#1819 nationals
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
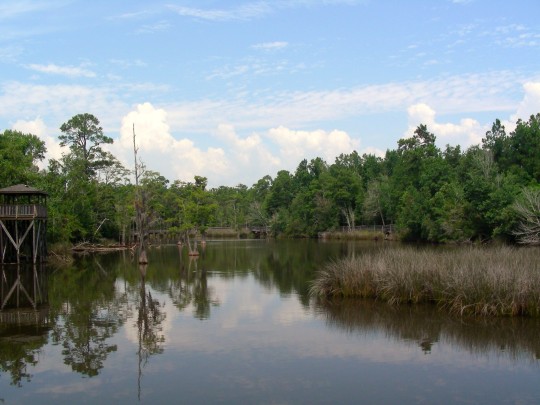
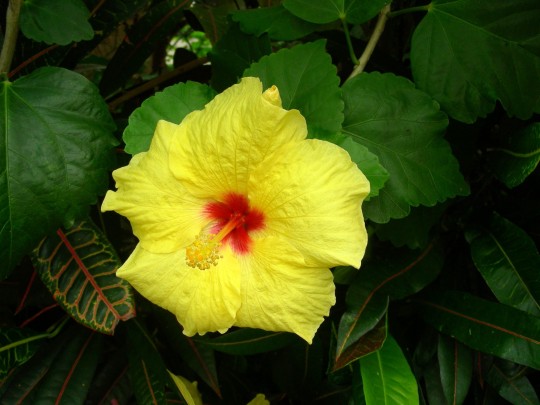
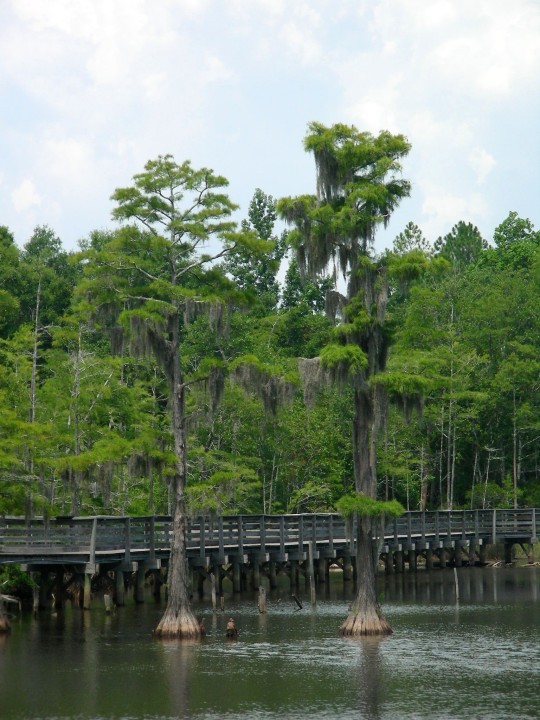
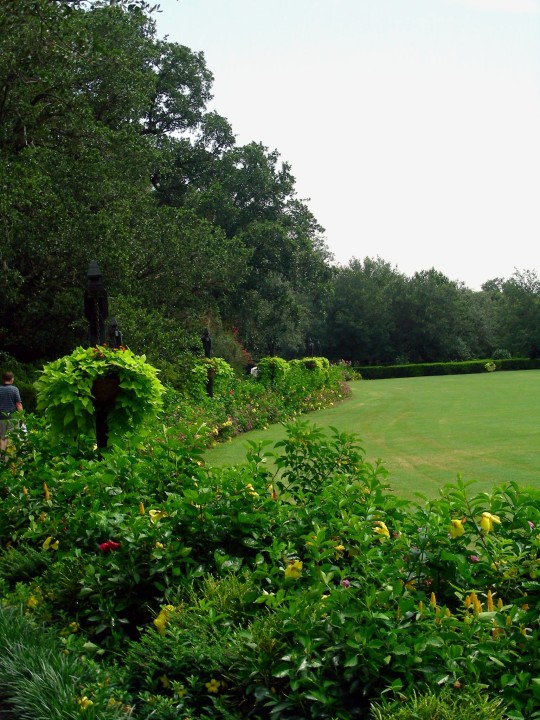
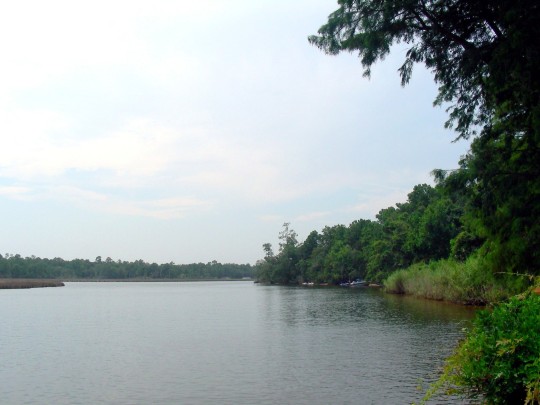
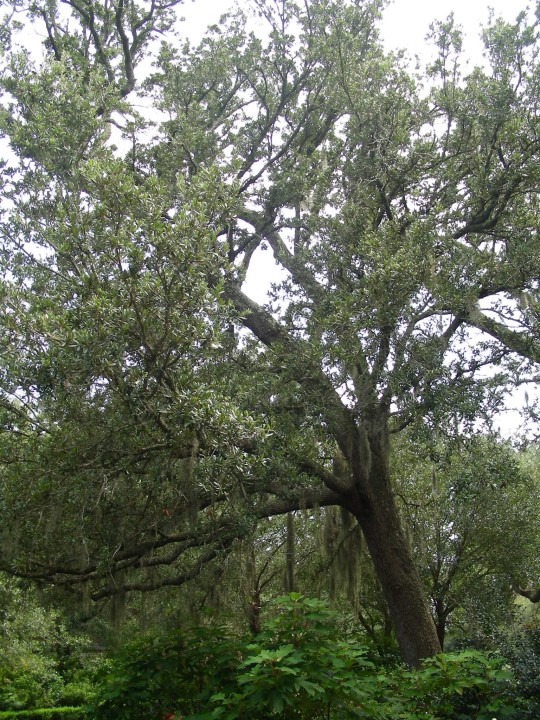
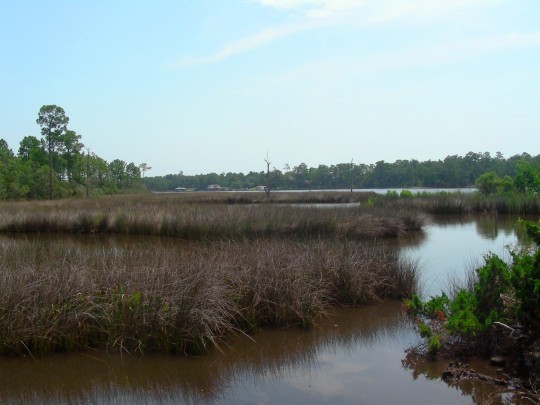
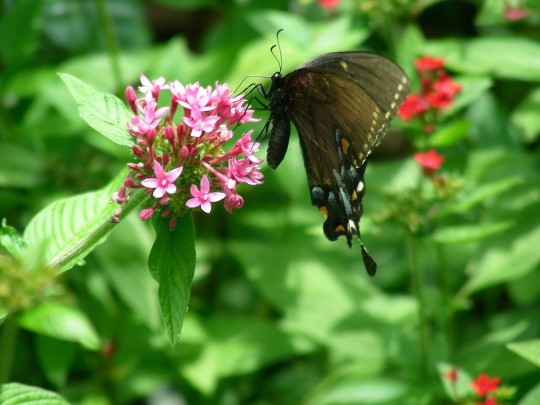
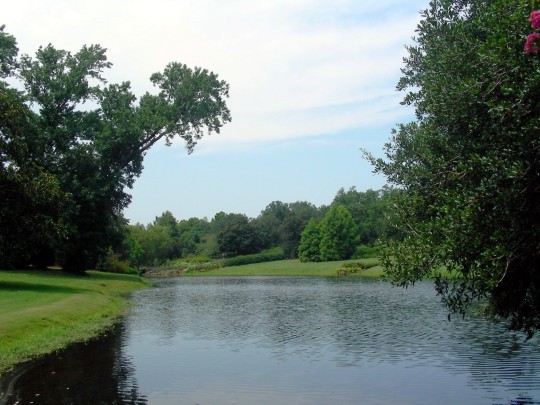
