#Canadian temperature records
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

ThisIsNotNormal ---
#ScottDuncanWX: "#Heatwave in Pacific Northwest & #BritishColumbia is breaking records.
British Columbia 🇨🇦 has just registered its #hottestAugustday on record with 42.2°C (108°F) at Lytton."
#This Is Not Normal#Climate Change#Protect The Planet#Climate Crisis#Hottest August Temperatures#Canada Heat Wave#Hot Temperatures In Canada#Canadian temperature records
0 notes
Text
Some alarming climate news as of June 2023
Antarctica, which is in the dead of winter, has unexpectedly failed to reform its winter sea ice. This is an exceptional deviation from the norm that has left scientists dumbfounded.
The entire NE Atlantic Ocean is experiencing its most significant marine heatwave ever…by far. That area had never been a full 1°C above the 1951-1980 average. It has suddenly jumped to 1.7°C above that average.
A powerful heatwave has overtaken southern North America for weeks on end, with places like Texas and northern Mexico breaking daily record high temperatures.
In the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico, sea surface temperatures are extremely high. Water temperatures are in the *90s* by the Florida coast, Miami keeps breaking daily record heat index values, and a major coral bleaching event will soon be underway.
The Canadian 2023 Wildfire Season will not let up, with nearly all annual records falling before we even reach the midpoint of the season. No Canadian wildfire season had ever produced 12 terawatts (TW) of fire radiative power. 2023 has produced 18TW.
Dramatic flood events have begun striking various countries around the world simultaneously this week.
El Niño has rapidly developed in recent months as sea surface temperatures across the equatorial east Pacific skyrocket. As of yet, El Niño has not impacted global weather conditions. That will change in a few months.
All of these events have culminated in June 2023, easily being the hottest June in Earth’s recorded history. Likely the hottest June in 115k-120k years when Earth was last this hot.
#important#current events#news#environment#climate#climate change#climate justice#environmentalism#environmental justice#global warming#activism#climate crisis#climate news
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
As of right now it’s predicted that the temperatures for the Las Vegas GP could be as low as 4C.
The record for the current coldest GP was the 1978 Canadian GP where it was 5C
This is genuinely going to be chaos, especially as there’s almost no proper corners on the track (and it’s corners that put temperature into the tyres) and instead there’s just straights which cool the tyres.
They’re just going to be tiptoeing around or swerving everywhere
832 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Burned to the Ground: the Canadian village incinerated by record temperatures, June 8, 2023
The small village of Lytton in British Columbia hit the global media when it smashed Canada's highest temperature ever recorded in June 2021, at 49.6 degrees centigrade. Two days later, the entire village had burned to the ground. In the ashes of their homes, this cohesive but diverse community which includes a majority of First Nations residents had to confront the realities of climate displacement by being relocated away from their ancestral lands. Through the stories of three main protagonists we find a community searching for answers while relying on a collective spirit to heal. The Guardian
@allthecanadianpolitics
#Lytton#British Columbia#Nlaka'pamux Nation#indigenous peoples#First Nations#Canada#landscape#climate change#documentary#climate emergency#wildfire#Wallop Film#film#The Guardian#short
436 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lessons From a Burning Forest. (New York Times)
As a reporter, I’ve experienced the aftermath of several disasters, including dam bursts, landslides and floods. But nothing quite prepared me to witness the extent of the destruction in Canada’s boreal forests that I saw in June, one year after the record-breaking wildfires of 2023.
At one point, my colleague Bryan Denton and I drove for an entire hour and saw almost no living trees in the forests we could see from the road. Much of the landscape was covered with blackened stumps of trees that burned last year. Residents told us the burned trees revealed hills, rivers and towns that they had never seen before.
I’ll be open with you: It was alarming.
We were there reporting how parts of North America’s boreal forests are failing to regrow because of the more frequent, bigger wildfires that have become a hallmark of our changing climate. One of the strongest pieces of evidence of this shift is the gradual decline of the black spruce, a humble species that has dominated these landscapes for thousands of years.
In short, my article shows how the dwindling number of black spruce trees is deeply transforming this vast ecosystem, which is one of the planet’s biggest storage systems for planet-warming carbon dioxide. What’s troubling is that black spruce evolved to exist with fire — just not fire that happens this often.
Losing any part of the black spruce forests will make the global struggle to keep temperatures below catastrophic levels harder, and it may mean our climate models are too optimistic.
But I also want to share what researchers and local Indigenous leaders told me: There is a lot we can do to adapt, particularly borrowing from traditional fire-management practices. These won’t save the immense boreal forests from global warming, but they could help communities adapt.
Indigenous people are some of the most directly affected by this new age of wildfires. According to government figures from April, 80 percent of First Nations communities in Canada are in wildfire-prone areas.
Many First Nations elders say they have been forced to change their traditional fire-management practices.
For centuries, Indigenous Canadians burned their lands during the spring, when the grass was dry and the forest was wet, in what are known as cultural burns. Elders looked for cues that can’t exactly be marked on a calendar, like signs the local snow was almost ready to melt, or when the ducks started to nest, as elders in Alberta explained in a 1979 documentary.
These burns protected their homes from insects, induced lush sprouting that attracted animals they hunted, and, perhaps most crucially, fireproofed their communities. The flames weren’t hot enough to kill the trees, just burn branches and leaves that, if left unattended, could fuel bigger fires during summer.
