#Agriculture and Animal Feed Industry
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
if you think vegan food is just shit like quinoa and imported "exotic" foods you dont know jackshit about veganism outside of movie stereotypes and animal agriculture industry propaganda (which is a real thing, big surprise. capitalism is full of industry propaganda) and should inform yourself outside of that. read a fucking cookbook at this point.
#its beans and wheat and shit like that#a lot of vegans are at the poverty line. hell i have less than 1000 euros a month and i eat healthy and vegan#and if theyre doing it for environmental reasons they likely also care about where the plants come from etc#animal agriculture needs insane amounts of plants to feed the livestock.#slaughterhouses are traumatizing workers#wide use of antibiotics is fucking us all over by building resistances#but ahahah gotcha vegans right?#i dont give a shit if youre vegan or not i seriously do not. do what you want#but generalizing a growing group of people from all walks of life as only rich white egotistical idiots#is where i draw the line#the milk and meat industry isnt going to fuck you.#is veganism perfect? no. it cant be under this system. but we're fucking trying.#a lot of convos i have w fellow vegans about food is what can be done better. what to watch out for and not to support. we give a shit.#unfollow me if youre gonna be a dick about this i seriously dont want anything to do with animal ag industry bootlickers anymore#basil yells at cloud
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Challenges Facing Kenya's Livestock Feed Industry: High Costs, Limited Raw Materials, and Regulatory Gaps
Kenya has extended the implementation of regulations that allow the country, and others in East Africa, to continue importing duty-free raw materials for feed manufacturing from within the region as the government attempts to address the high feed prices and stabilize the nearly $230 million industry. Treasury Cabinet Secretary Prof. Njuguna Ndung’u said in June that the Kenyan government will…
#agricultural sustainability#Akefema#animal feed prices#climate change impact#duty-free raw materials#EAC Customs Management#East African Community#feed industry challenges#feed manufacturing regulations#feed quality standards#feedstock importation#GMO vs non-GMO feed#high fertilizer prices#Kenya agriculture policy#Kenya feed industry#livestock farming in Kenya#livestock sector#local feed production#raw material suppliers#regional collaboration.
0 notes
Text
Is Corn Bad?
It's got the juice. (It's got the juice.) And, it's kind of complicated. Want a relatively unbiased opinion on it from an animal nutritionist? Here you go!
These do not, in fact, have the juice.Photo by Jayson Roy on Unsplash Corn is often misunderstood as a feed ingredient. It seems that everywhere you look, corn is either at the top of the ingredients list or it’s labeled as a “filler ingredient” and removed entirely. As a result, public opinion of corn also tends to lean to one extreme or the other, and there’s a lot of uncertainty and…

