#Biogas
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


A consortium linked to the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) has built a plant at the Mannheim wastewater treatment plant that cleans generated biogas and uses the resulting CO2 to produce climate-neutral marine fuel using green hydrogen. The process could help decarbonise the shipping sector, which is currently responsible for around three percent of global greenhouse gas emissions.
The demonstration plant uses a patented process to convert biogas produced during wastewater treatment into climate-neutral methanol. The biogas is first purified and the separated CO₂ can then be used with renewably-produced hydrogen to make methanol – a raw material that can be used as marine fuel or in the chemical industry. Methanol does release the CO2 back into the atmosphere when burned. However, because the carbon comes from the treatment plant and not from additional fossil sources, it is considered climate neutral.
There are some 80,000 wastewater treatment plants in Europe that offer considerable potential for the new process, wrote KIT. "To achieve our climate protection goals, we must keep all technological options open," said Volker Wissing, federal minister for digital affairs and transport. “In addition to electrification and hydrogen-based propulsion, we need climate-friendly fuels, especially in maritime shipping." Stressing that the sector represented a future growth market, Wissing said Germany should play a pioneering role in research and development. "It's also about making our country independent of energy imports."
Vidal Vazquez, co-founder of climate tech start-up ICODOS, a spin-off from the KIT, added, "In Germany alone, wastewater treatment plants could produce several million tonnes of sustainable methanol annually." The project shows that "wastewater treatment plants can serve as the heart of sustainable fuel production – a potential that has so far remained untapped," Vazquez said. ICODOS is currently in discussions with other wastewater treatment plants to set up other production facilities.
Renewables-based synthetic fuels could be necessary to decarbonise certain sectors such as shipping, where alternatives are not available today, or extremely costly. However, producing the rare fuels is energy-intensive and expensive and they should only be used where the direct use of electricity is not an option.
25 Mar 2025
#good news#environmentalism#science#environment#nature#animals#conservation#climate change#climate crisis#greenhouse gases#decarbonization#renewable energy#green energy#solar energy#clean energy#solar power#solar panels#green hydrogen#biogas#waste management#carbon footprint#carbon neutrality#maritime shipping
249 notes
·
View notes
Text
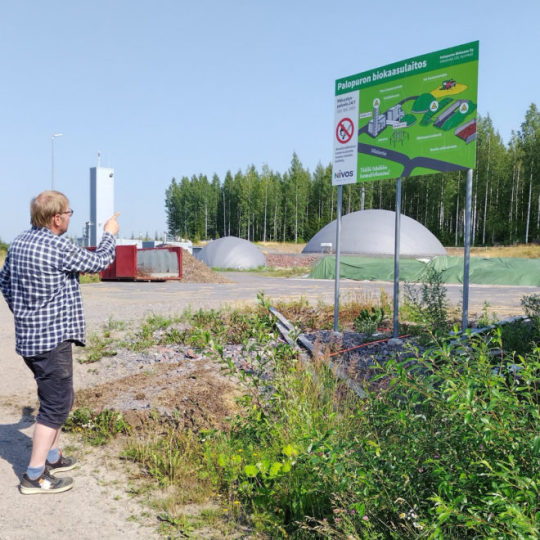

Self-sufficient organic Finnish farm grows its own fuel and a greener future
An award-winning farm has teamed up with Helsinki University to create a symbiotic food production system that is self-sufficient in energy and nutrients. It’s a trailblazer in sustainable agriculture.
Photo above: Farmer Markus Eerola shows visitors the biogas plant that helps make his farm an energy producer rather than an energy consumer.Photo: Wif Stenger
Organic Knehtilä Farm provides its own nutrients and energy, thanks to careful long-term planning and a small onsite biogas plant operated by energy utility Nivos.
The biogas powers his tractor, pickup truck and cars, and is available to others at a commercial filling station on the edge of the farm, although vehicles that can use biogas are still relatively rare. It offers a valuable alternative to meet the growing need for affordable, clean domestic energy.

