare it is not entirely unheard of. It is not unusal for a family to keep one or two horned-rabbits, raising them both for meat and for fur. Sheep and cattle are both quite common, as evidenced by the Sehaic love of cheese. Mutton and lamb are often consumed at celebrations. Jirbaha, is a beloved dish consisting of strips of lamb or mutton, cooked with a variety of herbs and spices as well as mustard. This is then wrapped in a cigar like fashion, along with various greens and cheese, in a thin dough and is either fried or baked. This is then typically cut into pieces or else is held in the hand.
Sehaic cuisine shows a deep reverence for freshwater fish, with eels, trout, and sturgeon being reserved for either special occasions or the diets of the wealthy/powerful. Smaller and less valuable fish act as occasional supplements to the common diet.
Insects and gastropods are eaten quite regularly. Locusts, cicadas, grubs, and snails are all common parts of the Sehaic diet, often added to other dishes. The favoured preparation for insects is fried in sesame or olive oil, and then heavily spiced and seasoned. During the harvest season, locusts with lisijir are a popular snack. Other agricultural pests, such as field rats and moles, may also be eaten, typically cooked over a fire.
Kipnakili is a comfort food, often eaten by farmers and river boat drivers, including pirates. It consists of soft cheese, nuts (typically pistachios or walunts or a mix), fruit (typically figs, with the addition of raspberries and sometimes pomegranate), and honey. This mixture is pounded into a fine paste, which is then spread onto flatbread or small round barley cakes, the Felic equivalent to kipsha.
Sehaic cuisine, and Felic cuisine in general, exhibits a strong influence from both native populations and ancient Shabalic cuisine, with some dishes, such as Birafepaha, having roots as far back as the time of Tamel.
3. The Western Coast : Chibal
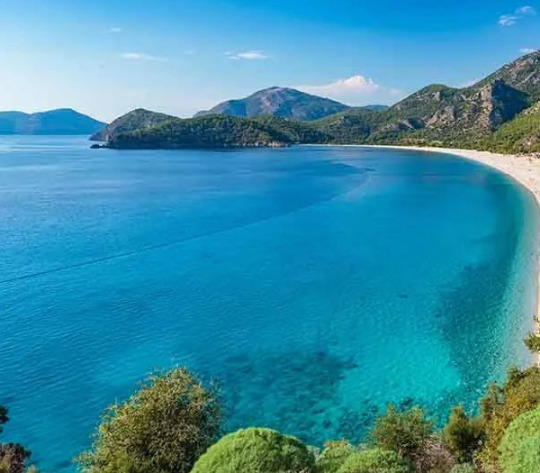

Pictured Above: The Western Coast near the city-state of Chibal
The Western Coast borders the Green Sea stretching from Bura in the north to Bisabal in the south. The climate here is warm and wet, defined by arid summers and stormy winters, similar to the Felic Plains but more intense on both counts. This has resulted in a culinary tradition with strong seasonal trends.
Room temperature of even cold dishes are popular in the summer months while more hearty soups and broths are popular in the winter and fall.
Chibal, the second largest city in Kishetal after Labisa, has become the most culturally and demographically diverse city in the region, thanks to its prominence as a major trading port. This rich diversity is reflected in Chibalian cuisine, which incorporates elements from Korithian, Apunian, Ikopeshi, Baalkic, Shabalic, and Makorian culinary traditions. This post will focus specifically on dishes which were developed and created in Chibal and not imported.
Due to this sheer variety of influences and sub-cultures it is hard to make any sweeping claims about the nature of Chibalian food. However in general Chibalian food puts an emphasis on the quality of individual ingredients, with Chibalian cooks and diners earning a reputation as being pretentious. As a result, generally Chibalian dishes tend to be less complex, while being fresher. The same applies for seasoning and spice. While not bland like Labisian cuisine, Chibalian cuisine in most instances lacks the complex melanges of spices and seasoning seen in Sehaic food. Rather it should be expected that a Chibalian dish, in most instances, will rely primarily on only one or two items as seasoning, aside from salt.
While legumes and grains(particularly the massive paper thin flatbread known as lakibi) make up the majority of the Chibalian diet, fish and meat also make a significant contribution.
Unsurprisingly a far larger portion of the diets of the people of Chibal and the Western Coast in general are composed of marine elements. Alongside fish and shellfish, the coast is home to many varieties of edible seaweed which appear in a number of dishes, particularly salads and soups. Chibal is additionally famous for its salt, produced in salt beds. This flaky salt is shipped around the entirety of the Green Sea, however the best is kept in Chibal and used to top a variety of dishes. Other popular condiments include cumin seeds, vinegar, olive oil, and a variety of Korithian fish sauce called wydram.
Bikerebi (water-leaf water) is a traditional soup, often served as a starter or side dish. It features a broth typically made from small fish or shrimp and various types of green sea algae. While the broth can be enjoyed on its own, it is usually enhanced with additional ingredients like salt, lisijir, vinegar, black pepper, and dill. A popular variation, known as Kibikerebi, involves crumbling stale or dried bread into the broth, creating a paste-like porridge. This heartier version is commonly eaten by fishermen and laborers as their first meal of the day.
Ovens are typically reserved only for bread, with roasted or baked dishes being relatively rare (though roasted meats and seafoods may be eaten on special occasions). Rather the majority of Chibalian food is boiled, pickled, sauteed, fried, or dried. Chibal is one of the only places in Kishetal with a penchant, particularly in the warmer months, for eating raw foods. This includes fruits and vegetables along with fish and shellfish.
