#COVID-19 recovery trends
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Double-Sided Tape Market: Key Applications, Industry Players, and Future Outlook

The double-sided tape market plays a pivotal role across various industries due to its versatility, offering innovative adhesive solutions for a multitude of applications. From packaging to healthcare, this industry is poised for substantial growth, driven by technological advancements and a rising demand for efficient bonding solutions. The market is growing at a high rate due to the increased demand from various sectors. The global double-sided tape market size was USD 11.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 17.2 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 6.7% between 2023 and 2028.
Key Applications
Packaging: Double-sided tape is extensively used in the packaging sector due to its strength and reliability. Its use is especially prevalent in e-commerce, where it provides secure sealing solutions for boxes and packages. This ensures the integrity of goods during transport and storage, making it a critical component in maintaining product quality throughout the supply chain.
Building and Construction: In construction, double-sided tape is employed for mounting signs, panels, mirrors, and other materials. It allows for clean, quick installations, offering flexibility in design and application. The rapid urbanization and ongoing infrastructure development worldwide have further fueled its demand in this sector.
Automotive: The automotive industry leverages double-sided tape for attaching interior trims and exterior components. This adhesive technology supports lightweight design, helping manufacturers enhance both assembly efficiency and vehicle performance, which is crucial given the increasing focus on fuel efficiency.
Electrical and Electronics: Double-sided tape is also widely used in the electronics industry due to its affordability and ease of use. It helps secure components and facilitate connections, contributing to the overall functionality of electronic devices.
Healthcare: With the growing trend toward minimally invasive medical devices, the healthcare sector has embraced double-sided tape for the assembly of wearable sensors, infusion pumps, and other medical equipment. These tapes are designed to be hypoallergenic and breathable, ensuring patient comfort while providing secure bonding.
Retail: In the retail sector, double-sided tape is often used to mount promotional materials such as posters and signs. Its ease of use allows for quick updates to displays, making it ideal for seasonal promotions and product launches, helping retailers create dynamic and engaging shopping experiences.
Major Industry Players
The global double-sided tape market features key players who lead the industry through innovation, sustainability efforts, and a focus on high-performance products.
3M Company: A pioneer in adhesive technologies, 3M provides a wide range of double-sided tape solutions catering to industries such as electronics and automotive.
Avery Dennison Corporation: Known for its diverse adhesive product portfolio, Avery Dennison continues to expand its offerings to meet rising market demand.
Lohmann GmbH & Co. KG: A strong player in the market, Lohmann offers tailored adhesive solutions for various industries.
Lintec Corporation: Specializing in high-quality adhesive products, Lintec leverages technological advancements to continuously enhance its product lineup.
Tesa SE (Beiersdorf AG): Tesa is well-known for its innovative adhesive solutions and its commitment to sustainability, catering to the eco-conscious consumer base.
Future Outlook
The double-sided tape market is expected to witness significant growth from 2024 to 2032. Technological innovations, rising consumer demand, and increased government investments in urbanization and infrastructure development are key factors driving this growth. The market is evolving rapidly to meet the specific needs of diverse sectors.
Technological Advancements: Continuous improvements in manufacturing processes are enabling the development of high-performance double-sided tape solutions for specialized applications.
Sustainability: As regulatory requirements and consumer preferences shift towards eco-friendly products, manufacturers are focusing on developing sustainable and green adhesive solutions.
Customization: Tailored solutions designed to meet specific consumer requirements are gaining traction, providing manufacturers with new avenues to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Regional Insights on the Double-Sided Tape Market
North America: North America, especially the United States and Canada, holds a significant share of the global double-sided tape market. This can be attributed to the region’s strong manufacturing and construction sectors, which demand high-quality adhesive solutions for a variety of applications. Additionally, North America's advanced distribution networks, innovative tape technologies, and strict quality standards bolster its position as a key hub for both the production and consumption of double-sided tape. Despite facing challenges during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, with manufacturing activities temporarily declining, the region has been recovering since 2021 as economic activities gradually resume.
Europe: Europe is another major player in the double-sided tape market, with notable contributions from countries like Germany, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Spain. The market in this region is characterized by a mature industrial base, high consumer demand, and diverse applications. European market players focus on developing advanced adhesive technologies to meet strict regulations and quality standards, driving innovation and growth across the region.
Asia-Pacific: Asia-Pacific is projected to see the fastest growth in the double-sided tape market, fueled by rapid urbanization and industrialization in countries like China and India. Government support and the availability of inexpensive raw materials contribute to this expansion. The region's booming automotive industry and increasing business investments further enhance its market potential, making it highly attractive for new entrants. Key contributors to this growth include Japan, South Korea, Australia, and emerging markets such as Indonesia and Thailand.
Latin America: Brazil and Mexico are the primary markets driving growth in the double-sided tape sector in Latin America. While the region is smaller compared to North America and Asia-Pacific, rising industrial activities and increasing consumer demand for adhesive products are contributing to its development.
Middle East and Africa: The Middle East and Africa are gradually gaining momentum in the double-sided tape market, though their market share remains relatively small. Factors such as ongoing infrastructural development and industrialization are expected to drive demand in this region in the coming years.
Download PDF Brochure :
The double-sided tape market is thriving, driven by rising demand for efficient bonding solutions across sectors such as packaging, construction, automotive, electronics, healthcare, and retail. Its versatility and efficiency have made it indispensable in modern industries, particularly as e-commerce and urbanization trends continue to rise. With innovations in adhesive technology, a shift towards sustainable products, and increasing regional demand, the double-sided tape market is well-positioned for significant growth in the coming years.
#North America adhesive market#Europe adhesive technologies#Asia-Pacific market growth#industrial adhesives#construction adhesives#rapid urbanization#COVID-19 recovery trends
0 notes
Text
Navigating Global Economic Recovery Amidst Turbulent Times
Understanding the Complexities of Global Economic Recovery

The world is currently grappling with a multitude of challenges that are hindering global economic recovery. As we strive to move past the unprecedented impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, new waves of infections continue to pose significant threats to economies worldwide. In addition, rising inflation rates, supply chain disruptions, policy uncertainties, and labor market challenges further compound the complexities. This article explores the interplay of these factors and delves into the measures required to overcome these hurdles and steer towards a resilient economic future.
The Ongoing Battle with COVID-19
Despite progress in vaccination efforts, COVID-19 remains a potent adversary to economic recovery. As new waves of infections emerge, countries are forced to grapple with imposing restrictions and lockdowns to curb the spread. Such measures, though essential for public health, have profound consequences for businesses and industries. Disruptions in workforce continuity, temporary closures, and reduced consumer demand impact economic growth.
The uncertainty surrounding the duration and intensity of these waves adds further strain to businesses' ability to plan and invest in the future. Moreover, as variants of the virus continue to evolve, adapting strategies to combat the virus becomes an ongoing challenge for governments and businesses alike.
Inflation: The Silent Eroder of Purchasing Power
Rising inflation rates present another obstacle to global economic recovery. The pandemic's economic fallout, coupled with supply chain disruptions, has caused an increase in the prices of goods and services. This phenomenon erodes consumers' purchasing power, as their income struggles to keep pace with the soaring costs of essential items.
Central banks and governments face the delicate task of balancing inflation control measures while simultaneously promoting economic growth. Tackling inflation requires a careful calibration of monetary policies and fiscal stimulus to prevent the economy from slipping into stagflation – a state of stagnant growth with soaring prices.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Bottlenecks in the Path to Recovery
The pandemic exposed the vulnerabilities of global supply chains. As nations went into lockdowns, the movement of goods and raw materials was severely impeded, causing bottlenecks and delays. While economies have gradually reopened, the challenges persist. Shortages of critical components and delays in production have far-reaching implications for various industries, from manufacturing to retail.
Efforts are being made to diversify and localize supply chains to enhance resilience. However, transforming complex global supply networks is no small feat and requires time and substantial investments.
Policy Uncertainties: A Hurdle for Investors
Policy uncertainties amplify the challenges faced during economic recovery. Governments worldwide have implemented various measures to tackle the pandemic's impact, often requiring businesses to adapt swiftly. However, the changing policy landscape introduces uncertainty for investors, deterring them from making long-term commitments.
Clarity and consistency in government policies are crucial to instill confidence in businesses and encourage investments that fuel economic growth. Transparent communication and collaboration between policymakers and industries can foster a conducive environment for economic recovery.
Labor Market Challenges: Finding the Right Balance
The labor market also faces its own set of challenges. Many sectors, particularly those heavily reliant on physical presence, were severely affected during the pandemic. As businesses resume operations, there is a demand for skilled workers to fill positions that have remained vacant for extended periods.
Simultaneously, the shift towards remote work and technological advancements has led to a mismatch in the skills demanded and those available in the labor pool. Addressing this gap requires retraining and upskilling the workforce to ensure a seamless transition into the post-pandemic job market.
Charting the Course for Economic Resilience
Navigating the complexities of global economic recovery requires a coordinated effort from governments, businesses, and individuals. To build economic resilience, several key strategies can be adopted:
Strengthening Healthcare Systems and Vaccination
Prioritizing public health is fundamental to economic recovery. Governments must focus on bolstering healthcare infrastructure, ensuring sufficient medical supplies, and accelerating vaccination campaigns. A healthy workforce will instill confidence in employees and consumers, ultimately fostering economic growth.
