#15 April 1865
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
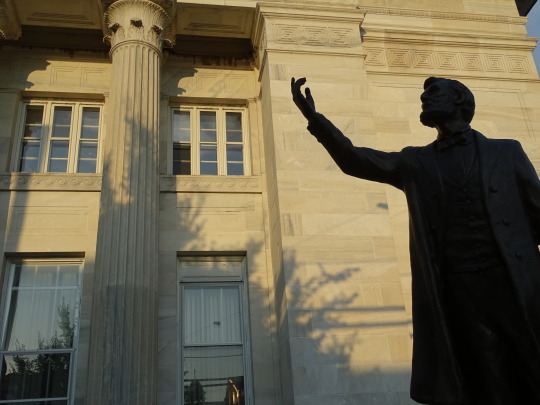
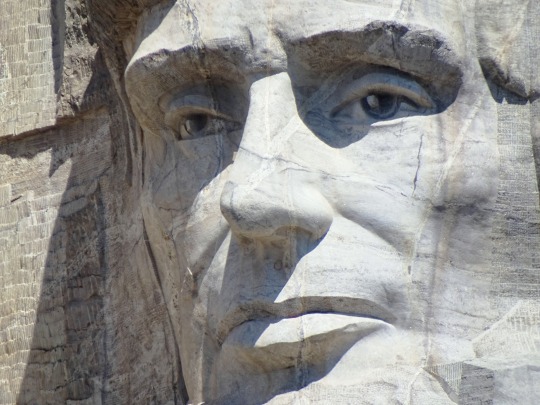
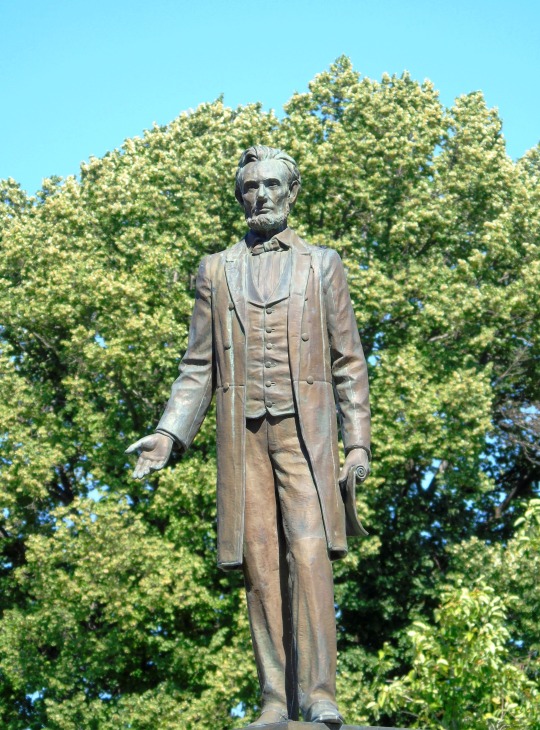
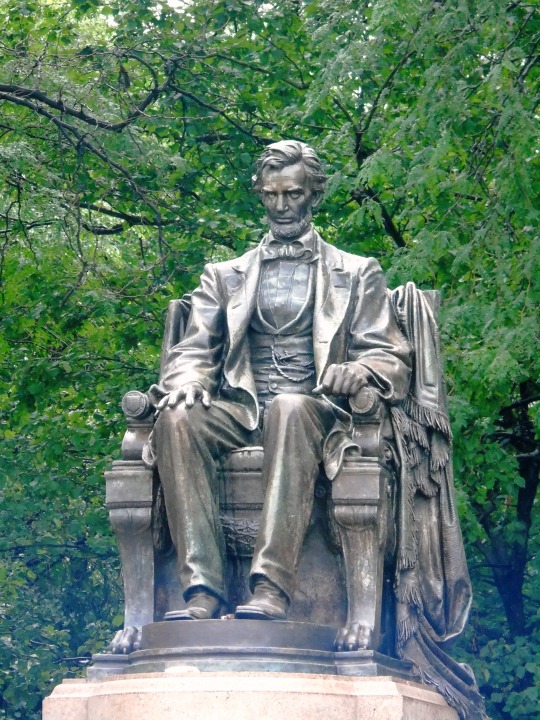
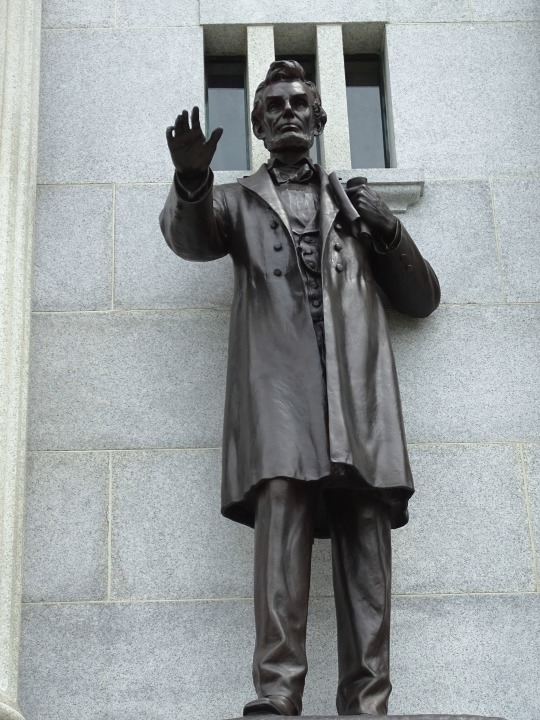













