#zinc corrosion
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Mailbag: How's the Build Quality of the Leica M6 TTL?
by Johnny Martyr My daughter and I checking out the selection at the Leica Store Paris – photo by Stephanie Lee Isaiah Hervé and I follow one another on Instagram. He takes beautiful, serene landscape photos that just blow me away. His work is very fine and nuanced and nothing that I have the patience or skill for! So, many thanks to him for taking an interest in my clumsy…

View On WordPress
#35mm leica#durability#larger shutter speed dial#Leica#Leica M#Leica M6#Leica M6 TTL#light meter#mailbag#Q&A#reliability#reverse shutter speed dial#technology#ttl version#zinc corrosion#zinc top plate#zinc vs brass
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Protect Cement Plant Structures from Corrosion and Its Benefits
Introduction
Cement plants operate in highly aggressive environments, where exposure to moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures leads to corrosion of steel structures, pipelines, and machinery. Corrosion can significantly impact the longevity, efficiency, and safety of a cement plant. Implementing effective corrosion protection strategies is crucial to maintaining operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
Causes of Corrosion in Cement Plants
Several factors contribute to corrosion in cement plant structures:
High Humidity & Moisture: The presence of water accelerates corrosion, especially in areas with high humidity or frequent exposure to rain.
Acidic and Alkaline Environments: Cement production involves exposure to chemicals such as sulfur dioxide, chlorides, and carbon dioxide, which can lead to acid corrosion.
High Temperatures: Extreme heat causes thermal stress on metal structures, leading to cracks and oxidation.
Abrasive Materials: Dust and particulate matter can wear down protective coatings, making metal surfaces more vulnerable.
Electrochemical Reactions: Exposure to different metals and stray electrical currents can cause galvanic corrosion.
Methods for Protecting Cement Plant Structures from Corrosion
To ensure long-term durability and reliability, several corrosion protection techniques should be employed:
1. Thermal Spray Coating (TSA & TSZ)
Thermal spray aluminum (TSA)coating and thermal spray zinc (TSZ) coatings create a strong protective barrier against corrosion. These coatings are particularly effective in harsh industrial environments.
2. Galvanizing
Hot-dip galvanizing applies a protective zinc layer to steel structures, preventing rust formation. This method provides long-term corrosion resistance, especially in outdoor installations.
3. Protective Paint Coatings
Applying high-performance industrial coatings, such as epoxy, polyurethane, and alkyd paints, helps to create an impermeable shield against moisture and chemicals.
4. Cathodic Protection
This method uses sacrificial anodes or impressed current systems to prevent corrosion by directing electric currents that neutralize oxidation reactions on metal surfaces.
5. Sealants and Waterproofing
Using sealants and waterproof coatings on concrete and steel structures reduces the penetration of water and chemicals, slowing down corrosion.
6. Regular Maintenance & Inspections
Routine inspections and preventive maintenance allow early detection of corrosion, helping to address potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs.
7. Environmental Controls
Installing proper ventilation systems and using dehumidifiers in enclosed spaces can help reduce humidity and moisture levels, slowing corrosion progression.
Benefits of Corrosion Protection
1. Extended Equipment Lifespan
Implementing corrosion protection methods increases the durability of structures and equipment, reducing the frequency of replacements.
2. Reduced Maintenance Costs
Preventive measures significantly lower maintenance costs compared to reactive repairs and replacements due to structural failures.
3. Enhanced Safety & Compliance
Corrosion can weaken structures, leading to accidents and operational hazards. Protecting against corrosion ensures compliance with safety regulations and reduces risks to workers.
4. Improved Operational Efficiency
Corrosion-resistant equipment operates more efficiently, reducing downtime and enhancing production output.
5. Cost Savings in the Long Run
While corrosion protection requires an initial investment, it minimizes costly repairs, equipment failures, and unplanned downtime, resulting in significant savings.
6. Environmental Benefits
By prolonging the life of structures and equipment, corrosion protection reduces waste and the environmental impact of frequent material replacements.
Conclusion
Corrosion in cement plant structures can lead to significant financial and operational setbacks if not addressed properly. By implementing effective corrosion protection strategies such as thermal spray coatings, galvanizing, protective paints, and regular maintenance, cement plants can extend equipment lifespan, reduce costs, and ensure safer operations. Investing in corrosion protection is not just about preventing deterioration—it’s about safeguarding the future of the plant’s infrastructure and ensuring long-term profitability.