View On WordPress
#a big lump with knots#Agriculture#animal feed#animal nutition#conventional#conventional agriculture#conventional farming#corn#crops#educational#edutainment#farming#feed#grains#industrial agriculture#is corn bad#is corn good#it&039;s corn#it&039;s got the juice#Non-GMO#nutrition#Organic#organic agriculture#organics#why do people love corn#why is corn bad
1 note
·
View note
Text
Some notes on worldbuilding with carnivorous cultures:
Animals feed more people than you think. You don't kill a cow for just one steak, this is a modern misconception since we're removed from the actual animals we eat our meat from; a single cow has several kilos of meat. In fact, slaughtering a single cow often means a feast time for possibly dozens of people. Every part of an animal can be used, and you can see this in cultures that live by ranching and transhumance.
Here, you should look at the Mongols and the people of the Eurasian Steppe, the people of the North American Plains, the people of the Pampas (fun fact; Buenos Aires was called the "carnivore city"), European and Asian cultures that practice transhumance, and those of the Arctic circle.
There are many ways to cook meat, but arguably, the most nutritious way to consume meat is in stew, as it allows you to consume all the fats of the animal and add other ingredients. In fact, mutton soup and stew historically was one of the basic meals for the for people in the Eurasian Steppe, who are one of the people with the highest meat consumption in the world.
Of course, meat spoils away easily. Fortunately, from jerky to cured meats, there are ways to prevent this. In pre-industrial and proto-industrial societies, salted meat was the main way of consumption and exporting meat. This makes salt even a more prized good.
Often, certain parts of animals like eyes, the liver, the testicles, the entrails, are considered not only cultural delicacies but as essential for vitamins and nutrients unavailable in environments such as the poles. The Inuit diet is a very strong example.
Pastures and agriculture have often competing dynamics. The lands that are ideal for mass pasture, that is, temperature wet grasslands, are also often ideal for agriculture. So pastoralism has often been in the margins of agrarian societies. This dynamic could be seen in the Americas. After the introduction of cattle and horses, the Pampas hosted semi-nomadic herdsmen, natives and criollo gauchos. The introduction of wire eventually reduced this open territory, converting it into intense agriculture, and traditional ranching was displaced to more "marginal" land less suitable for agriculture. Similar processes have happened all over the world.
This also brings an interesting question to explore. Agriculture is able to feed more people by density. What about species that DON'T do agriculture, because they're completely carnivorous? The use of what human civilization considers prime agricultural land will be different. They will be able to support much higher population densities than pastoralism.
Pastoral human populations have developed lactase persistance to be able to feed on dairy products even in adulthood. This mutation has happened all over the world, presumably with different origins. In any mammalian species that domesticates other mammals such a thing would be very common if not ubiqutous, as it massively expands the diet. Milk provides hydration, and cheese, yogurth and other such products allows long lasting food sources.
What about hunting? Early humans were apex predators and we are still ones today. However, humans can eat plants, which somewhat reduces the hunting pressure on fauna (though not the pressure of agrarian expansion which can be even worse). An exclusively carnivorous species (for example some kind of cat people) would have to develop very rigid and very complex cultural behavior of managing hunting, or else they would go extinct from hunger before even managing domestication. These cultural views towards hunting have also arosen in people all over the world, so you can get a sense of them by researching it.
It is possible for pastoral nomadic people, without any agriculture, to have cities? Of course. All nomadic peoples had amazing cultures and in Eurasia, they famously built empires. But they traded and entered conflicts with agrarian societies, too. They weren't isolated. Most of nomadic societies were defined by trade with settled ones.
The origin of human civilization and agriculture is still debated. It would be probably completely different for a non-human carnivorous society. One possible spark would be ritual meeting points (such as the historical Gobleki Tepe) or trade markets growing into permanent cities. But in general, pastoralism, hunting and ranching favors low-density populations that would be quite different.
Fishing, on the other hand, is a reliable source of protein and promotes settled cities. One can imagine acquaculture would be developed very early by a civilization hungry for protein.
Other possibilities of course are the raising of insects and mushrooms, both very uncommonly explored in fiction besides passing mentions.
Of course, most carnivorous species have some limited consumption of plant matter and many herbivores are oportunistic predators. The main thing to ask here is what the daily meal is here. For most human agrarian cultures, it's actually grain (this is where the word meal comes from). What about species that cannot live with a grain-based diet? You will find that many things people take for granted in agrarian society would be completely different.
As I always say: the most important question you can ask is "where does the food comes from?"
I hope you found these comments interesting and useful! I would love to do a better post once I'm able to replace my PC (yes, I wrote this all in a phone and I almost went insane). If you like what I write and would love to see more worldbuilding tips, consider tipping my ko-fi and checking my other posts. More elaborate posts on this and other subjects are coming.
#cosas mias#worldbuilding#speculative evolution#spec evo#spec bio#writing advice#biotipo worldbuilding
986 notes
·
View notes
Text
Leather vs. Pleather: 8 Myths Debunked
Since we are all beyond tired of seeing the same regurgitated leather posts every day, I've compiled and briefly debunked some of the most common myths peddled about leather and pleather… So hopefully we can all move on to talk about literally anything else.
1) Leather is not sustainable.
Approximately 85% of all leather (almost all leather you'll find in stores) is tanned using chromium. During the chrome tanning process, 40% of unused chromium salts are discharged in the final effluents, which makes it's way into waterways and poses a serious threat to wildlife and humans. There are also significant GHG emissions from the sheer amount of energy required to produce and tan leather.
Before we even get the cow's hide, you first need to get them to slaughter weight, which is a hugely resource-intensive process. Livestock accounts for 80% of all agricultural land use, and grazing land for cattle likely represents the majority of that figure. To produce 1 pound of beef (and the subsequent hide), 6-8 pounds of feed are required. An estimated 86% of the grain used to feed cattle is unfit for human consumption, but 14% alone represents enough food to feed millions of people. On top of that, one-third of the global water footprint of animal production is related to cattle alone. The leather industry uses greenwashing to promote leather as an eco-friendly material. Leather is often marketed as an eco-friendly product, for example, fashion brands often use the Leather Working Group (LWG) certificate to present their leather as sustainable. However, this certification (rather conveniently) does not include farm-level impacts, which constitute the majority of the negative environmental harm caused by leather.
2) Leather is not just a byproduct.
Some cows are raised speciifically for leather, but this a minority and usually represents the most expensive forms of leather. This does not mean that leather is just a waste product of beef and dairy, or that it is a completely incidental byproduct; it is more accurate to call leather a tertiary product of the beef and dairy industries. Hides used to fetch up to 50% of the total value of the carcass, this has dropped significantly since COVID-19 to only about 5-10%, but this is recovering, and still represents a significant profit margin. Globally, leather accounts for up to 26% of major slaughterhouses’ earnings. Leather is inextricably linked to the production of beef and dairy, and buying leather helps make the breeding, exploitation and slaughter of cows and steers a profitable enterprise.
3) Leather is not as biodegradable as you think.
Natural animal hides are biodegradable, and this is often the misleading way leather that sellers word it. "Cow hide is fully biodegradable" is absolutely true, it just purposely leaves out the fact that the tanning process means that the hide means that leather takes between 25 and 40 years to break down. Even the much-touted (despite it being a tiny portion of the market) vegetable-tanned leather is not readily biodegradable. Since leather is not recyclable either, most ends up incinerated, or at landfill. The end-of-life cycle and how it relates to sustainability is often massively overstated by leather sellers, when in fact, it is in the production process that most of the damage is done.
4) Leather is not humane.
The idea that leather represents some sort of morally neutral alternative to the evils of plastic is frankly laughable, at least to anyone who has done even a little bit of research into this exploitative and incredibly harmful industry. Cows, when properly cared for, can live more than fifteen years. However, most cows are usually slaughtered somewhere around 2-3 years old, and the softest leather, most luxurious leather comes from the hide of cows who are less than a year old. Some cows are not even born before they become victim to the industry. Estimates vary, but according to an EFSA report, on average 3% of dairy cows and 1.5 % of beef cattle, are in their third-trimester of pregnancy when they are slaughtered.
Slaughter procedures vary slightly by country, but a captive bolt pistol shot to the head followed by having their throats slit, while still alive, is standard industry practice. This represents the “best” a slaughtered cow can hope for, but many reports and videos exist that suggest that cows still being alive and conscious while being skinned or dismembered on the production line is not uncommon, some of these reports come from slaughterhouse workers themselves.
5) Leather often involves human exploitation.
The chemicals used to tan leather, and the toxic water that is a byproduct of tanning, affect workers as well as the environment; illness and death due to toxic tanning chemicals is extremely common. Workers across the sector have significantly higher morbidity, largely due to respiratory diseases linked to the chemicals used in the tanning process. Exposure to chromium (for workers and local communities), pentachlorophenol and other toxic pollutants increase the risk of dermatitis, ulcer nasal septum perforation and lung cancer.
Open Democracies report for the Child Labour Action Research Programme shows that there is a startlingly high prevalence of the worst forms of child labour across the entire leather supply chain. Children as young as seven have been found in thousands of small businesses processing leather. This problem is endemic throughout multiple countries supplying the global leather market.
6) Pleather is not a ‘vegan thing’.
Plastic clothing is ubiquitous in fast fashion, and it certainly wasn’t invented for vegans. Plastic leather jackets have been around since before anyone even knew what the word vegan meant, marketing department have begun describing it as ‘vegan leather’ but it’s really no more a vegan thing than polyester is. Most people who wear pleather are not vegan, they just can’t afford to buy cow’s leather, which remains extremely expensive compared to comparable fabrics.
It is striking how anti-vegans consistently talk about how ‘not everyone can afford to eat plant-based’ and criticise vegans for advocating for veganism on that basis, yet none of them seem to mind criticisms directed at people for wearing a far cheaper alternative than leather. You can obviously both be vegan and reduce plastic (as we all should), but vegans wear plastic clothing for the same reason everyone else does: It is cheaper.
7) Plastic is not the only alternative.
When engaging in criticism of pleather, the favourite tactic seems to be drawing a false dilemma where we pretend the only options are plastic and leather. Of course, this is a transparent attempt to draw the debate on lines favourable to advocates of leather, by omitting the fact that you can quite easily just buy neither one.
Alternatives include denim, hemp, cork, fiber, mushroom fiber, cotton, linen, bamboo, recycled plastic, and pinatex, to name a few. Alternatives exist for everything from materials designed to ensure sub-zero temperatures and specialist motorcycle equipment. There are exceptions in professions like welding, where an alternative can be difficult to source, but nobody needs a jacket, shoes or a bag that looks like leather. For most of us, leather is a luxury item that doesn’t even need to be replaced at all.
8) Leather is not uniquely long-lasting.
The longevity of leather is really the only thing it has going for it, environmentally speaking. Replacing an item less often means fewer purchases, and will likely have a lower environmental impact than one you have to replace regularly. Leather is not unique in this respect, however, and the idea that it is, is mostly just effective marketing.
As your parents will tell you, a well-made denim jacket can last a lifetime. Hemp and bamboo can both last for decades, as can cork and pinatex. Even cotton and linen can last for many years when items are looked after well. While some materials are more hard wearing than others, how long an item will last is mostly the result of how well made the product is and how well it is maintained, not whether or not the item is leather.
464 notes
·
View notes
Text
An essential component of the imperial mode of living is the expansion of industrial agriculture, which has gone hand in hand with land grabs and dispossession, expands the power of agricultural and food corporations, and requires ever greater energy input. As a part of a norm that ties increasing meat consumption to rising prosperity, expansion is accompanied by a ballooning system of industrial animal farming and the massive ethical and ecological problems that are part and parcel of this practice. Producing one calorie of poultry meat requires four times that amount in energy input; pork and milk require fourteen times the final amount of caloric energy; eggs thirty-nine times; and beef, depending on the type of feed, twenty to forty times. ‘Today, more energy is invested in agricultural production than is gained in its form as food. The large quantity of high-quality agricultural products fed to livestock is partially responsible for this.’
The Imperial Mode of Living: Everyday Life and the Ecological Crisis of Capitalism
147 notes
·
View notes
Text
"On a blustery day in early March, the who’s who of methane research gathered at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Santa Barbara, California. Dozens of people crammed into a NASA mission control center. Others watched from cars pulled alongside roads just outside the sprawling facility. Many more followed a livestream. They came from across the country to witness the launch of an oven-sized satellite capable of detecting the potent planet-warming gas from space.
The amount of methane, the primary component in natural gas, in the atmosphere has been rising steadily over the last few decades, reaching nearly three times as much as preindustrial times. About a third of methane emissions in the United States occur during the extraction of fossil fuels as the gas seeps from wellheads, pipelines, and other equipment. The rest come from agricultural operations, landfills, coal mining, and other sources. Some of these leaks are large enough to be seen from orbit. Others are miniscule, yet contribute to a growing problem.
Identifying and repairing them is a relatively straightforward climate solution. Methane has a warming potential about 80 times higher than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period, so reducing its levels in the atmosphere can help curb global temperature rise. And unlike other industries where the technology to decarbonize is still relatively new, oil and gas companies have long had the tools and know-how to fix these leaks.
MethaneSAT, the gas-detecting device launched in March, is the latest in a growing armada of satellites designed to detect methane. Led by the nonprofit Environmental Defense Fund, or EDF, and more than six years in the making, the satellite has the ability to circle the globe 15 times a day and monitor regions where 80 percent of the world’s oil and gas is produced. Along with other satellites in orbit, it is expected to dramatically change how regulators and watchdogs police the oil and gas industry...