President Abraham Lincoln died on April 15, 1865 after being shot the previous evening by actor John Wilkes Booth.
#Robert Russin#Mount Rushmore National Memorial#Gutzon Borglum#USA#J. Otto Schweizer#Gettysburg National Military Park#Henry K. Bush-Brown#Stanley J. Watts#Abraham Lincoln#died#death#15 April 1865#US history#anniversary#original photography#sculpture#tourist attraction#summer 2019#travel#vacation#Daniel Chester French#landmark#architecture#cityscape
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Fyodor Dostoevsky at Abraham Lincolns assassination, April 15, 1865!
403 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Crimson Peak Timeline
(based on the art book, documents shown onscreen in the movie, and the character bios GDT wrote- where the bios don't contradict film canon. I've attempted to combine the two where contradicting elements are unavoidable.
Sometime during the reign of Charles II (1660-1685). Edward Sharpe created Baronet for services to the crown in providing clay for construction projects. Allerdale Hall built in the parish of Above Derwent, Cumberland, England.
1841. Carter Everett Cushing born the second son of six in an impoverished family that traveled the eastern US for his father's masonry business.
1863. Beatrice Alexandra Chetwynde, eldest daughter of a large, wealthy family, marries Baronet James William Sharpe. The marriage is contracted solely for the Chetwyndes' land, which adjoins the Sharpe estate.
April 1, 1865. Lucille Sharpe born.
Sometime between 1865 and ~1873. Carter marries 18-year-old socialite Eleanor Wyndham-Beckford, to the immense disapproval of her family. Though she is disowned and the couple struggles to make ends meet for years, Carter ultimately becomes a successful developer.
February 18, 1867. Thomas Sharpe born.
C. 1867-1872. The Sharpes employ a wet nurse- and later nanny -named Theresa, who would become the only adult to care about the children in their lives. She would ultimately be sacked after Beatrice caught young Lucille snuggling with her for warmth on a winter's night (on the grounds that a noble child should not be close with servants- a "crime" for which Lucille was beaten severely).
1876. 11-year-old Lucille murders her father with poison distilled from mine tailings, after he took Thomas on a hunting trip and left him in the woods to die of exposure.
Late 1876? A mining vein near Allerdale Hall collapses, killing several child mine-workers. I could have sworn I read somewhere that James foolishly dug a mining tunnel under the house shortly before his death, and that's what destabilized it, but I can't find it now.
October 9, 1877. Edith M. Cushing born, after Eleanor had suffered several miscarriages.
1878. Thomas and Lucille begin a secret sexual relationship.
Early August, 1879. Beatrice catches Lucille and Thomas together; Lucille murders her to keep their secret. The siblings try to run away together but are caught and brought back. Thomas is sent to live with an aunt and uncle in Whitehaven (who in turn send him to boarding school), while Lucille is forced into a mental institution.
Probably summer, 1885. Thomas finishes his schooling and rescues Lucille; they return to Allerdale.
1887. The Sharpe siblings travel to London seeking investors for Thomas' venture to reopen the mines. A wealthy, terminally ill gentleman, Major Richard Upton, takes a liking to Thomas and begs Thomas to marry his disabled daughter, Pamela. At Lucille's urging- since they're running out of both options and money -Thomas agrees. The two attempt to poison Pamela to death, but Lucille ends up strangling her instead.
Sometime between October 1887 and October 1888. Eleanor Cushing dies of cholera and appears to Edith as a ghost.
Early-mid 1890s. Carter and the recently widowed Mrs. McMichael have a brief flirtation that both Edith and Eunice oppose. Though it goes nowhere, the rift between the two girls is never healed.
Late October or November 1892. Edith (age 15) becomes infatuated with a 25-year-old poet who is having marital difficulties. After convincing Carter to hire him as a tutor, all unknowing, she confesses her feelings to him. He not only takes his leave of the Cushing family, but of Buffalo itself, quickly moving away with his wife and children.
1893. The Sharpes travel to Edinbrugh, where Thomas again finds no investors but does attract the attention of a 36-year-old widow of means, Margaret McDermott. Once again, he marries her and helps Lucille poison her, though she is ultimately killed via blunt force trauma.
Summer 1893. Edith asks her best friend, Alan McMichael, to kiss her so she can write about kisses more accurately. It means nothing to her, but sparks an unrequited passion in Alan
1896. Lucille falls pregnant by Thomas. He travels with her to Italy, which he loves and she despises. There he meets a wealthy woman named Enola Sciotti, widowed and bereaved of her only child, and decides of his own accord to marry and murder her in their usual fashion. The Sharpes and Enola return to Allerdale.
1897. Lucille is delivered of a son, who may or may not be sickly. Enola tries to care for her and the child, promising she can save him. The baby either dies of natural causes or Lucille smothers him under the conviction that his cries mean something is terribly wrong with him and he can't live- this is one contradiction in the bios vs. the movie that I prefer to leave vague, since it's possible not even Lucille remembers what happened. Either way, she blames Enola and dispatches her by unknown means. Thomas patents his excavating machine.
Late summer(?) 1901. Alan returns from studying medicine in London and sets up an ophthalmology practice in Buffalo. Edith's debut novel, Figures In The Mist, is rejected for publication by Oglivie and Sons. Thomas seeks investment in the mines from Cushing and Co., unsuccessfully. Edith and the Sharpes begin a friendship. Edith sees her mother's ghost for the second time.
September 14, 1901. President William McKinley dies after being shot at the Pan-American Exposition in Buffalo. I include this because the fact that the movie doesn't is hilarious to me.
October 21, 1901. At the Cushings' dinner party, Carter bribes the Sharpes to leave, instructing Thomas to break Edith's heart or he'll tell her about the marriage to Pamela. A deleted scene reveals that he was on the verge of relenting and investing in the mines when he read the private investigator's report.
October 22, 1901. Lucille murders Carter at his club, then departs to return to England. Thomas and Edith become engaged.
Late October-early November 1901. Thomas and Edith are married and travel to Allerdale.
November-December 1901 (possibly into early 1902?). The rest of the movie's plot.
71 notes
·
View notes
Note
Was Trump's assassination attempt the first time people other than the president were also killed or hurt?
No, it definitely was not the first time. There have been a number of additional victims during Presidential assassinations or assassination attempts throughout American history.
Here are the incidents where someone other than the President was wounded in an assassination attempt on Presidents or Presidential candidates:
•April 14, 1865, Washington, D.C. At the same time that John Wilkes Booth was shooting Abraham Lincoln at Ford's Theatre, Booth's fellow conspirator, Lewis Powell, attacked Secretary of State William H. Seward at Seward's home in Washington. Seward had been injured earlier that month in a carriage accident and was bedridden from his injuries, and Powell viciously stabbed the Secretary of State after forcing his way into Seward's home by pretending to deliver medicine. Powell also attacked two of Seward's sons, a male nurse from the Army who was helping to care for Seward, and a messenger from the State Department. Another Booth conspirator, George Azterodt, was supposed to kill Vice President Andrew Johnson at the same time that Lincoln and Seward were being attacked in an attempt to decapitate the senior leadership of the Union government, but Azterodt lost his nerve and got drunk instead. A total of five people were wounded at the Seward home as part of the Booth conspiracy, but Lincoln was the only person who was killed.
•February 15, 1933, Miami, Florida Just 17 days before his first inauguration, President-elect Franklin D. Roosevelt was the target of an assassination attempt in Miami's Bayfront Park. Giuseppe Zangara fired five shots at Roosevelt as FDR was speaking from an open car. Roosevelt was not injured, but all five bullets hit people in the crowd, including Chicago Mayor Anton Cermak who was in the car with FDR. Roosevelt may have been saved by a woman in the crowd who hit Zangara's arm with her purse as she noticed he was aiming his gun at the President-elect and caused him to shoot wildly. Mayor Cermak was gravely wounded and immediately rushed to a Miami hospital where he died about two weeks later.
•November 1, 1950, Blair House, Washington, D.C. From 1949-1952, the White House was being extensively renovated with the interior being almost completely gutted and reconstructed. President Harry S. Truman and his family moved into Blair House, a Presidential guest house across the street from the White House that is normally used for visiting VIPs, for 3 1/2 years. On November 1, 1950 two Puerto Rican nationalists, Griselio Torresola and Oscar Collazo, tried to shoot their way into Blair House and attempt to kill President Truman, who was upstairs (reportedly napping) at the time. A wild shootout ensued on Pennsylvania Avenue, leaving White House Police Officer Leslie Coffelt and Torresola dead, and Collazo and two other White House Police Officers wounded.
•November 22, 1963, Dallas, Texas Texas Governor John Connally was severely wounded after being shot while riding in the open limousine with President John F. Kennedy when JFK was assassinated.
•June 5, 1968, Ambassador Hotel, Los Angeles, California When he finished delivering a victory speech after winning California's Democratic Presidential primary, Senator Robert F. Kennedy of New York was shot several times while walking through the kitchen of the Ambassador Hotel. While RFK was mortally wounded and would die a little over a day later, five other people were also wounded in the shooting.
•May 15, 1972, Laurel, Maryland Segregationist Alabama Governor George Wallace was paralyzed from the waist down after being shot by Arthur Bremer at a campaign rally when he was running for the Democratic Presidential nomination. Three bystanders were also wounded in the shooting, but survived.
•September 22, 1975, San Francisco, California A taxi driver in San Francisco was wounded when Sara Jane Moore attempted to shoot President Gerald Ford as he left the St. Francis Hotel. Moore's first shot missed the President by several inches and the second shot, which hit the taxi driver, was altered when a Vietnam veteran in the crowd named Oliver Sipple grabbed her arm as she was firing. Just 17 days earlier and 90 miles away, Lynette "Squeaky" Fromme, a member of the Charles Manson family, had tried to shoot President Ford as he walked through Capitol Park in Sacramento but nobody was injured.
•March 30, 1981, Washington, D.C. President Ronald Reagan was shot and seriously wounded by as he left the Washington Hilton after giving a speech. Three other people were wounded in the shooting, including White House Press Secretary James Brady who was shot in the head and partially paralyzed, Washington D.C. Police Office Thomas Delahanty, and Secret Service agent Tim McCarthy. Video of the assassination attempt shows that when the shots were fired, McCarthy turned and made himself a bigger target in order to shield the President with his own body. President Reagan was struck by a bullet that ricocheted off of the Presidential limousine.
#History#Presidential Assassinations#Presidential Assassination Attempts#Presidency#Politics#Political History#Assassinations#Attempted Assassinations#Lincoln Assassination#Assassination of Abraham Lincoln#Booth Conspiracy#Attempted Assassination of President-elect Franklin D. Roosevelt#FDR#Franklin D. Roosevelt#President Roosevelt#Puerto Rican Nationalists#Attempted Assassination of Harry S. Truman#President Truman#Secret Service#United States Secret Service#White House Police#Presidential History#Robert F. Kennedy#RFK Assassination#Assassination of Robert F. Kennedy#Attempted Assassination of George Wallace#Attempted Assassination of Gerald Ford#President Ford#Attempted Assassination of Ronald Reagan#President Reagan
23 notes
·
View notes
Photo