Targeted Fiscal Support
Governments can offer targeted fiscal support to industries most impacted by the pandemic. Financial aid and incentives can help businesses recover and protect jobs. By tailoring support to specific sectors, governments can maximize the impact of their interventions.
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience
Diversifying and strengthening supply chains will mitigate the risks posed by disruptions. Businesses can explore alternative sourcing options and collaborate with partners to build redundancy and flexibility into their supply networks.
Transparency and Consistency in Policies
Transparent communication from policymakers, coupled with consistent and predictable policies, will encourage businesses to plan for the future confidently. This stability fosters a conducive environment for investments and economic growth.
Investment in Skills Development
Investing in workforce skills development is crucial to bridge the labor market gap. Governments, educational institutions, and businesses can collaborate to provide training programs that equip individuals with the skills needed for evolving job opportunities.
Embracing Technology and Innovation
Technological advancements offer transformative solutions for businesses to adapt to the changing landscape. Embracing innovation can streamline operations, enhance productivity, and open new avenues for growth.
In conclusion, global economic recovery is indeed hampered by various challenges arising from new COVID-19 waves, inflation, supply chain disruptions, policy uncertainties, and labor market adjustments. However, by adopting comprehensive strategies and fostering collaborative efforts, nations can navigate these turbulent times and chart a course towards a more resilient and prosperous future. The road ahead may be challenging, but with determination and cooperation, we can overcome these hurdles and emerge stronger than ever before.
What's In It For Me? (WIIFM)
In this blog article, you will gain valuable insights into the critical factors obstructing global economic recovery. Discover how new waves of COVID-19, rising inflation, supply chain disruptions, policy uncertainties, and labor market challenges intertwine to create a complex web of obstacles. Learn about the impact these challenges have on businesses, economies, and individuals worldwide. Most importantly, find out how you can contribute to and navigate through these challenging times, ensuring a resilient economic future.
Call to Action (CTA)
Ready to equip yourself with essential knowledge about the challenges hindering global economic recovery? Click here to read the full blog article and gain a comprehensive understanding of how new waves of COVID-19, rising inflation, supply chain disruptions, policy uncertainties, and labor market challenges are shaping the economic landscape. Let's work together to build a stronger, more sustainable global economy.
Blog Excerpt
The road to global economic recovery is far from smooth. As the world attempts to overcome the far-reaching impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, new waves of infections continue to emerge, necessitating ongoing restrictions and lockdowns. Alongside this, rising inflation and supply chain disruptions add to the complexities, impacting the prices of goods and the smooth flow of essential resources. Policy uncertainties further exacerbate the challenges, creating an environment of hesitation for investors and businesses. To add to the mix, labor market adjustments bring their own set of obstacles. This blog delves into the intricate web of these issues and explores potential solutions for a resilient global economic recovery.
Meta Description (320 characters)
Discover the hurdles obstructing global economic recovery: COVID-19 waves, inflation, supply chain disruptions, policy uncertainties, and labor challenges. Gain insights and solutions for a stronger future.
#Global economic recovery challenges#New waves of COVID-19 impact#Rising inflation consequences#Supply chain disruptions analysis#Policy uncertainties effects#Labor market challenges solutions#Economic recovery post-COVID#Global economic outlook#COVID-19 pandemic effects#Economic resilience strategies#Inflation surge implications#Supply chain bottlenecks#Policy implications for businesses#Labor market trends post-COVID#Economic recovery measures#COVID-19 and inflation link#Supply chain risks and solutions#Policy decisions and economic growth#Labor market shifts and adjustments#Post-pandemic economic challenges#Inflation control methods#Enhancing supply chain resilience#Policy clarity for investors#Future of labor markets#Global economy and pandemic impact#Inflationary pressures on economies#Supply chain optimization strategies#Policy stability and business investments#Labor market upskilling and reskilling#Economic recovery amidst uncertainties
0 notes
Note
You need a grippy sock vacation for thinking that a fucking cold needs this much worrying about.
Grow up and get a fucking life
Objective brain injury and associated cognitive impairment were noted as long as 1 year after infection with SARS-CoV-2.
Some patients with acute COVID-19 develop encephalitis and associated cognitive deficits. In addition, even among people with mild acute COVID-19, residual brain damage has been reported: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) from before and after COVID-19 showed gray matter loss that was not seen in matched control patients who didn't have COVID-19 (NEJM JW Gen Med Jun 1 2022 and Nature 2022; 604:697), and objective tests of cognition showed deficits that lasted at least 1 year after acute illness (NEJM JW Gen Med Mar 15 2024 and N Engl J Med 2024; 390:806).
In a multi-institutional U.K. study, researchers followed 351 people who had been hospitalized for acute COVID-19 (with or without neurological findings) and 3000 matched controls who didn't have COVID-19. All patients were assessed with MRI, subjective reports of cognition, formal cognitive testing, and serum markers of injury to neurons and astrocytes. Compared with controls, post–COVID-19 patients were more likely to have global cognitive deficits (subjective and objective), reduced volumes in several brain regions, and multiple serum markers of neuronal and astrocyte injury. Risk for neurocognitive sequelae was greater in patients with more-severe initial infections, postacute psychiatric symptoms, and encephalopathy during acute COVID-19. Encouragingly, longitudinal follow-up in 106 patients revealed a trend toward recovery.
"Just a cold"
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#wear a respirator#still coviding#pandemic#covid#covid 19#coronavirus#sars cov 2
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Can Math Predict the Future? Exploring Mathematical Forecasting
The idea of predicting the future using mathematics has fascinated humans for centuries. From forecasting weather patterns to predicting economic trends and even understanding social dynamics, math provides the framework for making sense of the world and anticipating what comes next.
1. Weather Forecasting: A Battle with Chaos
One of the most obvious examples of mathematical forecasting is weather prediction. Meteorologists rely on complex differential equations to model atmospheric conditions. These models, based on physical principles like fluid dynamics and thermodynamics, simulate the behavior of the atmosphere. But here’s the kicker—weather systems are chaotic. This means that tiny changes in the initial conditions can lead to vastly different outcomes, a phenomenon famously described by Edward Lorenz in the 1960s.
Lorenz’s work led to the development of chaos theory, which showed that deterministic systems (those governed by fixed laws) could still be unpredictable due to their sensitivity to initial conditions. This is why forecasts beyond a few days are often inaccurate: small errors compound exponentially, making long-term weather predictions difficult. Still, thanks to sophisticated computing and more accurate data, we can predict weather patterns with reasonable accuracy for about a week, and even then, the models rely heavily on continuous updates and refinement.
2. Exponential Growth and the Spread of Disease
In the world of epidemiology, mathematical models are essential for understanding the spread of infectious diseases. SIR models (Susceptible-Infected-Recovered) use ordinary differential equations to model how diseases spread through populations. These models take into account the rate of infection and recovery to predict the future trajectory of a disease.
The exponential nature of disease spread—especially in the early stages—means that without intervention, the number of cases can explode. For example, during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, exponential growth was apparent in the number of cases. The key to controlling such outbreaks often lies in early intervention—social distancing, vaccinations, or quarantine measures.
Exponential growth isn’t limited to disease, either. It applies to things like population growth and financial investments. The classic compound interest formula,
A = P \left(1 + \frac{r}{n} \right)^{nt}
demonstrates how small, consistent growth over time can lead to huge, seemingly unstoppable increases in value.
3. Predictive Algorithms: Making Sense of Big Data
Data science is at the cutting edge of forecasting today. Algorithms powered by big data are now able to predict everything from consumer behavior to stock market fluctuations and political elections. By identifying patterns in large datasets, these algorithms can forecast outcomes that were previously unpredictable.
For example, Amazon uses predictive models to forecast demand for products, ensuring they have inventory ready for expected sales spikes. Similarly, Netflix uses recommendation systems to predict what shows or movies you’ll watch next based on your previous choices.
Despite all the advances in predictive analytics, uncertainty remains a fundamental part of the picture. Even the best models can't account for random events (think of a sudden market crash or an unexpected global pandemic). As a result, forecasting is always a balance of probability and uncertainty.
4. The Limits of Mathematical Predictions: Enter Uncertainty
At the core of any discussion about forecasting is the recognition that math cannot predict everything. Whether it’s the weather, the stock market, or even the future of human civilization, uncertainty is a constant. Gödel’s Incompleteness Theorem reminds us that even within a well-defined system, there are true statements that cannot be proven. Similarly, Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle in quantum mechanics tells us that there’s a limit to how precisely we can know both the position and momentum of particles—unpredictability is embedded in the fabric of reality.
Thus, while math allows us to make educated guesses and create models, true prediction—especially in complex systems—is often limited by chaos, uncertainty, and the sheer complexity of the universe.