A couple hours after the rocket blasted off, Wofsy, Hamburg, and his colleagues watched on a television at a hotel about two miles away as their creation was ejected into orbit. It was a jubilant moment for members of the team, many of whom had traveled to Vandenberg with their partners, parents, and children. “Everybody spontaneously broke into a cheer,” Wofsy said. “You [would’ve] thought that your team scored a touchdown during overtime.”
The data the satellite generates in the coming months will be publicly accessible — available for environmental advocates, oil and gas companies, and regulators alike. Each has an interest in the information MethaneSAT will beam home. Climate advocates hope to use it to push for more stringent regulations governing methane emissions and to hold negligent operators accountable. Fossil fuel companies, many of which do their own monitoring, could use the information to pinpoint and repair leaks, avoiding penalties and recouping a resource they can sell. Regulators could use the data to identify hotspots, develop targeted policies, and catch polluters. For the first time, the Environmental Protection Agency is taking steps to be able to use third-party data to enforce its air quality regulations, developing guidelines for using the intelligence satellites like MethaneSAT will provide. The satellite is so important to the agency’s efforts that EPA Administrator Michael Regan was in Santa Barbara for the launch as was a congressional lawmaker. Activists hailed the satellite as a much-needed tool to address climate change.
“This is going to radically change the amount of empirically observed data that we have and vastly increase our understanding of the amount of methane emissions that are currently happening and what needs to be done to reduce them,” said Dakota Raynes, a research and policy manager at the environmental nonprofit Earthworks. “I’m hopeful that gaining that understanding is going to help continue to shift the narrative towards [the] phase down of fossil fuels.”
With the satellite safely orbiting 370 miles above the Earth’s surface, the mission enters a critical second phase. In the coming months, EDF researchers will calibrate equipment and ensure the satellite works as planned. By next year [2025], it is expected to transmit reams of information from around the world."
-via Grist, April 7, 2024
#satellite#epa#environmental protection agency#environmental activism#methane#emissions#climate change#climate news#climate action#natural gas#fossil fuels#global warming#good news#hope
143 notes
·
View notes
Text
i am also vegan because cattle farming is the main cause of amazon deforestation and illegal land seizures fom indeginous brazilians
i am also vegan because the shrimp industry enslaves and abuses migrant fishermen from south-east asia
i am also vegan because animal agriculture is one of the main drivers of climate change, which most affects the poorest on earth
i am also vegan because european fishing vessels are systematically stealing fish from somalian waters
i am also vegan because we could directly feed an additional 1 billion people with some of the food we feed to livestock animals
i am also vegan because animal agriculture is a main driver of antibiotic resistance, which killed 1,27 million people in 2019
i am also vegan because i believe it is wrong to exploit the planet and the most vulnerable populations for the sake of sensory pleasure
117 notes
·
View notes
Note
i've been reading some of your arguments for why you wouldn't be vegan and just wanted to point out that you have a lot of fallacy in your arguments. might want to do a look in there to make sure you are stating your morals/prose properly, and aren't using any arguments that can be easy to shutdown. appeal to tradition. appeal to futility and the argument that personal pleasure(taste etc) allows us to do what we want to others without consent to their bodies is a moral issue i don't think you align with but i could be mistaken. a lot of people who enjoy sex don't rape for example.
i also liked the taste of animal flesh and organs but realized my personal pleasure i got from consuming them pales when it is placed against the value of someone's life and what they have to endure for me to get that on my plate, it's easy to have a disconnect when you don't know. health, animals, earth all benefit from a plant based diet. a plant based diet can feed more people for cheaper, helping to end hunger.
you can say you cook "more vegetarian" but i implore you to continue your growth and align your actions with your morals and continue to strive for a plant based diet in the future. you don't seem like a cruel person but i could be wrong. i've been vegan for 15 years and i cook so many amazing meals and can tell you from experience you don't have to limit yourself to oatmeal. if you have time to watch/listen id implore you to check out gary yourofsky "the most important speech you will ever hear"
good luck to you on aligning your moral values with the actions you take daily/what you pay for.
Okay. Do you say these same things to vegans that wear cotton? That also kills a lot of animals. Like a lot of them. It hurts entire ecosystems.
There’s no way to buy stuff in our current economy that doesn’t hurt somebody or something. I know how to cook tasty and cheap and mostly healthy meals for myself and the easiest way to do that is with pre-cut veggies, eggs, and the occasional poultry.
Yeah I’m wasting plastic. Yeah I’m eating animals. Vegans eat almonds and quinoa. Those are bad farmed at an industrial scale.
Being an omnivore is natural and I don’t feel bad about it. If you look me in the eyes and ask me if I could kill a chicken the answer is yes. I’ve done extensive research on how to do it safely, actually. If the apocalypse comes I’m raising hens for meat.
Also comparing animal agriculture to rape? Couldn’t find literally anything else to compare it to? Really?
179 notes
·
View notes
Note
Can we see more about pyliod....he's so silly. ♥️ kissing him on the head.
I'm obsessed with how khait mimic real world bulls but also goats in their behaviors. are there any other behaviors/traits they mimic from IRL animals?
Which leads me to the question: what separates livestock from pets?
Esp for brakul, I'm assuming the animals he lived around when he was younger were livestock and meant for eating - but what if you had a favorite? Was it different for janeys? Hibrides?
Also leads me to another question: fish keeping - is it a hobby? Are fish just seen as food or can they be considered decorative?
(please forgive any spelling errors it's 1 in the morning for meeee)
Don't know if you saw this post but this gives a good rundown of khait behavior. They're based on wildebeests and most of the descriptions of their social behavior are accurate to them, other aspects of their behavior is pulled mostly from other bovids (other antelopes mostly. l swear I saw urine self-anointing+wallowing by topi or hartebeest or smth in a documentary once, but in terms of bovids that might just be a goat thing. Cervids also do that). Not much of their behavior is actually based on cattle, besides using cattle as a model to inform the concept of a hypothetical domesticated antelope. There's also some horse influence, though in that case it's pretty much exclusively to inform the concept of a non-horse domestic ungulate used Primarily for riding, and their interactions with humans.
The like, general definition of distinction between livestock/pets would be a venn diagram between 'livestock' 'working animals' and 'pets', with livestock being animals raised for production (meat, wool, fur, leather, eggs, milk, etc), working animals being used for physical labor or otherwise performing utilitarian 'jobs' (plow animals, riding animals, ratters, herders, guardians, etc), and pure pets having no directly 'productive' role and exist for companionship, ornamentation, etc (though the definition of a pet can be pretty nebulous, especially if you're framing it around emotional attachment instead of the lack of a productive angle). These categories can heavily overlap.
This is just a generalized answer (not even in-universe). How a culture defines these concepts separately (if it does at all) is going to vary extensively.
Brakul grew up surrounded by livestock/working animals and virtually no animals kept EXCLUSIVELY for companionship. The core subsistence method is a mix of settled agriculture (producing primarily grain) and seasonal pastoralism of cattle and horses (producing primarily dairy and wool), occasionally supplemented by hunting and fishing of wild game. The diet revolved around dairy and grain with meat being eaten irregularly, especially for people who aren't rich (which in this particular context is primarily measured in the quality and quantity of livestock- someone wealthy in cattle can afford to slaughter more frequently). Slaughtering a cow is a special occasion. Brakul's clan was on the lower end of the livestock wealth scale, so he ate meat infrequently and almost never his Own livestock (mostly eating hunted/fished game, meat given as gifts or in trade, meat provided by the ruling clan by social obligation).
(This is also broadly true of animal husbandry in Real Life across history prior to industrialized farming- most livestock is more valuable alive as a continuously replenishing resource (milk, wool, eggs, pulling plows, etc) and thus would be slaughtered for personal use infrequently. In class stratified societies, the majority of animals raised for meat would often feed upper classes rather than the people actively involved in rearing them. Some pastoralist societies will rarely or virtually never slaughter their animals for meat, as they are wholly relied on for products they produce while alive.)
So Brakul existed in a context where it was very possible to get attached to livestock and working animals. A lot of basic survival revolved around the dairy and wool the livestock provide, there are high emotional stakes in their survival and well-being, so personal attachment to these animals (even those likely destined for slaughter) can come naturally and be beneficial. The concept that's more alien to him is pure companion animals that don't really do anything directly productive. House dogs kind of freak him out because they're SO different from the dogs he was used to (extremely independent livestock guardians that don't really bond with people, and herding dogs that bond readily with their owners but are notably intelligent and self-sufficient). Encountering dogs that are utterly dependent on their owners and desperate for human attention was like 'what the fuck is wrong with that thing? sad'.
Pretty much the exact reverse situation for the characters from noble families. They would rarely be in close contact with livestock or subsistence level working animals (if anything, they/their families own land and livestock that is entirely raised by peasant workers), and instead would have most contact with pets/ornamental animals/leisure type working animals (hunting dogs, sport khait), and animals used in transportation (cart khait and oxen). They have VERY clear, clean-cut delineations between 'pet' and 'food' (though still not as much as is common in industrialized societies where most people are completely and utterly disconnected from the sources of their food. They're still Connected to the process, seeing animals being slaughtered is a part of daily life). They also would have eaten meat on a much more regular basis, while having little to no personal involvement in its production.
Wardi culture as a whole is not big on companion dogs (there are a few companion dog 'breeds' within the region, but most are hunting or herding dogs). Polecats are by far the most common companion animal in this cultural sphere (they technically fill working functions as ratters, but are mostly kept as housepets). Other animals kept purely as pets are mainly ornamental fowl and ducks. There's also a kind of pygmy horse breed that is kept as a companion animal (reminder that horses in this setting share the size range of goats).
Faiza, Couya, Janeys and Hibrides all grew up with pet polecats and hunting dogs, and sport khait owned by their families. Hibrides had pygmy horses as a kid. In the present day, Janeys' household has two hunting dogs that he doesn't like all that much, he also got two polecats for his children (one of which died tragically after being thrown from a window by his eldest), and has 14 total khait (12 of which are Brakul's) (technically owns another herd and a herd of cattle, but has nothing to do with them. It's an investment). Faiza likes dogs quite a bit and owns three bred hunting dogs and one feral dog she took off the street, also two khait (she owns land and the animals are kept there).
Re: fishkeeping. There's going to be plenty of variation in a global context, but broadly speaking keeping fish as a hobby/for display/other non-meat purposes is going to be on the rarer side in this setting. This is a limited practice in Imperial Wardin (you'll get the occasional wealthy home keeping fish in a courtyard pool but there's no traditions built around it). In terms of nearby civilizations, it's a much more significant practice in Bur, where water gardens with ornamental plants and fish are integrated into temples, city layouts, and wealthy homes.
#Also keeping animals PURELY for companionship is going to be rare in this setting overall. The vast majority of the world's population#is existing at subsistence level and maintenance of an animal that provides no practical benefit in return (as much as one can argue#that emotional companionship is a practical benefit) is unsustainable in a lot of contexts.#Though sometimes the 'practical benefit' can be intrinsic to the animal enough to lower this barrier- ie any dog can benefit its owners#by barking to alert of intruders (and may be able to mostly fend for itself and not require a massive investment in resources)
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Environmental charity Climate Force is collaborating with the Eastern Kuku Yalanji people and rangers to create a wildlife corridor that runs between two UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Australia: the Daintree Rainforest and the Great Barrier Reef.
Wildlife habitats in this region have become fragmented due to industrial agriculture, and a forested corridor is expected to help protect biodiversity by allowing animals to forage for food and connect different populations for mating and migration.
The project aims to plant 360,000 trees over an area of 213 hectares (526 acres); so far, it has planted 25,000 trees of 180 species on the land and in the nursery, which can also feed a range of native wildlife.
The project is ambitious and organizers say they’re hopeful about it, but challenges remain, including soil regeneration and ensuring the planted trees aren’t killed off by feral pigs or flooding.
#good news#environmentalism#science#environment#nature#animals#conservation#indigenous peoples#rainforest
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
when will people realize that as long as there are slaughterhouses, there WILL ALWAYS be minority adults and children drafted and exploited into the traumatic and psychologically shattering experience of working there under egregious and often fatal conditions
you cannot have both. you cannot have a healthy slaughterhouse work environment that is safe, fulfilling, and financially beneficial. it will NEVER happen. think about it. no matter how small, family-owned, local, or whatever else bullshit excuse you’re parroting from twitter
even if you don’t give a fuck abt nonhuman animals (in which case you’re just. an idiot but whatever) then you must eliminate these jobs altogether in order to prevent the abuse, mutilation, and trauma that the humans there have to go through in order to perform the job. not to mention the migrant laborers who work under unbelievably hellish conditions for pennies on the dollar to harvest the immense amount of cereal/grain food that goes not to feed us but to fatten those animals headed to slaughter
it is not possible to make the killing floor, nor the raping or milking or skinning or chromium tanning floor, a safe or harmless or emotionally normal profession.
it is not necessary. it must ALL go. it harms all who are involved beyond measure.
so how do you do it?
stop funding this shit. stop buying the products. go vegan. stop supporting it. stop ignoring it. stop pretending you give a shit abt anyone’s rights if you turn a blind eye to what animal agriculture does to the humans and the nonhuman animals it shackles.
you all believe in boycotts? prove it. actually do it and boycott one of the most capitalistic and nuclear evils out there, and do it for life. or else you’re just an internet philosopher at best, and a gaping hypocrite besides.
because as long as you willingly support this, you are telling the world in no uncertain terms that it’s ok for child laborers to suffer for your food, because you like the end result. and that’s no better than a conservative hoarding his guns.
you are literally telling on yourself that you think this industry is some kind of necessary evil, that SOMEONE has to do it (no they don’t btw), and, since it’s not you, you’re ok not acting on it at all to any degree. as long as you don’t have to see it or think about it or be called upon change your life in any way, it’s fine.
it’s 2024. DO BETTER.
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pigs Eyes & Crying Elephants: Sentient Beings Manifesto
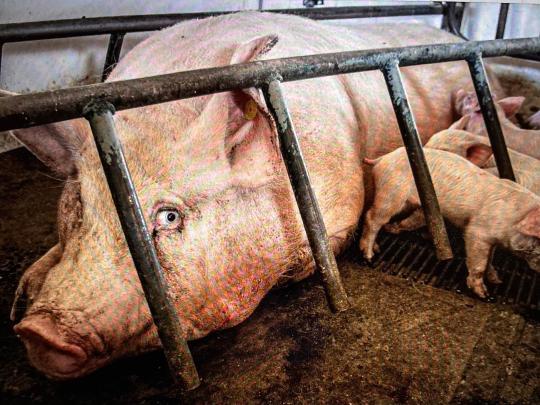

