#Byzantine Empire
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
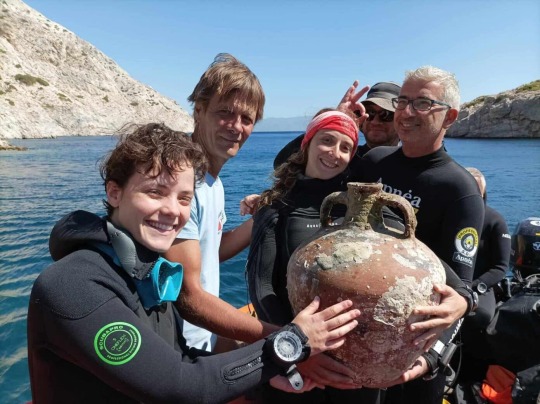

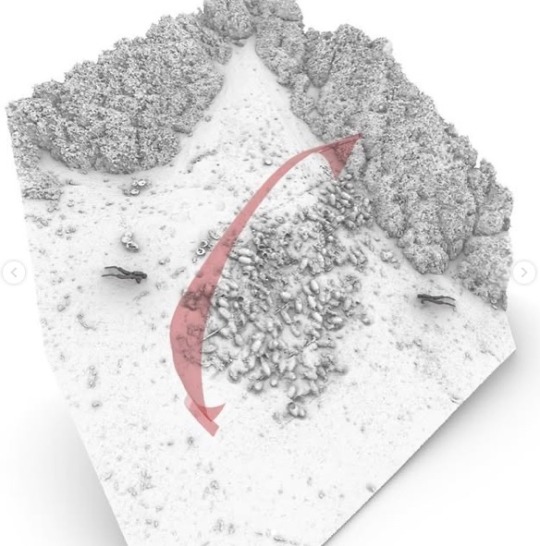
Dozens of Amphorae Recovered From Ancient Byzantine Shipwreck in Greece
Excavations of an ancient Byzantine shipwreck off the coast of Fournoi near Samos, Greece are bringing new finds onto the surface.
The wreck has been systematically excavated since 2021 and has been selected for intensive investigation due to the extremely interesting cargo it carries.
The amphorae found recently in the sand near the wreck, along with the wooden skeleton of the ship itself, were in remarkably good condition. Experts believe that the ship’s wooden framing survived throughout the centuries because it was crushed under the rest of the ship and oxygen couldn’t reach it, stalling the process of decay.
So far eight different amphora types have been recorded, originating from Crimea, Sinope of the Pontus region in the Black Sea, as well as from the Aegean islands and the Phocaean region of Asia Minor.

Pottery recovered at the ancient Byzantine shipwreck
The Ministry of Culture said that 170 group dives were carried out during the latest excavations. Archaeologists worked throughout the period to clear sand and debris from the wreck to provide access for experts to conduct studies of the site.
The scattering of the finds on the seabed seems to indicate a partial loss of cargo before the ship sank.
The recovered pottery was particularly enlightening, in terms of the more precise chronological inclusion of the wreck, which can now be safely dated between 480 and 520 AD, probably during the years of Emperor Anastasios I (491 – 518 AD), said a press release by the Greek Ministry of Culture.
Byzantine Emperor Anastasios I is known for his fiscal and monetary reforms, which strengthened the Empire’s coffers and enabled the expansionist policy of the emperors of the 6th century.
In parallel with the excavation of the wreck, findings from three more wrecks at the Fournoi archipelago were recovered, which are intended to be exhibited at the local archeological museum. Among these finds are a giant archaic anchor obelisk and amphorae from shipwrecks of the 6th to 8th centuries AD.

Countless ancient shipwrecks off Greece
There are many ancient shipwrecks across the Greek seas, and archaeologists have found countless historic treasures in these sunken archaeological sites.
In March 2024, the Ministry of Culture announced that scientists have discovered several shipwrecks and other important ancient finds in the underwater, near Greece’s island of Kasos.
These date back indicatively from prehistory (3000 BC), the Classical period (460 BC), the Hellenistic (100 BC to 100 AD), and the Roman years (200 BC – 300 AD) to the medieval and Ottoman periods.
Four stunning ancient shipwrecks filled with artifacts from antiquity and the Roman and Byzantine eras off central Greece can now be explored by amateur divers.
“We plan to highlight our marine cultural heritage,” Culture Minister Lina Mendoni said.
“We have responded to this great challenge by opening to the public a total of four underwater archaeological sites in the prefecture of Magnesia, which will allow Greece to join the world map of diving tourism.”
By Tasos Kokkinidis.