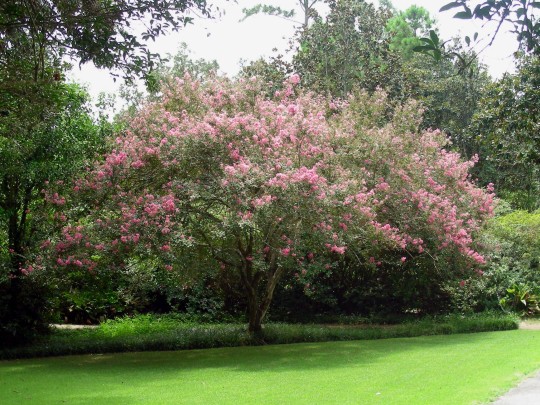
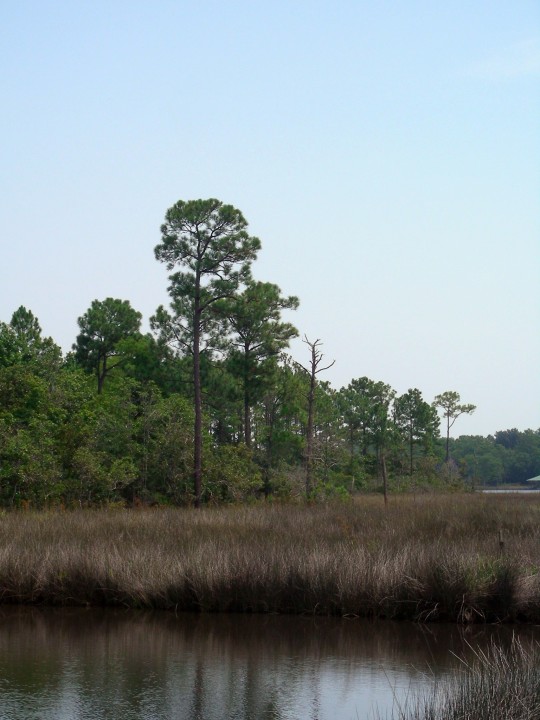
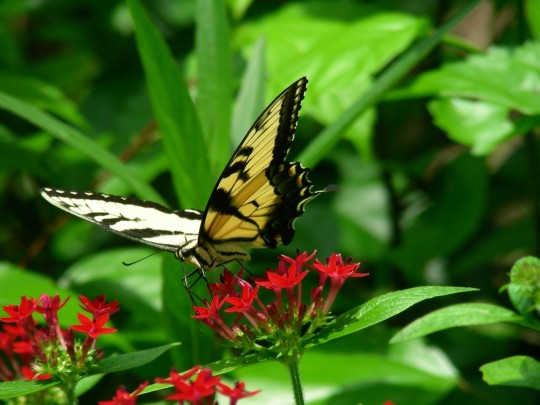
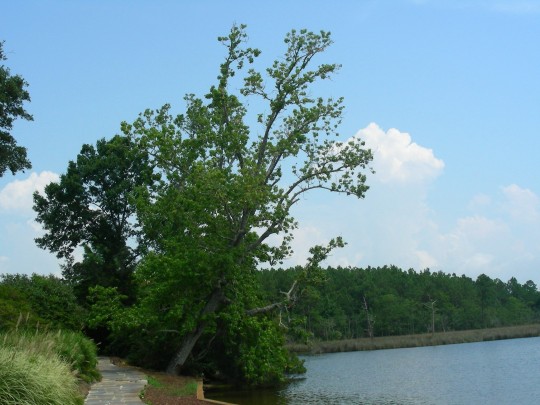
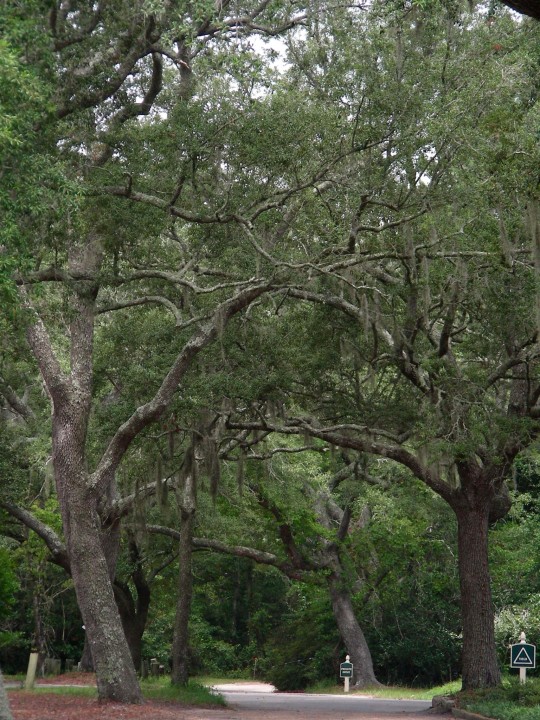
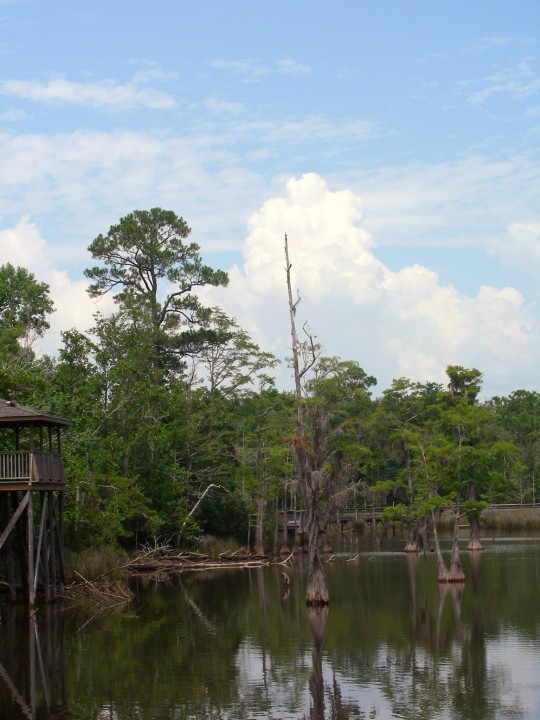
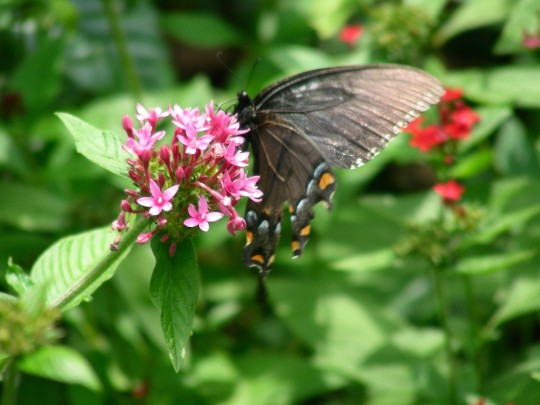
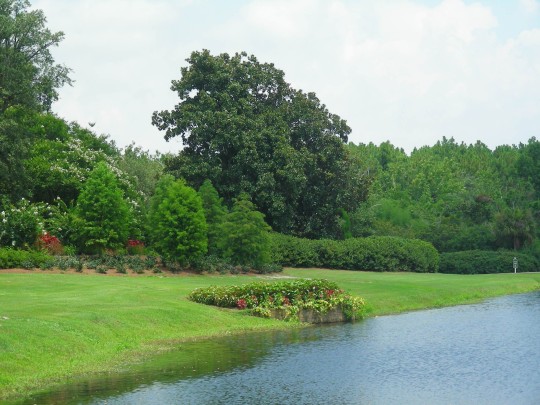
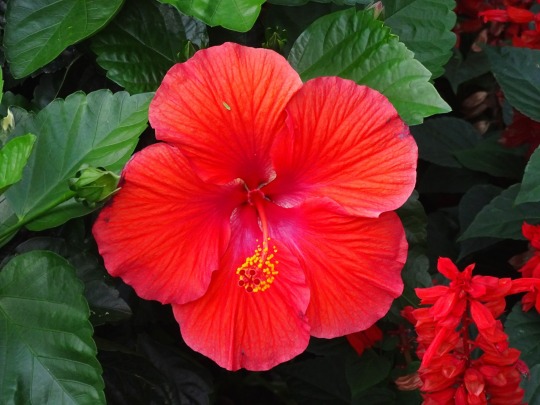
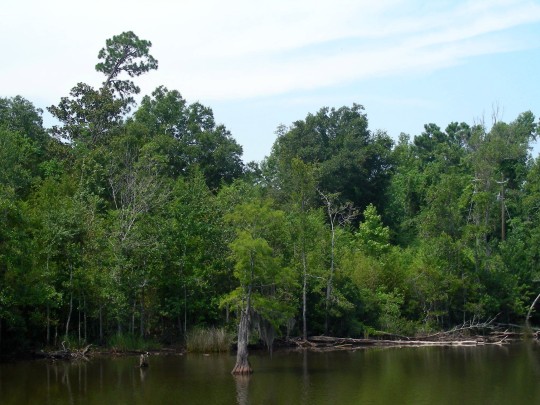



