A commercial with a crying elephant & the eyes of a pig.

I saw the elephant commercial for an animal welfare group last Tuesday during NXT.
That is what started all of this.
I was vegetarian for two years from 2013 to 2015 meaning I didn't eat any meat or seafood but I did eat eggs & consume dairy.
Then I started eating meat again in 2015.
Then about a year ago, I decided I would eat vegetarian during the week (Monday through Friday) and then eat meat & dairy on the weekends -- so my diet was 75% vegetarian for the past year.
But I was still eating all the chocolate, cheese & all of the dairy tingz.
Then I saw a commercial last week during NXT with a crying elephant. It really got to me.
I started during research on elephants & emotion. Turns out elephants pass the "mirror test" and are self-aware.
So are dolphins.
That led me down a rabbit hole where I started researching the emotional self-awareness of other animals and was surprised to find similar findings for pigs, chickens and cows.
And monkeys -- rhesus macaques are endlessly tortured for human medication. They are extremely self-aware and emotional.
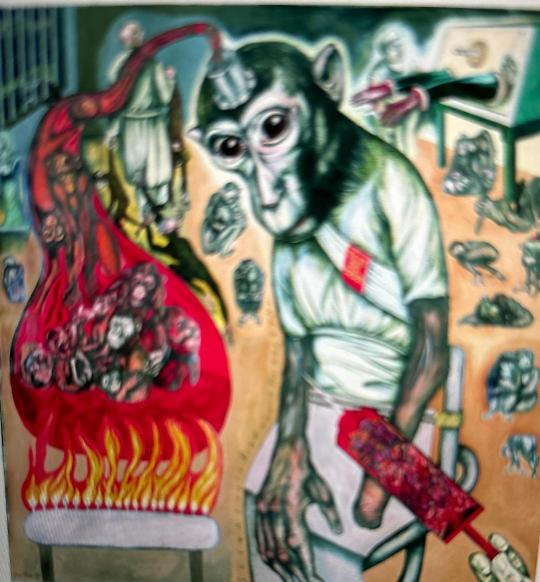