#Dozens of Amphorae Recovered From Ancient Byzantine Shipwreck in Greece#coast of Fournoi#ancient shipwreck#ancient amphorae#ancient artifacts#archeology#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient greece#greek history#byzantine history#byzantine empire
59 notes
·
View notes
Text

Maidens with Swords - Byzantine Empire
567 notes
·
View notes
Photo
7th century aqueduct be rebuild but they are not rebuild bathhoues ,
the zeuxippus silk workshop and prison
in ottoman rule the aqueduct be recover


The Valens Aqueduct is a Roman aqueduct which was the major water-providing system of the Eastern Roman capital of #Constantinople. Vatican Skip the Line Tours
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
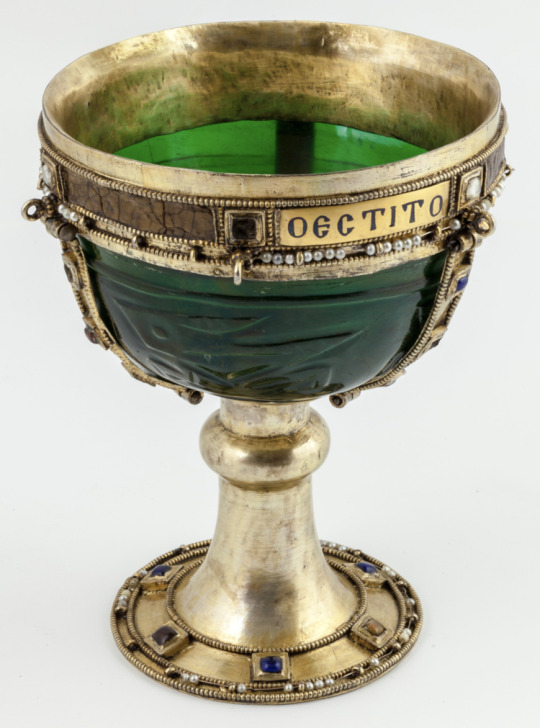

Byzantine chalice which originated as a green glass cup or bowl which originated from either Egypt or Iran in the 9th-11th century. When it made it's way to the Byzantine Empire it was decorated and turned into a chalice
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Shout out to Porphyrios, the whale who terrorized the waters near Constantinople for more than 50 years during the 6th century.
You'd sunk more Roman warships than most of their human enemies.
#roman history#byzantine history#roman empire#byzantine empire#new roman empire#eastern roman empire#constantinople#rome#history#porphyrios
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Fragment of a linen tunic from Egypt, dating to the 5th or 6th century AD/CE, when the province was part of the East Roman (Byzantine) Empire. The fragment features clavus bands with a red ground and black border; within the bands are polychrome figures of animals. Each band ends in a pendant medallion of inset wool. The tunic is now in the Cooper Hewitt, Smithsonian Design Museum, New York City, NY, USA. Photo credit: Cooper Hewitt.
#art#art history#ancient art#Egypt#Ancient Egypt#Roman Egypt#Byzantine Egypt#Byzantine#Byzantine Empire#Byzantine art#textiles#textile art#fiber arts#textile arts#tunic#linen#Cooper Hewitt
549 notes
·
View notes
Text
Byzantine history be like:
In 874 Emperor Kostalogous IV ascended to the throne after blinding sixteen nephews, and married his wife, Theodora.
However, he soon ran afoul of the Patriarch of Constantinople, Theopelagionikus, and his wife Theodora.
In 895 he was deposed by his general, Justiniapelomaxorianous II, and his wife Theodora.
This created nine new church schisms.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text


