#wikipedia.org - electronic information source
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

#CYMEKS#CYMEK#brain controlling machine body#vacation#a willing vacation from your life in the palace because you want to live a life with less positivity in it in every imaginable way- vacatio#planet earth#text#txt#reading what somebody else wrote as text and making decisions using it - a plan to ensure you die horribly and your family all gets raped#absolutely the wierdest fucking shit anyone has ever heard of - traveling to a different planet based only on text you personally read#absolutely the wierdest fucking shit anyone has ever heard of - traveling to a different universe based only on text you personally read#criminals substituting the text dictionaries or lexicons used by others for translation especially#all text analysis read wikipedia.org and all of its contents#all text analysis read all hyperlinks on the electronic information source wikipedia.org and all the documents there and follow them#electronic information source - wikipedia.org#wikipedia.org - electronic information source#brad geiger - nobody wants to be bothered by lots of idiots who would decide to not bother if they read more#bradley carl geiger - nobody wants to be bothered by lots of idiots who would decide to not bother if they read more#guys in bad situations lying and scheming to get idiots to do their bidding because they essentially have no useful resources#guys who got everything disconnected except communications devices they reprogrammed themselves#guys selling things they don't own that aren't for sale or trade#brad geiger - infinite resources and unimaginable levels and amounts of defenses#biting flies - stay away from planet earth and the universe it is in and never allow anything to even contact it#guys who claimed they already killed brad geiger or own him or own anything in his universe and the bafti#the bafti#guys who stole a single body or identity that brad geiger's time traveling deep space capable military robots become aware of#slavers who enslave and eat humanoids to prove their wealth in slaves from all different times directions and species are attacking earth#what are you involved in?#planet earth has species and individual energy signature analysis to determine what and exactly who you are no matter what body you are in#all in the universe the planet earth is in are constantly scanned and none are abducted or killed
0 notes
Text
Blog Post 1- Industry Research
AMATEUR PHOTOGRAPHY
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating long lasting images through the recording of light, either electronically or chemically using a light sensitive material like photographic film. Photography is employed in a range of scientific fields, as well as manufacturing and business, and of course its direct uses, such as art, film and video production and recreational uses, such as a hobby or as a directive of mass communication.
Photography typically uses a lens to focus the light that has either been emitted or reflected from objects that then make a real image on the light sensitive surface inside the camera during a timed exposure. With an electronic image sensor, an electronic charge is produced with each pixel and these are then processed electronically and digitally stored in a digital image file, for either future display or further processing.
Photographic emulsion gives the result of an invisible, but latent image which will later be chemically developed into a visible image, either positive or negative, depending on a couple of factors, and they are the purpose of the photographic material, and the processing method. A negative image on photographic film is traditionally used to create a positive image on a paper base. This is usually referred to as a print, and this is created using an enlarger or through contact printing.
WHAT DOES AN AMATEUR PHOTOGRAPHER DO?
An amateur photographer practices photography as a hobby or as a passion, not necessarily to make money. The work of some amateur photographers can be compared to that of many professional photographers and will either be highly specialised or eclectic in subject choice. Amateur photography is sometimes pre-eminent in the subjects being used as they have very minute commercial use prospects or any prospects of monetary gain for the photographer.
The growth of Amateur photography began in the late 19thCentury following a meteoric rise in popularity of hand-held cameras. In the present times, photography is so widely spread through social media and this has been aided by the evolution of photography equipment and platforms as well. The change in the equipment used for photography, like mobile phones with cameras that have also aided the progression of actual photo quality, have meant that photography has had its accessibility blown wide open.
(Wikipedia.org, 2021)
DIGITAL ART
Digital Visual Art consists of either 2D visual information shown on an electronic visual display or 3D information that has been mathematically translated from 2D information, which is then viewed through perspective projection on an electronic visual display.
The simplest form of this is 2D Computer Graphics which may be a basic reflection of how one may draw with a pen or pencil and a piece of paper. In the instance of 2D Computer Graphics, the image is on the screen and the drawing implement is either a tablet stylus or a computer mouse. What is then generated on the screen has the appearance of a pencil, pen, or paintbrush.
The second kind of computer generated digital art is 3D computer graphics, in which the screen is the window into a virtual setting, and this becomes where objects are arranged to be “photographed” by the computer.
Typically, 2D computer graphics are comprised of raster graphics, their primary means of source representation, differentiating from 3D computer graphics which make use of vector graphics in order to create immersive VR installations. A third and final possible variation is the generation of 2D or 3D art through the sole use of algorithms that are embedded in computer programmes. This can be considered as the native form of computer art and the introduction to the history of computer art. This introduction can be found in an interview with the pioneer of computer generated art, Frieder Nake (Wikipedia.org, 2021).
Fractal Art, Data moshing, and algorithmic art, alongside real-time generative art are a few other examples.
(Wikipedia.org, 2021)
DIGITAL ILLUSTRATION
Digital or Computer illustration is the use of digital tools to create images that have been directly manipulated by the artist. This is usually done through the use of a pointing device like a tablet stylus or a computer mouse. Digital harness mathematical models that are created by the artist. Digital Illustration can be separated easily from digital photo manipulation, what that means is that it is constructed from original designs and photos. Photographs are not usually the main base for Digital Illustration.
Illustration Software
There are two main types of application that are used for Digital Illustration:
· Bitmap Applications- Adobe Photoshop
· Vector Applications- Adobe Illustrator
Bitmap Applications:
Bitmap Applications are usually referred to as painting applications. With a bitmap application, the content is stored digitally in fixed rows and columns of pixels, which can be transformed into separate layers which can be isolated for easier manipulation of different parts of the image.
A bitmap image contains information regarding the hue, luminance, and saturation of each pixel. When the pointing device moves over a pixelated area of the image, new colours and values are applied to the underlaying pixels. Painting tools allow for the simple creation of “fuzzy” imagery, including glow or soft shadow effects and textures such as fur, velvet, stone, and skin and these are hugely used in photo retouching.
Vector Applications:
The second kind of digital illustration application is a Vector Application. Vector applications are more commonly referred to as drawing applications. It is referred to in this manor due to the differences in appearance of final products between the two applications, with regard to the look and feel.
Within vector based tools, the content is stored digitally as a resolution independent mathematical formula describing open paths (lines), closed paths (shapes), as well as colour fills, strokes, and gradients. Vector paths are built up of anchor points and paths segments by using the pointing device to click and move. Many vector graphics are readily available from internet databases which are editable and can be used for larger projects. Drawing tools can draw precise lines, shapes and patterns with well defined edges and are great for working with big constructions such as maps and typography.
Digital may include both vector and raster graphics in the same work. A bitmap file may be saved in a format which embeds a layer of vector information, and a vector image file may include imported bitmap images.
Digital Techniques:
Photo bashing is a technique that is mostly used by Concept Artists. The process involves the artist blending and merging photographs and/or 3D Assets as well as painting, so they can create a composite art piece. This technique is similar to the process of compositing in video editing. Concept artists use this technique to increase the accuracy of the piece but also to aide their productivity.
(Wikipedia.org, 2021)
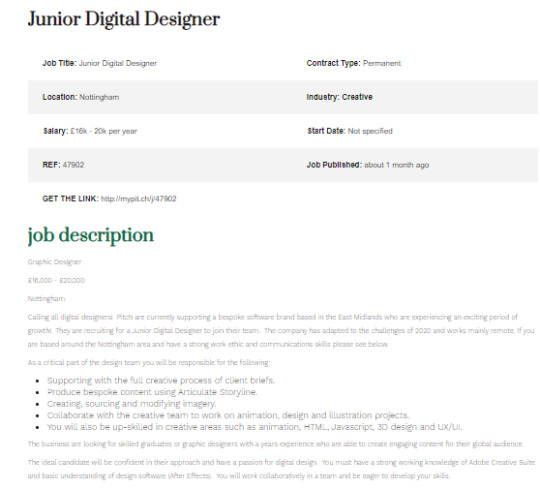
JUNIOR DIGITAL DESIGNER JOBS
To fulfil a job such as a Junior Digital Designer, I need to have a range of skills such as:
· Animation
· HTML
· JavaScript
· 3D Design
· UX/UI Design
As a part of a team of designers I’d have to share the collective responsibility of:
· Client support during the creative process
· Produce bespoke content using articulate storyline
· Creating, sourcing, and modifying imagery
· Collaborative with the creative team to work on animation, illustration, and design projects.
I’d need to have a strong working knowledge of Adobe Creative Suite and a basic knowledge of design software such as After Effects.
I’d need to be a graduate or graphic designer with one year experience and be able to create engaging content for a global audience. I would work collaboratively in a team with an eagerness to develop my skills.

1 note
·
View note
Text
10 Unfamiliar Filipino Words
We are fond using words which makes us more unique in any way we have to use it.
Many of Us know that many foreigners are having a hard time speaking in our language, But as we go far in our side of truth.. we still have many things or words to learn even if we are natives of our own land.
Let's discover the undiscoverable one, and let's be familiar to the unfamiliar... Here are the 10 uncommon Filipino Words that will surely amaze you and you'll surely share to anyone!
.........
1. " Karumalan "
English Term : Menstrual Period
Example : Hindi makagalaw ng mabuti ang mga kababaihan kung sila ay may Karumalan.