One famed, though expensive dish is Sibizu aka "cold-fish" typically made from white flesh fish, such as sea bass, flounder, mackerel, and scallops. Tuna species and swordfish are considered more luxurious, and are preferred by the wealthy. Fish meat is cut into thin pieces and covered in salt and herbs, typically dill. This can be done either in a bowl or pot or spread onto a tray or flat stone. This is then allowed to sit, typically for around 2 hours. After this the fish is removed from salt and rinsed in a mixture of water and vinegar, typically three times. After this the fish is served with a olive oil as well as various other toppings. In certain circumstances the fish may be served ontop of ice or snow as this is believed to improve the freshness and flavour.
Uncooked fish more often takes the form of pickled fish, left in a mixture of vinegar, salt, and herbs. Oysters and clams are regularly eaten raw, though they may also be shucked and added to soups or stews or on rare occasion baked.
Chibalian cuisine is defined by an intense interest in texture with the perfect meal preferable containing elements which are soft, slimy, creamy, crunchy, and chewy. For the last category cephalopods such as octopus and squid as well as stewed cartilage are popular ingredients.
Vegetables are typically served as sides, favored for their textural components rather than their flavor. Crisp lettuce or crunchy asparagus/cabbage often appear as part of broader meals, but are often ignored. Salads composed of lettuce, spinach, cabbage, and other greens including seaweed are often served at the end of the meal, after fruit.
Chibal is one of the only cities where pigs are consumed at a greater rate than sheep or goats, though still not as much as the horned-rabbit. Sausages, tripe, offal, and chops are all eaten regularly along with products made from the skin and blood.
4. The Northern Coast/Sheprian Forest: Shepra

The Sheprian forest in the northern part of Kishetal is primarily composed of deciduous trees with occasional conifer patches at areas with higher elevations. Common trees include oak, chestnut, birch, hornbeam, black pine, cedar, juniper, and beech.
The city of Shepra lies on the northern coast of Kishetal at the Delta of the Pesha River. The surrounding area is heavily forested. For this reason, Shepra is famed for the quality of its hunters and of its game. Sheprians are additionally famed for the quality of their wheat, said to be sweeter and more delicate than the more abundant Felic varieties. Sheprian bakers are famed for their fluffy yeasted breads, typically favouring wheat rather than the barley which reigns supreme in southern regions. As a result, Sheprian wheat bread has been called, Kipchilu or Bread of the Gods. Sheprian bread is so popular that it or at the very least, Sheprian wheat flour, may be shipped hundreds of miles by foot, donkey, and ship to the courts of cities like Labisa and Chibal where it is treated with great reverence, often as a desert. Sheprian bread is often added to sacrifices alongside meat and fat meant for Great Spirits and Gods, either left outside on special alters (for Great Spirits) or burnt (for Gods).
Shepra boasts a vast collection of communal ovens, located near the town's center alongside the central grain store. By paying taxes, serving in the city guard, or fulfilling other civic duties, a Sheprian household earns a clay tablet that grants them the right to use one of the ovens for the season. However, a persistent issue plagues the town: a group of counterfeiters producing fake tablets. If someone is caught using a counterfeit tablet, they face punishment through debt slavery for up to three years, usually tasked with cleaning and maintaining the ovens. The problem is so significant that the Sheprian King has established a dedicated bureaucratic office, the Chief of Ovens, to address it (not to be confused with the Chief of Bread, who oversees the baking of bread and the storage of grains within the Palatial Complex). Those found guilty of intentionally damaging an oven or stealing an oven tablet receive death.
Some families also own smaller ceramic ovens or braziers, which can be used inside the house or, more commonly, on the flat roofs. In addition to these, there are professional bakers who either own their own ovens or petition for special tablets that designate them as bakers, granting them unrestricted access to the communal ovens. The abundance of ovens, along with ample timber and coal, has shaped a cuisine centered around braising, roasting, and baking. Sheprian food often involves long, slow cooking times, resulting in dishes celebrated for their rich flavors but often criticized for their lackluster colors and textures. Stews and gravies play a central role in Sheprian cuisine.
Unsurprisingly, bread is a staple of Sheprian meals, with 126 distinct varieties produced in the region, 42 of which are entirely unique to that region, and 13 exclusive to the city of Shepra. One notable variety, ruyi (literally "plate"), is a large, dry, and dense flatbread typically made from a mixture of wheat and barley. Families usually bake ruyi in bulk every four to five days. To prevent spoilage, it is cooked to a cracker-like consistency, making it hard and tasteless in its natural state. The flatbread is then wrapped in cloth and stored for use as flatware during meals.
Food is served directly onto the ruyi, accompanied by vinegar, oil, cheese, and various sauces and toppings, including a chickpea and garlic paste known as Babilkipi. After the meal, once the bread has absorbed the liquids, it is either cut or broken into pieces and eaten. Ruyi is a common presence at most Sheprian meals, and it is not unusual for families to consume multiple types of bread, including ruyi, in a single meal.
Perhaps due to their preference for hearty, fatty meals—possibly to counter the cold winters—Sheprians, along with Labisians, are often stereotyped as being somewhat heavier than other Kishite groups. This trait is not viewed negatively; in fact, many consider both Sheprian men and women among the most attractive in Kishetal.
As previously mentioned, game such as venison and boar is consumed regularly in Shepria, alongside goat and pork. However, horned rabbits are rarely kept, making them a minor part of the Sheprian diet. Cattle and sheep are similarly uncommon, largely due to the dense, ancient forests that dominate the region, which are not well-suited to pastoralism. For this same reason the people of Shepria have historically had little use for horses and cavalry.
