#15 April 1850
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
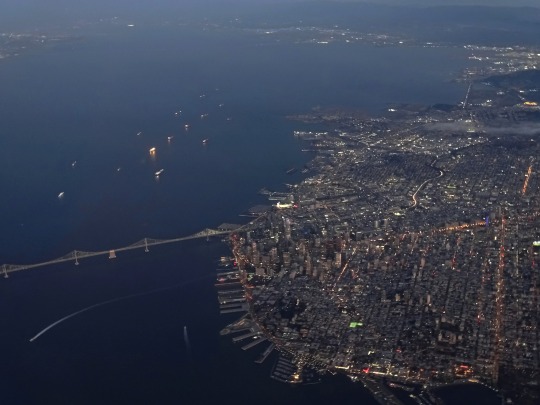
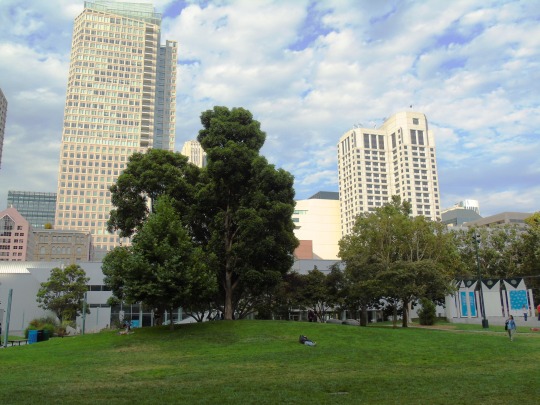
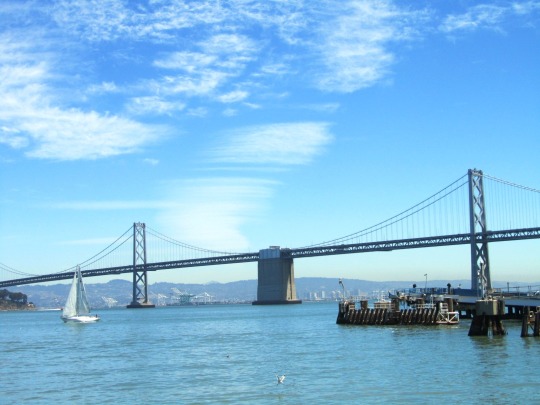
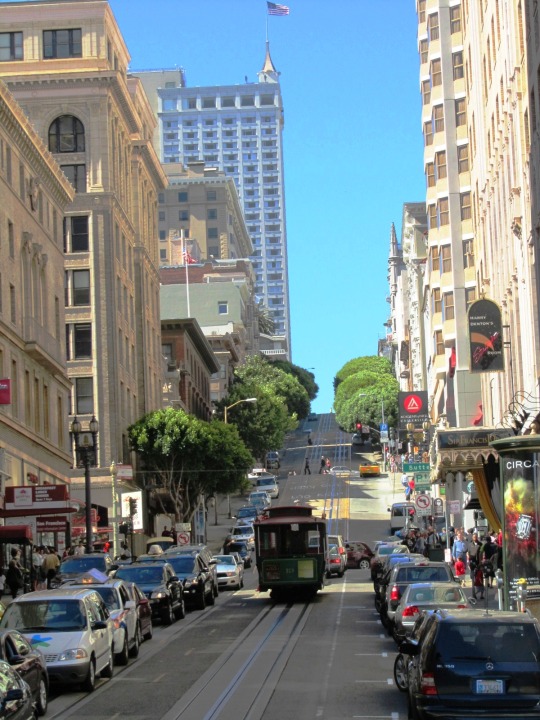
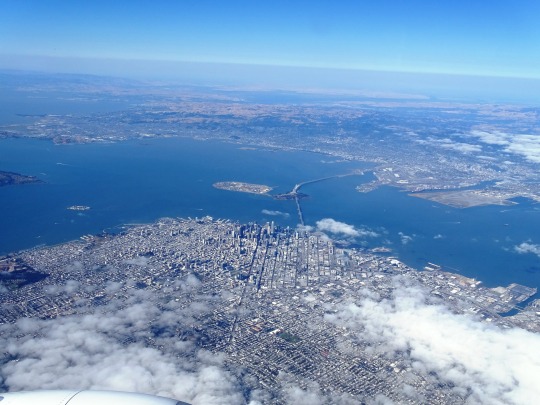
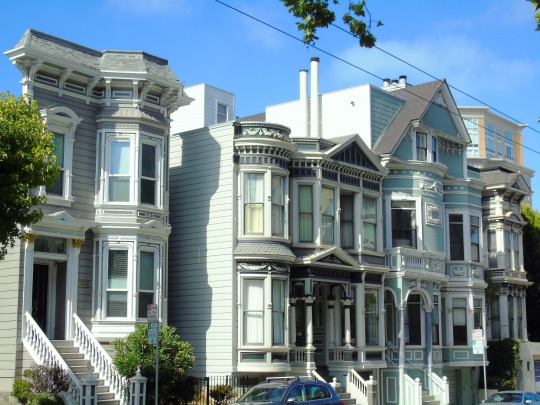
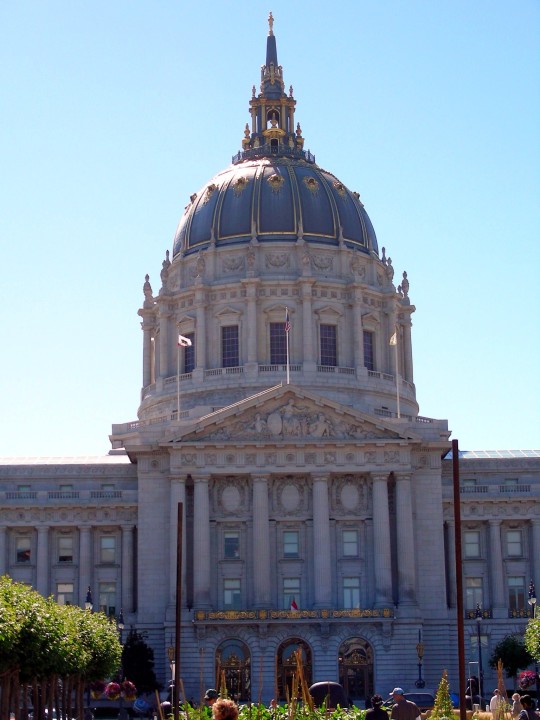
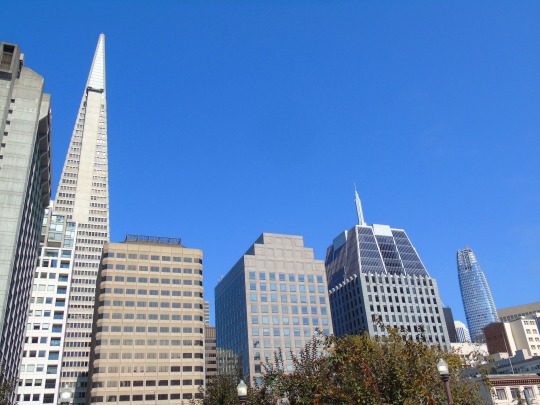
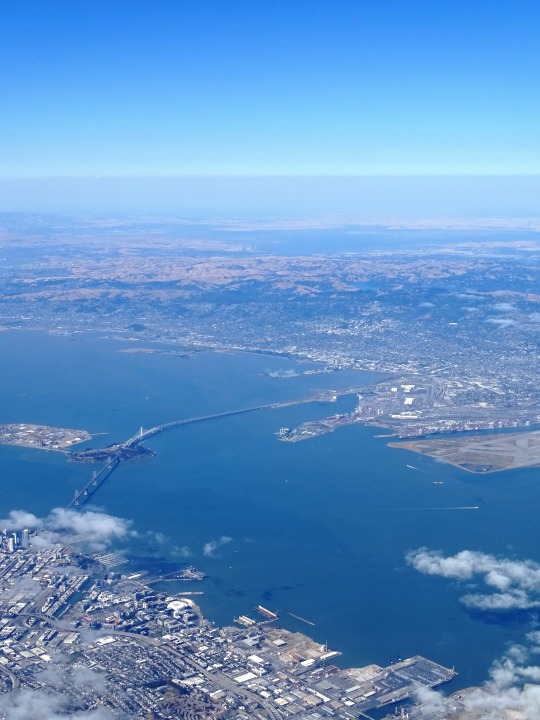
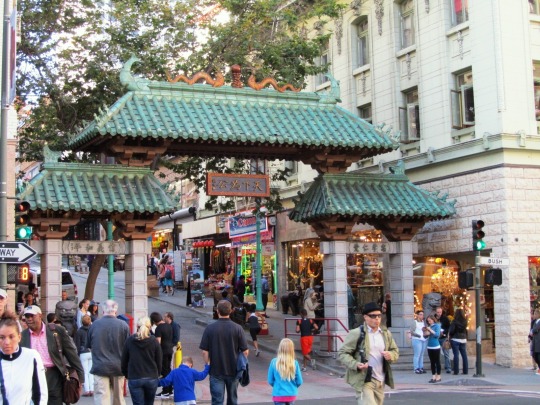
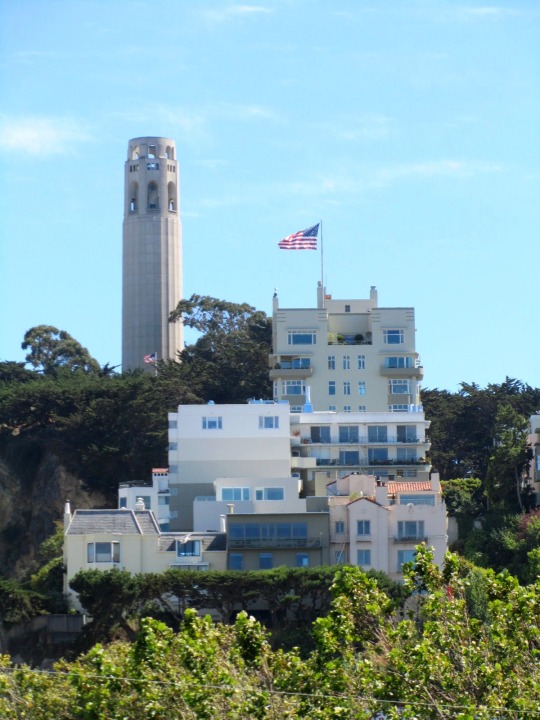
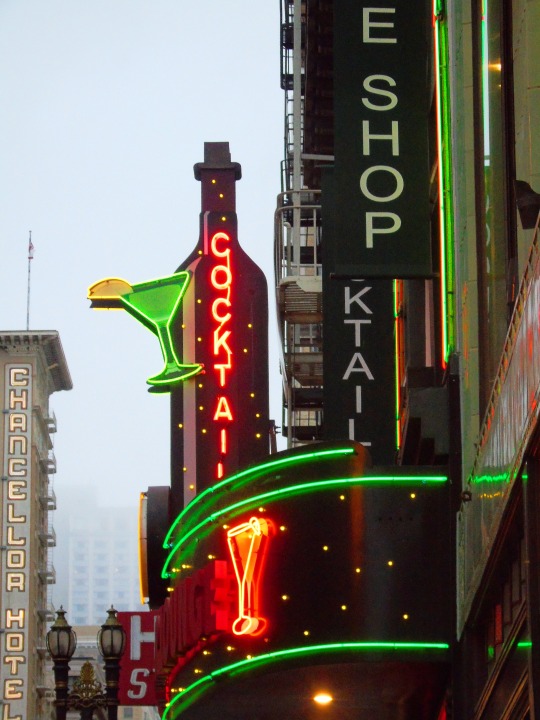
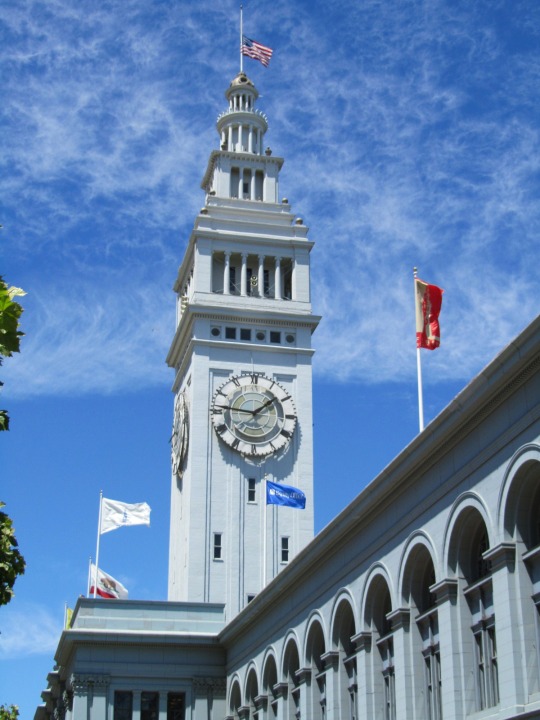
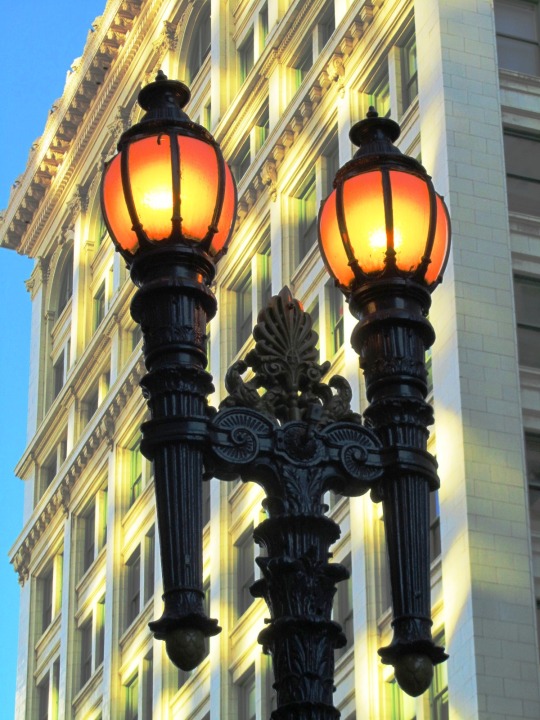
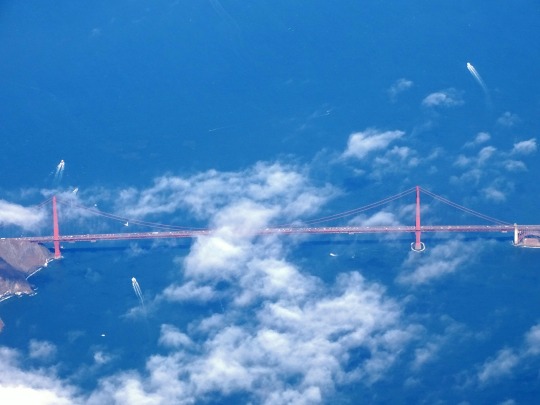
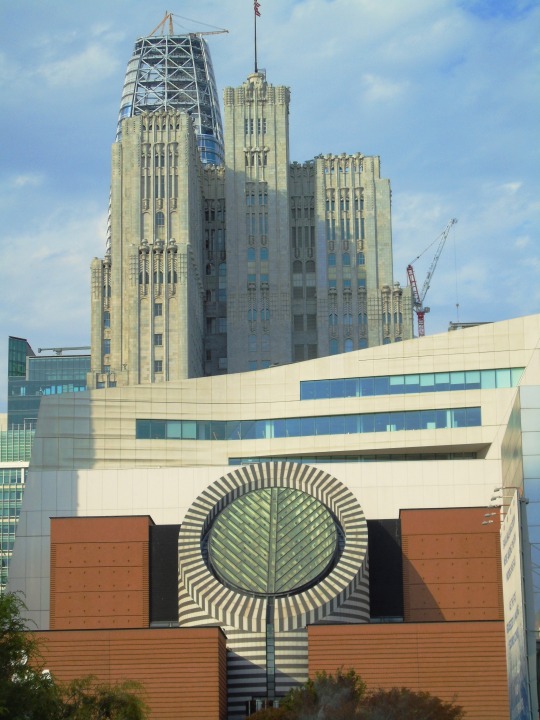
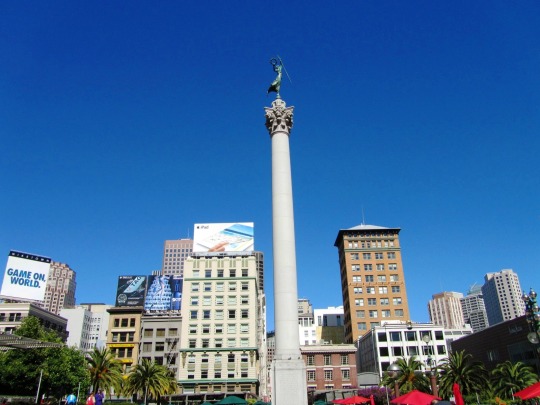
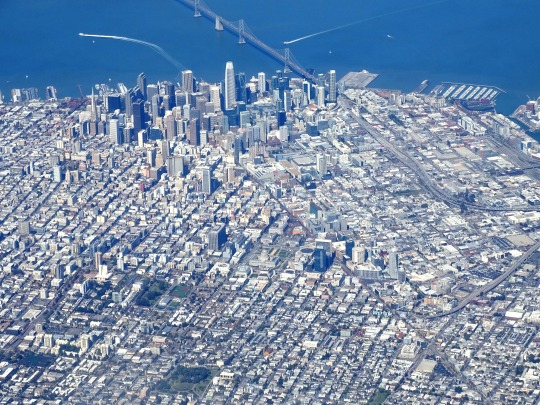
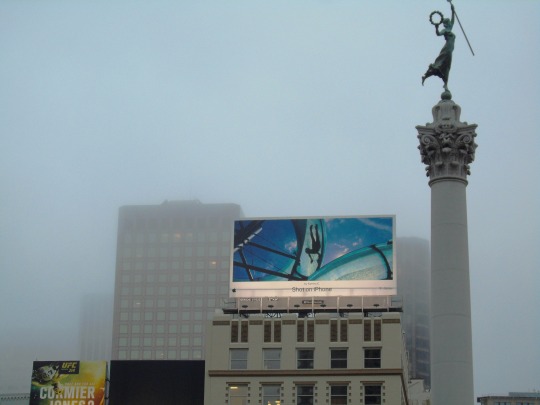
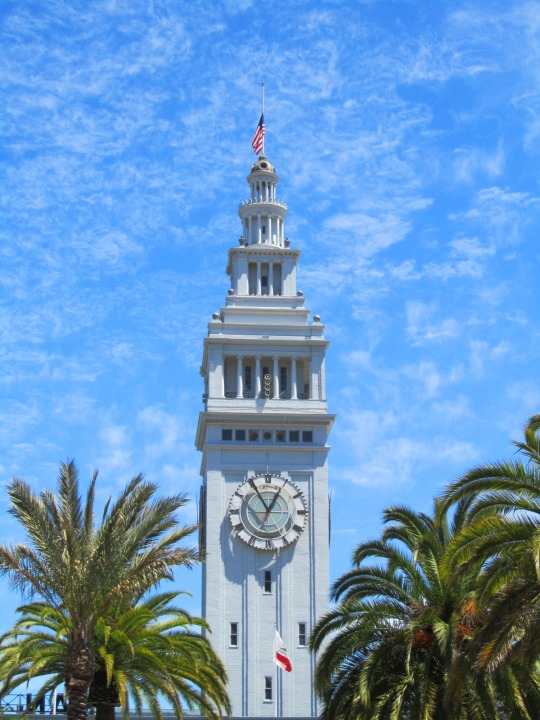






