#sandblasting#thermal spray coating#zinc coating#Alluminum coating#corrossion protection#cement plant#corrosion prevention
0 notes
Text
Top 15 Market Players in Global Zinc Phosphate Corrosion Inhibitors Market

Top 15 Market Players in Global Zinc Phosphate Corrosion Inhibitors Market
The zinc phosphate corrosion inhibitors market is competitive, driven by demand from industries like construction, automotive, and marine. Here are the top 15 players shaping the global market:
Heubach GmbH A market leader in corrosion inhibitors, Heubach provides high-performance zinc phosphate products designed for protective coatings and paints.
W.R. Grace & Co. Grace’s innovative solutions include zinc phosphate additives that enhance corrosion resistance for industrial applications.
BASF SE BASF delivers advanced zinc phosphate corrosion inhibitors that are widely used in marine and automotive coatings.
Nubiola (Ferro Corporation) Nubiola, a subsidiary of Ferro Corporation, specializes in anti-corrosion pigments, including zinc phosphate solutions tailored for harsh environments.
SNCZ Known for its expertise in anti-corrosion additives, SNCZ produces a broad range of zinc phosphate variants for industrial coatings.
Kerala State Industrial Enterprises (KSIE) A key player in the Indian market, KSIE offers high-quality zinc phosphate for domestic and international clients.
Chemetall GmbH (BASF subsidiary) Chemetall focuses on metal surface treatment and provides zinc phosphate products with excellent anti-corrosion properties.
Vanchem Performance Chemicals Vanchem is a recognized supplier of zinc phosphate inhibitors used in surface coatings for industrial and construction sectors.
Noelson Chemicals Specializing in anti-corrosion and anti-rust additives, Noelson offers innovative zinc phosphate products to meet diverse market needs.
Jiangsu Xinruida Chemical Co., Ltd. This Chinese company focuses on the production of zinc phosphate corrosion inhibitors for coatings and paints used in heavy industries.
Hanchang Industries Co., Ltd. Hanchang supplies zinc phosphate inhibitors designed for long-term corrosion protection in automotive and marine applications.
Kobo Products, Inc. Kobo Products provides functional pigments, including zinc phosphate, catering to advanced industrial coatings.
Halox (ICL Advanced Additives) Halox offers corrosion inhibitors such as zinc phosphate to enhance the durability of paints and coatings in aggressive environments.
Shijiazhuang Xinsheng Chemical Co., Ltd. A leader in the Chinese market, Xinsheng manufactures high-quality zinc phosphate products with a strong export focus.
Pigmentan Ltd. Based in Israel, Pigmentan produces zinc phosphate corrosion inhibitors that are widely used in protective coatings worldwide.
Request report sample at https://datavagyanik.com/reports/global-zinc-phosphate-corrosion-inhibitors-market/
Top Winning Strategies in Zinc Phosphate Corrosion Inhibitors Market
Market leaders in zinc phosphate corrosion inhibitors employ strategic approaches to remain competitive and address the increasing demand for high-performance protective solutions. Below are the top strategies:
Innovation in Product Development Companies are investing in R&D to develop advanced zinc phosphate variants that enhance performance while being eco-friendly. For instance, BASF has introduced low-toxicity products catering to strict environmental regulations.
Sustainability Initiatives With rising demand for environmentally friendly solutions, companies like Heubach are focusing on developing non-toxic and sustainable zinc phosphate products.
Targeting Emerging Markets Players are expanding their presence in emerging economies such as India, Brazil, and Southeast Asia, where industrialization and infrastructure development drive demand.
Collaborations with End-User Industries Collaborating with industries such as automotive, construction, and marine helps manufacturers tailor their products to specific customer needs. Chemetall’s partnerships with automotive OEMs exemplify this strategy.
Global Distribution Networks Expanding distribution networks ensures market players can meet global demand efficiently. Noelson Chemicals, for example, has strengthened its export capabilities in North America and Europe.
Focus on High-Growth Segments Companies are targeting high-growth applications, such as powder coatings and waterborne paints, which increasingly rely on zinc phosphate corrosion inhibitors.