Despite being located right next to the Shabalic Sea, seafood plays a relatively minor role in the Sheprian diet. Ironically, most of the prized Sheprian catch is sold to merchants and traders from cities like Chibal and Seha. The exception is shellfish, which the Sheprians consume in large quantities. The outskirts of the city are dotted with massive shell middens, some of which have become homes to various spirits and, on occasion, even monsters.
Sheprians use a wide range of spices and herbs, but their cuisine is particularly known for its heavy reliance on oregano, garlic, juniper, turmeric, and even imported ginger and cinnamon. To add heat to their dishes, Sheprians favor both horseradish and radishes, especially a specific breed of radish renowned for its intensity. This radish is often sliced thinly and used as a condiment. In other Kishite regions, bards and comedic poets like to tell exaggerated tales of Sheprian children wandering the streets and hills, gnawing on mustard seeds, radishes, and whole pieces of horseradish. While these stories are clearly hyperbolic, there is some truth to the Sheprian preference for this type of heat. Interestingly, despite their love for pungent flavors, Sheprians rarely use black pepper or lisijir in their cooking.
Kilakela, or "Field and Forest," refers to a category of layered dishes that might best be described as casseroles. These dishes typically involve finely chopped meat—often pork or various game birds—combined with additional fat, usually lard or olive oil, along with root vegetables like beets and parsnips, onions, an array of spices, wine, and sometimes honey. The mixture is placed in a special clay vessel and buried under coals at the back of the oven, where it cooks slowly throughout the day, allowing the ingredients to become tender and flavors to meld. Once the day's baking and other cooking tasks are complete, the vessel is retrieved, and the resulting stew or casserole is served atop ruyi. A variation of Kilakela, known as Kilala, excludes meat and is instead a vegetable stew, often fortified with chickpeas or lentils to add heartiness.
Northerners are one of the few groups which consume mushrooms on a regular basis, evidently not holding the same fears and superstitions as their southern cousins. One dish banalligu, sees mushrooms, doused in vinegar and olive oil, cooked on a skewer often with various other ingredients, depending on what is available such as whole cloves of garlic, small onions, vegetables including carrots, beets, and cabbage, game (most often duck or venison) or pork belly, and sometimes figs. This is cooked directly on the dying coals of the oven, charring the mushrooms and other components. After cooking the ingredients are removed from the skewer and may either be eaten as is or be wrapped in thin flatbread similar to Chibalic lakibi before being topped with a variety of ingredients.
Sheprian food shows strong influence from more recent Shabalic trends, with both favouring stews and hearty meals typically composed of many ingredients.
5. The Southern coast: Kotsa

The Southern Coast consists of three regions; the southern deciduous forest, the scrubland, and the plains. The climate in the south is quite warm, with summers being hot and dry and winters mild in both temperature and rainfall. On rare occasions, the southern coast may experience heavy snowfall.
Major cities are sparse however, many villages dot the southern coast, many of these villages rely on piracy, preying primarily on Apunian and Jezaani ships traveling to and from the Western Coast. The largest of the southern cities is Kotsa, founded on the ruins of a pre-Kishite civilization.
Kotsa is famed as the primary home of the Shobiashkun, a particular brand of priests and sages. While these priests are superficially said to serve the Deity of Writing and Knowledge, Shashuma (They are a minority, the largest temples in Kotsa belong to the storm God, Kotomah), in actuality this small collection of scholars and philosophers focus their interests on the Shobiash, the River of Creation and Time, thus looking behind the Heavenly Gods. A Shobiashku looks for patterns in existence, and seeks meaning and purpose in these patterns, typically through meditation or sometimes through drug assisted trances. The Shobiashku forgo sex, meat, and honey, save for in those instances in which those things may help with their musings. Numerous treatises pertaining to the nature of the universe, death, magic, and civil order have been produced by this small sect. Despite the fact that the Shobiashkun are a relatively small group, little more than 50 individuals at any time, they have had a major effect on the cuisine of Kotsa and the surrounding region.
As a result Kotsa is one of the few regions with a significant vegetarian population, particularly among the learned elite.
Kotsa has one of the most defined elite cuisines, separated from that of the commoners not only by the ingredients used, but also by how that food is prepared and presented. Particularly among the nobility of Kotsa, eating and food is viewed with a level of spiritual and medicinal reverence. At the palatial court for example the supposed symbolism and medicinal boon of each dish is announced each time one of the many small courses is presented, with some courses comprising of only a couple of bites of food. At a Ceremonial Kotsian Banquet, bread is always served first, unseasoned and alone. Most often this is a dense barley bread, its hearty nature meant to represent the soil and stone. Next comes water, or more rarely, beer. This is followed by a number of dishes with various representations; A charred onion spiced with lisijir and ginger (Hagugura) to represent fire, a small cake made from sheep’s cheese and wheatberries to represent the fields (Jiribikip), a piece of roasted turnip spiced with cardamom and salt to represent the walls of the city (Elmuhi), etc. Wine is drunk sparingly throughout the meal and often watered down to an extreme level (sometimes to the equivalent of 16 parts water to one part wine.) In these particular dishes, spice is used sparingly as it is believed that using too many additional ingredients may in some way dampen the medicinal properties of the dish. Of course, such rigid dining is mostly indicative of ceremonial affairs or of the most rigidly traditional nobles, it does not represent all cuisine.
