#ziyad al-aly
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
https://twitter.com/coffeeteanxiety/status/1736750299551826127 I’ll stop masking when the world’s leading researchers on Long C0vid do. Prof. Akiko Iwasaki: "I'm still wearing my 😷 everywhere." Michael Peluso, MD: "I'm very strict, actually, about 😷." Ziyad Ai-Aly, MD: "Yes, primarily because of Long C0vid. I don't want Long C0vid."
+
https://twitter.com/sri_srikrishna/status/1736460422499459115 Full of DEEP INSIGHTS ABOUT LONG COVID. At 1:01:15, panelists were asked if they continue to be covid-cautious by wearing masks 😷(even though many at infectious disease conferences no longer do), all three nodded yes with a smile 😃 and they MASK TO AVOID LONG COVID
#covid#long covid#twitter#commentary/opinion#long covid research#science#akiko iwasaki#ziyad al-aly#michael peluso#masking#winter 2023-24
306 notes
·
View notes
Text

ID :
“The burden of disease and disability from Long COVID, when you measure it, is on par with the burden of cancer and heart disease. Even if people emerge unscathed after having the first infection they can still get long covid after reinfection. Not enough people know this fact. The best way to prevent Long COVID is to prevent COVID in the first place. There is no Long COVID without COVID.”
World-renowned COVID-19 researcher Dr Ziyad Al-Aly, January 2024, Testimony before the U.S. Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor & Pensions
#long covid#HELPLongCovid#Dr Ziyad Al-Aly#burden of disability#reinfection#chronically ill#chronic illness#invisible illness#disability#chronic pain
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
.
#STUPIDEST THING ABOUT DOING AN ARTICLE ABOUT LONG COVID IS RUNNING INTO A TWEET YOU HAVE TO ADD TO YOUR LIT REVIEW#i gotta get outta here. just saw a guy clap his hands together and say 'the ten meta-analyses'#and everyone around him turned inside out and had their irbs revoked and disappeared#save me ziyad al-aly. ziyad al-aly save me
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Recently I have found a period drama about Tariq ibn Ziyad and the conquest of the Iberian Peninsula, so I thought it's an appropiate to share it now because of the bookscans of AL-ANDALUS. Historical figures. This period drama is a Kuwaiti-Syrian series from 2022, Fath Al-Andalus (The Conquest of Al Andalus), that has 30 episodes so far.


(There are ships on fire on the second poster, maybe in the series there's a scene or a reference about the legend of Tariq burning the ships after arriving to the Iberian Peninsula?)
I haven't watch it (yet), but in YouTube there's a watch list of the 30 episodes with subtitles.
As far as I know there has been controversies about this series in Morocco due to some historical inaccuracies, like erasing Tariq's Amazigh origins and undervalue the role of the Amazigh people in the conquest of Al Andalus.
Main cast
Suhail Jabei as Tariq ibn Ziyad
Taiseer Edris as Rodrigo, King of the Goths
Rafik Ali Ahmad as Musa ibn Nusayr
Pierre Dahger as Julián, Count of Ceuta
Marah Hijaz as Princess Florinda
Akef Najem as Abu Basir, the Judge
Creative and technical staff
Directors: Mohammad Alenezi and Saleh El Salty
Cinematography: Dragan Sisa
Editor: Mohamed Rageh
Visual effects: Momen Ebba and Eman Alshehabi
Productor: Al Buraq Production
Music: Nouamane Laholu