#mathematics#math#mathematician#mathblr#mathposting#calculus#geometry#algebra#numbertheory#mathart#STEM#science#academia#Academic Life#math academia#math academics#math is beautiful#math graphs#math chaos#math elegance#education#technology#statistics#data analytics#math quotes#math is fun#math student#STEM student#math education#math community
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
full article under the cut
A Visual Breakdown of America’s Stagnating Number of Births
By Anthony DeBarros
About 3.66 million babies were born in the U.S. in 2022, essentially unchanged from 2021 and 15% below the peak hit in 2007, according to new federal figures released Thursday.
The provisional total—3,661,220 births—is about 3,000 below 2021’s final count, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Health Statistics. Final government data expected later this year could turn that small deficit positive.
Experts have pointed to a confluence of factors behind the nation’s recent relative dearth of births, including economic and social obstacles ranging from child care to housing affordability.
Absent increases in immigration, fewer births combined with ongoing baby boomer retirements will likely weigh on the labor force supply within the next 10 years, said Kathy Bostjancic, chief economist at Nationwide, an insurance and financial-services company.
“You’re going to have a real shortage of workers unless we have technology somehow to fill the gap,” Bostjancic said.
A look at the trends in charts:
Births stay well off peak
The government tallied about 655,000 fewer births in 2022 than the 2007 high of 4.32 million, reflecting ongoing decreases. With still-elevated deaths due in part to the latter phase of the Covid-19 pandemic, the U.S. in 2022 saw only about 385,000 more births than deaths.
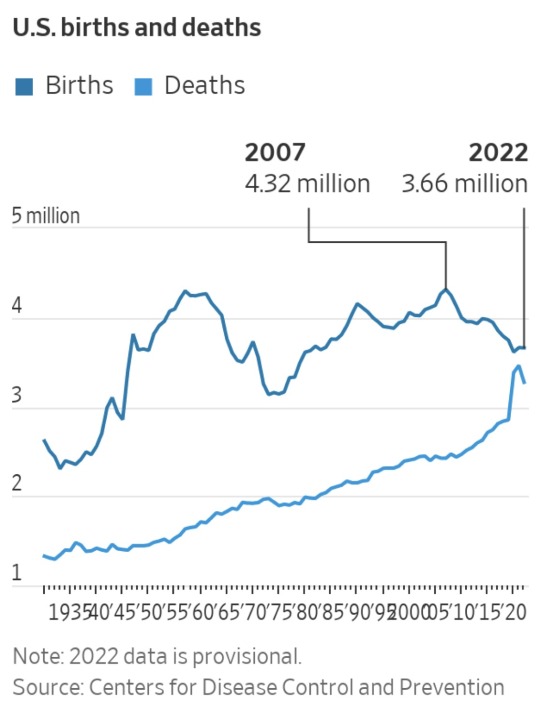
The 2022 total might tick higher when final data is tallied later this year. Final 2021 births were about 5,000 above the provisional number; for 2020, the final tally was about 8,400 greater.
Fertility remains below ‘replacement’ level
The total fertility rate—closely watched because a level of 2.1 children per woman is the “replacement rate” needed for a population to maintain current levels—was 1.665 in 2022. That was essentially unchanged from 1.664 in 2021 and only a slight recovery from a record low in 2020.
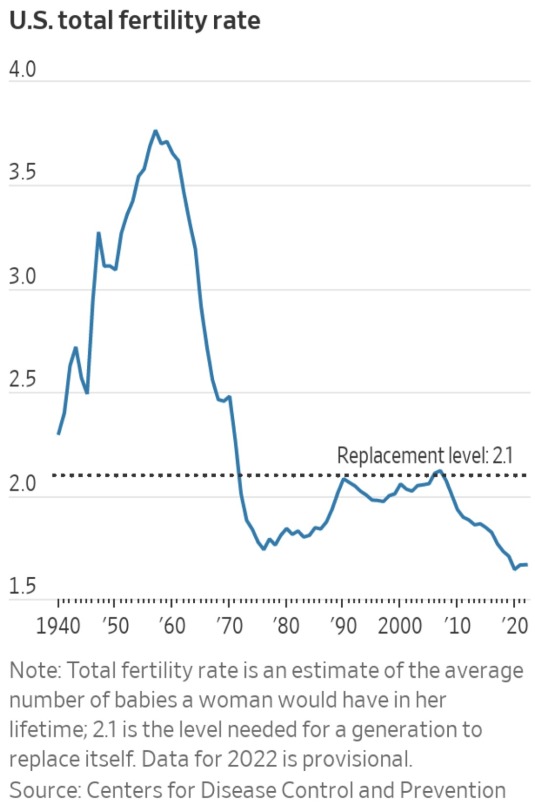
The U.S. has generally been below replacement level since the early 1970s.
Hispanic fertility rates climb
The general fertility rate for Hispanic mothers increased 4% in 2022, second only to people of Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander origin. Fertility rates among Asian women rose 3%; rates for all other groups fell.
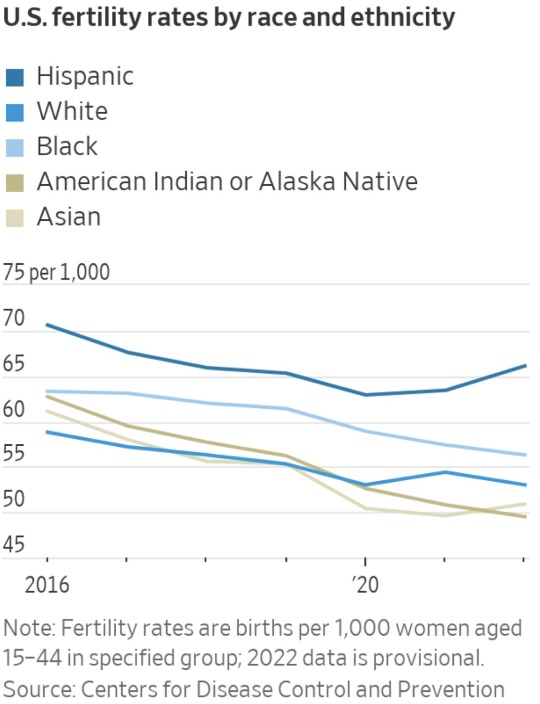
Hispanic mothers accounted for 25.5% of U.S. births in 2022, a record, while the shares of births from non-Hispanic white and Black women declined. White women accounted for 50.1% of births in 2022, Black women for 13.9%, and Asian women for 6%.
Birthrates continue declining among the young
The trend of decreasing birthrates among younger women continued in 2022. For teens ages 15 to 19, the birthrate fell 3%, and for ages 20 to 24 it was down 2%. The rate for the next oldest group, 25 to 29, edged up only slightly. Increases were mainly seen among women 35 to 44.

If trends continue, the birthrate for women ages 35 to 39 might soon eclipse the rate for ages 20 to 24.
#let’s go even lower!!!!!#deny this country a population!!!!#won’t even take care of the women they need sooo bad for incubating workers 😢#lots of contingencies to account for but still. this could be promising#esp since—as i would like to remind everyone—the U.S.’s maternal mortality rate rn is the highest it’s been since 1965
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
China’s recently announced GDP target for 2024 remains unchanged from last year, at 5 percent. But even if the country hits that number, its economic problems run deep. In January, China published economic data for the last quarter of 2023 which put its annual GDP growth rate at 5.2 percent, beating the government target. Yet, to put things in perspective, China’s real GDP growth rate from 2011 to 2019 averaged 7.3 percent while 2001-10 saw average growth of 10.5 percent.
After the figures dipped in 2020 to 2.2 percent owing to COVID-19, expectations for post-pandemic recovery were high. This was rooted in the assumption that China lifting its dynamic zero-COVID policy in January 2023 would unlock pent-up demand in the economy, which remained suppressed during the two-year-long lockdown. But that hasn’t happened. Some observers even doubt the recently released GDP data’s authenticity and suspect the numbers are far below the official figures.
But even if the figures are accurate, the wider trends of the Chinese economy suggest a worrying state of affairs. To begin with, this was the first time since 2010 that China’s real GDP growth rate exceeded its nominal GDP growth rate (4.8 percent). The nominal growth rate is calculated on the previous year’s numbers without accounting for inflation. Discounting inflation is necessary to remove any distortion arising from a mere increase in the prices of goods and services. Thus, the real GDP figure is calculated after adjusting for inflation to reflect the increase in output of goods and services. This is also the number economists and governments refer to when stating GDP growth numbers.
Usually, the nominal growth rate should be higher than the real growth rate. But in a deflationary year, the real growth rate can give a distorted picture, because deflation or negative inflation amplifies the real numbers. Thus, the fact that China’s real GDP number exceeded its nominal number indicates that Beijing’s gross value of output in real terms was amplified thanks to negative inflation, i.e. a general decrease in the prices of goods and services. If not for deflation, China’s real GDP growth in 2023 would have been even lower and would have certainly missed the national target of 5 percent.
The news on China’s gross fixed capital formation (GFCF) isn’t encouraging either. The term refers to the acquisition of fixed assets such as land and machines or equipment intended for production of goods and services. It is one of the four components of GDP (besides exports, household consumption, and government expenditure) and a measure of investment in the economy. For decades, China relied on a high GFCF rate to power its economy, but it has witnessed a sustained decline under President Xi Jinping’s leadership. For reference, the GFCF growth rate in the last 9 years (2014-22) averaged 6.7 percent as compared to 13 percent in the 21 years before that (1994-2014). It hit over 10 percent only on four occasions in the last nine years, once in 2021 thanks only to a significantly low base due to the pandemic year.