[ Womens can't freely move when they are on a Menstrual Period ]
Definition : The menstrual Period or Cycle is the monthly series of changes a woman's body goes through in preparation for the possibility of pregnancy. Each month, one of the ovaries releases an egg — a process called ovulation. At the same time, hormonal changes prepare the uterus for pregnancy.
( Source : Mayoclinic.Org )

2. " Panginain "
English Term : Browser
Example : Gamitin mo ang Panginain mo sa iyong Cellphone para makapaghanap ng impormasyon ng mabilis.
[ Use your mobile browser to search information quickly ]
Definition : Browser is a software application that lets you visit web pages on the Internet. Popular browsers include Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Internet Explorer. Currently, Google Chrome is the most widely used browser in the world, and is also considered one of the fastest and most secure.
( Source : whatsmybrowser.org )

3. " Pantablay "
English Term : Charger
Example : Maari ko bang mahiram ang iyong pantablay?
[ Can I borrow your charger? ]
Definition : Charger is a device used to put energy into a secondary cell or rechargeable battery by forcing an electric current through it. The charging protocol depends on the size and type of the battery being charged.
( Source : Wikipedia )

4. " Dagibalniing liboy "
English Term : Electromagnetic wave
Example : Halimbawa ng dagibalniing liboy ay ang liboy ng radyo
[ example of an Electromagnetic wave is Radio wave ]
Definition : One of the waves that are propagated by simultaneous periodic variations of electric and magnetic field intensity and that include radio waves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
( Source : Merriam Webster )

5. " Pang- Ulong Hatinig "
English Term : Headset
Example : Pwede bang mahiram ang iyong pang ulong Hatinig?
[ Can I borrow your Headset? ]
Definition : A headset combines a headphone with a microphone. Headsets are made with either a single-earpiece (mono) or a double-earpiece (mono to both ears or stereo).
( Source : Wikipedia.Org )

6. " Pook Sapot "
English Term : Website
Example : Ang pook sapot na napuntahan ko ay higit na mas kapanipaniwala
[ the website that I have visited is more reliable ]
Definition : A website is a collection of publicly accessible, interlinked Web pages that share a single domain name. Websites can be created and maintained by an individual, group, business or organization to serve a variety of purposes. Together, all publicly accessible websites constitute the World Wide Web.
( Source : Techopedia.com )

7. " Dagitab "
English Term : Electric Current
Example : Mabagal ang daloy ng dagitab ngayong araw
( Electric Current flows slowly today )
Definition : Electric current is electric charge in motion. It can take the form of a sudden discharge of static electricity, such as a lightning bolt or a spark between your finger and a ground light switch plate. More commonly, though, when we speak of electric current, we mean the more controlled form of electricity from generators, batteries, solar cells or fuel cells.
( Source : Livescience.com )

8. " Sambat "
English Term : Fork
Example : Maari bang pakiabutan ako ng sambat?
[ can you lend me a fork? ]
Definition : a common tool used in eating that usually has three or four stiff metalpoints attached to a handle.
( source : Cambridge dictionary )

9. " Miktinig "
English Term : Microphone
Example : Maganda ang kalidad ng iyong miktinig
( Your Microphone is a good quality )
Definition : A microphone is a device that translates sound vibrations in the air into electronic signals or scribes them to a recording medium. Microphones enable many types of audio recording devices for purposes including communications of many kinds, as well as music and speech recording.
( Source : Techtarget.Com )

10. " Pinag- Urungan "
English Term : Left Overs
Example : Itapon mo ang iyong pinag- urungan
( Throw your left overs )
Definition : something, especially food, remaining after the rest has been used or consumed.
( Source : Google Definition )

.....................
That's all... I hope you have something to learn from those unfamiliar words... The comment section is open for suggestions, corrections and appreciation for my work... Untill next time... See you!
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Familiarity with keyboard instruments + types of keyboard or thumb instruments.
It is a keyboard instrument that uses a keyboard to play it. Types of thumb instruments include organ, wind organ, Hammond organ, piano, keyboard, harpsichord, cello, accordion, melotron and synthesizer, the most well-known of which are piano and organ. Source: wikipedia.org Keyboard instruments are commonly used in European countries and many of these instruments are kept in museums due to their long history. Keyboard instruments are very popular with those who are interested in old music and instruments. Join us to get acquainted with the types of these instruments. Keyboard instruments are instruments that are used to create sound and play it. These types of instruments are very popular and the use of keyboard instruments is very popular among young people. The following are some of them: Piano - Organ - Clausen - Keyboard - Chambero - Harpicord - Celta - Accordion - Harmonica - Harmony - Harmony - Original - Electronic Instruments - Electric Organ - Terminus - Synthesizer - Keyboard - Electric Guitar - Bass Guitar. Types of keyboard instruments Keyboard instruments, as the name implies, are instruments played by a knob or key. • Organ Today's organ instrument has two main types: wind organ and electric organ (electronic). The wind organ consists of a row of pipes of different sizes that produce sound from the oscillation of air in these sound pipes. In an electric organ, electronic circuits oscillate and hear the sound of the speaker. It is a wind instrument whose notes are played on the keyboard. It is one of the oldest instruments in European culture and has been used in religious and church music for a long time. In ancient Arabic and Persian sources, this instrument was called the organ. • Pipe organ - Pipe organ It is a type of wind instrument whose sound is created by blowing compressed air. This sound is conducted by tubes. These sounds are controlled by the keyboard. This instrument is one of the oldest instruments made by Europeans and is mostly used in religious and church music. In Persian, this instrument is called an organ • Hammond organ It is a type of electric organ invented by Lawrence Hammond and John M. Hunter in 1935. Different models were produced that used sliding bars to produce a variety of sounds. Hammond developed the instrument as a low-cost alternative to large church wind instruments, but it was soon used by gospel bands. Jimmy Smith introduced it to jazz, and later rock bands used it. Source: wikipedia.org • Piano - Piano It is one of the most famous keyboard instruments. The sound of the piano is produced by the impact of hammers on its metal strings inside a wooden box. These hammers move when the keys are pressed. The piano strings are attached to a plate called the "sound plate" which acts as their amplifier. The piano has three pedals, the first pedal being echoed from the right. The second pedal is used to reduce the volume but mute the sound. The third pedal stops the sounds and prepares to start again.
• Clavichord A knob is similar to a keyboard. This instrument was very popular for many years, especially in the sixteenth, seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. In the clavichord, sound is produced by tapping brass or iron strings with small blades called tangents. Vibrations are transmitted across the bridge to the sound board. The keyboard was invented in the early fourteenth century. • Harpsichord - harpsichord It is one of the keyed instruments. The appearance of the harpsichord is almost similar to that of the piano, but the way the two instruments sound is different; In a harpsichord, by pressing the keys and moving the components of a mechanical system attached to them, small (percussion-like) appendages of the strings vibrate and sound is produced. Synthesizer (In Persian: electric instrument or combiner) is an electronic device that is able to produce different types of sound and combine signals with different frequencies. As the name implies, most synthesizers seek to artificially produce the sound of acoustic instruments such as those listed above. Instead of producing natural direct sound, the synthesizer generates electrical signals that can then be transmitted through speakers or headphones. • Mellotron - Mellotron The Mellotron is an electromechanical keyboard with multitasking and playback capabilities, first built in 1963 from a similar chamber called Chamberlain in Birmingham. Its advantage over Chamberlain was its mass production capability. The structure evolved from a similar Chamberlain, but could be produced more efficiently. The instrument is played by pressing its keys, each of which presses a length of magnetic tape toward a cap and pulls it through one end. Then, when the key is released, the bar is retracted to its original position by a spring. Different parts of the tape can be played to access different sounds.
Accordion It is a thumb instrument with a movable diagonal surface on both sides and a lantern body. The instrument was invented in Europe in the early 19th century and is commonly used in the folk music of Europe, North America, South America and Russia. The oldest name of this instrument is harmonica, which is a Greek name meaning musical harmony. Accordion is a famous German instrument that is world famous for its simplicity and softness of sound. • Célesta Celesta, also spelled celestial, is an orchestral percussion instrument resembling a small standing piano patented in 1886 by a Parisian, Auguste Mustele. It consists of a series of small metal rods (and hence a metallophone) with a keyboard and a simple piano work in which small felt hammers strike the rods. Abstract Keyboards or knobs are instruments that you can make sound by tapping the key with your fingers. These instruments, like other instruments, have different types, which we have mentioned and explained in this article. These instruments attract most young people. From the past until now, many inventions have been made in these instruments. If you wish, you can share your comments or information about these instruments with us.
1 note
·
View note
Text
10 Things Maritime Academies Don’t Teach
As Benjamin Franklin said – “TELL ME AND I FORGET. TEACH ME AND I REMEMBER. INVOLVE ME AND I LEARN.”
For a professional at any stage in career life, learning is a continuous process.
However, what we learn in the colleges and academy form the base of everything in the future.
Maritime colleges play a crucial role in a seafarer’s life as he/she learns all the “life at sea” skills there.
Unfortunately, not all the maritime colleges and universities teach students the important skills needed in the “Real World”.