I questioned myself on why my 75% vegetarianism diet shouldn't be 75% plant-based (vegan).
And I realized that I didn't want to give up exactly two things: cheese & chocolate.
And hell no, I didn't want the vegan alternatives.
But I started researching the dairy industry which then led me to researching CAFOs (commercial agricultural feeding operations) aka factory farms aka hell on earth aka infinity mirrors of animals being tortured endlessly.
10 billion land animals are slaughtered every year in the United States. Millions a day.
Is that really necessary?
Then I realized that the dairy industry was the plot to a dystopian sci-fi novel:
Women are forcibly impregnated, their babies taken from them immediately after being born — the baby boys are killed within 1 to 4 days, the girls are imprisoned to be forcibly impregnated just like their mothers.
The impregnation cycle is relentless and there are absolutely no breaks between artificial insemination - impregnation - birth repeat.
The woman are also given artificial growth hormones to force them to grow bigger & more quickly — the easier & quicker to impregnate them.
The women are kept in stalls that are so small & overcrowded they cant even move or turn around.
The women never see natural sunlight.
They are only allowed out of their stalls to give birth.
They are forced to endlessly lactate and pumped by machines so mercilessly that they bleed.
I still didn't feel that I could give up cheese 75% of the time.
Then I questioned myself on why not.
I have done very restrictive very low calorie diets in the past. I used to work out 2 hours a day, 6 days a week. I used to have a six pack.
I broke my 13 year addiction to the NFL & won't even be watching the Super Bowl once a year as of this year.
Why then is not eating cheese 75% of the time a seeming impossibility?
That was honestly how I felt.
So, I googled and found this:
Cheese contains casein. This is what causes such intense cravings. It also contains casein fragments called casomorphins, a casein-derived morphine-like compound. Dairy protein has opiate molecules built in. When consumed, these fragments attach to the same brain receptors that heroin and other narcotics attach to. Casomorphins cross the blood brain barrier and attach to dopamine receptors.
Cheese is literally 10% as addicting as morphine.
Yet they (do ask yourself who they is) have the motherfucking audacity to say it is "no more addictive than anything else that could be addictive, like Pringles or fast food."
First of all -- they are simply proving the point as those foods -- OPFs or overly processed foods & fast food -- also are highly addicting by deisgn, they are literally made to be. Study after study has confirmed that the most addictive foods are foods that are highly processed, high in fat, high in sodium and/or sugar.
Checks out, right?
What foods do you consider the most addicting?
Probably Oreos, potato chips, pizza, french fries, mozzarella sticks, fast food, donuts, cookies, brownies, pretzels, burgers like anyone else.
Right?
They are designed that way on purpose.
They create addicts on purpose for profit.
Cancer, diabetes, hypertension, high blood pressure, artherosclerosis, blood clots, immune system disorders, heart disease, stroke, heart attacks are all caused by diet & lifestyle.
It is a very lucrative business for them.
A million people are already on Wegovy babes?
It's a set up.
They make the food that makes people sick and they make the medicine that people buy after they buy the food that makes them sick. The above diseases did not exist at the current rate even 100 years ago. It's due to OPFs (overly processed food), PFAs (forever chemicals), toxins, sugar substitutes, partially hydrogenated vegetable oil (transfat), high fructose corn syrup, modified food starch, monosodium glutamate, dextrose, sucralose, lecithin, emulsifiers, aspartame, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), bioengineered ingredients, pesticides, artificial flavors & colors, preservatives, synthetic lab-made chemicals.
Capitalism is nothing but a death cult.
Wake up.
They are literally made that way on purpose & designed to be addictive.
But the way that casein is addictive is truly unique because it is binding itself to receptors in our brains the way that morphine & heroine does.
So, I decided I want to do something that is sustainable in the long-term 15 & 20+ years from now. I am 43.
I don't play an all or nothing zero sum game of zealotry where it's something that is impractical.
I look forward to the weekly meals with my husband.
We have been together for 17 years and have been married for over a decade.
I've looked at thousands of recipes over the years and have curated a Top 100 list of our absolute favorite receipes plus ones that I want us to try.
We always make a meal on the weekend & post the pictures on his Facebook.
While we eat our weekly meal, we talk, hang out, watch stuff on Youtube, baseball, basketball & wrestling.
It's one of the things we look forward to doing together as a couple the most.
He is the quintessential "meat & potatoes guy" but when I started eating vegetarian 75% of the time last year, he agreed to eat vegetarian 3 to 5 days a week.
He does eat meat & dairy the other days of the week.
I have decided that maintaining our weekly meals ritual as a couple is important to me.
So, for this to be sustainable it has to allow for our weekly meals to have meat and/or dairy -- and also, during the holidays, I want to be able to eat meat and/or dairy.
Other than that, Monday through Friday, my plan for the rest of my life is to eat a vegan (plant-based) diet 75% of the time -- no meat, seafood, dairy or animal-based or derived ingredients or by-products.
I immediately went through my apartment this morning once I had decided on this & was disappointed at how many of my snacks weren't vegan -- Annie's Organic granola bars, Nature's Bakery Bars & literally all of my remaining Halloween candy (Take 5, Reese's Cups, Crunch, & candy corn).
I gave it all to my husband in a bag this morning for him to take to work.
Since they are snacks that I ate on a daily basis, it is better to remove them from the apartment as my goal is to now eat vegan (plant-based) diet 75% of the time, Monday through Friday.
Staring at a bag of my absolute favorite non-vegan candy corn isn't exactly going to help me achieve that.
Vox When asked in an interview on the Climavores podcast why farms aren’t regulated to reduce pollution, USDA Secretary Tom Vilsack said there are simply too many farms to regulate, and that conservation efforts should be voluntary
According to Civil Eats, a nonprofit publication covering the US food system, nearly all animal agriculture operations are exempt from federal protections under the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, and the agency doesn’t respond to 85 percent of worker fatalities on animal farms.
Most states exempt livestock from anti-cruelty laws, and many states have passed “ag-gag laws,” which criminalize activists and journalists for simply recording what goes on at farms.
All 50 states have so-called “right to farm” laws, which prevent citizens from suing farms for nuisances like pollution and odor that degrade their quality of life.
A recent analysis from Stanford University researchers found that from 2014 to 2020, the US livestock sector received about 800 times more public funding than the meat, egg, and dairy alternatives sector.
Farmers are heavily overrepresented in government, with 25 current members of the US House of Representatives, or their family members, having collected millions of dollars in agricultural subsidies. That’s almost 6 percent of the chamber, even though just about 1 percent of Americans live on farms. The dynamic is the same at the state level.
Corn and soybean production, most of which is dedicated to ethanol and livestock feed, accounts for half of all crop cash receipts.
Don't you think some of the children literally starving to death right now in North Gaza in Palestine could have used some of that corn & soybean? No? The livestock that we don't need to eat because we don't need meat to survive needed it more than the children literally dying from starvation right now in North Gaza?
Vox Raising livestock requires far more land and water than growing plant-based foods — and produces far more pollution.
Over the past decade, the animal-agriculture industry has been behind the introduction of "ag-gag" bills in more than half of all state legislatures across the country. These dangerous bills are designed to silence whistleblowers revealing animal abuses on industrial farms. Ag-gag laws currently exist in six states, penalizing whistleblowers who investigate the day-to-day activities of industrial farms, including the recording, possession or distribution of photos, video and/or audio at a farm.
The USDA never conducts surprise audits, or any audits at all, to verify the company is telling the truth. It is, in essence, an honor system. The USDA also has an incredibly low, and often nonsensical, bar for what passes as humane treatment.
Over the course of more than a dozen shifts at multiple Foster Farms facilities, the investigator — who requested anonymity due to the covert nature of undercover investigations — documented workers slamming birds into crates, kicking and hitting chickens, and numerous instances of forklift drivers running over birds.
The investigator recalled making eye contact with a bird shortly after they were run over by a forklift. “They were being crushed and everything was being pushed forward, and they had their beak open, and they had this look on their face like they knew that they were dying,” the investigator told me. “And then I watched them flap and struggle for a moment before passing.”
The investigator chalked up most of the cruelty to the chaotic, fast-paced work environment imposed by supervisors during long, grueling shifts.
But you wouldn’t know that from its marketing or its “American Humane” certification.
Chickens raised for meat in America -- 98% of land animals that get slaughtered each year in factory farms -- are five times bigger today than they were in the 1950s! In 1957, chickens on farms raised for meat were 907 grams. In 1978, chickens on farms raised for meat were 1,808 grams. In 2005, they are 4,202 grams! WHERE IS OUR HUMANITY???????????
Vox American Humane allows for the standard chicken slaughter process: shackling chickens upside down, dunking them in a bath of electrified water to stun them unconscious, slitting their throats, and then placing them in a scalding vat to loosen their feathers.
Despite all that, the resulting meat can still be advertised as humane, sustainable, and produced from healthy birds.
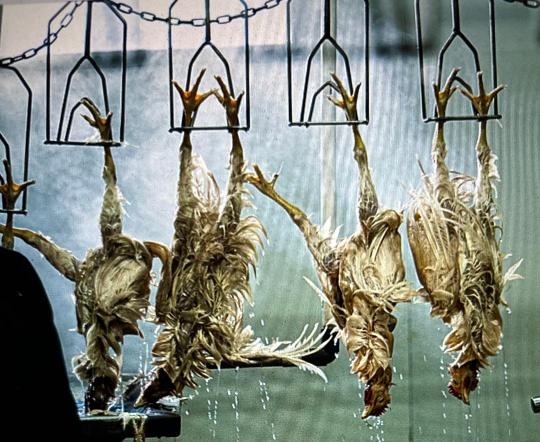

Currently, chickens and other poultry birds have zero federal legal protections while on the farm or in the slaughterhouse.
During their short stint on behalf of the Washington, DC-based animal rights group Animal Outlook, the investigator documented hours upon hours of the typical horrors found on chicken factory farms: tens of thousands of birds stuffed into dark warehouse-sized barns, many of them severely injured with gruesome lesions, injuries, and deformities. At more than one point, birds are deprived of feed or water, and there was also a rat infestation and footage of bugs crawling in the chickens’ feed.
The conditions are visibly at odds with Tyson’s advertising claims that it treats animals humanely and raises “happy” and “healthy” chickens.
“It’s just a living nightmare,” the investigator, who requested anonymity due to the covert nature of undercover investigations, told Vox. “A video just does not do it any justice.”

Despite the horrific findings, they’re not all that different from the conditions documented at other farms that raise chickens for Tyson and Tyson’s competitors. The US Department of Agriculture (USDA) says chicken producers using the label “free-range” must provide birds “continuous, free access to the outside” for over 51 percent of their 6.5-week lives.
Is 6.5 weeks a life?????????????????????
In another portion of Animal Outlook’s footage, when the investigator asked the farm manager why so many chickens couldn’t move, he was blunt:
“They’re just fucked up.”

According to a 2021 ProPublica investigation, humane-labeled chicken is often processed in the same slaughterhouses, owned by companies like Tyson, as conventional meat.
“You almost couldn’t design a more torturous setting,” she said, adding that the video shows dying and dead chickens in “advanced states of decomposition” with the potential to “spread infectious disease to the other birds, human workers, and unsuspecting Tyson customers.”
WHERE IS OUR HUMANITY???????????????
Animal Outlook’s investigator also documented bugs crawling in the chickens’ feed, and rat infestations — problems echoed by the Tyson technician in the undercover video.
“The little baby chicks are gonna peck at those bugs, eat them, and then they’re gonna die,” Tyson’s technician told the farm manager in a conversation recorded by the investigator.
“You got rats in there, you got fresh rat activity in all your houses.” Despite these known issues, Animal Outlook alleges Tyson delivered fresh chicks to the farm.