#fath al andalus#period dramas#the conquest of al andalus#series#tariq ibn ziyad#king rodrigo#musa ibn nusayr#conde don Julián#count don julián#julián de ceuta#rey rodrigo#florinda#princess florinda#abu basir#suhail jabei#taiseer edris#rafik ali ahmad#pierre dahger#marah hijaz#akef najem#al andalus#mohammad alenezi#dragan sisa#mohamed rageh#momen ebba#eman alshehabi#nouamane laholu#book scans related
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dr. Ziyad Al-Aly @zalaly, one of TIME 100’s most influential people in health, has published 20 research studies that have helped shape the world’s understanding of the long-term effects of COVID-19, which range from debilitating fatigue and brain fog to increased risks of chronic conditions.
#LongCOVID
https://time.com/6966812/ziyad-al-aly/
0 notes
Text
One day I'm going to stop posting about this but I can't tell you how surreal it feels to be one of the only people living in reality. A friend of mine had strep throat six times in six months. That's not normal. The amount of sickness and death all around us. I would have an easier time facing it all if 90% of the population wasn't in absolute denial of it. There's strength in solidarity.
We had that back in 2020. We don't have it now.
#what happened to society. genuinely man#it's been mind-blowing to see our governments openly embrace not only eugenics but also genocide#personal#anyway. i'm okay <3#and i'm sorry if these posts are repetitive to see#but genuinely i think they've helped me to process it all#also like. thank god for doctors like ziyad al-aly who are pushing for public health and policy reforms re: covid#i think we will see a change. but there's going to be so much death before that. unfortunately!
0 notes
Text
also preserved on our archive
By Erica Sloan
These days, it’s tempting to compare COVID-19 with the common cold or flu. It can similarly leave you with a nasty cough, fever, sore throat—the full works of respiratory symptoms. And it’s also become a part of the societal fabric, perhaps something you’ve resigned yourself to catching at least a few times in your life (even if you haven’t already). But let’s not forget: SARS-CoV-2 (the virus responsible for COVID) is still relatively new, and researchers are actively investigating the toll of reinfection on the body. While there are still a lot of unknowns, one thing seems to be increasingly true: Getting COVID again and again is a good deal riskier than repeat hits of its seasonal counterparts.
It turns out, SARS-CoV-2 is more nefarious than these other contagious bugs, and our immune response to it, often larger and longer-lasting. COVID has a better ability to camouflage itself in the body, “and it has the keys to the kingdom in the sense that it can unlock any cell and get in,” says Esther Melamed, PhD, an assistant professor in the department of neurology at Dell Medical School, University of Texas Austin, and the research director of the Post-COVID-19 program at UT Health Austin. That’s because SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2 receptors, which exist in cells all over your body, from your heart to your gut to your brain. (By contrast, cold and flu viruses replicate mostly in your respiratory tract.)
It only follows that a bigger threat can trigger an outsize immune response. In some people, the body’s reaction to COVID can turn into a “cytokine storm,” Dr. Melamed tells SELF, which is characterized by an excessive release of inflammatory proteins that can wreak havoc on multiple organ systems—not a common scenario for your garden-variety cold or flu. But even a “mild” case of COVID can throw your immune system into a tizzy as it works to quickly shore up your defenses. And each reinfection is a fresh opportunity for the virus to win the battle.
While you develop some immunity after a COVID infection, it doesn’t just grow with each additional hit. You might be thinking, “Aren’t I more protected against COVID and less likely to have a serious case after having been infected?” Part of that is true, to an extent. In the first couple years after COVID burst onto the scene, reinfections were generally (though not always) milder than a person’s initial bout of the virus. “The way we understand classic immunology is that your body will say to a virus [it’s seen before], ‘Oh, I know how to deal with you, and I’m now going to deal with you in a better way the second time around,’” says Ziyad Al-Aly, PhD, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine and the chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System.
But any encounter with COVID can also cause your immune system to “go awry or develop some form of dysfunction,” Dr. Al-Aly tells SELF. Specifically, “immune imprinting” can happen, where, upon a second (or third or fourth) exposure to the virus, your immune cells launch the same response as they did for the initial infection, in turn blocking or limiting the development of new antibodies necessary to fight off the current variant that’s stirring up trouble. So, “when you get hit an [additional] time, your immune system may not behave classically,” Dr. Al-Aly says, and could struggle with mounting a good defense.
Pair that dip in immune efficiency with the fact that your antibody levels also wane with time post-infection, and it’s easy to see how another hit can rock your body in a new way. Indeed, the more time that passes after any given COVID infection, the less of a “competitive advantage” you’ll have against any future one, Richard Moffitt, PhD, an associate professor at Emory University, in Atlanta, tells SELF. His research found that, while people who got sick initially during the delta phase were less likely to get reinfected during the first omicron wave (as compared to folks who were infected in a prior period), that benefit leveled off with following omicron variants.