But near the end of the 19th century, Canada started banning cultural burns and fining anyone who practiced them. Slowly, what were meadows became flammable forests, and blazes grew harder to control, Cardinal Christianson said. “This idea of fire suppression or fire exclusion has got us in this problem,” she told me.
In 2020, a paper published in the journal Nature found that fire suppression increased the risk of wildfires for many communities in the Canadian boreal forest.
32 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Highest and Lowest recorded temperature in US States and Canadian Provinces and Territories.
159 notes
·
View notes
Photo
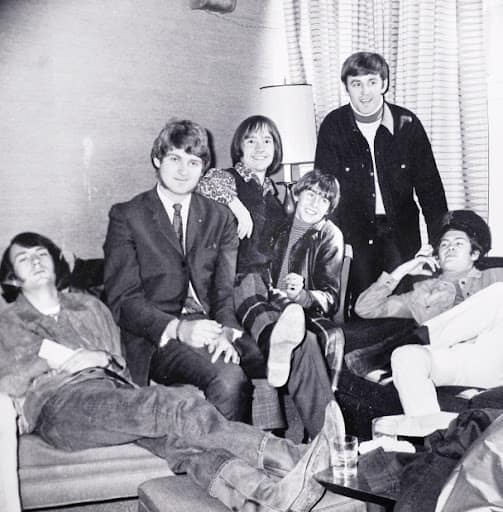

The Monkees with CFUN DJ's Terry David Mulligan and John Tanner in Vancouver, April 1, 1967.
“Regina: CKCK’s Terry David Mulligan claims to be the first Canadian air personality with an interview with the Monkees and he has a tape to prove it. Anyone wishing a copy can take Mulligan up on his boast by sending him a blank tape and he will return a dub to sender. Terry also did a 30 minute Christmas show with Peter Tork, his sister and brother. They sang cuts from the Monkees new LP (Mulligan sings too)[,] sang a few carols and just chit-chatted in a relaxing mood.” - RPM Canada, January 28, 1967 (this Christmas 1966 anecdote was previously posted here and more about Christmas 1967 here)
“History records that The Monkees played their first Canadian concert in Winnipeg on April 1/1967. What never gets mentioned is that the first time all four Monkees set foot on Canuck soil was many hours earlier, in Vancouver, while en route to Manitoba’s capital city. Top 50 radio station CFUN assigned two deejays—Terry David Mulligan and John Tanner—to meet Micky Dolenz, Davy Jones, Michael Nesmith and Peter Tork at Vancouver International Airport. A photo op ensued in a private waiting area as the lads waited, shortly after sunrise, to board a connecting flight. 'If you study that picture, you could tell two of the guys (Davy and Peter) were really into it and the other two (Micky and Mike) didn’t really want to be there,' recalls Mulligan (second from right in photo). 'They weren’t pissed off at us. They were just tired and weren’t particularly into having their picture taken that early in the morning.' Nevertheless, all six exchanged pleasantries. Despite the early hour, Davy Jones seemed friendly and 'Mike Nesmith was so whip smart, while Micky Dolenz had this interesting Hollywood vibe about him,' remembers Mulligan. Terry and Peter got the opportunity to renew acquaintances. The previous year, when Mulligan was spinning discs at CJME Regina, 'who should walk in but Peter Tork. Of course, I asked: "What are YOU doing here?" And Peter answered: "My dad (Halsten John Thorkelson) teaches at the University of Saskatchewan and I dig your radio program."' Peter would take a couple of additional breaks from Monkees commitments to visit his family. Each time, he’d visit Mulligan at CJME. 'We’d always have really good off-air chats, in between as I was playing records.' For his part, CFUN deejay John Tanner (second from left in photo) boarded the plane bound for Winnipeg with The Monkees. 'I remember being at the tail of the plane while The Monkees and their entourage were much further forward. I walked up there at one point and noticed some of them were sleeping. So I went back to my seat as I didn’t want to bother anyone.' Prior to the late afternoon Monkees concert at the Winnipeg Arena, Tanner said he killed some time walking 'what seemed to be the coldest streets in Winnipeg.' Indeed, band insider David Price would mention the frigid 17 degrees Fahrenheit daytime temperature when he subsequently wrote a four-page article titled My Life With The Monkees—That Wild Canadian Weekend for 16 magazine that detailed the April 1 concert in Winnipeg and the ensuing show in Toronto on April 2. Price, who also served as a decoy for Davy Jones (in addition to other band duties), claimed The Monkees came to Canada aware of rumours that attempts might be made on their lives during the two concerts. In the 16 magazine piece, Price wrote: 'Mike asked me and his friend Charlie Rockett and Mike’s wife Phyllis’s brother Bruce Barbour to make sure that any packages that landed onstage were thrown off again, because one of them might contain a bomb.' In the end, the only ‘bomb’ at the Winnipeg show was a water bomb hurled at Micky Dolenz atop the seven-foot high stage just before opening song Last Train To Clarksville. Seconds before, the four Monkees burst out of phoney amplifiers on either side of the stage, with the boys having hidden themselves within when the house lights were momentarily turned off. Likely backing up The Monkees onstage was Candy Store Prophets. If so, that band’s members—including guitarist Tommy Boyce and keyboardist Bobby Hart—had played on many early Monkees studio tracks that Boyce and Hart produced. Winnipeg-based Electric Jug & Blues band opened the show. Press reports later revealed that before the concert, rambunctious fans charged past about 30 police officers as the band left the Hotel Fort Garry for the arena. Monkees publicist Don Berrigan described the incident as a 'near riot' adding 'Mike and Davy were knocked down. It was really nasty.' There were apparently well over 400 police and security inside the arena. Perhaps it was the security concerns that resulted in Winnipeg and Toronto fans receiving slightly shorter concerts than about a dozen previous American shows in late 1966 and early ‘67—13-song setlists, three less than south of the border. The Winnipeg concert marked the first time Peter Tork-sung Your Auntie Grizelda, was played publicly. 