#trastamara
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text



Reign | The Spanish Princess
Francis and Henry meet their future Brides
#francis de valois#henry tudor#francis ii#henry viii#dauphin#duke of york#mary stuart#catalina de aragon#catherine of aragon#queen of scots#spanish princess#trastamara#ruairi o'connor#toby regbo#charlotte hope#adelaide kane#frary#cathry#reign#the spanish princess#castilla y aragon#meeting#engagement#hubby and wifey#face expression#love#en vray amoure#musician king#renaissance#Spotify
12 notes
·
View notes
Photo






Elizabeth of York and Katherine of Aragon
In 1501, Queen Elizabeth would help organize the wedding of her eldest son, Prince Arthur, and Katherine of Aragon.On October 2, the Spanish princess at last arrived in England, coming ashore at Plymouth after a stormy voyage. Ladies and officials had been appointed “to give their attendance upon the princess at her landing,” summoned by letters sent by the Queen herself. When Katherine set out on her journey eastward to London, she received a rapturous welcome from the people who flocked to see her on the way. Elizabeth must have been delighted to hear that her son’s bride was pretty and golden-haired, with a pleasing dignity. Preparations for the coming wedding advanced briskly.
On November 12, as all the bells of London rang out, banners fluttered from windows, crowds packed the streets, music sounded from every side, and the conduits ran with free wine, Katherine made her formal entry into the City. She was greeted by a series of lavish pageants in the Burgundian style as she passed along the processional route; all were designed to underline the success of the Tudor dynasty in obtaining such a highborn princess for the heir to the throne. The King, the Queen, Prince Arthur, Lady Margaret Beaufort and many other notables watched the procession from the windows of the home of a haberdasher in Cornhill. It was from her window that Elizabeth glimpsed her new daughter-in-law for the first time, as Katherine’s procession passed below; looking out, she would have seen a young girl riding “a great mule richly trapped after the manner of Spain,” flanked by Prince Henry and the papal legate, and wearing “rich apparel” in the Spanish mode:
“a little hat fashioned like a cardinal’s hat of pretty braid with a lace of gold to stay it, her hair hanging down about her shoulders, which is fair auburn, and a coif between her head and her hat of a carnation color.”
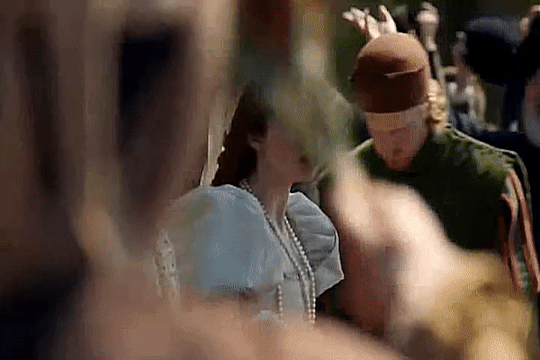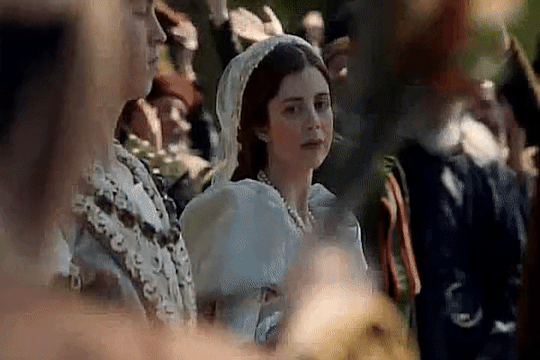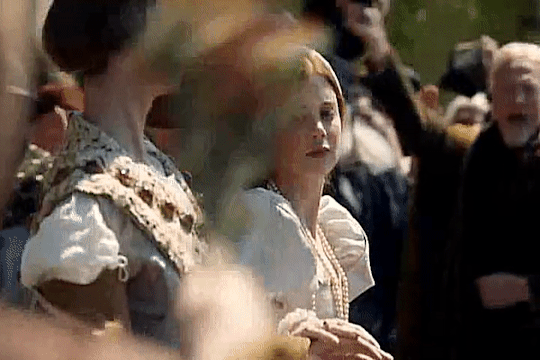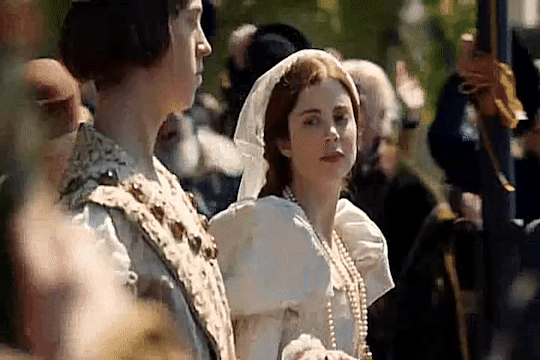
Arthur and Katherine were married on November 14 at Old St.Paul’s Cathedral in London. Katherine was now second lady in the land after the Queen. Afterward the Prince and Princess of Wales were conducted in a grand procession led by Prince Henry to the Bishop’s Palace, where a great feast was prepared.The previous afternoon and evening Katherine had been spent at the recently rebuilt royal residence of Baynard’s Castle, on the riverside, getting to know her mother-in-law. During her audience, Katherine and Elizabeth both spoke in Latin.They enjoyed themselves with pleasant and goodly communication, dancing and disports. Already Elizabeth had begun the process of preparing her successor for the role she would one day occupy, and probably Katherine was glad to have the guidance of a kindly mother-in-law who could initiate her into realities and mysteries of English court life. After the wedding, Elizabeth and Katherine shared days of celebrations with tournaments, disguisings and pageants.
The plan therefore was for Katherine to remain in London, under the tutelage of her mother-in-law (not forgetting her dominating grandmother-in-law), while Arthur was to be allowed to continue his growing-up undisturbed by the distractions of a wife, in the Marches of Wales at Ludlow Castle. But this plan was not carried out. Instead, Katherine and Arthur left together for Ludlow on December 21. Less than five months after their wedding, at the end of March 1502, Arthur and Katherine both fell ill. It took several weeks for her to recover from her illness. However, Arthur died on 2 April at the age of fifteen. He was buried in Worcester Cathedral. The news of Arthur’s death caused Henry VII to break down in grief, as much in fear for his dynasty as mourning for his son. Elizabeth comforted him, telling him that he was the only child of his mother but had survived to become King, that God had left him with a son and two daughters, and that they were both young enough to have more children.