There’s also the fact that no matter how your immune system has responded to a prior strain (or strains!) of the virus, it could react differently to a new mutation. “We tend to think of COVID as one homogeneous thing, but it’s really not,” Dr. Al-Aly says. So even if your body successfully thwarted one of these intruders in the past, there’s no guarantee it’ll do the same for another, now or in the future, he says.
Getting COVID again and again is especially risky if it previously made you very ill. Dr. Moffitt’s study above also found that the “severity of your first infection is very predictive of the severity of a reinfection,” he says. Meaning, you’re more likely to have a severe case of COVID—for instance, requiring hospitalization or intensive care, such as ventilation—when reinfected if you had a rough go of it the first time around.
It’s possible that some folks are more prone to an off-kilter immune response to the virus, which could then happen consistently with reinfections. The antibodies created in people who’ve had severe cases “may not function as well as those in folks who’ve had mild infections or were able to fight the virus off,” Dr. Melamed says. Though researchers don’t fully understand why, some people’s immune systems are also more likely to overreact to COVID (remember the cytokine storm?), which can cause serious symptoms—like fluid in the lungs and shortness of breath—whenever they’re infected.
Being over the age of 65, having a chronic illness or other medical condition, and lacking access to health care have all been shown to spike your risk of serious outcomes with a COVID infection, whether it’s your first or fifth fight with the virus.
But you’re not home free if you’ve only had, say, a brief fever or cough with COVID in the past; Dr. Moffitt points out that a small subset of people in his research who had minor reactions with their initial infection went on to be hospitalized with a repeat hit. The probability of that might be lower, but it’s still a possibility, he says.
Even if you’ve only had “mild” cases, each reinfection strains your body, upping your chances of developing long COVID. A 2022 study led by Dr. Al-Aly found that COVID reinfections also increase your risk of complications across the board, regardless of whether you recovered just fine in the past or got vaccinated. In particular, it showed that reinfection raises the likelihood that you’ll need hospitalization; have heart or lung problems; or experience, among other possible issues, GI, neurological, mental health, or musculoskeletal symptoms. “We use the term ‘cumulative effects,’” Dr. Al-Aly says, “so, multiple hits accrue and then leave the body more vulnerable to all the potential long-term health effects of COVID.”
That doesn’t mean your experience of a second (or third or fourth) infection will necessarily be worse, in and of itself, than what you felt during a prior case. But with each new hit, a fresh batch of the virus seeps into your system, where, even if you have a mild case, it has another chance to trigger any of the longer-term complications above. While the likelihood of getting long COVID (a constellation of symptoms lingering for three months or longer post-infection) is likely greatest after initial infection, “The bottom line is, people are still getting diagnosed with long COVID after reinfection,” Dr. Moffitt says.
Researchers don’t totally know why one person might deal with lasting health effects over another, but it seems that, in some folks, the immune system misfires, generating not only antibodies to attack the virus but also autoantibodies that go after the body’s own healthy cells, Dr. Al-Aly says. This may be one reason why COVID has been linked to the onset of autoimmune conditions like psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis.
A different hypothesis suggests that pieces of the virus could linger in the body, even after a person has seemingly “recovered” (reminder that SARS-CoV-2 is scarily good at weaseling its way into all sorts of cells). “Maybe the first time, your immune system was able to fully clear it, but the second time, it found a way to hang around,” Dr. Al-Aly posits. And a third theory involves your gut microbiome, the community of microbes in your GI tract, including beneficial bacteria. It’s conceivable that “when we get sick with COVID, these bacteria do, too, and perhaps they recover [on initial infection], but not on the second or third hit,” he says, throwing off your balance of good-to-bad gut bugs (which can impact your health in all sorts of ways).
Another unnerving possibility: The shock to your system triggered by COVID may “wake up” a latent (a.k.a. dormant) virus or two lurking in your body, Dr. Melamed says. We all carry anywhere from eight to 12 of these undetected bugs at a time—things like Epstein-Barr, varicella-zoster (which causes chickenpox and shingles), and herpes simplex. And research suggests their reactivation could be a contributing factor in long COVID. Separately, the systemic inflammation often created by COVID may spark the onset of high blood pressure and increased clotting (which can up your risk of stroke and pulmonary embolism), as well as type 2 diabetes, Dr. Melamed says.