There is a vast gap between what the students are taught in the Maritime academies and what’s needed for a successful tenure at sea.
But not all seafarers are aware of it.
Maritime institutes, along with the theoretical knowledge must also introduce soft skills, which would make students ready to face unwanted situations and to succeed in life in general.
Related Read: Maritime Training System In India Needs Urgent Reforms And Changes
1. Time Management
Time management may be defined as utilizing the time effectively and productively.
This is something very critical and imperative onboard.
Some people don’t exercise this due to lack of interest or knowledge and things/situations get out of their hand sooner or later.
Photograph by Jr.Engineer Divya Raj
Maritime institutes don’t focus on teaching this part of the professional life onboard, and this is something which is never talked about in maritime academies.
In the maritime world where there is always various kind of pressures from all around, i.e., commercial or work-related, it is imperative to manage one’s time and not just stumble on the tasks you get.
We too have people onboard who well plan their jobs and stay happier giving results on time or accomplishing their jobs with good results. Life onboard for them who exercise proper time management is always high on the hog.
Related Read: How to Stay Fit and Focused on Ships?
2. Task Prioritization
Prioritization is something which helps you to decide relative importance or urgency of things.
It helps you to analyse your jobs and grade them in a sequence of importance so that you can anchor your energy and concentration on the things that matter. It is something that can show your strength of handling multiple tasks in your professional life.
As you keep escalating in your rank, task prioritization will matter the most and will help you at all times.
Related Read: 10 Professional Mistakes Seafarers Should Never Make Onboard Ships
3. Adaptability
To cope up with the advancements in various things in the shipping industry, including the changes in the maritime laws and convention, it is essential to stay updated all the time.
The competency level required for any job onboard is changing rapidly along with the technology.
Even though so much around us has changed, in Maritime institutes still the same things are taught which were being taught a decade earlier.
It is foremost essential to be with the flow of the current to sustain in a highly competitive market.
4. Balancing Social and Professional Life
Many people say for mariners, it’s challenging to maintain a proper balance between Professional and Social life. This difficulty is only with the seafarers who wholeheartedly focus on work to escalate their career leaving no time for their friends and families.
Related Read: 10 Ways to Ensure WellBeing Of Seafarers At Sea
However, many seafarers do not know how to handle their careers and social life. Though it is essential to focus on work, it is equally important to finding a perfect and healthy balance between the two.
Officer with Chief cook and OS.
5. Financial management
As a seafarer, it is essential to manage your finances/money to ensure yours and your family’s financial wellbeing at all times and at times of critical situations. We have to be prepared for the day when we will not be able to work.
Consider the below as 3 essential tips for your financial planning:
Personal Medical, health, and Life insurance
Do not overspend
Savings and Investments
Many of us choose this profession for money.
We all want to earn as much money as possible, and we work too hard to earn. It’s therefore very important to manage your finance.
6. Cyber Security
Being connected with friends, family and the world via the internet is now a necessity. However, with the technological advancements, shipping companies are providing internet facilities to its crew onboard to make them feel connected to the family and the world.
With the power of technology also comes the risk of using it. MAERSK fell victim to a major cyber-attack caused by the Not Petya malware, leading to a loss of approx. USD 300 million.
Related Read: Download New FREE Guide – Cybersecurity For Seafarers
As a budding seafarer, the maritime institutes can play a vital role in teaching social media usage and cyber security when at sea, which will not only save shipping companies from such financial cyber-attacks but also save the crew from maritime pirates.
7. Dealing With People With Different Nationalities
Going on the ship for the first time and finding oneself among a bunch of other nationals is very common.
However, we have our percipience how a particular nationality behaves, without knowing the facts accurately.
Photograph by Captain Manish Nayyar
For e.g., many nationalities do not appreciate loud communication or pointing fingers while communication, which may make the situation sore.
Related Read: 6 Ways to Improve Interpersonal Relationship among Seafarers on board Ships
There are a handful of nations which are dominating the maritime industry and teaching the students about the culture, communication practices, and behaviours, in brief, will help them improve the inter-personnel relationships at sea which will ultimately make a successful team on ship.
8. Life Beyond Sea
If you are an experienced seafarer, you must have met someone who is planning to move ashore (or it might be you) after a long (or a brief) stint at sea.
With the qualification a marine engineer or a deck officer holds, there are different shore jobs which can be opted for.
However, seafarers are always in a dilemma about what kind of shore job they will get if they want to quit life at sea or settle ashore in the same industry. The maritime institutes can bridge this knowledge gap by providing a few essential lectures or classes at the end of the course.
Related Read: How Not To Choke When Making The Transition From Ship To Shore
9. Inter-communication Between Departments
Many institutes provide both nautical science and marine engineering courses on one campus. A ship runs safely and on time due to the teamwork of deck and engine department.
Related Read: 10 Situations Wherein Engine and Deck Officers Must Maintain Efficient Communication
This teamwork can be practised right from the institution level where the MTI can arrange intercommunication classes between navigation and engineering departments, improving the operational awareness.
10. Digital Disruption In The Industry
Digital changes in the shipping industry are often and highly advanced.
Credits: kevin huges /wikipedia.org
From electronic engine to autonomous ships, the industry is adapting to automation at a pace higher than what is taught in the maritime academies.
For seafarers, there is no other alternative but to adapt to the changes as they come.
To make it a gradual adaptation (which will help them learn the process), additional automation and machine learning courses should be provided by the maritime academies, explaining how the seafarers will need to work in co-operation with the Remote Operating Centres (ROC) in the near future.
Related Read: Can Futuristic Unmanned Cargo Ships Sail Without Seafarers?
This is to ensure that future technologies are not disruptive but further help in the overall advancements for decades.
Over to you..
Do you know about any other things that maritime academies don’t teach?
Let’s know in the comments below.
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Report an Error
from Storage Containers https://www.marineinsight.com/careers-2/10-things-maritime-academies-dont-teach/ via http://www.rssmix.com/
0 notes
Video
youtube
What is VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM? What does VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM mean? VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM meaning - VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM definition - VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM explanation. Source: Wikipedia.org article, adapted under http://ift.tt/yjiNZw license. A vehicle tracking system combines the use of automatic vehicle location in individual vehicles with software that collects these fleet data for a comprehensive picture of vehicle locations. Modern vehicle tracking systems commonly use GPS or GLONASS technology for locating the vehicle, but other types of automatic vehicle location technology can also be used. Vehicle information can be viewed on electronic maps via the Internet or specialized software. Urban public transit authorities are an increasingly common user of vehicle tracking systems, particularly in large cities. Several types of vehicle tracking devices exist. Typically they are classified as "passive" and "active". "Passive" devices store GPS location, speed, heading and sometimes a trigger event such as key on/off, door open/closed. Once the vehicle returns to a predetermined point, the device is removed and the data downloaded to a computer for evaluation. Passive systems include auto download type that transfer data via wireless download. "Active" devices also collect the same information but usually transmit the data in near-real-time via cellular or satellite networks to a computer or data center for evaluation. Many modern vehicle tracking devices combine both active and passive tracking abilities: when a cellular network is available and a tracking device is connected it transmits data to a server; when a network is not available the device stores data in internal memory and will transmit stored data to the server later when the network becomes available again. Historically, vehicle tracking has been accomplished by installing a box into the vehicle, either self-powered with a battery or wired into the vehicle's power system. For detailed vehicle locating and tracking this is still the predominant method; however, many companies are increasingly interested in the emerging cell phone technologies that provide tracking of multiple entities, such as both a salesperson and their vehicle. These systems also offer tracking of calls, texts, web use and generally provide a wider range of options. Major constituents of the GPS-based tracking are: 1. GPS tracking: The device fits into the vehicle and captures the GPS location information apart from other vehicle information at regular intervals to a central server. Other vehicle information can include fuel amount, engine temperature, altitude, reverse geocoding, door open/close, tire pressure, cut off fuel, turn off ignition, turn on headlight, turn on taillight, battery status, GSM area code/cell code decoded, number of GPS satellites in view, glass open/close, fuel amount, emergency button status, cumulative idling, computed odometer, engine RPM, throttle position, GPRS status and a lot more. Capability of these devices actually decide the final capability of the whole tracking system; most vehicle tracking systems, in addition to providing the vehicle's location data, feature a wide range of communication ports that can be used to integrate other on board systems, allowing to check their status and control or automate their operation. 2. GPS tracking server: The tracking server has three responsibilities: receiving data from the GPS tracking unit, securely storing it, and serving this information on demand to the user. 3. User interface: The UI determines how one will be able to access information, view vehicle data, and elicit important details from it. Vehicle tracking systems are commonly used by fleet operators for fleet management functions such as fleet tracking, routing, dispatching, on-board information and security. Along with commercial fleet operators, urban transit agencies use the technology for a number of purposes, including monitoring schedule adherence of buses in service, triggering changes of buses' destination sign displays at the end of the line (or other set location along a bus route), and triggering pre-recorded announcements for passengers.
0 notes
Text
10 Things Maritime Academies Don’t Teach
As Benjamin Franklin said – “TELL ME AND I FORGET. TEACH ME AND I REMEMBER. INVOLVE ME AND I LEARN.”
For a professional at any stage in career life, learning is a continuous process.
However, what we learn in the colleges and academy form the base of everything in the future.