Alabama became the 22nd U.S. state on December 14, 1819.
National Alabama Day
National Alabama Day celebrates the rich culture and contributions of the state known as the Heart of Dixie.
It honors Alabama’s significant role in the nation, from its natural beauty and historical landmarks to its vibrant traditions and unique cuisine.
This day encourages everyone to appreciate what makes Alabama special, fostering a sense of state pride and unity.
The day recognizes Alabama’s impact on American history and culture. It highlights the state’s importance in events like the Civil Rights Movement and showcases its role in shaping the nation.
Celebrating this day also means acknowledging Alabama’s natural wonders, such as the Appalachian Mountains and Gulf Coast, along with its famous southern hospitality and delicious dishes like barbecue and fried green tomatoes.
National Alabama Day is a time for residents and visitors to explore the state’s diverse attractions and enjoy community gatherings.
People can visit national parks, attend local music festivals, and indulge in traditional Alabama foods.
These activities celebrate the state’s heritage and bring communities together, making it a memorable and cherished occasion for all.
History of National Alabama Day
National Alabama Day celebrates Alabama’s admission to the Union as the 22nd state. This day acknowledges the state’s journey from being part of the Mississippi Territory to becoming its entity.
The process started with a constitutional convention in Huntsville in July 1819, leading to statehood on December 14 of the same year. The first governor was William Wyatt Bibb, and the initial capital was in the town of Cahawba. While Alabama Day was celebrated unofficially all over the state starting in 1903, the state officially declared the day in 1923.
The celebration of this day reflects on Alabama’s significant historical milestones and contributions to the nation. Alabama played a crucial role in events like the Civil Rights Movement, which began in Montgomery.
This period marked important strides towards equality and justice in the United States, making the state a central figure in American history.
National Alabama Day also celebrates the state’s rich cultural heritage, including its music, cuisine, and natural beauty.
From southern hospitality to delicious barbecue and sweet tea, Alabama offers a unique blend of traditions that are cherished nationwide.
This day serves as a reminder of the state’s enduring spirit and its importance in the tapestry of American culture.
How to Celebrate National Alabama Day
Celebrate National Alabama Day with these fun and engaging activities. Each suggestion offers a unique way to appreciate Alabama’s heritage, natural beauty, and cultural richness.
Dive into History
Visit historical sites to explore Alabama’s rich past. Check out the Civil Rights Memorial in Montgomery. Tour the USS Alabama Battleship Memorial Park in Mobile.
Dive into the tales these landmarks tell. They offer a fascinating glimpse into the state’s history.
Feast on Southern Delights
Cook up some Alabama specialties. Fire up the grill for some BBQ ribs. Whip up a batch of fried green tomatoes.
Don’t forget to try the famous Alabama white sauce. Enjoy a sweet ending with a slice of pecan pie. Your taste buds will thank you.
Enjoy the Great Outdoors
Take advantage of Alabama’s natural beauty. Hike through the Appalachian Mountains, lounge on the sandy beaches of the Gulf Coast, and explore underground caves.
Nature enthusiasts will find plenty to love in Alabama’s varied landscapes.
Attend Local Events
Join in the community festivities. Parades, music festivals, and street fairs are common. Enjoy traditional music and dance performances.
These events bring the vibrant culture of Alabama to life, and it’s a great way to experience local traditions firsthand.
Show Your State Pride
Wear Alabama colors and gear, decorate your home with the state flag, share fun facts about Alabama with friends, and celebrate the unique aspects of the Heart of Dixie.
It’s all about showing your love for this amazing state.
National Alabama Day FAQs
What unique role did Alabama play in the history of Mardi Gras?
Mobile, Alabama, hosted the first American Mardi Gras in 1703, predating New Orleans’ celebrations. The city continues this tradition with vibrant parades and festivities each year.
Is it true that Alabama was the birthplace of the windshield wiper?
Yes, in 1903, Mary Anderson from Alabama invented the first operational windshield wiper, enhancing driver visibility and safety.
How did Alabama contribute to the development of the 911 emergency system?
In 1968, Haleyville, Alabama, made the first-ever 911 call, pioneering the emergency response system now standard across the U.S.
What is Alabama’s official state dance, and how does it reflect the state’s culture?
The square dance is Alabama’s official state dance, highlighting the state’s rich traditions in folk music and community gatherings.
Did Alabama have a unique method of mail delivery that’s still in use today?
Yes, Magnolia Springs, Alabama, maintains the only year-round water-based mail delivery route in the U.S., with mail delivered by boat since 1915.
What is the significance of the Pine Burr Quilt in Alabama’s history?
The Pine Burr Quilt is Alabama’s official state quilt, recognized for its intricate design and cultural importance in the state’s quilting heritage.
How did Alabama’s constitution set a record?
Alabama’s state constitution, with over 300,000 words and 775 amendments, is the longest in the world, reflecting the state’s complex legal history.
What unique natural feature does Alabama possess regarding its waterways?
Alabama has more navigable waterways than any other U.S. state, totaling over 1,500 miles, which have been vital for transportation and commerce.
How did Alabama’s city of Fort Payne set a world record?
In 1989, Fort Payne built the world’s largest cake to celebrate its centennial, weighing over 128,000 pounds, though this record was later surpassed.
What is the story behind Alabama’s state motto?
Alabama’s state motto, “Audemus jura nostra defendere,” translates to “We dare defend our rights,” reflecting the state’s historical emphasis on sovereignty and self-determination.
Source
#Giant Swallowtail#Alabama#22nd US state#14 December 1819#US history#205th anniversary#insect#animal#original photography#nature#bayou#Bellingrath Gardens and Home#Mirror Lake#tree#flora#fauna#lawn#summer 2009#vacation#travel#road trip#flower#Spanish Moss#tourist attraction#landmark#landscape#National Alabama Day#NationalAlabamaDay#USA
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
it's national poetry month. thank you poems for sometimes saving my life when i need it the most