Demand for organic food continues to grow. “The price gap between organic and standard production is narrowing, partly because we don’t need fertiliser. Our farm has its own product line of oat and buckwheat products, which are produced here using a proven cultivation method known as agroecological symbiosis, where nutrients and energy are efficiently recycled.”
The sprawling 380-hectare farm’s carefully balanced circular economy has developed over a decade and a half, earning a WWF award in 2015 as a model of nature-friendly agriculture. In 2021, the Finnish Organic Association chose Knehtilä for the honour of Organic Business of the Year.
“Biogas production can convert farms from being energy consumers to energy producers, and play an important role in the transition away from fossil fuels. When it’s done in a smart way, it’s also possible to increase biodiversity in farming systems.”
Knehtilä forms part of the Global Network of Lighthouse Farms, a project led by Wageningen University in the Netherlands, involving commercially viable farms that offer “radical solutions to address sustainability challenges.” International visitors frequently come to Knehtilä to learn about unique system.
The rich, vibrant cycle of life at Knehtilä is visible in not only the lush fields, but also in the insects and frogs that frequent them, and in a few animals such as horses, sheep, goats, chickens and rabbits. The farm is also a lively event venue; a high-ceilinged, 80-year-old barn has been converted to a space for up to 100 people for weddings, theatre performances and concerts.
#solarpunk#solar punk#indigenous knowledge#reculture#self reliant farming#agroecology#biogas#finland#organic farming#design
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Weg von Erdgas und Öl, hin zur nachhaltigen Produktion: Keine leichte Aufgabe vor allem für die Industrie mit ihrem hohen Energieverbrauch. In einer Pommes-Fabrik in Rain am Lech gibt es dafür eine außergewöhnliche Lösung: Biogas aus Pommes-Abwasser.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
#business#branding#industrial pumps#pumps#oil & gas industry#food industry#mining equipment#chemical industry#biogas#beverage industry
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Panasonic destaca compromisso ambiental na COP-30 no Brasil
A COP-30, que se realiza pela primeira vez em solo brasileiro, surge em um contexto em que as preocupações relacionadas às mudanças climáticas se tornam cada vez mais urgentes. Nesse cenário, a Panasonic reafirma seu comprometimento com questões ambientais, destacando a relevância dessa pauta para a empresa. Em suas palavras, Sergei Epof, um dos executivos da Panasonic, enfatiza que a sustentabilidade está intrínseca à filosofia da companhia, que possui um legado centenário e atua em mais de 80 países, sempre com um foco em práticas responsáveis, muito antes do conceito de ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) ganhar popularidade.(...)
Leia a noticia completa no link abaixo:
https://www.inspirednews.com.br/panasonic-destaca-compromisso-ambiental-na-cop30-no-brasil

#cop-30#panasonic#sergeiepof#mudancasclimaticas#energiasustentavel#biogas#reciclagem#desenvolvimentosustentavel#economiacircular#tecnologiasverdes#brasil
0 notes
Text

Save the Planet, One Flame at a Time
#renewableenergy#greenenergy#cleanpower#ecofriendly#cleanenergy#tricklebiopower#renewablepower#sustainableenergy#biogas#electicity
0 notes
Text

