#1939 films of the United States
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Movita_Castaneda_in_Wolf_Call_(1939).jpg
#wikimedia commons#1930s#1939#Movita Castaneda#1939 films of the United States#Monogram Pictures films#PD US no notice#PD-US missing SDC copyright status
1 note
·
View note
Photo





Love Affair Leo McCarey. 1939
Accident 5th Ave #338, New York, NY 10118, USA See in map
See in imdb
#leo mccarey#love affair#irene dunne#accident#empire state#empire state building#manhattan#new york#united states#taxi#movie#cinema#film#location#google maps#street view#1939
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
A copy of the first reading list, if you dislike clicking on Google docs links:
The liberal news media is working overtime to silence Palestinian voices. As we sit thousands of miles away, witnessing the massacre through social media, the least we can do is educate ourselves and work to educate others. Apartheid threatens all of us, and just to reiterate, anti-Zionism ≠ antisemitism.
Academic Works, Poetry and Memoirs
The Revolution of 1936-1939 in Palestine: Background, Details, and Analysis, Ghassan Kanafani (1972)
Palestinians: From Peasants to Revolutionaries, Rosemary Sayegh (1979)
Popular Resistance in Palestine: A History of Hope and Empowerment, Mazin Qumsiyeh (2011)
My Life in the PLO: The Inside Story of the Palestinian Struggle, Shafiq al-Hout and Jean Said Makdisi (2019)
My People Shall Live, Leila Khaled (1971)
Poetry of Resistance in Occupied Palestine, translated by Sulafa Hijjawi (Baghdad, Ministry of Culture and Guidance, 1968)
On Palestine by Ilan Pappé and Noam Chomsky (2015)
Gaza in Crisis: Reflections on the US-Israeli War Against the Palestinians, Noam Chomsky and Ilan Pappé (2013)
The Politics of Dispossession: The Struggle for Palestinian Self-Determination, 1969-1994, Edward W. Said (2012)
Queer Palestine and the Empire of Critique, Sa’ed Atshan (2020)
Stone Men: The Palestinians Who Built Israel, Andrew Ross (2019)
Ten Myths About Israel, Ilan Pappé (2017)
Blaming the Victims: Spurious Scholarship and the Palestinian Question, Christopher Eric Hitchens and Edward W. Said (2001)
Palestinian Walks: Notes on a Vanishing Landscape, Raja Shehadeh (2010)
The Gun and the Olive Branch: The Roots of Violence in the Middle East, David Hirst (1977)
Gaza: An Inquest into Its Martyrdom, Norman Finkelstein (2018)
Fateful Triangle: The United States, Israel and the Palestinians, Noam Chomsky (1983)
Israel and Palestine: Reappraisals, Revisions, Refutations, Avi Shlaim (2010)
Politicide: Ariel Sharon’s War Against the Palestinians, Baruch Kimmerling (2006)
The Holocaust Industry: Reflections on the Exploitation of Jewish Suffering, Norman G. Finkelstein (2015)
Light in Gaza: Writings Born of Fire, Jehad Abusalim (2022)
Nakba: Palestine, 1948, and the Claims of Memory, Ahmad H. Sa’di and Lila Abu-Lughod (2007)
Peace and its discontents: Essays on Palestine in the Middle East peace process, Edward W. Said (2012)
Three Poems by Yahya Hassan
Articles, Papers & Essays
“Palestinian history doesn’t start with the Nakba” by PYM (May, 2023)
“What the Uprising Means,” Salim Tamari (1988)
“The Palestinians’ inalienable right to resist,” Louis Allday (2021)
“Liberating a Palestinian Novel from Israeli Prison,” Danya Al-Saleh and Samar Al-Saleh (2023)
Women, War, and Peace: Reflections from the Intifada, Nahla Abdo (2002)
“A Place Without a Door” and “Uncle Give me a Cigarette”—Two Essays by Palestinian Political Prisoner, Walid Daqqah (2023)
“Live Like a Porcupine, Fight Like a Flea,” A Translation of an Article by Basel Al-Araj
Films & Video Essays
Fedayin: Georges Abdallah’s Fight (2021)
Naila and the Uprising (2017)
Off Frame AKA Revolution Until Victory (2015)
Tell Your Tale Little Bird (1993)
The Time That Remains (2009)
“The Present” (short film) (2020)
“How Palestinians were expelled from their homes”
Louis Theroux: The Ultra Zionists (2011)
Born in Gaza (2014)
5 Broken Cameras (2011)
Little Palestine: Diary of a Siege (2021)
Al-Nakba: The Palestinian catastrophe - Episode 1 | Featured Documentary
Organisations to donate to
Palestine Red Crescent Society - https://www.palestinercs.org/en
Anera - https://support.anera.org/a/palestine-emergency
Palestinian American Medical Association - https://palestinian-ama.networkforgood.com/projects/206145-gaza-medical-supplies-oct-2023
You First Gaza - https://donate.gazayoufirst.org/
MAP - Medical Aid for Palestinians - https://www.map.org.uk/donate/donate
United Nations Relief and Works Agency - https://donate.unrwa.org/-landing-page/en_EN
Palestine Children’s Relief Fund - https://www.pcrf.net/
Doctors Without Borders - https://www.doctorswithoutborders.org/what-we-do/where-we-work/palestine
AP Fact Check
https://apnews.com/article/israel-hamas-gaza-misinformation-fact-check-e58f9ab8696309305c3ea2bfb269258e
This list is not exhaustive in any way, and is a summary of various sources on the Internet. Please engage with more ethical, unbiased sources, including Decolonize Palestine and this list compiled by the Palestinian Youth Movement.
390 notes
·
View notes
Text
the Zionists and the Nazis AUGUST 8, 2024

THE HAAVARA AGREEMENT
Immediately following Hitler’s rise to power in 1933, the Nazis wasted no time in passing antisemitic legislation, including a boycott of Jewish businesses, and, between 1933-1938, a process known as “voluntary Aryanization” (which later became “mandatory Aryanization”) transferred Jewish businesses and assets to Germans. German Jews became increasingly desperate to flee, but no countries wanted to take in Jewish refugees, and this economic marginalization made emigration virtually impossible.
In 1933, Eliezer Hoofein, the director of the Anglo-Palestine Bank, and the Reich Economics Ministry negotiated the Haavara Agreement. Under the terms of the agreement, Jews fleeing persecution in Germany could use their assets to purchase German goods for export, thus salvaging their assets and facilitating emigration to Palestine under the immigrant investor visa, in spite of severe British antisemitic immigration restriction policies.
Even so, the Haavara Agreement was met with staunch opposition, both among Zionist and anti-Zionist Jews. In response to the Nazi boycott of Jewish businesses, Jews worldwide enacted a boycott on German goods themselves. The Haavara Agreement was not in line with the Jewish anti-German boycott, as the Jewish community in both Germany and Palestine would be purchasing German goods. German public opinion also opposed the agreement. The Haavara Agreement was dissolved after World War II broke out in 1939.
The Haavara Agreement, though deeply controversial, ultimately saved the lives of some 60,000 German Jews. For context, the Haavara Agreement was similar to making a hostage deal with Hamas…making a deal with a hostile, genocidal enemy to save the lives of your own people. It wasn’t Zionist-Nazi “collaboration” by any stretch of the imagination.
LEHI-NAZI TIES
Lehi, pejoratively known as the “Stern Gang,” was an extremist right wing Jewish terrorist group in Mandatory Palestine. Believing that the British occupation of the Land of Israel was a much bigger threat to world Jewry than Nazism, they tried to establish contact with the Nazis twice, hoping to establish an alliance. The Nazis rejected them both times, because the Nazis would not ally with Jews, regardless of their views.
Lehi constituted no more than 300 members, whose views were fringe and non-representative of the Jewish community.
Ultimately, the Nazis never would’ve allied with any Zionist group.
In 1937, a Nazi document on foreign policy read, “(1) The formation of a Jewish state or a Jewish-led political structure under British mandate is not in Germany’s interest…(2) Germany therefore has an interest in strengthening the Arab world as a counterweight against such a possible increase in power for world Jewry.”
JEWISH PARTISANS
The organized Jewish resistance during the Holocaust was predominantly Zionist. In fact, Zionism was a major motivator for Jews joining the resistance.
In Poland, the main partisan organization, Żydowska Organizacja Bojowa (ZOB), meaning “Jewish Combat Organization,” was formed out of Zionist youth groups.
The first Jewish resistance organization in Nazi-occupied Europe, the Lithuanian Fareynikte Partizaner Organizatsye (FPO), meaning “United Partisan Organization,” had a strong Zionist presence. Two of its three leaders, Abba Kovner and Josef Glazman, were prominent figures in the Zionist movement.
In France, Jews, who comprised one percent of the total French population, formed between 15-20 percent of the resistance. In 1942, French Jewish partisans founded the Zionist Armée Juive, meaning “Jewish Army.”
Among the most recognizable Jewish partisan groups during the Holocaust were the Bielski brothers, who hid in the forest and rescued over a thousand Jews, and whose story was depicted in the film Defiance. The oldest Bielski brother and commander of the group, Tuvia, had long been interested in the Zionist youth movement.
WARSAW GHETTO UPRISING
The Warsaw Ghetto Uprising, which lasted from April 16 to May 16, 1943, was the largest Jewish uprising against the Nazis during the Holocaust.
In March of 1942, a number of Zionist Jewish youth groups inside the Warsaw Ghetto first proposed the creation of a Jewish self-defense force.
After 250,000+ Warsaw Jews were deported to the Treblinka death camp in the summer of 1942, two Zionist organizations — the left-wing socialist Jewish Combat Organization and the right-wing Jewish Military Union — formed and began training.
The Warsaw Ghetto Uprising was a last-ditch effort to resist the Nazi liquidation of the Warsaw Ghetto — that is, the deportation of all of Warsaw’s Jews to extermination camps to be gassed or worked to death. The uprising was led by the Jewish Combat Organization and the Jewish Military Union, which, again, were both Zionist groups.
According to German records, the only German casualties in 29 days of fighting during the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising were 17 Nazi soldiers. The Germans responded by burning the entirety of the ghetto, resulting in 13,000 Jewish deaths, most of whom suffocated to death or were burnt alive. Another 36,000 Jews were sent to death camps.
THE YISHUV

The Jewish community in British Mandatory Palestine fiercely opposed the Nazis, so much so that the Jewish paramilitaries, the Haganah and the Irgun, temporarily halted their resistance operations against the British and instead joined the British war effort against Germany. In 1944, the British established the Jewish Brigade, comprised of Jewish citizens of Palestine, seen in the above photo. Some 30,000 Jews volunteered to join the Brigade.
The Yishuv sent a number of paratroopers to Europe to rescue Jews from deportation to death camps, most notably Hannah Szenes, who was captured and executed.
Despite temporarily halting most anti-British operations, the Haganah continued carrying out Aliyah Bet to the best of their ability, illegally smuggling Jewish Holocaust refugees to Palestine with varying success.
Chaim Weizmann, the future first president of Israel, played an important role in convincing the British government to accept the Kindertransport, the organized rescue of 10,000 Jewish children, who were given refuge in the United Kingdom.