On this day, 19 April 1882, hundreds of women, men and children fought police on the mountainous Isle of Skye in northwest Scotland. It was the start of a widespread land revolt that required a military invasion to restore order. In 1865 a landowner let out Ben Lee hill to a sheep farmer. It was a devastating blow for his already impoverished tenants, who traditionally had local grazing rights. For 15 years they stoically endured the confiscation of their grazing rights, but when the sheep farm’s lease expired, they petitioned the landlord to reinstate them for a fair rent. When the petition went ignored, the crofters declared a rent strike and drove their animals onto the hill in violation of the law. So the sheriff's office delivered eviction notices to some of the most senior and troublesome tenants. Sheriffs were met by a jeering mob of 150 women, men, and children who burned the eviction notices and chased them off. So on April 19 the Sheriff returned with his own officers plus police from Glasgow. They marched into the Braes and seized prisoners in Balmeanach. The crofters, initially taken by surprise, soon ran from their homes and fields carrying whatever weapons they could find. In heavy wind and rain, the crofters began to chuck stones, while others attacked with branches and agricultural tools. The police baton-charged unsuccessfully and soon they too resorted to hurling stones. A local journalist described how “Stones were coming down like hail, while huge boulders were hurled down… Here and there a constable might be seen actually bending under the pressure of a well-directed boulder, losing his footing, and rolling down the hill, followed by scores of missiles.” Eventually the exhausted police had to flee with just five prisoners, but the revolt spread and was only quelled by warships and hundreds of troops over two years later. More information, sources and map: https://stories.workingclasshistory.com/article/9059/Battle-of-the-Braes https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=611307024375850&set=a.602588028581083&type=3
170 notes
·
View notes
Text
—The Peale’s: An illustrious lineage.










Charles Willson Peale (April 15, 1741 – February 22, 1827) was an American painter, scientist, naturalist and inventor, famous for painting figures from the American Revolution like John Laurens and baron Frederick von Steuben and making the most famous portrayals of president George Washington. His children (many of whom received names of Peale’s favourite artists) and grandchildren would go down in history as influential artists, ornithologist and polymaths. They were:
Raphaelle (also known was Raphael) Peale (1774–1825), widely considered he first professional still-life painter born in America.
Remembrandt Peale (1778–1860), author of more that 600 paintings and museum keeper, whose most notable painting was “Rubens Peale with a Geranium”.
Rubens Peale (1784–1865), museum administrator, who due to his weak eyesight would not practice painting seriously until the last decade of his life, when he became an still-life artist.
Sophonisba Angusciola Sellers, née Peale (1786–1859), ornithologist and mother of engineer Coleman Sellers II.
Titian Ramsay Peale I (1780–1798), ornithologist.
Franklin Peale (1795–1870), Chief Coiner at the Philadelphia Mint.
Titian Ramsay Peale II (1799–1885), ornithologist, scientific illustrator, photographer and explorer.
His granddaughters would also be known as:
Mary Jane Peale (1826–1902), Rubens’ third child and only daughter, a painter.
Rosalba and Eleanor Peale, Remembrandt’s daughters, of ehom Rosalba would be known as a painter.
#Charles Willson Peale#Raphaelle Peale#Remembrandt Peale#Rubens Peale#Sophonisba Angusciola Peale#Titian Ramsay Peale I#Titian Ramsay Peale II#Franklin Peale#Mary Jane Peale#Rosalba Peale#Eleanor Peale#Art post#art
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think that April 14, 1865, 10:15 pm, is a great date and time to attend a theatre
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ch 42: As Long as They Don't Forget

They call him Captain Puppy Eyes

Did she atone by founding the Sunflower Nursery??
Andy tells her to pour Anheuser beer on his crew's graves to find forgiveness, and Fuuko sets out alongside him. He claims that he wants to make the saloon woman suffer, but Fuuko sees another side to his motivation. And then we get:
🐎COWBOY ANDY MONTAGE🐎

We see the four seasons representing the passage of time between them. In the first one, they're both shooting at a group of normal-looking old-timey Western guys. In the second, they're walking through the desert.
In the third, there's falling leaves and an angel in the background. It looks like they've got a child fighting with them. They're fighting two guys wearing suits and masks that resemble the Union Negator hunters from Chapter 1. The angel doesn't quite match up with the statue in the chapel in Longing, either. I'm so curious about this one!!
Angel comparison:
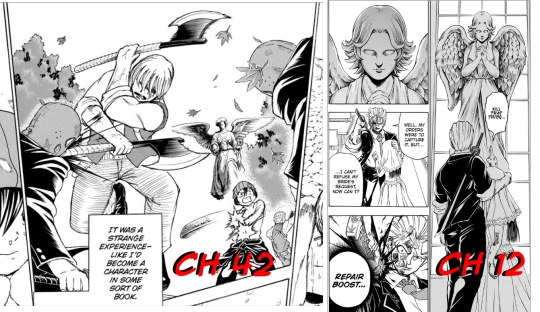
In the fourth, Andy has buried a friend in the wintertime. There are two other people dressed like Andy and Fuuko.
I love the way the narration boxes explain Fuuko's POV here. Describing the time as eons that passed quickly, like a dream, both rich and deep but also instantaneous--- that's a lot like the effect authors want to create when writing a good flashback.