🏭 Vil du arbejde for @Danfoss? Burner Components, en del af Danfoss Climate Solutions, søger en produktingeniør til deres produktions-, udviklings- og applikationsteam i Nordborg. Der er en video om arbejdspladsen og et link til jobopslaget på vores blog.
https://arnenielsen.dk/2025/05/06/danfoss-soeger-medarbejder-til-burner-components/
0 notes
Text
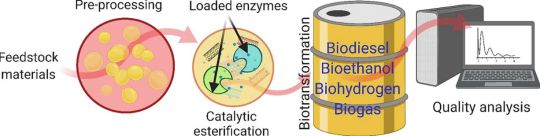
⚗️ Powering the Green Revolution: Nanomaterials Accelerate Biofuel Production from Lignocellulosic Biomass
By Hafiz Muhammad Husnain Azam Researcher, Brandenburg University of Technology Cottbus-Senftenberg 📘 Published 🔗 Read Full Study on Elsevier
The Biofuel Bottleneck—and the Nanotech Breakthrough
With fossil fuel dependency driving climate change, geopolitical instability, and economic volatility, the world is racing to scale up renewable energy solutions. Among these, biofuels—biodiesel, bioethanol, biogas, bio-oil, and biohydrogen—are gaining momentum as scalable, low-carbon alternatives.
However, biofuel production from lignocellulosic biomass—agricultural waste, forestry residues, and organic by-products—has historically been hampered by complex conversion processes and low yields. Our latest article addresses this challenge with a cutting-edge solution: nanomaterials.
How Nanomaterials Are Revolutionizing Biofuel Efficiency
Nanomaterials possess extraordinary physicochemical properties—high surface area, catalytic efficiency, and tunable morphology. These qualities make them ideal for enhancing biomass-to-biofuel conversion processes like:
Transesterification (for biodiesel)
Hydrolysis and fermentation (for bioethanol and biogas)
Pyrolysis and gasification (for bio-oil and biohydrogen)
They act as nano-catalysts, replacing harsh chemicals and enabling cleaner, faster, and more efficient transformations. This drastically improves both yield and cost-efficiency while reducing environmental impact.
Bridging the Gap Between Energy Demand and Sustainability
With global leaders striving to meet Net-Zero targets, biofuels play a critical role in the transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy. Yet, for biofuels to become a backbone of this transition, the production systems must be radically optimized. This is where nanotechnology emerges as a strategic enabler.
Our review reveals:
Enhanced metabolic and catalytic activity via nanomaterials
Improved thermal stability and recyclability of catalysts
Lower activation energy for biomass breakdown
Reduced process time and chemical waste
Future Outlook: Opportunities and Challenges
Despite their game-changing potential, the commercial deployment of nanomaterials faces hurdles:
High production costs
Limited scalability
Safety and environmental concerns
Regulatory gaps
Addressing these through targeted research, policy frameworks, and interdisciplinary collaboration will be key to unlocking the full potential of nanotech in renewable energy.
Let’s Drive the Conversation Forward
This research is a call to action for materials scientists, chemical engineers, policy leaders, and energy stakeholders. Nanomaterials are not just a lab innovation—they are a viable industrial solution in the making.
📖 Explore the full article: Elsevier – Nanomaterials in Biofuel Production
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122840
https://go.nature.com/4j0ywq
#Nanomaterials#Biofuels#Biodiesel#Bioethanol#Biogas#Biohydrogen#LignocellulosicBiomass#GreenEnergy#CleanTech#SustainableEnergy#Nanotechnology#Catalysis#RenewableEnergy#EnvironmentalEngineering#EnergyTransition#CircularEconomy#CarbonNeutral#WasteToEnergy#FutureFuels#AdvancedMaterials#ClimateTech#Decarbonization#GreenInnovation#FuelTheFuture#ScienceForSustainability#EnergyResearch#ZeroCarbonFuels#NetZero2050#NanoCatalysts#BiomassConversion
1 note
·
View note
Text
Biogas Plant in Kerala: A Green Energy Initiative for Sustainable Development
Abstract
The biogas plant in Kerala is rapidly becoming an essential component of the state’s strategy for renewable energy and sustainable waste management. With Kerala facing challenges related to increasing organic waste and rising energy demands, the biogas plant in Kerala presents an eco-friendly solution that converts biodegradable waste into usable biogas and organic fertilizer. This article explores the relevance, application, and potential of the biogas plant in Kerala, emphasizing its environmental, economic, and social benefits.
Introduction
The biogas plant in Kerala has emerged as a sustainable model for addressing waste management and clean energy production. Given Kerala’s dense population, agricultural activities, and growing urban centers, the state produces significant amounts of organic waste daily. The installation of a biogas plant in Kerala offers an effective solution by recycling this waste into biogas, which can be used for cooking, electricity, and other energy needs, thereby promoting a circular economy and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Main Body
The adoption of the biogas plant in Kerala is driven by the state’s commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting renewable energy sources. Various government and private initiatives encourage households, institutions, and industries to install a biogas plant in Kerala to manage organic waste efficiently while producing sustainable energy. The tropical climate of Kerala, combined with a high generation of food and agricultural waste, makes the biogas plant in Kerala a viable and practical technology.

The government has played a pivotal role in promoting the biogas plant in Kerala by offering subsidies, technical guidance, and awareness programs. The Suchitwa Mission and Haritha Keralam initiatives actively promote the biogas plant in Kerala as a part of their integrated waste management systems. These efforts aim to improve waste disposal practices, minimize the use of landfills, and promote decentralized energy production through the biogas plant in Kerala.
Communities and institutions that have adopted the biogas plant in Kerala have reported reduced household energy costs and improved sanitation practices. The slurry produced as a byproduct of the biogas plant in Kerala serves as a high-quality organic fertilizer for agricultural purposes. As a result, the biogas plant in Kerala not only addresses energy and waste management issues but also contributes to sustainable agricultural development.
In rural areas, the biogas plant in Kerala has empowered small farmers by providing a reliable and low-cost energy source, which is especially useful for cooking and lighting. Urban centers have also embraced the biogas plant in Kerala through community-based models, where multiple households collectively process their organic waste and share the biogas output. This model has helped strengthen Kerala’s efforts to become a zero-waste state, positioning the biogas plant in Kerala as a cornerstone of environmental policy.