Outside of the world of ceremonial dining, Kotsian cuisine is known for its freshness and its love of spices, though its relative disdain for heat (lisijir, horseradish, radish, etc.) Cardamom, ginger, garlic, bay, turmeric, and saffron all appear regularly in Kotsian dishes. The South of Kishetal is famed as being one of the only places west of Sinria to have successfully planted and cultivated the cinnamon tree, with five small groves near Kotsa, accounting for nearly all Kishite Cinnamon. Cinnamon features in both savory and sweet dishes and may even be added to wine and beer. As a result, cinnamon appears in much of Kotsian cooking. One popular dessert, Jakeresha consists of a cake made from dates, cheese, and flour, wrapped in several layers of thin dough. This is then heavily seasoned in a mixture of ground cinnamon, honey, and sesame seeds. The savory version of this dish, Jakereshu replaces the dates typically with a mixture of mashed chickpeas and fava beans, and replaces the honey usually with oil, while retaining the heavy use of cinnamon.
Kotsian food is noteworthy among Kishite cuisines for its fragrance, due to its heavy use of aromatics. It is said the ruler of the country of Apuna, the Fapacha, once hired Kotsian cooks to work in his kitchens, only so that the smell of Kotsian food could perfume his halls.
Kotsian food doesn't seem to demonstrate any particular tendencies or preferences when it comes to cooking styles, with baking, sautéing, frying, and boiling all appearing. Aside from the Makurian Steppe region, and is the most distinct from other Kishite styles. In terms of preparation and ingredients, Kotsian and southern cuisine in general seems to have more in common with that of foreign lands like Jezaan and even Apuna, than it does with places like Labisa or Seha.
While vinegar does appear, it and its use in pickling and preservation are far less common than in other regions. Dried foods are common however, with fruits and vegetables and fish often dried on reed mats as a way to intensify flavor.
For the purpose in general the treatment of meat within the Kotisan diet is similar to that of Seha, with meat being eaten only on rare occasions. When meat is served, it is typically done simply, roasted or boiled and cut into thin pieces. Sheep are the most common form of livestock, with significant cattle herds also being present. Horned-rabbits are relatively common, though not to the extent of the mountainous regions. Pigs are all but absent. Due to the relatively arid environment, game is also a relatively rare part of the diet, with the exception of gazelle.
Kotsians, and the south in general are famed for their love of yogurt, or Ishjir, often eaten as a mid-day meal, mixed with fruit or honey. Yogurt may also function as a condiment of sorts, with a variety of sauces comprised of yogurt mixed with various herbs and spices, utilized depending on the circumstance.
Fish is eaten regularly, particularly fish like seabream, which is often salted and left to dry. This dried fish is then stored and may be rehydrated in soups or else used as a travel food.
One dish that is unique to the region but that is quickly spreading both to other regions of Kishetal and to other parts of the Green Sea is Talakili which while its name literally translates to "flat bread" is actually more comparable to pasta, typically made from wheat flour mixed with water and oil, rolled flat, cut into either small squares or circles and then boiled and served with a variety of sauces. Talakili with salt, cheese, and cinnamon is a popular comfort food among Kotsian children.
6. The Kipsian Desert : Kipsa

The Kipsian Desert, with its rocky terrain and sparse vegetation, is the least populated regions of Kishetal, and is also the region with the largest pre-Kishite genetic and cultural influence. As a result, the Kipsian dialect of Kishite, is often quite difficult for other Kishites to understand as it is heavily influenced by other languages such as Mageryu and Duluqi. Despite these challenges, the city of Kipsa, the largest in the region, has cultivated a distinctive culinary tradition that reflects its unique environment and cultural heritage. Kipsa is well known for the ferocity of its warriors and as the center of rakeshim production. Rakeshim is a fabric, woven from thin strands of gold interwoven with either linen or silk. Its construction is incredibly complex and the secret to its creation, a jealously guarded secret among the five families which produce it.
Central to Kipsian cuisine is the use of local herbs and spices, hearty grains, and a pronounced affinity for sweetness. A defining feature of Kipsian cooking is the use of large subterranean ovens called Bahasayu. The Bahasayu enables slow, even cooking, ideal for preparing the region’s staple dishes. These ovens, essential for traditional cooking, are found in nearly every home, typical appearing either in courtyards or in front of homes. On rare occasions two or more homes may share one Bahasayu. When a couple marries, it is customary for them to dig a Bahasayu as part of claiming their new home. Additionally, in some cases, the remains of deceased ancestors are interred beneath these ovens, after their customary exposure to the elements, linking the living with their ancestors. Because these ovens are so central to domestic life, they are often the target of curses. A disgruntled Kipsian may place a or crack a curse tablet over a rival’s Bahasayu in order to bring them misfortune.
Kipsian cuisine uses many of the same spices and herbs as their Kotsian cousins, though with a distinct preference from cumin and coriander over cinnamon.
Due to the arid environment and lack of major irrigation, vegetable cultivation is relatively sparse, and what vegetables and fruits are available are often preserved in some way. Fresh vegetables are a luxury typically reserved for the wealthy. Rather Kipsian cuisine has come to rely on a particularly robust strain of barley. While it is able to withstand the dry and hot climate, this barley produces an often chewy and unpleasant product. As a result, Kipsian cuisine is often maligned for the poor quality of its bread and those that can afford it prefer to import wheat from the Felic Plains and Kotsa. One use of this otherwise unpleasant barley is Takuriha (stemming from the Duluqi language, meaning “beer soup”), a soup made from fermented grains mixed with yogurt and herbs and spices. The resulting dish is served cool or room temperature and is typically eaten after the sun has set. The soup is mildly alcoholic. Kipuhi, is a salad also featuring barley pearls mixed with chopped herbs, olive oil, and regalu juice. This may be supplemented with dried or shredded meats as well as chickpeas or other vegetables in order to create a more complete and hearty meal.