Acquisitions and Mergers Acquisitions of smaller players help market leaders enhance their product portfolio and expand their geographic presence. W.R. Grace’s acquisition of regional suppliers has bolstered its market share.
Digital Marketing and Branding Leveraging digital platforms to showcase product benefits and applications has become a key strategy for companies looking to attract industrial clients globally.
Cost Optimization in Production Implementing efficient production techniques and sourcing raw materials strategically helps companies reduce costs and remain competitive in price-sensitive markets.
Customizable Solutions Offering tailored zinc phosphate products for specific coatings and paints enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty. SNCZ excels in this approach with its industry-specific solutions.
Adapting to Regulatory Changes Ensuring compliance with global environmental and safety standards is critical. Companies like Vanchem are proactively reformulating products to meet evolving regulations.
Enhancing Supply Chain Efficiency Optimizing supply chains through regional manufacturing facilities and digital tools has helped companies like BASF improve delivery times and reduce costs.
Educational Initiatives Conducting workshops and training sessions for customers to highlight the application and benefits of zinc phosphate products builds trust and long-term partnerships.
Technological Integration Integrating advanced technologies like nanotechnology into product formulations enables companies to offer superior anti-corrosion performance. Halox has leveraged such innovations effectively.
Focus on Long-Term Performance Emphasizing the durability and extended lifecycle benefits of zinc phosphate corrosion inhibitors helps companies attract industries prioritizing cost-effective maintenance solutions.
These strategies are enabling market leaders to drive innovation, capture emerging opportunities, and address evolving customer needs in the zinc phosphate corrosion inhibitors market.
Request a free sample copy at https://datavagyanik.com/reports/global-zinc-phosphate-corrosion-inhibitors-market/
#Zinc Phosphate Corrosion Inhibitors Market#Zinc Phosphate Corrosion Inhibitors Production#market share#market growth#market players#market size#revenue#average price#top trends#competitive pricing strategies
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Thermal Diffusion Zinc Coating Solutions for Steel Products
Distek is one of the leading players in the field of coating technologies. We offer cutting-edge thermal diffusion zinc coating solutions to meet the unique needs of various enterprises. Read more: https://medium.com/@distekg/the-ultimate-guide-to-thermal-diffusion-zinc-coating-solutions-for-steel-products-fa5873389aa3
#Zinc Coating Solutions for Steel Products#Anti corrosion coating lines#Coating steel products with zinc#Zinc coated steel corrosion resistance
0 notes
Text
Why Coating is Essential to Protect Metals
Metal has been very precious for human beings since the era of the medieval period. We gain knowledge of the anti corrosion coating of steel products. various types of coating are available, their application process, and how to preserve the longevity and good performance of steel. Contact us Now.
0 notes
Text
Cathodic protection is a concept used to protect large objects, such as ships, pipelines and buildings, from rusting (figure 12.24).

"Chemistry" 2e - Blackman, A., Bottle, S., Schmid, S., Mocerino, M., Wille, U.
#book quotes#chemistry#nonfiction#textbook#cathodic protection#zinc#anode#cathode#electrochemistry#bronze#rudder#ship#boat#pipeline#building#rust#corrosion#protection
0 notes
Text
If you’re dealing with rust on iron or metal surfaces, you’re not alone. Rust is a common issue that affects the appearance and structural integrity of various objects, from household tools to industrial equipment. But fear not, for we are here to guide you through the best way to Rust removal services from iron and metal, ensuring your possessions regain their former glory.
Metal finishing services offer a range of solutions, including rust and corrosion removal services. They have the expertise, equipment, and experience to restore your metal items to their former glory. Whether it’s automotive parts, antiques, or industrial machinery, these experts can tackle rust issues with precision.
#Rust removal services#Rust and Corrosion Removal#Zinc Rack Plating#Rust Removal#Metal finishing services
0 notes
Text
Zinc Chemicals are Mostly Used in Automotive and Tire Industries
Zinc chemicals are extensively used in the production of automotive tubes and tires. You all are familiar with the increasing number of vehicles on the road because of increasing disposable income of the people. And, zinc chemicals are used in the production of tires and tubes, so it is not that hard to imagine the mammoth demand for these chemicals.