Conclusion
The biogas plant in Kerala exemplifies how simple yet innovative technologies can transform waste into a valuable resource, supporting both environmental sustainability and energy security. With increasing government support, public participation, and technological advancements, the biogas plant in Kerala is poised to become a widespread solution across the state. The future of waste management and clean energy in Kerala depends significantly on the adoption and integration of the biogas plant in Kerala into both rural and urban infrastructure.
0 notes
Text
Hyundai Motor Group Presents Action Plans for Waste-to-Hydrogen Ecosystem in Indonesia
Hyundai Motor Group to collaborate with Pertamina and West Java Province to build a waste-to-hydrogen ecosystem, advancing sustainable hydrogen solutions By 2027, the Group plans to launch an on-site hydrogen refueling station utilizing Pertamina’s CNG infrastructure Building on its successful W2H model in Korea, the Group plans to expand the ecosystem in Indonesia as its first overseas…
0 notes
Photo

PRIMA PAGINA Il Gazzettino di Oggi martedì, 15 aprile 2025
#PrimaPagina#ilgazzettino quotidiano#giornale#primepagine#frontpage#nazionali#internazionali#news#inedicola#oggi venezia#gratis#della#capitaneria#pagina#gazzettino#ancora#muore#autista#lutto#llosa#addio#allo#scrittore#reso#luogo#quotidiano#nordest#mestre#corsa#biogas
0 notes
Text
Decentralized Power: IoT is the Glue in Smart Grid
#BioGas#BioMass#Charge#Dynamic Demand#Energy#Energy Balancing#Energy Market#Energy Trading#Grid#Hydro#Power#Remote Management#Water
0 notes
Text
What is the Efficiency of a Bio CNG Plant?

Introduction
Bio CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) is emerging as a sustainable alternative to conventional fuels, offering an eco-friendly solution for energy needs. The efficiency of bio CNG plants plays a crucial role in determining their viability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits. Understanding the factors that influence efficiency can help industries and governments optimize operations for maximum output.
Understanding Efficiency in Bio CNG Production
Efficiency in a bio CNG plant is measured by the ratio of energy output to input, methane yield, and overall resource utilization. A well-optimized plant can achieve an energy output-to-input ratio of approximately 25:1, meaning it produces significantly more energy than it consumes. This high efficiency makes bio CNG a competitive option compared to fossil fuels.
Key Factors Influencing Bio CNG Plant Efficiency
Several factors impact the efficiency of bio CNG plants, including:
1. Feedstock Quality and Composition
Organic waste, agricultural residues, and animal manure serve as raw materials.
High-methane-yield feedstocks, such as Napier grass or food waste, enhance gas production.
Proper pre-treatment removes impurities and maximizes methane potential.
2. Digestion Process and Retention Time
Anaerobic digestion is the core process in bio CNG production.
Longer retention times (typically 20–40 days) allow for complete breakdown of organic matter.
Maintaining an optimal temperature (35–55°C) improves bacterial activity and gas yield.
3. Advanced Purification Technologies
Water scrubbing, pressure swing adsorption (PSA), membrane separation, and cryogenic separation enhance methane purity.
High-quality purification systems ensure methane levels reach 90% or higher, improving fuel quality and efficiency.
4. Energy Consumption in the Process
Efficient pumps, mixers, and blowers reduce overall energy consumption.
Using biogas-generated electricity within the plant enhances sustainability.
Comparing Bio CNG Efficiency with Other Renewable Energy Sources
Bio CNG vs. Biogas: Bio CNG is a more refined version of biogas, with higher methane content and better combustion efficiency.
Bio CNG vs. Solar and Wind: Unlike intermittent solar and wind energy, bio CNG offers continuous energy production, making it a reliable fuel source.
Bio CNG vs. Fossil Fuels: Producing bio CNG reduces greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90% compared to diesel and petrol.
Challenges in Maximizing Bio CNG Efficiency
Despite its advantages, certain challenges must be addressed:
High initial investment costs for setting up purification and compression units.
Logistics and transportation hurdles for collecting and processing raw materials.
Variability in feedstock supply, affecting consistency in methane yield.
Future Innovations to Enhance Bio CNG Plant Efficiency
To further improve efficiency, ongoing research focuses on:
Hybrid purification techniques that combine multiple separation technologies.
AI-driven process optimization for real-time monitoring and control.
Carbon capture and utilization (CCU) for reusing CO₂ separated during purification.
Conclusion
The efficiency of bio CNG plants depends on factors such as feedstock quality, digestion process, purification methods, and energy management. With an energy output-to-input ratio of 25:1, bio CNG is proving to be a highly efficient renewable fuel. Investing in advanced technologies and innovative processes will further enhance its sustainability and commercial viability, making it a key player in the transition to cleaner energy.
0 notes
Text
Government Initiatives Supporting Biogas in Kerala