ORIGIN OF THE ZIONISM = NAZISM LIBEL
The accusation that Zionists are Nazis has its roots in the British Foreign Office during the period of the British Mandate of Palestine. In March of 1945 — about two months before the Nazis even surrendered— the High Commissioner of Palestine, Lord Gort, told the Colonial Secretary in London that “the establishment of any Jewish State in Palestine…will almost inevitably mean the rebirth of National Socialism [i.e. Nazism] in some guise.”
In 1969, the United Nations passed the International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination. Both the United States and Brazil wanted to add a clause including antisemitism. The Soviet Union, which had been heavily oppressing its Jewish population, worried that such a clause would be used to rebuke them for persecuting Soviet Jews. As such, they included a counter proposal, which was a clause that equated Zionism to Nazism. That way, they could say they were persecuting Zionists, not Jews. Neither clause passed.
In 1985, the Anti-Zionist Committee of the Soviet Public published a propagandist brochure known as the “Criminal Alliance of Zionism and Nazism,” which claimed that there was irrefutable proof that the Zionists not only had collaborated with the Nazis, but were also responsible for the genocide of Jews, Slavs, and others in Europe. When Israel captured and tried Adolf Eichmann in the 1960s, the Soviets painted the Israel-West Germany relationship as “evidence” that the Zionists had colluded with the Nazis. Soviet anti-Zionist propaganda in the Arab world was so pervasive that it even influenced the dissertation of current so-called “moderate” Palestinian Authority President Mahmoud Abbas, titled “The Other Side: The Secret Relationship between Nazism and Zionism.” According to Abbas, Israel captured Eichmann “to prevent the ‘sacred secrets’ of this [Zionist-Nazi] collaboration from becoming public.”
rootsmetals
Hannah Szenes wasn’t tortured and executed for your disrespectful ass to come and say the Zionists collaborated with the Nazis 🙄
93 notes
·
View notes
Photo
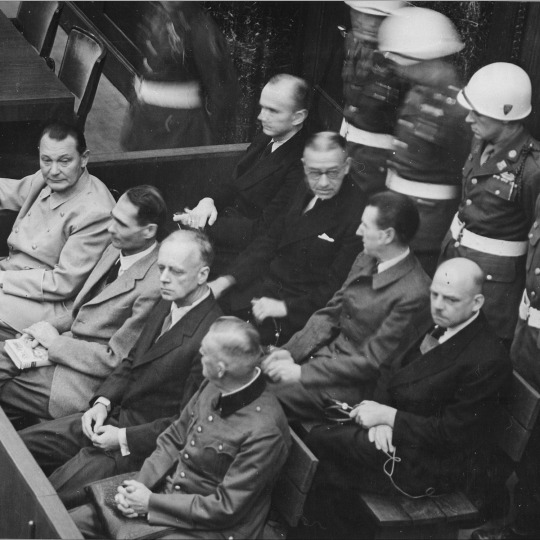

Nuremberg Trials
The Nuremberg trials (1945-6), held in Nürnberg (Nuremberg), Germany, were a series of trials involving the senior surviving Nazis to hold them accountable for waging war and committing war crimes and crimes against humanity during the Second World War (1939-45). 22 Nazis were tried, with 19 found guilty and sentenced to either death by hanging or lengthy prison terms.
The first Nuremberg trials were conducted from November 1945 to October 1946, and then, a second phase, which involved a much larger number of defendants, was conducted from November 1946 to April 1949. The Nuremberg trials were the first in history where the victors in a war sought to make senior figures from the losing side accountable for their actions. The trials were filmed and contributed greatly to our understanding of how WWII was conducted and revealed both the irrefutable evidence for and enormous scale of such atrocities as the Holocaust. The first month of the trials, the initial proceedings only, were hosted in the Supreme Court Building in Berlin, but they moved on 20 November to the Palace of Justice in Nuremberg. The Palace of Justice was selected because it had been the heart of Nazi show trials against enemies of the Third Reich, the city was the home of the Nuremberg Rally, the infamous annual Nazi Party congress, and the complex had the practical advantage of an adjoining prison where the defendants were detained.
The International Military Tribunal
At the close of WWII, the victorious Allies of France, Britain, the United States, and the USSR, as agreed by their respective leaders at a conference in Moscow back in October 1943, jointly formed an International Military Tribunal (IMT) to bring German Nazi war criminals to justice. There were some calls to have judges from neutral nations head the IMT, but the allied leaders were determined to be directly involved in getting their pound of flesh. The idea of the trials was supported by a number of other nations besides the four main powers.
The panel that would decide the fate of the defendants brought before the IMT consisted of one judge and one prosecutor from each of the four nations mentioned above. The judging panel was presided over by the British judge Lord Justice Geoffrey Lawrence, described by one American lawyer as "like God...Hollywood would have cast him" (MacDonald, 23). The chief Soviet judge was I. T. Nikitchenko, the French lead judge was Henri Donnedieu de Vabres, and the US judge was Francis B. Biddle. The legal proceedings followed the common law practice applied in the United States and Britain. Translators worked in the courtroom, and everyone present had access to a set of headphones. There was a large screen to show the court relevant film clips and statistical information. 250 journalists attended the court sessions, and the whole proceedings were filmed and sound recorded.
Nuremberg Trials Judges
U.S. Army (CC BY-NC-SA)
In the closing stages of the war, Adolf Hitler (1889-1945), Joseph Goebbels (1897-1945), and Heinrich Himmler (1900-1945) had all committed suicide, but there remained 24 senior Nazi figures whom the Allies were determined to bring to justice. The group was selected not only for their individual roles but also as representatives of particular Nazi institutions. Before the trials could begin, Robert Ley (1890-1945), head of the German Labour Front, committed suicide, and Gustav Krupp (1870-1950), an industrialist who had used forced labour, was considered too physically frail to stand trial. The 22 remaining defendants faced four charges, as expressed in the Oxford Companion to World War II, they were:
Count 1: Contributing to a common plan or conspiracy to wage war
Count 2: Crimes against peace
Count 3: War crimes (e.g. violations of the Geneva Convention such as the abuse and murder of prisoners of war, use of prisoners for labour, destruction of private property, and devastation of property and places with no military justification)
Count 4: Crimes against humanity (e.g. the murder of civilian populations, use of slave labour, the forced deportation of civilians, and the persecution of specific social, political, religious, and racial groups)
Counts 1 and 2 proved problematic to define, and therefore it was difficult to find the defendants either innocent or guilty of them. This is hardly surprising considering the debate amongst historians ever since as to why and how WWII started and how far one should go back exactly in order to discover the causes of WWII, causes which could be attributed in some cases to both the victors and losers. The court essentially considered counts 1 and 2 as involving actions such as breaking international treaties and invading and occupying free countries. Much easier to establish were cases of counts 3 and 4, although even here there was the added complication that the victors had themselves been guilty of what would today be called war crimes, for example, the Allied bombing of Germany, submarine attacks on unarmed vessels, and the Katyn Forest massacre of Polish prisoners of war by USSR forces. Certain facts were taken as given, such as that Hitler had fully intended to start a world war. In addition, such Nazi organisations as the Gestapo (secret police), the SS (Schutzstaffel), and SA (Sturmabteilung) were condemned as criminal organisations.
Palace of Justice, Nuremberg
US Army (Public Domain)
The judges not only benefitted from the cross-examination of the defendants but also the testimony of around 360 witnesses (including both victims of and members of the Nazi regime) and a huge quantity of incriminating documents, official and otherwise, including indisputable photographs, sound recordings, and films, such as those taken at concentration and death camps. As noted by Dr Robert Kempner, a lawyer who had fled the Nazi regime:
One of the biggest helps to us was the German bureaucratic sense – they kept everything and they even made publications and films and lot of material had been discovered by our Allied search teams. Some of the people like General Governor Frank of Poland was so anxious to show his friend Hitler after the war what he has done that he kept diaries, volumes and volumes and volumes. In fact he had written his own indictment.
(Holmes, 593)
It is important to note, however, that the documentation for Nuremberg was compiled in order to support the legal case that the defendants were guilty of one or more of the four counts (and not to create a comprehensive reconstruction of past events as, say, a historian would do). There was, too, a degree of negotiation between the various national judges regarding particular defendants – the USSR judge, for example, wanted Rudolf Hess hanged while his fellow judges preferred a prison sentence – but there was a conscious effort on all parties to deliberate with as much fairness as possible given the seriousness of the trials and the world's scrutiny of them. To this end, the defendants were collectively represented by a legal counsel, Otto Kranzenbühler, and permitted individual lawyers to present their defence.
Camp Guard Giving Evidence at Nuremberg
Imperial War Museums (CC BY-NC-SA)
Continue reading...
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
THIS DAY IN GAY HISTORY
based on: The White Crane Institute's 'Gay Wisdom', Gay Birthdays, Gay For Today, Famous GLBT, glbt-Gay Encylopedia, Today in Gay History, Wikipedia, and more … December 14



c.530 – Venantius Fortunatus (d.circa 600/609) was a Latin poet and hymnodist in the Merovingian Court, and a Bishop of the early Catholic Church. He was never canonised but was venerated as Saint Venantius Fortunatus during the Middle Ages.
Born in Treviso, near Ravenna in Italy, he spent his time as court poet to the Merovingians. After visiting the tomb of St. Martin of Tours at St. Hilary at Poitiers, he decided to enter a monastery.
He continued to write poetry, some of which have a permanent place in Catholic hymnody, for instance the Easter season hymns "Vexilla Regis" and the "Pange Lingua" (Sing, O my tongue, of the battle). Three or four years before he died he was made bishop of Poitiers. Although never canonized, he was venerated as a saint in the medieval church, and his feast day is still recognized on 14th December each year.
Like Paulinus of Nola, St Venantius's poetry also includes some decidedly secular verse of the romantic sort. That this celebrates male love is clear from its inclusion in the Penguin Book of Homosexual Verse.
"Written on an Island off the Breton Coast" You at God's altar stand, His minister And Paris lies about you and the Seine: Around this Breton isle the Ocean swells, Deep water and one love between us twain. Wild is the wind, but still thy name is spoken; Rough is the sea: it sweeps not o'er they face. Still runs my lover for shelter to its dwelling, Hither, O heart, to thine abiding place. Swift as the waves beneath an east wind breaking Dark as beneath a winter sky the sea, So to my heart crowd memories awaking, So dark, O love, my spirit without thee.
Fortunatus died in the early 600s. He was called a saint after his death, but was never formally canonized.