#poems are#daddy by sylvia plath#catalogue of unabashed gratitude by ross gay#england in 1819 by percy shelley#the orange by wendy cope#hope is the thing with feathers by emily dickinson#mrs midas by carol ann duffy#dark academia#dark academia vibes#dark acadamia aesthetic#poerty#national poetry month#light academia#light acadamia aesthetic#books#book blog#booklr
10 notes
·
View notes
Text









Wolf Hall + Art (2/2) Henry VII, Elizabeth of York, Henry VIII and Jane Seymour Remigius van Leemput | circa 1667 Wolf Hall: The Mirror and The Light | Episode three 'Defiance'
This small painting was copied by the Flemish artist Remigius van Leemput for Charles II from the life-size mural on the wall of the Privy Chamber in Whitehall which was painted by Holbein for Henry VIII in 1537. The wall-painting was destroyed by the fire at Whitehall Palace on 4 January 1698 and this is the only complete record of the mural. Holbein's original preparatory cartoon for the left half of the composition is in the National Portrait Gallery. The first part of the Latin inscription on the plinth in the centre of the composition translates: ‘If it pleases you to see the illustrious images of heroes, look on these: no picture ever bore greater. The great debate, competition and great question is whether father or son is the victor. For both, indeed, were supreme'. The painting appears in Pyne's illustrated 'Royal Residences' of 1819, hanging in The Queen's Closet at Kensington Palace. (source)
#wolf hall#the mirror and the light#wh#periodramaedit#jane seymour#henry viii#art#tudor era#tudorerasource#kate phillips#damian lewis#tudor england#art history#tudor history#dailyflicks#tvgifs#mediagifs#tv shows#tv series#bbc one#bbc drama#by fefa#book adaptation#adaptationsdaily#artwh
566 notes
·
View notes
Text
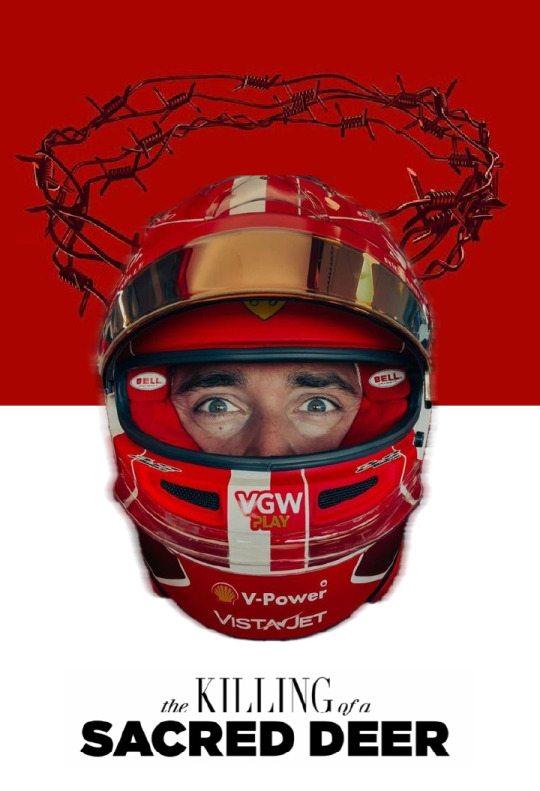