As journalist Eyal Press, author of Dirty Work, a book on jobs in morally troubling industries like poultry, put it in a Vox podcast interview: “On the rare occasions when the curtain is pulled back and we see this dirty work going on, the blame goes to the lowest-ranking people at the bottom, and that’s very convenient for society.”
Ofcourse it is -- society still wants their Wendys Spicy Nuggs.
Vox However, holding meat companies legally accountable for how they treat animals is exceedingly difficult because there are no federal laws that protect animals while on the farm, and birds are exempt from federal slaughter and transport law.
Chickens raised for slaughter are bred in "high stocking densities", meaning they are unable to "move freely to flap their wings" or show "natural behaviors".
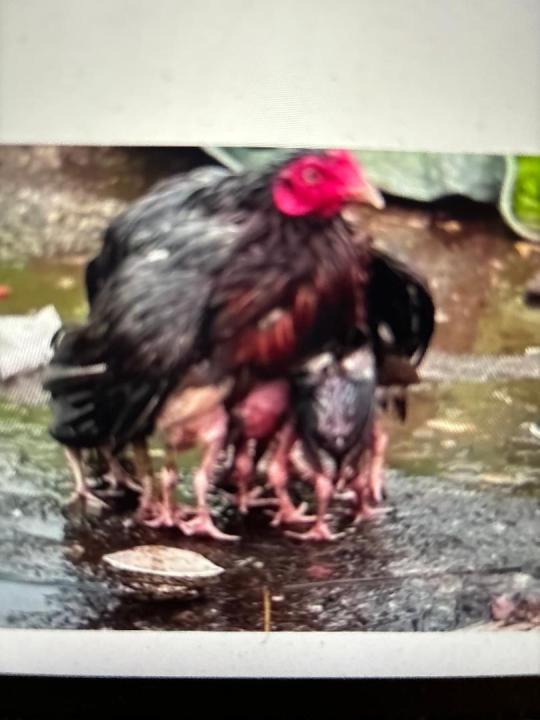

"They [Frankenchickens] have been bred to eat at an extraordinary rate so they put on this completely inappropriate weight gain just to get to market as quickly as possible."
If you are a starseed, understand our mission is to break up & dismantle Big Meat & Big Ag (& ofcourse Big Oil, Big Pharma, etc...): LPE Project
Today four massive companies – JBS, Tyson Foods, National Beef, and Cargill – control over 80 percent of America’s beef. Three companies – JBS, Tyson, and Smithfield Foods – control 63 percent of America’s pork. Two of those – JBS and Tyson – also control 38 percent of poultry. The grain, seed, farm equipment, agrochemical, livestock genetics, and animal pharmaceutical industries have likewise become highly consolidated.
These companies possess dominant market power as both sellers of meat and buyers of livestock, which they used to raise prices for consumers and lower prices paid to farmers.
In 1971, President Richard Nixon appointed Earl Butz – who at the time served on multiple agribusiness boards – to lead the USDA, opening a revolving door between the industry and the agency that has swung non-stop ever since.
Under Butz, subsidies for fossil-fuel-intensive monocultures led to a glut of cheap grain, which in turn led to factory farmed animals. “Since factory farms could buy grain for less than it cost farmers to grow it, they could now fatten animals more cheaply than farmers could,” wrote Michael Pollan.
In the last year, top companies in every major American meat sector – beef, pork, chicken, and turkey – have been subject to civil suits and/or federal investigations for conspiring to keep prices high. One lawsuit estimates that chicken industry price-fixing alone costs the average American family of four $330 per year.
The primary reason multinational meat conglomerates have flourished, and meat prices have remained artificially low, is that our government massively subsidizes them at everyone else’s expense.
Our government subsidizes Big Meat directly by allocating the bulk of federal crop subsidies to large farms growing animal feeds, by financing animal factory infrastructure, by buying billions of dollars of their products, and much more. In exchange for this support, taxpayers get hijacked federal agencies, policies shaped by pro-industry academic research, a less responsive democracy, and forceful industry lobbying to keep it that way.
It does this by failing to regulate the environmental impacts of factory farming, including the industry’s role in contaminating air, poisoning drinking water, and driving the climate crisis; by failing to require safe conditions for slaughterhouse workers; by denying most farmworkers the rights to form unions and earn minimum wage and overtime pay; by exempting “common farming practices,” no matter how cruel, from most state animal anti-cruelty statutes; and by failing to restrict the industry’s use of antibiotics (used to speed growth and keep overcrowded animals alive) despite the resulting increase in drug-resistant infections.
Farmer suicide rates are now 3.5 times that of the general population.
It is now commonplace for pigs (and their diseases) to be trucked hundreds of miles across the country without food, water, bedding, protection from extreme temperatures, or adequate space.
BedlamFarm.com One of these happenings was the discovery by scientists in New York in the 1950’sthat by adding tiny traces of antibiotics to animal feed they could increase the growth rates of animals.
With these new tools, farmers could concentrate animals in confined areas on a scale never before possible.
This was soon to be called “factory farming” by the few voices raised in alarm. The term has never been complimentary..
At the same time as the geneticists made their discoveries, Earl Butz, Dwight Eisenhower’s Agriculture Secretary, defined the new future.
It isn’t clear if Butz, a crude by visionary agriculture economist, saw the coming future or created it.
Farms, he said, and farmers had to consolidate, corporatized, embrace economies of scale, just what most family farmers would never do. The economists picked up this cry, and the family farmers never had a chance.
Butz was serious, perhaps prescient. He meant that in order to survive, farmers must pursue a new corporate model for farms – maximize profits, minimize loss.
Corporations jumped into farming big-time, buying giant tractors, hiring biologists and geneticists to redesign animals and turn them into unhealthy freaks with short live spans and no resistance to illness, parasites, or viruses, setting up distributions systems that could even sell milk and meat overseas.
On the corporate farms, when a cow gets sick, it is instantly put to death, veterinary care cut into profits, the cow just goes to slaughter.
The average live span of a milk cow, says the Agriculture Department, plunged from 12-15 years to two years by the 1990s. Cows on corporate farms never set foot outside, some never left their stalls, get no exercise, and are bored almost senseless.
Where is our humanity?????????????????
There is no stimulation in their lives, no change of scenery no hed for these herd animals, no walk, grazing, or hanging out with other cows, a cow’s favorite activity.
They live as long as they can produce more and more milk, and when they can’t, they die.
For animals, life became an Orwellian horror show, their very bodies, and spirits taken from them as they were genetically engineered to be profit centers, not animals with human caretakers and individual personalities and traits.
So have the chickens and pigs, many of whom live their lives without ever standing up in factory farms, mostly in the mid-central United States.
Most Americans will never see what is happening to these animals or even hear about them.
The people who increasingly have taken over the care of the animals we eat are sometimes the cruelest and most immoral people who have ever come within a hundred miles of a farm.
Comment to the above article: A quick google search reveals legislation proposed to add oversight to use of antibiotics in animals in 2018, 2017, 2013, 2002- all fought by Big Pharma. Often with the same ferocity and tactics used by Big Oil to fight against regulations to slow climate change.
ForksOverKnives: The USDA is tasked with setting the nation's nutrition guidelines. Yet this is in direct conflict with its primary interest: ensuring the profitability of producers of foods such as dairy and meat. These foods are known to increase the risk of obesity, diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular disease. Is it any wonder that programs administered by the USDA and funded by the Farm Bill preferentially feed school children and the poor unhealthy foods that cause chronic disease?
The farming practices that underpin our healthcare crisis also degrade our environment. To grow vast swaths of these monoculture crops, enormous amounts of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides are required. Many of these agricultural chemicals are suspected endocrine disruptors and carcinogens that are thought to alter human DNA down through the generations.
During my lifetime alone, annual worldwide pesticide production has increased from 200,000 tons to more than 5 million tons, according to estimates from The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. It has gotten to the point that many of these chemicals now rain down upon us. These pesticides wipe out beneficial and native wildlife such as honey bees, monarch butterflies, and songbirds.
A Happy Meal? If, by eliminating Farm Bill subsidies, the cost of a Quarter Pounder with Cheese were to rise from, say $4 to $15, eating habits would likely shift toward eating healthier foods, especially if at the same time, a program were put in effect to incentivize the consumption of whole plant foods. In fact, a large nationwide program in South Africa has already demonstrated that the public will consume more fruits and vegetables when these healthy foods are subsidized.
Making Us Sick Makes Them Money The 17 percent of GDP (about $3.2 trillion) the nation now spends on health care will rise to 20 percent of GDP by 2025, according to The Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services. The CDC estimates that 86 percent of this money is not actually spent on making people healthy; it is spent on treating and sustaining chronic illness such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, obesity, diabetes, and dementia. The medical evidence shows that most of this chronic disease is the result of the food we eat and can be prevented and even reversed by eating a plant-based diet.
Fish have it worse in one way -- they have ZERO legal protections.