There’s no guarantee that any given COVID infection snowballs into something debilitating, but each hit is like another round of Russian roulette, Dr. Al-Aly says. From a sheer numbers standpoint, the more times you play a game with the possibility of a negative outcome, the greater your chances are of that bad result occurring. And because every COVID case has at least some potential to leave you very ill or dealing with a host of persistent symptoms, why take the risk any more times than you need to?
Bottom line: You should do your best to avoid COVID reinfection and bolster your defenses against the virus. At this stage of the pandemic’s progression, it’s not realistic to suggest you can avoid any exposure to the virus, given that societal protections against its spread have been rolled back. But what you should do is take some common-sense precautions, which can help you avoid any contagious respiratory virus. (A cold or the flu may not pose as many potential health risks as COVID, but being sick is still not fun!)
It’s a good idea to wear a mask when you’re in a crowded environment (especially indoors), choose well-ventilated or outdoor spaces for group hangouts, and test for COVID if you have cold or flu-like symptoms, Dr. Al-Aly says. If you do get infected, talk to your doctor about whether your personal risk of a severe case is enough to qualify for a Paxlovid prescription (which you need to take within the first five days of symptoms for it to be effective).
The other important thing you should do is get the updated COVID vaccine (the 2024-2025 formula was recently approved and released). Unlike getting reinfected, the vaccine triggers “a very targeted immune response…because it’s [made with] a specific tiny part of the virus,” Dr. Melamed says. Meaning, you get the immune benefit of a little exposure without the potential of your whole system going haywire. Getting the current shot also ensures you restore any protection that has waned since you received a prior jab and that you have an effective shield against the dominant circulating strains. Plus, research shows that being vaccinated doesn’t just lower your chances of catching the virus; it also reduces your risk of having a severe case or winding up with long COVID if you do get it.
So, too, can the deceivingly simple act of keeping up with healthy habits—like exercising regularly, eating nutritious foods, and clocking quality sleep. Maintaining this kind of lifestyle can help you stave off other health issues that could increase your risk of harm from COVID, Harlan Krumholz, PhD, a cardiologist at Yale University and founder of the Yale Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation (CORE), tells SELF. “Given that we will be repetitively exposed to the virus, the best investments we can make are in our baseline health,” he says.
Doing any (or all!) of the above is a big act of compassion for yourself, the people you love, and your greater community. “For the average person, it’s like, ‘Oh, COVID is gone,’ but they’re just not seeing the impact,” Dr. Al-Aly says, noting the invisibility of long COVID symptoms like disorienting brain fog and crushing fatigue. The truth is, in plenty of people, just one more infection could be the difference between living their best life and facing a devastating chronic condition.
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator#lokng covid
245 notes
·
View notes
Text
For months, governmental officials around the world have appeared to want to forgo discussing the specter of long COVID. As a new review makes clear, that is wishful thinking—and the latest COVID variants may well kick long COVID into overdrive, a scenario that researchers and experts have been warning about for some time.
“I think they (government agencies) are itching to pretend that COVID is over and that long COVID does not exist,” says Ziyad Al-Aly, director of the Clinical Epidemiology Center at Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System and lead author of the review. “It is much more pleasant topretend as if emergency department visitsand hospitalizations haven’t been rising sharply thissummer.”
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
A senior Palestinian resistance leader said that the Palestinian people could not stand against Israel if not for Iran's full support.
Secretary General of the Palestinian Islamic Jihad movement Ziyad al-Nakhaleh made the remarks at a joint press conference with Iranian Foreign Minister Hossein Amir-Abdollahian in Tehran on Saturday.
He praised Iran's important role in supporting the resistance of the Palestinian people since the start of Israel's genocidal war against the people of Gaza in early October 2023.
Iran's active diplomacy played a leading role in clarifying the position of Palestine's resistance, he added.
The Islamic Jihad leader emphasized that the Palestinian people will achieve a final victory in their fight against Israel, saying the steadfastness of the Palestinians will be a model for all the people of the world.
Nakhaleh added that Iran has paid the price for its constant support for the resistance of the Palestinian people and its defense of the Palestinians' rights as numerous sanctions have been imposed against Tehran.
He thanked the Leader of the Islamic Revolution Ayatollah Seyyed Ali Khamenei and the Iranian officials and nation for supporting Palestine.
#Ayatollah Khamenei#Free Palestine#Gaza#Gaza Genocide#Iran#Tehran#Sanctions#Resistance#Keep Talking About Palestine
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Government confirms at least 100 Israelis held captive in Gaza