DEER THEORY
WORDS: ‘The Deer’ by Terrance Hayes / ‘I’m Not Calling You a Liar’ (Florence + the Machine) / Aaron O’Hanlon / The Killing of a Sacred Deer (2017) dir. Yorgos Lanthimos / ‘The Stag and the Quiver’ by Richard Siken / mine / ‘Salvage’ by Hedgie Choi / ‘A Letter to My Mother That She Will Never Read’ by Ocean Vuong / ‘Little Deer’ (SPELLLING) / ‘Grendel’ by Roger Reeves / ‘Herd of ‘panicked’ deer filmed jumping to their deaths from motorway’ by Tanveer Mann (Metro UK) / ‘Kinder Than Man’ by Althea Davis / ‘Anecdote of the Pig’ by T. Adkisson / ‘Ferrari Drivers Charles Leclerc and Carlos Sainz Are Racing Back to the Top of F1’ by Tom Lamont (GQ Sports) / Deuteronomy 12:23 / ‘‘It’s a kind of religion’ - Ferrari’s popularity and following in Italy dissected’ by Akshat Kabra (Sportskeeda) / ‘Abstract (Psychopomp)’ (Hozier) / ‘Not Strong Enough’ (boygenius) / The Favourite (2018) dir. Yorgos Lanthimos / Enzo Ferrari / ‘Killer’ (Phoebe Bridgers) / CL for ‘Charles Leclerc talks about his “Red Passion”’ by Roberto Croci (L’Officiel Ibiza) / ‘The fragility of a predestined | FormulaPassion.it’ by admin_l6ma5gus (Pledge Times) / ‘Kinder Than Man’ by Althea Davis / Carmen Maria Machado, In the Dream House / ‘Rabbit Heart (Raise It Up)’ (Florence + the Machine) / ‘Ferrari Needs to Sign Charles Leclerc for the 2018 Formula One Season’ by Gabriel Loewenberg (The Drive) IMAGERY: Styrian GP (2020) / ? (antlers) / ? (crown of thorns) / Scuderia Ferrari Press Office (2023) / @velvetbambi (x) / Saint Maud (2019) dir. Rose Glass / white-tailed buck shedding its antlers (via Deer & Deer Hunting) / Azerbaijan GP (Baku, 2019) / post-French GP (2022) / Jules Bianchi (via F1 TV) / George Shiras III for National Geographic (1906) / ? (young CL) / ‘Driver-Deer Collisions On The Rise: State Farm’ (WSLM RADIO) / Male Red Deer (antlers) / post-Bahrain GP (2019) (CL looking up from hands) / ‘roadkill’ by Loso (via Flickr) (x) / Saturn Devouring His Son (1819-23) Francisco Goya / post-Belgian GP (Spa, 2019) (CL pointing upwards) / The Banshees of Inisherin (2022) dir. Martin McDonagh / Italian GP (Monza, 2020) / Nathan Sandwell @cuchulainn-4 (x) / ? (camcorder) / ‘Deer Caught Gnawing on Human Bones’ by Jason Daley (Smithsonian Magazine) / A Fragment of Ourselves Returning (2018) Beatrice Wanjiku / @nightcorp-archive (x) / Brazilian GP (2023) (CL figure walking) / Singapore GP (2022) / post-Qatar GP (2021) / The Deer Hunter (1978) dir. Michael Cimino / ? (dogmouth doe) / Brazilian GP (2023) / French GP (2022)
265 notes
·
View notes
Text

John Faed (Scottish , 1819-1902) The Evening Hour (The Misses Bennie and Mr J. Noble Bennie), n.d. National Galleries of Scotland
#John Faed#scottish art#scottish#scotland#victorian#regency#brunet#blonde#brunette#1800s#art#fine art#european art#classical art#europe#european#fine arts#oil painting#europa#aristocrat#aristocracy#noble#nobles#the evening hour#The Misses Bennie and Mr J. Noble Bennie#black hair
116 notes
·
View notes
Text

"No class of artists excels the hummingbirds. Their nests are wonders of beauty, delicacy, and architecture-plant down and dried flower petals hold together with silvery spider's web, exquisitely decorated with greyish-white lichens." ~ Royal Dixon, "Feathered Artists," The Human Side of Birds, 1917
Brazilian Hummingbirds
Artist: Martin Johnson Heade (American, 1819-1904)
The American painter Martin Johnson Heade started out as a portraitist and took up landscape painting late in life. He spent three years travelling around Europe during his formative years. This first Grand Tour marked the start of an itinerant lifestyle which he continued to lead throughout his entire existence. From 1840 to 1859 he lived in Philadelphia, New York, Saint Louis, Chicago, Trenton and Providence. His second trip to Europe at the end of the 1840s brought about a shift in his style towards a more sophisticated type of genre painting. He moved to New York about 1859; there he came into contact with other landscape artists such as his lifelong friend Frederic E. Church and began to paint landscapes. Despite exhibiting his work at the National Academy of Design on several occasions, he never became a member and nor was he particularly involved in the New York art scene.
Heade’s mature style, characterised by great precision and luminosity and influenced by the work of Lane, whom he may have known, was later dubbed Luminism. The numerous scenes conveying the calm and splendour of the salt marshes are the compositions that have earned him greater fame. This marshy ground provided Heade with the opportunity to capture changes in the atmosphere and light.
Possibly encouraged by his friend Church, Heade travelled to Central and South America (Brazil, Colombia, Panama and Jamaica) three times between 1860 and 1870. During these trips he painted exotic flowers and birds, in addition to scenery. The combination of these motifs resulted in his original still-life paintings of orchids and hummingbirds in tropical settings, which are acknowledged as the most original part of his oeuvre.
In 1883, at the age of sixty-four, Heade married and moved to Saint Augustine, Florida, where he continued to paint the tropical flowers that grew there. He died there years later, completely forgotten by the art world.
#quotes#hummingbird quotes#hummingbird painting#tropics#hummingbird nest#royal dixon quotes#brazilian hummingbirds#martin johnson heade#luminosity#calm#splendor#artwork#fine art
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
Her name was Julia Chinn, and her role in Richard Mentor Johnson’s life caused a furor when the Kentucky Democrat was chosen as Martin Van Buren’s running mate in 1836.
She was born enslaved and remained that way her entire life, even after she became Richard Mentor Johnson’s “bride.”
Johnson, a Kentucky congressman who eventually became the nation’s ninth vice president in 1837, couldn’t legally marry Julia Chinn. Instead the couple exchanged vows at a local church with a wedding celebration organized by the enslaved people at his family’s plantation in Great Crossing, according to Miriam Biskin, who wrote about Chinn decades ago.
Chinn died nearly four years before Johnson took office. But because of controversy over her, Johnson is the only vice president in American history who failed to receive enough electoral votes to be elected. The Senate voted him into office.
The couple’s story is complicated and fraught, historians say. As an enslaved woman, Chinn could not consent to a relationship, and there’s no record of how she regarded him. Though she wrote to Johnson during his lengthy absences from Kentucky, the letters didn’t survive.
Amrita Chakrabarti Myers, who is working on a book about Chinn, wrote about the hurdles in a blog post for the Association of Black Women Historians.
“While doing my research, I was struck by how Julia had been erased from the history books,” wrote Myers, a history professor at Indiana University. “Nobody knew who she was. The truth is that Julia (and Richard) are both victims of legacies of enslavement, interracial sex, and silence around black women’s histories.”
youtube
Johnson’s life is far better documented.
He was elected as a Democrat to the state legislature in 1802 and to Congress in 1806. The folksy, handsome Kentuckian gained a reputation as a champion of the common man.
Back home in Great Crossing, he fathered a child with a local seamstress, but didn’t marry her when his parents objected, according to the biography “The Life and Times of Colonel Richard M. Johnson of Kentucky.” Then, in about 1811, Johnson, 31, turned to Chinn, 21, who had been enslaved at Blue Spring Plantation since childhood.
Johnson called Chinn “my bride.” His “great pleasure was to sit by the fireplace and listen to Julia as she played on the pianoforte,” Biskin wrote in her account.
The couple soon had two daughters, Imogene and Adaline. Johnson gave his daughters his last name and openly raised them as his children.
Johnson became a national hero during the War of 1812. At the Battle of the Thames in Canada, he led a horseback attack on the British and their Native American allies. He was shot five times but kept fighting. During the battle, the Shawnee chief Tecumseh was killed.
In 1819, “Colonel Dick” was elected to the U.S. Senate. When he was away in Washington for long periods, he left Chinn in charge of the 2,000-acre plantation and told his White employees that they should “act with the same propriety as if I were home.”
Chinn’s status was unique.
While enslaved women wore simple cotton dresses, Chinn’s wardrobe “included fancy dresses that turned heads when Richard hosted parties,” Christina Snyder wrote in her book “Great Crossings: Indians, Settlers & Slaves in the Age of Jackson.”
In 1825, Chinn and Johnson hosted the Marquis de Lafayette during his return to America.
In the mid-1820s, Johnson opened on his plantation the Choctaw Academy, a federally funded boarding school for Native Americans. He hired a local Baptist minister as director. Chinn ran the academy’s medical ward.
“Julia is as good as one half the physicians, where the complaint is not dangerous,” Johnson wrote in a letter. He paid the academy’s director extra to educate their daughters “for a future as free women.”
Johnson tried to advance his daughters in local society, and both would later marry White men. But when he spoke at a local July Fourth celebration, the Lexington Observer reported, prominent White citizens wouldn’t let Adaline sit with them in the pavilion. Johnson sent his daughter to his carriage, rushed through his speech and then angrily drove away.
When Johnson’s father died, he willed ownership of Chinn to his son. He never freed his common-law wife.
“Whatever power Chinn had was dependent on the will and the whims of a White man who legally owned her,” Snyder wrote.
Then, in 1833, Chinn died of cholera. It’s unclear where she is buried.
Johnson went on to even greater national prominence.
In 1836, President Andrew Jackson backed Vice President Martin Van Buren as his successor. At Jackson’s urging, Van Buren — a fancy dresser who had never fought in war — picked war hero Johnson as his running mate. Nobody knew how the Shawnees’ chief was slain in the War of 1812, but Johnson’s campaign slogan was, “Rumpsey, Dumpsey. Johnson Killed Tecumseh.”
Johnson’s relationship with Chinn became a campaign issue. Southern newspapers denounced him as “the great Amalgamationist.” A mocking cartoon showed a distraught Johnson with a hand over his face bewailing “the scurrilous attacks on the Mother of my Children.”