'He really dug it, and so did the audience,' wrote Price. [...] Back in Winnipeg, after final song I’m A Believer, the band rushed to limos to return to the hotel, before taking an evening flight to Toronto. A subsequent Canadian Press article noted that one policeman was taken to hospital after a wire retaining fence collapsed on him when 'thousands of fans surged towards the rear exits in an unsuccessful bid to catch a glimpse of their departing idols.' The officer was treated for cuts and abrasions and released. The official capacity of Winnipeg Arena was 11,800. But Price claimed that several hundred additional tickets were sold just before showtime, resulting in an attendance closer to 12,500. Later that Saturday night, The Monkees checked out of the hotel and headed to the airport in what Price described as near-blizzard conditions. For his part, CFUN deejay John Tanner got a kick out of the 'wild and crazy' show he had just witnessed. 'It was kind of a thrill being there.' The photo taken back in Vancouver earlier that day would be published in the April 8 copy of the C-FUNTASTIC FIFTY survey given away at Greater Vancouver record stores. Part of the photo ID read 'They said it couldn’t be done' — likely a veiled reference to doubts that The Monkees would trek north for concerts so soon into their existence.” - Richard Skelly, Facebook, April 1, 2022 [x]
#Peter Tork#Tork quotes#Davy Jones#Micky Dolenz#Michael Nesmith#The Monkees#Monkees#60s Tork#1960s#1967#long read#Terry David Mulligan#John Tanner#David Price#et al#Monkees fans#where is that tape of Peter and his siblings now?#what if... of Tork history#'sang a few carols and just chit-chatted in a relaxing mood' (if that tape still exists it'd be such a gem)#hope those radio tapes were preserved#can you queue it
32 notes
·
View notes
Text

Northwest Territories Ablaze
The boreal forests of northern Canada have evolved to burn. These forests are dominated by black spruce, a type of evergreen that is not just tolerant of fire but dependent on it.
Black spruce has waxy, resinous needles adapted to ignite during lightning storms and burn vigorously. The forests thrive if they burn every century or so because fires open the canopy up to light, stimulate new growth, and help maintain biodiversity. Fires also melt away the waxy coating on cones of black spruces allowing them to deposit seeds uniquely designed to thrive in charred, acidic soils. But Canada’s black spruce boreal forests have been burning more frequently in recent decades, putting even these fire-loving forests under strain.
When the VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) on the NOAA-20 satellite captured this image of smoke streaming throughout the region on August 11, 2024, the sensor detected nearly 100 active fires burning in the Northwest Territories, according to data posted by the territory’s government. The Canadian government, including the Northwest Territories, uses hotspot data from the Fire Information for Resource Management System (FIRMS), a fire monitoring system developed by NASA, to help detect and track wildfires.The image below, captured by NASA’s EPIC (Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera) on NOAA’s DSCOVR satellite, shows a river of smoke from the fires in western Canada winding its way over the Hudson Bay.

Most fires in the Northwest Territories burn far from towns or infrastructure, so authorities let many of them burn themselves out, a process that can take weeks or even months depending on the weather. Of the 96 fires active on August 11, Canadian authorities reported that 88 of them burned unhindered by firefighting efforts. Firefighters had controlled five fires and were in the process of suppressing one, according to the territory’s government. None of the fires were close enough to settlements to trigger evacuation orders. However, dense smoke has triggered air quality warnings for fifteen Northwest Territories communities, including settlements in the North Slave, South Slave, Dehcho, and Sahtu regions.
The fires coincided with a drought classified as moderate to extreme by the North American Drought Monitor and a week of extreme warmth that broke temperature records in several places in the Northwest Territories, including the towns of Aklavik, Inuvik, Fort McPherson, and Tuktoyaktuk. All four communities surpassed 30 degrees Celsius (86 degrees Fahrenheit); Fort McPherson’s temperature soared to a remarkable 34.9°C (94.8°F) on August 7 and 8.
Though Canada’s black spruce forests are accustomed to fire, ecologists who study them are finding that some forests in the region are struggling to recover after fires due to the increasing frequency and size of fires in the region. One study led by Jennifer Baltzer, an ecologist at Wilfrid Laurier University, found that black spruce’s ability to regenerate declined at 38 percent of the 1,500 recently burned forest sites included in the study and failed to regenerate entirely at 18 percent of the sites—unusually high percentages compared to the historic norm. The analysis was based on tree regeneration data compiled and analyzed as part of NASA’s Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE).