The City of San Francisco was incorporated on April 15, 1850.
#Yerba Buena Gardens#Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary#San Francisco#USA#United States Penitentiary Alcatraz Island#Transamerica Pyramid#architecture#Powell Street#Golden Gate Bridge#Chinatown#Telegraph Hill#Coit Tower#incorporated#15 April 1850#anniversary#US history#original photography#summer 2017#2012#cityscape#tourist attraction#landmark#street scene#travel#vacation#Pacific Ocean
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
RDR Event Timeline (Canon + Headcanon)
This is the timeline I have constructed and use for all of my Red Dead writings. Canon event dates/ages are taken from the Red Dead Wiki, and headcanon estimations for more ambiguous events/characters are based on their approximate ages in-game by 1899 and what makes the most logical sense to me based on that timeline.
Please feel free to use this as a reference for your own works too, if it helps. (Canon events are noted as such, and my headcanons are labeled "HC.")
1839 - Uncle born (HC)
1844 - Hosea Matthews born (Canon)
1845 - Rains Fall born (HC)
1846 - Leopold Stauss born (HC)
1850 - Susan Grimshaw born (HC)
1853 - Orville Swanson born (HC)
1855 - Dutch Van der Linde born (Canon)
1857 - Josiah Trelawney born (HC)
1860 - Micah Bell III born (Canon) (newspaper clipping mentions Micah Bell Jr. robbing with his 17-year-old son in 1877)
1861 - Simon Pearson born (HC)
1863 - Arthur Morgan born (Canon)
1866 - Bill Williamson born (Canon)
1870 - Dutch leaves home aged 15 (Canon); Kieran Duffy born (HC)
1871 - Sadie Adler born (HC)
1872 - Charles Smith born (HC) (based on est. age of 27 in 1899)
1873 - John Marston born (Canon); Javier Escuella born (HC)
1874 - Lyle Morgan arrested and hanged, Arthur orphaned (Canon); Molly O'Shea born (HC)
1875 - Karen Jones born (HC)
1876 - Dutch and Hosea meet outside of Chicago, IL (Canon); Sean MacGuire born (HC)
1877 - Abigail Roberts born; Arthur joins the gang, aged 14 (Canon)
1878 - Eagle Flies born (HC)
1879 - Tilly Jackson and MaryBeth Gaskill born (HC)
1880 - Lenny Summers born (Canon)
1881 - John Marston's father dies, John orphaned (Canon)
1882- Annabelle and Bessie join the gang (HC)
1883 - Bessie and Hosea marry and leave the gang (Canon); Arthur meets and begins dating Mary Gillis (HC) (Jamie Gillis references both Annabelle and Bessie during the mission in Chapter 2, so IMO this would've been the most likely time for all 3 to have met one another.)
1884 - Dutch kills Colm O'Driscoll's unnamed brother, Annabelle killed by Colm in retaliation; Hosea returns to the gang (HC)
1885 - John Marston and Susan Grimshaw join the gang (Canon); Charles Smith leaves home, aged 13 (HC) (based on est. DOB 1872)
1886 - Arthur proposes to and subsequently breaks up with Mary in the springtime; Arthur meets Eliza (19) later in the year, and Isaac is conceived (HC)
1887 - Lee & Hoyt Bank Robbery, April (Canon); Isaac Morgan born (HC) (According to Arthur in-game, Eliza only knew who he was after she got pregnant. Based on this they most likely met in late 1886 or very early 1887, with the bank robbery in April '87 and Isaac born that autumn.)
1888 - Death of Bessie Matthews (HC) (based on the assumption that she passed some time before Arthur lost his son. Her cause of death is never specified in canon, but I HC it was a fairly quick battle with pneumonia over the winter.)
1891 - Isaac Morgan (4) and Eliza (23) killed in a home robbery (HC)
1892 - Bill Williamson dishonorably discharged from the U.S. Army (Canon); Uncle joins the gang (HC)
1893 - Bill Williamson joins the gang (Canon)
1894 - Abigail Roberts joins the gang, introduced to them by Uncle (Canon)
1895 - Jack Marston born; Javier joins the gang (Canon)
1896 - John Marston leaves the gang; Jake and Sadie Adler marry in September (Canon)
1897 - John Marston returns to the gang after a year (Canon)
1898 - Micah Bell, Charles Smith, Lenny Summers, and Jenny Kirk join the gang (Canon)
1899 - Blackwater Massacre; dissolving of the Van der Linde gang; deaths of Jenny Kirk, Mac and Davey Callender, Sean MacGuire, Kieran Duffy, Hosea Matthews, Lenny Summers, Molly O'Shea, Eagle Flies, Susan Grimshaw, and Arthur Morgan (Canon)
1907 - Construction of Beecher's Hope ranch; John and Abigail marry; death of Micah Bell III (Canon)
1911 - Kidnapping of Abigail and Jack Marston by the U.S. Government in exchange for John's cooperation; deaths of Bill Williamson, Javier Escuella, Dutch Van der Linde, Uncle, and John Marston (Canon)
1914 - Death of Abigail Marston; Jack Marston kills Edgar Ross to avenge his father's murder (Canon)