This political cartoon was a racist attack on Johnson because of his relationship with Julia Chinn. (Library of Congress)
Van Buren won the election, but Johnson’s 147 electoral votes were one short of what he needed to be elected. Virginia’s electors refused to vote for him. It was the only time Congress chose a vice president.
When Van Buren ran for reelection in 1840, Democrats declined to nominate Johnson at their Baltimore convention. It is the only time a party didn’t pick any vice-presidential candidate. The spelling-challenged Jackson warned that Johnson would be a “dead wait” on the ticket.
“Old Dick” still ended up being the leading choice and campaigned around the country wearing his trademark red vest. But Van Buren lost to Johnson’s former commanding officer, Gen. William Henry Harrison.
Johnson never remarried, but he reportedly had sexual relationships with other enslaved women who couldn’t consent to them.
The former vice president won a final election to the Kentucky legislature in 1850, but died a short time later at the age of 70.
His brothers laid claim to his estate at the expense of his surviving daughter, Imogene, who was married to a White man named Daniel Pence.
“At some point in the early twentieth century,” Myers wrote, “perhaps because of heightened fears of racism during the Jim Crow era, members of Imogene Johnson Pence’s line, already living as white people, chose to stop telling their children that they were descended from Richard Mentor Johnson … and his black wife. It wasn’t until the late 20th century that younger Pences, by then already in their 40s, 50s, and 60s, began discovering the truth of their heritage.”
#He Became the Nation’s Ninth Vice President. She Was His Enslaved Wife.#enslaved people#Richard Johnson#Julia Chinn#Youtube
230 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gallery Collection 001

Published: 2-21-2024 | Updated: N/A SUMMARY This is the first in a series of upcoming investment objects for Sims 2 – things your sims can use to generate income over time. From 1975-2000, Anheuser-Busch, Inc. commissioned 30 paintings of African kings and queens for an extended outreach and marketing campaign. This set of paintings features artwork from this amazing series. Celebrate Black History Month 2024! #co2bhm #bhm2024 #sims2bhm. *No copyright infringement intended – I own no rights to these images.


DETAILS Requires Sims 2. Requires Apartment Life for shiftability. §1K-15K | Buy > Deco > Wall Hangings Paintings are centered on 1-tile but cover more tiles than that. They come in various gallery sizes and images have been edited to fit the mesh. After purchase, their value increases by approximately 2% daily – watch out for burglars! Files with “MESH” in their name are REQUIRED. Frame recolors include EA/Maxis and yeti textures. Frame and painting recolors are merged into two files so you’ll have to take them or leave them. ITEMS Great Kings & Queens of Africa: Paintings 001-006 (92-764 poly) DOWNLOAD (choose one) from SFS | from MEGA


IMAGES
Akhenaton Pharaoh of Egypt (1375-1358 BC) by Barbara Higgins Bond
Alfonso I King of the Kongo (circa 1486-1543) by Carl Owens (1929-2002)
Askia Muhammaed Toure King of Songhay (1493-1529) by Leo Dillon
Benhanzin Hossu Bowelle—The King Shark (1841-1906) by Thomas Blackshear II
Cleopatra VII Queen of Egypt (69-30 BC) by Ann Marshall
Hannibal Ruler of Carthage (247-183 BC) by Charles Lilly
Hatshepsut The Ablest Queen of Far Antiquity (1503-1482 BC) by Dean Mitchell
Idris Alooma Sultan of Bornu (1580-1617) by Charles Lilly (1949-)
Ja Ja King of the Opobo (1821-1891) by Jonathan Knight
Khama III The Good King of Bechuanaland (1819-1923) by Carl Owens
Makeda Queen of Sheba (960 BC) by Debra Edgerton
Mansa Kankan Musa King of Mali (1306-1337) by Barbara Higgins Bond
Menelek II King of Kings of Abyssinia (1844-1913) by Dow Miller
Moshoeshoe King of Batsutoland (circa 1786-1870) by Jerry Pinkney
Mwana Ngana Ndumba Tembo—Ruler of the Angolan Tchokwe (1840-1880 circa) by Kenneth Calvert
Nandi Queen of Zululand (1778-1826 AD) by HM Rahsaan Fort II
Nefertari Nubian Queen of Egypt (192-1225 BC) by Steve Clay
Nehanda of Zimbabwe (1862-1898) by Lydia Thompson
Nzingha—Amazon Queen of Matambo (1582-1663) by Dorothy Carter
Osei Tutu King of Asante (circa 1650-1717) by Alfred Smith
Queen Amina of Zaria (1588-1589) by Floyd Cooper
Samory Toure The Black Napoleon of the Sudan (1830-1900) by Ezra Tucker
Shaka-King of the Zulus (1787-1828) by Paul Collins
Shamba Bolongongo African King of Peace (1600-1620) by Roy LaGrone
Sunni Ali Beer King of Songhay (circa 1442-1492) by Leo Dillon
Taharqa King of Nubia (710-664 BC) by John Thomas Biggers
Tenkamenin King of Ghana (1037-1075 AD) by Alexander Bostic
Thutmose III Pharaoh of Egypt (753-712 BC) by Antonio Wade
Tiye The Nubian Queen of Egypt (circa 1415-1340 BC) by Leonard Jenkins
Yaa Asantewa Queen of Ghana (1863-1923) by Barbara Higgins Bond CREDITS No copyright infringement intended – I own no rights to these images. Artwork and trademarks are the property of their respective creators and/or owners. If this exceeds fair use, please contact me via private message. Thanks: Simming and Sketchfab Communities. Sources: Any Color You Like (CuriousB, 2010), Beyno (Korn via BBFonts), Console Certificates (d_dgjdhh, 2019; 2011), EA/Maxis, Gyeongbokgung Sajeongjeon Painting (National Heritage Administration, 2024 via CCA; Sketchfab), Great Kings and Queens of Africa Series (Anheuser-Busch, Inc., 1975-2000; Kentake, 2016), Offuturistic Infographic (Freepik), Painting by Zdzislaw Beksinski (Sosnowski, 2018 via CCA), Yeti Metals (Shastakiss, 2017).
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
Below are 10 articles from Wikipedia's featured articles list. Links and descriptions are below the cut.
On Saturday, May 1, 1920, the Brooklyn Dodgers and the Boston Braves played to a 1–1 tie in 26 innings, the most innings ever played in a single game in the history of Major League Baseball. Both Leon Cadore of Brooklyn and Joe Oeschger of Boston pitched complete games, and with 26 innings pitched, jointly hold the record for the longest pitching appearance in MLB history.
Clarence 13X, also known as Allah the Father (born Clarence Edward Smith) (February 22, 1928 – June 13, 1969), was an American religious leader and the founder of the Five-Percent Nation, sometimes referred to as the Nation of Gods and Earths.
Henry Edwards (27 August 1827 – 9 June 1891) was an English stage actor, writer and entomologist who gained fame in Australia, San Francisco and New York City for his theatre work.
The law school of Berytus (also known as the law school of Beirut) was a center for the study of Roman law in classical antiquity located in Berytus (modern-day Beirut, Lebanon). It flourished under the patronage of the Roman emperors and functioned as the Roman Empire's preeminent center of jurisprudence until its destruction in AD 551.
Minnie Pwerle (also Minnie Purla or Minnie Motorcar Apwerl; born between 1910 and 1922 – 18 March 2006) was an Australian Aboriginal artist. Minnie began painting in 2000 at about the age of 80, and her pictures soon became popular and sought-after works of contemporary Indigenous Australian art.
Ove Jørgensen (Danish pronunciation: [ˈoːvə ˈjœˀnsən]; 5 September 1877 – 31 October 1950) was a Danish scholar of classics, literature and ballet. He formulated Jørgensen's law, which describes the narrative conventions used in Homeric poetry when relating the actions of the gods.
Legends featuring pig-faced women originated roughly simultaneously in The Netherlands, England and France in the late 1630s. The stories tell of a wealthy woman whose body is of normal human appearance, but whose face is that of a pig.
The Private Case is a collection of erotica and pornography held initially by the British Museum and then, from 1973, by the British Library. The collection began between 1836 and 1870 and grew from the receipt of books from legal deposit, from the acquisition of bequests and, in some cases, from requests made to the police following their seizures of obscene material.
Qalaherriaq (Inuktun pronunciation: [qalahəχːiɑq], c. 1834 – June 14, 1856), baptized as Erasmus Augustine Kallihirua, was an Inughuit hunter from Cape York, Greenland. He was recruited in 1850 as an interpreter by the crew of the British survey barque HMS Assistance during the search for John Franklin's lost Arctic expedition.
Sophie Blanchard (French pronunciation: [sɔfi blɑ̃ʃaʁ]; 25 March 1778 – 6 July 1819), commonly referred to as Madame Blanchard, was a French aeronaut and the wife of ballooning pioneer Jean-Pierre Blanchard. Blanchard was the first woman to work as a professional balloonist, and after her husband's death she continued ballooning, making more than 60 ascents.
#Wikipedia polls#people said they liked the summaries-first format but it got fewer votes in total so i think I'll stick with summaries-after-the-cut#i would recommend checking out the readmore before you vote though. or don't I'm not your boss
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
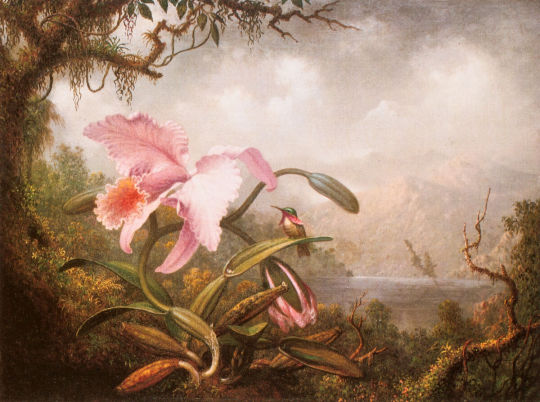