We see some crumbs about Andy's current crew, and that he's drinking a Budweiser, which came out in 1876 IRL.
Andy and Fuuko's conversation about death raises some questions about Victor. When he's being suppressed, is he "alive?" Can you be alive if you can't challenge? If you can't change?

We see how Andy's crew formed. When they met him, everyone was wearing tattered clothes and looking like they were just in a battle. I'll bet Andy helped them out and then they started following him like Fuuko.
Fuuko tells him that she believes people who have passed remain alive in our hearts and talks about how she feels her parents guiding her.

Andy knows that he won't be alone anymore and he smiles. And then all readers collectively gasp at the next page:

FIRST OF ALL, {ohrwepo%9Ksd46<2[LJS:Fqj3nq4rwe^isdfah!

I can't believe it! The realest, non-battle-related, most solemn and serious moment of major romance, and they still don't kiss!

And she's right-- It's not really the same person and he doesn't really know her as well as she knows him at this point.
The line, "As long as I don't forget, then people won't die" is impactful to this story in so many ways.
First, Juiz has to remember to find people every loop. If she forgets to how to seek out the Negators or forgets who they are, she'll waste opportunities to defeat God.
Second, what does it mean when the story seals off Victor's memories? Are those memories "dead?"
Third, Andy has to remember Fuuko so he can find her in the future.
Also, Andy/Victor serves as a "witness" to the story to remember all the people and events that have happened. If they forget, they'll be missing valuable information that can help everyone.
In one way, it's really sweet that Andy now has a philosophy that he never really has to say goodbye to people bc they live on as long as he remembers them. But in another sense, it's horrifically tragic bc he's already forgotten so much. Everyone from before April 15, 1865 is dead to him, in all senses of the word.
What was the reason she began to fade away? Was it because she told him she loved him? Because he smiled? Because they almost kissed? And what will she find at the next stop in the book?