The bulk of this investment came from the real estate sector, which constituted a quarter of China’s total investments in fixed assets. Between 1994 and 2014, the sector witnessed a year-on-year growth rate of around 30 percent. But in the last eight years, the property sector has witnessed average growth of only 4.2 percent—and shrank by 10 percent from 2021 to 2022.
In part, the drop in investment can be attributed to the conscious decision of the central leadership under Xi to deflate the property bubble, which had become unsustainable, and reallocate and redirect capital from speculative to more productive forces. The decelerating impact this decision has had on China’s GDP has forced leadership to reverse its policies to some degree, trying to prop up the bubble. But the forced deflation is now proving too resistant to change, as is evident from the 2023 numbers that suggest the real estate sector shrunk by 9.6 percent.
But that’s not the only reason for the drop in investment. In the past year, China’s economy has witnessed an increasing securitization of its development. On numerous occasions, including at the 20th Party Congress in 2022 and the Two Sessions in 2023, Xi has underlined that the idea of development cannot be isolated from that of security. In a meeting of the Chinese Communist Party’s National Security Commission last year, Xi reiterated the need to “push for a deep integration of development and security.”
Consequently, in the first half of 2023, Chinese authorities carried out a series of crackdowns on foreign and domestic consultancy companies that offered consultancy services to help overseas businesses navigate China’s challenging regulatory environment. The infamous instances included raids on U.S. companies Mintz in March and Bain & Company in April. In May, Shanghai-based consultancy Capvison saw its offices raided for stealing state secrets and transferring sensitive information to its foreign clients. Weeks later, China’s Cyberspace Administration announced that U.S. chip giant Micron failed to obtain security clearance for its products.
This need to put security over the economy further became apparent in China’s revision of its counter-espionage law, which came into effect in July 2023. The updated law not only broadens and dilutes the definition of espionage but also confers wide-ranging powers on local authorities to seize data and electronic equipment on account of suspicion. China’s new developmental security approach, which manifested in its crackdown on foreign and domestic consultancies alike, has spooked private investors since then.
The government has issued repeated assurances to both domestic and foreign investors to improve the business environment and spur investment. However, investment in fixed assets by private holding companies has been declining since 2018. It briefly rebounded in 2021, only to drop again in 2022. The data for 2023, although not yet updated, is unlikely to pick up.
In contrast, investment by the state has gone up to compensate for the decline in private investment. But this can’t be a substitute in the long run for two reasons. First, rising government debt at a time when private investment is declining can lead to crowding out of capital, thereby shrinking the resource pool for private businesses. And second, the government has already stretched itself as its debt-to-GDP ratio rose to 55.9 percent in 2023. Given the mounting debt situation, there exists very little room for the government to even sustain, let alone expand, its current expenditure.
The data on China’s net exports suggests their contribution to GDP, although steadily picking up since recording a low in 2018, is unlikely to return to the glory years of 2001-14. While China will continue to be a leading export nation, the contribution of net exports to its growth rate might not be high. Poor external demand also means that export-oriented investments will see a decline, thereby pulling the overall investment rates further down albeit with a lag.
China’s strategy in the wake of this situation has been to seek to boost domestic consumption and household spending. Yet for domestic consumption to emerge as a new engine of growth requires not only sustaining its previous momentum but also increasing its share as a percentage of GDP to compensate for the loss of growth due to falling investment (in property and export-oriented sectors) rate.
However, a look at China’s household consumption expenditure as a percentage of GDP suggests that it has remained significantly low compared to other consumption-driven advanced and emerging economies. For instance, in both the United States and India, household consumption makes up more than 55 percent of GDP. In contrast, China’s household consumption has historically hovered around 40 percent—and dropped to 37 percent in 2022.
To add to the misery, the growth of China’s household consumption expenditure is also declining in the wake of a pandemic that left the public deeply insecure about their financial future. For ten years (2010-19), growth remained stable at around 10 percent before the pandemic forced the household consumption growth rate to drop to zero in 2020. After recording an uptick in 2021from that low, the growth rate dropped again in 2022. The negative difference between the nominal and real GDP in 2023, indicative of deflation, further confirmed the sluggish demand in the economy.
Thus, domestic consumption seems unlikely to be able to fuel China’s growth. The rising unemployment rate, declining consumer confidence, aging population, and rising dependence ratio will further burden any attempt to raise China’s consumption.
These trends may be baked in the near to medium term. China will not see a return to the high growth rates witnessed in 1980-2010 and will instead stabilize near 4 percent. This will likely derail China’s plan to transition from a middle- to a high-income country and certainly dent Xi’s dream of transforming China into an advanced socialist country. The much-dreaded fear of the “middle-income trap” is real for China.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Class 2: Corona vs. Heineken
I must preface this blog post by saying that I do not drink very often, and I can probably count the number of times I have had Corona and Heineken brand products on one hand. Even though I am not a subject matter expertise on this topic, I still felt the case was quite interesting, and I am excited to explore and analyze the learnings of this case in class on Thursday. After reading this week's case on Corona beer, three main ideas came to mind.
Firstly, I thought it was fascinating to read that even though this case was written years ago, it identified a decline in alcohol consumption. This challenged my assumptions about drinking trends over the past 30 years. It is a common phrase nowadays to discuss how people drink much less than they used to, and in fact, there is a record low level of alcohol use among generation Z. The question remains whether this generation in general has converted to alternative substances or whether society is taking health and wellness more seriously than in generations past. Many scientific studies are showing the negative effects of alcohol consumption, even as little as one standard drink, on recovery and sleep. I am curious to hear an update on the case and how Heineken and Corona are addressing this trend. I know that Heineken has created and promoted a non-alcoholic beer, however from a sales and revenues perspective, I am not confident in the success metrics of this new product. I would also be fascinated to see quantitative evidence of this trend especially throughout the Covid-19 pandemic and the years following.
Second, I learned that the relatively recent misconceptions about the Corona brand are not the first instance where this brand has had to handle unfortunate press. The article mentioned a few cases of false contamination of the product which led to marketing damage control and the rebuilding of trust within the brand. With the Covid-19 pandemic being referred to as 'Corona,' I do recall hearing media stories of the Corona beer products dropping in sales.
Finally, I was shocked when the case mentioned that selling beer is just marketing and not actual skill in making the product itself. The case discussed the relative ease in which beers can be made, so beer companies are in fact selling a brand, feeling, association, and confidence. As mentioned above, I am not an expert on the brand differences between Heineken and Corona, so I will be quite interested to hear from my classmates of the markets and demographics that each brand is attempting to target.
#MITSloanBranding2024A
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tourism Market: Trends, Growth, and Industry Players
Introduction
The global tourism market is a dynamic sector that continually evolves in response to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and global events. As we delve into the current landscape, it is crucial to explore the tourism market size, growth patterns, industry trends, and key players that shape the sector's trajectory.
Tourism Market Size and Growth
The tourism market has witnessed remarkable growth over the past decade. According to the latest data the global international tourist arrivals reached 1.5 billion in 2022, marking a 4% increase from the previous year. The tourism industry's robust growth is attributed to factors such as increased disposable income, improved connectivity, and a growing middle class in emerging economies.

The COVID-19 pandemic, however, significantly impacted the industry in 2020 and 2021. International tourist arrivals plummeted by 74% in 2020, representing the largest decline in the industry's history. As the world recovers from the pandemic, tourism is experiencing a resurgence. The UNWTO estimates that international tourist arrivals will surpass pre-pandemic levels by 2023, emphasizing the sector's resilience.
Tourism and Hospitality Industry Trends
The tourism and hospitality industry is undergoing transformative changes driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer behaviors. One notable trend is the rise of sustainable tourism. Travelers are increasingly prioritizing destinations and businesses that adopt eco-friendly practices. Hotels, airlines, and tour operators are responding by implementing sustainable initiatives to meet the demands of environmentally conscious travelers.
Another trend shaping the industry is the integration of technology. From mobile apps for seamless bookings to virtual reality experiences, technology is enhancing the overall travel experience. The use of artificial intelligence and big data analytics is also becoming prevalent, enabling businesses to personalize services, predict consumer preferences, and optimize operations.
Tourism Industry Players
The tourism market is comprised of a diverse range of players, including governments, international organizations, tour operators, airlines, hotels, and online travel agencies (OTAs). Notable industry players such as Airbnb, Expedia, and Booking. com have disrupted traditional hospitality models, offering travelers a wide array of accommodation options and personalized experiences.
Governments play a crucial role in shaping the tourism landscape through policies, infrastructure development, and destination marketing. Collaborations between public and private sectors are essential to foster sustainable growth and address challenges such as over-tourism and environmental impact.

Tourism Market Analysis
A comprehensive analysis of the tourism market involves assessing key factors such as market dynamics, competitive landscape, and regulatory environments. The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a powerhouse in the tourism sector, with countries like China, India, and Japan experiencing substantial growth. In contrast, established destinations in Europe and North America continue to attract millions of tourists annually.