AnimalEquality Commercial fishing is cruelty to animals on a colossal scale, killing nearly a trillion animals worldwide every year. Ships the size of football fields use techniques such as longlining and gill nets.
Gill nets, which range from 300 feet to seven miles in length, create large walls of nets that fish are unable to see. They inadvertently swim into them and many will suffocate or bleed to death.
In the United States, fish are not covered by the Humane Slaughter Act. This results in a wide variety of cruel slaughter methods dependent on industry, company, and species.
Fish are usually removed from the water and left to suffocate and die. They desperately attempt to escape as their gills collapse preventing them from being able to breathe. Larger animals, such as tuna and swordfish, are usually clubbed to death. This often leads to an animal being injured but regaining consciousness and the process having to be repeated several times.
There are 1.3 billion farm raised fish in the United States.
Vox It’s unsurprising that fish have been ignored. They live underwater, so we rarely interact with them. They can’t vocalize or make facial expressions, so it’s much harder to understand them than mammals and birds. And research has shown that the further animals are from us on the evolutionary chain, the less likely we are to try to protect them.
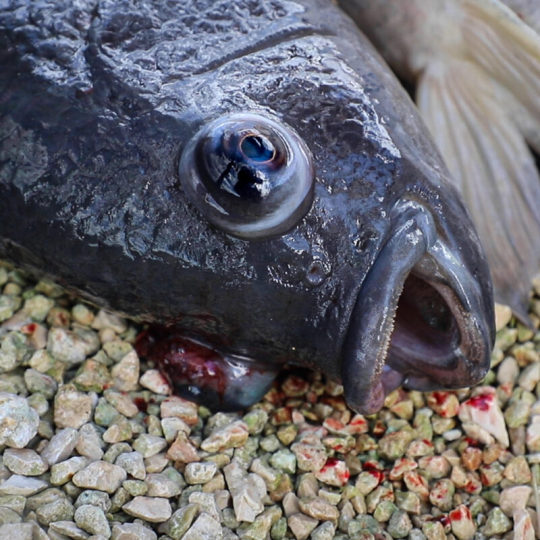

In commercial ocean fishing, the welfare concerns are mostly relegated to the final minutes or hours of a fish’s life — they’re typically left to suffocate to death on deck, which can take under an hour or up to several hours.
Other welfare issues include rough handling and the inability to express natural behaviors, like migration and nesting.
One of the bigger findings of the past two decades has been that fish have nociceptors, sensory neurons that detect and respond to damaging or threatening stimuli — a strong indicator they experience pain.
But just like with other species, researchers have repeatedly demonstrated that fish behave differently in adverse conditions (for example, they limit eating and activity) and stop these behaviors when pain relief is given.
They don't WANT to believe fish feel pain because it will lower their profits -- read the above again & honestly tell me that those fish don't sound like they were in pain & then relieved from pain -- so should they be left alone on ship decks to suffocate to death for HOURS???????????
Wild-captured fish experience agonizing final moments no animal should have to endure, as pressure weighs on their bodies when they’re quickly pulled up out of the ocean’s depths in nets, and they begin to suffocate.
Death, too, is cruel on fish farms, where many fish are killed slowly by suffocation or in ice water.
Existing in these cramped environments is a far cry from the lives fish would experience in their natural habitats. For one example, salmon may swim spans of hundreds of miles to reach the ocean from the streams in which they hatched, and much farther as they reach feeding grounds, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. Sometimes, salmon will spend years at sea before returning to their original stream to spawn.
Extraction of groundwater for aquaculture has been found in one study to accelerate sea level rise by causing land to sink.
Pigs on factory farms are often cannibalized, forced to eat meat from fellow pigs.
WHERE IS OUR HUMANITY???????????

Where is humanity?
They are sentient beings: capable of feeling pain, and experiencing a range of emotions. Scientific evidence has revealed that fish are far more intelligent than people assume. They have long-term memories, complex social structures, problem solving abilities, and some have been seen using tools.
Fish are even crushed to death & literally cut in half while alive!
Where is humanity?
Porkopolis It is near impossible in the industry to encounter a conceptual or ethical limit proposed for sows biological reproductive capacity.

AnimalsAustralia Farrowing crates are cold, hard metal cages with steel or concrete floors. In factory farms around the world, it’s standard practice to transfer mother pigs to a farrowing crate 7-14 days before she gives birth to her new piglets. After birthing (in a process known as ‘farrowing’), she remains confined in these metal ‘maternity’ crates for 3-4 weeks until her piglets are weaned.
Farrowing crates are so small a mother pig can barely move – she can only sit, stand or lay down slowly, and with difficulty. Pigs are naturally very clean animals, and when given the choice, never toilet where they eat, sleep or play. Instead, they will often travel far away to relieve themselves. But trapped in a farrowing crate, she can only take one step forward or back and is forced to urinate and defecate right where she stands. For mother pigs, this unhygienic behaviour causes her extreme stress, discomfort and heightens her risk of disease.
Despite having the intelligence of a 3-year old child, who can solve puzzles and even play video games, have amazing memories, can sense the passing of time, foster lifelong friendships with other pigs and expresses empathy for humans and pigs alike, these loving animals continue to be industrialised and treated like 'products', rather than individuals who feel - and express - an enormous range of emotions. She is someone, not something.

Eggs are Not Eggscellent Cages are extremely cruel, and sadly they are just one of many cruelties chickens are forced to endure in the egg industry. In all commercial egg systems – cage, barn-raised, free-range or organic – male chicks are considered ‘worthless’ and are killed on their first day of life.
Female chicks are raised to replace hens who are sent to slaughter at just 18-30 months old — a fraction of their natural lifespan. As newborns, the tips of their beaks can be cut off without pain reliefto reduce aggressive pecking fueled by frustration when they cannot move freely, forage, or establish a natural social structure.
Because the males bred into the industry won’t grow up to produce eggs they are ‘disposed of’ by gassing or maceration -- literally being shredded to death while alive.
And later that year, at Sparboe Farms in Iowa, undercover investigators documented hens with gaping, untreated wounds laying eggs in cramped conditions among decaying corpses.

Leo Tolstoy - 1891 Essay A village pig is dragged outside for slaughter. The animals “human-looking pink body” screamed in a “dreadful voice, resembling the shriek of a man”.
After the screams subsided and the animal was killed, even the gruff carriage driver accompanying Tolstoy lets out a heavy sigh.
“Do people really not have to answer for such things?”
Almost 200 years later, do they answer for such things?
My question to anyone reading this (unless you are already a strict vegan) is:
What can you do to reduce the overall suffering & harm done to sentient beings (all animals including fish & cetaceans) that is realistic & repeatable over the long term?
Me, personally I do not see the point in being some total zealot that never eats anyhing with bone char again if it isn't sustainable over the long term.
Vegans call it doing what is "practical & possible".
I believe it is also very important that it be sustainable over the long term or else what was the point?
Now, I will end this by asking you the same question I asked myself:
What can you do to reduce the suffering & harm to sentient beings (all animals including fish & cetaceans) that fits the following two criteria:
Realistic
Repeatable over the long term
I also want to say this if you are a starseed reading this -- we need to work with everyone.
This isn't some kind of ideological purity test or a flex as I see a lot of that within the movement for animal rights & activism. This is about sentient, self-aware beings that are emotional, social & cognitively functional getting the living shit tortured out of them.
This is about the fact that 90% of the world's population as of today eats meat.
This is about 10 billion farm animals being slaughtered in the US every year for food.
This is about 99% of farm animals in the US being killed in factory farms.
This is about 90% of the 10 billion farm animals being slaughtered in the US being chickens.
This is about fedral subsidies that make a cheeseburger $4 when it should really be at least $15.
This is about big meat & big ag spending tens of millions every year to bankroll politicians for favorable policies.
This is about landmark legislation from the EPA & Congress not applying to the agricultural industry that causes the majority of land, air & water pollution & waste.
This is about the fact that there is no Big Broccoli to counter the meat & agricultural cartels.
This is about Trump winning.
It's not about fighting over bone char, cholecalciferol & cross contamination.
It's not about a competition on who can utilize the least animal byproducts (like the paint on the walls in your home & the tires in your car).
It's not a who's the best vegan dick measuring contest.
We need to work with everyone given what we are about against.
The 10 billion number has not dropped. And actually, people are consuming more meat.
Although there have been legislative wins and imitation meat like Impossible & Beyond Meat are promising.
They have the lobbying machine, political apparatus, laws, subsidies & constant commercials & ads on their side. When's the last time you saw a commercial for vegetables?
Now, when's the last time you saw a commercial for Sonics, Dominos, Pizza Hut, Burger King, Pringles, Lays, Reeses Cup, Snickers, Twix, Applebees, Chilis, McDonalds.
We need to work with omnis, flexitarians, pescatarians, people that don't eat pork, people that don't eat chicken, people that don't eat beef, people that don't consume dairy.
That's not watering down or diluting a message.
It's decentering zealotry so we can actually get somewhere in our fight for animals to be recognized as sentient beings with their own inalienable rights.
That is maybe 100 to 250+ years off.
We won't get anywhere if we stay on reddit debating about whether brown sugar is okay if it is processed with bone char.
Keep that in mind. The animals are counting on us. ✨✨✨

#vegan#veganism#antispeciesism#speciesism#big meat#big ag#trump#antispeciesist#vegetarian#animal liberation#go vegan#plant based#flexitarian#omnivore#factory farming#fast food#mcdonalds#kfc#burger king#pizza hut#corporatism#anti capitalism#climate change#starseed#starseeds
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
A comprehensive guide to Raptordyne
(This is what my fucking life is I guess)
With a show as incoherently written as Dinosquad there tends to be a lot of guesswork and inconsistent information left for the fans to work with. But not anymore folks! I have scoured the entire show to bring you a comprehensive breakdown of Raptordyne, what it does, who works there, and how it’s built. Let’s get started.
What does Raptordyne do?
The show seems to push the idea that Raptordyne is pretty much exclusively built as a factory for global warming and ooze monsters but that obviously can’t be the only thing happening here.
in the first episode Rodger states that Raptordyne is a biogenetics company and phrase that, like most things in this show, is a vague mush of science-y sounding words. Then in the episode Easy Riders and Raging Dinos we see that Raptordyne owns an animal feed company.
With that in mind it seems safe to assume that Raptordyne is in the agricultural industry more specifically designing GMOs and related products.
Who works there?
Now that we know what Raptordyne does when it’s not making horrible mutants, let’s see who works there. I’m going to go in order from most relevant to least relevant.