Masterpost
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
The napoleonic marshal‘s children
After seeing @josefavomjaaga’s and @northernmariette’s marshal calendar, I wanted to do a similar thing for all the marshal’s children! So I did! I hope you like it. c: I listed them in more or less chronological order but categorised them in years (especially because we don‘t know all their birthdays). At the end of this post you are going to find remarks about some of the marshals because not every child is listed! ^^“ To the question about the sources: I mostly googled it and searched their dates in Wikipedia, ahaha. Nevertheless, I also found this website. However, I would be careful with it. We are talking about history and different sources can have different dates. I am always open for corrections. Just correct me in the comments if you find or know a trustful source which would show that one or some of the dates are incorrect. At the end of the day it is harmless fun and research. :) Pre 1790
François Étienne Kellermann (4 August 1770- 2 June 1835)
Marguerite Cécile Kellermann (15 March 1773 - 12 August 1850)
Ernestine Grouchy (1787–1866)
Mélanie Marie Josèphe de Pérignon (1788 - 1858)
Alphonse Grouchy (1789–1864)
Jean-Baptiste Sophie Pierre de Pérignon (1789- 14 January 1807)
Marie Françoise Germaine de Pérignon (1789 - 15 May 1844)
Angélique Catherine Jourdan (1789 or 1791 - 7 March 1879)
1790 - 1791
Marie-Louise Oudinot (1790–1832)
Marie-Anne Masséna (8 July 1790 - 1794)
Charles Oudinot (1791 - 1863)
Aimee-Clementine Grouchy (1791–1826)
Anne-Francoise Moncey (1791–1842)
1792 - 1793
Bon-Louis Moncey (1792–1817)
Victorine Perrin (1792–1822)
Anne-Charlotte Macdonald (1792–1870)
François Henri de Pérignon (23 February 1793 - 19 October 1841)
Jacques Prosper Masséna (25 June 1793 - 13 May 1821)
1794 - 1795
Victoire Thècle Masséna (28 September 1794 - 18 March 1857)
Adele-Elisabeth Macdonald (1794–1822)
Marguerite-Félécité Desprez (1795-1854); adopted by Sérurier
Nicolette Oudinot (1795–1865)
Charles Perrin (1795–15 March 1827)
1796 - 1997
Emilie Oudinot (1796–1805)
Victor Grouchy (1796–1864)
Napoleon-Victor Perrin (24 October 1796 - 2 December 1853)
Jeanne Madeleine Delphine Jourdan (1797-1839)
1799
François Victor Masséna (2 April 1799 - 16 April 1863)
Joseph François Oscar Bernadotte (4 July 1799 – 8 July 1859)
Auguste Oudinot (1799–1835)
Caroline de Pérignon (1799-1819)
Eugene Perrin (1799–1852)
1800
Nina Jourdan (1800-1833)
Caroline Mortier de Trevise (1800–1842)
1801
Achille Charles Louis Napoléon Murat (21 January 1801 - 15 April 1847)
Louis Napoléon Lannes (30 July 1801 – 19 July 1874)
Elise Oudinot (1801–1882)
1802
Marie Letizia Joséphine Annonciade Murat (26 April 1802 - 12 March 1859)
Alfred-Jean Lannes (11 July 1802 – 20 June 1861)
Napoléon Bessière (2 August 1802 - 21 July 1856)
Paul Davout (1802–1803)
Napoléon Soult (1802–1857)
1803
Marie-Agnès Irma de Pérignon (5 April 1803 - 16 December 1849)
Joseph Napoléon Ney (8 May 1803 – 25 July 1857)
Lucien Charles Joseph Napoléon Murat (16 May 1803 - 10 April 1878)
Jean-Ernest Lannes (20 July 1803 – 24 November 1882)
Alexandrine-Aimee Macdonald (1803–1869)
Sophie Malvina Joséphine Mortier de Trévise ( 1803 - ???)
1804
Napoléon Mortier de Trévise (6 August 1804 - 29 December 1869)
Michel Louis Félix Ney (24 August 1804 – 14 July 1854)
Gustave-Olivier Lannes (4 December 1804 – 25 August 1875)
Joséphine Davout (1804–1805)
Hortense Soult (1804–1862)
Octavie de Pérignon (1804-1847)
1805
Louise Julie Caroline Murat (21 March 1805 - 1 December 1889)
Antoinette Joséphine Davout (1805 – 19 August 1821)
Stephanie-Josephine Perrin (1805–1832)
1806
Josephine-Louise Lannes (4 March 1806 – 8 November 1889)
Eugène Michel Ney (12 July 1806 – 25 October 1845)
Edouard Moriter de Trévise (1806–1815)
Léopold de Pérignon (1806-1862)
1807
Adèle Napoleone Davout (June 1807 – 21 January 1885)
Jeanne-Francoise Moncey (1807–1853)
1808: Stephanie Oudinot (1808-1893) 1809: Napoleon Davout (1809–1810)
1810: Napoleon Alexander Berthier (11 September 1810 – 10 February 1887)
1811
Napoleon Louis Davout (6 January 1811 - 13 June 1853)
Louise-Honorine Suchet (1811 – 1885)
Louise Mortier de Trévise (1811–1831)
1812
Edgar Napoléon Henry Ney (12 April 1812 – 4 October 1882)
Caroline-Joséphine Berthier (22 August 1812 – 1905)
Jules Davout (December 1812 - 1813)
1813: Louis-Napoleon Suchet (23 May 1813- 22 July 1867/77)
1814: Eve-Stéphanie Mortier de Trévise (1814–1831) 1815
Marie Anne Berthier (February 1815 - 23 July 1878)
Adelaide Louise Davout (8 July 1815 – 6 October 1892)
Laurent François or Laurent-Camille Saint-Cyr (I found two almost similar names with the same date so) (30 December 1815 – 30 January 1904)
1816: Louise Marie Oudinot (1816 - 1909)
1817
Caroline Oudinot (1817–1896)
Caroline Soult (1817–1817)
1819: Charles-Joseph Oudinot (1819–1858)
1820: Anne-Marie Suchet (1820 - 27 May 1835) 1822: Henri Oudinot ( 3 February 1822 – 29 July 1891) 1824: Louis Marie Macdonald (11 November 1824 - 6 April 1881.) 1830: Noemie Grouchy (1830–1843) —————— Children without clear birthdays:
Camille Jourdan (died in 1842)
Sophie Jourdan (died in 1820)
Additional remarks: - Marshal Berthier died 8.5 months before his last daughter‘s birth. - Marshal Oudinot had 11 children and the age difference between his first and last child is around 32 years. - The age difference between marshal Grouchy‘s first and last child is around 43 years. - Marshal Lefebvre had fourteen children (12 sons, 2 daughters) but I couldn‘t find anything kind of reliable about them so they are not listed above. I am aware that two sons of him were listed in the link above. Nevertheless, I was uncertain to name them in my list because I thought that his last living son died in the Russian campaign while the website writes about the possibility of another son dying in 1817. - Marshal Augerau had no children. - Marshal Brune had apparently adopted two daughters whose names are unknown. - Marshal Pérignon: I couldn‘t find anything about his daughters, Justine, Elisabeth and Adèle, except that they died in infancy. - Marshal Sérurier had no biological children but adopted Marguerite-Félécité Desprez in 1814. - Marshal Marmont had no children. - I found out that marshal Saint-Cyr married his first cousin, lol. - I didn‘t find anything about marshal Poniatowski having children. Apparently, he wasn‘t married either (thank you, @northernmariette for the correction of this fact! c:)
#Marshal‘s children calendar#literally every napoleonic marshal ahaha#napoleonic era#Napoleonic children#I am not putting all the children‘s names into the tags#Thank you no thank you! :)#YES I posted it without double checking every child so don‘t be surprised when I have to correct some stuff 😭#napoleon's marshals#napoleonic
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
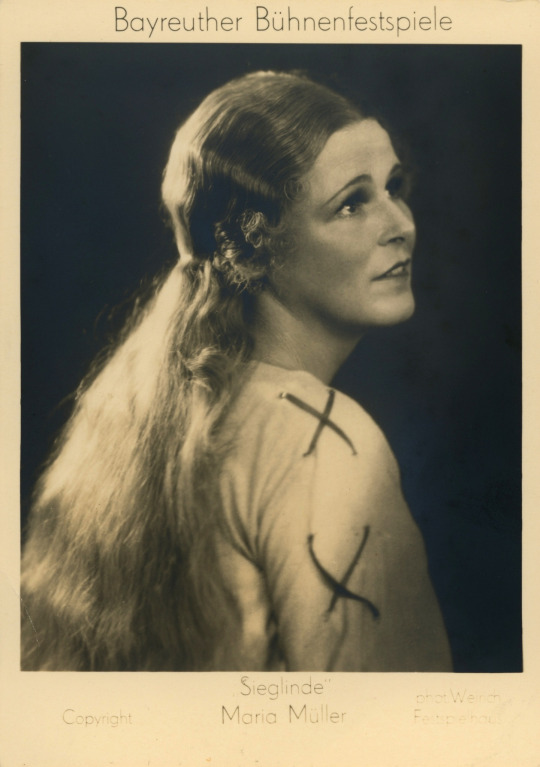
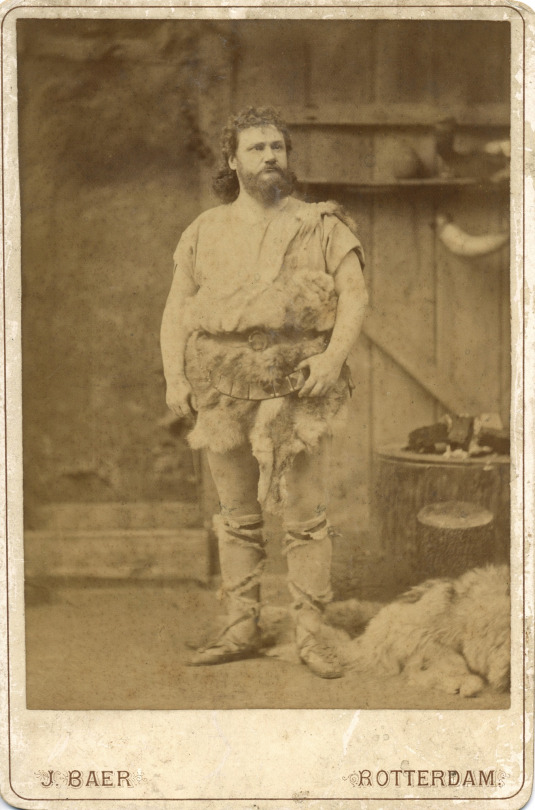
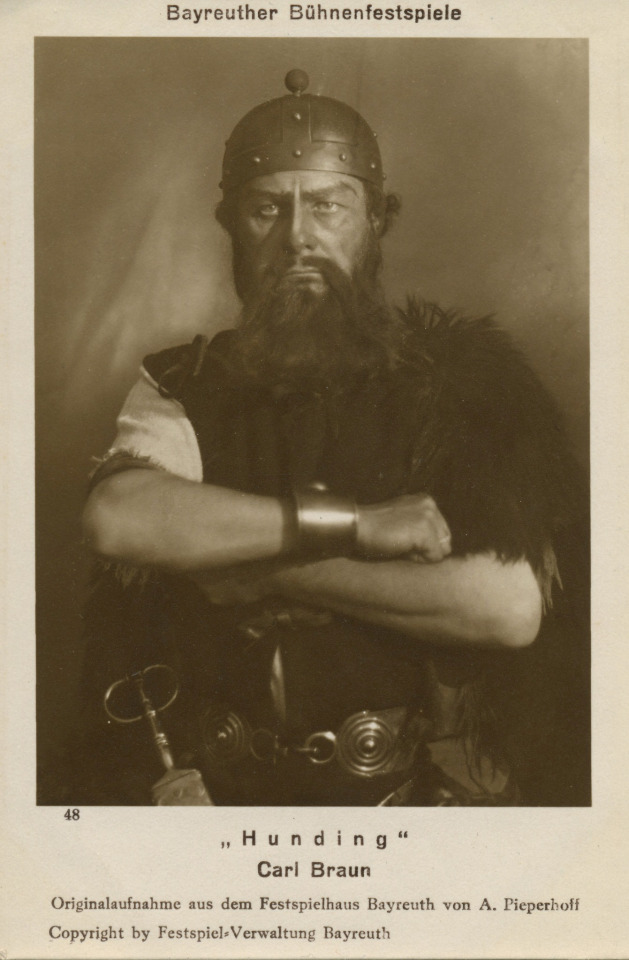