The post-pandemic recovery has prompted a shift in travel preferences, with a surge in demand for domestic and outdoor experiences. Travelers are seeking off-the-beaten-path destinations, contributing to the diversification of the tourism market.
Travel and Tourism Industry Outlook
Looking ahead, the outlook for the travel and tourism industry is optimistic. The industry is expected to rebound strongly, driven by pent-up demand, increased vaccination rates, and the easing of travel restrictions. The global tourism market is projected to reach $11.38 trillion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.1% from 2020 to 2027.
In conclusion, the tourism market is a vibrant and resilient sector that continues to adapt to changing circumstances. Understanding the market size, growth trends, industry players, and emerging dynamics is crucial for stakeholders navigating the evolving landscape. As the world reopens for travel, the industry's ability to innovate and embrace sustainable practices will play a pivotal role in shaping its future success.
#market research#business#ken research#market analysis#market report#market research report#travel and tourism sector#travel and tourism market#travel and tourism industry#tourism sector#tourism market trends#tourism market size#tourism market players#tourism market forecast
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Crowdsourcing: not a new concept

what is crowdsourcing?
By using the Internet, social media, and smartphone apps, a huge number of individuals can contribute their work, information, or opinions through a process known as crowdsourcing.
While some crowdsourcing participants carry out menial jobs willingly, others work as paid freelancers. For instance, in order to give app users access to up-to-date, real-time information, traffic applications such as Waze incentivize drivers to self-report accidents and other traffic occurrences. (Hargrave, 2022) Crowdsourcing is a collaborative approach that involves sourcing information, ideas, or services from a wide and diverse group of individuals, known as the "crowd." This decentralized method relies on the collective intelligence and varied expertise of contributors, often facilitated through online platforms. Crowdsourcing is characterized by an open call for participation, inviting individuals to provide solutions, ideas, or content to address specific challenges or tasks.

Crowdsourcing in crisis
Amid the global, ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, among the tireless work of health care workers, policy makers, and government officials across various nations, there is another player with “skin in the game” if you will—crowdsourcing projects. Crowdsourcing is a model whereby individuals or organizations obtain goods and services, including ideas, from a large, relatively open community of digital media, Internet users, and an entire array of diverse stakeholders sharing a common interest from a range of perspectives and experiences.1 Although crowdsourcing originated long before the advent of digital age, in the current era of social media and other digital outlets, crowdsourcing has become a fairly commonplace solution. (Desai, 2020) Crowdsourcing in health and medical mostly started in the bioinformatics and technology fields about 2010. Its broad usefulness in disaster crisis management has, however, mostly gone unutilized. We address the ongoing and present uses of crowdsourcing in the COVID-19 era from this point of view. The COVID-19 pandemic, which has infected > 5 million people worldwide and caused > 330,000 deaths at the time of this writing, is no less than a disaster crisis, albeit biological. A disaster life cycle consists of the steps taken in planning for and responding to a particular disaster (Fig 1). This disaster cycle is used throughout the emergency management community, from the local to the national and international levels. We saw similar disaster mitigation (social distancing), preparedness (quarantine restrictions), response (masking), and recovery efforts during the 1918-1920 seasonal H1N1 flu pandemic. (Kuderer, 2020)
Community for creatives
Crowdsourcing funding for projects, businesses, and causes is expected to grow to be a $300 billion industry in the near future, according to estimations made by the crowdfunding trends blog Fundly. In 2017, Stanford University student Nicholas Benavides, the creator of the Blue Ocean Entrepreneurship Competition for Students, conducted an analysis of over 2,000 Kickstarter project data to identify the elements of a successful crowdfunding campaign. Benavides surveying the terms used in a campaign's title and blurb using the Kaggle Kickstarter dataset developed a model that could predict a campaign's success with 75% accuracy. (Sickler, 2020) Among his major findings was that the most common words–game, new, design, world–appeared equally in both funded and unfunded campaigns. The major point of differentiation was not in word choice but between those categories inherently more social in nature, such as Comics, Dance, Music, Theater and Design, and solo practices like Craft and Journalism. Social categories were simply a more natural fit for the success criteria of crowdfunding.
Role of crowdsourcing in Web3
Crowdsourcing in Web3 refers to the decentralised process of obtaining goods or services from a large, undefined group of people via the internet, rather than from traditional employees or suppliers. The role of crowdsourcing in Web3 is to empower individuals and communities to collaborate and contribute their skills, knowledge, and resources to create and maintain decentralised applications and services that are more equitable, transparent, and secure. This can lead to increased innovation, collaboration, and democratisation in the development and deployment of new technologies, as well as in the creation of new forms of governance and value exchange. (Reffell, 2023)
Crowdsourcing in Web3 examples:-
DAOs: Decentralised autonomous organisations (DAOs) are organisations that are run through rules encoded as computer programs on a blockchain network. DAOs are governed by their members, who vote on proposals and make decisions collectively. Examples of DAOs include MakerDAO and Aragon.
Prediction Markets: Prediction markets are decentralised platforms that allow users to make predictions on the outcome of events and earn rewards for accurate predictions. Examples of prediction markets include Augur and Gnosis
Decentralised Exchanges (DEXs): Decentralised exchanges are platforms for trading cryptocurrencies and tokens without the need for a central authority or intermediaries. Examples of DEXs include Uniswap and Curve.
Decentralised Identity Systems: Decentralised identity systems are platforms that allow users to control and manage their personal information and data, rather than relying on central authorities or intermediaries. Examples of decentralised identity systems include Sovrin and uPort.
In conclusion, by utilising the combined knowledge of many participants, crowdsourcing has the potential to revolutionise creativity and problem-solving. Its capacity to combine a variety of viewpoints and abilities not only encourages innovation but also offers an economical way to address difficult problems. Its attractiveness stems from the speed at which solutions are generated and the active participation of communities, which fosters the growth of unorthodox ideas. But obstacles like upholding quality control and handling moral issues like equitable recompense and privacy issues highlight the necessity of cautious execution. With the integration of intelligent algorithms and automation in technology, crowdsourcing looks to have a bright future ahead of it, providing even more effective and significant collaboration in a variety of disciplines.

REFERENCE
Desai, A., Kuderer, N. M., & Lyman, G. H. (2020). Crowdsourcing in crisis: Rising to the occasion. JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics, (4), 551–554. https://doi.org/10.1200/cci.20.00054
Hargrave, M. (n.d.). Crowdsourcing: Definition, how it works, types, and examples. Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/crowdsourcing.asp#:~:text=While%20crowdsourcing%20often%20involves%20breaking,samples%20for%20a%20small%20fee.
Reffell, C. (2023, February 7). What is the role of crowdsourcing in web3?. Crowdsourcing Week. https://crowdsourcingweek.com/blog/crowdsourcing-in-web3/#:~:text=Crowdsourcing%20in%20Web3%20is%20made,transactions%20and%20interactions%20between%20participants.
Sickler, E., & Erin Sickler Erin Sickler is a mindfulness & creativity coach living in the Hudson Valley. A former NY art curator. (2020, September 2). How to launch a Creative Crowdfunding Campaign for your next art project. art journal. https://artrepreneur.com/journal/creative-crowdfunding-for-artists/#:~:text=A%20well%2Ddesigned%2C%20online%20crowdfunding,win%20you%20fans%20for%20life.

3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Aluminium Wire Prices, News, Trend, Graph, Chart, Monitor and Forecast
The aluminium wire market has experienced significant fluctuations in recent years, driven by a complex interplay of factors that influence supply, demand, and pricing dynamics. Aluminium wire, widely used across industries such as electrical transmission, construction, automotive, and telecommunications, remains a crucial commodity in the global economy. The pricing trends of aluminium wire are inherently linked to the performance of the broader aluminium market, which is influenced by global economic conditions, raw material availability, energy costs, and geopolitical factors. As a lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and highly conductive material, aluminium wire continues to see robust demand, particularly with the growing adoption of renewable energy infrastructure and electric vehicles.
The primary driver of aluminium wire prices is the cost of raw aluminium, which is derived from bauxite ore through energy-intensive processes like Bayer refining and Hall-Héroult smelting. The availability and price of bauxite, along with energy costs, significantly impact production expenses. Additionally, market prices are influenced by factors such as import-export policies, trade restrictions, and tariffs. In recent years, disruptions in bauxite supply chains, particularly from major producers like Australia, Guinea, and China, have led to price volatility. Political instability in resource-rich regions and policy changes in key markets have further added to the unpredictability in aluminium wire pricing.
Get Real time Prices for Aluminum Wire: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Pricing-data/stainless-steel-1502
Global economic growth plays a crucial role in determining aluminium wire prices. During periods of strong economic expansion, infrastructure projects and industrial activities increase, driving up the demand for aluminium wire. Conversely, economic slowdowns, like the one witnessed during the COVID-19 pandemic, lead to reduced demand and downward pressure on prices. The pandemic-induced disruptions to global supply chains caused significant fluctuations in aluminium prices, with initial declines followed by sharp recoveries as industries resumed operations and governments implemented stimulus packages to boost infrastructure development.