#rdr2#red dead redemption#red dead redemption 2#rdr#fanfiction#rdr fanfiction#rdr2 fanfiction#rdr fanfic#red dead redemption timeline#writing resources#canon compliant#heacanons#zanazirawrites
132 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Terror: When, How, Where... (PART 1)
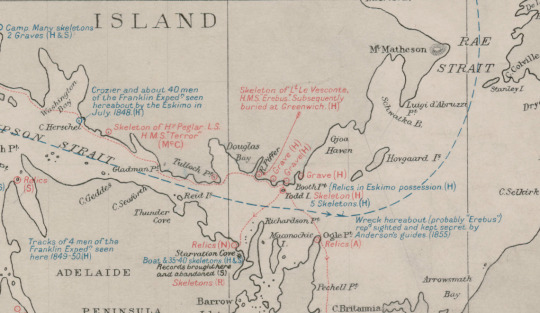
See part 2 for the end of my sanity (ep 6 through 9. Wasn't enough characters left on the post for ep 10)
See part 3 (and episode 10)
As I am writing the fic, I was getting frustrated at trying to figure out the timeline of the expedition. More specifically, what happens after they dropped the Victory Point Note.
Therefore, in order to organize my ideas, and also because it might be of interests to some of you, I will document here what I got.
Episode 1 through 5 for now.
Methodology
If we agree that the showrunners (and Dan Simmons to an extent) made their research, we should be able to match some of the event of the story with notable point of interests where artefacts and/or remains were found over the numerous searches made to ascertain the fate of the Franklin Expedition
I also tried to take note of all indications of time passing so that I might document their speed travel and the dates when they are not mentioned.
... And the death count. (Departing Beechey Island with 24 officers and 102 men)
Finally, I also used the following website to keep track of sunrises and sunsets: https://www.timeanddate.com/
1927 Admiralty Map
I may be an amateur in this kind of research but I find myself frustrated that the most complete map I've been able to find showing all that was found between 1850 and 1926 is shown on this map from 1927

To be noted, we now know that the Skeleton of H. Peglar was more probably W. Gibson or T. Armitage
The Skeleton of Lt. Le Vesconte has also been reevaluated and is now believed to be that of Harry Goodsir ( :( )
Also, as it happens, if we compare to 2024 maps, we can say that this is not the actual shape of KWI (close enough!).
Therefore, for my own sanity, I recreated with modern maps. Is it accurate? Well, I wouldn't publish it but I think it gives a good enough view of where they went and where they were going:

Where the Ships had drifted to in June 1847 (According to G. Gore's coordinates left on the Victory point note)
Where the Ships had drifted with the Pack by April 1848 (Victory Point Note)
Victory Point
McClintock's Boat Place (proposed to be same location as NgLJ-1)
Camp with Many skeletons
From D. Simmons' The Terror - The Hospital Camp
Peglar Skeleton
Starvation Cove
A Bunch of cairns in the area
Harry Goodsir
Gjoa Haven (Netsilik Settlement)
Fort Resolution (Dear God... look at how far they wanted to walk/Canoe/make portage...)
Matching the Show
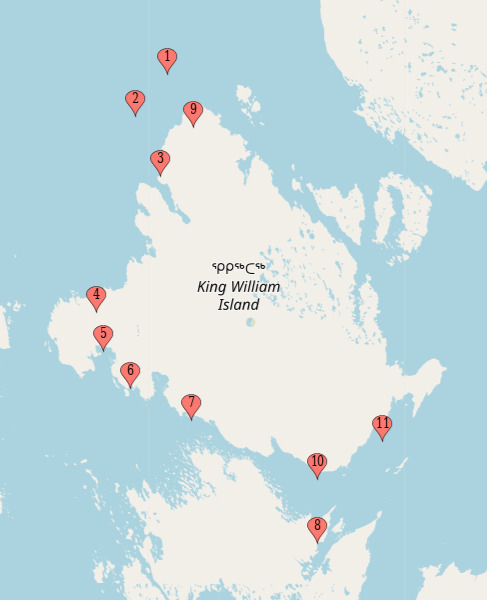
Episode 1 - Go for Broke
Location 1 - David Young's grave (71.22, -96.60)
Date: September 5th 1846
Nighttime - None
Daylight - 14h 57 min
Twilight - 9h 03 min
Sunset: 7:51 PM - Sunrise: 4:55 AM
David Young was buried 7 days before they were beset in the ice (see point 3 on the map below).
During the dinner in which we were regaled by the tale of Mr. Fitzjames' Holes, Franklin discuss that they were approaching a bigger channel, which is now know as the McClintock Channel (see point 1 on the map below), meaning that at the time, they were still in the Franklin Strait.
On the day after his death, Franklin discuss their next course and assure that they must be 'nearly in sight of KW Land'. Crozier suggests it might take them weeks to actually make it to KWI. This would confirm what was infer above.
As we can see the two ships fitting in a cozy little cove while the grave is being dug, I would like to propose Point 4 on the map below as Ficitonal David Young's final resting place, on Tasmania Islands
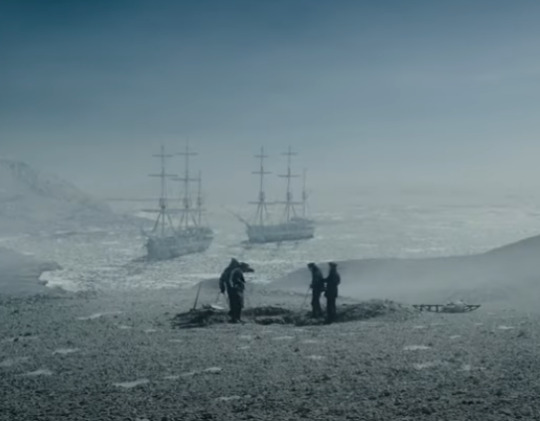

Location 2 - Ships September 1846 (70.25, -98.00)
Date: September 12th 1846
Nighttime - None
Daylight - 13h 45 min
Twilight - 10h 15 min
Sunset: 7:19 PM - Sunrise: 5:34 AM
Well, for this one, we need to use the extrapolation provided by the 1927's Admiralty map by tracing the line from where the ships were known to be in 1847 and 1848 (Point 5 and 6). (see point 3)

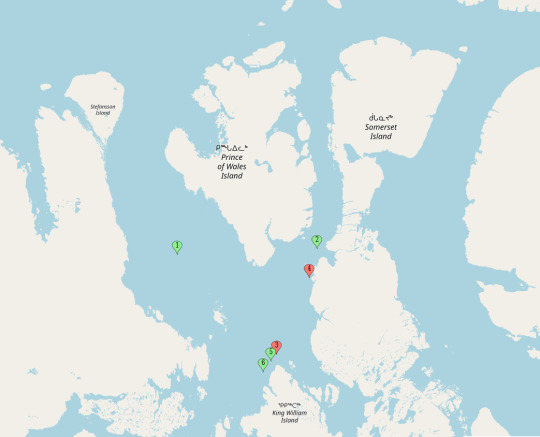
For Future Reference:
Travel Time between Loc 1 and Loc 2 - 7 days
Distance between Loc 1 and Loc 2 :70 NM / 80 Miles / 130 km
Average Travel Speed - 11.4 miles a day
Travel Condition - Ice breaking
DEATH COUNT: 2 + 3 (Total 5)
24 Officers and 100 Men remaining
Episode 2 - Gore
Location 3 - The Ships in 1847 (70.15, -98.30)
Date: May 24th 1847
Nighttime - None
Daylight - 24h min
Twilight - None
Sunset: N/A - Sunrise: N/A
Coordinates and Date From the Victory Point Note (see Point 1)

Location 4 - The Cairn (69.66, -98.27)
Date: May 28th 1847
Nighttime - None
Daylight - 24h min
Twilight - None
Sunset: N/A - Sunrise: N/A
From the ships, Gore lead his party to James Clark Ross' Cairn.
Now, in the Show, they found JCR's Cairn without an issue. In reality, while Gore had found the Cairn just fine, Crozier and Fitzjames did not. One of the reason for it is that JCR had, apparently, made a miscalculation in reporting where he had erected the Cairn by several miles. Honestly, the way that Fitzjames had written the words was so confusing, I appreciate that the show made the whole thing so much simpler, ahah. So let's say that it matches what we know now as Victory Point. Easy Peasy! (see Point 2)
To be Noted, we know the dates of departure from ships and arrival at cairn from the Victory Point Note.

Location 5 - The Ice Camp (69.665, -98.32)
Date: May 28th 1847
Nighttime - None
Daylight - 24h min
Twilight - None
Sunset: N/A - Sunrise: N/A
The Camp was raised just beyond the ice ridge that blocked the way form the shore and the Cairn was only a mile or so away. (see Point 3... hidden between point 2)
Of Note: That hail storm's cloud coverage was intense to say the least... So dark :')

Back to Loc 3 (70.15, -98.30)
Date: June 2nd 1847
Nighttime - None
Daylight - 24h min
Twilight - None
Sunset: N/A - Sunrise: N/A
Wednesday is a good day to drink with the Captain :D which makes it the Wednesday following May 28th 1847! So it's June 2nd!