Increasing E-Vehicles Power the Demand for Zinc Chemicals
What’s more, there is an increase in the number of e-vehicles as well on top of the conventional vehicles. Likewise, higher zinc oxide loadings can advance hot air properties, while too low a zinc oxide concentration can give rise to problems. It also decreases heat buildup and wear and tear of tire, making it a significant part of the tire manufacturing industry. Consequently, with the expansion of the tire industry, the demand for zinc oxide. Will also grow leaps and bounds.

Talking of automotive tires, they are mostly manufactured in the Asia Pacific region. The major countries of the region are the key automobile producers; therefore, the requirement for the zinc chemicals will only rise. This is because, there is absolutely no stopping to the demand for vehicles.
China and India are Major Users of Zinc Chemicals
We have talked about the APAC being the largest end user of zinc chemicals earlier, it is not only because of the automotive and tire industry.
China produces the most chemicals all over the world. The chemical manufacturing sector will only grow with time, as a result of a lot of initiatives carried out by the government and also because there is a large base of end-users as well base. The growth in chemical production will bring about a lot of promising prospects for the industry to grow.
The booming agrochemical sector and economic boom in China and India will power the requirement for zinc chemicals. Chemical fertilizers are lower-priced and ease of accessibility are important for the growth of the industry. Zinc sulphate is used as an additive in chemical fertilizers, boosting the industry for zinc chemicals.
Zinc chemicals are also used in decorative coatings and India is home to a lot of decorative and industrial coating manufacturers. Due to the increased requirement for coatings, companies have boosted their production. This will power the demand for synthetic rubber, boosting the requirement for zinc chemicals in the years to come as well.
#zinc chemicals market#industrial applications#chemical compounds#market analysis#corrosion protection#market trends#zinc oxide#industry players#market insights#market segmentation#emerging trends#zinc plating#market dynamics
1 note
·
View note
Text
Writing Notes: Poison

References (Forms, Actions & Examples of Poison; Route of Administration; Some Symptoms; What to do if a Poisoning Happens)
400 years back, Paracelsus stated that, “All substances are poisons; there is none which is not a poison.”
If the right dose is taken, it could become a remedy, otherwise poisonous.
Poison - a substance which when administered, inhaled or swallowed by living organism causes ill effects on the body. It is defined also as a medicine in a toxic dose. Toxic substance may be solid, liquid, gas or any environmental agent.
Forms of Poison
Physical form: Gaseous/volatile/vaporous forms of poisons act faster than liquid poisons as they are quickly absorbed. Similarly, liquid poisons act faster than solid poisons. Gaseous or volatile > liquid > solid. For solid poisons, powdered poisons act quickly than the lumps. For example, there are certain seeds that escape the gastrointestinal tract as they are solid, but when crushed, they can be fatal. For solids: powdered > lumps
Chemical form: Few substances like mercury or arsenic are not poisonous as they are insoluble and cannot be absorbed when they are in combination with other substances like mercuric chloride, arsenic oxide, etc. In other cases, the action is vice versa. For example, there are some substances that become inert in combination with silver nitrate and hydrochloric acid and are deadly and poisonous when present in pure forms.
Mechanical combination: The effect of poisons is significantly altered when they are combined with inert substances.
Action of Poisons
Local action: Direct action on the affected site of the body. Examples include irritation and inflammation in strong mineral acids and alkalis, congestion and inflammation by irritants, the effect on motor and sensory nerves, etc.
Remote action: Affects the person due to absorption of that poison into the system of that person. For example, alcohol is absorbed in the system and then it affects the person.
Local and remote actions: Some poisons can affect both local and remote organs. Thus, they not only affect the area with contact to the poison but also cause toxic effect after absorption into the system.
General action: The absorbed poison affects more than one system of the body, for example, mercury, arsenic, etc.
Route of Administration
The route of administration is the path through which a drug, toxin, or poison is taken or administered into the body of a person which is distinguished by the location where any drug is applied. It is mostly classified on the basis of its target:
Topical—has a local effect
Enteral—has a wide effect, i.e., affect the whole system
Parental—follows a systemic action
Poisons are given or taken so that death can occur at once by shock due to stoppage of body’s vital systems.
Route of administration plays a very important role in determination of death by poison as time in which death occurs are fastest in inhaled poisons, relatively slow in injected and lastly when ingested orally.