Maritime colleges play a crucial role in a seafarer’s life as he/she learns all the “life at sea” skills there.
Unfortunately, not all the maritime colleges and universities teach students the important skills needed in the “Real World”.
There is a vast gap between what the students are taught in the Maritime academies and what’s needed for a successful tenure at sea.
But not all seafarers are aware of it.
Maritime institutes, along with the theoretical knowledge must also introduce soft skills, which would make students ready to face unwanted situations and to succeed in life in general.
Related Read: Maritime Training System In India Needs Urgent Reforms And Changes
1. Time Management
Time management may be defined as utilizing the time effectively and productively.
This is something very critical and imperative onboard.
Some people don’t exercise this due to lack of interest or knowledge and things/situations get out of their hand sooner or later.
Photograph by Jr.Engineer Divya Raj
Maritime institutes don’t focus on teaching this part of the professional life onboard, and this is something which is never talked about in maritime academies.
In the maritime world where there is always various kind of pressures from all around, i.e., commercial or work-related, it is imperative to manage one’s time and not just stumble on the tasks you get.
We too have people onboard who well plan their jobs and stay happier giving results on time or accomplishing their jobs with good results. Life onboard for them who exercise proper time management is always high on the hog.
Related Read: How to Stay Fit and Focused on Ships?
2. Task Prioritization
Prioritization is something which helps you to decide relative importance or urgency of things.
It helps you to analyse your jobs and grade them in a sequence of importance so that you can anchor your energy and concentration on the things that matter. It is something that can show your strength of handling multiple tasks in your professional life.
As you keep escalating in your rank, task prioritization will matter the most and will help you at all times.
Related Read: 10 Professional Mistakes Seafarers Should Never Make Onboard Ships
3. Adaptability
To cope up with the advancements in various things in the shipping industry, including the changes in the maritime laws and convention, it is essential to stay updated all the time.
The competency level required for any job onboard is changing rapidly along with the technology.
Even though so much around us has changed, in Maritime institutes still the same things are taught which were being taught a decade earlier.
It is foremost essential to be with the flow of the current to sustain in a highly competitive market.
4. Balancing Social and Professional Life
Many people say for mariners, it’s challenging to maintain a proper balance between Professional and Social life. This difficulty is only with the seafarers who wholeheartedly focus on work to escalate their career leaving no time for their friends and families.
Related Read: 10 Ways to Ensure WellBeing Of Seafarers At Sea
However, many seafarers do not know how to handle their careers and social life. Though it is essential to focus on work, it is equally important to finding a perfect and healthy balance between the two.
Officer with Chief cook and OS.
5. Financial management
As a seafarer, it is essential to manage your finances/money to ensure yours and your family’s financial wellbeing at all times and at times of critical situations. We have to be prepared for the day when we will not be able to work.
Consider the below as 3 essential tips for your financial planning:
Personal Medical, health, and Life insurance
Do not overspend
Savings and Investments
Many of us choose this profession for money.
We all want to earn as much money as possible, and we work too hard to earn. It’s therefore very important to manage your finance.
6. Cyber Security
Being connected with friends, family and the world via the internet is now a necessity. However, with the technological advancements, shipping companies are providing internet facilities to its crew onboard to make them feel connected to the family and the world.
With the power of technology also comes the risk of using it. MAERSK fell victim to a major cyber-attack caused by the Not Petya malware, leading to a loss of approx. USD 300 million.
Related Read: Download New FREE Guide – Cybersecurity For Seafarers
As a budding seafarer, the maritime institutes can play a vital role in teaching social media usage and cyber security when at sea, which will not only save shipping companies from such financial cyber-attacks but also save the crew from maritime pirates.
7. Dealing With People With Different Nationalities
Going on the ship for the first time and finding oneself among a bunch of other nationals is very common.
However, we have our percipience how a particular nationality behaves, without knowing the facts accurately.
Photograph by Captain Manish Nayyar
For e.g., many nationalities do not appreciate loud communication or pointing fingers while communication, which may make the situation sore.
Related Read: 6 Ways to Improve Interpersonal Relationship among Seafarers on board Ships
There are a handful of nations which are dominating the maritime industry and teaching the students about the culture, communication practices, and behaviours, in brief, will help them improve the inter-personnel relationships at sea which will ultimately make a successful team on ship.
8. Life Beyond Sea
If you are an experienced seafarer, you must have met someone who is planning to move ashore (or it might be you) after a long (or a brief) stint at sea.
With the qualification a marine engineer or a deck officer holds, there are different shore jobs which can be opted for.
However, seafarers are always in a dilemma about what kind of shore job they will get if they want to quit life at sea or settle ashore in the same industry. The maritime institutes can bridge this knowledge gap by providing a few essential lectures or classes at the end of the course.
Related Read: How Not To Choke When Making The Transition From Ship To Shore
9. Inter-communication Between Departments
Many institutes provide both nautical science and marine engineering courses on one campus. A ship runs safely and on time due to the teamwork of deck and engine department.
Related Read: 10 Situations Wherein Engine and Deck Officers Must Maintain Efficient Communication
This teamwork can be practised right from the institution level where the MTI can arrange intercommunication classes between navigation and engineering departments, improving the operational awareness.
10. Digital Disruption In The Industry
Digital changes in the shipping industry are often and highly advanced.
Credits: kevin huges /wikipedia.org
From electronic engine to autonomous ships, the industry is adapting to automation at a pace higher than what is taught in the maritime academies.
For seafarers, there is no other alternative but to adapt to the changes as they come.
To make it a gradual adaptation (which will help them learn the process), additional automation and machine learning courses should be provided by the maritime academies, explaining how the seafarers will need to work in co-operation with the Remote Operating Centres (ROC) in the near future.
Related Read: Can Futuristic Unmanned Cargo Ships Sail Without Seafarers?
This is to ensure that future technologies are not disruptive but further help in the overall advancements for decades.
Over to you..
Do you know about any other things that maritime academies don’t teach?
Let’s know in the comments below.
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Report an Error
from Storage Containers https://www.marineinsight.com/careers-2/10-things-maritime-academies-dont-teach/ via http://www.rssmix.com/
0 notes
Text
30 Types of Navigation Equipment and Resources Used Onboard Modern Ships
Gone are the days when a ship navigation officer had to take help of unconventional ways to plan and navigate a voyage at sea. Today, a ship officer has myriad of marine navigation equipment which makes his life a lot simpler, thanks to the advancement in technology. Moreover, present-day seafarers are trained so as to know the functioning and operation of all modern day navigational equipment that has made the journey at sea smoother and safer.
With modern day facilities and automation, a ship today has several advanced navigation equipment systems which give accurate data for the voyage.
Image for Representation Purpose only; Credits: wikimedia.org
Herein, we have enlisted 30 types of navigational equipment, both old and new, which are present on all merchant ships.
1. Gyro Compass
It is used for finding the right direction. Unlike magnetic compass, gyro compass is not hampered by an external magnetic field. It is used to find the correct North Position, which is also the earth’s rotational axis to provide a stable directional source. Its repeater system must be present in the steering platform for emergency steering.
Read more about Gyro Compass here
Related Read: Top 3 Free Marine Compass Apps for Android Smart Phones
2. Radar
The seagoing vessels depend on S-band and X-band frequency radar system for navigation as it can detect targets and display the information on the screen such as the distance of the ship from land, any floating objects (an island, rocks, iceberg etc.), other vessels, and obstacles to avoid a collision. It is a rotating antenna which discovers the surrounding area of the ship.
Credits: kelvin hughes/wikipedia.org
Read more about ECDIS here.
Related Read: 15 Things To Consider While Using Radar On Ships
3. Magnetic Compass
The magnetic compass work in conjunction with the magnetic field of the earth and is the essential means of the direction indicating device. It is used to get a planned course for the voyage. This ship navigation equipment is usually fitted at the centre line of the ship on the monkey island. A transmitting magnetic type compass is fitted so that the output can be displayed in the bridge panel.
Related Read: What is a Binnacle On Ships?
4. Auto Pilot
The ship bridge layout is filled with equipment and tools used for navigation. The autopilot is considered to be one of the most effective bridge navigational equipment as it assists the human operator in controlling the ship by keeping the steering in autopilot, which allows them to concentrate on broad aspects of the operation.
It is a combination of hydraulic, mechanical, and electrical system and is used to control the ship’s steering system from a remote location (Navigation bridge).
Related Read: 10 Things to Consider While Using Auto-Pilot System on Ships
5. ARPA
Automatic Radar Plotting Aid displays the position of a ship and other vessels nearby. The radar displays the position of the ships in the vicinity and selects the course for the vessel by avoiding any kind of collision.
This bridge navigational equipment constantly monitors the ship’s surrounding and automatically acquires the number of targets, in this case; ships, boats, stationary or floating objects etc., and plot their speeds and courses respectively. It also presents them as vectors on the display screen and constantly update the parameters with each turn of the antenna by calculating their nearest points of approach to own ship and also the time before this will occur.
6. Automatic Tracking Aid
Just like ARPA, automatic tracking aid displays the information on tracked targets in graphic and numeric to generate a planned layout for a safer and collision-free course.