Kelami, a local variety of flatbread, is historically baked on hot stones or now more commonly, on the roof of the bahasayu. To counteract the quality of the barley, it is typically served with various dips and spreads, such as Muhamara, a rich paste made from roasted chickpeas, walnuts, and olive oil.
Cucumbers are beloved as a snack, particularly during the hotter season, as they are thought to cool the body. They are served typically in salad composed of cucumber, mint, vinegar, and garlic. When fresh cucumbers are not available, they are pickled in vinegar, alongside various herbs and spices. Pickled vegetables and meats, as well as bird’s eggs and fruits, are integral the Kipsian diet. Pickled vegetables and herbs often act as condiments of sorts, placed on the table to be added to other dishes. Pickled foods are so common that they typically act in place of vinegar as a topping.
Meat, though not a daily staple, is carefully prepared when used. Goats are the primary source of protein. One dish, Ishukjiraru, is a dish made with intentionally spoiled meat. Goat meat is packed in herbs, vinegar, and fat (typically rendered goat fat) inside of a large jar and is allowed to sit, sometimes for weeks at a time. The resulting product is cleaned and then utilized in a number of dishes, including stews and as a shredded meat added to salads and on flatbreads. The taste is quite sour and funky and can be an acquired taste. Kipsiansalso raise a unique breed of horned-rabbit well-suited to the desert environment. Heards of these wiry creatures can be seen roaming from bush to bush, guided by desert shepherds. Gukeki (from the Mageryu for “gift”), is served for special occasions, as its use of fresh vegetables make it a relative luxury. It is a vegetable stew made with ingredients like eggplant and onions, which is cooked in large clay pots and may also include the shredded goat, spinach, and other ingredients.
Honey is a prominent ingredient in Kipsian cuisine, the Kipsa itself being famed for its many hives. It is used as a condiment in various forms, including Habazibi, a salted and spiced variety with a hint of Lisijir for subtle heat. One result of this abundance of honey is the Kipsian love of mead and honeyed wine or beer. Kipsians have a reputation as heavy drinkers, drinking more of these beverages than any other Kishite people. The god of beer, Fepaha, is honored, and many banquets are dedicated to celebrating this drink.
Kipsians have a notable sweet tooth, with foods often heavily sweetened with honey or date syrup. Desserts such as Kepechi (the Kipsian equivalent of kipsha), barley cakes soaked in a honey and regalu syrup, and Gelukepi, a sweet treat made from slow-cooked fruits (primarily dates and figs), are popular and enjoyed with a strong tea made from mint and coriander, with “laughing leaf” a mild intoxicant, also occasionally added.
Kipsian food shows a heavy influence from indigenous cuisines.
7. The Makurian Steppe: Shebal

The Makurian steppe is massive, spreading over most of western Macia. Only a tiny sliver of that vast extent falls in Kishetal. Trees are almost entirely absent. Vast expanses of grass-covered hills define the area. To the north of the steppe is the Shabalic forest, and to the south is the Jezaaic desert. The largest of the Makurian cities is Shebal, once the homeland of the Ugri Tribe, the city still is the target of many repeated attacks by Makurian tribes. Despite its remoteness, silver mines and soil rich in gems, have made Shebal uncharacteristically rich, particularly considering that it is the least populous of all the regional "capitals".
Perhaps unsurprisingly, Shebalian cuisine takes heavy inspiration from that of the western Makurian tribes. This translates to a cuisine heavily built on the consumption of meat and dairy, and a prevalence towards soups and stews. It is said derisively of the Shebalians, that they eat horse meat stew for dinner and horse bone soup for dessert. It is true that the Shebalians, and the people of the east in general, are the only region of Kishetal in which horse and donkey/ass are eaten regularly. Meat, cheese, and milk from these animals are eaten in large quantities. Despite this the Shebalians are known for their deep connection with the horses, famed as charioteers and riders. The slaughtering of a horse is a sober affair, typically attended to by a priest of the god Ikeshpaha (the God of wealth and the steppe) and undertaken with the utmost care. The first dish to be prepared from the horse or ass, is Jabolibi a thick porridge consisting of blood as well as either wheat berries or rice. This is typically consumed by warriors, kings, and pregnant women.
Shebalians and eastern Kishites in general eat more dairy than any other Kishites, with cheese, yogurt, butter, milk, and various fermented curd products accounting for much of the diet. Jiraba is a variety of curd, first heavily fermented and then dried until hard and crunchy. This is then crushed and sprinkled on other dishes.
Fresh vegetables are rare as the environment is ill-suited to agricultural, as a result most vegetables are imported from the west or from lands to the south. As a result of this, green vegetables with short shelf-lives are highly rare and are seen as a delicacy. Root vegetables like carrots, beets, turnips, and parsnips are common and appear often in Shebalian dishes or may be served as a side. Shebalians cuisine does make use of lentils as their primary legume of choice.
One food item unique to Shebal and the surrounding area, is rice. Rice is an import from the east, typically carried over vast miles by traders from Sinria, Mu, and other places. The palace buys vast quantities of rice and use it often as a form of payment. Rice is steamed and served with meat, butter, and spices, or else may be added to broths to make them hearty and filling.