Some Symptoms
Sore throat
Trouble breathing
Drowsiness, irritability, or jumpiness
Nausea, vomiting, or stomach pain without fever
Lip or mouth burns or blisters
Unusual drooling
Strange odors on breath
Unusual stains on clothing
Seizures or unconsciousness
Examples
Poisons Based on Mode of Action
1. Corrosive poisons
Strong Acid - sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid
Strong Base - sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, ammoniumhydroxide
2. Irritant poisons
(a) Inorganic:
Metallic - lead, arsenic, mercury, antimony, copper, zinc
Non-metallic - chlorine, bromine, iodine
(b) Organic:
Vegetable - croton oil, castor oil
Animal - snake venom, scorpion venom, spider venom
(c) Mechanical: powder glass, diamond dust
3. Neurotic poisons
Cerebral - alcohol, opium, barbiturates, benzodiazepines
Spinal - strychnine
Peripheral - curare
4. Cardiac poisons
5. Asphyxiants - CO2, CO
Poisons Based on Medicolegal Classification
Homicidal poisons - aconite, abrus precatorius, strychnos nux vomica
Suicidal poisons - opium, barbiturate, organophosphorous, organochloro compounds
Accidental poisons - snake bite, CO, dhatura's seeds as it resembles capsicum seeds
Abortifacient poisons - quinine, calotropis
Stupefying agents - dhatura, chloral hydrate
Agents used to cause body injury - corrosive acids
Cattle poison - abrus precatorius, calotropis
Used for malingering - semicarpus anacardium
Poisons Based on Toxico-analytical Classification
1. Gaseous poisons: methanol, ethanol, benzene, toluene, acetone
2. Volatile substances: ethane, butane
3. Organic Non-volatile substances:
Drugs - opiates and synthetic narcotics, sedatives and hypnotics, stimulants, depressants
Pesticides - insecticides, fungicides, herbicides, rodenticides, nematocides
4. Metallic poisons: arsenic, lead, mercury, antimony, zinc, copper
5. Anion poisons: bromide, cyanide, fluoride, hypochlorite, nitrate, phosphate, sulfide, sulfate
Poisons Based on Physical State
1. Solid: lead, arsenic, mercury
2. Liquid:
Organic - ethanol, methanol, chloroform, acetone
Inorganic - liquid ammonia, liquid sulfur dioxide
3. Gaseous: carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide
Poisonous Fumes or Gases
In the home, poisonous fumes can be emitted from the following sources:
A car running in a closed garage
Leaky gas vents
Wood, coal, or kerosene stoves that are not working properly
Mixing bleach and ammonia together while cleaning, which makes chloramine gas
Strong fumes from other cleaners and solvents
Common Household Products
Oily hydrocarbon products are thin and slippery and can easily suffocate if the substances are drawn into the lungs when ingested. The products can cause chemical pneumonia by coating the inside of the lungs. Products that are required to have a safety lid include:
Baby oils
Sunscreens
Nail enamel dryers
Hair oils
Bath, body, and massage oils
Makeup removers
Some automotive chemicals (gasoline additives, fuel injection cleaners, and carburetor cleaners)
Cleaning solvents (wood oil cleaners, metal cleaners, spot removers, and adhesive removers)
Some water repellents containing mineral spirits used for decks, shoes, and sports equipment
General-use household oil
Gun-cleaning solvents containing kerosene
Oil products that are thicker and more "syrupy" are not as problematic, since they are not as easily inhaled into the lungs.
What to do if a poisoning happens
Swallowed poisons
Stay calm, act quickly, and follow these guidelines:
Get the poison away
If the substance is still in the mouth, make them spit it out or remove it with your fingers (keep this along with any other evidence of what was swallowed)
Do not make them vomit
Do not follow instructions on packaging regarding poisoning because these are often outdated. Instead, call Poison Help to get connected to a local poison center.
Take or send the poison container with you to help the healthcare provider find out what was swallowed.
Poisons on the skin
If someone spills a chemical on his or her body, remove his or her clothes and rinse the skin with lukewarm—not hot—water.
If the area shows signs of being burned, continue rinsing for at least 15 minutes, no matter how much they may protest.
Then call the poison control center for further advice.
Do not use ointments or grease.
Poison in the eye
Flush the eye by holding the eyelid open and pouring a steady stream of lukewarm—not hot—water into the inner corner of the eye.