„WALKÜRE“ R. Wagner / FIRST ACT
Some Sieglindes, Siegmunds and Hundings
Maria Müller (29 January 1898 – 15 March 1958); Czech-Austrian lyric/dramatic soprano, Emanuel List (22 March 1888 - 21 June 1967; Austrian-American bass and Franz Völker (31 March 1899 – 4 December 1965); dramatic tenor, Bayreuth, 1933
Maria Müller as Sieglinde, Bayreuth, 1937
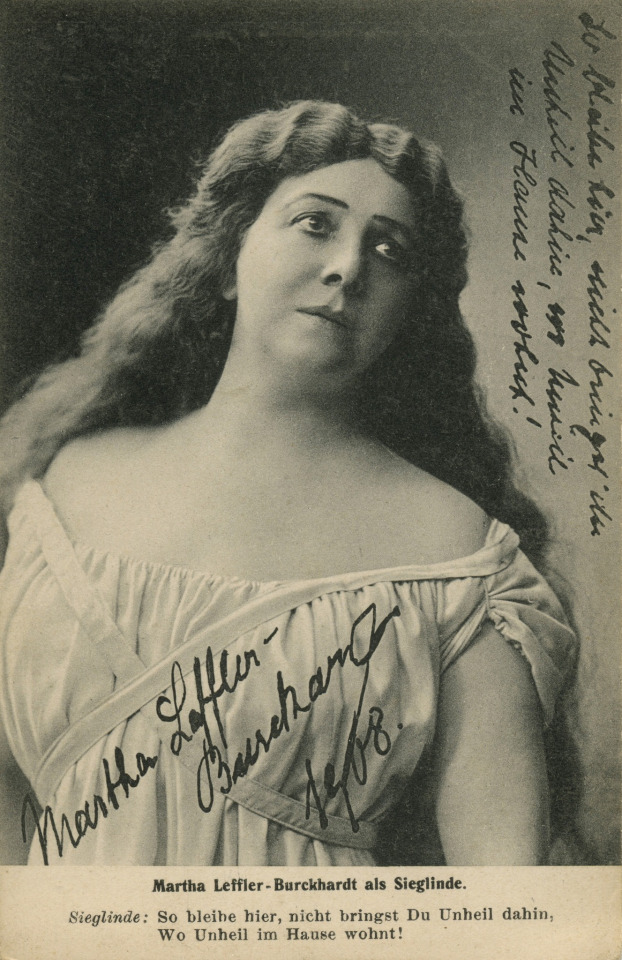
Martha Leffler-Burckhardt (16 June 1865 -14 May 1954); German soprano as Sieglinde, Bayreuth, 1908
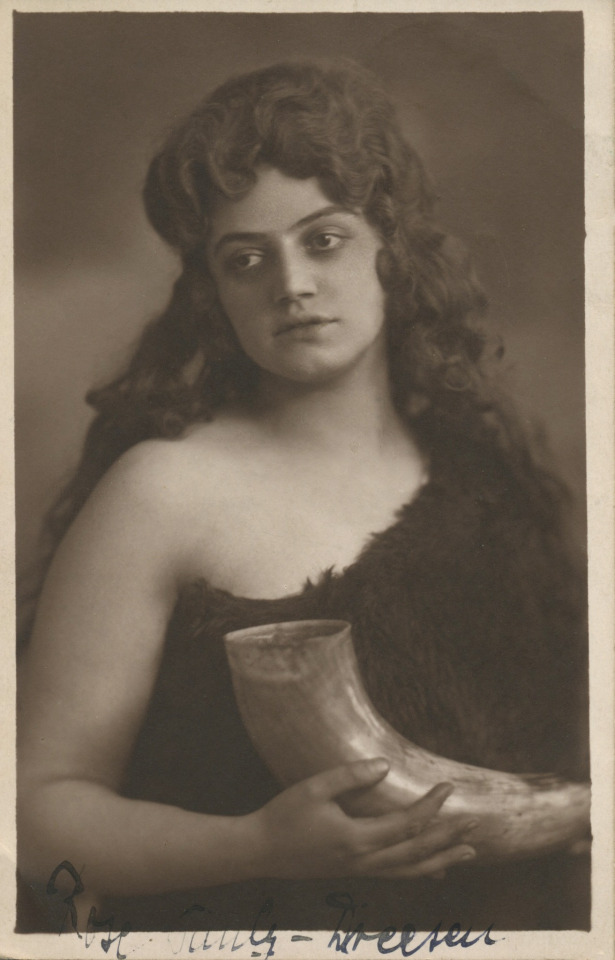
Rose Pauly-Dressen (15 March 1894 – 14 December 1975); Hungarian dramatic soprano as Sieglinde, Frankfurt, ?
Martha Selle as Sieglinde, Breslau, ?
Florence Easton (25 October 1882 – 13 August 1955); English dramatic soprano as Sieglinde, Berlin, ?
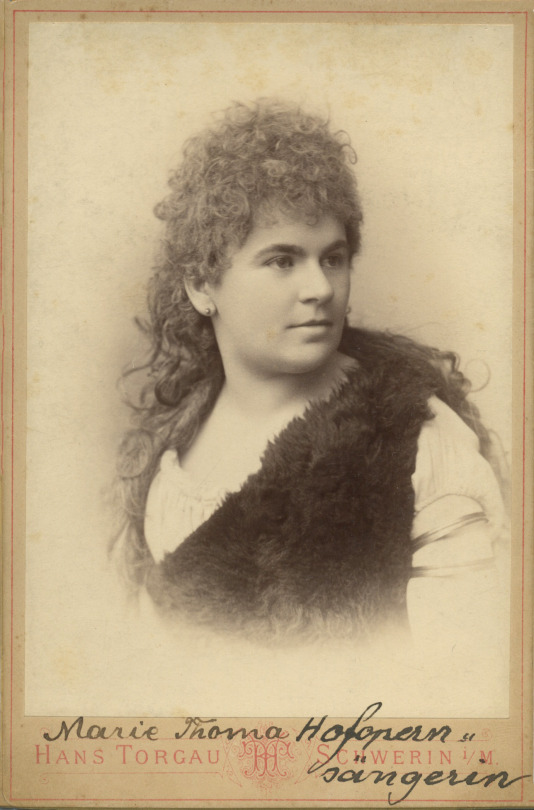
Marie Thoma as Sieglinde, Schwerin, ?
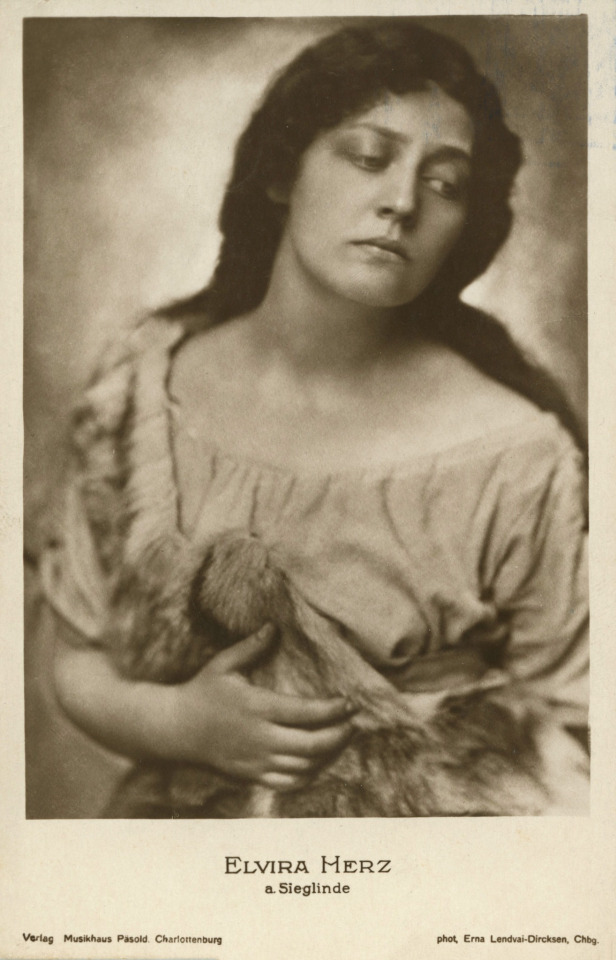
Elvira Herz as Sieglinde, Berlin, ?
Adolf Gröbke ? (26.5.1872 -16.9.1949); German tenor as Siegmund, Rotterdam, ?
Lauritz Melchior (20 March 1890 – 18 March 1973); Danish-American heldentenor as Siegmund, Bayreuth, 1924, 1925 and 1931
Fiorenzo Tasso (1901 - 29. 3. 1976); French tenor as Siegmund, Milan, 1945
Carl Braun (2 June 1886 – 24 April 1960); German bass as Hunding, Bayreuth, 1925, 1927, 1928 and 1930
Lorenz Corvinus (20 July 1870 - 18 January 1952); German bass as Hunding, Bayreuth, 1908
#classical music#opera#music history#bel canto#composer#classical composer#aria#classical studies#maestro#chest voice#Die Walküre#The Valkyrie#Richard Wagner#Wagner#Der Ring des Nibelungen#The Ring of the Nibelung#Norse mythology#Völsunga saga#Poetic Edda#Sieglinde#classical musician#classical musicians#classical voice#musician#musicians#music education#music theory#history of music#historian of music#classical
25 notes
·
View notes
Text