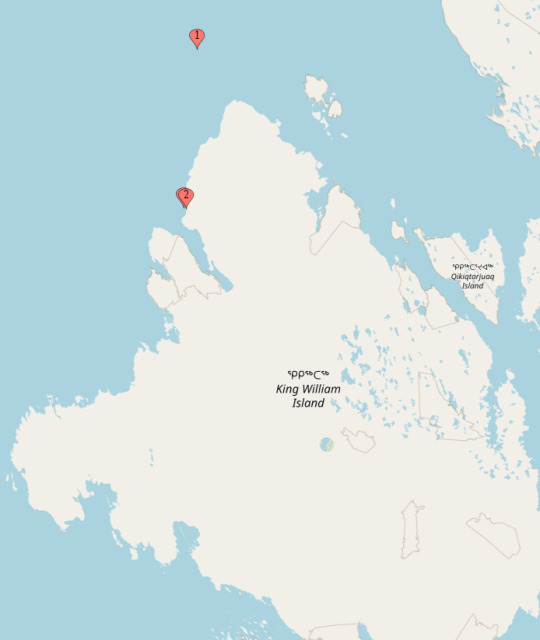
For Future Reference:
Loc 2 to Loc 3
Travel time - 8 months, 12 days or 254 days
Travel Distance: 8.6 NM / 10 miles / 16 km
Average Travel Speed - 0.04 miles a day
Travel Condition - Pack drifting
Loc 3 to Loc 4/5
Travel time - 5 days
Travel Distance: 29 NM / 33.5 miles / 54 km
Average Travel Speed - 6.7 miles a day
Travel Condition - 6 Men hauling Sledge on Ice
Loc 4/5 Back to Loc 3
Travel time - 4 days
Travel Distance: 29 NM / 33.5 miles / 54 km
Average Travel Speed - 8.4 miles a day
Travel Condition - 6 Men hauling ASS and Sledge on Ice
DEATH COUNT: 1 (Total: 6)
23 Officers and 100 Men remaining
Episode 3 - The Ladder
This one is fun because, well... they're not moving! I could point out where Silna ends up but it looks like she remain close enough to the ships that it doesn't matter all that much. So, let's just make note of the date and events:
Location 3 - Ships in June 1847 (70.15, -98.30)
For the duration of the episode:
Nighttime - None
Daylight - 24h min
Twilight - None
Sunset: N/A - Sunrise: N/A
Date: between June 2nd and June 10th 1847
- Silna makes her igloo a few miles away from the Ships
Date: June 11th 1847
- Franklin Dies
- Crozier drafts his resignation letter
Date: June 12th 1847
- Franklin's leg is buried :')
- Lieutenant Fairholme is sent to KWI.
DEATH COUNT: 2 (Total: 8)
22 Officers and 99 Men remaining
Episode 4 - Punished, As a Boy
Another fun bottle Episode!
Location 3 - Ships in same approx position as June 1847 (70.15, -98.30)
Date: November 23rd 1847
Nighttime - 12h 35 min
Daylight - None
Twilight - 11h 25min
Sunset: 11:47 am - Sunrise: 10:51 am
- William Strong's birthday :)
- We know because it's the last sunrise of the year!
- Evans and Strong die :(
They searched for a long time if it was just before 4 pm when they got the alarm and then they came back in time for last sunrise at 11 am...

Date: November 24th 1847 to November 25th 1847
Nighttime - 12h 35 min
Daylight - None
Twilight - 11h 25min
Sunset: N/A - Sunrise: N/A
- Hickey has a communion with Tuunbaq (supposedly next day or so)
- Then Hickey gets evily booped.
DEATH COUNT: 2 + Hickey's postern (Total: 10)
22 Officers and 97 Men remaining
Episode 5 - First Shot the Winner, Lads
More fun in a bottle. These boys are not going far...
Honestly, for this one, the trouble was figuring out how much time had passed. For one, we know it's not yet Christmas because Christmas is, in fact, mentioned in Episode 6 (And Lady Jane's Christmas Pudding, hear hear) as part of the meeting between the officer and there was not yet a cooperation between the Terror Lts and Fitzjames for counting the supplies.
ALSO! That scene where Mr. Wentzell got killed dead over his nail... well, it gave me the feeling that either the review of the crew is not daily or that they've been on Erebus for a short time because 1) Fitzjames doesn't know their names and 2) He has to repeat the instructions about cleanliness... Perhaps they sent the Terrors in waves and not all 50 of them at once.
Other details to be mentionned:
Hickey is not recovered yet and Goodsir suspects he might reopen his wounds from working.
Goodsir has had time to be quite good at speaking inuktitut. Now, he could have had a continuous learning experience from Dr. McDonald since June 47 and before but considering that Dr. McDonald is stationed in Terror and Goodsir in Erebus, I suspect they did not have much time to have a class together...
Finally. Crozier suggests that he would be 2, perhaps, perhaps more... sick from sobering up. He got up just in time for First sunrise (Jan 17th).
So! We can infer that the episode might have spanned over 1 or 2 days (what's with the movement between the ships and the whole Rat Wedding).
My best guess is that the dates for this whole episode would be:
Date: December 14th 1847 to December 18th 1847
Nighttime - 13h 32 min
Daylight - None
Twilight - 11h 28min
Sunset: N/A - Sunrise: N/A
Why December 14th? Because it would be Edward Little's Birthday and I feel like it is appropriate for his character to have his boss send him back to the killing cold for more booze :') (December 16th to December 20th seems more likely but...)

This would give Crozier a full month to recover from sobering up and 22 days for Goodsir to learn inuktitut (impressive!), for Hickey backside to feel better and for Fitzjames to NOT learn the name of his new Terrors.
DEATH COUNT: 3 + Blanky's leg (Total: 13)
22 Officers and 94 Men remaining
That's it for now. I'll do the last 5 episodes soonish...
Conclusion to the first sets of episode: Sunsets and Sunrises were whacky in June 1847 but, so far, distance and travel times make good sense. If the accuracy holds up until episode 10, we might be able to have a pretty good idea of what, when and where everything happened in episodes 6 through 10.
#The Terror#The Terror AMC#Reference#The Terror Timeline#19th century dead sailors#At least now it's written somewhere that is not 120301923 word files...#Might need later editing#Super duper long post
51 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hon. Emma (Crewe) Cunliffe, later Emma Cunliffe-Offley
Artist: Thomas Lawrence (British, 1769-1830)
Date: c. 1809-1830
Medium: Oil on canvas
Collection: The Huntington Library, Art Museum, and Botanical Gardens, San Marino, CA, United States
Hon. Emma (Crewe) Cunliffe, later Emma Cunliffe-Offley British, 1780 - 1850
Elizabeth Emma Crewe was born February 15, 1780, the only surviving daughter of John Crewe (1742-1829) of Crewe Hall, Cheshire, and his wife Frances Anne Greville Crewe (1744-1818). Her father was created 1st Baron Crewe in 1806 in recognition of loyal service to the Whig party during forty-eight years as a member of parliament. But it was her mother's legendary beauty, intelligence, and political zeal that attracted a galaxy of political and cultural luminaries to the family circle.
As a young girl, Emma Crewe garnered high praise from Fanny Burney, who found her "extremely well bred, sensible, attentive, & intelligent" and "promising to resemble mentally her charming Mother." She delighted in music and often performed as a singer at social gatherings. Numerous contemporary accounts attest to her considerable ability.
On March 16, 1809 the painter Thomas Lawrence reported to a friend that Emma Crewe had refused a marriage proposal from Sir W.W. Wynne. One month later, on April 21, 1809, she married Foster Cunliffe (1782-1832) of Acton Park, Wrexham, elder son of Sir Foster Cunliffe (1755-1834), 3rd Baronet, and his wife Harriet. Having no children of their own, she and her husband later assumed responsibility for raising their young niece, the Hon. Annabella Crewe (1814-1874), daughter of Emma's elder brother John, 2nd Baron Crewe (1772-1835).
1829, on inheriting the property of Madeley, Staffordshire, her husband adopted the surname Offley, by which her own family had been known prior to the early eighteenth century. Following her husband's death on April 19, 1832, Emma Cunliffe-Offley spent several years traveling with her niece in Germany, Austria, and Italy. She returned briefly to England on the death of her mother in December 1835, when it was observed that she would have perished from grief, had it not been for the affectionate support of her niece. It was to Annabella that Emma Cunliffe-Offley left the present painting (together with furnishings at Madeley and at her house in Upper Brook Street) when she died on February 15, 1850.
#portrait#woman#painting#oil on canvas#british culture#three quarters length#white empire dress#white lace hood#gold mantle#dog#landscape#thomas lawrence#british painter#british art#british history#artwork#european art
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Suggested song
youtube
"The Frozen Logger" The Weavers, 1951
"The Frozen Logger" was originally written and performed in 1929 by Jim Stevens (the man who popularized the folk legend Paul bunyan in his 1925 book "Paul Bunyan"
for his program on the ABC seattle network "The Histories of Paul Bunyan"
here's a segment of Jim Stevens talking about that himself:

Oregon Historical Quarterly Vol. 50, No. 4 (Dec., 1949) pp.235-242
it's possible that the song was performed by Ivar Haglund (notable for his prolific seafood themed songs and clam restaurant) in the early to mid 1940s on his radio show "Around the Sound" where he would sing folk music for 15 minutes, and I found a couple sources listing him as either the copyright owner of the song, or the writer (he did not write the song). He was friends with Jim Stevens, and it's likely that Stevens taught him the song.


Radio Daily, July 1944 and KJR flyer, 1942
Many secondhand sources mentioned that "The Frozen Logger" was based on an old tune or an old ballad, with words that were originally written by Jim Stevens, including Jim Stevens himself though he's not specific. I think i might be the first person ever to point out that the ballad it was based on belongs to the folk song family of "The Unfortunate Rake"/ "The Unfortunate Lad" (recorded here in the 1960s and performed by A.L. Lloyd) it has a similar story structure, similar characters, similar rhymes, and similar composition.
in " 'The Unfortunate Rake' and His Descendants" by Kenneth Lodewick, the original song is dated as being from ireland in 1790, and one of its earliest printings was in England in 1850 as a folk ballad

as you might be able to guess if you're familiar with cowboy ballads, this song is also the origin of "Streets of Laredo" or "The cowboys lament" which emerged in the late 1800s from cowhand workers. A cowhand in the late 1870s named Frank H. Maynard has claimed to write the song in 1876 and published his version in "Cowboy's Lament: A Life on the Open Range" in 1911 after it was published in Alan Lomax's "Cowboy Songs and Other Frontier Ballads" in 1910. in my opinion, i think this song could have multiple origins.
the oldest recording i could find was by Harry McClintock in 1928
as an aside, there was also ANOTHER lumberjack version of the song collected by John C. French called "The Wild Lumberjack" from Pennsylvania logging camps dated between 1870-1904/1905. performed here by Kenneth S Goldstein (1960s). This song isn't the origin of "The Frozen Logger" but it's interesting that there are two songs like this.
I believe that "The Frozen Logger" is an adaptation from the cowboy version. Jim Stevens grew up in Idaho and worked in Montana (where he mentions learning many songs) and in 1959, he gave an interview with Ivar Harglund about how he used traditional folk and country music and created new and topical lyrics for the Keep Washington Green Campaign in the 1940s
The first ever publishment and recording (That I could find) of "The Frozen Logger" was in 1947 by Earl Robinson in his Keynote Album, commented upon by the Chicago star by Raeburn Flerlage that same year.