Many of the areas burning in this image also burned in 2023, during Canada’s worst wildfire season on record. However, the total number of fires and the number of hectares burned in the Northwest Territories through mid-August 2024 are below the 10-year average so far, according to data released by Canadian authorities. The extent of burning in neighboring British Columbia and Alberta through mid-August 2024, however, was above average.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Lauren Dauphin, using VIIRS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE, GIBS/Worldview, and the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) and data from DSCOVR EPIC. Story by Adam Voiland.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
So-called zombie fires in the peatlands of Alaska, Canada, and Siberia disappear from the Earth’s surface and smolder underground during the winter before coming back to life the following spring. These fires puzzle scientists because they appear in early May, way ahead of the usual fire season in the far north, and can reignite for a number of years.
Most scientists believe that zombie fires are the remnants of fires on the surface, but we have identified an alternative cause. Our research suggests that rapid atmospheric warming aboveground can cause peat soils to suddenly heat up to smoldering temperatures underground, all without any spark or other ignition. These zombie fires may be a case of climate-change-driven spontaneous combustion.
Reports of such fires date back to the 1940s, when they were rare events. However, the frequency and intensity of these fires have increased significantly in the past two decades, hand in hand with accelerated warming in the Arctic, the fastest-warming region on the planet.
At the start of 2024, more than 100 zombie fires were active in the Canadian province of British Columbia. Zombie fires have even been recorded near the coldest village on Earth, Oymyakon in north eastern Siberia, where they carried over through multiple winters and account for around 3.5 percent of area burned in the wider region each year.
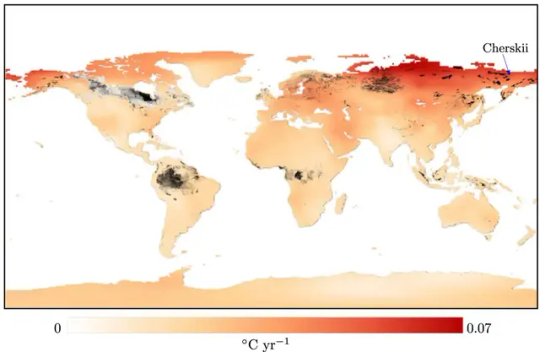
Red areas are warming fastest, while black and gray areas show carbon-rich peat soils. There is significant overlap between the two, such as in Cherskii in northern Siberia. Map: O’Sullivan et al./Royal Society A; data from Berkeley Earth/PEATMAP
More carbon is trapped in temperature-sensitive Arctic peat soils than is found in the entire atmosphere, and these fires are releasing gigatons of it into the atmosphere. We wanted to know if sudden warming might be directly responsible.
Two Remarkable Results
We developed a mathematical model to explore different what-if scenarios, including how the temperature and carbon content of peat soils respond to changes in the weather and climate. Crucially, our model captures how certain microbes generate heat while breaking down soil and releasing its carbon into the atmosphere.
We obtained two remarkable results:
The first is that those microbes can generate so much heat that underground peat can smolder at around 80 degrees Celsius (176° F) over the winter, ready to ignite in spring. And this can happen without there ever having been a fire in that spot aboveground and without the weather aboveground reaching the sorts of temperatures that would normally be needed for soil to burn.
We call this new state the hot metastable state of peat soils. In this context, “metastable” means a long burn—the hot state lasts for a long but finite time, up to 10 years, until the peat burns out.
Our other key finding is that a sudden transition from the regular cold state to the hot metastable state can be triggered by realistic climate patterns alone, including summer heat waves and global warming scenarios. Most interestingly, the increase in the atmospheric temperature has to be faster than some critical rate to trigger the transition. If the atmospheric temperature increases by the same amount but at a slower rate, bioactive peat soil remains in the regular cold state and never transitions to the hot metastable state.
We still do not have proof of this happening in the real world, and it hasn’t been demonstrated in a lab—for now, this is a phenomenon seen only in our models. But we do know that compost (very similar to peat) can catch fire in the same way. For instance a large fire on the outskirts of London during a heatwave in 2022 was probably caused by a pile of compost spontaneously combusting.
All this suggests that atmospheric temperature is not actually the key critical factor for zombie fires. Rather, it is the rate of atmospheric warming that triggers long burns of underground peat. Put simply, it is not the heat, it is the rate.
How to Fight the Zombies
As the climate warms, the weather is becoming more extreme, and these are precisely the conditions that can lead to more and more zombie fires. This is concerning, as it could kick off a vicious cycle: The gigatons of carbon released from ancient peat soils into the atmosphere are likely to make the climatic changes even worse, which means more fires, so more extreme weather, and so on.
Indeed, zombie fires are an example of a rate-induced tipping point, where a system fails to adapt to too-fast changes in external conditions and transitions from its regular state to a different, often undesired state. It is possible that the contemporary climate is approaching—or has already exceeded—dangerous rates of change for certain natural system, such as bioactive peat soils, which could explain the recent increase in zombie fires.