An Israeli family arrives to a police station in Lod, Israel, to provide DNA samples to help identify a relative missing since a Hamas militant attack near the Gaza border, Oct. 8, 2023. (AP Photo/Maya Alleruzzo)
Israel’s Government Press Office confirms that at least 100 Israelis are currently being held captive in Gaza.
Posting an infographic on its Facebook page, GPO writes that “100+ kidnapped, 2,000+ injured, 600+ murdered.”
Until now Israel has refused to confirm the number of civilians or soldiers being held hostage. Media reports have suggested that at least 170 may be being held captive in Gaza.
Iran’s Raisi speaks to Hamas, Islamic Jihad as Tehran hails terror onslaught as ‘victory’
By AFP

Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi speaks during a news conference on the sidelines of the 78th United Nations General Assembly, at UN headquarters in New York City on September 20, 2023. (Ed Jones/AFP)
Iran’s President Ebrahim Raisi speaks with leaders of Palestinian terror groups Hamas and Islamic Jihad, official media say, a day after Hamas launched a surprise attack on Israel.
“Raisi discussed the developments in Palestine in separate phone calls with Ziyad al-Nakhalah, secretary general of the Islamic Jihad Movement, and Ismail Haniyeh, the head of the [Hamas] political bureau,” state news agency IRNA reported, without giving further details.
Iran hails the Palestinian attack, calling it a “proud operation” and a “great victory.”
“This victorious operation, which will facilitate and accelerate the collapse of the Zionist regime, promises the impending destruction of the Zionist regime,” says Ali Akbar Velayati, a senior adviser to Iran’s supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei.
“I am congratulating this great and strategic victory, which is a serious warning to all compromisers in the region,” he adds in a letter to Hamas and Islamic Jihad, referring presumably to Arab countries that have normalized ties with Israel.
15 notes
·
View notes
Photo
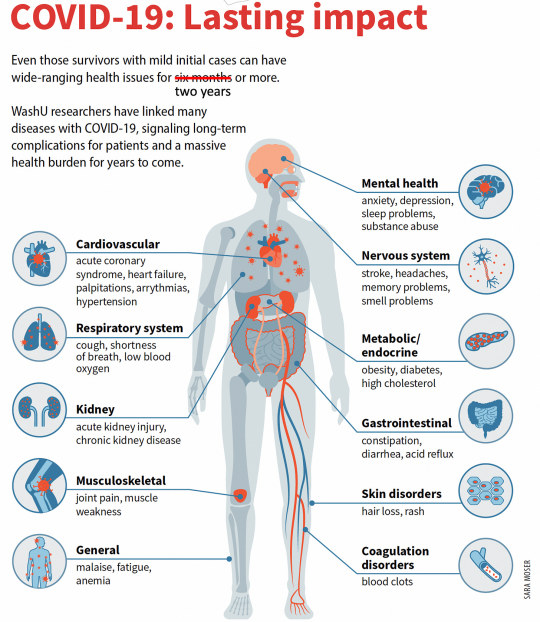
Long-Term Long Covid - by Eric Topol
Unfortunately, what was seen at 6 months largely continues out to 2 years.
... [New paper at] Nature Medicine addresses what happened 2 years later to nearly 140,000 people who had Covid, compared with almost 6 million people non-infected controls.
... in the non-hospitalized group a substantial proportion— about 30%— of the 80 sequelae, including GI and neurologic, remained significantly elevated.
... I’d like to point out the data analyzed in this study was enormous, as I tried to capture with one of the supplemental tables below, representative of many others. The authors took on many advanced analytic approaches with weighting, conditional modeling, and sensitivity analyses that I’m not going to review here.
... While this is the first comprehensive and systematic study of Covid at 2 years, it unfortunately is within a highly skewed population. The demographics of nearly 90% men, with a mean age 61 years, is far different than the prototypic person with Long Covid who is more apt to be female and age 30-39 years. Furthermore, to get 2 year follow-up it meant studying a population who had Covid early in the pandemic, before vaccines or the marked evolution of the virus with new variants, including Delta, which was more virulent that the ancestral or Alpha strains that preceded it. So please keep this in mind—the results are important but they may well not be representative of the real world, broader population, of Covid and Long Covid. That’s already a major hole in our knowledge base since there is no other report yet to systematically address a more representative population.
...
Summary
At two years after Covid, there’s a persistent and considerable burden of symptoms and multi-system organ involvement in an important subgroup of people. It’s also unpredictable who will be afflicted with protracted symptoms and new medical diagnoses. While there still is no validated treatment (the Big Miss, as recently reviewed), Long Covid marches on, not just over time for most of those already suffering, but also among newly infected or re-infected individuals — like we are seeing now with increase in cases in the United States and many other countries. The main emphasis here, beyond the enduring and very concerning symptoms and organ dysfunction, is that we are still in the dark. It will take many years to fully know the sequelae of Covid, be it from unforeseen, delayed adverse outcomes like what occurred many years after influenza or polio, or the secondary outcomes of organ systems that are clearly affected, or via promotion of autoimmune conditions or pro-inflammatory pathways, potentially exacerbating risk of atherosclerosis. We’re going to need many more years of careful follow-up to fully understand the ways and extent Covid has hurt us. Meanwhile, beyond the known strategies for prevention of infection, we must consider finding effective ways to treat people who suffer from Long Covid as an urgent and foremost priority.
#long covid#research#data#eric topol#covid#summer 2023#Ziyad Al-Aly#VA study#nature medicine#sequelae
102 notes
·
View notes
Text
On 26 October, the Palestinian Ministry of Health released the list of names of Palestinians killed since 7 October. Among them, from the Abu Omra family, are:
Fatima Muhammad Ali (91);
Rabaa Ayada Hamidan (74);