The Chicago Star (Chicago, III.) April 5, 1947 (p.13). Library of Congress
Pete seeger, one of the Weavers, was (for some reason that escapes me) friends with Ivar Haglund (who was friends with Jim Stevens) and, like with the song "the Old Settler" , it is likely that Haglund taught the song to Pete Seeger who then, with the rest of the Weavers, performed it in 1951, popularizing the song.
for @slowtraincumming
#Youtube#Jim Stevens#ivar haglund#harry Mcclintock#alan lomax#pete seeger#the weavers#Frank H Maynard#paul bunyan#cowboy ballads#traditional folk#folk history#american folk#the unfortunate rake#american history#folklore#oregon#Washington#american folk revival#folk#suggested songs
13 notes
·
View notes
Note
Has there ever been a time when we haven't had a vice president?
John Adams was sworn in as our first Vice President in 1789 and in the 234 years since then, we've gone without a VP for 37 years and 290 days.
Until the ratification of the Twenty-Fifth Amendment, there was no mechanism for filling a vacancy in the Vice Presidency, so in several instances we've gone almost entire Presidential terms without a Vice President.
7 Vice Presidents Died In Office: •George Clinton (Jefferson's second VP & Madison's first VP), died April 20, 1812, leaving the Vice Presidency vacant for 318 days. •Elbridge Gerry (Madison's second VP), died November 23, 1814, leaving a vacancy for 2 years, 101 days. •William Rufus DeVane King (Pierce's VP), died April 18, 1853, leaving a vacancy for 3 years, 320 days. •Henry Wilson (Grant's second VP), died November 22, 1875, leaving a vacancy for 1 year, 102 days. •Thomas A. Hendricks (Cleveland's first VP), died November 24, 1885, leaving a vacancy for 3 years, 99 days. •Garret A. Hobart (McKinley's first VP), died November 21, 1899, leaving a vacancy for 1 year, 103 days. •James S. Sherman (Taft's VP), died October 30, 1912, leaving a vacancy for 125 days.
2 Vice Presidents Resigned: •John C. Calhoun (VP under John Quincy Adams and Jackson's first VP), resigned on December 28, 1832, leaving a vacancy for 66 days. •Spiro Agnew (Nixon's first VP), resigned on October 10, 1973, leaving a vacancy for 57 days.
9 Vice Presidents Succeeded to the Presidency: •John Tyler (William Henry Harrison's VP), assumed office upon President Harrison's death on April 4, 1841, leaving a VP vacancy for 3 years, 333 days. •Millard Fillmore (Taylor's VP), assumed office upon President Taylor's death on July 9, 1850, leaving a VP vacancy for 2 years, 238 days. •Andrew Johnson (Lincoln's second VP), assumed office upon President Lincoln's death on April 15, 1865, leaving a VP vacancy for 3 years, 323 days. •Chester Arthur (Garfield's VP), assumed office upon President Garfield's death on September 19, 1881, leaving a VP vacancy for 3 years, 166 days. •Theodore Roosevelt (McKinley's second VP), assumed office upon President McKinley's death on September 14, 1901, leaving a VP vacancy for 3 years, 171 days. •Calvin Coolidge (Harding's VP), assumed office upon President Harding's death on August 2, 1923, leaving a VP vacancy for 1 year, 214 days. •Harry S. Truman (FDR's third VP), assumed office upon President Roosevelt's death on April 12, 1945, leaving a VP vacancy for 3 years, 283 days. •Lyndon B. Johnson (JFK's VP), assumed office upon President Kennedy's death on November 22, 1963, leaving a VP vacancy for 1 year, 59 days. •Gerald Ford (Nixon's second VP), assumed office upon President Nixon's resignation on August 9, 1974, leaving a VP vacancy for 132 days.
Only two Vice Presidential vacancies have been filled under the provisions of the 25th Amendment. Gerald Ford was appointed to the Vice Presidency by President Nixon following Spiro Agnew's resignation in October 1973 and was confirmed by Congress in December 1973 (a nominee to fill a Vice Presidential vacancy must be confirmed separately by a majority vote of both chambers of Congress). On August 9, 1974, Nixon resigned as President and Ford succeeded to the White House, leaving the Vice Presidency vacant for the second time in less than a year. President Ford nominated Nelson Rockefeller as Vice President on August 20 and he was confirmed by Congress in December 1974.
#History#Vice Presidency#Vice President of the United States#Vice Presidents#Vice Presidential Vacancies#Constitution#Twenty-Fifth Amendment#Vice Presidential nominees#VPs#VPOTUS#Vice Presidential History#Presidents#Presidency#Presidential History#Presidential Succession
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
The napoleonic marshal‘s children
After seeing @josefavomjaaga’s and @northernmariette’s marshal calendar, I wanted to do a similar thing for all the marshal’s children! So I did! I hope you like it. c: I listed them in more or less chronological order but categorised them in years (especially because we don‘t know all their birthdays). At the end of this post you are going to find remarks about some of the marshals because not every child is listed! ^^“ To the question about the sources: I mostly googled it and searched their dates in Wikipedia, ahaha. Nevertheless, I also found this website. However, I would be careful with it. We are talking about history and different sources can have different dates. I am always open for corrections. Just correct me in the comments if you find or know a trustful source which would show that one or some of the dates are incorrect. At the end of the day it is harmless fun and research. :) Pre 1790
François Étienne Kellermann (4 August 1770- 2 June 1835)
Marguerite Cécile Kellermann (15 March 1773 - 12 August 1850)
Ernestine Grouchy (1787–1866)
Mélanie Marie Josèphe de Pérignon (1788 - 1858)
Alphonse Grouchy (1789–1864)
Jean-Baptiste Sophie Pierre de Pérignon (1789- 14 January 1807)
Marie Françoise Germaine de Pérignon (1789 - 15 May 1844)
Angélique Catherine Jourdan (1789 or 1791 - 7 March 1879)
1790 - 1791
Marie-Louise Oudinot (1790–1832)
Marie-Anne Masséna (8 July 1790 - 1794)
Charles Oudinot (1791 - 1863)
Aimee-Clementine Grouchy (1791–1826)
Anne-Francoise Moncey (1791–1842)
1792 - 1793
Bon-Louis Moncey (1792–1817)
Victorine Perrin (1792–1822)
Anne-Charlotte Macdonald (1792–1870)
François Henri de Pérignon (23 February 1793 - 19 October 1841)
Jacques Prosper Masséna (25 June 1793 - 13 May 1821)
1794 - 1795
Victoire Thècle Masséna (28 September 1794 - 18 March 1857)
Adele-Elisabeth Macdonald (1794–1822)
Marguerite-Félécité Desprez (1795-1854); adopted by Sérurier
Nicolette Oudinot (1795–1865)
Charles Perrin (1795–15 March 1827)
1796 - 1997
Emilie Oudinot (1796–1805)
Victor Grouchy (1796–1864)
Napoleon-Victor Perrin (24 October 1796 - 2 December 1853)
Jeanne Madeleine Delphine Jourdan (1797-1839)
1799
François Victor Masséna (2 April 1799 - 16 April 1863)
Joseph François Oscar Bernadotte (4 July 1799 – 8 July 1859)
Auguste Oudinot (1799–1835)
Caroline de Pérignon (1799-1819)
Eugene Perrin (1799–1852)
1800
Nina Jourdan (1800-1833)
Caroline Mortier de Trevise (1800–1842)
1801
Achille Charles Louis Napoléon Murat (21 January 1801 - 15 April 1847)
Louis Napoléon Lannes (30 July 1801 – 19 July 1874)
Elise Oudinot (1801–1882)
1802
Marie Letizia Joséphine Annonciade Murat (26 April 1802 - 12 March 1859)
Alfred-Jean Lannes (11 July 1802 – 20 June 1861)
Napoléon Bessière (2 August 1802 - 21 July 1856)
Paul Davout (1802–1803)
Napoléon Soult (1802–1857)
1803
Marie-Agnès Irma de Pérignon (5 April 1803 - 16 December 1849)
Joseph Napoléon Ney (8 May 1803 – 25 July 1857)
Lucien Charles Joseph Napoléon Murat (16 May 1803 - 10 April 1878)
Jean-Ernest Lannes (20 July 1803 – 24 November 1882)
Alexandrine-Aimee Macdonald (1803–1869)
Sophie Malvina Joséphine Mortier de Trévise ( 1803 - ???)
1804
Napoléon Mortier de Trévise (6 August 1804 - 29 December 1869)
Michel Louis Félix Ney (24 August 1804 – 14 July 1854)
Gustave-Olivier Lannes (4 December 1804 – 25 August 1875)
Joséphine Davout (1804–1805)
Hortense Soult (1804–1862)
Octavie de Pérignon (1804-1847)
1805
Louise Julie Caroline Murat (21 March 1805 - 1 December 1889)
Antoinette Joséphine Davout (1805 – 19 August 1821)
Stephanie-Josephine Perrin (1805–1832)
1806
Josephine-Louise Lannes (4 March 1806 – 8 November 1889)
Eugène Michel Ney (12 July 1806 – 25 October 1845)
Edouard Moriter de Trévise (1806–1815)
Léopold de Pérignon (1806-1862)
1807
Adèle Napoleone Davout (June 1807 – 21 January 1885)
Jeanne-Francoise Moncey (1807–1853)
1808: Stephanie Oudinot (1808-1893) 1809: Napoleon Davout (1809–1810)
1810: Napoleon Alexander Berthier (11 September 1810 – 10 February 1887)
1811
Napoleon Louis Davout (6 January 1811 - 13 June 1853)
Louise-Honorine Suchet (1811 – 1885)
Louise Mortier de Trévise (1811–1831)
1812
Edgar Napoléon Henry Ney (12 April 1812 – 4 October 1882)
Caroline-Joséphine Berthier (22 August 1812 – 1905)
Jules Davout (December 1812 - 1813)
1813: Louis-Napoleon Suchet (23 May 1813- 22 July 1867/77)
1814: Eve-Stéphanie Mortier de Trévise (1814–1831) 1815
Marie Anne Berthier (February 1815 - 23 July 1878)
Adelaide Louise Davout (8 July 1815 – 6 October 1892)
Laurent François or Laurent-Camille Saint-Cyr (I found two almost similar names with the same date so) (30 December 1815 – 30 January 1904)
1816: Louise Marie Oudinot (1816 - 1909)
1817
Caroline Oudinot (1817–1896)
Caroline Soult (1817–1817)
1819: Charles-Joseph Oudinot (1819–1858)
1820: Anne-Marie Suchet (1820 - 27 May 1835) 1822: Henri Oudinot ( 3 February 1822 – 29 July 1891) 1824: Louis Marie Macdonald (11 November 1824 - 6 April 1881.) 1830: Noemie Grouchy (1830–1843) —————— Children without clear birthdays:
Camille Jourdan (died in 1842)
Sophie Jourdan (died in 1820)
Additional remarks: - Marshal Berthier died 8.5 months before his last daughter‘s birth. - Marshal Oudinot had 11 children and the age difference between his first and last child is around 32 years. - The age difference between marshal Grouchy‘s first and last child is around 43 years. - Marshal Lefebvre had fourteen children (12 sons, 2 daughters) but I couldn‘t find anything kind of reliable about them so they are not listed above. I am aware that two sons of him were listed in the link above. Nevertheless, I was uncertain to name them in my list because I thought that his last living son died in the Russian campaign while the website writes about the possibility of another son dying in 1817. - Marshal Augerau had no children. - Marshal Brune had apparently adopted two daughters whose names are unknown. - Marshal Pérignon: I couldn‘t find anything about his daughters, Justine, Elisabeth and Adèle, except that they died in infancy. - Marshal Sérurier had no biological children but adopted Marguerite-Félécité Desprez in 1814. - Marshal Marmont had no children. - I found out that marshal Saint-Cyr married his first cousin, lol. - I didn‘t find anything about marshal Poniatowski having children. Apparently, he wasn‘t married either (thank you, @northernmariette for the correction of this fact! c:)
#Marshal‘s children calendar#literally every napoleonic marshal ahaha#napoleonic era#Napoleonic children#I am not putting all the children‘s names into the tags#Thank you no thank you! :)#YES I posted it without double checking every child so don‘t be surprised when I have to correct some stuff 😭#napoleon's marshals#napoleonic
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
November 27, 2024
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
NOV 28
Thanksgiving is the quintessential American holiday…but not for the reasons we generally remember.
The Pilgrims and the Wampanoags did indeed share a harvest celebration together at Plymouth in fall 1621, but that moment got forgotten almost immediately, overwritten by the long history of the settlers’ attacks on their Indigenous neighbors.
In 1841 a book that reprinted the early diaries and letters from the Plymouth colony recovered the story of that three-day celebration in which ninety Indigenous Americans and the English settlers shared fowl and deer. This story of peace and goodwill among men who by the 1840s were more often enemies than not inspired Sarah Josepha Hale, who edited the popular women’s magazine Godey’s Lady's Book, to think that a national celebration could ease similar tensions building between the slave-holding South and the free North. She lobbied for legislation to establish a day of national thanksgiving.
And then, on April 12, 1861, southern soldiers fired on Fort Sumter, a federal fort in Charleston Harbor, and the meaning of a holiday for giving thanks changed.
Southern leaders wanted to destroy the United States of America and create their own country, based not in the traditional American idea that “all men are created equal,” but rather in its opposite: that some men were better than others and had the right to enslave their neighbors. In the 1850s, convinced that society worked best if a few wealthy men ran it, southern leaders had bent the laws of the United States to their benefit, using it to protect enslavement above all.
In 1860, northerners elected Abraham Lincoln to the presidency to stop rich southern enslavers from taking over the government and using it to cement their own wealth and power. As soon as he was elected, southern leaders pulled their states out of the Union to set up their own country. After the firing on Fort Sumter, Lincoln and the fledgling Republican Party set out to end the slaveholders’ rebellion.
The early years of the war did not go well for the U.S. By the end of 1862, the armies still held, but people on the home front were losing faith. Leaders recognized the need both to acknowledge the suffering and to keep Americans loyal to the cause. In November and December, seventeen state governors declared state thanksgiving holidays.
New York governor Edwin Morgan’s widely reprinted proclamation about the holiday reflected that the previous year “is numbered among the dark periods of history, and its sorrowful records are graven on many hearthstones.” But this was nonetheless a time for giving thanks, he wrote, because “the precious blood shed in the cause of our country will hallow and strengthen our love and our reverence for it and its institutions…. Our Government and institutions placed in jeopardy have brought us to a more just appreciation of their value.”
The next year, Lincoln got ahead of the state proclamations. On July 15 he declared a national day of Thanksgiving, and the relief in his proclamation was almost palpable. After two years of disasters, the Union army was finally winning. Bloody, yes; battered, yes; but winning. At Gettysburg in early July, Union troops had sent Confederates reeling back southward. Then, on July 4, Vicksburg had finally fallen to U. S. Grant’s army. The military tide was turning.
President Lincoln set Thursday, August 6, 1863, for the national day of Thanksgiving. On that day, ministers across the country listed the signal victories of the U.S. Army and Navy in the past year and reassured their congregations that it was only a matter of time until the United States government put down the southern rebellion. Their predictions acknowledged the dead and reinforced the idea that their sacrifice had not been in vain.
In October 1863, President Lincoln declared a second national day of Thanksgiving. In the past year, he declared, the nation had been blessed.
In the midst of a civil war of unequaled magnitude and severity, he wrote, Americans had maintained their laws and their institutions and had kept foreign countries from meddling with their nation. They had paid for the war as they went, refusing to permit the destruction to wreck the economy. Instead, as they funded the war, they had also advanced farming, industry, mining, and shipping. Immigrants had poured into the country to replace men lost on the battlefield, and the economy was booming. And Lincoln had recently promised that the government would end slavery once and for all. The country, he predicted, “with a large increase of freedom,” would survive, stronger and more prosperous than ever. The president invited Americans “in every part of the United States, and also those who are at sea, and those who are sojourning in foreign lands” to observe the last Thursday of November as a day of Thanksgiving.
In 1863, November’s last Thursday fell on the 26th. On November 19, Lincoln delivered an address at the dedication of a national cemetery at Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. He reached back to the Declaration of Independence for the principles on which he called for Americans to rebuild the severed nation:
”Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.”
Lincoln urged the crowd to take up the torch those who fought at Gettysburg had laid down. He called for them to “highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain—that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom—and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.”
The following year, Lincoln proclaimed another day of Thanksgiving, this time congratulating Americans that God had favored them not only with immigration but also with the emancipation of formerly enslaved people. “Moreover,” Lincoln wrote, “He has been pleased to animate and inspire our minds and hearts with fortitude, courage, and resolution sufficient for the great trial of civil war into which we have been brought by our adherence as a nation to the cause of freedom and humanity, and to afford to us reasonable hopes of an ultimate and happy deliverance from all our dangers and afflictions.”
In 1861, Americans went to war to keep a cabal from taking control of the government and turning it into an oligarchy. The fight against that rebellion seemed at first to be too much for the nation to survive. But Americans rallied and threw their hearts into the cause on the battlefields even as they continued to work on the home front for a government that defended democracy and equality before the law.
And in 1865, at least, they won.
Happy Thanksgiving.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Minot’s Ledge Lighthouse, Scituate, MA