It appears that the only solution to prevent further zombie fires is to limit climate variability. While policymakers focus on dangerous levels of atmospheric temperature (the heat), climate variability (the rate of change) could be equally or even more relevant to our resilience in the short term.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
climate change blackpill megapost
there are several climate tipping points identified in the united nations intergovernmental panel on climate change sixth assessment report (chapter 3, specifically). tipping points refer to critical thresholds in a system that, when exceeded, can lead to a significant change in the state of the system, often with an understanding that the change is irreversible. they are:
the greenland ice sheet
the west antarctic ice sheet
the atlantic meridional overturning current
monsoon systems
el niño-southern oscillation
tropical rainforests
northern boreal forests
thawing permafrost
extreme heat
current (2022) global warming of ~1.1°C above preindustrial temperatures already lies within the lower end of some tipping point uncertainty ranges. several tipping points may be triggered in the paris agreement range of 1.5 to <2°C global warming, with many more likely at the 2 to 3°C of warming expected on current policy trajectories.
greenland's ice sheet is in disequilibrium and we are committed to 2-3 meters of sea level rise from its melt alone in the next 200 years.
greenland's ice sheets have been melting twice as fast in the last twenty years as they were during the previous century.
rapid increase in the rate of melting of the west antarctic ice sheet is unavoidable.
the west antarctic ice sheet is retreating twice as fast as previously predicted
because of widespread seawater intrusion beneath the grounded ice of the thwaites glacier.
the west antarctic ice sheet will raise sea levels by four meters when it melts.
this is causing the atlantic meridional overturning current to collapse.
the gulf stream (aka amoc) is weakening. 99% confidence. measured volume through the florida straits has declined by 4% in the past 40 years
the gulf stream will collapse between 2025 and 2095. 95% confidence.
the north atlantic is four standard deviations above its historic temperatures.
when the amoc collapses, the arctic sea-ice pack will extend down to 50°n. the vast expansion of the northern hemispheric sea-ice pack amplifies further northern hemispheric cooling via the ice-albedo feedback.
a collapse of the atlantic meridional overturning circulation would have substantial impacts on global precipitation patterns, especially in the vulnerable tropical monsoon regions in west africa, east asia, and india where they will experience shorter wet seasons and longer dry seasons with an overall decrease in precipitation
although recent studies indicate that the amazon will experience net benefit from the collapse of the amoc with cooler temperatures and increased rainfall
increased el niño intensity will increase the frequency and severity of droughts in the amazon rainforest.
even if we were able to stabilize global mean temperature at 1.5º C, el niño intensity will continue to increase for a century
and the amazon rainforest is currently in the worst drought on record, which may indicate it has passed its threshold to maintain its own wet climate.
while widespread and persistent warming of permafrost has been observed in polar regions and at high elevations since about 1980, the highest permafrost temperatures in the instrumental record were recorded in 2018–2019 (data from 2019-2020)
as of 2019 the southern extent of permafrost had receded northwards by 30 to 80km
soil fires in the canadian arctic are burning the peat underground and melting the permafrost. stat from the study 70% of recorded area of arctic peat affected by burning over the past forty years has occurred in the last eight and 30% of it was in 2020 alone.
nasa finds that tundra releases plumes of methane in the wake of wildfires.
in 2023 eight times more land burned in canada than average.
russian siberia experienced a similarly massive fire season in 2021.
a methane source we weren’t expecting was warmer, wetter conditions to increase organic decomposition in tropical wetlands which is releasing ever increasing amounts of methane.
we have been experiencing exponential rise in atmospheric methane since 2006. historical data indicates that we may have entered into an ice age termination event fueled by these methane releases.
we have been over 1.5º C above pre-industrial temperatures since the beginning of 2023.
this may be because of the extreme el niño conditions of the 2023-24 cycle, but breaches of 1.5°C for a month or a year are early signs of getting perilously close to exceeding the long-term limit
and the world meteorological organization expects us to permanently break 1.5º C of warming from pre-industrial levels within the next five years.
the united nations environmental programme (unep) emissions gap report found that current fossil fuel extraction commitments leave no credible path to keeping warming below 1.5º C. based on current policies we will experience 2.8ºC of warming by 2100. even if all current pledges were implemented and followed through with (which they never have been), we will only be able to limit that to 2.4-2.6ºC of warming.
#this isn't even touching on the anthropological or ecological impacts#just the physics of the predicament#climate change#climate crisis#climate emergency#ipcc#extinction rebellion#last generation#just stop oil#it's the end of the world as we know it
11 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey Mama, are you doing okay????? In class today we were looking at polar vortex in North America rn and one of the places my teacher talked about was the province i think you live in (you're Canadian, right???) and he said it was like -40 Degrees Celsius there!!!!! I don't even know how to comprehend those temperatures!!!! Like, are you still alive out there???
Hello my sweet summer child! <3 You're right, I am Canadian! And im not going to lie to you, its been rough out here. And more importantly, its been CONSISENTLY COLDER THAN THE SURFACE OF MARS HERE.
My area of the province has set several temperature records in the past few days:
January 14, 2024: New record of -45.1, Old record of -41.6 set in 2020
January 13, 2024: New record of -45.3, Old record of -41.7 set in 1972
January 12, 2024: New record of -45.9, Old record of -39.4 set in 1969
This doesn't account for the Windchill factor which effectively made the temperatures closer to -55 degrees or colder. To put it into context the only way I can think to, According to Environment Canada at:
-28 to -39 degrees Celsius exposed skin can freeze in 10-30 minutes.
-40 to -47 degrees Celsius exposed skin can freeze in 5-10 minutes.
-48 to -54 degrees Celsius exposed skin can freeze in 2-5 minutes.
Literally not a single car in my family's worked, no matter what we did. This is including extended family, so like, 13 cars. Its just too damn cold for them. Hospitals were literally wrapping their ambulances with heated blankets in between calls so that the entire engine wouldn't freeze. In their heated garage.