Muhammad Ibrahim Nassar (72) and his brother Mahmud Ibrahim Nassar (62);



Hamidan Muhammad Ayada (68) and his sons Muhammad Hamidan Muhammad (35) and Abdullah Hamidan Muhammad (32);



Hamidan’s son Imad Hamidan Muhammad (38) and his son Hamza Imad Hamidan (6);
and Hamidan’s son Ziyad Hamidan Muhammad (34), his wife Hind Talbani, and their son Tariq Ziyad Hamidan (1);
Najah Ali Muhammad (47);
Ikram Hamidan Muhammad (40);
Islam Sabah Khalil (33);
Nihad Ismail Ibrahim (29);
Salim Suleiman Ahmed (28);
Nur al-Din Muhammad Salman (27);
Nur Ibrahim Muhammad (21) and her brothers Muhammad Ibrahim Muhammad (16) and Ali Ibrahim Muhammad (11);
Samiya Ahmed Saleh (18) and her brother Ibrahim Ahmed Saleh (7);
Muhammad Salim;
Atiya Salman, a baby;
Yahya Muhammad, a child;

Nur Muhammad;

and Mustafa Anwar.
You can read more about the human lives lost in Palestine on the Martyrs of Gaza Twitter account and here.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bir Şii Gazetecinin tespitleri.
“Biz arlanmaz, utanmaz bir toplumuz. Ve tarihi gerçekler asla unutulmamalı!
1) Şam, İran ve Irak’ı kim fethetti?
Ömer bin el-Hattab, Sünni.
2) Pakistan, Hindistan ve iki nehir ardındaki ülkeyi kim fethetti? Muhammed bin Kasım, Sünni.
3) Kim Kuzey Afrika’yı fethetti?
Kuteybe bin Müslim, Sünni.
4) Endülüs’ü kim fethetti?
Tarık bin Ziyad ve Musa bin Nasr, Sünni.
5) İstanbul’u kim fethetti?
Fatih Sultan Mehmet, Sünni.
6) Sicilya’yı kim fethetti? Esed bin Furat, Sünni.
7) Kim Endülüs medeniyetini kurdu ve ilim yuvası yaptı? Emevi Halifeleri, Sünni.
8) Hıttin’de Müslüman lider kim idi?
Salahaddin Eyyubi, Sünni.
9) Ayn Calut’ta Müslümanlar’a kim liderlik etti ve Moğollar’ı hezimete uğrattı?
Seyfeddin Kutuz ve Rukneddin Baybars, Sünni.
10) Kim İspanya’yı bozguna uğrattı Fas’ta?
Abdulkerim al-Hattâbi, Sünni.
11) Kim İtalya’yı hesap vermeye zorladı Libya’da?
Ömer el-Muhtar, Sünni.
12) Ve yakında kim Rusları perişan etti Çeçenistan’da? Şeyh Şamil, Dudayev, Şamil Basayev ve Hattab, Sünni.
13) Kim Rusya’yı (SSCB) Afganistan’da hezimete uğrattı? Afganistanlı Sünniler.
14) Kim yine Afganistan’da NATO’nun yüzünü toprağa sürttü? Sünnîler
15) Kim Amerika’nın Irak’tan çekilmesini sağladı?
Sünnîler.
Lakin biz Şiî olarak çocuklarımıza ne bıraktık?
1) Kim Hz.Hüseyin’e ihanet etti ve Kerbela’da yalnız bıraktı? el-Muhtar es-Sekafî, Şii.
2) Abbasi Halifesi Râdî Billah’a kim ihanet etti?
Buveyhiyyûn, Şii.
3) Irak’ı Moğollar’a satan kim? İbnü’l-Alkami, Şii.
4) Kim Hülagü’nün pis işlerini örtbas ederdi?
Nasır al-Tusi, Şii.
5) Kim Moğollar’a Şam işgalinde yardım etti? Şiiler.
6) Kim Fransızlar’a yardım etti Müslümanlara karşı?
Fatimiyyun Şiileri.
7) Selçuklu Sultanı’na kim ihanet etti?
Tuğrul al-Basasiri, Şii
8) Kudüs’ü işgalde Haçlılar’a kim yardım etti?
Ahmet bin Ata’, Şii.
9) Kim Salahaddin Eyyubi’nin ölümünü organize etti? Kenzü’d-Devle, Şii.
10) Hülagü’yü Şam’da kim ağırladı?
Kemaleddin bin Bedr al-Tiflis, Şii.
11) Suriye’de kanlı rejimle kim birlik oldu ve Rusya’ya destek verdi? Ali Hamaney, Şii.
Görülüyor ki, Şiilerin kalemleri, kılıçları ve dilleri hep Sünni Müslümanlara karşı olmuştur. Ve her ne kadar biz Kâfirlere karşıyız deseler de kalpleri Kâfirlerle beraberdir."
Siyaset Bilimci ve Gazeteci Mehmet Dağıstanlı
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
As I promised, let's start with the bookscans:
Al-ANDALUS. PERSONAJES HISTÓRICOS
(Al Andalus. Historical figures)
Concepción Masiá