The Minot’s Ledge Lighthouse was built in 1849, and first lit January 1st, 1850. The frequent storms of the area proved dangerous to the keepers throughout first year and the light eventually fell to the Minot’s Light Storm in April 1851, but was rebuilt in 1860. On May 1st, 1894 a second-order fresnel lens was installed and in 1947 was replaced with a third-order fresnel lens. The Minot’s Ledge Light stands at 85 feet tall and can be seen from 15 miles away.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Thanksgiving History
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
November 23, 2023
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
Thanksgiving is the quintessential American holiday…but not for the reasons we generally remember.
The Pilgrims and the Wampanoags did indeed share a harvest celebration together at Plymouth in fall 1621, but that moment got forgotten almost immediately, overwritten by the long history of the settlers’ attacks on their Indigenous neighbors.
In 1841 a book that reprinted the early diaries and letters from the Plymouth colony recovered the story of that three-day celebration in which ninety Indigenous Americans and the English settlers shared fowl and deer. This story of peace and goodwill among men who by the 1840s were more often enemies than not inspired Sarah Josepha Hale, who edited the popular women’s magazine Godey’s Lady’s Book, to think that a national celebration could ease similar tensions building between the slave-holding South and the free North. She lobbied for legislation to establish a day of national thanksgiving.
And then, on April 12, 1861, southern soldiers fired on Fort Sumter, a federal fort in Charleston Harbor, and the meaning of a holiday for giving thanks changed.
Southern leaders wanted to destroy the United States of America and create their own country, based not in the traditional American idea that “all men are created equal,” but rather in its opposite: that some men were better than others and had the right to enslave their neighbors. In the 1850s, convinced that society worked best if a few wealthy men ran it, southern leaders had bent the laws of the United States to their benefit, using it to protect enslavement above all.
In 1860, northerners elected Abraham Lincoln to the presidency to stop rich southern enslavers from taking over the government and using it to cement their own wealth and power. As soon as he was elected, southern leaders pulled their states out of the Union to set up their own country. After the firing on Fort Sumter, Lincoln and the fledgling Republican Party set out to end the slaveholders’ rebellion.
The early years of the war did not go well for the U.S. By the end of 1862, the armies still held, but people on the home front were losing faith. Leaders recognized the need both to acknowledge the suffering and to keep Americans loyal to the cause. In November and December, seventeen state governors declared state thanksgiving holidays.
New York governor Edwin Morgan’s widely reprinted proclamation about the holiday reflected that the previous year “is numbered among the dark periods of history, and its sorrowful records are graven on many hearthstones.” But this was nonetheless a time for giving thanks, he wrote, because “the precious blood shed in the cause of our country will hallow and strengthen our love and our reverence for it and its institutions…. Our Government and institutions placed in jeopardy have brought us to a more just appreciation of their value.”
The next year, Lincoln got ahead of the state proclamations. On July 15 he declared a national day of Thanksgiving, and the relief in his proclamation was almost palpable. After two years of disasters, the Union army was finally winning. Bloody, yes; battered, yes; but winning. At Gettysburg in early July, Union troops had sent Confederates reeling back southward. Then, on July 4, Vicksburg had finally fallen to U. S. Grant’s army. The military tide was turning.
President Lincoln set Thursday, August 6, 1863, for the national day of Thanksgiving. On that day, ministers across the country listed the signal victories of the U.S. Army and Navy in the past year and reassured their congregations that it was only a matter of time until the United States government put down the southern rebellion. Their predictions acknowledged the dead and reinforced the idea that their sacrifice had not been in vain.
In October 1863, President Lincoln declared a second national day of Thanksgiving. In the past year, he declared, the nation had been blessed.
In the midst of a civil war of unequaled magnitude and severity, he wrote, Americans had maintained their laws and their institutions and had kept foreign countries from meddling with their nation. They had paid for the war as they went, refusing to permit the destruction to cripple the economy. Instead, as they funded the war, they had also advanced farming, industry, mining, and shipping. Immigrants had poured into the country to replace men lost on the battlefield, and the economy was booming. And Lincoln had recently promised that the government would end slavery once and for all. The country, he predicted, “with a large increase of freedom,” would survive, stronger and more prosperous than ever. The president invited Americans “in every part of the United States, and also those who are at sea, and those who are sojourning in foreign lands” to observe the last Thursday of November as a day of Thanksgiving.
In 1863, November’s last Thursday fell on the 26th. On November 19, Lincoln delivered an address at the dedication of a national cemetery at Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. He reached back to the Declaration of Independence for the principles on which he called for Americans to rebuild the severed nation:
”Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.”
Lincoln urged the crowd to take up the torch those who fought at Gettysburg had laid down. He called for them to “highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain—that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom—and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.”
The following year, Lincoln proclaimed another day of Thanksgiving, this time congratulating Americans that God had favored them not only with immigration but also with the emancipation of formerly enslaved people. “Moreover,” Lincoln wrote, “He has been pleased to animate and inspire our minds and hearts with fortitude, courage, and resolution sufficient for the great trial of civil war into which we have been brought by our adherence as a nation to the cause of freedom and humanity, and to afford to us reasonable hopes of an ultimate and happy deliverance from all our dangers and afflictions.”
In 1861, Americans went to war to keep a cabal from taking control of the government and turning it into an oligarchy. The fight against that rebellion seemed at first to be too much for the nation to survive. But Americans rallied and threw their hearts into the cause on the battlefields even as they continued to work on the home front for a government that defended democracy and equality before the law.
And in 1865, at least, they won.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Thanksgiving history#Heather Cox Richardson#Letters from An American#American History#Civil war#Thanksgiving#Abraham Lincoln
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
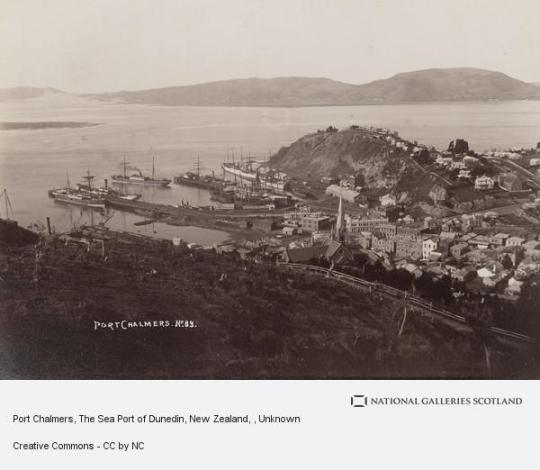