Energy costs are another critical factor in aluminium wire pricing. The aluminium production process requires substantial electricity, and any fluctuations in energy prices, particularly for fossil fuels and electricity, directly impact production costs. In regions where energy prices are high, aluminium wire producers face higher production costs, which are often passed on to consumers through increased prices. The global push toward cleaner energy sources and the associated costs of transitioning to renewable energy have also affected the aluminium market. As more aluminium producers adopt sustainable practices and invest in energy-efficient technologies, production costs may stabilize, potentially influencing aluminium wire prices.
The automotive industry, particularly the rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs), has significantly influenced aluminium wire demand and pricing. Aluminium wire is essential for lightweight wiring systems in EVs, contributing to improved energy efficiency and vehicle performance. With major automakers committing to electrification and governments worldwide promoting EV adoption through incentives and regulatory measures, the demand for aluminium wire has surged. This growing demand has contributed to upward pressure on prices, especially as manufacturers compete for high-quality aluminium products.
In the construction sector, aluminium wire is extensively used in electrical wiring, structural components, and infrastructure projects. Urbanization, population growth, and infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies like India, China, and Southeast Asia, have driven consistent demand for aluminium wire. Large-scale infrastructure projects, such as smart city initiatives, renewable energy installations, and high-speed rail networks, have further boosted market growth. However, fluctuations in construction activity, driven by factors like interest rate changes and economic policies, have led to periodic price variations in the aluminium wire market.
Geopolitical factors, including trade tensions, sanctions, and international agreements, have also played a significant role in aluminium wire pricing. The imposition of tariffs and sanctions on major aluminium producers, such as Russia and China, has led to supply chain disruptions and increased prices in certain regions. Trade policies implemented by the United States, the European Union, and other major economies have influenced the flow of aluminium products across borders, impacting regional price disparities. Additionally, currency fluctuations and changes in global trade dynamics contribute to the complexity of pricing in the aluminium wire market.
Technological advancements and innovations in aluminium wire manufacturing have introduced new market dynamics. The development of high-performance alloys, improved production techniques, and the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes have enhanced product quality and efficiency. As manufacturers invest in research and development to create aluminium wires with superior conductivity, strength, and durability, production costs and pricing strategies may evolve accordingly. Furthermore, the increasing focus on recycling and the circular economy has led to the growth of secondary aluminium production. Recycled aluminium requires significantly less energy compared to primary production, potentially mitigating price increases and contributing to more sustainable pricing trends.
Regional variations in aluminium wire prices reflect differences in supply chain structures, production capacities, and demand patterns. Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, remains a dominant player in the aluminium wire market due to its vast manufacturing base and ongoing infrastructure development. North America and Europe, while also significant markets, experience price variations influenced by energy costs, environmental regulations, and import policies. In Latin America and Africa, the availability of raw materials like bauxite and growing industrialization efforts contribute to regional price dynamics.
The outlook for aluminium wire prices remains subject to the interplay of these multifaceted factors. As the world transitions toward cleaner energy sources, the demand for aluminium wire in solar, wind, and electric grid applications is expected to rise. However, potential supply chain disruptions, energy price fluctuations, and geopolitical developments could lead to continued price volatility. Market participants, including manufacturers, traders, and consumers, must stay attuned to these dynamics to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the aluminium wire market effectively.
Get Real time Prices for Aluminum Wire: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Pricing-data/stainless-steel-1502
Contact Us:
ChemAnalyst
GmbH - S-01, 2.floor, Subbelrather Straße,
15a Cologne, 50823, Germany
Call: +49-221-6505-8833
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.chemanalyst.com
#Aluminium Wire#Aluminium Wire Price#Aluminium Wire Prices#Aluminium Wire Pricing#India#united kingdom#united states#Germany#business#research#chemicals#Technology#Market Research#Canada#Japan#China
0 notes
Text
Harvesting Opportunities: A Strategic Analysis of the Wine Tourism Market
The global wine tourism market size is anticipated to reach USD 106.74 billion by 2030 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.9% from 2024 to 2030, to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. This growth is primarily attributed to increasing consumer interest in unique and immersive travel experiences, the expanding global wine culture, and the rising popularity of wine-related activities such as tours and tastings. Enhanced digitalization and online booking platforms also drive market growth by improving accessibility and convenience for travelers.
According to the Arizona Wine Tourism Industry Survey 2023, the growth in the wine tourism market in the U.S. is highlighted by high levels of repeat visitation, with 80% of winery visitors returning frequently and 42% of festival-goers attending multiple times. This trend highlights the sector's strong customer loyalty and sustained appeal. Additionally, the presence of out-of-state and international visitors, including from Canada and Mexico, indicates expanding regional and global interest, further driving market growth and diversification.
The global wine tourism market is expanding, with emerging destinations such as Moldova, Croatia, and Georgia gaining prominence. These regions are leveraging their unique cultural and historical assets to attract visitors. Moldova is noted for its extensive underground cellars, Croatia combines wine with agritourism and gastronomy, and Georgia is capitalizing on its ancient winemaking traditions. Bulgaria and Ethiopia are also making strides, with Bulgaria’s historic wineries and Ethiopia’s new wine production venture showing growing appeal.
Millennials are a key driver of this growth, favoring immersive wine experiences and value-focused wines. Despite budget constraints, they actively seek out winery tours and tastings, often using online tools for planning. In Arizona, a significant portion of wine tourists are repeat visitors, and wine festivals are increasingly popular for purchases and extending travel experiences. Word of mouth and social media play crucial roles in promoting wineries and festivals, with the Verde Valley region standing out for its high visitor spending.
The Global Report on Covid-19’s impact on wine tourism revealed significant disruption across the industry, with the majority of wineries experiencing drastic declines in turnover and international visitors. In 2020, over 80% of wineries reported losses in revenue, with 47% facing a decrease of more than 90% in international visitors. Despite these setbacks, wineries were optimistic about a recovery, with 90% expecting wine tourism to return to pre-pandemic levels by 2022. The majority were planning to maintain or increase their investment in wine tourism, indicating a long-term positive outlook for the sector.
Wine Tourism Market Report Highlights
Based on service, wine tastings and tours dominated the wine tourism market with over 57% of the revenue share in 2023. This is due to their unique appeal, offering immersive experiences in vineyards, insights into winemaking, and opportunities to sample exclusive wines. Growing consumer interest in authentic travel and the rise of premium wineries have further boosted the demand for these experiences.
The demand for wine tourism among international tourists is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.3% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is driven by heightened global interest in unique cultural experiences, the growing popularity of wine regions as vacation spots, and targeted marketing by wineries. Improved infrastructure and expanded direct flights to emerging wine regions are also enhancing accessibility, fueling this growth.
Based on booking mode, direct bookings accounted for over 38% of revenue share in 2023, reflecting a preference for personalized booking experiences and the ease of accessing winery websites. These bookings provide consumers with better control over their itineraries, immediate confirmation, and often exclusive deals, driving their significant contribution to market revenue.
In 2023, Europe led the global wine tourism market with over 51% of total revenue, owing to its rich wine culture and attractive wineries in Spain, Italy, and France. Innovations such as France's Vignobles & Découvertes label, which features 72 destinations, and the U.K.'s 55% increase in vineyard visits in 2024, have significantly driven market growth.
Key companies in the wine tourism market are expanding their market share by leveraging a strong brand presence and innovative offerings, supported by digital marketing and travel agency partnerships. They are focusing on personalized and exclusive experiences, such as private vineyard tours and curated tastings, and are bundling wine tours with cultural and gastronomic activities to meet the growing demand for experiential travel.
In July 2024, Domaine de la Dourbie in France launched new immersive experiences to celebrate its 20th anniversary, including wine tastings, an interactive wine tour, and an open-air brunch with a DJ. The estate, located in the Hérault Valley, now features a modernized winery and collaborations with local producers for organic wine products. The interactive tour, developed with VinoWays, enhances visitor engagement through a digital platform with videos and an audio guide, reflecting a growing trend in wine tourism towards immersive and experiential activities.
Wine Tourism Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global wine tourism market based on service, tourist type, booking mode, and region:
Wine Tourism Service Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
Wine Tastings and Tours
Wine Festivals and Events
Others
Wine Tourism Tourist Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
Domestic
International
Wine Tourism Booking Mode Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
Direct Booking
Travel Agencies
Online Marketplaces
Wine Tourism Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
North America
US
Canada
Mexico
Europe
Germany
UK
France
Italy
Spain
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
Australia
Central & South America
Brazil
Argentina
Middle East & Africa
South Africa
Key Players in the Wine Tourism Market
The Prisoner Wine Company
VIAVINUM, S.L
Wine Paths
Grape Escapes
Cellar Tours
BKWine Tours
Pure Luxury Transportation
Backcountry Wine Tours
Sula Vineyards
Wine Compass
Order a free sample PDF of the Wine Tourism Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
In a recent study published in The Lancet, researchers updated their analysis from the original Eight Americas study to reflect current life expectancy disparities in the United States.