In addition to Elizabeth’s other burdens, she was concerned for her daughter-in-law, and seems to have felt—as the Spanish sovereigns would when they heard the news of Arthur’s death— that Katherine of Aragon “must be removed without loss of time from the unhealthy place where she is now.” To this end Queen Elizabeth had sent an escort to bring the bereft and isolated young widow back to London, as soon as she was well enough to travel, and herself provided a black velvet litter, with valances and fringes also of black made by her own tailor, to convey her convalescent daughter-in-law. In this mournful equipage Katherine was brought to Richmond Palace. When she reached Richmond, she was conducted at once to the Queen, with whom she shared a mutual sorrow. After a short stay with the King and Queen, Katherine was given the choice of two residences: Durham House, the Bishop of Durham’s palace on London’s Strand, and Croydon Palace, the Archbishop of Canterbury’s residence in Surrey. Katherine chose Croydon and, by 4 May, was lodging there.
Late in May, Elizabeth of York sent Edward Calvert, her page, to Croydon, possibly to check on the Princess’s health, and perhaps discreetly to ask her servants if there were signs of any pregnancy. During the months Katherine stayed at Croydon, her future remained under discussion and her stay must have been shadowed by sorrow and anxiety. If Katherine had conceived a child by Arthur, the baby would be the new heir to the English throne and her union with Prince Henry would contravene canon law. Doña Elvira, her duenna, was adamant that the marriage had not even been consummated and wrote to Queen Isabel insisting that the Princess remained a virgin. Katherine was not pregnant with Arthur’s child. With her future still uncertain, Katherine has moved to Durham House.
In September Elizabeth sent Katherine books. In October sixteen oarsmen rowed her barge to the Durham House steps.They took Katherine the short distance to the Court of Westminster, where she seems to have stayed several weeks.The kindness offered by Elizabeth of York dried up abruptly ten months after Arthur’s death.The Queen had immediately got pregnant.The baby was a girl named Katherine, who died shortly after her birth. Succumbing to a post partum infection, Elizabeth died nine days later. It was her 37th birthday. Protocol suggests it is unlikely that Katherine attended the solemn funeral, where Elizabeth’s full-length effigy lay upon a coffin draped with black velvet and topped by a white gold cross. With Elizabeth’s death Katherine would have lost an ally, an alternative mother figure, and witnessed the effects of grief upon the king and his son Henry. Now the whole court was in mourning again.
Sources:
Elizabeth of York: A Tudor Queen and Her World by Alison Weir
The Six Wives of Henry VIII by Antonia Fraser
Catherine of Aragon: Henry’s Spanish Queen by Giles Tremlett
The Six Wives and Many Mistresses of Henry VIII: The Women’s Stories by Amy Licence
#catherine of aragon#katherine of aragon#catalina de aragon#elizabeth of york#arthur tudor#henry VII#tudor#trastamara#english history
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
So was nobody going to tell me that Queen Mary I and Rory Gilmore apparently have the same Myers-Briggs Type, or was I just supposed to find that out for myself? Because now I feel obligated to draw some Trastamara house/Gilmore Girls mashups.
#rory gilmore#mary i#queen mary i#mary tudor#trastamara#catherine of aragon#isabella of castile#myers briggs#mbti#isfj#isfj personality
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
CARLOS II de Navarra el rey que pudo dominar Europa
La apasionante vida de Carlos II de Navarra llena de intrigas, luchas, acuerdos, decepciones y a veces brutalidades.
Por otro lado, su vida se fué llenando en enfrentamientos personales con los más altos dignatarios de su época.