If this is a child, you may need help from another adult to hold the child while you rinse the eye.
Continue flushing the eye for 15 minutes, and call the poison control center for further instructions.
Do not use an eyecup, eyedrops, or ointment unless the poison center tells you to do so.
Poisonous fumes or gases
If someone breathes in fumes or gases, get him or her into fresh air right away.
If they are breathing without a problem, call the poison center for further instructions.
If they are having difficulty breathing, call 911 or your local emergency service (EMS).
If they have stopped breathing, start CPR and do not stop until they breathe on their own or someone else can take over.
If you can, have someone call 911 right away.
If you are alone, perform CPR for 2 minutes and then call 911.
Be prepared for a poisoning emergency by posting the poison center telephone number by every telephone in your home.
Sources: 1 2 3 ⚜ Writing Notes & References
Writing Notes: Fictional Poisons
#writing notes#poison#fiction#writing reference#writing inspiration#spilled ink#writeblr#creative writing#writers on tumblr#dark academia#literature#poets on tumblr#writing prompt#poetry#light academia#jean béraud#writing resources
220 notes
·
View notes
Text
smth about the corrosion of metals being described in an almost living way,,,, bronze disease,,,, zinc rot…. tin plague….. corrosion as a living breathing thing that is eating inorganic substances alive,,,,,,
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
revolutionary robot girls galvanized into action (given a protective coating of zinc to prevent corrosion)
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
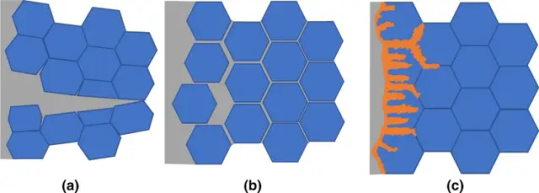
Liquid Metal Embrittlement
Ductile metals can turn brittle after contact with liquid metal and the presence of an applied stress (usually) in a phenomenon known as liquid metal embrittlement. (Also sometimes thought of as a collection of phenomena, based on the mechanisms involved.) Liquid metal embrittlement tends to occur with specific combinations of metals: zinc, mercury, and lithium are common liquid metals, with zinc able to embrittle some steels and aluminum alloys, mercury aluminum and copper alloys, and lithium some steels and copper alloys, for example. Mercury is the most common culprit of liquid metal embrittlement, which is one reason the metal is prohibited on commercial aircraft.
Sources/Further Reading: (Image source - 2021 article) (Corrosion Clinic) (TWI) (Wikipedia)
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Are There Different Styles of Fasteners for Residential Metal Roofing?
Regarding residential metal roofing, you may wonder about the various components contributing to a secure and durable installation. One important aspect is the fasteners that attach the roofing panels to your home. In this article, we’ll explore the different styles of fasteners available for residential metal roofing and help you understand how each option can impact the longevity and performance of your roof.
Understanding Residential Metal Roofing
Before we discuss fasteners, let’s briefly define residential metal roofing. Metal roofing consists of panels or tiles made from steel, aluminum, or copper. Known for their durability and resistance to harsh weather conditions, metal roofs are increasingly popular among homeowners. They can endure everything from heavy rains and snow to intense sunlight, making them a practical choice for various climates.
The Role of Fasteners in Residential Metal Roofing
Fasteners are essential for securing roofing panels to the underlying structure of your home. They ensure the panels remain in place and can effectively handle environmental stresses like wind, snow, and rain. When choosing a metal roofing system, understanding the different fastener styles is important for installation and long-term maintenance.
Types of Fasteners for Residential Metal Roofing
Let’s explore the various styles of fasteners commonly used in residential metal roofing. Each option has unique features and benefits, making it essential to choose the right one for your needs.
1. Exposed Fasteners
Exposed fasteners are popular for many homeowners due to their straightforward installation and lower cost. As the name suggests, the fasteners are visible on the surface of the roofing panels, penetrating them directly. Here are some key points to consider about exposed fasteners:
Installation Ease: Exposed fastener systems are generally easier to install, making them a great option for DIY enthusiasts or budget-conscious homeowners.
Cost-Effectiveness: This fastener style is typically less expensive, lowering overall material and labor costs.
Potential Leak Points: One drawback of exposed fasteners is that each penetration represents a possible leak point. Regular maintenance is needed to check for any corrosion or loosening over time.