1901 – King Paul of Greece (d.1964) reigned as king of Greece from 1947 to 1964. He may have been bi-sexual.
Paul was born in Athens, the third son of King Constantine I of Greece and his wife, Princess Sophia of Prussia. He was trained as a naval officer. On 9 January 1938, Paul married Frederika of Hanover at Athens. They had three children.
Before his marriage he is alleged to have invited the homosexual literary muse, Denham Fouts, on a cruise of the Aegean Sea, perhaps because they were lovers. However, Fouts's friend John B. L. Goodwin said Fouts often made up stories about his life, and literary critic Katherine Bucknell thought many of the tales about him were myth.
During most of World War II, when Greece was under German occupation, he was with the Greek government-in-exile in London and Cairo. From Cairo, he broadcast messages to the Greek people.
Paul returned to Greece in 1946. He succeeded to the throne in 1947, on the death of his childless elder brother, King George II.


David Lewis (L) with Producer Irving Pichel
1903 – David Lewis (d.1987 ), born David Levy, was a Hollywood film producer who produced such films as Dark Victory (1939), Arch of Triumph (1948), and Raintree County (1957).
He was also the longtime companion of director James Whale from 1930 to 1952. Although they were separated at the time of Whale's death in 1957, Lewis later released the contents of Whale's suicide note.
Lewis was portrayed in the 1998 film Gods and Monsters by David Dukes.


1915 – The American actor and dancer Dan Dailey was born on this date (d.1978). Dailey was born and raised in New York City and appeared in vaudeville before his Broadway debut in 1937 in Babes in Arms. In 1940, he was signed by MGM to make movies and, although his past career had been in musicals, he was initially cast as a Nazi in The Mortal Storm. However, the people at MGM realized their mistake quickly and cast him in a series of musical films.
He served in the United States Army during World War II, was commissioned as an Army Officer after graduation from Signal OCS at Ft Monmouth, NJ, after which he served with distinction until the war ended. Then returned to more musicals. Beginning with Mother Wore Tights (1947) Dailey became the frequent and favorite co-star of movie legend Betty Grable. His performance in their film When My Baby Smiles at Me in 1948 garnered him an Academy Award nomination for Best Actor. In 1950, he starred in A Ticket to Tomahawk, often noted as one of the first screen appearances of Marilyn Monroe, in a very small part as a dance-hall girl. In 1953, Dailey starred in Meet Me at the Fair. One of his notable roles was in There's No Business Like Show Business (1954) which featured Irving Berlin's music and also starred Ethel Merman, Marilyn Monroe, Donald O'Connor, and Johnnie Ray.
In 1950 the notorious "Confidential" Magazine (the National Enquirer of its day) printed a picture of him wearing female clothing. His studio, 20th Century Fox, rushed to repair the damage; gossip columnists were told that Dailey had simply been snapped on his way to a fancy dress party. But Andre Previn, the composer, tells in his biography No Minor Chords how Dailey turned up drunk and in female clothing for the press screening of It's Always Fair Weather in 1954. In the mid '70s, gossip columnist Joyce Haber was on television promoting a novel about Hollywood. Asked to dish some gossip, she mentioned that one of the top dancer-actors was a closet transvestite with a costly and beautiful wardrobe that many women would envy.
He had three failed marriages with women, but also was known to hang out in Gay bars. After the suicide of his only son, he was an embittered alcoholic. He died three years later, just after he playing boyfriend Clyde Tolson in (the unintentionally hilarious *and bad*) The Private Files of J.Edgar Hoover (1977). He appeared in over 60 films in his career.


1932 – George Furth (d.2008) was an American librettist, playwright, and actor.
Born in Chicago with the name of George Schweinfurth (he dropped the "schwein" on becoming an actor).
Furth made his Broadway debut as an actor in the 1961 play A Cook for Mr. General, followed by the musical Hot Spot two years later. He was also known for his collaborations with Stephen Sondheim: the highly successful Company, the ill-fated Merrily We Roll Along and the equally ill-fated drama, Getting Away with Murder. Furth penned the plays Twigs, The Supporting Cast and Precious Sons, and wrote the book for the Kander and Ebb musical, The Act.
Company has been revived many times over the years, sometimes updated to the Aids era, although requests from producers to give the show a homosexual slant were turned down by the unmarried Sondheim and Furth, although both of them were gay.
Frequently cast as a bespectacled, ineffectual milquetoast, Furth appeared in such films as The Best Man, Myra Breckinridge, Hooper, Blazing Saddles, Oh God!, Shampoo, The Cannonball Run, Young Doctors in Love, Doctor Detroit, Bulworth and Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid. His many television credits include Tammy, McHale's Navy, Ironside, I Dream of Jeannie, That Girl, Green Acres, The Monkees, Batman, The Odd Couple, Bonanza, Happy Days, All in the Family, Murphy Brown, L.A. Law, Dr. Quinn, Medicine Woman, Murder, She Wrote, Little House on the Prairie, Love, American Style, Adam-12, F Troop and the made-for-TV film The Scarlett O'Hara War, in which he portrayed famed film director George Cukor. He was a regular in the cast of the short-lived 1976 situation comedy The Dumplings.
He adapted his play Twigs as a 1975 television production, starring Carol Burnett. He also worked as a voice actor in several episodes of the animated television series The Adventures of Don Coyote and Sancho Panda for Hanna-Barbera Productions.
One of Furth's last writing projects was a foray into an area where he had not previously endeavored. Furth penned the lyrics for a musical revue, with music by Doug Katsaros. Furth and Katsaros shaped the work with San Francisco director Mike Ward into "The End - a new musical revue". The piece was performed at San Francisco's New Conservatory Theatre Center during the summer of 2004 and was billed as a "Pre-U.S. Tour Workshop Production". The piece was reworked twice, with the title changing to Last Call and Happy Hour, respectively.
Furth died on August 11, 2008 at the age of 75. The exact cause of death is unknown, although he had been hospitalized for a lung disease at the time.


1955 – Hervé Guibert (d.1991) was a French writer and photographer. The author of numerous novels and autobiographical studies, he played a considerable role in changing French public attitudes to AIDS. He was a close friend and lover of Michel Foucault.
Guibert was born in Saint-Cloud, Hauts-de-Seine, to a middle-class family and spent his early years in Paris, moving to La Rochelle from 1970 to 1973. In his teens Hervé Guibert lied about his age to work at the magazine 20 ans eventually leading to a job with Le Monde. After working as a filmmaker and actor, he turned to photography and journalism. In 1978, he successfully applied for a job at France's prestigious evening paper Le Monde and published his second book, Les aventures singulières (published by Éditions de minuit). In 1984, Guibert shared a César Award for best screenplay with Patrice Chéreau for L'homme blessé. Guibert had met Chéreau in the 1970s during his theatrical years.
Guibert's writing style was inspired by the French writer Jean Genet. Three of his lovers occupied an important place in his life and work: Thierry Jouno, director of an institute for the blind whom he met in 1976, and which led to his novel Des aveugles; Michel Foucault, whom he met in 1977; and Vincent Marmousez, a teenager of fifteen who inspired his novel Fou de Vincent.
In January 1988 Guibert was diagnosed with AIDS. From then on, he worked at recording what was left of his life. In June the following year, he married Christine, the partner of the late Thierry Jouno, so that his royalty income would eventually pass to her and her two children. In 1990, Guibert publicly revealed his HIV status in his roman à clef "À l'ami qui ne m'a pas sauvé la vie" (published in English as To the Friend Who Did Not Save My Life). Guibert immediately found himself the focus of media attention, featured in newspapers and appearing on several television talk shows.
Two more books also detailing the progress of his illness followed: Le Protocole compassionnel (published in English as The Compassionate Protocol) and L'Homme au chapeau rouge (published in English as The Man In The Red Hat), which was released posthumously in January 1992, the same month French television screened La Pudeur ou l'impudeur, a home-made film by Guibert of his last year as he lost his battle against AIDS. Almost blind as a result of disease, he attempted to end his life just before his 36th birthday, and died two weeks later.