The state of Kerala is making significant strides in promoting biogas as a renewable energy source for waste management and sustainability. The government, both at the state and central levels, has introduced various initiatives, subsidies, and schemes to encourage the adoption of biogas in Kerala among households, farmers, and industries.
This article explores the key government programs supporting biogas in Kerala and how individuals and businesses can benefit from them.
1. State Government Schemes for Biogas in Kerala
The Kerala government actively promotes biogas plants through various initiatives:
✅ Suchitwa Mission — This is the state’s flagship sanitation and waste management program that encourages decentralized biogas plants in homes, institutions, and local communities. ✅ Kerala State Renewable Energy Policy — Provides incentives for adopting biogas systems to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. ✅ Subsidized Household Biogas Plants — The government provides financial assistance for small-scale domestic biogas plants, helping households convert organic waste into cooking fuel.
2. Central Government Support for Biogas in Kerala
Apart from state programs, several central government schemes promote biogas in Kerala, including:
🔹 National Biogas and Organic Manure Programme (NBOMP) — A scheme by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) that provides subsidies for setting up family-sized biogas plants. 🔹 Waste to Energy Scheme — Promotes biogas projects in industries and urban areas to convert organic waste into energy. 🔹 GOBAR-Dhan Yojana — Aimed at rural areas, this scheme helps farmers and dairy units generate biogas from cattle dung and organic farm waste.
3. Financial Assistance and Subsidies for Biogas in Kerala
💰 Subsidy for Household Biogas Plants — Eligible households can get up to ₹10,000 — ₹20,000 in subsidies for setting up small-scale biogas plants. 💰 Industrial Biogas Plant Incentives — Large-scale biogas plants for commercial use can receive funding support and tax benefits. 💰 Bank Loans and Grants — Various government-backed loans and grants are available to farmers, self-help groups, and industries interested in biogas in Kerala.
4. How to Apply for Government Support?
To avail of subsidies or financial aid for biogas in Kerala, follow these steps:
1️⃣ Contact the Suchitwa Mission office or local panchayat for subsidy details. 2️⃣ Submit an application along with project details and cost estimates. 3️⃣ Get approval from the Kerala State Renewable Energy Board or other relevant bodies. 4️⃣ Install the biogas plant through authorized vendors and claim the subsidy.
5. Benefits of Government-Supported Biogas Plants
✔ Reduced Cooking Fuel Costs — Families using biogas save on LPG expenses. ✔ Waste Management — Helps in managing household and agricultural waste effectively. ✔ Eco-Friendly — Reduces methane emissions and reliance on non-renewable energy. ✔ Additional Income — Farmers can sell surplus biogas or use bio-slurry as organic fertilizer.
Conclusion
Government initiatives supporting biogas in Kerala are transforming the way waste is managed and energy is produced. With financial incentives, policy support, and awareness programs, more households and businesses are encouraged to adopt biogas technology. Taking advantage of these schemes can lead to long-term savings, sustainability, and a cleaner environment.
#biogas in kerala#biogas plant for home#incinerator manufacturers in kerala#biogas#kerala#portable biogas plant for home#incinerators in kerala
0 notes
Text
Como a Coreia do Sul Transformou Resíduos em Recursos: Um Modelo de Reciclagem Exemplar
Yuna Ku, uma jornalista que reside em Seul, capital da Coreia do Sul, tem uma relação peculiar e consciente com seus restos de comida. "Já estou acostumada. Para mim, é um hábito", afirma, ao explicar como paga para reciclar seus resíduos alimentares por meio de máquinas equipadas com sensores distribuídas pelo seu condomínio, que abriga 2.000 apartamentos. Este sistema de reciclagem de resíduos alimentares da Coreia do Sul pode parecer inusitado à primeira vista, mas transformou o país em um exemplo a ser seguido por nações ao redor do mundo.(...)
Leia a noticia completa no link abaixo:
https://www.inspirednews.com.br/como-a-coreia-do-sul-transformou-residuos-em-recursos-um-modelo-de-reciclagem-exemplar

#coreiadosul#reciclagem#residuosalimentares#sustentabilidade#yunaku#jae-cheoljang#tecnologia#desperdiciodealimentos#meioambiente#onu#fao#biogas#racaoanimal#gestaoderesiduos
0 notes
Text

Buy Reliable Biogas for a Greener Future
Trickle Bio Power offers high-quality biogas for clean energy solutions.
#renewableenergy#greenenergy#cleanpower#cleanenergy#ecofriendly#renewablepower#tricklebiopower#sustainableenergy#biogas#electicity
0 notes