2. Concealed Fasteners
Concealed fasteners offer a more refined look and can provide better protection against leaks. Unlike exposed fasteners, these are hidden beneath the seams of the roofing panels, which means they don’t come into direct contact with the elements. Here’s what to know about concealed fasteners:
Enhanced Aesthetics: Since concealed fasteners are hidden from view, they provide a clean, streamlined appearance.
Leak Prevention: Concealed fasteners generally have a lower risk of leaks because they are not directly exposed to weather conditions.
Installation Complexity: This type of fastener can be more complicated to install, often requiring professional assistance to ensure proper sealing and alignment.
Fastener Materials and Coatings
The choice of fastener material and coating can also significantly influence the performance and durability of your residential metal roofing. Here are some common options:
1. Galvanized Steel Fasteners
Galvanized steel fasteners are coated with zinc to protect against corrosion. They’re durable, but the zinc coating can wear away over time, especially in humid or coastal environments. Regular inspections can help identify issues before they become significant concerns.
2. Stainless Steel Fasteners
Stainless steel fasteners are highly resistant to rust and corrosion, making them an excellent choice for areas with harsh weather conditions. They tend to have a longer lifespan but can be more expensive than galvanized options.
3. Aluminum Fasteners
Aluminum fasteners are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making them suitable for many residential metal roofing applications. However, they may not be as strong as steel fasteners, so they’re typically used in less demanding situations.
Choosing the Right Fastener Style for Your Home
When selecting the right fastener style for your residential metal roofing, consider the following factors:
Roof Design and Slope: The design and slope of your roof can influence the type of fastener best suited for your home. Steeper roofs may benefit from concealed fasteners to minimize water pooling and potential leaks.
Climate Conditions: Assess your local climate. If you live near the coast or in an area with heavy rainfall, prioritize corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel.
Budget: Weigh your budget against the benefits of different fastener types. While exposed fasteners may save you money upfront, the potential for leaks could lead to higher maintenance costs later.
Maintenance Tips for Fasteners in Residential Metal Roofing
Regardless of the type of fasteners you choose, regular maintenance is essential to ensure your metal roof remains in good condition. Here are some maintenance tips:
Annual Inspections: Schedule yearly inspections of your roof, focusing on fasteners. Look for loose, damaged, or corroded fasteners that need attention.
Tighten Loose Fasteners: If you notice any loose fasteners, tighten them promptly to prevent leaks and further damage.
Check for Corrosion: Pay close attention to any signs of corrosion on your fasteners, especially if they’re made from galvanized steel. Replace any corroded fasteners to maintain the integrity of the roof.
Sealant Application: Consider applying a sealant around fasteners to enhance their leak resistance, particularly for exposed fasteners.
Consult a Professional: If you’re unsure about the condition of your fasteners or how to maintain them, consult a qualified roofing contractor for assistance.
Choose the Best Fasteners for Your Metal Roof
Understanding the different styles of fasteners for residential metal roofing is essential for making informed decisions about your roofing project. By considering the pros and cons of each type and the materials used, you can select the best option for your home that meets both your aesthetic preferences and functional needs.
If you're ready to enhance your home’s roofing system, visit Lastime Exteriors. They offer various services and can provide expert guidance on energy-efficient roofing solutions tailored to your specific needs. Explore your options today and ensure your home is protected with a high-quality metal roof!
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Type of Screws Should Be Used for Residential Metal Roofing?
If you're considering upgrading to residential metal roofing, you’re likely wondering about a few key aspects—like the types of screws you'll need to use. Choosing the right screws isn’t just a matter of aesthetics; it plays a significant role in the durability and longevity of your roof. Let’s dive into the details so that you can make informed decisions for your home improvement project.
Understanding Residential Metal Roofing
Residential metal roofing is gaining traction among homeowners due to its incredible longevity and durability. Unlike traditional asphalt shingles, metal roofs can last 50 years or more when properly installed. They are also highly resistant to weather conditions, making them a smart choice for various climates. However, the installation process requires the right materials, particularly when it comes to screws.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Screws
When installing residential metal roofing, the type of screws you select matters. Using the wrong screws can lead to leaks, corrosion, and reduced lifespan of your roofing system. Specifically, metal roofing screws are designed to accommodate the expansion and contraction that occurs with temperature changes. They’re manufactured to offer a secure fit while minimizing the risk of damage to the panels.