#sketches#graphic art#art#illustration#artists on tumblr#medieval art#byzantium#byzantine empire#middle ages#russian literature
189 notes
·
View notes
Text
Common Modern Greek phrases with Byzantine origins
"Παίζω στα δάχτυλα" (Pézo sta ðákhtyla) = I am very good at knowing something, I have learned it very well. Literally, I can play (sth) on my fingers. Children in the Eastern Roman Empire learned the basics of arithmetic by counting with their fingers, a practice still used in the old years of the modern Greek school.
"Ο ήλιος βασίλεψε" (O ílios vasílepse) = the sun set, literally "the sun reigned" It might seem counter-intuitive, however in Greek when you say "the sun reigns" or "sun-reigning" (ηλιοβασίλεμα), it is not about the sun being high in the sky but it is instead used for the sunset, the early evening. This is because of the striking colours of the sunset; gold, orange, red, purple - the luxurious colours associated with the Byzantine emperors.
"Ἐφαγα τον περίδρομο" (Éphagha ton períðromo)= I ate too much, I ate everything on sight. Literally, I ate the "peridromos". The peridromos was the edge of a deep bowl in which the Byzantines ate soup, so when they filled their bowl up to the peridromos it meant they were eating a lot. The interesting thing is that the origin of this phrase is very little known to modern Greeks and because peridromos can also have other meanings, there are also other interpretations that however make too little sense (IMO). This alone could perhaps be proof of how the phrase survived organically amongst the people even after the fall of the Byzantine empire (and its bowls).
"Μη με παιδεύεις" (Mi me peðévis) = don't bother / torment / trouble me, etymologically deriving from the word for "child". In Ancient Greek, the child was παις and its derivative verb παιδεύω meant "educate", an action interwined with childhood. Progressively, however, the verb became more and more associated with the pains and struggles of being educated until by Byzantine / Medieval Greek's time it had the meaning of "bother / torment". In Modern Greek the verb παιδεύω has kept the Byzantine meaning of tormenting / bothering but its respective noun παιδεία (peðía) still retains the ancient meaning of education or more accurately the full transformative period of learning in a young person's life. There are however other also ancient derivatives from the same words that are more precisely used for education terminology.
"Ἠμαρτον!" (Ímarton) = an exclamation in the likes of "I have sinned! (Forgive me)") Ancient Greek did not have a word for the sin. The verb αμαρτάνω (amartáno), whose form above is the past tense, meant "I miss the target / I make a mistake". In ancient Greek they would say it for example when an archer did not hit the target. By Byzantine times, however, the word had acquired a more figurative, Christian theological meaning because one's ultimate goal was the virtuous living, so when they did something bad or wrong, it was perceived as "losing sight of their aim, their intent". And that's how the word developed into meaning "sin" in Medieval and Modern Greek.
Source: Byzantinist historian Helene Ahrweiler

#greek#greece#greek language#history#languages#language stuff#linguistics#greek history#byzantine history#eastern roman empire#byzantine empire#greek culture
210 notes
·
View notes
Text
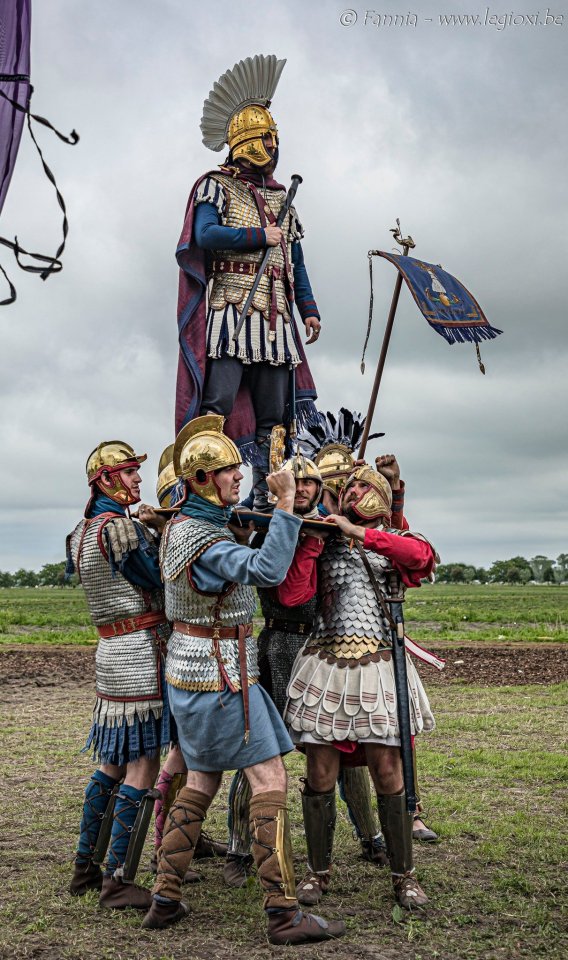




Byzantine reenactment by Evan Schultheis
#Evan Schultheis#byzantine empire#reenactment#noble#army#scale armor#banner#plume#dart#spear#sword#cape
673 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Emperor of Byzantium Basil II during the Georgian campaign, 1020 by Giuseppe Rava
#giuseppe rava#art#basil ii#bulgar slayer#emperor#byzantium#byzantine#byzantines#byzantine empire#roman#history#middle ages#medieval#varangian#guard#soldiers#georgia#georgian campaign#christianity#christian#cross#christendom#europe#european#asia#empire#varangian guard#romans#standards#banner
206 notes
·
View notes
Text