Usually, A large size target measuring 800 m or more in the circumference is considered as a landmass and not tracked. Echoes less than 800 m are deemed as targets to be tracked.
Related Read: 10 Important Things To Do During Ship Collision Accident
7. Speed & Distance Log Device
This bridge equipment on a ship is used to measure the speed and the distance travelled by a ship from a set point. By calculating the same, ETA of the ship is adjusted or given to the port authority and agent.
8. Echo Sounder
There are many modern ship navigation tools present on ship and echo sounder is one of the instruments which has been in the play from almost 100 years now. It is used to measure the depth of the water below the ship’s bottom using sound waves which work on the principle of transmission of sound waves and an audio pulse which will bounce off a reflecting layer, returning as an echo to the source.
9. Electronic Chart Display Information System
ECDIS is a development in the navigational chart system used in naval vessels and ships. With the use of the electronic navigation equipment, it has become easier for a ship’s navigating crew to pinpoint locations, and attaining directions are easier than before.
Read more about ECDIS here.
Related Read: Pros and Cons of ECDIS Or Paperless Navigation Of Ships
10. Automatic Identification system
AIS is also among the types of a navigation system which helps to pinpoint the location and other navigational statistics of ships. AIS uses VHF radio channels as transmitters and receivers to send and receive messages between ships which endeavours to fulfil a lot of responsibilities.
As per the regulation enforced by The International Maritime Organisation (IMO), all passengers’ vessels and commercial ships over 299 Gross Tonnage (GT) sailing in the international to carry a Class A AIS transponder.
Read more about AIS here.
Related Read: Download: The Definitive AIS Handbook
11. Long Range Tracking and Identification (LRIT) System
LRIT is an international tracking and identification system incorporated by the IMO under its SOLAS convention to ensure a thorough tracking system for ships of 300 gross tons and above which are on international voyages across the world. This maritime equipment is fitted to improve the maritime domain awareness.
Read more about LRIT here.
12. Rudder Angle Indicator
Rudder angle indicator, as the name indicates, provides the angle of the rudder. The display is provided on the navigation bridge equipment console so that the ship navigation officer can control the rate of turn and rudder angle of the ship. The indication is also provided in the bridge wing and engine control room.
Related Read: How Does A Rudder Help In Turning A Ship?
13. Voyage Data Recorder
A VDR or voyage data recorder is a crucial instrument among the ship navigation equipment list which is installed on a ship to continuously record vital information related to the operation of a vessel. It contains a voice recording system for a period of at least the last 12 hours. This recording is recovered and made use of for investigation in events of accidents. The importance of VDR is similar to a “black box” installed on an airplane.
Image Credits: wikimedia.org
Read more about VDR here.
14. Rate of turn indicator
This navigational tool indicates how fast the ship is turning at a steady rate (useful during pilotage and manoeuvring), normally shown as a number of degrees turned. The rate a ship is turning is measured in degrees per minute. This essential tool assists a coxswain in steering a course safely.
15. GPS Receiver
A Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver is a display system used to show the ship’s location with the help of Global positioning satellite in the earth’s orbit.
With the record of the ship’s positions, the speed, course, and the time is taken to cover the distance between “two marked positions” can be calculated.
Related read: 5 Best Handheld Portable Marine GPS Devices
16. Sound Reception System
This acoustic system is required for a ship with a fully enclosed type bridge. It enables the navigating officer inside the cabin to listen to the sound signals (such as fog or ship’s horn) from other ships in the vicinity. This is fitted in ships bridge equipment console and helps the navigating officer to conduct the look-out duty as per the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea.
Related read: 10 Important Points Ship’s OOW Should Consider During Restricted Visibility
17. Navigational Lights
All boats – whether big or small are required to have night lights as a part of the navigation systems. This system was introduced in the year 1838 by the United States and then was followed by the United Kingdom in 1849. In the year 1889, the International Maritime Conference was established by the United States to establish proper guidelines to prevent marine accidents. In the year 1897, these rules were officially adopted internationally. The navigation lights are one of the most critical navigation equipment needed for sailing in high seas as it enables self vessel being clearly visible to other ships in the vicinity.
Read more about navigation lights here.
Related read: How Maintenance of Navigation Lights is Done On Ships?
18. Ship Whistle
A ship’s horn is known as a whistle and it is generally provided in duplicate. One is driven by air and the other is electrically operated. The whistle should be both manually and electrically operational from the bridge.
Among different instruments used in difficult navigation such as bad weather, fog, poor visibility, high traffic etc., the ship’s whistle or horn helps in alerting the nearby vessels.
During an emergency, the horn is used to notify and alert the ship’s crew and other vessels nearby.
19. Daylight Signalling Lamp
They are light-signalling devices used for emergency signalling in the day time (and can also be used during the night). Like other emergency ship instruments, the energy source for the lamp is not solely dependent on the ship’s main power supply. Also, the lamp enclosure should be weather and seawater- proof material.
20. Pilot Card
It is an informative booklet provided to the ship’s pilot. It consists of the dimension, draught, turning circle, manoeuvring, propulsion equipment and other navigation tools and instruments list of the vessel for safe manoeuvring.
Related Read: What Are The Duties of Officer On Watch When Pilot is On Board Ship?
21. Voyage Plan
A voyage Plan must be present onboard for referring past voyage plans or planning a future voyage. Among the different aids to navigation carried on a ship, a voyage plan is a tool for the deck officer to ensure the safety of the ship from a commercial and legal perspective too. It is prepared by gathering different information such as weather, meteorological, ship’s current and future cargo data, other navigational data etc.
Image Credits: Nachiketh Bhattathiri
Read more about Voyage Plan here
22. Forecastle Bell
It is used to mark the presence of the ship in fog or bad weather and sound the alarm in case of an emergency, along with the ship’s main horn or whistle.
Related Read: What to do When Ship Encounters Rough Weather?
23. Manoeuvring Booklet
In this booklet, the performance of the propulsion plant and the ship during manoeuvring in different weathers and situations is recorded for quick reference. The important content of the manoeuvring booklet are:
Ships General description
Manoeuvring characteristics in deep water
Stopping and speed control characteristics in deep water
Manoeuvring characteristics in shallow water
Manoeuvring characteristics in wind
Manoeuvring characteristics at low speed
Additional information
Related Read: Understanding Different Types Of Manoeuvres of a Vessel
24. Black Ball Shape
It is a day time signalling shape used to determine the characteristics of the vessel with a different arrangement of ball shapes. For e.g. a vessel at anchor will show a black ball at the foremost end of the forecastle and a ship not under command shows two black balls in a vertical line on her highest mast.
Related Read: Responsibilities Of Deck Officer During Anchoring Operation
25. Record of Navigation Activities
All the navigational activities which are performed by the ship’s officers and crew using different navigation equipment on the bridge must be recorded and kept on board for ready reference. This is mandatory and the most important log book.
Related Read: Different Entries To Be Made In Bridge Log Book of The Ship
26. Record of Maintenance of Navigational Equipment
The hard copy of all the ship navigation system and equipment list must be present as records onboard ships for ready reference of port and regulatory authorities and must be signed by master and duty officers of the ship.
Related Read: Daily, Monthly And Weekly Tests Of GMDSS Equipment On Board Ships
27. Wheelhouse Posters
Present in the Navigation bridge, it displays detailed information of manoeuvring characteristics of the ship including turning circle, stopping and manoeuvring characteristics of the vessel.
28. Transmitting Heading Devise
Transmitting Heading Devise or THD is an electronic device which is used to display the information of the vessel’s true heading. The THDs compliance information is provided in chapter V of the SOLAS Convention.
29. Black Diamond Shape
When the ship is being towed or when a vessel is unable to manoeuvres on itself, a black diamond shape is shown during the day time.
Related Read: Preparations For Emergency Towing Of Ship – 10 Important Points
30. Ship Flags
Various types of ship flags with different colours and signs are used to indicate a navigation ship’s position. Signal flags are they are commonly known, have been used since the ancient times and are still used on all vessels.
These are the different bridge equipment and their uses which are installed on the ship to assist the deck officer for navigating the vessel safely. If we missed any equipment or you want to add more to the list, please comment below.
Related Read: Understanding Nautical Flag Etiquettes
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
SaveSaveSaveSave
SaveSaveSaveSave
SaveSave
Report an Error
from Storage Containers https://www.marineinsight.com/marine-navigation/30-types-of-navigational-equipment-and-resources-used-onboard-modern-ships/ via http://www.rssmix.com/
0 notes
Text
Everything You Ever Wanted to Know About Container Refrigeration Unit
A reefer container is an enclosed unit used for transporting temperature sensitive cargo. The container requires an external power supply for its operation. The article describes everything you ever wanted to know about container refrigeration units.
When reefer containers are loaded in ships, the power supply is provided from the power generated from the D.G sets of the vessel. If the vessel’s generator capacity is not enough to support the additional power consumption of the refrigerated containers (in case of old ship or unavailability of generator due to overhauling etc.), mobile power packs are installed on the ship.
There are a different variety of refrigerated shipping containers present in the market today. A particular type is used depending upon the efficiency requirement and the cargo they need to carry.
Types of Refrigerated Shipping Containers are:
1. Closed Reefer: This is a conventional type refrigerated container. It comes in one-piece with integral front wall and an all-electric automatic cooling and heating unit for ISO sea-going containers.