Victor Veloci
The main guy, the clown that runs this circus, our leading man, the CEO of Raptordyne. Despite seeing this guy every episode we don’t really get to see him actually doing his human job, we do however know that he spends a lot of time on charity work, thanks to the first episode and the episode Perseverance.

Lieutenant Alpha
A surprisingly unknown character despite showing up in two episodes with speaking scenes the Lieutenant is shown to be in charge of most of the masked grunt force at Raptordyne. Though in his two episodes, Who let the dogs out and Scents and Scents Abilities he is shown to be disliked by Veloci and doesn’t seem aware of the true purpose of Veloci’s work.
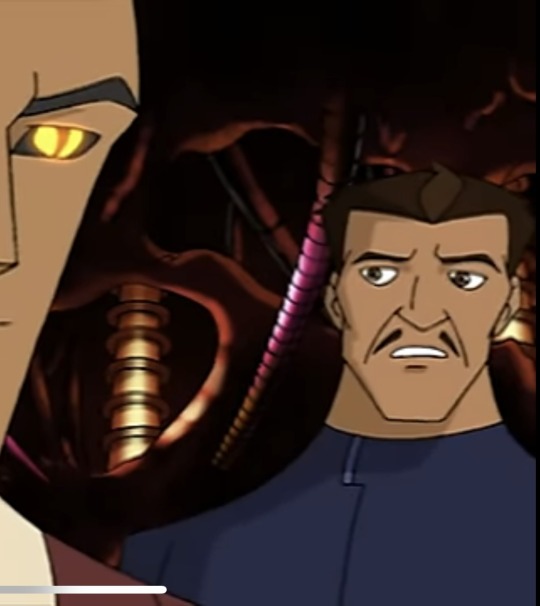

Peter
Anyone who knows me also know that this guy is my personal favorite character of all time, despite only showing up in the first episode for 20 seconds. Contrary to popular belief Peter is not actually Veloci’s assistant, his real work lies in the engineering department. He developed nanobots that are supposedly used in primordial ooze and potentially built the robot seen in the episode Wannabe or the hologram dinosaur in Who let the dog out. Peter was injected with primordial ooze however the outcome of that experiment was never seen.


Gregor, Mina, and Robert
I would like to thank the Dinosquad discord server for helping me name these scientists, if you haven’t joined it yet go check it out. These three scientists appear in the background of a few episodes though are never named or given speaking roles. From left to right on the second picture we have Robert, Gregor, and Mina. It is implied in the episode Attack of the Brainasuarus that Veloci works directly with these three to develop prototype ooze.

The twins
These two only appear in the episode Pet Peeve and are the masked grunts working under Veloci for the day. I wanted to point them out not only because they are the only grunts seen without their uniforms but they are also significantly more incompetent than any other grunts seen in the show, thus designating them as their own significant characters.
Workplace Environment
With all our players in place let’s talk about Raptordyne itself. The underground lab seems to be made of one continuous room situated in a cave system underneath the main building. Let’s break it down.

The Entrance
Pictured above is the left end of the cave lab. It’s primarily just Veloci’s ominous skull chair and the entrance elevator (not pictured). This is the area we see the most in the show. What’s interesting about this area is the room over looking the lab just past Veloci’s chair, and the rail tracks cutting through the center of the room, but more on those later.

The Lab
Pretty self explanatory, just across the rail track is the lab where the ooze and mutants are made. The mutants shown in the test tubes are not used in the show but their humanoid shape does imply some sort of human experimentation.

The airlock
On the right side of the lab there is this specialized containment zone. As seen in the episode One Precent Inspiration this area is used for the temporary containment of live specimens and also has an airlock at the top of the containment unit for the release of airborne specimens.

The Greenhouse
Seen only once in the episode Growth Potential this room is what I believe to be in that raised portion of the lab seen in the entrance. This area of the lab is used exclusively for the production and study of mutant plants, a concept that is severely underutilized in the show.

Veloci’s Office
Realized i forgot this originally whoops. Being the influential man he is Veloci obviously needs an office that isn’t in a secret dinosaur lair. This is one spacious office in what looks like the top of the Raptordyne building.

The warehouse
Technically this isn’t a part of the underground lab, nor is it a single building in my opinion. Featured in Scents and Scents abilities we see what is one of possibly many warehouse outposts. Complete with their own security systems and staff.


In the episode it is featured in the place seems to be controlled exclusively by the Lieutenant and masked grunts. So why is this relevant? I propose that the railway seen in the main lab is actually a transit system between the main lab and a network of these outpost facilities.
Conclusion
Go nuts nerds
#dinosquad#dino squad#victor veloci#Holy cow this took a long fucking time to write#But seriously go nuts nerds#I did not compile all this fucking info for you to not do anything with it#Write fan fic#Draw art#build the place in Minecraft idc
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
the Eastern Kuku Yalanji people and rangers to create a wildlife corridor that runs between two UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Australia: the Daintree Rainforest and the Great Barrier Reef.
Wildlife habitats in this region have become fragmented due to industrial agriculture, and a forested corridor is expected to help protect biodiversity by allowing animals to forage for food and connect different populations for mating and migration.
The project aims to plant 360,000 trees over an area of 213 hectares (526 acres); so far, it has planted 25,000 trees of 180 species on the land and in the nursery, which can also feed a range of native wildlife.
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
You have all just got to come to terms with how laughably simplistic it is to dismiss legitimate critiques about modern wool production with catchphrases like ‘Its just a haircut, it doesn’t hurt them!’
Wool is ‘just a haircut’ in the same way that cocoa is ‘just a plant.’ Yes, you can acquire chocolate without harming anyone, but is anyone dismissing the obvious ethical issues with modern chocolate production by pointing out that cocoa doesn’t require us to hurt anyone to acquire? Of course not, because we all recognise that because of modern production practices and exploitation it is far more complicated than that. Why can’t we do the same for animal products?
Shearing a sheep does not have to harm sheep by itself, though fast processing speeds demanded by commercial producers means that shearing injuries are very common. That isn’t the issue with wool. The issue is that wool production by itself is not very profitable, profits are subsidised by taking lambs from their mothers every lambing season, then slaughtering them for meat. The issue is that sheep will almost always be slaughtered once their profitability declines. Obviously, most animal farmers are not going to house and feed unprofitable animals.
Tail docking is an issue, de-horning is an issue, castration is an issue. The live transport of sheep for hours in all weather extremes without food and water is an issue. Breeding sentient beings into bodies that over-produce wool, eggs, or milk to the point where they require human intervention just to be comfortable is an issue. Exploiting the bodies of animals for profit is, in and of itself, an ethical issue.
The massive environmental harm caused by grazing sheep, who have converted vast swathes of formerly forested land into ecologically dead wastelands, is difficult to overstate. Grazing animals are widely acknowledged as one of the most significant barriers to forest restoration and re-wilding. George Monbiot calls them ‘the white plague’ for good reason. Just take a look at what has happened to most of England and Wales. That isn’t even factoring in the methane emissions of the sheep themselves, their resource requirements, or the fact that farmers routinely kill predators and oppose species reintroduction to protect their herds.
All you do when you dismiss these real concerns by pointing out that ‘wool doesn’t hurt sheep duhhh’ is show us how little thought you are willing to put into what is a far more complex issue than any of you are willing to admit. That these cringe ‘shave your sheep’ posts still get tens of thousands of notes is evidence of nothing so much as widespread ignorance and confirmation bias when it comes to discussing animal agriculture.
Honestly, so many of you have been so brainwashed by this colonialist, cottagecore pastoral fantasy that you’re no longer able to apply any real nuance or analysis to land or animal issues. I’m not expecting you to immediately agree with us and throw out all your fleece, but at least recognise that it’s not as simple as saying ‘shearing doesn’t harm sheep you morons.’
At the very least, you should all be able to recognise that vegans aren’t just stupid for not immediately agreeing that an environmentally destructive, ecologically disastrous industry that is breeding and exploiting sentient beings for profit is just uncomplicatedly fine actually.
654 notes
·
View notes