What is the Eight Americas study? The Eight Americas study was published nearly two decades ago to provide crucial insights into life expectancy inequities in the United States. Herein, the U.S. population was categorized into eight groups based on race, geographical location, urbanicity, income per capita, and homicide rates.
In 2001, the Eight Americas study reported gaps of 12.8 years for females and 15.4 years for males in life expectancy, with the observed disparities in mortality particularly large for young and middle-aged males.
In the current study, scientists update and expand the original Eight Americas study by examining trends in life expectancy between 2000 and 2021 for ten Americas categorized by age, sex, and age group. The ten Americas included analogs to the original eight groups, as well as two additional groups comprising the U.S. Hispanic or Latino population.
Important observations The ten categories of Americas included Asian individuals, Latino individuals in other counties, White, Asian, and American Indian or Alaska Native (AIAN) individuals in other counties, White individuals in non-metropolitan and low-income Northlands, Latino individuals in the Southwest, Black individuals in other counties, Black individuals in highly segregated metropolitan areas, White individuals in low-income Appalachia and Lower Mississippi Valley, Black individuals in the non-metropolitan and low-income South, and AIAN individuals in the West.
The lowest life expectancy in 2000 was among Black Americans residing in non-metropolitan and low-income counties in the South and highly segregated metropolitan regions, as well as AIAN individuals in the West. The second lowest life expectancy was observed for White Americans in low-income counties in Appalachia and the Lower Mississippi Valley.
Between 2000 and 2010, life expectancy increased for all Americas except for AIAN individuals in the West, who experienced a one-year reduction.
Further reduction in life expectancy was observed for AIAN individuals in the West between 2010 and 2019. A smaller reduction was observed among White Americans residing in low-income counties in Appalachia and the Lower Mississippi Valley, Black Americans in non-metropolitan and low-income counties in the South, as well as White Americans in non-metropolitan and low-income counties in the Northlands.
During the first year of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, life expectancy significantly decreased across the Americas. However, the extent of this decline varied widely among Americans.
A slight recovery of life expectancy was observed for Black Americans in highly segregated metropolitan areas, Asian Americans, and Latino Americans in other countries between 2020 and 2021. However, for other Americans, life expectancy continued to decline during this period.
In some cases, significant variations in life expectancy rates were observed by sex and age group. Significant variations in income and educational attainment were also observed between the ten Americas.
These differences had varying impacts on life expectancy. For example, AIAN individuals residing in other counties had the highest income and educational attainment in most years; however, these individuals were ranked fourth or fifth in life expectancy before 2020.
These disparities reflect the unequal and unjust distribution of resources and opportunities and have profound consequences for the wellbeing and longevity of marginalized populations."
Conclusions In 2000, a 12.6-year gap in life expectancy was observed among the Americas, which gradually increased by 2010 and accelerated to 20.4 years after the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
AIAN individuals in the West were the only Americans who experienced a reduction in life expectancy over the two-decade period preceding the COVID-19 pandemic. Low healthcare accessibility, unemployment, low education attainment, and systemic discrimination may contribute to reduced life expectancy among AIAN individuals in the West.
A significant improvement in life expectancy was observed among the three categories of Black Americans during the study period. A significant improvement in educational facilities, reduction in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- and cardiovascular disease-related deaths, and reduced homicide rates likely contributed to the improved longevity and reduced life expectancy disparities among Black Americans.
A significantly longer life expectancy was observed among Latino Americans as compared to that of White Americans. The longer life expectancy might be associated with the higher life expectancy, specifically among foreign-born Latino individuals.
The largest reduction in life expectancy during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic was observed among AIAN, Black, and Latino Americans, which may be attributed to systemic racism and racial inequities observed during the pandemic. Considerable inequalities among White Americans by geographical location and income level were also observed, which may be due to variations in income and educational attainment among these individuals.
These findings emphasize the importance of addressing and analyzing the different factors contributing to life expectancy disparities in the U.S. to ensure that all Americans can live healthy lives, regardless of their geographical location, race, ethnicity, or income.
It is time for us to take collective action; to invest in equitable health care, education, and employment opportunities; and to challenge the systemic barriers that create and perpaetuate these disparities."
Journal reference: Dwyer-Lindgren, L., Baumann, M. M., Li, Z., et al. (2024). Ten Americas: a systematic analysis of life expectancy disparities in the USA. The Lancet. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01495-8 www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(24)01495-8/fulltext
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#covid#covid 19#wear a respirator#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Detailed Report on H.8 - Balance Sheet of Commercial Banks in the U.S.
Date: February 8, 2025 Intended for: Small Investors and Beginner Bankers Source: Federal Reserve H.8 Report (February 7, 2025)
1. Introduction
The Federal Reserve's H.8 report is an essential indicator for understanding the financial health of commercial banks in the United States. It provides weekly data on the evolution of banks' assets and liabilities, enabling detailed analyses of trends in credit, deposits, and sector liquidity. These data are fundamental for investors and financial professionals, as they allow for assessments of credit trends, liquidity, and banking system stability.
This document delves into the analysis of banking sector trends in 2024 using economic theories such as the Monetary Multiplier Theory, the Quantity Theory of Money, and the Efficient Market Hypothesis, helping small investors and beginner bankers make more informed decisions.
2. Key Banking Trends in 2024
2.1. Growth of Bank Credit and the Monetary Multiplier Theory
Bank credit grew 3.8% in 2024, recovering after a slight decline in 2023 (-0.3%). According to the monetary multiplier theory, this growth can amplify the money supply in the economy, boosting consumption and investment.
If banks continue to expand credit, there is a potential risk of increased inflation, as predicted by the Quantity Theory of Money (MV=PY), where an increase in the monetary base can lead to rising prices. A recent example of this relationship was observed during the COVID-19 pandemic, when the Federal Reserve and other central banks significantly expanded the monetary base to support the economy. This expansion, combined with supply chain disruptions, contributed to rising inflation in the subsequent years. Similarly, the expansionary monetary policy of the early 1970s led to the so-called 'Great Inflation,' reinforcing the relationship between credit growth and rising prices. More recently, the post-pandemic economic recovery in 2021 also demonstrated this relationship, when extensive liquidity injections by central banks contributed to sustained inflation. According to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. inflation reached 7% in 2021, the highest level in four decades, driven by increased money supply and global supply shocks.
2.2. Investments in Securities and Markowitz's Portfolio Theory
The volume of securities in banks' portfolios increased by 6.5%, suggesting a more conservative approach and reduced exposure to credit risk.
According to Markowitz's portfolio theory, this asset allocation shift indicates that banks are maximizing risk-adjusted returns, favoring lower-volatility assets such as government securities.
This also suggests potential concerns over private market volatility, leading banks to seek more predictable assets. This shift may negatively impact high-innovation sectors such as technology and startups, which heavily rely on risk financing. Conversely, sectors such as infrastructure and public services may attract more investment flows due to their financial stability.
2.3. Loans and Monetary Policy
Loans and leases grew 2.7%, a slight increase from 2023 (2.0%). This expansion may result from more restrictive monetary policy, which slowed credit growth by raising interest rates.
Loans to businesses (commercial and industrial) grew only 0.8%, suggesting that the Fed’s high-interest-rate policy is limiting private investment.
As described by the IS-LM Curve, rising interest rates reduce aggregate investment, impacting corporate credit demand.
2.4. Deposits and Bank Debt
Bank deposits grew 2.7%, after a decline of -2.7% in 2023, which may be explained by rising interest rates making deposits more attractive to investors.
Term deposits increased by 6.6%, signaling that consumers are seeking security in fixed-income investments.
Bank debt fell -6.9%, potentially indicating lower dependence on external financing and a more resilient banking sector. This reduction may be linked to the Federal Reserve’s more restrictive monetary policies, which raised interbank credit costs, encouraging banks to adjust their funding strategies. Additionally, recent regulatory changes may have led financial institutions to strengthen their balance sheets and reduce leverage to meet new capital requirements.
2.5. Bank Asset Quality and the Efficient Market Hypothesis
Loan loss provisions increased 4.5%, indicating that banks are becoming more cautious about default risks.
According to the Efficient Market Hypothesis (Fama, 1970), this precaution is already priced into financial markets, affecting the value of bank stocks.
If asset quality continues to deteriorate, there may be greater volatility in banking asset prices.
3. What Small Investors and Beginner Bankers Should Watch For
3.1. For Investors and Keynes’ Liquidity Preference Theory
Deposits and liquidity: The growth in deposits suggests that banks have sufficient liquidity, reducing systemic risks.
Securities profitability: The demand for government securities may indicate a higher perception of risk in the private sector, suggesting caution in capital allocation.
Credit for businesses: The low demand for commercial loans may slow economic growth, requiring prudence when investing in sectors dependent on bank financing.
3.2. For Beginner Bankers and Banking Regulation
Risk management: The increase in loan loss provisions suggests that banks should strengthen their credit risk assessments to mitigate default risks.
Credit supply and interest rates: The slowdown in loan growth indicates that the cost of credit is high, reducing financing attractiveness.
Deposit collection: The recovery of deposits may present an opportunity to offer more sophisticated financial products, attracting investors seeking security in fixed income.