Happy National Orchid Day!
Orchid and hummingbird Heade, Martin Johnson, 1819-1904, American ca.1885 Oil on canvas 15 x 20 1/8"
Repository: Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco, San Francisco, San Francisco, California, United States HOLLIS Number: olvwork199203
This image is part of FAL’s Digital Images and Slides Collection (DISC), a collection of images digitized from secondary sources for use in teaching and learning. FAL does not own the original artworks represented in this collection, but you can find more information��at HOLLIS Images.
#NationalOrchidDay#Orchid#Painting#HarvardFineArtsLibrary#FineArtsLibrary#Harvard#HarvardLibrary#DigitalImages
65 notes
·
View notes
Text

LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
November 29, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Nov 30, 2024
In 2008, Congress passed and President George W. Bush signed into law an act making the day after Thanksgiving National Native American Heritage Day.
About a month ago, on Friday, October 25, President Joe Biden became the first president to visit Indian Country in ten years when he traveled to the Gila River Indian Community in Maricopa County, Arizona, near Phoenix. Secretary of the Interior Deb Haaland traveled with him. The trip was designed to highlight the investments the Biden-Harris administration has made in Tribal Nations.
At a press gaggle on Air Force One on the way to Arizona, White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre noted that under Biden, Tribal Nations have seen the largest direct federal investment in history: $32 billion from the American Rescue Plan and $13 billion through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to build roads and bridges, bring clean water and sanitation, and build high-speed Internet in Tribal communities.
Jean-Pierre added that First Lady Jill Biden has also championed Native communities, visiting them ten times to highlight investments in youth mental health, the revitalization of Native languages, and to improve access to cancer screening and cancer care in Native communities.
Secretary Haaland, herself a member of the Pueblo of Laguna, agreed that the Biden-Harris administration has brought “transformational change” to Native communities: “electricity on the Hopi Reservation in Arizona for homes that have never had electricity; protecting cultural resources, like salmon, which Pacific Northwest Tribes have depended on for thousands of years; new transportation infrastructure for the Mescalero Apache Nation in New Mexico that will provide a safer travel route and boost their economic development, their local economy; addressing toxic legacy pollution and abandoned oil and gas infrastructure that pollutes our air and water for the Osage Nation in Oklahoma; providing clean drinking water for Fort Peck in Montana.”
“Tribal leaders are experiencing a new era,” Haaland added. “They’re at the table. They’re being consulted.”
When Biden spoke at the Gila Crossing Community School, he said he was there “to right a wrong, to chart a new path toward a better future for us all.” As president of the United States, Biden formally apologized to the Native peoples—Native Americans, Native Hawaiians, Native Alaskans—for the U.S. government policy that forced Native children into federal Indian boarding schools.
The apology comes after the release of an Interior Department study, The Federal Boarding School Initiative, that Secretary Haaland directed the department to undertake in 2021. According to Assistant Secretary of the Interior Bryan Newland, a citizen and former president of the Bay Mills Indian Community (Ojibwe), the initiative was “a comprehensive effort to recognize the troubled legacy of Federal Indian boarding school policies with the goal of addressing their intergenerational impact and to shed light on the traumas of the past.”
The initiative set out to identify federal Indian boarding schools and sites, to identify the children who attended those schools and to identify their Tribal identities, to find marked and unmarked burial sites of the remains of Indian children near school facilities, and to incorporate the viewpoints of those who attended federal Indian boarding schools and their descendants into the story of those schools.
The report looked at the Indian education system from 1819 to 1969 as a whole, bringing together federal funding for religious schools in the early 1800s with later explicitly federal schools and their public school successors during and after the 1930s. But historians generally focus on the period from 1879 to the 1930s as the boarding school era.
In 1879, the government opened the Carlisle Indian Industrial School, a boarding school for American Indian children in Carlisle, Pennsylvania, explicitly designed to separate children from their families and their culture and to train them for menial jobs.
The boarding school era was the brainchild of Army officer Richard Henry Pratt, a Civil War veteran who, in the years after the war, commanded the 10th United States Cavalry, a Black regiment stationed in the American West whose members Indigenous Americans nicknamed the “Buffalo Soldiers.” Pratt fought in the campaigns on the Plains from 1868 through 1875, when he was assigned to oversee 72 Cheyenne, Kiowa, Comanche, Arapaho, and Caddo prisoners of war at Fort Marion in St. Augustine, Florida (now known as the Castillo de San Marcos National Monument).
Many Indigenous prisoners at Fort Marion, taken from the dry Plains to the hot and humid coast of Florida where they were imprisoned in a cramped stone fort, quickly sickened and died. Pratt worked to upgrade conditions and to assimilate prisoners into U.S. systems by teaching them English, U.S. culture, Christianity, and how the American economy worked. He cut their hair, dressed them in military-type uniforms, and urged them to make art for sale to local tourists—it’s from here we get the world-famous collection of ledger art by the artists of Fort Marion—but focused on turning the former warriors and their families into menial workers.
After the Battle of the Little Bighorn in 1876 and the subsequent pursuit and surrender of leading Lakota bands throughout that year and the next, leading to the murder of Crazy Horse in 1877, popular opinion ran heavily toward simply corralling Indigenous Americans on reservations and waiting either for their assimilation or extermination. At the same time, with what seemed to be the end of the most serious of the Plains Wars, Army officers like Pratt had reason to worry that the downsizing of the U.S. Army would mean the end of their careers.
Indigenous survivors of Fort Marion returned home to see that the American government had no real plans for a thriving American Indian populace. There was little infrastructure to link them to the rest of the country to sell their art, and Indian agents rejected tribal members for jobs in favor of white cronies.
But Pratt considered his experiment at Fort Marion a great success, and he came to believe he could make his system work even more thoroughly by using a loophole in the treaties between Plains Tribes and the U.S. government to force Indigenous Americans to assimilate as children. He planned, he said, to “Kill the Indian and save the man.”
Treaties between Plains Indian Tribes and the government required the U.S. government to educate American Indian children—something their parents cared deeply about—but the treaties didn’t actually specify where the schools would be. So Pratt convinced the U.S. Army and officials at the Interior Department to give him the use of the Carlisle Barracks to open an industrial school, designed to teach American Indian children the skills necessary to be servants and menial workers.
In summer 1879, Pratt traveled to western reservations of the Lakotas and Dakotas, primarily, to gather up 82 children to begin his experiment in annihilating their culture from their minds. He forbade the practice of any aspect of Indigenous culture—language, religion, custom, clothing—and forced children to change their names, use English, practice Christianity, and wear clothing that mirrored that of Euro-American children.
Crowded together, many children died of disease; bereft of their family and culture, many died of heartache. Some found their newfound language and lessons tolerable, others ran away. For the next fifty years, the Carlisle model was the central model of government education for Indigenous children, with tens of thousands of children educated according to its methods.
In the 1920s the Institute for Government Research, later renamed the Brookings Institution, commissioned a study funded by the Rockefeller Institute—to make sure it would not reflect government bias—to investigate conditions among Indigenous Americans.
In 1928 that study, called the Meriam Report, condemned the conditions under which American Indians lived. It also emphasized the “deplorable health conditions” at the boarding schools, condemned the schools’ inappropriate focus on menial skills, and asserted that “[t]he most fundamental need in Indian education is a change in point of view.” In 1934 the Indian Reorganization Act reversed the policy of trying to eradicate Tribal cultures through boarding children away from their families, and introduced the teaching of Indian history and culture in federal schools.
But the boarding schools remain a central part of the experience of American Indians since the establishment of the U.S. government in North America, and the Federal Boarding School Initiative recommended that “[t]he U.S. Government should issue a formal acknowledgment of its role in adopting a national policy of forced assimilation of Indian children, and carrying out this policy through the removal and confinement of Indian children from their families and Indian Tribes and the Native Hawaiian Community and placement in the Federal Indian boarding school system.”
It continued: "The United States should accompany this acknowledgment with a formal apology to the individuals, families, and Indian Tribes that were harmed by U.S. policy."
On October 25, 2024, President Joe Biden delivered that apology.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Heather Cox Richardson#Letters From An American#American History#native Americans#American Indians#Federal Boarding School Initiative#Indian Children#Indian Reorganization Act#American Heritage Day
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Singapore’s prosperity has long set it apart from many other former British colonies. There is another difference, too: Singapore has clung to honouring its former colonial ruler — and it wants to keep doing so.
Special accolade has gone to Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles, who is considered to have founded modern Singapore in the early 1800s. For decades, Singapore’s textbooks credited Raffles with transforming the island from a “sleepy fishing village” into a thriving seaport. He has been the central character in a larger official narrative that says imperial Britain had set up Singapore for success as an independent nation.
Dedications to Raffles dot the landscape of Singapore. A business district, schools and dozens of other buildings bear his name. Two 2.5-metre likenesses of the man loom large in downtown Singapore.
But a new statue of Raffles, installed in a park in May, has revived a debate about the legacy of colonialism in Singapore. On one side is the broader establishment, which has held up British colonial rule positively. On the other are those who want a closer inspection of the empire that Raffles represented and the racial inequity he left behind, even as Singapore became wealthy.
This divide has surfaced before, perhaps most prominently a few years ago when Singapore celebrated the bicentennial of Raffles’ arrival on the island. Now, the new statue has set off a fresh debate, with critics pointing out that other countries have for years been taking down monuments to historical figures associated with slavery or imperialism, or both.
“The thing about Raffles is that, unfortunately I think, it has been delivered as a hagiography rather than just history,” said Alfian Sa’at, a playwright who wants to see the Raffles statues destroyed. “It’s so strange — the idea that one would defend colonial practice. It goes against the grain on what’s happening in many parts of the world.”
The new statue of Raffles stands next to one of his friend Nathaniel Wallich, a Danish botanist, at Fort Canning Park. Tan Kee Wee, an economist who pooled $330,000 with his siblings to commission the statues, said he wanted to commemorate the pair’s role in founding Singapore’s first botanic gardens, which were his frequent childhood haunt. He donated the sculptures in his parents’ name to the National Parks Board.
Opponents have also criticised the government for allowing the statue to go up at the park because it was the site of the tomb of precolonial Malay kings. The parks board said it considered historical relevance in the installation of the sculptures.
Questions about the statue have even been raised in Singapore’s parliament. In June, Desmond Lee, the minister for national development, responded to one by saying that Singapore did not glorify its colonial history. At the same time, Lee added, “We need not be afraid of the past.”
The plaque for the Raffles statue explains how Singapore’s first botanic gardens “cultivated plants of economic importance, particularly spices”. That, critics said, was a euphemism for their actual purpose: cash crops for the British Empire.
Tan defended the legacy of British colonialists in Singapore, saying they “didn’t come and kill Singaporeans”.
He added: “Singapore was treated well by the British. So why all this bitterness?”
Far from benign
But colonial Britain was far from benign. For instance, it treated nonwhite residents of Singapore as second-class citizens. Raffles created a town plan for Singapore that segregated people into different racial enclaves. And he did not interact with the locals, said Kwa Chong Guan, a historian.
“He was very much a corporate company man, just concerned with what he assumed to be the English East India Co’s interests,” Kwa said.
Raffles landed in Singapore in 1819 as Britain was looking to compete with the Dutch in the Malacca Strait, a crucial waterway to China. At the time, Singapore was under the sway of the kingdom of Johor in present-day Malaysia. Raffles exploited a succession dispute in Johor to secure a treaty that allowed the East India Company to set up a trading post in Singapore.
Within a handful of years, Singapore was officially a British territory. Convict labour, largely from the Indian subcontinent, was crucial to its economic development. So, too, were Chinese immigrants, which included wealthy traders and poor labourers.
Singapore achieved self-governance in 1959, then briefly joined Malaysia before becoming an independent republic in 1965. It has since built one of the world’s most open economies and among its busiest ports, as well as a bustling regional financial hub.
In recent years, the government has acknowledged, in small ways, the need to expand the narrative of Singapore’s founding beyond Raffles. Its textbooks now reflect that the island was a thriving centre of regional trade for hundreds of years before Raffles arrived.
In 2019, officials cast the commemoration of Raffles’ arrival as also a celebration of others who built Singapore. A Raffles statue was painted over as if to disappear into the backdrop. Placed next to it, though only for the duration of the event, were four other sculptures of early settlers, including that of Sang Nila Utama, a Malay prince who founded what was called Singapura in 1299.
To some historians and intellectuals, such gestures are merely symbolic and ignore the reckoning Singapore needs to have with its colonial past. British rule introduced racist stereotypes about nonwhites, such as that of the “lazy” Malay, an Indigenous group in Singapore, that has had a lasting effect on public attitudes. Colonialism led to racial divisions that, in many ways, persist to this day in the city-state that is now dominated by ethnic Chinese.
“If you only focus on one man and the so-called benevolent aspect of colonialism, and you don’t try to associate or think about the negative part too much, isn’t that a kind of blindness, or deliberate amnesia?” said Sai Siew Min, an independent historian. (Story continues below)
Role of race
Race relations played a role in Raffles’ ascension in Singaporean lore. Soon after Singapore became independent, the governing People’s Action Party — which remains in power decades later — decided to officially declare Raffles the founder of Singapore. Years later, S Rajaratnam, who was then the foreign minister, said that anointing a Malay, Chinese or Indian as its founder would have been fraught.
“So we put up an Englishman — a neutral, so there will be no dissension,” Rajaratnam said.
The decision was also meant to indicate that Singapore remained open to the West and free markets.
In a 1983 speech, Rajaratnam acknowledged that Raffles’ attitude toward the “nonwhite races was that without British overlordship the natives would not amount to much”.
Critics of the Raffles statues also argue that his legacy should reflect his time on the island of Java. Although Raffles outlawed slavery in Singapore, he allowed trading of slaves in Java, including children as young as 13, according to Tim Hannigan, who wrote a book about Raffles.
The new statues of Raffles and Wallich were created by Andrew Lacey, a British artist. The sculptures evoke the two men as apparitions — symbolism that Lacey said represented the world’s evolution away from the West.
Lacey said he had “wrangled” with the public reaction toward his sculptures and he had no qualms if Singaporeans wanted to take them down, destroy them or replace their heads with the Malay gardeners who were instrumental in creating the botanic gardens.
“I was cognisant of the complexities of making any dead white male,” he said of Raffles. “I wasn’t cognisant of the degree of complexity around him.”
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
The elections aren't even recognized by Europian countries but these traitors of a government are already pushing censorship.
Changes made to the Georgian national exam history program:
Previously, a topic in the program had the following wording: “Uprisings in Georgia against Tsarism” and the Georgian uprisings of 1802, 1804, 1812, 1819-1820, and 1932 against the Russian Empire were included in it.
“The Conquest of Georgia by Russia” is now the only thing written in the program. Only the 1932 uprising is listed.
This formulation, “the conquest of Georgia by Russia,” refers to the history of the conquest and abolition of the Georgian kingdoms and principalities by Russia, which are the gradual events of the years 1802-1867.
The authors of the program have singled out and left only the 1932 uprising. 1802, 1804, 1812, 1819-1820 are not mentioned.
They have also removed many very famous works of patriotic authors and poets from Georgian language national exam.
These were taught even during Stalin. They're trying to bring back censorship last seen during Tsarist rule.
#georgia#saqartvelo#georgia 🇬🇪#🇬🇪#russia is a terrorist state#russia is the occupier#slava ukraini#საქართველ���
11 notes
·
View notes
Text