1960 – Bob Paris, American bodybuilder and Gay rights advocate, born; The former Mr. Universe, and International Federation of BodyBuilders professional bodybuilder, Bob Paris is a writer, public speaker and civil rights activist. He acknowledged his sexuality in the July 1989 issue of Ironman magazine and has graced the covers of scores of magazines worldwide. After Paris officially came out as a Gay man in the media, he and his then-partner, Rod Jackson, became involved in marriage equality advocacy, started successful non-profits, lectured on a wide variety of Gay civil rights issues, and made many television, radio, newspaper and magazine appearances. The two separated in 1995. Today, Paris lives with his spouse of eleven years, Brian, on an island near Vancouver, British Columbia. Bob and Brian were legally married after Canada equalized the marriage laws in 2003.
In addition to his writing career, Bob Paris remains a committed civil rights advocate as well as a motivational speaker, model and actor. In 1998, he made his New York stage debut, starring at Carnegie Hall opposite Bea Arthur, Sandy Duncan and Tyne Daly in the Broadway musical, Jubilee as the character Mowgli. He is one of the subject of photographer Herb Ritts' gorgeous book, Duo. His official website is: http://www.bobparis.com/


1966 – James Earl Hardy, born in Bedford-Stuyvesant, Brooklyn, New York, is an American playwright, novelist, and journalist.
Generally considered the first to depict same-sex love stories that take place within the hip-hop community, his writing is largely characterized by its exploration of the African-American LGBTQ experience.
Hardy's best-known work is the B-Boy Blues series. The B-Boys Blues series comprises six novels and one short story. B-Boy Blues was adapted into a play in 2013 and into a film, directed and co-written by Jussie Smollett, in 2021.
Hardy attended undergraduate school at St. John's University and afterward went on to graduate from the Columbia Graduate School of Journalism in 1993. From 1992 to 1994, he wrote for Entertainment Weekly as a music journalist.


1968 – Yotam Ottolenghi is an Israeli-English chef, restaurateur, and food writer. He is the co-owner of six delis and restaurants in London, as well as the author of several bestselling cookbooks, including Ottolenghi (2008), Plenty (2010), Jerusalem (2012) and Ottolenghi Simple (2018).
Ottolenghi was conscripted into the Israeli Defense Forces in 1989, serving three years in IDF intelligence headquarters. He then studied at the Adi Lautman Interdisciplinary Program for Outstanding Students of Tel Aviv University, where in 1997, he completed a combined bachelor's and master's degree in comparative literature; his thesis being on the philosophy of the photographic image. While working on his thesis, Ottolenghi served as a night copy editor for Haaretz.
In 1997, Ottolenghi and his then-partner Noam Bar moved to Amsterdam, where he edited the Hebrew section of the Dutch-Jewish weekly NIW and considered getting his doctorate in comparative literature. Instead, he moved to London to study French cooking at Le Cordon Bleu.
Ottolenghi met his partner Karl Allen in 2000; they married in 2012 and live in Camden with their two sons, Max and Flynn. In 2013, Ottolenghi "came out as a gay father" in a Guardian essay that detailed the lengthy process of conceiving Max via gestational surrogacy, an option that he believes should be more widely available to those who cannot conceive naturally.
Ottolenghi served as a pastry chef at three London restaurants: the Michelin-starred Capital Restaurant, Kensington Place, and Launceston Place in Kensington New Town. In 1999, he became head pastry chef at the artisanal pastry shop Baker and Spice, where he met the Palestinian chef Sami Tamimi, who grew up in Jerusalem's Old City. Ottolenghi and Tamimi bonded over a shared language—Hebrew—and a joint "incomprehension of traditional English food".
His debut cookbook Ottolenghi was published in 2008 and has sold over 100,000 copies. Six volumes have followed: the all-vegetable cookbooks Plenty (2010) and Plenty More (2014); Jerusalem (2012); Nopi (2015); the dessert cookbook Sweet (2017); and Ottolenghi Simple (2018).
Ottolenghi's bestselling cookbooks have proven influential, with The New York Times noting that they are "widely knocked-off for their plain-spoken instructions, puffy covers, and photographs [that Ottolenghi] oversees himself, eschewing a food stylist". In 2014, the London Evening Standard remarked that Ottolenghi had "radically rewritten the way Londoners cook and eat", and Bon Appetit wrote that he had "made the world love vegetables".


1988 – The movie version of Harvey Fierstein's play "Torch Song Trilogy" opened in New York.


1989 – Amini Fonua is a Tongan competitive swimmer.
Fonua was born and raised in Ponsonby, Auckland, New Zealand to Tongan lawyer Sione Fonua and British-born mother Julie. He holds dual Tongan and New Zealand citizenship. His family includes two other sisters.
Fonua's swimming career began at the Roskill Swimming Club based at Cameron Pool in Auckland, coached by Sandra Burrow from 1999–2007. He broke numerous Auckland and New Zealand Age Group Records under Burrow's tenure. He then moved to West Auckland Aquatics in 2007, and was coached by Donna Bouzaid. In the Fall of 2008, Fonua enrolled at Texas A&M on a swimming scholarship. While at Texas A&M he was a peer voted Team Captain, Big XII Conference Champion, NCAA All-American, and recipient of The Aggie Heart Award. He graduated with a Telecommunication and Multi-Media degree, with a Minor in Creative Writing in May 2013.
He was the first Tongan swimmer to win a gold medal in international competition, when he took gold in the 50 metre breaststroke at the 2010 Oceania Swimming Championships.
In preparation for the 2012 London Olympics Fonua was trained by New Zealander and designated head coach for Tonga, Jon Winter. He served as his nation's flag-bearer in the 2012 Summer Olympics Parade of Nations. As a swimmer at the 2012 Summer Olympics, he competed in the Men's 100 metre breaststroke, failing to reach the semifinals.
Fonua made an international comeback at the 2015 Pacific Games in Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea. He created history by becoming the first ever Tongan athlete to ever win 3 Gold medals at a Pacific Games by sweeping the Breaststroke events, setting 2 Games Records in the process (50 m and 100 m Breaststroke). He is the only Tongan athlete in history to ever hold dual Oceania and Pacific Games titles.
Fonua is openly gay and an advocate for LGBT rights.


1993 – In Denver Colorado, Judge Jeffrey Bayless ruled Amendment 2 unconstitutional. The amendment to the Colorado state constitution sought to eliminate all gay rights laws in the state and prevent any more from being passed.


21 notes
·
View notes
Text
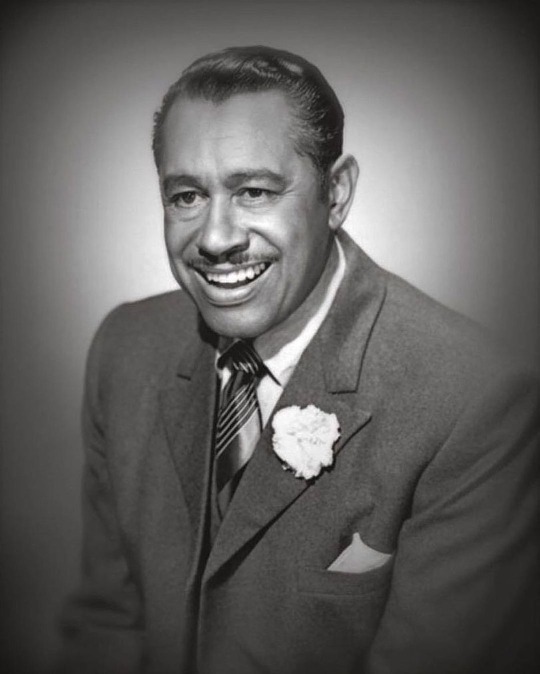

Today In History
Cabell “Cab” Calloway, accomplished bandleader, singer, dancer, songwriter, and author, was born in Rochester, NY, on this date December 25, 1907.
He learned the art of scat singing before landing a regular gig at Harlem’s famous Cotton Club. Following the enormous success of his song “Minnie the Moocher” (1931), Calloway became one of the most popular entertainers of the 1930s and ‘40s.
With other hits that included “Moon Glow” (1934), “The Jumpin’ Jive” (1939) and “Blues in the Night” (1941), as well as appearances on radio, Calloway was one of the most successful performers of the era.
He appeared in such films as The Big Broadcast (1932), The Singing Kid (1936) and Stormy Weather (1943). In addition to music, Calloway influenced the public with books such as 1944’s The New Cab Calloway’s Hepster’s Dictionary: Language of Jive, which offered definitions for terms like “in the groove” and “zoot suit.”
Calloway and his orchestra had successful tours in Canada, Europe and across the United States, traveling in private train cars when they visited the South in order to escape some of the hardships of segregation. With his enticing voice, energetic onstage moves and dapper white tuxedos, Calloway was the star attraction.
The standout musicians Calloway performed with include saxophonist Chu Berry, trumpeter Dizzy Gillespie and drummer Cozy Cole.
CARTER™ Magazine
#carter magazine#carter#historyandhiphop365#wherehistoryandhiphopmeet#history#cartermagazine#today in history#staywoke#blackhistory#blackhistorymonth#cab calloway
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
Carmen Miranda - The Brazilian Bombshell
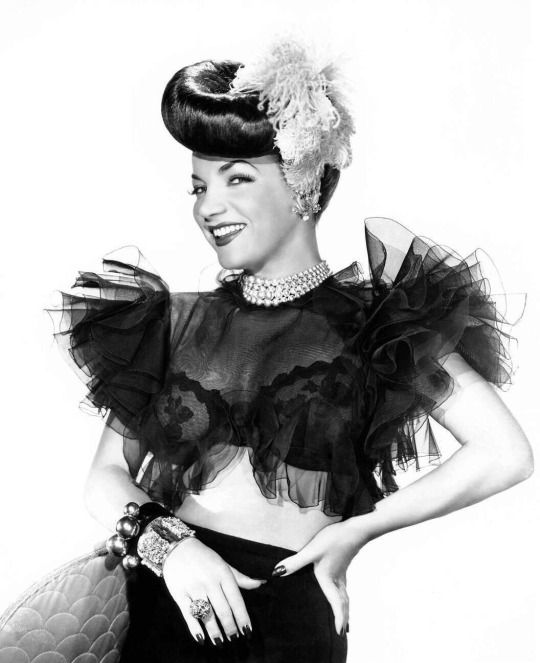
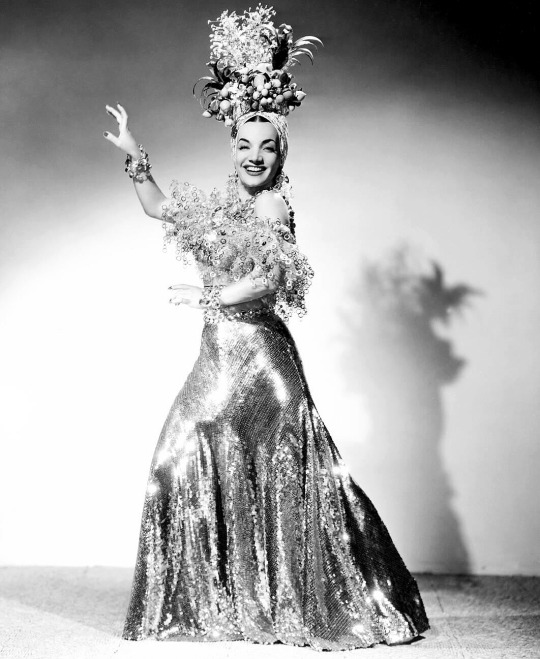
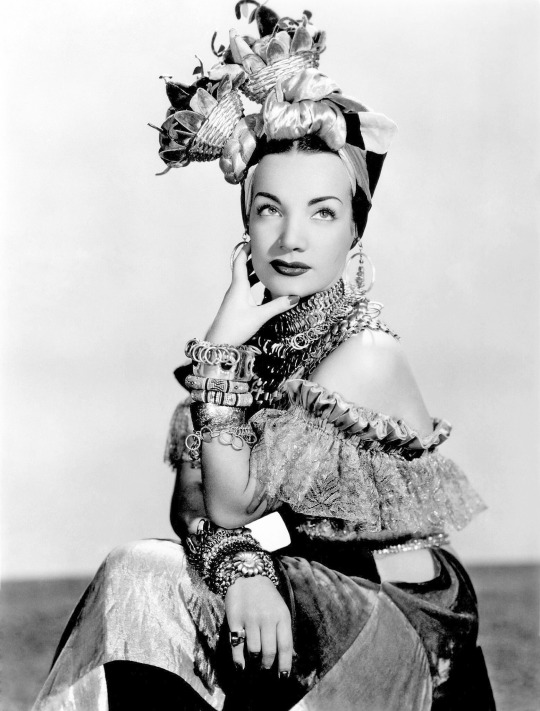
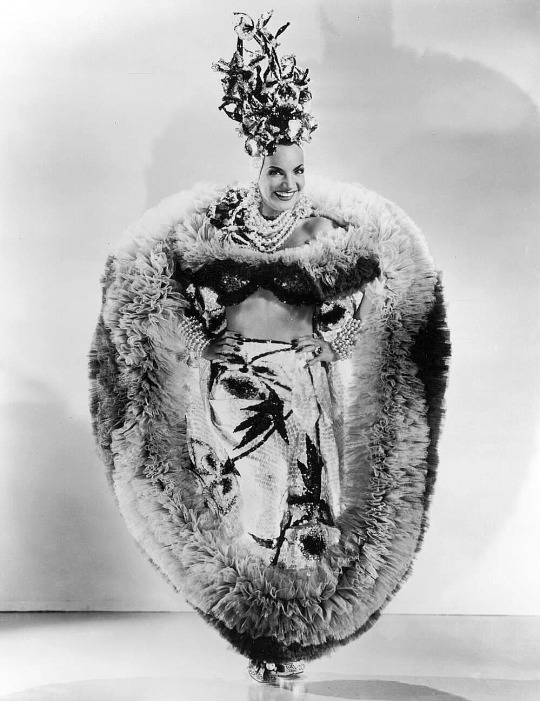