Types of Screws for Residential Metal Roofing
1. Self-Drilling Screws
Self-drilling screws, often referred to as “tek screws,” are one of the most popular options for residential metal roofing. These screws come with a drill bit tip, allowing them to pierce the metal without requiring pre-drilling. This can save time during installation since you can avoid the extra step of making pilot holes.
Benefits of Self-Drilling Screws:
Easy and quick installation.
Excellent for various metal thicknesses.
Reduces the risk of misalignment during installation.
2. Galvanized Screws
Galvanized screws are coated with a layer of zinc, which provides excellent rust resistance. This is particularly important for roofs exposed to harsh weather conditions, as metal roofs can be prone to corrosion if not properly protected.
Benefits of Galvanized Screws:
Enhanced durability against rust and corrosion.
Suitable for both residential and commercial applications.
Available in various lengths and diameters to fit different needs.
3. Stainless Steel Screws
For homeowners looking for the ultimate in corrosion resistance, stainless steel screws are an excellent choice. They are perfect for coastal areas where saltwater can accelerate corrosion. Although they are typically more expensive, their longevity can justify the investment.
Benefits of Stainless Steel Screws:
Exceptional resistance to rust and corrosion.
Ideal for challenging environments, such as coastal regions.
Lower maintenance costs over the lifespan of your roof.
4. EPDM Washers
While not a screw type, it’s essential to consider the washers you’ll use with your screws. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) washers provide a reliable seal that prevents water leaks. When paired with metal roofing screws, they create an effective barrier against moisture, ensuring the integrity of your roofing system.
Benefits of EPDM Washers:
Flexible and durable, allowing for thermal expansion and contraction.
Offers excellent weather resistance.
Helps to prevent leaks in metal roofing applications.
Other Considerations for Residential Metal Roofing Screws
Length and Diameter
When selecting screws for residential metal roofing, pay attention to the length and diameter. The length should be sufficient to penetrate through the metal panel and into the underlying structure, typically a wooden or metal frame. Generally, screws should extend at least 1 inch into the substrate to ensure a secure hold.
Color Match
Aesthetics also play a role in your screw selection. Many manufacturers offer color-matched screws that blend seamlessly with your metal roofing panels. This not only enhances the visual appeal of your roof but also ensures that any exposed screw heads do not detract from the overall design.
Installation Tips for Using Screws in Residential Metal Roofing
To ensure a successful installation, consider the following tips:
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always consult the metal roofing manufacturer's instructions regarding screw types, lengths, and installation practices.
Avoid Over-Tightening: When installing screws, be careful not to over-tighten them. This can lead to the deformation of the metal panels and compromise their integrity.
Stagger Your Screws: For improved water resistance and stability, stagger your screws in each panel. This technique provides better support and minimizes the potential for leaks.
Check for Alignment: Regularly check that your panels are aligned properly as you install the screws. Misalignment can lead to unnecessary strain on the panels and screws.
Secure Your Home’s Future
When it comes to choosing screws for residential metal roofing, making the right decisions will significantly impact the roof's performance and longevity. Self-drilling screws, galvanized or stainless steel options, and EPDM washers are all excellent choices to consider. Paying attention to the type, size, and installation techniques ensures that your metal roofing project stands the test of time.
Are you ready to explore residential metal roofing more and learn the best practices for installation? Visit Lastime Exteriors today to learn about our services and find energy-efficient roofing solutions tailored to your needs. Make sure to invest in your home's future!
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Distek company developed and patented a new non-polluting technology of anti-corrosion protection for steel parts, based on a thermal-diffusion zinc-coating process using powder mixtures.
#Zinc coating corrosion resistance#Anti corrosion coating solution#Zinc corrosion resistance coating#In-House Anti corrosion coating lines#Corrosion resistance coating#Anti corrosion coating for steel
0 notes
Text
What Makes Zinc Coating a Superior Metal Coating Option
We know metals are prone to corrosion. And we also know of its negative impacts, such as damaging the metal structure and entailing financial losses. Therefore, we should consider an effective method to guard metals against corrosion. Zinc coating is an effective technique to protect metals from corrosion. Due to zinc coating corrosion resistance, metal life becomes long.
0 notes