Its about an eight day wait for any kind of towing or boosting services. From any provider.
We out here, we cant see anything through the ice fog because the air itself is frozen, but we out here.
Also, I feel like this is the perfect opportunity to give the rest of you much farther south than me tips for surviving other wandering polar vortex's in the future, because at least we're prepared up here:
YOU NEED SURVIVAL EQUPMENT IN YOUR CAR!!! I CANNOT STRESS THIS ENOUGH!!!! I'm talking heavy duty gloves, hats, socks, blankets, those heat reflective thermal blankets. If possible, have enough for at least two people but if you're a family ensure there's clothes for every member of your family. I also highly recommend that you get hand and feet warmers to put into your boots and gloves to prevent frostbite
Here is a good checklist to keep, and is very similar to what I have in my car:
https://todayshomeowner.com/weather/guides/winter-survival-kit-for-your-vehicle/
On that note, dressing for seriously cold weather is no fucking joke either, okay? There's an art to it, and that art is L A Y E R S . More layers than you think you need, and then one more. If you can bend your arms or legs without struggling at least a little bit, put another sweater on, underneath your windproof thick outer layer. And another pair of socks. Never leave the house without a hat and your ears covered.
Here's a good guide, which includes the warning signs, symptoms, and suggested actions for each stage of frostbite and hypothermia. Which, in case you didn't know happen in three stages of severity similar to burns but on the opposite side of the temperature scale.
Sorry to turn this into a Winter Weather Safety PSA but I genuinely cannot stress enough how important it is to be prepared in extreme cold. And please, for the love of everything good on this earth, do not and do not let your friends or anyone else walk anywhere when they've been drinking. Do. Not.
Every year in my city at LEAST several collage kids freeze to death because "their place isn't that far" "I have a good jacket." "Ive done it before."
People have frozen to death outside bars because they fell in a snowbank and were too drunk to get out and nobody saw them, because they tried to walk home.
Anyways, stay safe (and warm) out there everyone!!!!
#answered asks#haleigh speaks#not tolkien#but very important!!!!!#winter safety#winter safety tips#extreme cold#I'm from northern Canada okay i know what I'm talking about#polar vortex
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
The chill is gone
Arctic sea ice cover retreated rapidly in July 2024, pushing the daily ice extent at the end of the month to the third lowest in the 46-year satellite record. Extensive low-concentration areas of sea ice are found in the Beaufort and East Siberian Seas, reaching 85 degrees North. In the Southern Ocean, sea ice is nearing the extreme low record extent set just last year, caused mostly by a large ice-free area in the southwestern Indian Ocean. As a result, global sea ice extent is at record lows for this time of year.
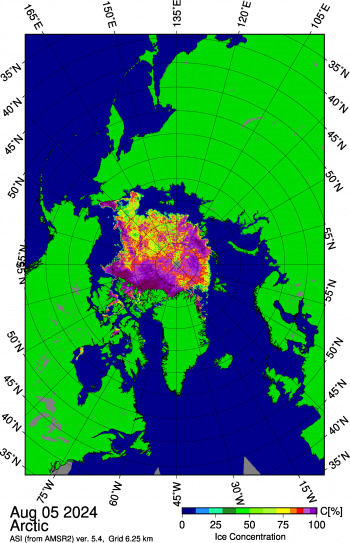
Figure 1c. This image from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer 2 (AMSR2) shows sea ice concentration in the Arctic Ocean on August 5, 2024, highlighting areas of low concentration ice stretching north from the Beaufort and East Siberian Seas, and north of Greenland.
Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, courtesy University of Bremen
Overview of conditions
Arctic sea ice extent averaged for July 2024 was 7.89 million square kilometers (3.05 million square miles), the sixth lowest in the 46-year passive microwave satellite record (Figure 1a and 1b). As of August 1, daily sea ice extent is third lowest behind 2019 and 2020, and just below 2012, the record low year. The July sea ice extent was 1.58 million square kilometers (610,000 square miles) below the 1981 to 2010 average and 600,000 square kilometers (232,000 square miles) above 2020, the record low July.
Ice loss during the month was greatest in the Kara and East Siberian Seas, Baffin Bay, Hudson Bay, and the Canadian Archipelago. Extensive low-concentration areas of sea ice are found in the Beaufort and East Siberian Seas (Figure 1c). A small patch of ice remains in western Hudson Bay, unusual for this time of year. There is still sea ice in both the northern and southern Northwest Passage routes according to passive microwave satellite data. On the Siberian side, the unusually packed area of sea ice south of Wrangel Island remains. Note that icebreakers and ice-capable liquefied natural gas (LNG) carriers routinely traverse the Northern Sea route along the Russian coast even with fairly thick sea ice.
Arctic sea ice retreat in July proceeded at a pace of 113,000 square kilometers (44,000 square miles) per day, faster than the 1981 to 2010 average pace of 87,000 square kilometers (34,000 square miles) per day and only slightly slower than the record pace of 117,000 square kilometers (45,000 square miles) per day set in 2020.