The Origins of Rice in Shebal
According to legend the origins of rice in Shebal come from not long after the foundation of Kishetal by the demigod Tamel. The first king of Shebal, then a vassal of Tamel, was Haman the Thrice-Bearded. Haman had one son, Hiru the Brilliant. Said to be blessed with all the radiance of the silver of the steppe, it is typically agreed among scholars and poets that Hiru was the most beautiful of all Kishites. His statues and images can be found throughout Kishetal, and particularly in the east. Said to have the strength and size of a great warrior, and the face of a lovely maiden, many flocked to see Hiru. Men and women alike from countless nameless land, travelled many miles, bearing gifts of gold and silver, perfume and spice, to marry or just to sit with the beautiful prince. Even spirits and forestfolks came before him, the dragon, Eker, offered the entirety of the land of Ukat just to have the beautiful prince in his home. Those that were not cowed by his beauty, plead and promised him wealth, love, and many children. They sang of his beauty. Hiru, however refused all gifts, and turned away all suitors, for all they could see was his beauty.
One day the Sinrian King, Jiparitu (Juparvi in his own tongue) came to play his own card, wishing for Hiru to be his lover and cupholder. Jiparitu, who the called The Mount of Rendigra (A Sinrian Thunder God), was the son of the Demigod, Ranaya. He was broad as an ox, the hands like bear paws. He was great warrior who had killed his 5 older brothers in battle for the right to sit upon the throne of his father's city. He presented the youth with the three elephants, ten rolls of silk, five pounds of saffron, and three golden statues, each as large as a man. Yet, Hiru refused. Enraged, Jiparitu stormed from the palace, only to return later that night, along with his plantbrew. They drugged Hiru and ferried him away, over the steppe and the high mountain, to his palace in Sinria. There he bedecked the prince in flowers and silks, and cherished his beauty, and made him his lover, though unwilling. But soon he grew jealous as he saw the looks of awe and lust on the faces of his servants and court. And so he had Hiru's face, bound tight in cords of silk and wool, locked with chains of bronze and copper, so that none could look upon his face but he. He ordered that his body be covered in filth and dressed , save for when it came time for the king to look upon him, so that no other could see his treasure. He then locked the prince in a tower of white stone and gold.
When King Haman heard of his son's abduction, he marched, joined by his brother's the rulers of Bur and Kutar, and 67 of Hiru's former suitors and their men to the lands of king Jiparitu. There they laid siege to the castle for 67 days, and on each day, it is said that one of the suitors was killed.
While the siege raged outside Hiru remained trapped in his tower, his only company being wicked Jiparitu and the slave, Safeniri (Savanri in her own tongue). Both could enter the tower only by an entrance, hidden so that none but they could find it. Safeniri, a peasant girl, born of two rice farmers, fed him scraps of the jungle fowl (chicken), crusts of bread, and green leaves, for these are all that Jiparitu permitted he be fed, lest the beauty of his body be marred by fat. And yet, in secret, she also brought to him, a porridge, made from rice, cinnamon, milk, waweshi (sugar, native to the kingdoms of Sinria, but quite rare in Kishetal) and coconut which she called kerumipiya (Kerumpaja in her native tongue) as well as bowls of rice and butter, for this is all that she, a slave, could afford. She had never seen Hiru's face, and knew nothing of his famed beauty. Hiru longed for her company, and though he had never seen her face, blinded as he was by the cloth around his face, he began to fall in love with her, and she with him.
When word of the siege reached the ears of Hiru and Safeniri, together they concocted a plan to free Hiru and to return him to his father. Outside of the tower, in great bunches, grew "laughing leaf" which dulls the mind and weakens the balance. Its effects are strong but its taste is bitter. When next Jiparitu came into his tower to gaze upon his treasure, Safeniri waited there with Hiru. As always Jiparitu insisted that his guards wait outside of the tower, lest they recieve the pleasure of gazing upon Hiru's beauty. It was only as Jiparitu ordered the clothes removed and the filth wiped away, that Safeniri finally saw him truly. And though she was awed, she had already long since fell in the love with the imprisoned prince.
Though still handsome beyond measure, his face had been marked by seven cuts where the cloth had been bound too tight, and from then on he was known as Hiru of the Seven Scars. While Jiparitu marveled over his captive, Safeniri approached him and offered him a bowl of the kerumipiya, one which she had tainted with the laughing leaf, its bitterness covered by the sweet sugar and milk. The king ate and as he ate, he became joyous and wild. So wild that he spilled the rice upon his fine clothes. Safeniri then suggested that the king undress, less his expensive clothing be ruined by his rice. And so he did, undressed down to his undergarments, his heavy robe falling at his feet. And Safeniri sang and pounded upon the bottom of the clay pot like a drum. Saferniri then opened the door, beyond which were the stairs which spiralled up the tower. Jiparitu danced, entranced by her beautiful voice. His feet became tangled in his discarded robe, and his mind too clouded to stop himself, he fell, tumbling down the hundred stairs of the tower, until he lie at the bottom, dead.
Saferniri then took the kings discarded robe, and tore the jewels and gold from it, she smeared it with filth and grime, until it looked like a beggars cape. This she covered Hiru in and guided him down the tower and through the secret entrance. When they people looked, they saw only a peasant woman, guiding a beggar, his face hidden.
She lead him past the city walls, to where his father and uncles sat in their camp, bereft, for the last of the suitors had been slain by arrow and sling. King Haman was so joyous upon seeing his son that he fell to his knees and sang praises to the gods of Kishetal and the Steppe. And yet he was shocked, when the first words that Hiru spoke to him, were to say that he had found a wife.
Haman was scandalized by the suggestion that his son, the prince, would marry a slave girl. He demanded to know what Safeniri’s family could possibly offer to warrant such a union with one as magnificent and beautiful as Hiru when all other suitors had offered gold, silver, and land. Love and rice, was all that Safeniri could offer. Haman was unimpressed by this seemingly simple answer.