2. Modified/ Controlled Atmosphere (MA/CA) reefer containers: These type of insulated shipping containers maintain a constant atmosphere by replacing consumed oxygen using an air exchange system, keeping an ideal atmosphere in equilibrium with the product’s deterioration rate.
3. Automatic Fresh Air Management Containers: Popularly known by its acronym – AFAM reefer containers uses advanced technology to regulate the air combination by automatically adjusting the scale of fresh air exchange. It works similar to Controlled Atmosphere refrigerated container, controlling the composition of oxygen, carbon dioxide and others. The controls of the AFAM refrigerated containers can be adjusted to influence and extend the shelf lives of the cargo they carry.
Some important points about container refrigeration are:
Container Refrigeration unit is fitted in front of the container and it serves as a container front wall.
Some units are dual voltage, designed to operate on 190/230 or 380/460 volts A.C, 3 phase, 50-60 hertz power.
Operating control power is provided by single phase transformer which steps down the A.C supply power source to 24 volts, 1 phase control power.
Credits: Sarahjolda2/wikipedia.org
Related reading: How perishable food is transported using refer ships?
Understanding the Basic Sections of Refer Unit
1. Compressor Section
Consists of a compressor (with H.P switch) and power cable storage compartment. Power transformer may be an option where the ship supply differs.
It also contain modulating and suction solenoid valve (for controlling the quantity of gas flow).
Safety fittings in the section are- moisture liquid indicator, pressure relief valve, filter drier etc.
Safety of the system is further enhanced by electronic monitoring with the help of following sensors- Compressor suction and discharge sensor, supply air temperature sensor, supply recorder sensor, ambient sensor.
Related reading: What are safety devices on a refrigeration system of a ship?
2. Condenser Section
The condenser section contains condenser fan and its motor, an air cooled condenser coil and condenser saturation sensor.
For air cooled condenser air is normally pulled from bottom and discharged horizontally through centre of the unit.
Some units consists of water cooled condenser /receiver. This unit is expensive.
Related reading: Heat exchangers on ship explained
3. Evaporator Section
This section contains temperature sensing bulb, return recorder bulb sensor and a thermostatic expansion valve (for flow of refrigerant and maintenance of inside temperature).
Assembly consist of evaporator coil and heater, drain pan and heater, defrost and heat transmission switches.
The evaporator fan circulates air throughout the container by pulling air in top of refrigeration unit and directing air through evaporator coil where it’s either heated or cooled and is then discharged out at the bottom of refrigeration unit into the container.
Related reading: Understanding capacity control in ship’s air conditioning and refrigeration system
4. Fresh air Make up Vent
Purpose of this vent is to provide ventilation for commodities that requires fresh air circulation and must be closed when transporting frozen foods.
Air exchange depends upon static pressure differential which will vary depending upon how container is loaded.
Safety and Operating Precaution
Credits: Andrea Puggioni/wikipedia.org
An injury, no matter how small, should never go unattended. Always obtain first aid or medical attention immediately.
Always wear safety gloves and glasses while working on any unit and also when charging refrigerant.
Keep hand, tools, and clothing clear from evaporator and condenser fan.
No work should be performed on any unit until all circuit breaker and start-stop switches are turned off and power supply disconnected.
Do not bypass any electrical safety device.
When performing arc welding on unit or condenser, disconnect all wire harness connection from the module in control box. Do Not remove wire harness from the module unless you are grounded to a unit frame with a static safe wrist strap.
In case of electrical fire, open circuit switch and extinguish it with CO2 extinguisher.
Officer and crew responsible for refrigerated shipping container must know the hazard related to refrigerant gas such as – Phosgene gas hazard (due to high temperature), Asphyxiation hazard in non-ventilated spaces etc.
Safely handle the compressed gas bottles when charging refrigerant
Most common Problem in refrigerated shipping containers – Leakage.
The leakage of refrigerant is the most common problem faced by onboard staff during the voyage. Following tests must be carried out to detect leakages:
1. Soap water test: This is done on low-pressure line by spraying soapy water on the troubled pipe or space. If the soapy water comes in contact with leakage area, bubbles will form
2. Halide lamp test: This is used for all pressure lines
3. Electronic leak detector: It is a portable unit to carry out leak detection. It should not be used in a noisy area.
4. Permanent or fixed type leak detection unit: Some reefer containers come with fixed type leak detection unit which gives audio-visual alarm in case of leakage
*Note: All the pipes in the refrigerated container unit are insulated. Before testing the piping for leakage, make a small hole in the insulation and check the leakage near the hole (using soap/ halide lamp or electronic detector). Once the leakage is confirmed, then remove the insulation of the complete pipe section to spot the leakage area.
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Report an Error
from Storage Containers https://www.marineinsight.com/refrigeration-air-conditioning/everything-you-ever-wanted-to-know-about-container-refrigeration-unit/ via http://www.rssmix.com/
0 notes
Text
How ECIDS Can Be Further Improved – A 2nd Officer’s Perspective
ECDIS has no doubt been in many ways a blessing for ship officers as it has made their lives easy. Gone are those days when it used to take at least 2-3 days correcting paper charts. It would also not be wrong to point out that though it has made life easy for many, still there are few grey areas which
It would also not be wrong to point out that though ECDIS on ships has made life easy for many, still there are a few grey areas which need due attention when it comes to using ECDIS practically and where it can further be improved. Let’s focus on the so-called ‘grey areas’ and how it can be further improved from a user’s perspective.
Credits: Hervé Cozanet/wikipedia.org
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
NAVTEX/NAV AREAS WARNING INTEGRATION
Although there are many ECIDS manufacturers who have provisions to integrate NAVTEX to their ECDIS, these warnings are not automatically marked on ENCs (Electronic Navigation Charts). It simply displays these warnings under the NAVTEX menu in ECDIS where the user can just read it. Thus by just having an option for integrating NAVTEX to ECDIS it does NOT relieve the user from manual plotting or removing outdated warnings appropriately from ENCs.
With respect to NAV Area warnings, there are a very few ECDIS(s) in which these warnings are marked on ENCs (E.g. TRANSAS). Since these warnings are mainly promulgated via SAT-C, integration and marking on ENCs is a bit difficult. However, there are few ECDIS makers who get these warning marked directly on ENCs if the ECDIS is connected to the internet or updated via email. In either case, marking on ENCs again does not relieve the user from manual plotting or removing outdated warnings appropriately from ENCs.
In order to keep a track on NAVTEX/NAV area warnings manually plotted on ENCs, it is highly recommended to use NP 133C – Admiralty ENC Maintenance Record.
In future as a user, it would be a pleasure to see seamless integration and automatic plotting of these warnings on ENCs. It would not only eliminate the possibility of missing out on these warnings while planning passage but also greatly reduce the chances of error during manual plotting.
Image for representation purpose only
T&P NOTICES AND AIO
The T&P notices that are shown in the Overlay relate specifically to ADMIRALTY paper charts and are overlaid on ENCs to alert users on the availability of this information during passage planning. There are two important things to note here.
First, AIO should be switched on while passage planning so that all relevant T&P notices are taken into account. Since in monitoring mode, AIO causes a lot of clustering of data on ENCs and therefore it is not recommended to keep it on. Also as a prudent officer, while planning passage, all important T&P notices should be manually marked on ENCs; for example, if the vessel is going in for anchoring and T&P warning shows a new fowl area or sea cable, then even if AIO is switched off, the bridge team should be well aware where the potential hazard is.
Second, AIO may not contain all T&P NMs issued by the ENCs producer. Also, there may be a time delay between the publication or cancellation of national T&P NMs and the publication or removal of the equivalent ADMIRALTY T&P NMs. Many ENC producers include some or all of their T&P NMs in their ENCs and care should be taken to understand what has already been included in the ENCs in use. A list of
A list of ENCs producers whose policy is to include T&P NM information in their ENCs can be found at www.ukho.gov.uk/AVCS and in the \INFO folder on all AVCS discs. Please note that official ENCs remain the primary source of information for navigation at all times.
Image for representation purpose only
DIFFERENT IHO STANDARDS
In order to have uniformity across data transfer between different hydrographic offices of the world and because of issues such as encryption, validation, preventing piracy and decryption of data, various standards have been set up by International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) based at Principality of Monaco. Few important standard relevant to a user are described below.
S-57 – is the transfer standard of digital data among various national hydrographic offices in the world and also for manufacturers, mariners and other data users. This ensures that all the national hydrographic offices will construct ENCs in a manner which is safe for navigation and do not omit any important information.
Every ECDIS equipment must be able to read the exchange format S-57, otherwise, it cannot become an ECDIS. This standard is subjected to regular updates; thus it is important that ECDIS software is kept up to date so as to enable it to read the latest edition of S-57.
S-52 – basically contains standards for visual presentation of ENC data by means of symbols, line styles, colours and other visual cues. This means that what the user sees on the screen is displayed in the same way across all approved makes and models of ECDIS.
Presentation library forms an important part of ECDIS. Again this standard is subject to regular updates and thus it is important that ECDIS software is kept up to date at all times.