On November 29th 1813 a campaign was launched in Dumfries to raise public subscriptions to fund a mausoleum for the poet Robert Burns.
The first attempt to have a memorial erected to Burns was made as far back as 1812, by John Forbes Mitchell of Bombay, and it is ironic that the first expression of a national, as opposed to a local, nature, should have come from overseas. Although Mitchell eventually collected a large sum of money for this purpose, it was not until he returned to Britain in 1819 that he could take practical steps to implement his proposals. In the meantime, plans for monuments to Burns had been maturing elsewhere.
In 1813, John Syme, who had been a close friend of Burns, campaigned to raise funds for the Mausoleum. The structure was designed by Thomas Frederick Hunt while sculptor Peter Turnerelli created the scene in marble of Burns at the plough contained inside.
On 19th September 1815 the poet`s remains were exhumed and re interred in the mausoleum. The service was attended by his wife Jean Armour, who had been unable to attend the original service as she was giving birth to Burns` son.
It was actually built by a local stonemason named John Milligan at a cost of just over £300. Though the structure was completed in 1817 Burns' body was moved to its new home in 1815 while the mausoleum was being built.Burns' wife Jean Armour was interred beside her husband in 1834. At this time a plaster cast was made of Burns' skull. Also buried in the mausoleum is the couple's son Maxwell Burns, who died in 1799 at just 2 years and 9 months old, and Francis Burns, another son who died in 1803 at 14 years old.
The mausoleum takes the form of a neoclassical rotunda with pairs of Ionic columns supporting an octagonal drum with a dome at the top. Within the mausoleum is a group of sculptures by Peter Turnerelli.
The sculptures show the ancient Muse 'Colla', a representation of the Ayrshire region of Kyle where Burns was born, throwing her mantle over Burns while he ploughs a farm field. The cloak is a mantle of inspiration, a reflection of how Burns' life early life in Ayrshire inspired his poetry. Colla's mantle of inspiration summons Burns the ploughman to become Burns the poet.
The original sculptures were replaced by copies sculpted by Hermon Cawthra in 1936. They were installed as part of an effort to restore the mausoleum and were unveiled by Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald.
The mausoleum is made of local red sandstone. Around 1880 the structure was painted bright white, with the dome a pale green. The base of the mausoleum is open on three sides, but each of these sides is now protected by an iron gate so that you can see within but cannot actually enter the building.During the 19th century the Dumfries Burns Club began a custom of laying a wreath at the mausoleum on Burns' birthday (25th January) and the custom continues to this day.
The Burns Mausoleum is listed Grade A for its heritage value.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
SET SIXTEEN FINAL - ROUND FOUR


"Unfinished Painting" (1989 - Keith Haring) / "Saturn Devouring His Son" (c. 1819–1823 - Francisco Goya)
UNFINISHED PAINTING: A self-portrait left intentionally "incomplete". I'm roughly the same age as Haring was when AIDS ended his life and I can only begin to imagine how it must feel to know that your life has been cut short a third of the way through. I get such a lump in my throat each time I look at this. (louisianna)
SATURN DEVOURING HIS SON: This painting already gave me the heebie jeebies a bit but I got the chance to see it in person a while back and WOW. I was just filled with such deep dread and discomfort standing in the gallery, like there was just a gaping hole in my gut. The detail that really was the cherry on top of the experience is honestly how goopy his eyes are. You feel like he's staring right at your soul to be honest. Beyond terrifying (100000/10 would recommend) (broke-on-books)
("Unfinished Painting" is an acrylic on canvas painting by Keith Haring. It measures 39 x 39 in (99 x 99 cm) and is located in National Portrait Gallery, in Washington DC. This was Haring’s last painting and it was intentionally left incomplete.
"Saturn Devouring His Son" is a 1819-23 mixed media mural transferred to canvas (originally painted on the wall of his dining room) by Spanish artist Francisco Goya during one of the darkest periods of his life. It measures 143.5 cm × 81.4 cm (56.5 in × 32.0 in) and is displayed at the Museo del Prado in Madrid.)
#art that fucks you up tournament#polls#atfyu polls#id in alt text#cw eye contact#cw nudity#cw blood#cw gore
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
National personification
The UK has Britannia. France has Marianne. The US have Uncle Sam. National personifications, summing up supposed collective qualities and passing on a message, both to citizens and foreigners alike. Instantly recognizable by just about anyone. To be found everywhere, from city halls (busts, frescoes, tapestries) to subway walls (Army conscription posters - of course it rings a bell!).
Romania has this:

This is Revolutionary Romania, as seen by C.D. Rosenthal, an Austrian painter who found both friendship and an avid clientele among the Romanian young rebels who tried and failed to overthrow the corrupted Ottoman rule, in 1848. Following them in exile and probably also spying on their behalf, Rosenthal was finally arrested in Budapest and tortured to death by the Imperial authorities: a normal occurrence in troubled times. His memory went on and on and on, because the same friends were soon to come back home and become ministers, bankers, newspaper owners: a modern democracy slowly emerged.
This is his most famous portrait and it quickly became our Britannia of sorts. Ceaușescu had it placed in his office, for inspiration - it did not help much, though.
The woman painted by Rosenthal holds the red, yellow and blue flag and is dressed in a Southern peasant costume, as it was worn at the time. She gazes with strength, determination and confidence towards a future that spells free press, parliamentary elections, industrialization and capitalist speculation. In real life, she is Maria Rosetti, a personal friend and sponsor of his. The wife of C.A. Rosetti, an authentic Prince of Genoese and Greek stock, one of the leaders of both the rebellion and the future Liberal Party. Also a many times removed relative of this blogger - but let's not insist. 😉
There is a catch, however, in all this fine and dandy story. Our national personification, the woman I just mentioned, is Scottish. Her life begins in Guernsey in 1819, as Marie Grant, the daughter of Captain Edward Grant, a ship-owner businessman and member of the Clan Grant of Carron and Spey and Marie La Lacheur, a French Huguenot woman.
These people, who fought as Jacobites at Prestonpans and Culloden and whose motto was 'Stand Fast':


Marie came to Wallachia, or what is now the Southern part of Romania, around 1837, following her younger brother, Effingham Grant, who just managed to find a lucrative job as the private secretary of another Scot (Glaswegian, even), Robert Gilmour Colquhoun, the newly appointed British Consul-General. At the time, these were long term postings, not unlike a long sojourn on a space station of sorts: Colquhoun remained in Bucharest from 1835 to 1854, when he eventually was posted to Bosnia.
Because she needed to support herself, Marie found a well paid live-in job as a governess for the family of Ion Odobescu, a high ranking Police honcho (also a far removed relative, this time on my maternal grandmother's side - the world is really, really small). The rest was easy enough: having met Rosetti through her brother, they fell in love, eloped to Plymouth and got married there, for what was to become a life long equal political and business partnership. Because they owned several newspapers, she is our first female journalist. A truly remarkable woman, a philanthropist and an indispensable voice advocating for the dispossessed. Effingham went on to establish the biggest foundry in the country, along with a real estate company, a tobacco manufacture, an orchid greenhouse and a bread factory - all prospered beyond any expectations. A heavy traffic steel bridge in Bucharest still bears his name. Enduring legacies.
For those brave enough or bored enough to look for more, here is the best detailed account on her I could find, based on Guernsey sources (but not only): https://www.priaulxlibrary.co.uk/node/386 .
36 notes
·
View notes