Determined to prove her worth, Safeniri crept back into the city, and returned to her home. With the help of her parents, prepared a pot of kerumipiya, the finest ever made. They used fruit plucked from the trees, milk fresh from the cow, and sugar as white as snow. When she presented this exceptional dish to Haman and his brothers, they were astonished by its exquisite taste, unlike anything they had ever eaten.
Haman, along with his brothers, was deeply moved by the dish and by Hiru's story of Safeniri's cunning and dedication. Relenting, he agreed that a spouse capable of creating such a remarkable meal deserved to be wed to his son. However, he imposed one condition: Safeniri was to see that Hiru was presented with a bowl of kerumipiya every day until he was guided into the next life.
The wedding that followed was a grand celebration. To meet Haman's stipulation, rice and other eastern goods were brought from distant lands to Shebal. Soon, rice, and particularly kerumipiya, became symbols of wealth and love, often featured at weddings. When Haman passed away, Hiru ascended to the throne and ruled with wisdom and kindness, particularly towards slaves and captives. Safeniri honored her promise, and upon Hiru’s death, it was said that she joined him on the very same day.
Many stories of both Hiru and Safeniri now fill Kishite Folklore, with the wisdom of Safeniri being particularly renowned. Many queens and princesses, particularly those in the east of Kishetal may take the title Lusafeniri or "Of Safeniri/ Safeniri-Like" in order to emphasis their wisdom and prowess.
In Shebal today, while still reliant on imported rice, kerumipiya has adapted to local ingredients. Instead of sugar and coconut, it’s sweetened with honey and flavored with dried fruits such as figs and apricots, and often uses horse or donkey milk as opposed to cow milk.
A sprinkle of ground cinnamon might be added for extra flavor. Kerumipiya is commonly eaten as a dessert, or during special occasions. It remains a popular dish at weddings and many lovesick youths may try to woe potential partners with a steaming bowl.
Rice is often used a sacrifice to the god of wealth, Ikeshpaha, its many grains believed to represent plenty. Rice sprinkled around the house is believed to ward of wicked spirits, and disease as it is believed that it "absorbs" evil.
One benefit of its eastern location is that Shebal and the surrounding cities are often the first to receive exotic spices carried from Mu and Sinria, often at far less cost than their western cousins. This is led to a cousin, which well simplistic at first glance, is highly complex in its flavors. Soups such as the goat-based, Habisichiarsoni (The Soup that Awakens the Sleeping God) may use dozens of different spices including turmeric, cumin, pepper (long and black), mustard, cardamom, lime leaf, etc, in a complex and masterful way. Easterners who journey to the west, well excited by the access to wheat and vegetables, often bemoan the perceived blandness, with only Sehaic food being seen as "properly spiced". Shebalian cuisine's heavy use of lisijir and other spices make it perhaps the only cuisine which could be considered "spicy" by Earthly standards.
Another quirk of Shebalian cuisine and of the steppe is that it is the only region which prefers butter as its primary fat, this has earned easterners the somewhat derogatory nickname "butter-eaters" by their western cousins, where the use of butter is often viewed as barbaric. Butter is often used as a condiment, melted and added to soups, bread or other dishes.
The diet of the Shebalians is the least reliant on bread of any Kishite culture, with some families going several days without eating bread. When bread is consumed, it often uses rye, rather than the barley or wheat preferred on the other side of the mountains. The result is dense and nutty and works well with the fatty and meaty cuisine of the steppe. Errikili is a knotted bread made from rye flour, often noted for its somewhat phallic appearance. It is typically used to dip in soups, or else may be eaten with butter and imported spices.
Talakili has become increasingly common in Shebalian cuisine, imported from Kotsa. In Shebal it is often added to soups and broths and is thicker and heartier then its southern equivalent. One particular rendition of Shebalian Talakili called Irkipikiki (literally "pregnant thing") is stuffed with meat and cheese, somewhat similar to a ravioli.
While still identifiably Kishite in its presentation and cooking styles, the components of Shebalian cuisine are largely foreign. Its base ingredients are of the Makurian steppe, while its use of spice shows heavy influence from the lands of the Great Southern Kingdoms (Baban and Ukkaria), Sinria, and even lands far to the east like Pya, Mu, and Xianti.
And that's that! A pretty barebones explanation of the differences between the cuisines of different parts of Kishetal. Let me know if you have any other questions about any of these cuisines/dishes! Maybe one day I'll do something similar with the regional cuisines of places like Korithia, Shabala, Pyria, and Apuna.
Taglist (let me know if you want to be added or removed!)
illarian-rambling, @mk-writes-stuff, @kaylinalexanderbooks, @willtheweaver, @patternwelded-quill
@elsie-writes, @elizaellwrites, @the-ellia-west, @the-octic-scribe, @the-golden-comet
@finickyfelix, @theprissythumbelina, @autism-purgatory, @diabolical-blue , @tildeathiwillwrite
@katenewmanwrites, @leahnardo-da-veggie, @paeliae-occasionally, @melpomene-grey
@drchenquill, @marlowethelibrarian, @phoenixradiant, @pluttskutt
@dyrewrites, @unrepentantcheeseaddict, @roach-pizza, @rivenantiqnerd, @pluppsauthor
@flaneurarbiter, @dezerex, @axl-ul, @surroundedbypearls
@treesandwords, @the-golden-comet
#testamentsofthegreensea#writeblr#worldbuilding#fantasy world#writing#fantasy writing#world building#fantasy food#fantasy#creative writing
29 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Maiores Grupos de Imigrantes em CABO VERDE
0 notes
Text
Listen to the southern right talk about violence in America and you’d think New York City was as dangerous as Bakhmut on Ukraine’s eastern front.