Olga Boznanska, Natalie Barney, ca. 1900, oil on fiberboard, 30 5⁄8 x 19 5⁄8 in. (77.8 x 49.8 cm.), Smithsonian American Art Museum, Gift of Mme. Yvonne Guehennec and Mr. William E. Huntington, 1976.153.26
Olga Boznańska (15 April 1865 – 26 October 1940) was a Polish painter of the turn of the 20th century. She was a notable painter in Poland and Europe, and was stylistically associated with the French impressionism, though she rejected this label. Via wikipedia
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo










President Abraham Lincoln died on April 15, 1865 after being shot the previous evening by actor John Wilkes Booth.
#Robert Russin#Mount Rushmore National Memorial#Gutzon Borglum#USA#J. Otto Schweizer#Gettysburg National Military Park#Henry K. Bush-Brown#Stanley J. Watts#Abraham Lincoln#died#death#15 April 1865#US history#anniversary#original photography#sculpture#tourist attraction#summer 2019#travel#vacation#Daniel Chester French
0 notes
Text
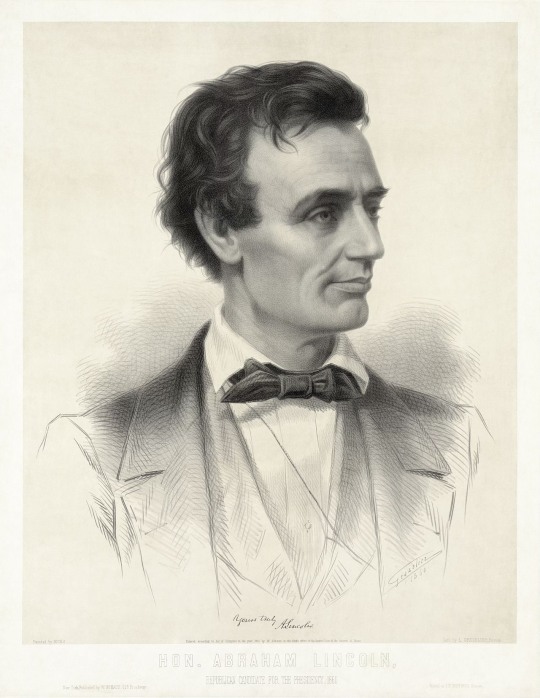