Carmen Miranda (born Maria do Carmo Miranda da Cunha in Marco de Canaveses, Porto on February 9, 1909) was a Portuguese-born Brazilian singer. Nicknamed "The Brazilian Bombshell", she was known for her sass and signature fruit hat outfit that she wore in her American films.
Miranda was introduced to a composer while working at her family's inn and soon recorded her first single in 1929. She then signed a two-year contract with Rádio Mayrink Veiga, the most popular Brazilian station of the 1930s. Her rise to stardom in Brazil was linked to the growth of a native style of music: the samba.
At the invitation of US show business impresario, Lee Shubert, who saw her perform in Rio's Cassino da Urca, she came to Broadway and starred in hit musicals.
When news of Broadway's latest star reached Hollywood, Twentieth Century-Fox offered her a contract in 1941. Her most memorable film performances are in the musical numbers of films such as Week-End in Havana (1941) and The Gang's All Here (1943). After World War II, Miranda's films at Fox were produced in black-and-white, indicative of Hollywood's diminishing interest in her. As a result, she produced her own films to limited success. Although her film career was faltering, her musical career remained solid and she was still a popular nightclub attraction. She continued to tour the US, Europe, and Latin America.
After filming a segment for the NBC variety series The Jimmy Durante Show, where complained of feeling unwell, she died at home in Beverly Hills, California from a heart attack. She was 46 years old.
Legacy:
Was the first contract singer in Brazilian radio history; subsequently, the highest-paid radio singer in Brazil in the 1930s
Chosen by former Brazilian president Getúlio Vargas as a goodwill ambassador to the United States in 1939
Was the first Latin American star to have a block in the forecourt of Grauman’s Chinese Theatre in 1941
Was Hollywood's highest-paid entertainer and the top female taxpayer in the US in 1945, earning more than $200,000 that year
Has a museum in Rio de Janeiro, Museu Carmen Miranda, established in her honor in 1976
Received the Ordem do Infante Dom Henrique Grande Oficial, a Portuguese order of knighthood, in 1995
Has a square in Hollywood named Carmen Miranda Square with a ceremony headed by honorary mayor of Hollywood Johnny Grant and attended by Brazilian consul general Jorió Gama in 1998
Was one of 500 stars nominated for the American Film Institute's 50 greatest screen legends in 1999
Honored by the Museum of Modern Art in Rio de Janeiro in 2005 and the Latin America Memorial in São Paulo in 2006 with a Carmen Miranda Forever exhibit to commemorate the 50th anniversary of her death
Bestowed the Ordem do Mérito Cultural by the Ministry of Culture of Brazil in 2009
Was a part of a set of commemorative US Postal Service Latin Music Legends stamps, painted by Rafael Lopez, in 2011
Commemorated in the 2016 Summer Olympics closing ceremony with a tribute
Honored with a Google Doodle on her 108th birthday in 2017
Was the first South American honored with a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame at 6262 Hollywood Blvd for motion picture

#Carmen Miranda#The Brazilian Bombshell#Brazilian Bombshell#Samba#Chiquita Banana#Cantora Do It#Ditadora Risonha do Samba#A Pequena Notável#Silent Films#Golden Age of Hollywood#Film Classics#Old Hollywood#Vintage Hollywood#Hollywood#Hollywood Walk of Fame#Walk of Fame#Movie Legends#movie stars#1900s#28 Hollywood Legends Born in the 1900s
39 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Women 1939
The Women is a 1939 American comedy-drama film directed by George Cukor. The film is based on Clare Boothe Luce's 1936 play of the same name and was adapted for the screen by Anita Loos and Jane Murfin, who had to make the film acceptable for the Production Code for it to be released.
The film stars Norma Shearer, Joan Crawford, Rosalind Russell, Paulette Goddard, Joan Fontaine, Lucile Watson, Mary Boland, Florence Nash, and Virginia Grey. Marjorie Main and Phyllis Povah also appear, reprising their stage roles from the play. Ruth Hussey, Virginia Weidler, Butterfly McQueen, Theresa Harris, and Hedda Hopper also appear in smaller roles. Fontaine was the last surviving actress with a credited role in the film; she died in 2013.
The film continued the play's all-female tradition—the entire cast of more than 130 speaking roles was female. Set in the glamorous Manhattan apartments of high society evoked by Cedric Gibbons, and in Reno, Nevada, where they obtain their divorces, it presents an acidic commentary on the pampered lives and power struggles of various rich, bored wives and other women they come into contact with.
Filmed in black and white, it includes a six-minute fashion parade filmed in Technicolor, featuring Adrian's most outré designs; often cut in modern screenings, it has been restored by Turner Classic Movies. On DVD, the original black-and-white fashion show, which is a different take, is available for the first time.
Throughout The Women, not a single male character is seen or heard. The attention to detail was such that even in props such as portraits, only female figures are represented, and several animals which appeared as pets were also female. The only exceptions are a poster-drawing of a bull in the fashion show segment, a framed portrait of Stephen Haines as a boy, a figurine on Mary's night stand, and an advertisement on the back of the magazine Peggy reads at Mary's house before lunch that contains a photograph of Douglas Fairbanks, Jr.
In 2007, The Women was selected for preservation in the United States National Film Registry by the Library of Congress as being "culturally, historically, or aesthetically significant".
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
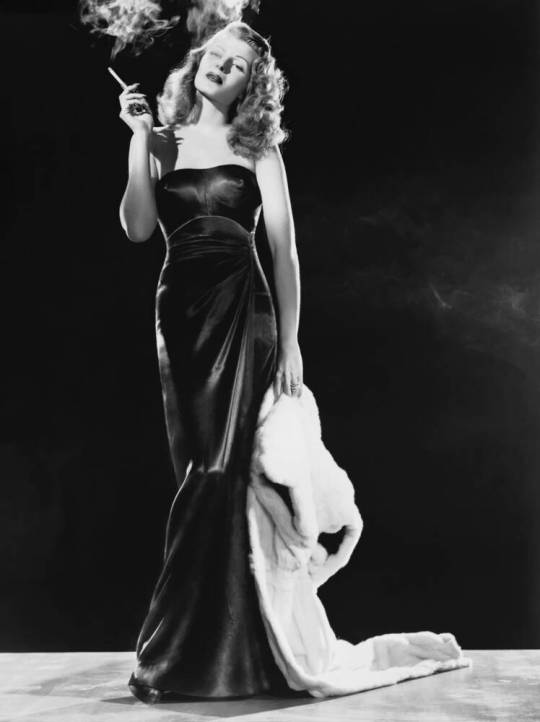

