#LignocellulosicBiomass
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
⚗️ Powering the Green Revolution: Nanomaterials Accelerate Biofuel Production from Lignocellulosic Biomass
By Hafiz Muhammad Husnain Azam Researcher, Brandenburg University of Technology Cottbus-Senftenberg 📘 Published 🔗 Read Full Study on Elsevier
The Biofuel Bottleneck—and the Nanotech Breakthrough
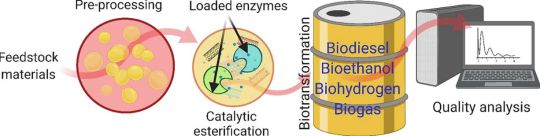
With fossil fuel dependency driving climate change, geopolitical instability, and economic volatility, the world is racing to scale up renewable energy solutions. Among these, biofuels—biodiesel, bioethanol, biogas, bio-oil, and biohydrogen—are gaining momentum as scalable, low-carbon alternatives.
However, biofuel production from lignocellulosic biomass—agricultural waste, forestry residues, and organic by-products—has historically been hampered by complex conversion processes and low yields. Our latest article addresses this challenge with a cutting-edge solution: nanomaterials.
How Nanomaterials Are Revolutionizing Biofuel Efficiency
Nanomaterials possess extraordinary physicochemical properties—high surface area, catalytic efficiency, and tunable morphology. These qualities make them ideal for enhancing biomass-to-biofuel conversion processes like:
Transesterification (for biodiesel)
Hydrolysis and fermentation (for bioethanol and biogas)
Pyrolysis and gasification (for bio-oil and biohydrogen)
They act as nano-catalysts, replacing harsh chemicals and enabling cleaner, faster, and more efficient transformations. This drastically improves both yield and cost-efficiency while reducing environmental impact.
Bridging the Gap Between Energy Demand and Sustainability
With global leaders striving to meet Net-Zero targets, biofuels play a critical role in the transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy. Yet, for biofuels to become a backbone of this transition, the production systems must be radically optimized. This is where nanotechnology emerges as a strategic enabler.
Our review reveals:
Enhanced metabolic and catalytic activity via nanomaterials
Improved thermal stability and recyclability of catalysts
Lower activation energy for biomass breakdown
Reduced process time and chemical waste
Future Outlook: Opportunities and Challenges
Despite their game-changing potential, the commercial deployment of nanomaterials faces hurdles:
High production costs
Limited scalability
Safety and environmental concerns
Regulatory gaps
Addressing these through targeted research, policy frameworks, and interdisciplinary collaboration will be key to unlocking the full potential of nanotech in renewable energy.
Let’s Drive the Conversation Forward
This research is a call to action for materials scientists, chemical engineers, policy leaders, and energy stakeholders. Nanomaterials are not just a lab innovation—they are a viable industrial solution in the making.
📖 Explore the full article: Elsevier – Nanomaterials in Biofuel Production
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122840
https://go.nature.com/4j0ywq
#Nanomaterials#Biofuels#Biodiesel#Bioethanol#Biogas#Biohydrogen#LignocellulosicBiomass#GreenEnergy#CleanTech#SustainableEnergy#Nanotechnology#Catalysis#RenewableEnergy#EnvironmentalEngineering#EnergyTransition#CircularEconomy#CarbonNeutral#WasteToEnergy#FutureFuels#AdvancedMaterials#ClimateTech#Decarbonization#GreenInnovation#FuelTheFuture#ScienceForSustainability#EnergyResearch#ZeroCarbonFuels#NetZero2050#NanoCatalysts#BiomassConversion
1 note
·
View note