Summary
Introduction.................................. 9
The precursors of al-Andalus.....13
Count Don Julián....................13
Tarif ben Malluk. ....................15
Musa ben Nusayr and Tariq ben Ziyad: the conquerors of Spania...........16
Abd al-Aziz: a good governor with an unfortunate fate ..........................25
The Odyssey of Prince Abd al-Rahman the Immigrant......................................29
Abd al-Rahman was only twenty-five years old.........................................36
Sulayman ben Yaqzan ben al-Arabi: Charlemagne's deceived "deceiver" ........................... ...........41
Amrus ben Yusuf: the muladí of Huesca
.............................................................47
The “rabadies”: adventurous spirits.. ..............................................53
Ziryab: the singer of Baghdad........61 Tarub: the favorite of Abd al-Rahman II...............,...........................................67 Abbas ben Firnas: the first aviator............................ ......................73 Yahya ben Hakan al-Bakri: the miserly poet.....................................................77

Abd al Chabbar and Sulayman ben Martin: the rebels of Mérida..........................81 Eulogio and Álvaro de Córdoba: pursuing martyrdom..........................85 The Andalusian Vikings..................... 95 The emir Abd Allah distrust and death...............................….................... 101 Musa ben Musa ben Qasi: the third king of Spain.......................................................107 Ibn Hafsun: the unredeemed rebel.....115 Abu Alí al-Sarrach: the Andalusian missionary. ...........................................125 Ibn Masarra: a freethinker in Spanish Islam.......,...........,...................................131 Abd al-Rahman III: the first independent caliph of al-Andalus. ...........,................................137 Hasday ibn Shaprut: the Jewish doctor of Abd al-Rahman III............ ....... ...................... ................... 145 Andalusians in France: the “Moorish kingdom” of Fraxinetum....................... 151 Rabbi ben Zayd: Bishop Recemundo............................................. 157 Al-Hakam al-Mustansir bi-llah: passion for culture.................................. 161
Ibn Abd Rabbhi, the encyclopedist, and Ibn Futais, the collector.................. 167 Al-Mansur “the Victorious” ...................171 Hisham II and Sanchuelo: misrule. .......191
Abu Muhammad Ali ibn Hazm: The pigeon neackle................................209

Hisham III al-Mu'tadd: the end of the Umayyad caliphate...............................215
Ibn al-Wafid: the gardener doctor.....221
Avempace. The supreme good: wisdom...................................................225
Zaida: the Moorish Queen of Leon and Castile........................................................227
Ibn Tufayl of Guadix: the best disciple of Avempace................. ............................ .231 Averroes: the universal Andalusian....233 Moseh ben Maimon: Maimonides..... ..239 Abu Yusuf Yaqub: the winner of Alarcos......................................................243 Ibn Arabi: the Sufi mystic.....................249 Avenzoar: a long dynasty of doctors. ...................................................253 Al-Ahmar: Abenámar, Moor of the Morería. ...,...............................................255 The Abencerrajes. ..................................261 Boabdil the Younger: the last Moorish king ............................................................267 Aben Humeya: the last Muslim leader of Spain................ ..........................................275 Bibliography .............................................285
Note: The spelling of Muslim names is taken from the works of: Levy Provençal, Muslim Spain, and González Ferrín, General History of al-Andalus.

Introduction
In the long eight hundred years that the Muslims remained in Spain, there were many personalities who, in all the fields of knowledge, sciences, letters and arts, stood out unequivocal, marking a milestone not only in the culture of al-Andalus, but that had a relevant character in universal culture.
On the other hand, the almost constant struggle between Christians and Muslims would also generate a whole series of great warriors who, for example, the infante Don Juan Manuel considered the best gifted for the war of all those who existed in the East and the West of their time.
The date that we all know as the arrival of the Muslims to Gothic Spania dates back to the year 711. Its expansion throughout the territory was so rapid as had been the conquest of the Persian empire and its presencein large areas of Asia or North Africa, but from a cultural point of view, the 8th century was totally sterile. The new conquerors who arrived from beyond the Strait of Gibraltar, were men at arms, mostly illiterate, who could do little contribute to a Christian Spania whose culture continued to develop under the dictates of the wisdom of Saint Isidore of Seville. Still they were left on the Peninsula