Rita Hayworth (born Margarita Carmen Cansino; October 17, 1918 – May 14, 1987) was an American actress, dancer, and pin-up girl. She achieved fame in the 1940s as one of the top stars of the Golden Age of Hollywood, and appeared in 61 films in total over 37 years. The press coined the term "The Love Goddess" to describe Hayworth, after she had become the most glamorous screen idol of the 1940s. She was the top pin-up girl for GIs during World War II.
Hayworth is perhaps best known for her performance in the 1946 film noir Gilda, opposite Glenn Ford, in which she played the femme fatale in her first major dramatic role. She is also known for her performances in Only Angels Have Wings (1939), The Strawberry Blonde (1941), Blood and Sand (1941), The Lady from Shanghai (1947), Pal Joey (1957), and Separate Tables (1958). Fred Astaire, with whom she made two films, You'll Never Get Rich (1941) and You Were Never Lovelier (1942), once called her his favorite dance partner. She also starred in the Technicolor musical Cover Girl (1944), with Gene Kelly. She is listed as one of the top 25 female motion picture stars of all time in the American Film Institute's survey, AFI's 100 Years...100 Stars.
Hayworth was a top glamour girl in the 1940s, a pin-up girl for military servicemen and a beauty icon for women. At 5 ft 6 in (1.68 m) and 120 lb (54 kg), she was tall enough to be a concern for dancing partners such as Fred Astaire. She reportedly changed her hair color eight times in eight movies.
In 1949, Hayworth's lips were voted best in the world by the Artists League of America. She had a modeling contract with Max Factor to promote its Tru-Color lipsticks and Pan-Stik make-up.
For her contribution to the motion picture industry, Hayworth received a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame at 1645 Vine Street in 1960.
In 1980, Hayworth was diagnosed with early-onset Alzheimer's disease, which contributed to her death in 1987 at age 68. The public disclosure and discussion of her illness drew attention to Alzheimer's, and helped to increase public and private funding for research into the disease.
The public disclosure and discussion of Hayworth's illness drew international attention to Alzheimer's disease, which was little known at the time, and it helped to greatly increase federal funding for Alzheimer's research.
The Rita Hayworth Gala, a benefit for the Alzheimer's Association, is held annually in Chicago and New York City. The program was founded in 1985 by Princess Yasmin Aga Khan, in honor of her mother. She is the hostess for the events and is a major sponsor of Alzheimer's disease charities and awareness programs. As of August 2017, a total of more than $72 million had been raised through events in Chicago, New York, and Palm Beach, Florida.
On October 17, 2016, a press release from the Springer Associates Public Relations Agency announced that Rita Hayworth's former manager and friend, Budd Burton Moss, initiated a campaign to solicit the United States Postal Service to issue a commemorative stamp featuring Hayworth. Springer Associates also announced that the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences would be lobbied in hopes of having an honorary Academy Award issued in memory of Hayworth. The press release added that Hayworth's daughter, Princess Yasmin Aga Khan, the Alzheimer's Association of Greater Los Angeles, and numerous prominent personalities of stage and screen were supporting the Moss campaign. The press release stated the target date for fulfillment of the stamp and Academy Award to be on October 17, 2018, the centennial of Hayworth's birth.
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at Just for Books…?
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Stanley Anderson

Physique: Stocky build Height: 5'8½" (1.74 m)
Stanley Albin Anderson, Jr. (October 23, 1939 – June 24, 2018; aged 78) was an American character actor who played Drew Carey's father on The Drew Carey Show. His film career included roles as the President of the United States in two Michael Bay movies, Armageddon and The Rock. His television career included The X-Files, Dangerous Minds, L.A. Law, and Law & Order.





I first came across him while watching the movie Primal Fear and I’ve had a hard-on for him ever since. And why not? I thought he was handsome and had a nice set of man tits on him.


Most of Stanley’s childhood was spent in Billings, Montana, and1fe graduating from Billings Senior High School. In 1957, he joined the United States Army where he served most notably as a radio announcer in Korea. He was honorably discharged in 1960. He attended San Jose City College and, later, San Jose State College, where he earned a Bachelor’s Degree in Drama.

Anderson was married 52 years with one son and passed away at his home in Santa Rosa, California on June 24, 2018, six weeks after being diagnosed with brain cancer. Even though he may not have been the most well known name in Hollywood, Stanley Anderson still left his mark and will truly be missed. His work in over 50 movies and TV shows, in addition to his theatrical and political work, marked his place in the world.

RECOMMENDATIONS: The Drew Carey Show (TV Series 1995–2004) Runaway Jury (2003) Seinfeld (TV Series 1989–1998) The Lake (1998) Primal Fear (1996)
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
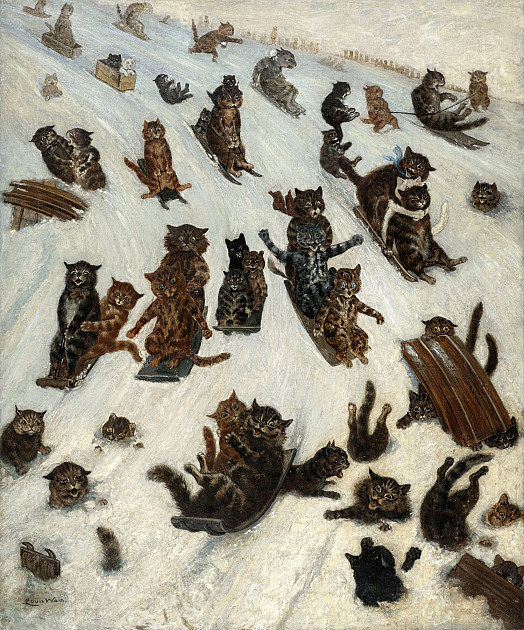

Snow time; Downhill all the way!
Louis Wain (1860-1939)
"At the turn of the century, Louis Wain became a household name as ‘The Man Who Drew Cats’. His drawings of cats appeared in periodicals and his own annuals and then, increasingly on prints and postcards. While his early work was already distinctive, in a gently humorous way, the onset of schizophrenia gradually transformed his style, making it bright, highly patterned and apparently in keeping with Jazz Age Modernism.
Louis Wain was born in London on 5 August 1860. His father was a textile salesman and his mother designed carpets and church fabrics. A sickly child, he was educated at the Orchard Street Boys and Infant School, South Hackney, and at St Joseph’s Academy, Kennington. He trained at the West London School of Art (1877-80), remaining there as an assistant master until 1882. From his father’s death in 1880, he had to support first his mother and five younger sisters and soon after a sick wife. He supplemented his income by working as a freelance illustrator (initially influenced by Caldecott and May), and in 1882 he joined the staff of the Illustrated Sporting and Dramatic News. He began to make his name with humorous cat drawings, primarily in the Illustrated London News, the staff of which he joined in 1886. He was the first to work consistently within the convention of depicting clothed and standing animals. His anthropomorphic vision of the world soon brought him much fame and as a result he was elected President of the National Cat Club in 1891. However, he was not a good businessman, and in 1907 he may have been sued for debt. In the same year, he moved to the United States to make a new start, producing strip cartoons for the New York American (1907-10). Back in England, he experimented with animation in 1917, in the films, The Golfing Cat and The Hunter and the Dog. After the death of his sister Caroline in the same year, he began to suffer a mental decline, becoming a schizophrenic, as his work clearly revealed. ‘His cats became frenzied and jagged, sometimes disappearing into kaleidoscopic shapes’ (Frances Spalding). When, in 1925, he was found in the paupers’ ward of Middlesex County Asylum, an appeal was launched on his behalf, and he was transferred to a comfortable room with his paints in the Bethlem Royal Hospital, Southwark. The appeal reached twice the target sum in a month, a sign of the public’s continuing affection. He died in the Middlesex County Asylum, Napsbury, near St Albans, on 4 July 1939.
Chris Beetles Gallery
48 notes
·
View notes
Text

John Amos in his 1958 East Orange High School yearbook photo.
John Allen Amos Jr. (born December 27, 1939) is an American actor known for his role as James Evans, Sr., on the CBS television series Good Times. Amos's other television work includes The Mary Tyler Moore Show, a recurring role as Admiral Percy Fitzwallace on The West Wing, and the role of Washington, D.C., Mayor Ethan Baker in the series The District. Amos has appeared on Broadway and in numerous films in his five-decade career. He has been nominated for a Primetime Emmy Award and an NAACP Image Award. On film, he has played numerous supporting roles in movies such as The Beastmaster (1982), Coming to America (1988), Die Hard 2 (1990) and Coming 2 America (2021).
John A. Amos, Jr. Was born in Newark, New Jersey. He grew up in East Orange, New Jersey, and graduated from East Orange High School in 1958. He enrolled at Long Beach City College and graduated from Colorado State University, qualifying as a social worker with a degree in sociology. Amos also played on the Colorado State Rams football team. After college, he was a Golden Gloves boxing champion.
In 1964, Amos signed a free agent contract with the American Football League's Denver Broncos. Unable to run the 40-yard dash because of a pulled hamstring, he was released on the second day of training camp. He then played with the Canton Bulldogs and Joliet Explorers of the United Football League. In 1965, he played with the Norfolk Neptunes and Wheeling Ironmen of the Continental Football League. In 1966, he played with the Jersey City Jets and Waterbury Orbits of the Atlantic Coast Football League.
In 1967, Amos signed a free agent contract with the American Football League's Kansas City Chiefs. Coach Hank Stram told him, "You're not a football player, you're a man who is trying to play football." He returned to the Continental League, where he played that year with the Victoria Steelers
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Valeska Gert, Munich, 1918 | @abwwia
Born Gertrud Valesca Samosch (11 January 1892 – c. 16 March 1978) was a German dancer, pantomime, cabaret artist, actress and pioneering performance artist.
In 1933, Gert's Jewish heritage resulted in her being banned from the German stage. Her exile from Germany sent her to London for some time, where she worked both in theatre and film. In London, she worked on the experimental short film Pett and Pott, which long stood as her last movie.
Beginning of 1939, she emigrated to the United States, where she was cared for by a Jewish refugee community.
By the end of 1941, she had opened the Beggar's Bar in New York City. It was a cabaret/restaurant that was filled with mismatched furniture and lamps.
In 1947 she returned to Europe. After stays in Paris and Zurich, where she ran a cabaret café called Valeska und ihr Küchenpersonal (Valeska and her kitchen staff) for half a year in 1948, she went back to Blockaded Berlin. There she first opened the cabaret Bei Valeska in the former Opernkeller (Opera cellar) at the Theater des Westens in 1949–1950, after that the cabaret Hexenküche (Witch's Kitchen) in 1950. It was active every winter until April 1956. Via wikipedia
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Stepin Fetchit
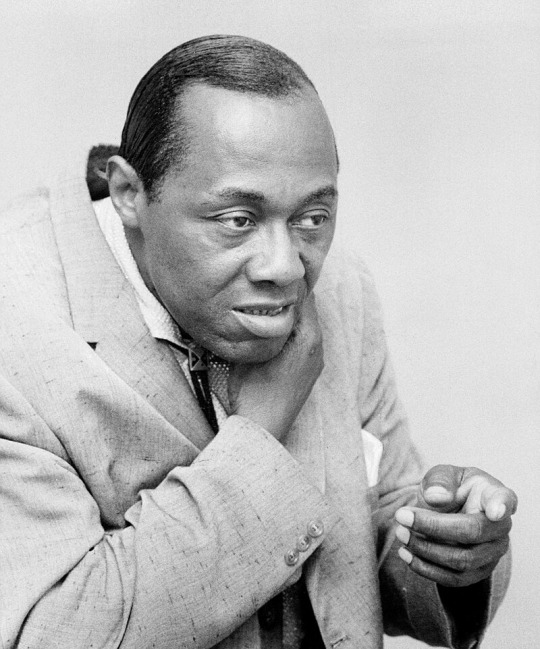