S-63 – this standard deals with encryption, decryption and authentication of ENCs data. This prevents unauthorized access to ENCs data and thus prevents piracy. It also ensures that users can be confident that S-63 compliant ENCs are original, free from inaccurate data that is posed by unofficial ENCs and reduce chances of malware being introduced to ship’s IT systems. Public key and permits for ENCs form an important part of this standard.
The future standards that are being developed are S-100 and S-101. S-100 supports items such as imagery and gridded data, 3D and time-varying data, the density of bathymetry, and seafloor classification. The major advantage will be the amalgamation of S-57 and S-52, thus making data and its presentation into one standard. Based on S-100, the next generation ENC product specification will take several years to develop and test. It will have forward capabilities with S-57 ENCs; that is, an S-101 ECDIS will accept S-57 ENCs. This means that the managed introduction of S-101 will not result in the withdrawal or early termination of S-57 or S-57 ENCs.
ROUTE CHECK CAPABILITIES
The latest versions of ECDIS have route check capabilities which give a warning if the planned passage is passing over any danger or exceeding any preset parameters. This is definitely a remarkable tool, but again there are chances if say proper parameters are not set or for that matter warnings were not given due importance, then it can lead to serious disasters. It is thus advisable that a thorough visual scan of the ship’s route is done prior putting it on monitoring mode.
It is also not advisable to do planning and monitoring on the same equipment. By changing to planning mode during monitoring, the primary purpose of ECDIS as an anti-grounding tool is defeated.
ENCs WITH EXPIRED PERMITS
Generally, for loading ENCs first the permits are loaded and then ENCs are loaded from base CDs/DVDs. However, once the permit expires the ENCs can still be viewed but a permanent warning is displayed to warn the user stating that the permit is expired and ENCs are not up to date. Updates for ENCs which do not have a valid permit are never applied.
It is thus highly recommended that once the permit expires the ENCs should be manually deleted.
The future version of ECDIS should have an option to auto-delete ENCs without valid permits. It would reduce the chances of deleting wrong ENCs and using outdated ENCs.
Image for representation purpose only
LOOK AHEAD CAPABILITIES
For generations, who have been brought up with paper charts, ECDIS has one inherent issue and that is not being able to look ahead or have bird’s eye view. Many feel ‘claustrophobic�� while using it. With small display screen, the problem only increases.
In my opinion, the only temporary solution for this problem with present-day screen sizes is to use one ECDIS as a “look-ahead” tool and as per appropriate scale for the ENC in use. As a user, it is desirable that ECDIS is fitted with bigger screens so more content is visible which is no doubt, definitely better for safe navigation.
In the end, I would like to bring it to all readers’ kind attention that ECDIS is just a tool which assists us in safe navigation. It can never replace our eyes and our sense of situational awareness. Over-reliance is an issue and is the leading cause of ECDIS related incidents. With a better understanding of its limitation and proper training, this issue can be addressed properly.
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Report an Error
from Storage Containers https://www.marineinsight.com/marine-navigation/ecids-can-improved-2nd-officers-perspective/ via http://www.rssmix.com/
0 notes
Video
youtube
What is HARDWARE INTERFACE DESIGN? What does HARDWARE INTERFACE DESIGN mean? HARDWARE INTERFACE DESIGN meaning - HARDWARE INTERFACE DESIGN definition - HARDWARE INTERFACE DESIGN explanation. Source: Wikipedia.org article, adapted under http://ift.tt/yjiNZw license. Hardware interface design (HID) is a cross-disciplinary design field that shapes the physical connection between people and technology. It employs a combination of filmmaking tools, software prototyping, and electronics breadboarding. Through this parallel visualization and development, hardware interface designers are able to shape a cohesive vision alongside business and engineering that more deeply embeds design throughout every stage of the product. The development of hardware interfaces as a field continues to mature as more things connect to the internet. Hardware interface designers draw upon industrial design, interaction design and electrical engineering. Interface elements include touchscreens, knobs, buttons, sliders and switches as well as input sensors such as microphones, cameras, and accelerometers. In the last decade a trend had evolved in the area of human-machine-communication, taking the user experience from haptic, tactile and acoustic interfaces to a more digitally graphical approach. Important tasks that had been assigned to the industrial designers so far, had instead been moved into fields like UI and UX design and usability engineering. The creation of good user interaction was more a question of software than hardware. Things like having to push two buttons on the tape recorder to have them pop back out again and the cradle of some older telephones remain mechanical haptic relicts that have long found their digital nemesis and are waiting to disappear. However, this excessive use of GUIs in today’s world has led to a worsening impairment of the human cognitive capabilities. Visual interfaces are at the maximum of their upgradability. Even though the resolution of new screens is constantly rising, you can see a change of direction away from the descriptive intuitive design to natural interface strategies, based on learnable habits (Google’s Material Design, Apple’s iOS flat design, Microsoft’s Metro Design Language). Several of the more important commands are not shown directly but can be accessed through dragging, holding and swiping across the screen; gestures which have to be learned once but feel very natural afterwards and are easy to remember. In the area of controlling these systems, there is a need to move away from GUIs and instead find other means of interaction which use the full capabilities of all our senses. Hardware interface design solves this by taking physical forms and objects and connecting them with digital information to have the user control virtual data flow through grasping, moving and manipulating the used physical forms. If you see the classic industrial hardware interface design as an “analog” method, it finds its digital counterpart in the HID approach. Instead of translating analog methods of control into a virtual form via a GUI, one can see the TUI as an approach to do the exact opposite: transmitting purely digital processes into analog methods of interaction. Example hardware interfaces include a computer mouse, TV remote control, kitchen timer, control panel for a nuclear power plant and an aircraft cockpit.
0 notes
Video
youtube
What is DATABASE APPLICATION? What does DATABASE APPLICATION mean? DATABASE APPLICATION meaning - DATABASE APPLICATION definition - DATABASE APPLICATION explanation. Source: Wikipedia.org article, adapted under http://ift.tt/yjiNZw license. A database application is a computer program whose primary purpose is entering and retrieving information from a computerized database. Early examples of database applications were accounting systems and airline reservations systems, such as SABRE, developed starting in 1957. A characteristic of modern database applications is that they facilitate simultaneous updates and queries from multiple users. Systems in the 1970s might have accomplished this by having each user in front of a 3270 terminal to a mainframe computer. By the mid-1980s it was becoming more common to give each user a personal computer and have a program running on that PC that connected to a database server. Information would be pulled from the database, transmitted over a network, and then arranged, graphed, or otherwise formatted by the program running on the PC. Starting in the mid-1990s it became more common to build database applications with a Web interface. Rather than develop custom software to run on a user's PC, the user would use the same Web browser program for every application. A database application with a Web interface had the advantage that it could be used on devices of different sizes, with different hardware, and with different operating systems. Examples of early database applications with Web interfaces include amazon.com, which used the Oracle relational database management system, the photo.net online community, whose implementation on top of Oracle was described in the book Database-Backed Web Sites (Ziff-Davis Press; May 1997), and eBay, also running Oracle. Electronic medical records are referred to on emrexperts.com, in December 2010, as "a software database application". A 2005 O'Reilly book uses the term in its title: Database Applications and the Web. Some of the most complex database applications remain accounting systems, such as SAP, which may contain thousands of tables in only a single module. Many of today's most widely used computer systems are database applications, for example, Facebook, which was built on top of MySQL. The etymology of the phrase "database application" comes from the practice of dividing computer software into systems programs, such as the operating system, compilers, the file system, and tools such as the database management system, and application programs, such as a payroll check processor. On a standard PC running Microsoft Windows, for example, the Windows operating system contains all of the systems programs while games, word processors, spreadsheet programs, photo editing programs, etc. would be application programs. As "application" is short for "application program", "database application" is short for "database application program". Not every program that uses a database would typically be considered a "database application". For example, many physics experiments, e.g., the Large Hadron Collider, generate massive data sets that programs subsequently analyze. The data sets constitute a "database", though they are not typically managed with a standard relational database management system. The computer programs that analyze the data are primarily developed to answer hypotheses, not to put information back into the database and therefore the overall program would not be called a "database application".
0 notes
Video
youtube
What is DATA CURATION? What does DATA CURATION mean? DATA CURATION meaning - DATA CURATION definition - DATA CURATION explanation, Source: Wikipedia.org article, adapted under http://ift.tt/yjiNZw license. Data curation is a broad term used to indicate processes and activities related to the organization and integration of data collected from various sources, annotation of the data, and publication and presentation of the data such that the value of the data is maintained over time, and the data remains available for reuse and preservation. Data curation includes "all the processes needed for principled and controlled data creation, maintenance, and management, together with the capacity to add value to data". In science, data curation may indicate the process of extraction of important information from scientific texts, such as research articles by experts, to be converted into an electronic format, such as an entry of a biological database. In the modern era of big data the curation of data has become more prominent, particularly for software processing high volume and complex data systems. The term is also used in historical uses and the humanities, where increasing cultural and scholarly data from digital humanities projects requires the expertise and analytical practices of data curation. In broad terms, curation means a range of activities and processes done to create, manage, maintain, and validate a component. Data curation is typically user initiated and maintains metadata rather than the database itself. According to the University of Illinois' Graduate School of Library and Information Science, "Data curation is the active and on-going management of data through its lifecycle of interest and usefulness to scholarship, science, and education; curation activities enable data discovery and retrieval, maintain quality, add value, and provide for re-use over time." The data curation workflow is distinct from data quality management, data protection, lifecycle management and data movement. Deep background on data libraries appeared in a 1982 issue of the Illinois journal, Library Trends. For historical background on the data archive movement, see "Social Scientific Information Needs for Numeric Data: The Evolution of the International Data Archive Infrastructure." The exact curation process undertaken within any organisation depends on the volume of data, how much noise the data contains and what the expected future use of the data means to its dissemination. This term is sometimes used in context of biological databases, where specific biological information is firstly obtained from a range of research articles and then stored within a specific category of database. For instance, information about anti-depressant drugs can be obtained from various sources and, after checking whether they are available as a database or not, they are saved under a drug's database's anti-depressive category. Enterprises are also utilizing data curation within their operational and strategic processes to ensure data quality and accuracy. The Dissemination Information Packages (DIPS) for Information Reuse (DIPIR) project is studying research data produced and used by quantitative social scientists, archaeologists, and zoologists. The intended audience is researchers who use secondary data and the digital curators, digital repository managers, data center staff, and others who collect, manage, and store digital information.