Conditions in context
Air temperatures at the 925 hPa level (approximately 2,500 feet above the surface) were near average overall, with several areas slightly below average. Relatively warm conditions prevailed over the Barents Sea with temperatures 2 to 3 degrees Celsius (4 to 5 degrees Fahrenheit) above average. In the Kara Sea, temperatures were only 1 degree Celsius (2 degrees Fahrenheit) above average. Below average temperatures persisted in a wide swath extending from the East Siberian Sea, over the Beaufort Sea, and onto the Canadian Archipelago and northern Labrador with temperatures 2 degrees Celsius (4 degrees Fahrenheit) below average.
July featured a large area of low sea level pressure centered over Greenland and the Canadian Archipelago, but covering much of the Arctic Ocean.
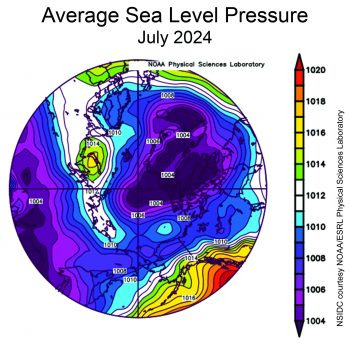
Figure 2b. This plot shows average sea level pressure in the Arctic in millibars for July 2024. Yellows and reds indicate high air pressure; blues and purples indicate low pressure.
Credit: NSIDC courtesy NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory Physical Sciences Laboratory
To continue reading click here
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Once
I have done many things in my lifetime and like most people when I find something that I enjoy doing I will do it more again. Like eating hamburgers. I love eating hamburgers so I have been fortunate enough to repeat this activity several thousand times in my life. For the record I have no regrets.
There have been (however) times upon occasion that I have tried something new and it turned out to be a one time thing. This has been for many reasons, sometimes outside of my control. If you are young and reading this (Why?) learn from my experience. If you are old and reading this either you have also tried some of these and stopped or you were smart enough never to consider doing it in the first place. I envy your fortitude.
Walk with me down memory lane and learn.
Skiing. We had to do this for P.E. class. Besides my lips flapping uncontrollably as I hurtled down the hillside I came to the realization that this accomplished the same thing as tobogganing in that it got me from the top of the hill to the bottom very fast. At least on a toboggan it wasn't far to fall when you wipe out.
Curling. I liked this. I found that when I used all of my strength the rock would go shooting out of my hand and when it hit the little rubber things you start your feet in at the other end the rocks launched majestically into the air. They asked me to never come back again.
Riding a loop-de-loop roller coaster. When it finally stopped I was so disoriented that I attempted to ride a horse from the merry-go-round home. I didn't seem to get anywhere.
I ran a 10K race. I am as shocked as you are but there I was seemingly in the peak of my physical prowess. When the race was over I threw up food I had never eaten.
Went to Mexico. Aside from the fact that they lost our luggage, we saw sea snakes that kept us out of the ocean and two men tried to pick me up at a swim up bar (not that there is anything wrong with that) it was an ok time but that was before all of the kidnappings, murders and other mayhem that is happening now.
Smoked weed. I distinctly remember this. I inhaled June 17th 1973 and exhaled August 22 1975. The rest is kind of fuzzy, but I swear I only tried that one puff.
Traveled by train with family to the east coast. I had the upper bunk and knocked myself silly every time I tried to sit up. I was standing when the train made a sharp turn putting me butt first into the corner of a table, and all cars were smoking cars back then. No wonder Agatha Christie set a murder on a train. I was ready to kill somebody on my sole trip.
Drank warm Guinness. Let me set the table for this one. I was sixteen and we were visiting family in England. The pubs didn't care about ID as long as you paid. A PINT (22 ounces) of Guinness sold for 4 pence which was 10 cents Canadian. I spent a dollar (you can do the math on how many ounces that was) and it was served at room temperature. Everything else that happened that night I blame on the greasy peanuts I ate.
Had gas in front of a Bishop. I was twelve and an altar boy. He was visiting for the 11:30 mass. I had beans and eggs for breakfast at 8:00am (not smart now that I reflect on this) and, well that was that. I believe I did set a record for the youngest person ever excommunicated from the Catholic church.
Got lost in Montreal at Expo 67. Was it my fault that none of the people there spoke English? On the upside I did eat a whale steak and a buffalo steak, both also one time things so I hit the trifecta.
THOUGHT OF THE WEEK: Life is to be experienced and that is great as long as you learn from each experience.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text


Smoke in the Northwest
"Extreme heat, bouts of strong winds, and a prolonged drought are fueling large forest fires in western Canada and the United States.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite acquired this image of smoke spreading across parts of British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and Montana on August 16, 2023. That same day, astronauts aboard the International Space Station captured the detailed photograph below, which shows smoke in valleys in British Columbia near the towns of Golden and Revelstoke.
The surge in fire activity follows the peak of an extreme heat wave that broke dozens of heat records in British Columbia on August 14. But even as temperatures cooled some in the following days, lightning storms triggered new fires, and strong winds turned small blazes into fast-moving, smoky infernos. Authorities in both the United States and Canada issued air quality alerts and, in some cases, calls to evacuate as smoke and fire threatened communities.
The recent heat and winds add to the existing problem of a prolonged drought that has affected the area since last year and primed vegetation to burn. According to the North American Drought Monitor, much of the Pacific Northwest was either abnormally dry or in moderate to extreme drought in mid-August 2023.