In October, Florida’s Republican governor Ron DeSantis proclaimed crime in New York City was “out of control” and blamed it on George Soros. Another Sunshine State politico, former president Donald Trump, offered his native city up as a Democrat-run dystopia, one of those places “where the middle class used to flock to live the American dream are now war zones, literal war zones.” In May 2022, hours after 19 children were murdered at Robb Elementary in Uvalde, Texas, Republican Gov. Greg Abbott swatted back suggestions that the state could save lives by implementing tougher gun laws by proclaiming “Chicago and L.A. and New York disprove that thesis.”
In reality, the region the Big Apple comprises most of is far and away the safest part of the U.S. mainland when it comes to gun violence, while the regions Florida and Texas belong to have per capita firearm death rates (homicides and suicides) three to four times higher than New York’s. On a regional basis it’s the southern swath of the country — in cities and rural areas alike — where the rate of deadly gun violence is most acute, regions where Republicans have dominated state governments for decades.
269 notes
·
View notes
Text
The fact that Haitian immigrants are eating pets in Ohio isn't even the worst part.
The Biden-Harris administration has secretly flown in over 320,000 unvetted Haitian immigrants into the United States.
Then, in June 2024, Mayorkas gave them special protective status to prevent them from being deported.
This represents an influx of people, sadly, from an inferior culture, and they are bringing their 3rd world values here:
- The average IQ in Haiti is ~78. (Context: An IQ of at least 75 is required to be considered competent in a court of law.)
- Haiti is by far the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere, with a GDP per capita $1,748
- Haiti is the 20th most deadly country in the world, with 40.9 homicides per 100,000
- Haiti's education system is ranked 177th globally in terms of national spending on education, with a literacy rate of 61%
- Haiti has one of the highest prevalence's of communicable diseases in the world, and the highest STD and tuberculosis rates in the Western Hemisphere
- Nearly 40% of Haitians practice some form of Voodoo, which involves witchcraft and animal sacrifice
- Haiti ranked lowest on the Human Development Index in the Region of the Americas
In no way does this make our country better

31 notes
·
View notes
Text
by Daniel Greenfield
The Associated Press recently made headlines by falsely claiming that the Israeli campaign against Hamas “sits among the deadliest and most destructive in recent history” and was even worse than “the Allied bombing of Germany in World War II”.
The Washington Post argued that “Israel has waged one of this century’s most destructive wars in Gaza” while The Wall Street Journal contended that it was “generating destruction comparable in scale to the most devastating urban warfare in the modern record.”
That’s all the more impressive since even accepting the Hamas casualty figures (tainted and inflated numbers in which there are no terrorists, only civilians, and fighting age men are really children) as the media does, this is still probably one of the least violent conflicts in the region.
In 2016, the Washington Post described the Syrian Civil War, with a possible 250,000 deaths, as “the most destructive conflict in the region”. In 2020, the UN had called the Yemeni Civil War, with 150,000 deaths, “the most destructive conflict since the end of the Cold War”.
And then there’s the current phase of the war in Sudan (which the media is currently uninterested in) in which 15,000 people have been killed over the course of last year, as part of a larger conflict that may have claimed as many as 2 million lives.
The Tigray War in Ethiopia over the last three years (which you may have missed because the media chose not to hysterically cover every single bomb dropped and protesters stayed home knitting instead of blocking traffic) may have cost the lives of between 80,000 to 600,000 people.
(El Pais, Spain’s newspaper, which did report on Ethiopia’s civil war, described it as “the deadliest of the 21st century” and then had to pivot to argue later that Israel was worse in, “25,000 deaths in Gaza: Why the destruction of this war exceeds that of other major conflicts”.)
In reality, every significant war and civil war in the region had a much higher death toll than the Hamas war: including the Iraq-Iran War with an estimated 500,000 to 2 million deaths. And in nearby Africa, the Congo War has been blamed for 6 million deaths since 1996.
How does the media justify arguing that 25,000 is more than 2 million?
There are plenty of statistical gimmicks available to anyone who wants to argue that 2 + 2 is really 5. Media “analyses” that claim that Israel’s campaign against Hamas is the deadliest and most destructive, and might even be worse than WWII, adjust their claims accordingly.
As the author of every dubious research study knows, to get the results you want, you manipulate your parameters. Media analyses selectively compare Israel’s campaign to battles, rather than wars, they narrowly focus on very specific timetables, they try to estimate per capita rather than gross figures. But drawing a circle around a particular area and going per capita works both ways. The Hamas attack of Oct 7 killed 10% of the population of Kibbutz Be’eri making it far worse per capita than anything in Israel’s response to those atrocities.
But statistical fudging is all in where the line is drawn to achieve a particular agenda.
For example, the New York Times declares that, “Gaza Deaths Surpass Any Arab Loss in Wars With Israel in Past 40 Years”. Of course the last major Arab-Israeli war took place 50 years ago.
The 40 year figure is based on the Lebanon War, but the actual numbers for that war vary wildly from the thousands according to Israel, 10,000 according to the CIA, 18,000 according to Lebanon and 30,000 according to Arafat and the PLO.
While the media at the time emphasized the highest estimates, in order to criticize the Israeli campaign against the PLO, they now use lower estimates to attack the Gaza campaign.
63 notes
·
View notes