On March 23rd 1848, the Free Church of Scotland settlement at New Edinburgh, New Zealand was founded, it is known today as Dunedin.
It was the poet’s uncle, Rev Thomas Burns, who was among the first settlers to arrive in Dunedin, the Gaelic for Edinburgh, having been appointed by the Free Church to lead a new Presbyterian settlement in the South Pacific
One passenger on the John Wickliffe, the fist ship to carry Scottish settlers to the South Island of New Zealand, wrote in his diary: “All seemed pleased and called it a goodly land – Port Chalmers and around is truly beautiful – rich in scenery – its slopes and shores are fertile, and wooded to the water’s edge.”
Every year in Dunedin, the arrival of these first settlers from Scotland is marked by Otago Anniversary Day, the public holiday falling this year on Monday just gone.
A second boat sent by the Otago Association, founded by the Free Church to broker land sales in South Island for its followers, arrived on April 15 with more than 200 people on board. They had spent 114 days at sea since leaving Greenock.
On board were people such as Adam James, 25, a boatbuilder; James Blackie, 21, a school teacher, James Brown, 23, a calico printer and Mary Pollok, 19, a servant.
By the end of the 1850s, around 12,000 Scots had joined them in this new flourishing city, many from the industrial lowlands.
Artisans, small traders and industrial workers were to make up a third of all Scottish migrants to New Zealand with almost 70 per cent of this group coming from the Edinburgh and Glasgow area.
A number left Paisley in the early 1840s when its weaving industry was in trouble with the south part of the city to become known as “Little Paisley”.
It was George Rennie MP, born in East Lothian, who first proposed a Scottish settlement in 1842 when he declared “We shall found a New Edinburgh at the Antipodes that shall one day rival the old.”
Chief operators of the church-led plan included William Cargill, a former British Army captain who commanded the John Wickliffe and became the first superintendent of Otago.
Edinburgh solicitor John McGlashan, became the Otago scheme’s chief organiser and promoter who commandeered residents for the new colony and organised ships.
His office at 27 South Hanover Street was open 10 hours a day as people turned up at his door to organise their passage.
Conditions were tough on arrival with relentless hard graft required to transform mud and bush into even the most primitive settlement. A number of wattle and daub cottages were constructed with the place dubbed “Mud-edin” given the coarse conditions.
Still, the Free Church, in an 1853 publication, had the highest praise of the new Scots residents who were “mostly of the labouring classes who had the aim of becoming landowners.”
The author noted the “very high character” of the residents and the “very serious regard to their religious duties.”
The extreme piousness of the settlement is made startling clear.
“The silent religious aspect of our Sabbath, the solemn seriousness, the death-like stillness, and the reverential attention in the house of God strike every stranger and are unequalled by anything of my experience,” the account added.
Despite the growth of Dunedin, the Otago Association folded in 1852 after repeatedly failing to meet is sales targets with its assets and liabilities taken over by the British Government.
McGlashan took a ship to join the settlers in Otago. He and Captain Cargill were to become major players in the governance of the region with the moral authority delivered by Rev Burns, a foundation chancellor of the University of Otago who some disliked for his heavy handed puritanical ways. Anglicans were referred to as “Little Enemy” by the Ayrshire-born minister.
As Tom Devine noted in To the Ends of the Earth, one anonymous correspondent to the New Zealand Otago Times, writing under the pseudonym a Staunch Englishman, described the Scots settlers as a “mean, close, bigoted, porridge-eating” lot who were prone to “minding the sixpences.”
The legacy of those first settlers is, however, ample. Otago Boys’ High School was set up in 1864, the University of Otago in 1869 and Otago Girls’ High School, one of the first state-run schools of its type in the world, opened in 1871.
John McGlashan College, Dunedin’s Presbyterian boys’ school, was founded in 1918 from a bequest to the Church by McGlashan’s daughters.
The stiff presbyterian tone of Dunedin is also said to have spurred a “creative rebellion” with works by Dunedin poet James K Baxter considered among the country’s finest.
Today, whisky, pipe band sand the city’s own Haggis Ceremony continue to mark the impact of those first Scottish settlers who arrived.
Shops on the main street stock Dunedin tartan, tweeds and Scottie dog trinkets and sign posts point to places such as Leith Valley, Corstorphine, Musselburgh and Calton Hill.
Bars pride themselves on their selections of fine malts, churches have an air of architectural familiarity and the municipal chambers looks as if it could have been transported from any Scottish town. A statue of Robbie Burns stands in the main square.
Mark Twain, after visiting Dunedin in 1895, wrote of them: “The people are Scotch. They stopped here on their way from home to heaven thinking they had arrived.”
For millions of Scots scattered worldwide, Scotland remains the homeland. It's the place they look towards for inspiration, with affection, or with an air ticket to renew that sense of Scottish identity. The internet has made the world a lot smaller for us all, which is why many enjoy the posts here, it gives them a wee sense of belonging, even if it less than a dram of Scottish blood you have flowing through you.
8 notes
·
View notes
Photo










The City of San Francisco was incorporated on April 15, 1850.
#Yerba Buena Gardens#Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary#San Francisco#USA#United States Penitentiary Alcatraz Island#Transamerica Pyramid#architecture#Powell Street#Golden Gate Bridge#Chinatown#Telegraph Hill#Coit Tower#incorporated#15 April 1850#anniversary#US history#original photography#summer 2017#2012#cityscape#tourist attraction#landmark#street scene
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
For Half A Century, Cincinnati Goldfish Thrived Because Of Our Untreated Water
Just south of the Mount Airy water towers lies a large, grass-covered lawn with a small playground tucked away in the corner. No historic marker identifies this plot, although it is an important site in the history of a long-forgotten Cincinnati industry. For fifty years, up until the 1970s, this meadow was occupied by a dozen ponds filled with goldfish because Cincinnati was among the largest producers of goldfish in the United States. It's true. Here is the Cincinnati Enquirer [4 August 1929]:
“Few of the people who buy fish realize that Cincinnati is one of the centers for goldfish breeding. More than 100 goldfish breeding ponds surround Cincinnati within a radius of 15 miles. Many of these are transient, the owner raising stock during the season and draining the pond during the winter, but several of them almost outdistance Japanese rivals in quality and output.”
It was estimated that Cincinnati pet stores sold nearly 5,000 goldfish every day in the late 1920s, most locally raised. Twenty years later, according to the Cincinnati Post [30 April 1946] Maryland was the largest producer of goldfish in the United States, but second place was held by southwest Ohio and southeast Indiana. At that time, according to the Post, there were approximately 50 permanent goldfish breeding ponds in the Cincinnati region.
Goldfish were first introduced to Cincinnati in the later 1850s and Cincinnatians soon became avid collectors. The first vendors to sell goldfish in Cincinnati were florists who appeared to think of these colorful fish as an adjunct to home décor, sort of a living bouquet, if you will.
Goldfish thrived in Cincinnati because our water supply was pumped unfiltered and untreated straight from the Ohio River. Cincinnati goldfish fanciers developed the opinion that goldfish never needed to be fed, because Cincinnati’s water was so loaded with worms and other tiny critters. A local newspaper, the Star In The West [19 November 1859] chastised those who did not feed their goldfish:
“Every other pet is expected to eat, but these gold-carp are expected to subsist on – nothing! ‘But don’t they eat the animalculae?’ Nonsense! Give them a few small earthworms, or anglers’ gentles, twice a week.”
Despite such advice, the belief persisted that Ohio River water contained enough living matter to feed our finny friends. The Cincinnati Gazette [17 March 1875] in a column about goldfish, insisted that “small worms, such as are common to the water, suffice for their food in general.” It appears that our ancestors were perfectly happy to quaff tap water in which small worms (or animalculae) were common!

Wormy or not, Ohio River water was clear enough to cause household hazards, as the Cincinnati Star [8 January 1875] reported:
“A goldfish globe, filled with water, hanging in the window of a house, set the casement on fire one morning recently; the globe acting as a burning glass. Had the family been absent, a conflagration might have resulted, and its origin unaccountable.”
A decade later, goldfish had become big business in Cincinnati as proved by one of the regular Ohio River floods. Hugo Mulertt was a florist with shops downtown on Race Street and on Freeman Avenue in the West End. Like many Cincinnati florists, he sold a lot of goldfish along with bouquets and nosegays. He operated his own fishery out near Spring Grove Cemetery and, according to the Cincinnati Enquirer [24 February 1884], lost most of his exotic stock when the floodwaters that year overwhelmed his fish ponds.
“The backwater from Millcreek flooded Hugo Mulertt’s gold-fish nursery out back of Spring Grove and carried away some thousands of fish of all kinds – Japanese fringe-tails, telescopes, double-tails, hog-noses, tumblers, piebalds, mottled beauties, and a hundred other rare kinds that you and I have never heard of.”
With all these delectable and collectable fish swimming around in open ponds, it is no surprise that Cincinnati goldfish-mongers encountered a veritable menagerie of critters gathering to eat up their profits. Mr. Mulertt kept a rifle to shoot hungry snakes, but listed among his enemies geese, herons, ducks, turtles, muskrats, cranes, kingfishers and crawdads. The crawdads, he said, didn’t eat his fish, but their burrows undermined his ponds.
Robert C. Dolle, whose grandfather excavated those Mount Airy ponds, contended with mud turtles, kingfishers, herons and mink. At Coldstream Farms in Northern Kentucky, the animals responsible for “shrinkage” included mink, snakes, mice, rats, racoons, cats and even insects. According to the Enquirer [4 August 1929]:
“A certain insect will catch a fish between the dorsal fin and the tail, leaving a small mark which is quickly filled with silver scales. These spots are often seen in aquaria.”
The Schlosser family, who managed Coldstream’s fishery for nearly a century, killed as many as a dozen mink every year to save their exotic goldfish.
And let’s not forget human predation. The late 1930s brought a fad that you can blame on your grandparents – goldfish swallowing. Medical experts quoted in the Cincinnati Post [8 April 1939] advised collegiate faddists not to swallow too many live goldfish at all. Or, if peer pressure overwhelmed them, to scale the little suckers first.
In addition to the Schlossers in Fort Mitchell and Mr. Dolle in Mount Airy, there was also a large fishery on Compton Road in Wyoming. That operation was owned by Dr. Charles Goosmann, a radiologist with offices on Seventh Street. In November 1930, Dr. Goosmann learned that predators included humans because a thief or thieves walked off with more than 1,500 goldfish from his breeding pools.
How would one put a value on that theft? This proved to be more than an academic question when tax time rolled around. In 1958, the Ohio Board of Tax Appeals considered the case of James C. Denier, who had taken over Mr. Dolle’s Mount Airy ponds while maintaining a large breeding pond on Poole Road in Colerain Township. According to the Cincinnati Enquirer [25 July 1958], the state tax commissioner just “guesstimated” the value of goldfish in Mr. Denier’s many ponds and decided that the tax bills for 1953 and 1954, amounting to less than ten dollars in total, were wildly out of whack and determined that Mr. Denier owed $24,000 for 1953 and $42,000 for 1954. Mr. Denier appealed and managed to get his tax bill lowered to $1,700 for each year.
By then, the market for goldfish had softened considerably. Cincinnati breeders turned their ponds into sheep pastures. Sheep grazed among the Denier ponds in Mount Airy for a decade or more until the City of Cincinnati acquired the property and drained the goldfish ponds in 1977. Despite an appeal by the Mount Airy Town Council for ideas, the land remains mostly vacant.