Lincoln Theodore Monroe Andrew Perry (May 30, 1902 – November 19, 1985), better known by the stage name Stepin Fetchit, was an American vaudevillian, comedian, and film actor of Jamaican and Bahamian descent, considered to be the first black actor to have a successful film career. His highest profile was during the 1930s in films and on stage, when his persona of Stepin Fetchit was billed as the "Laziest Man in the World".
Perry parlayed the Fetchit persona into a successful film career, becoming the first black actor to earn $1 million. He was also the first black actor to receive featured screen credit in a film.
Perry's film career slowed after 1939 and nearly stopped altogether after 1953. Around that time, Black Americans began to see his Stepin Fetchit persona as an embarrassing and harmful anachronism, echoing negative stereotypes. However, the Stepin Fetchit character has undergone a re-evaluation by some scholars in recent times, who view him as an embodiment of the trickster archetype.
Little is known about Perry's background other than that he was born in Key West, Florida, to West Indian immigrants. He was the second child of Joseph Perry, a cigar maker from Jamaica (although some sources indicate the Bahamas) and Dora Monroe, a seamstress from Nassau, The Bahamas. Both of his parents came to the United States in the 1890s, where they married. By 1910, the family had moved north to Tampa, Florida. Another source says he was adopted when he was 11 years old and taken to live in Montgomery, Alabama.
His mother wanted him to be a dentist, so Perry was adopted by a quack dentist, for whom he blacked boots before running away at age 12 to join a carnival. He earned his living for a few years as a singer and tap dancer.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
THIS DAY IN GAY HISTORY
based on: The White Crane Institute's 'Gay Wisdom', Gay Birthdays, Gay For Today, Famous GLBT, glbt-Gay Encylopedia, Today in Gay History, Wikipedia, and more … January 18



1726 – Frederick Heinrich Louis, more commonly known as Prince Henry of Prussia was born in Berlin (d.1802). He also served as a general and statesman, and, in 1786, was suggested as a candidate for a monarch for the United States, but before he could make up his mind on the offer, the U.S. had opted to be a Republic.
The younger brother of King Frederick II of Prussia, Henry's conflicts with "Frederick the Great" are almost legendary.
In 1752 Henry married Princess Wilhelmina of Hesse-Kassel in Charlottenburg, but they had no children. Henry lived in Rheinsberg after receiving it as a gift from his brother. Despite the marriage, he scarcely concealed his passion for other men and developed intimate friendships with the actor Blainville and the French emigre Count La Roche-Aymon. One favourite, Major Kaphengst, exploited the prince's interest in him to lead a dissipated, wasteful life on an estate not far from Rheinsberg.
Henry successfully led Prussian armies as a general during the Seven Years' War (1756-1763), in which he never lost a battle. After the Prussian Army's initial success against one wing of the joint Russian and Austrian Armies in the Battle of Kunersdorf, Henry urged his brother Frederick to stop attacking. The king, who had already sent a message of victory to Berlin, pressed the attack. The day ended with a virtually destroyed Prussian army, a virtually defenseless Kingdom of Prussia, and a complete victory by the Russo-Austrian force. Afterwards, Henry reorganized the routed Prussian forces. Frederick came to rely on his brother as commander of the Prussian forces in the east, Frederick's strategic flank. Henry later won his most famous victory at Freiberg in 1762.
After the Seven Years' War, Henry worked as a shrewd diplomat who helped plan the First Partition of Poland through trips to Stockholm and St. Petersburg. In the 1780s he made two diplomatic trips to France. He was a friend of Jean-Louis Favier.
Henry attempted to secure a principality for himself and twice tried to become King of Poland, but was opposed by a displeased Frederick. The king frustrated Henry's attempt to become ruler of a kingdom Catherine II of Russia planned to create in Wallachia.
In 1786 either Nathaniel Gorham, then President of the Continental Congress, or Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben, the Prussian general who served in the Continental Army, suggested to Alexander Hamilton that Henry should become President or King of the United States, but the offer was revoked before the prince could make a reply.


1904 – Cary Grant, born Archibald Alexander Leach, (d.1986), was an English actor who later took U.S. citizenship. Known for his transatlantic accent, debonair demeanor and "dashing good looks", Grant is considered one of classic Hollywood's definitive leading men. His good looks, charisma, and ambiguous sexuality enchanted women and men alike. As the star-struck comedian Steve Lawrence once said, "When Cary Grant walked into a room, not only did the women primp, the men straightened their ties."
Born Archibald Alexander Leach on January 18, 1904, near Bristol, England, Grant began his career in vaudeville. In 1932 he signed with Paramount and moved to Hollywood, where he developed the debonair persona that made him famous. After appearing in half a dozen films, his big break came when the sultry Mae West handpicked him to star with her in She Done Him Wrong (1933). Based on West's Broadway hit Diamond Lil, the film made Grant a bankable star.
Grant's best-known films include The Awful Truth (1937), Bringing Up Baby (1938), Gunga Din (1939), The Philadelphia Story (1940), His Girl Friday (1940), Arsenic and Old Lace (1944), Notorious (1946), To Catch A Thief (1955), An Affair to Remember (1957), North by Northwest (1959) and Charade (1963).
Grant was married five times. But there were well-founded rumours that he was bisexual or gay. Homosexual screenwriter Arthur Laurents wrote that Grant "told me he threw pebbles at my window one night but was luckless". Grant allegedly was involved with costume designer Orry-Kelly when he first moved to Manhattan, and lived with Randolph Scott off and on for twelve years.
Richard Blackwell wrote that Grant and Scott were "deeply, madly in love", and alleged eyewitness accounts of their physical affection have been published. Alexander D'Arcy, who appeared with Grant in The Awful Truth, said he knew that Grant and Scott "lived together as a gay couple", adding: "I think Cary knew that people were saying things about him. I don't think he tried to hide it." The two men frequently accompanied each other to parties and premieres and were unconcerned when photographs of them cozily preparing dinner together at home were published in fan magazines. Biographer Roy Moseley claims that Grant and Scott were seen kissing in a public carpark outside a social function both attended in the 1960s. William J. Mann's book Behind the Screen: How Gays and Lesbians Shaped Hollywood, 1910-1969 recounts how photographer Jerome Zerbe spent "three Gay months" in the movie colony taking many photographs of Grant and Scott, "attesting to their involvement in the Gay scene." Zerbe says that he often stayed with the two actors, "finding them both warm, charming, and happy."

Cary Grant (R) with Randolph Scott
For more pictures and backround of this 1930s 'bromance' see Cary Grant and Randolph Scott: A Love Story.
Barbara Harris, Grant's widow, has disputed that there was a relationship with Scott. When Chevy Chase joked about Grant being gay in a television interview Grant sued him for slander; they settled out of court. However, Grant did admit in an interview that his first two wives had accused him of being homosexual. Betsy Drake commented: "Why would I believe that Cary was homosexual when we were busy fucking? He lived 43 years before he met me. I don't know what he did. Maybe he was bisexual."
Although most of his career was spent playing a static archetype, Grant was unafraid to take risks, professionally or privately. He is credited with using the word "gay" for the first time in a homosexual context on screen. In Bringing Up Baby (1938), Grant plays a shy paleontologist against Katharine Hepburn's spoiled New York heiress. During one scene, Grant appears in a frilly pink dressing gown and to incredulous observers delivers his famous line "because I just went gay all of a sudden."
Knowing his audience did not want to see him age, Grant retired from films in the 1960s, secure as one of Hollywood's brightest stars. He died on November 29, 1986.


1913 – Danny Kaye, born David Daniel Kaminsky, (d.1987) was a celebrated American actor, singer, dancer, and comedian. His best known performances featured physical comedy, idiosyncratic pantomimes, and rapid-fire nonsense songs.
Kaye starred in 17 movies, notably The Kid from Brooklyn (1946), The Secret Life of Walter Mitty (1947), The Inspector General (1949), Hans Christian Andersen (1952), and — perhaps his most accomplished performance — The Court Jester (1956). His films were extremely popular, especially his bravura performances of patter songs and children's favorites such as The Inch Worm and The Ugly Duckling. He was the first ambassador-at-large of UNICEF and received the French Legion of Honor in 1986 for his many years of work with the organization.
Kaye and his wife, Sylvia Fine, both grew up in Brooklyn, living only a few blocks apart, but they did not meet until they were both working on an off-Broadway show in 1939. They were married on January 3, 1940.
During World War II, the Federal Bureau of Investigation investigated rumors that Kaye dodged the draft by manufacturing a medical condition to gain 4-F status and exemption from military service. FBI files show he was also under investigation for supposed links with Communist groups. The allegations were never substantiated, and he was never charged with any associated crime.
After Kaye and his wife became estranged, he was allegedly involved with a succession of women, though he and Fine never divorced. The best-known of these women was actress Eve Arden.
There are persistent rumors that Kaye was either homosexual or bisexual, and some sources claim that Kaye and Laurence Olivier had a ten-year relationship in the 1950s while Olivier was still married to Vivien Leigh. A biography of Leigh states that the alleged relationship caused her to have a breakdown. The alleged relationship has been denied by Olivier's official biographer, Terry Coleman. Joan Plowright, Olivier's widow, has dealt with the matter in different ways on different occasions: she deflected the question (but alluded to Olivier's "demons") in a BBC interview. However, in her memoirs Plowright denies that there had been an affair between the two men. Producer Perry Lafferty reported: "People would ask me, 'Is he gay? Is he gay?' I never saw anything to substantiate that in all the time I was with him." Kaye's final girlfriend, Marlene Sorosky, reported that he told her, "I've never had a homosexual experience in my life. I've never had any kind of gay relationship. I've had opportunities, but I never did anything about them."