Canada is facing one of the worst fire years it has seen in decades, according to data published by the Canadian Interagency Forest Fire Centre. More than 13.7 million hectares (33.9 million acres) had burned as of August 17, more than seven times the 25-year average. The United States has had a quieter wildfire season, with 1.7 million acres burned by mid-August. On average, 4.4 million acres have usually burned by mid-August, according to the U.S. National Interagency Fire Center.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Lauren Dauphin, using MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE and GIBS/Worldview. Astronaut photograph ISS069-E-61356 was acquired on August 17, 2023, with a Nikon D5 digital camera using an 50 millimeter lens and is provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations Facility and the Earth Science and Remote Sensing Unit, Johnson Space Center. The image was taken by a member of the Expedition 69 crew. The image has been cropped and enhanced to improve contrast, and lens artifacts have been removed. The International Space Station Program supports the laboratory as part of the ISS National Lab to help astronauts take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth. Story by Adam Voiland."
Source: NASA Earth Observatory
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Alberta will block renewable energy projects on “prime” agricultural land and limit the placement of wind turbines to preserve “pristine viewscapes”, a decision that increasingly pits the western Canadian province against environmental groups pushing green energy – and the companies investing in it.
The decision, announced by the premier, Danielle Smith, and utilities minister, Nathan Neudorf, on Wednesday, follows a controversial six-month ban on new renewable energy projects that is due to expire on 29 February.
Alberta’s moratorium, announced in August, left energy companies uncertain about billions in future investment, even as the region, with its clear skies and an abundance of wind, led the country in new renewable projects.
Nearly a third of Alberta’s grid is now powered by renewables and the province has shifted away from coal at a far faster rate than expected.
But Smith has pushed back against federal rules that aim to reduce the greenhouse-gas emissions of provincial power grids.
Last month, amid recording-breaking winter temperatures, Albertans were sent emergency alerts asking them to conserve power as the electrical grid buckled from the cold. Smith and others in the province used the cold snap to express skepticism about the feasibility of renewable energy.
On Wednesday, she framed the decision to put limits on new projects as one designed to grow the industry in a “well-defined and responsible” way.
“Alberta has led the country in renewable energy investment, and we will continue to lead the country,” she told reporters.
Under its new rules, Alberta will ban renewable projects on private lands that it believes have “excellent or good irrigation capability” as well as land that can grow specialty crops.
Landowners can request an exemption if they can show crops or livestock can thrive alongside the project. Developers of projects will be responsible for cleanup costs and must secure a bond with the government.
Smith said that the new rules reflect what she called “errors” in the way liability for oil and gas companies was structured in the past – and has since led to mounting crisis in the province as officials contend with roughly 170,000 “orphaned” oilwell sites.
“You don’t correct a problem by compounding it,” the premier said.
In order to preserve its vast open prairie landscapes and sight lines of the Rocky Mountains, the province will put in buffer zones at least 35 kilometres (22 miles) separating what the government believes is a “pristine viewscape” and wind turbines.
Neudorf admitted there was no “universal definition” of the term, but cited other jurisdictions, including the United Kingdom, with rules surrounding buffer zones.
Neudorf also said the policy would apply to the “vertical footprint” of all wind turbines – but that other industries that physically alter the landscape, such as coal projects or clearcut logging, would be assessed on a case-by-case basis.
The government decision was met with skepticism by renewable energy analysts, who warned the vagueness of the new rules amounted to a second “soft moratorium”.
“By introducing three new regulatory frameworks without details, investors and developers are left wondering what this actually means for their projects. Investors required certainty, and the government offered confusion,” Jorden Dye, director of the Business Renewables Centre-Canada, said in a statement.
He called the “unprecedented” 35km buffer zone a “backdoor land ban” that could eliminate the possibility of projects in three-quarters of southern Alberta.
“Overall, today’s announcement extends the climate of uncertainty and leaves us with the task of analyzing how many projects and how much investment Alberta will lose to other provinces,” he said. “Further details are needed to pin down exactly what the fallout will be. Failure to provide those details in a timely manner will also shift investment to other provinces and countries.”
#this is a conservative premier btw#imagine thinking coal pits or oil fields are not an atrocious eyesore#how much is oil and gas paying her to delay renewable energy projects is the question#embarrassing#not to mention the ongoing drought conditions#and renewables use no water#vs oil and gas using massive amounts
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
It’s Been the Hottest Summer on Record, European Officials Say. (New York Times)
Excerpt from this New York Times story:
The summer of “brat,” the Paris Olympics and political conventions may be winding down, but the heat in 2024 is still going strong.
The southwestern United States’ sizzling triple-digit temperatures this week mark the tail end of the hottest summer on record, according to a new European climate report.
“We know that the warming of the planet leads to more intense and extreme climate events, and what we’ve seen this summer has been no exception,” said Julien Nicolas, a climatologist with the Copernicus Climate Change Service, the European Union agency that published the assessment on Wednesday.
Since 2018, the agency has been combining data like weather observations from balloons and satellites with computer models that simulate temperature and precipitation to get a picture of what’s happening around the world. It pairs that picture with past weather conditions reconstructed back to 1940 to compute a global average temperature.
June and August were the hottest June and August on record, according to the models, while July is not quite as clear.
That heat increases the likelihood of extreme weather events like heat waves, heavy rainfall and flooding, and wildfires. Last year, Canadian wildfires were so expansive that they released more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than all but three countries: the United States, China and India.
4 notes
·
View notes