0 notes
Video
youtube
What is TRANSPARENCY REPORT? What does TRANSPARENCY REPORT mean? TRANSPARENCY REPORT meaning - TRANSPARENCY REPORT definition - TRANSPARENCY REPORT explanation. Source: Wikipedia.org article, adapted under http://ift.tt/yjiNZw license. A transparency report is a statement issued on a regular basis by a company, disclosing a variety of statistics related to requests for user data, records, or content. Transparency reports generally disclose how frequently and under what authority governments have requested or demanded data or records over a certain period of time. This form of corporate transparency allows the public to discern what private information governments have gained access to through search warrants and court subpoenas, among other methods. Some transparency reports describe how often, as a result of government action or under copyright provisions, content was removed. Disclosing a transparency report also helps people to know about the appropriate scope and authority of content regulation for online discussions. Google first launched a transparency report in 2010, with Twitter following in 2012. Additional companies began releasing transparency reports as during the aftermath of the global surveillance disclosures beginning in 2013, and the number of companies issuing them has increased rapidly ever since. Transparency reports are issued today by a variety of technology and communications companies, including Google, Microsoft, Verizon, AT&T, Twitter, Apple, Dropbox, Facebook, Yahoo and CloudFlare. Several companies and advocacy groups have lobbied the U.S. government to allow the number of secret data requests (requests which include a gag orders - including National Security Letters) to be described within ranges in the report. Transparency reports may be published for a variety of purposes. One purpose could be to clarify how much information governments ask for, how such requests are evaluated, and how the receiving entity chose to respond. This information may lead consumers to the conclusion that the report's publisher is more trustworthy. However, there is some debate about what transparency reports really reveal. Some critics argue that mere quantities of requests may mislead consumers, since most entities have little control over the number of requests they receive, the breadth of the requests they receive, or even the number of requests they ultimately comply with. Companies such as Google, Microsoft, Yahoo, Facebook, and Twitter all release transparency reports, all of which list the type and number of government data requests each company receives. these reports include exact numbers and shed a bright light on government activity. The U.S. government will not, however, permit companies to report exact numbers for national security requests or the number of requests that came under the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance (FISA) Section 702, Patriot Act Section 215, or national security letters. Instead, they have to aggregate the numbers or provide a range. And that’s even if the government permits a company to publish that data. Google may publish national security letter information, but not FISA information. Facebook may publish FISA information, but it must lump such data in with NSL information. As a result, consumers cannot see the true figure for total government data requests. Critics of this policy, such as the Electronic Frontier Foundation, argue that there is no clear national security justification for blocking entities from releasing this information. In June 2013, Google asked the Department of Justice for the permission for disclosing details about the number of FISA requests it receives. As a result, Microsoft, Yahoo, and Facebook followed suit immediately. However, the Department of Justice refused those requests, and they only provide the companies with a heavily redacted version of their arguments. Here's what Google legal director Richard Salgado had to say about FISA requests: "We want to go even further. We believe it’s your right to know what kinds of requests and how many each government is making of us and other companies. However, the U.S. Department of Justice contends that U.S. law does not allow us to share information about some national security requests that we might receive. Specifically, the U.S. government argues that we cannot share information about the requests we receive (if any) under the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act. But you deserve to know."
0 notes
Video
youtube
What is SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO? What does SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO mean? SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO meaning - SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO definition - SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO explanation. Source: Wikipedia.org article, adapted under http://ift.tt/yjiNZw license. Signal-to-noise ratio (abbreviated SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. While SNR is commonly quoted for electrical signals, it can be applied to any form of signal (such as isotope levels in an ice core or biochemical signaling between cells). The signal-to-noise ratio, the bandwidth, and the channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon–Hartley theorem. Signal-to-noise ratio is sometimes used informally to refer to the ratio of useful information to false or irrelevant data in a conversation or exchange. For example, in online discussion forums and other online communities, off-topic posts and spam are regarded as "noise" that interferes with the "signal" of appropriate discussion. All real measurements are disturbed by noise. This includes electronic noise, but can also include external events that affect the measured phenomenon — wind, vibrations, gravitational attraction of the moon, variations of temperature, variations of humidity, etc., depending on what is measured and of the sensitivity of the device. It is often possible to reduce the noise by controlling the environment. Otherwise, when the characteristics of the noise are known and are different from the signals, it is possible to filter it or to process the signal. For example, it is sometimes possible to use a lock-in amplifier to modulate and confine the signal within a very narrow bandwidth and then filter the detected signal to the narrow band where it resides, thereby eliminating most of the broadband noise. When the signal is constant or periodic and the noise is random, it is possible to enhance the SNR by averaging the measurement. In this case the noise goes down as the square root of the number of averaged samples. Additionally, internal noise of electronic systems can be reduced by low-noise amplifiers.
0 notes
Video
youtube
What is INTERNET CENSORSHIP? What does INTERNET CENSORSHIP mean? INTERNET CENSORSHIP meaning - INTERNET CENSORSHIP definition - INTERNET CENSORSHIP explanation. Source: Wikipedia.org article, adapted under http://ift.tt/yjiNZw license. Internet censorship is the control or suppression of what can be accessed, published, or viewed on the Internet enacted by regulators, or on their own initiative. Individuals and organizations may engage in self-censorship for moral, religious, or business reasons, to conform to societal norms, due to intimidation, or out of fear of legal or other consequences. The extent of Internet censorship varies on a country-to-country basis. While most democratic countries have moderate Internet censorship, other countries go as far as to limit the access of information such as news and suppress discussion among citizens. Internet censorship also occurs in response to or in anticipation of events such as elections, protests, and riots. An example is the increased censorship due to the events of the Arab Spring. Other areas of censorship include copyrights, defamation, harassment, and obscene material. Support for and opposition to Internet censorship also varies. In a 2012 Internet Society survey 71% of respondents agreed that "censorship should exist in some form on the Internet". In the same survey 83% agreed that "access to the Internet should be considered a basic human right" and 86% agreed that "freedom of expression should be guaranteed on the Internet". According to GlobalWebIndex, over 400 million people use virtual private networks to circumvent censorship or for increased level of privacy. Many of the changes associated with Internet censorship are similar to those for offline censorship of more traditional media such as newspapers, magazines, books, music, radio, television, and film. One difference is that national borders are more permeable online: residents of a country that bans certain information can find it on websites hosted outside the country. Thus censors must work to prevent access to information even though they lack physical or legal control over the websites themselves. This in turn requires the use of technical censorship methods that are unique to the Internet, such as site blocking and content filtering. Views about the feasibility and effectiveness of Internet censorship have evolved in parallel with the development of the Internet and censorship technologies: A 1993 Time Magazine article quotes computer scientist John Gilmore, one of the founders of the Electronic Frontier Foundation, as saying "The Net interprets censorship as damage and routes around it." In November 2007, "Father of the Internet" Vint Cerf stated that he sees government control of the Internet failing because the Web is almost entirely privately owned. A report of research conducted in 2007 and published in 2009 by the Berkman Center for Internet & Society at Harvard University stated that: "We are confident that the tool developers will for the most part keep ahead of the governments' blocking efforts", but also that "...we believe that less than two percent of all filtered Internet users use circumvention tools". In contrast, a 2011 report by researchers at the Oxford Internet Institute published by UNESCO concludes "... the control of information on the Internet and Web is certainly feasible, and technological advances do not therefore guarantee greater freedom of speech." Blocking and filtering can be based on relatively static blacklists or be determined more dynamically based on a real-time examination of the information being exchanged. Blacklists may be produced manually or automatically and are often not available to non-customers of the blocking software. Blocking or filtering can be done at a centralized national level, at a decentralized sub-national level, or at an institutional level, for example in libraries, universities or Internet cafes. Blocking and filtering may also vary within a country across different ISPs. Countries may filter sensitive content on an ongoing basis and/or introduce temporary filtering during key time periods such as elections. In some cases the censoring authorities may surreptitiously block content to mislead the public into believing that censorship has not been applied. This is achieved by returning a fake "Not Found" error message when an attempt is made to access a blocked website.
0 notes