1955 – Francis Warren Nicholls, Jr., better known by his stage name Frankie Knuckles (d. 2014), was an American DJ and record producer.
Knuckles was born in The Bronx, New York; he later moved to Chicago. He played an important role in developing and popularizing house music in Chicago during the 1980s, when the genre was in its infancy. Due to his importance in the development of the genre, Knuckles was often known as "The Godfather of House Music." Chicago named a stretch of street and a day after Knuckles in 2004 for this role. His accomplishments earned him a Grammy Award in 1997. Knuckles was inducted into the Dance Music Hall of Fame in 2005 as recognition for his achievements.
While studying textile design at the FIT in New York, Knuckles began working as a DJ, playing soul, disco, and R&B at two of the most important early discos, The Continental Baths and The Gallery, with childhood friend and fellow DJ Larry Levan.
In the late 1970s, Knuckles moved from New York City to Chicago, where Robert Williams, an old friend was opening what became the Warehouse. When the Warehouse club opened in Chicago in 1977, he was invited to play on a regular basis, which enabled him to hone his skills and style. This style was a mixture of disco classics, unusual indie-label soul, the occasional rock track, European synth-disco and all manner of rarities, which would all eventually codify as "House Music." The style of music now known as house was of course named after a shortened version of the Warehouse.
Knuckles was so popular that the Warehouse, initially a members-only club for largely black gay men, began attracting straighter, whiter crowds. He continued DJing at the Warehouse until November 1982, when he started his own club in Chicago, The Power Plant.
When the Power Plant closed in 1987, Knuckles played for four months at Delirium in the United Kingdom. Chicago house artists were in high demand and having major success in the UK with this new genre of music. Knuckles also had a stint in New York, where he continued to immerse himself in producing, remixing, and recording. 1988 saw the release of Pet Shop Boys' third album, Introspective, which featured Knuckles as a co-producer of the song "I Want a Dog."
Openly gay, Knuckles was inducted into the Chicago Gay and Lesbian Hall of Fame in 1996


1973 – The Chilean journalist Juan Manuel Astorga was born today. Astorga is a major media personality having hosted radio, television and cable shows in his long and storied career. In 2008, Astorga gave an interview to Caras magazine, in which he discussed his homosexuality .
He chose to disclose his sexuality before he was outed by an attorney who was a member of the Fascist-connected Catholic order Opus Dei. The attorney attempted to extort money from Astorga by threatening to out him. Astorga beat him to the punch. The Movement for Homosexual Integration and Liberation of Chile supported Astorga and condemned this kind of blackmail.


1974 – Maulik Pancholy is an American actor of Indian heritage known for his recurring role as Sanjay Patel on Weeds, his role as Jonathan on 30 Rock, voice acting as Baljeet Tjinder in Phineas and Ferb, and as Neal during the first season of Whitney. He also voices a different character also named Sanjay Patel in the Nickelodeon animated series Sanjay and Craig.
Pancholy's television work includes guest roles on Tracey Takes On..., The Sopranos, Law & Order: Criminal Intent and The Comeback. He also has several stage acting credits in New York City including the Culture Project's production of Guantanamo: Honor Bound to Defend Freedom in 2004, a workshop of the play Morbidity & Mortality at the historic Cherry Lane Theatre in 2005, and the lead role in India Awaiting at the Samuel Beckett Theatre.
Pancholy came out as gay in a November 2013 interview with Out magazine in which he discussed his partner of nine years. He announced his engagement to caterer Ryan Corvaia on January 9, 2014.


1984 – (Benjamin) Benji Schwimmer is an American professional dancer, choreographer and actor. On August 16, 2006 he was announced as the winner of the second season of So You Think You Can Dance and has choreographed for both the U.S. and the international versions of the show. He co-starred in the 2010 film Leading Ladies.
Schwimmer is known for his versatility in mixing the arts of solo dance and partnering. He works for the non-profit group, Dancers Everywhere Making a Needed Difference (D.E.M.A.N.D), and is the songwriter, producer, and vocalist for pop-rock band The Weekend Forecast.
Schwimmer grew up in a Latter-day Saint (Mormon) household in Moreno Valley, California. He is the son of choreographer and West Coast Swing dancer Buddy Schwimmer. His mother, Laurie Schwimmer, and sister, Lacey Schwimmer, are also west-coast swing dancers.
He started competing when he was five years old. Some of his early experiences included singing and dancing in "Sunshine Magic", a children's troupe.
Schwimmer put dancing on hold to serve a two-year mission for The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in the Mexican state of Oaxaca. He returned afterwards to the dance circuit. He founded D.E.M.A.N.D., a non-profit organization that helps the less fortunate and provides health care for dancers with HIV/AIDS and other illness.
Schwimmer is openly gay. He left the LDS church in 2011 due in part to the church's position on not allowing homosexuals to work with youth. He came out publicly in 2012, after struggling with his homosexuality for a number of years. The catalyst for his decision was the death by suicide of three gay friends.


1986 – Eugene Lee Yang is an American filmmaker, actor, and internet celebrity, best known for his work with BuzzFeed (2013–2018) and The Try Guys (2014–present). Yang is also known for his work with various human rights and LGBT advocacy charities such as The Trevor Project.
Yang, the only son of Korean immigrants Min-Young and Jae Yang, was born and raised in Pflugerville, Texas. He is the middle child of two sisters. Growing up in Pflugerville, Yang's family was one of the few Asian Americans in their community. He struggled with body image issues and low self-esteem as, in his own words, no one looked like him, and suffered bullying due to his appearance.
At school, he engaged in artistic activities including visual arts, illustration, theater, choir, and dance. However, a seventh-grade teacher recommended that he should consider studying filmmaking. He later went to the University of Southern California and, during his studies, had written and directed six short films discussing wide-ranging social and political topics, including mental health care, gay marriage, and school shootings. He graduated with a B.A. in cinema production degree in 2008. On June 15, 2019, Yang came out as gay in a video titled "I'm Gay" which he wrote, directed, and choreographed with the song "A Moment Apart" by Odesza.
In 2013, he started working for the video branch of the internet media company, BuzzFeed, at the recommendation of a colleague who saw his potential in creating short format videos. He was given free control on experimental video productions and exploring new modes of storytelling.Reaction to some of his early works was positive particularly on their distinct candor and reliability, which led to more provocative sketches such as
The Try Guys, which was established in Buzzfeed in 2014, together with co-stars Ned Fulmer, Keith Habersberger, and Zach Kornfeld. The show is a mix of social commentary and humor depicting scenarios such as men going through labor pains and prostate cancer check at a doctor's office. The cast initially were hesitant about stepping out from behind the camera as they had limited acting experience, but they continued producing videos for the show after receiving positive feedback.
Yang is the only openly gay member among the cast of The Try Guys, which also produced LGBTQ-themed videos such as season 1 episode 3 The Try Guys Try Drag for the First Time. On October 31, 2018, he published the video, My Dad’s First Drag Show (Featuring Kim Chi), where he adopted a similar approach into exploring drag culture by inviting his father and stepmother to a drag show.
He also executively produced and hosted Buzzfeed's Queer Prom five-part video series that documented the journey of eight high school seniors who attended the company's first LGBTQ-themed prom together with other students.
On October 11, 2018, commemorated as the 30th year of National Coming Out Day, he took over the website of the advocacy group Human Rights Campaign, publicly sharing his experience growing up as a young queer man and advocating for LGBTQ representation in the media. Furthermore, he collaborated with The Trevor Project, a non-profit LGBTQ suicide prevention organization, to raise awareness on the incidence of suicide among LGBTQ youth and in inviting volunteers in the video Eugene Volunteers at the Trevor Project, which was posted on December 3, 2018.
He referred to himself as queer and LGBT, however, on June 15, 2019, Yang explicitly came out as gay in a music video. Two days later, Yang released an accompanying video documenting the creation of the video, his feelings, and his thoughts surrounding his coming out process.
In 2019, he announced that he is in a relationship with Matthew McLean.


2009 – On this date the Right Reverend Gene Robinson, the bishop of New Hampshire, and the first openly gay bishop of any denomination opened the inaugural festivities of Barack Obama's presidency when he gave the opening prayer at the Lincoln Monument. HBO, which had paid for exclusive rights to the event did not broadcast Bishop Robinson's prayer. So those watching the event live or later in replay would never have known it had occurred.
Curiously, National Public Radio chose not to air the prayer live either. There was no record of Bishop Robinson or his prayer in images placed on the sites of Getty Images, the New York Times and the Washington Post.
Very curious indeed. After some lame excuses HBO later aired a complete version of the afternoon's proceedings with Bishop Robinson's prayer included. No good excuse was ever given by the inaugural committee.
On an added note the Gay Men's Chorus of Washington also performed at the event but there was no announcement or caption of any sort to identify the group performing (perhaps to not upset any viewers out there).


2010 – Undercover cops are working Dubai's chat rooms to bust gay men for trying to hookup online. The National reports that one 22 year old man is charged with prostitution, consensual homosexual sex, producing pornographic material, cross-dressing and insulting religion, while the second, an 18-year-old student, is facing prostitution charges. Homosexuality is illegal in the United Arab Emirates, and if found guilty both face a minimum of three and a maximum of 15 years in prison.





11 notes
·
View notes