4. Conclusion
The H.8 report of February 2025 reveals a stable banking sector, with moderate growth and strengthened reserves against default risks. Bank behavior reflects the impact of monetary policy and the search for greater investment security. The Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes, for example, have led banks to adopt a more cautious approach to lending, resulting in lower market liquidity. Additionally, monetary tightening has driven a shift toward lower-risk assets such as government securities, reinforcing the importance of monetary policy in capital allocation within the financial sector.
Small investors should consider opportunities in fixed-income securities and the banking sector, while new bankers should focus on risk management and attracting new deposits.
Regularly monitoring these data is essential for making informed decisions and ensuring sound financial planning. Additionally, investors can follow reports such as the Federal Reserve's Beige Book, FDIC banking performance data, and market analyses from reputable financial institutions to enhance their understanding of the sector.
Disclaimer: This report is based on public data from the Federal Reserve and should not be considered official financial advice.
For consultancy services via Telegram, contact: +55 11 97610-6005.
0 notes
Text
Measured productivity growth per worker in advanced economies increased sharply at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic and then dropped sharply. Using data on productivity since 1950, John Fernald of INSEAD and Huiyu Li of the San Francisco Federal Reserve find that productivity post-COVID followed predictable trends and that the rise of telework since 2020 has not notably impacted worker productivity. They argue that the surge in productivity growth and subsequent decline in 2020 and 2021 was not a sign of faulty productivity measures, but instead in line with the general pattern since the mid-1980s of productivity growth increasing in downturns and falling in recoveries. Comparing productivity growth across U.S. industries, they find no correlation between productivity growth and “teleworkability,” suggesting that the pandemic did little to alter the long-term, slow productivity trajectory in advanced economies.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Respiratory Heaters Market Growth and Future Trends: A Comprehensive Outlook for the Coming Decade
The respiratory heaters market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for efficient respiratory support devices across various industries. These heaters are crucial in providing warmth and moisture to inhaled air, particularly for patients with respiratory issues. The rising prevalence of respiratory diseases, including asthma, COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), and the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, has significantly accelerated the demand for respiratory heaters. The integration of advanced technologies and the growing healthcare infrastructure also play pivotal roles in the market's expansion.

Technological Advancements and Innovations
One of the key trends in the respiratory heaters market is the continuous improvement of heating technologies. Manufacturers are incorporating advanced systems, including smart heating devices that can adjust temperature and humidity levels according to patient needs. These heaters help in maintaining the optimum air temperature, crucial for comfort and efficient respiratory function. Furthermore, the miniaturization of respiratory heating devices is becoming more prominent, making them easier to use and more convenient for both patients and healthcare providers.
Healthcare Sector Demand and Growth
The healthcare sector remains the primary driver of demand for respiratory heaters. With an aging population and increasing chronic respiratory conditions, the need for therapeutic devices that provide constant airflow and warmth is on the rise. Hospitals, clinics, and home care settings are the main environments where respiratory heaters are utilized. In addition, the growth of the home healthcare industry is further boosting market opportunities as patients prefer using such devices at home for enhanced comfort during recovery.
Adoption of Portable Respiratory Heaters
Another notable trend is the growing adoption of portable respiratory heaters. Patients requiring respiratory support in non-hospital settings can benefit greatly from these portable solutions, which offer flexibility and ease of use. These devices can be used at home, on the go, or in emergency situations, making them essential for providing respiratory relief when needed. The compact design and improved battery life of portable respiratory heaters are key factors contributing to their increasing popularity.
Regulatory Landscape and Product Safety
As the demand for respiratory heaters continues to grow, regulatory bodies are focusing on ensuring product safety and quality. Manufacturers are required to adhere to stringent standards and guidelines set by authorities such as the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and CE (Conformité Européene) to ensure the safety and reliability of respiratory devices. These regulations ensure that respiratory heaters are safe for long-term use, with minimal risks to users. Compliance with these standards not only enhances market growth but also builds consumer trust in the products.
Market Competition and Key Players
The respiratory heaters market is becoming increasingly competitive, with numerous companies striving to capture market share. Leading players are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products that cater to diverse consumer needs. Some key players in the market include Philips Healthcare, ResMed, and Fisher & Paykel Healthcare. These companies focus on offering energy-efficient, cost-effective, and user-friendly solutions to meet the growing demand for respiratory devices.
Regional Market Analysis
Geographically, North America dominates the respiratory heaters market due to the high adoption of advanced healthcare technologies and the presence of key market players. However, the Asia Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth due to the expanding healthcare sector, rising healthcare expenditures, and the increasing prevalence of respiratory diseases. The European market is also showing significant growth, driven by the high demand for home healthcare solutions and technological advancements in respiratory devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the respiratory heaters market is poised for significant growth due to increasing healthcare demand, technological advancements, and the need for effective respiratory support devices. As the market continues to evolve, the focus on patient-centric innovations, portable solutions, and regulatory compliance will shape the industry's future trends.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Exploring the Global Growth of the Sex Reassignment Surgery Market: Key Insights and Trends
Exploring the Global Growth of the Sex Reassignment Surgery Market: Key Insights and Trends
As society moves towards greater inclusivity and acceptance of diverse identities, the global market for sex reassignment surgery (SRS) has witnessed substantial growth. According to recent data, this market was valued at $8.4 billion in 2023 and is expected to skyrocket to $111.718 million by 2031, growing at an impressive CAGR of 31.6% from 2024 to 2031. This surge underscores the increasing demand for gender-affirming healthcare worldwide.
Understanding Sex Reassignment Surgery
Sex reassignment surgery (SRS) refers to a collection of surgical procedures designed to align an individual's physical characteristics with their gender identity. This can include vaginoplasty, phalloplasty, breast augmentation, and facial feminization surgery, depending on whether the transition is from male to female (MTF) or female to male (FTM). Beyond surgery, this transition often involves hormone therapy and psychological support to ensure a holistic transformation, aiming to improve quality of life and reduce gender dysphoria.
Browse Link : https://www.statsandresearch.com/report/40446-global-sex-reassignment-surgery-market/
Market Dynamics and Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic had a notable impact on the healthcare sector, including the SRS market. With disruptions in elective surgeries and medical services, the market faced challenges. However, as healthcare systems adapt and prioritize gender-affirming care, the market shows a resilient recovery trajectory.
Regional Insights: Global Footprint
The SRS market spans across North America, Asia-Pacific, Europe, the Middle East and Africa, and South America. Key countries like the United States, China, Japan, India, and Brazil lead in market activity, driven by growing awareness and improved medical facilities. Each region presents unique dynamics, from the advanced healthcare infrastructure in North America and Europe to the increasing acceptance and medical tourism in Asia-Pacific.
Get A Free Sample Here : https://www.statsandresearch.com/request-sample/40446-global-sex-reassignment-surgery-market
Competitive Landscape: Key Players Shaping the Market
Leading the charge in this evolving market are key players such as:
Cleveland Clinic
Mayo Clinic
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Massachusetts General Hospital
Stanford Health Care
The Gender Confirmation Center
Chrysalis Health
Beverly Hills Plastic Surgery
Dr. Toby Meltzer
Dr. Sherman Leis
These institutions and professionals are at the forefront, offering cutting-edge procedures and compassionate care. Their role is critical in advancing both the medical and social aspects of gender-affirming healthcare.
Procedure Types: MTF and FTM Surgeries
Procedures vary widely based on the transition pathway:
Male-to-Female (MTF): Common surgeries include vaginoplasty, breast augmentation, and facial feminization surgery. These procedures help align an individual’s body with their gender identity, enhancing both physical appearance and psychological well-being.
Female-to-Male (FTM): Surgeries like top surgery (chest reconstruction), phalloplasty, and metoidioplasty are key. They focus on creating a masculine physique and, in some cases, reconstructing genitalia for functional and aesthetic alignment.
The Role of Medical Professionals
A successful transition requires a multidisciplinary team:
Surgeons: Perform the actual procedures, ensuring alignment with the patient’s identity and medical needs.
Endocrinologists: Manage hormone therapy to develop secondary sexual characteristics.
Psychiatrists/Psychologists: Provide mental health support, preparing individuals for surgery and assisting with emotional resilience.
Where the Surgeries Take Place
SRS is conducted in various settings, from comprehensive hospitals to specialized clinics and general healthcare facilities. Each offers a unique approach, balancing personalized care with medical excellence.
For Enquiry : https://www.statsandresearch.com/enquire-before/40446-global-sex-reassignment-surgery-market
The Road Ahead
With a projected CAGR of 31.6% from 2024 to 2031, the SRS market is set for rapid expansion. As societal acceptance grows and medical technologies advance, more individuals are seeking these life-changing procedures.
The journey towards comprehensive gender-affirming care continues, driven by both market forces and a deepening understanding of the needs of transgender individuals. This growing market not only reflects economic potential but also the human stories behind each transition, advocating for a world where everyone can live authentically.
Find Out Top Trending Reports Here :
Global Sex Reassignment Surgery Market
Global Enzyme Engineering Market
Global Neuroelectronic Devices Market
Global Vitamin K2 Market Insights
Global Defibrillator Market Insights
1 note
·
View note