many areas where Christianity had not taken root and its importance regarding the assimilation of Islam.
The first governors of al-Andalus, dependent on Caliphate of Damascus, during the first years of occupation had to face many enormous internal problems, originated by the different origins of their own people, Arabs and berebers, mostly, while cultural issues occupied a very secondary level. But, possibly for purely practical reasons, Arabic as a language was introduced into the Christian field. According to Juan Vernet, it is possible to find some codices from times as early as the 9th century, that in its margins appear apostilles or comments in Arabic, and it seems that this language was already rooted among the Mozarabs, that is, the Christians who continued to live and preserve their religion in Muslim-dominated territories, in times before Abd al-Rahman II.
But it will be Abd al-Rahman I the Immigrant, who arrived in al-Andalus from Syria as the only survivor of the exterminated Umayyad dynasty, the one who will be concerned with introducing the principles of oriental culture in Spain, limiting itself to the legal-religious sciences that, in those moments, were the most important for the newly Muslims arrived. It was during the time of Abd al-Rahman II that the first wise men, who can be called that, enrich the cultural landscape of al-Andalus.

Poets, doctors, philosophers, mathematicians, geographers, undefeated generals...All of them will give al-Andalus and Europe a series of works that, by their importance will be translated, searched, accepted and will serve as a basis for the western culture and Renaissance ideas, in such a way that many of the great sages of the Italian Renaissance considered that all knowledge of the time came from Muslim Spain, which all the wise men were of Andalusian origin. And when the political decline and the disintegration of the caliphate, will not stop birth, grow and develop distinguished minds that will continue to maintain,for a long time, the prestige of al-Andalus. Curiously, this situation will be repeated throughout the history of Spain, when the Arab occupation just be a memory. The Spanish Golden Age will coincide with decadence of the Austrias, when the country loses its pre-ponderance in Europe, and with the disaster of '98, with the loss for Spain of its last colonies, will produce a cultural and scientific renaissance that has been called the Silver age.
Through the pages of this book we want to highlight those figures who occupied a predominant place in the history of al-Andalus, although not all of them were necessarily Muslims, since that in that cultured and tolerant al-Andalus, many Jews and some other Christians showed their genius, and of those who, often, we know more about his works than about his biography. But whatever religion they had, they were all, after all, Andalusians, born and raised in the extensive lands of al-Andalus. As a matter of curiosity we will include some groups of characters anonymous people who, due to their surprising

actions, on occasions dictated by necessity, they reveal the ingenuity or character of the Andalusians. Such would be the case of the "rabadíes", of the Moors who, for a time, established a small kingdom in France, or those Normans who ended up becoming Andalusians and Muslims to save their lives.
Perhaps this way we will learn a little more about that crossbred Spain, in which despite so many years of struggle, truces and battles, mutual loves and hates, numerous characters belonging to the three cultures, Moors, Christians and Jews shared knowledge, affinities and forms of life, making al-Andalus the cultural beacon of the West.

The precursors of al-Andalus
Count Don Julián
The conquest of Morocco had been carried out quickly, but shallow. The Berbers were only subdued after a fierce resistance, defeated by an ambitious general who had just been appointed governor of Ifriqiya and Maghrib. His successes in these lands They would prepare the ground for him to be the one to set his eyes and, also his troops, over Gothic Spania. It was Musa ben Nusayr. Musa, with the help of one of his sons, took possession of Tangier, and demanded that the subjugated tribes hostage to educate them in the new faith, which in turn, became propagandists of Islam, leaving in the conquered Morocco Arab lieutenants, including General Tariq ben Ziyad, he turned to Ifriqiya. But it seems that the Ceuta square remained in the hands of a Christian, the so-called Count Don Julián, who would have a determining role in this entire story. We could consider it as a precursor of that al-Andalus that was about to be born.
#bookblr#book scans#historyblr#history books#al andalus#al andalus. personajes históricos#al andalus. historical figures#history#spanish history#musa ibn nusayr#tariq ibn ziyad#conde don julián#count don julián#count julian
28 notes
·
View notes
Text

Solving the puzzle of Long Covid, published in Science @ScienceMagazine on 22 Feb 2024 | written by Dr. Ziyad Al-Aly @zalaly and Dr. @EricTopol
More than 90% of cases occur in people who have mild SARS-CoV-2 infection.
#CovidIsAirborne #MaskUp #WashHands
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adl0867
44 notes
·
View notes
Text

This is a very informative podcast. Take a listen.
4 notes
·
View notes