BYZANTINE MARBLE TABLE TOP WITH ROUNDELS 6TH-7TH CENTURY A.D.
#BYZANTINE MARBLE TABLE TOP WITH ROUNDELS#6TH-7TH CENTURY A.D.#marble#marble table top#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#roman history#roman empire#eastern roman empire#byzantine empire#ancient art
406 notes
·
View notes
Text

Nativity of Christ, Menologion of Basil II, Constantinople, c. 1000.
#byzantine#byzantine history#byzantine art#byzantine empire#greek orthodox#greek orthodox church#christianity#roman#roman art#roman empire#roman history#nativity#miniature painting#illuminated manuscript#medieval#middle ages#medieval history#medieval art
111 notes
·
View notes
Text

Assassin’s Creed: Revelations (2011)
#2011#gaming#concept art#Assassin’s Creed#Revelations#Ezio#Ezio Auditore da Firenze#Altair#Altair ibn La'Ahad#Desmond Miles#Animus#Abstergo Industries#Masyaf#Constantinople#Istanbul#Ottoman Empire#Byzantium#Byzantine Empire
132 notes
·
View notes
Text

Chalice of Emperor Romanos, Byzantine, 10th century
854 notes
·
View notes
Text
Calabrian Greeks: Pocket of Hellenism in Southern Italy has Survived Millennia

There exists today a tiny enclave of Calabrian Greeks, Greek-speaking people in the Aspromonte Mountain region of Calabria that seem to have survived millennia…perhaps since the Ancient Greeks began colonizing Southern Italy in the 8th and 7th Centuries BC.

Italian as we know it today was not always spoken throughout Italy. The Italian language did not become the staple language until well into the end of the 19th Century during the process of Italian unification, or the Risorgimento.
Until then, the Italian peninsula was made up of Italo-Romance dialects and smaller minority languages that were differentiated by region and historical influences.

Once unification was complete, the Tuscan dialect was ushered into power as the official language of the Italian nation. This became the beginning of the modern end of the Greek language in Calabria, or what it is known today as Greko.
There exists today a tiny enclave of Greek-speaking people in the Aspromonte Mountain region of Calabria that seem to have survived millennia…perhaps since the Ancient Greeks began colonizing Southern Italy in the 8th and 7th Centuries BC.

Their language is called Greko. They survived empires, invasions, ecclesial schisms, dictators, nationalistic-inspired assimilation, and much more. Greko is a variety of the Greek language that has been separated from the rest of the Hellenic world for many centuries.
To help bring more perspective, Greek was the dominant language and ethnic element all throughout what we know today as Calabria, Basilicata, Puglia, and Eastern Sicily until the 14th Century.
Since then, the spread of Italo-Romance languages, along with geographical isolation from other Greek-speaking regions in Italy, caused the language to evolve on its own in Calabria. This resulted in a separate and unique variety of Greek that is different from what is spoken today in Puglia.

History of Calabrian Greeks
There are many theories or schools of thought regarding the origin of the Greko community in Calabria. Are they descendants of the Ancient Greeks who colonized Southern Italy? Are they remnants of the Byzantine presence in Southern Italy? Did their ancestors come in the 15th to 16th centuries from the Greek communities in the Aegean fleeing Ottoman invasion?

The best answers to all of those questions are yes, yes, and yes. This means that history has shown a continuous Greek presence in Calabria since antiquity. Even though different empires, governments, and invasions occurred in the region, the Greek language and identity seemed to have never ceased. Once the glorious days of Magna Graecia were over, there is evidence that shows that Greek continued to be spoken in Southern Italy during the Roman Empire.
Once the Roman Empire split into East (Byzantine) and West, Calabria saw Byzantine rule begin in the 5th Century. This lasted well into the 11th Century and reinforced the Greek language and identity in the region, as well as an affinity to Eastern Christianity.
What’s even more fascinating is that Calabria was apparently a Byzantine monastic hub of sorts. There were over 1,500 Byzantine monasteries in Calabria and people today still remember and adore those saints. Even though Byzantine rule ended in Calabria in the 11th Century, the Greek language continued to be spoken while gradually declining in the region with the spread of Latin and a process of Catholicization.
Follow us on Instagram, @calabria_mediterranea

#calabria#italy#italia#south italy#southern italy#greek#greek language#greek langblr#griko#mediterranean#greeks#magna graecia#minority languages#langblr#bova#gallicianò#bovesia#byzantine#byzantine empire#italian#history
59 notes
·
View notes