An original document signed by President Abraham Lincoln four days before his assassination on 15 April 1865. Photograph: Raab Collection
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
February 18, 2024
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
On the third Monday in February, the U.S. celebrates Presidents Day, a somewhat vague holiday placed in 1968 near the date of George Washington’s birthday on February 22, 1732, but also traditionally including Abraham Lincoln, who was born on February 12, 1809. This year, that holiday falls on February 19.
That the American people in the twenty-first century celebrate Abraham Lincoln as a great president would likely have surprised Lincoln in summer 1864, when every sign suggested he would not be reelected and would go down in history as the man who had permitted a rebellion to dismember the United States.
The news from the battlefields in 1864 was grim. In May, General U. S. Grant had taken control of the Army of the Potomac and had launched a war of attrition to destroy the Confederacy. In May and June, more than 17,500 Union soldiers were killed or wounded at the Battle of the Wilderness, 18,000 at Spotsylvania, and another 12,500 at Cold Harbor. As the casualties mounted, so did criticism of Lincoln.
Those Republican leaders who thought Lincoln was far too conservative both in his prosecution of the war and in his moves toward abolishing enslavement had plotted with the humorless Treasury Secretary Salmon P. Chase, who perennially hankered to run the country, to replace Lincoln with Chase on the 1864 ticket.
In February they went so far as to circulate a document signed by Senator Samuel Pomeroy of Kansas, a key party leader, saying that “even were the re-election of Lincoln desirable, it is practically impossible against the union of influences which will oppose him.” Even if he could manage to pull off a reelection, the Pomeroy circular said, he was unfit for office: “his manifest tendency towards compromises and temporary expedients of policy” would make the “dignity and honor of the nation…suffer.”
This was no small challenge: Chase had been in charge of remaking the finances of the United States, and he had both connections and Treasury employees all over the country who owed their jobs to him. In an era in which political patronage meant political victories, he had a formidable machine.
Lincoln managed to quell the rebellion from the radicals. In June 1864, soon after the party—temporarily renamed the National Union Party to make it easier for former Democrats to feel comfortable voting for Republicans—met to choose a presidential candidate, Chase threatened to resign from the Cabinet, as he had done repeatedly. In the past, Lincoln had appeased him. This time, Lincoln accepted his resignation.
But conservatives, too, were in revolt against Lincoln.
Crucially, Thurlow Weed, New York’s kingmaker, thought Lincoln was far too radical. Weed cared deeply about putting his own people into the well-paying customs positions available in New York City, and he was frequently angry that Lincoln appointed nominees favored by the more radical faction.
That frustration went hand in hand with anger about policy. Weed was upset that the Republicans were remaking the government for ordinary Americans. The 1862 Homestead Act, which provided western land for a nominal fee to any American willing to settle it, was a thorn in his side. Until Congress passed that law, such land, taken from Indigenous tribes, would be sold to speculators for cash that went directly to the Treasury. Republicans believed that putting farmers on the land would enable them to pay the new national taxes Congress imposed, thus bringing in far more money to the Treasury for far longer than would selling to speculators, but Weed foresaw national bankruptcy.
Even more than financial policy, though, Weed was unhappy with Lincoln’s 1863 Emancipation Proclamation, which moved toward an end of human enslavement far too quickly for Weed.
On August 22, Weed wrote to his protégé Secretary of State William Henry Seward that he had recently “told Mr. Lincoln that his re-election was an impossibility…. [N]obody here doubts it; nor do I see anybody from other states who authorises the slightest hope of success.”
“The People are wild for Peace,” he wrote, and suggested they were unhappy that “the President will only listen to terms of Peace on condition Slavery be ‘abandoned.’” Weed wrote that Henry Raymond, another protégé who both chaired the Republican National Committee and edited the New York Times, “thinks Commissioners should be immediately sent to Richmond, offering to treat for Peace on the basis of Union.”
On August 23, 1864, Lincoln asked the members of his Cabinet to sign a memorandum that was pasted closed so they could not read it. Inside were the words:
“This morning, as for some days past, it seems exceedingly probable that this Administration will not be re-elected. Then it will be my duty to so co-operate with the President elect, as to save the Union between the election and the inauguration; as he will have secured his election on such ground that he can not possibly save it afterwards. — A. Lincoln”
But then his fortunes turned.
Just a week after Weed foretold his electoral doom, the Democrats chose as a presidential candidate General George McClellan, formerly commander of the Army of the Potomac, in a transparent attempt to appeal to soldiers. But to appease the anti-war wing of the party, they also called for an immediate end to the war. They also rejected the new, popular measures the national government had undertaken since 1861—the establishment of state colleges, the transcontinental railroad, the new national money, and the Homestead Act—insisting on “State rights.”
Americans who had poured their lives and fortunes into the war and liked the new government were not willing to abandon both to return to the conditions of three years before.
Then news spread that Rear Admiral David Farragut had taken control of Mobile Bay, the last port the Confederates held in the Gulf of Mexico east of the Mississippi River. On September 2, General William T. Sherman took Atlanta, a city of symbolic as well as real value to the Confederacy, and set off on his March to the Sea, smashing his way through the countryside and carving the eastern half of Confederacy in half again.
Reelecting Lincoln meant committing to fight on until victory, and voters threw in their lot. In November’s election, Lincoln won about 55% of the popular vote compared to McClellan’s 45%, and 212 electoral votes to McClellan’s 12. Lincoln won 78 percent of the soldiers’ vote.
After his reelection, Lincoln explained to a crowd come to serenade him why it had been important to hold an election, even though he had expected to lose it:
“We can not have free government without elections; and if the rebellion could force us to forego, or postpone a national election it might fairly claim to have already conquered and ruined us.”
Happy Presidents Day.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#History#Abraham Lincoln#Heather Cox Richardson#Letters from An American#defense of democracy#American Civil War
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Abraham Lincoln (/ˈlɪŋkən/ LINK-ən; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War, defending the nation as a constitutional union, defeating the insurgent Confederacy, playing a major role in the abolition of slavery, expanding the power of the federal government, and modernizing the U.S. economy.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
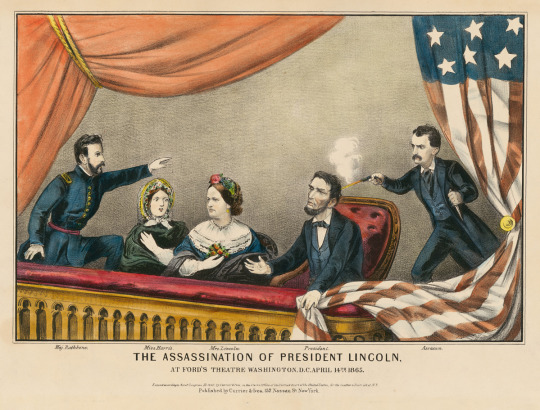

Today is the 159th anniversary of Abraham Lincoln's death, which took place at 7:22 AM on April 15, 1865, about nine hours after he was shot in the head by John Wilkes Booth at Ford's Theatre. So check back throughout the day for a few posts about Lincoln, the assassination, and Booth.

#History#Abraham Lincoln#President Lincoln#Assassination of Abraham Lincoln#Lincoln Assassination#Death of Abraham Lincoln#Presidents#Presidential History#John Wilkes Booth#Presidential Assassinations#Presidential Assassins#Civil War#Civil War History#Anniversary of Lincoln's Death#Presidential Deaths
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

MWW Artwork of the Day (2/19/24) George Peter Alexander Healy (American, 1813–1894) Abraham Lincoln (1869) Oil on canvas, 187.3 x 141.2 cm. The White House, Washington DC
This portrait of Abraham Lincoln was created by George Peter Alexander Healy (sometimes known as G. P. A. Healy) in 1869, not long after Lincoln's assassination on April 15, 1865. Lincoln originally sat for Healy in 1864, and the artist depicted Lincoln in this pose in a painting entitled The Peacemakers, an 1868 work that showed Lincoln conferring with Union military leaders during the final days of the Civil War. After Lincoln's death, Healy realized that the painting made an impressive portrait of Lincoln alone and painted three replicas, one of which became part of the White House collection. Lincoln became president on March 4, 1861 and had served in the House of Representatives earlier in his life.
6 notes
·
View notes