8 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Pearl Incident in 1848 was the single largest recorded escape attempt by enslaved people in US history. On April 15, 1848, 77 enslaved attempted to flee DC by sailing away on a schooner called The Pearl. They planned to sail south along the Potomac River and north up the Chesapeake Bay and to the free state of New Jersey.
The mass escape attempt was organized by both Black and white abolitionists in DC. Paul Jennings, the former enslaved of President James Madison, and Paul Edmonson, whose wife and 14 children were still enslaved, were the initiators of the escape. They enlisted the help of William Chaplin, a DC white abolitionist who in turn contacted Philadelphia abolitionist Daniel Drayton, Captain and owner of The Pearl, and pilot Edward Sayres. Abolitionist Gerrit Smith of New York provided financial backing for the escape.
With the help of numerous members of DC’s free Black community, slipped away from their places of work or residence on the evening of April 15 and made their way to The Pearl at a wharf on the Potomac. They boarded the ship which set sail. After realizing their enslaved and The Pearl were missing, sent out an armed posse of 35 men on the steamboat Salem. They caught up with The Pearl near Point Lookout, Maryland, boarded the vessel, and took the enslaved and the ship back.
An angry mob formed and for the next three days lashed out at suspected white abolitionists and the entire free Black community of DC in what would be known as the first DC Riot. The mob focused much of its wrath on Gamaliel Bailey and his antislavery newspaper The New Era.
Once the DC Riot ended, the slaveowners sold the attempted escapees to slave traders from Georgia and Louisiana, who took them to New Orleans. Two of the Edmonson children, Mary and Emily, were purchased and freed.
A provision of the Compromise of 1850 enacted by Congress ended the slave trade in DC although it did not abolish slavery. The Pearl incident is said to have inspired Harriet Beecher Stowe in her writing of Uncle Tom’s Cabin. #africanhistory365 #africanexcellence
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Religion of Ancient Greece by J. E. Harrison


The Religion of Ancient Greece The Religion of Ancient Greece by J. E. Harrison. The Religion of Ancient Greece is an inquiry into the nature of Greek religion ; an attempt to discover its origin how it resembles and how it differs from other religions. Especially its object is to ask and, if it may be, to answer the question : " What in Greek religion is characteristically Greek ?" From the book: "Plato says that the earliest inhabitants of Greece, like many of the barbarians, had for their gods the sun, moon, earth, the stars, and heaven, and that these were called gods because they were always 'running about' (theein = run). His statement as to the existence of these primitive gods is instructive, though his etymology is only amusing. The word for gods, 'theoi,' is more probably merely a variation of a root, meaning, in the different derivatives, 'prayer,' 'spell,' 'sacred,' or 'taboo' (festus). The theos is the being at the back of these magical or religious processes; the being whose existence is implied by them; the sanction of the prayer, the spell, the curse, the taboo. The study of comparative religion shows that man does not at the outset attribute complete personality to the things he worships. Personality comes with the giving of human or animal form. Before complete impersonation, we have 'animism,' when the gods are intangible Things, powerful but not personal, dwelling anywhere, everywhere. These Things are scarcely, in our sense, gods; but they become gods when man enters into relation with them, localizes them, fixes them by some form of worship." This book was first published London in 1913, download it here:

The religion of ancient Greece (1913) You can buy the print version here: Link
About the author J. E. Harrison
J. E. Harrison, whose full name is Jane Ellen Harrison, was a prominent British classical scholar and linguist. She was born on September 9, 1850, and died on April 15, 1928. Jane Ellen Harrison is best known for her work in the fields of classical studies, archaeology, and anthropology, particularly her research on ancient Greek religion, mythology, and art. One of her most influential works is the book titled "Prolegomena to the Study of Greek Religion," published in 1903. In this book, Harrison explored the origins and development of Greek religious beliefs and practices, emphasizing the role of rituals and symbolism in ancient Greek religion. Her work contributed significantly to the understanding of the connections between ancient Greek art, mythology, and religion. Harrison's approach to studying religion and mythology was groundbreaking for her time. She applied anthropological and sociological methods to the study of ancient cultures, offering new perspectives on the significance of rituals, symbols, and the evolution of religious thought. Overall, Jane Ellen Harrison is remembered as a pioneering figure in the study of classical antiquity, and her writings continue to be influential in the fields of classics and religious studies. Read the full article
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Power of Being a Heretic: The Forgotten Visionary Jane Ellen Harrison on Critical Thinking, Emotional Imagination, and How to Rehumanise the World
If we are to be true and worthy heretics, we need not only new heads, but new hearts, and, most of all, that new emotional imagination… begotten of enlarged sympathies and a more sensitive habit of feeling.
When the Inquisition persecuted Galileo for advancing the rude truth that Earth is not the centre of the universe, the charge against him was heresy—the same charge on which Joan of Arc was burned at the stake for her crusade for political reform. We have had many words for heretics over the epochs—rebels, radicals, freethinkers—but they have always been the ones to dislodge humanity from the stagnation of the status quo, to illuminate our blind spots, dismantle our unexamined biases, and jolt us out of our herd mentality. Without those devoted to seeing reality more clearly and possibility more wildly, we would still live in a world haunted by superstition and governed by dogma.
The power and dignity of this most courageous human mindset is what the pioneering classicist Jane Ellen Harrison (September 9, 1850–April 15, 1928), who brought the culture of Ancient Greece to the modern world, explores in her magnificent essay “Heresy and Humanity,” found in Alpha and Omega (public library) — the out-of-print essay collection that gave us Harrison on the art of growing older, published just as humanity was being dehumanised by its first World War.
Harrison writes:
“The word “heretic” has still about it an emotional thrill—a glow reflected, it may be, from the fires at Smithfield, the ardours of those who were burnt at the stake for the love of an idea.
Heresy, the Greek hairesis, was from the outset an eager, living word. The taking of a city, its expugnatio, is a hairesis; the choosing of a lot in life or an opinion, its electio, is a hairesis; always in the word hairesis there is this reaching out to grasp, this studious, zealous pursuit—always something personal, even passionate… To be a heretic today is almost a human obligation.”
In a sentiment Bertrand Russell would echo in timeless manifesto for freedom of thought, Harrison adds:
“The gist of heresy is free personal choice in act, and specifically in thought—the rejection of traditional faiths and customs.”
A century and a half after Emerson inveighed that “masses are rude, lame, unmade, pernicious in their demands and influence,” she considers what makes heresy so difficult yet so necessary to the health of society:
“All traditional views are held with such tenacity, such almost ferocity, because they belong to the class of views induced, not by individual experience, still less by reason, but by collective, or, as it is sometimes called “herd,” suggestion. This used to be called “faith.” The belief so held may or may not be true; collective suggestion is not in the least necessarily collective hallucination. Mere collective suggestions—that is the interesting point—have the quality of obviousness; they do not issue from the individual, but seem imposed from outside, and ineluctable; they have all the inevitableness of instinctive opinion… Hence they are held with an intensity of emotion far beyond any reasoned conviction. To doubt them is felt to be at once idiocy and irreverence. Inquiry into their rational bases is naturally, and in a sense rightly, resented, because they are not rationally based, though they may be rationally supported. It is by convictions such as this that a society of the homogenous kind—a society based on and held together by uniformity—lives and thrives. To attack them is to cripple and endanger its inmost life.”
Observing that the development of science is what pivoted heresy from damnable to desirable in society, Harrison contrasts sensemaking by empiricism with sensemaking by authority:
“Science classifies, draws ever clearer distinctions; herd-suggestion is always in a haze. Herd-suggestion is all for tradition, authority; science has for its very essence the exercise of free thought. So long as we will not take the trouble to know exactly and intimately, we may not—must not—choose… We must follow custom; we must accept the mandates of [those] who enforce tradition.
[…]
Science opens wide the doors that turned so slowly on tradition’s hinges, and opens them on clean, quiet places where we breathe larger air… It is well to remember our debt to science—our inward and spiritual as well as material debt.”
And yet, Harrison argues, the heretic needs more than science—the heretic needs humanity. She writes:
“Science broke the binding spell of herd-suggestion. For that great boon let us now and ever bless and praise her holy name. She cleared the collective haze, she drew sharp distinctions, appealing to individual actual experience, to individual powers of reasoning. But by neither individual sense—perception nor ratiocination alone do we live. Our keenest emotional life is through the herd, and hence it was that, at the close of the last century, the flame of scientific hope, the glory of scientific individualism that had blazed so brightly, somehow died down and left a strange chill. Man rose up from the banquet of reason and law unfed. He hungered half unconsciously for the herd. It seemed an impasse: on the one side orthodoxy, tradition, authority, practical slavery; on the other science, individual freedom, reason, and an aching loneliness.
[…]
We live now just at the transition moment; we have broken with the old, we have not quite adjusted ourselves to the new. It is not so much the breaking with the old faiths that makes us restless as the living in a new social structure.”
At the root of this new social structure, she observes, is not the old cult of homogeneity but the recognition of individuality, and the diversity of individualities, as the wellspring of vitality and social harmony—“differentiation that would unite, not divide.” With the World War flaming around her, waged on the herd-versus-herd collision of nationalisms and ideologies, she writes:
“Only through and by this organic individuality can the real sense and value of Humanity emerge. We are humane so far as we are conscious or sensitive to individual life. Patriotism is collective herd-instinct; it is repressive of individuality. You feel strongly because you feel alike; you are reinforced by the other homogenous unites; you sing the same song and wave the same flag. Humanity is sympathy with infinite differences, with utter individualism, with complete differentiation, and it is only possible through the mystery of organic spiritual union. We have come, most of us, now, to a sort of physical union by sympathy and imagination. To torture even an enemy’s body would be to us physical pain, physical sickness. There will come the day when to hurt mentally and spiritually will be equally impossible, because the spiritual life will by enhanced sympathy be one. But this union is only possible through that organic differentiation that makes us have need one of the other.”
A generation before Albert Camus, in the midst of the next World War, called for the superhuman duty to “mend what has been torn apart, make justice imaginable again in a world so obviously unjust, give happiness a meaning once,” Harrison concludes:
“In a word, if we are to be true and worthy heretics, we need not only new heads, but new hearts, and, most of all, that new emotional imagination, joint offspring of head and heart which is begotten of enlarged sympathies and a more sensitive habit of feeling. About the moral problem there is nothing mysterious; it is simply the old, old question of how best to live together. We no longer believe in an unchanging moral law imposed from without. We know that a harder incumbency is upon us; we must work out our law from within.”
Noting that we have outgrown the easy shorthand for morality offered by religious dogma, she contours what is asked of us if we are to rehumanise humanity:
“We must adventure a harder and higher spiritual task… a steady and even ardent recognition of the individual life, in its infinite variety, with its infinite interactions. We decline to be ourselves part of an undifferentiated mass; we refuse to deal with others in classes and masses… We are dissatisfied now not only with the herd-sanctions of religion, but with many of those later sanctities of law to which some even emancipated thinkers ascribe a sort of divinity. We feel the inherent savagery of law in that it treats individuals as masses… Yet all the time we know that we can, with spiritual safety, rebel only in so far as we are personally sensitive to the claims of other individual lives that touch our own. The old herd-problem remains of how to live together; and as the union grows closer and more intricate the chances of mutual hurt are greater, and the sensitiveness must grow keener. Others are safe from and with us only when their pain is our pain, their joy ours.”
Couple with E.E. Cummings on the courage to feel, then revisit Albert Camus on what it means to be a rebel, the radical Russian dissident prince Peter Kropotkin on the spirit of revolt, and the pioneering X-ray crystallographer and peace activist Kathleen Lonsdale on moral courage and our personal power in world change.
Source: Maria Popova, themarginalian.org (8th July 2023)
#quote#love#life#humanity#meaning#existential musings#all eternal things#love in a time of...#intelligence quotients#depth perception#understanding beyond thought#essential thinking#perspective matters#the science of things#kind is my love today#tomorrow kind#this is who we are#stands on its own#elisa english#elisaenglish
2 notes
·
View notes