También le tocó vivir en una época llena de cambios en un periodo de transición, como el nuestro ahora, en el que trató de transitar de la mejor manera posible, a veces y durante un tiempo lo consiguió, en otros momentos fracasó.

La lectura del libro de Fernando Sanchez Aranaz de la editorial Mintzoa es muy entretenida, apasionante más bien, está llena de todo lujo de detalles y referencias como para hacer un recorrido por todos los lugares de Europa y Navarra por donde fue gobernando Carlos II de Narvarra el rey que pudo dominar Europa y casi lo consigue.
#Navarra#HistoriaNavarra#Evreux#Castilla#Aquitaine#Bretagne#Albania#LaconquistadeAlbania#principenegro#trastamara#Nafarroa#Navarre#Vascones#vascos#navarros
0 notes
Text

#juana i of castile#art#digital illustration#taniata's art#women in history#spanish history#the rightful queen!#mother of the one of greatest dynasty#house of trastamara
92 notes
·
View notes
Text
No more Tudors, please—unless it’s Mary I or Edward VI. Let’s focus on the Trastámaras, especially Catherine of Aragon, and delve into the Habsburgs, like Margaret of Austria and her nieces: Eleanor, Isabella, Maria, and Catalina. And don’t forget Charles V and his brother Ferdinand! We need more content on the Trastámara and Habsburg dynasties, as well as Stuart topics that aren’t about Mary, Queen of Scots or Stuart England.
#history#tudor era#mary i of england#mary i#catherine of aragon#catalina de aragon#margaret of austria#eleanor of austria#isabella of austria#maria of austria#charles v#ferdinand i#mary queen of scots#mary stuart#stuart dynasty#trastamara dynasty#enoug with the elizabeth i stuff#gimme mary i
37 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, I love your work, and wanted to ask if I could request dividers and support banners featuring blue purple iris flowers like the ones from Vincent Van Gogh’s painting?
hello! @thecutestgrotto had a Famous Art Collection line, and she did a beautiful set of Iris dividers here! I’d love to rec those instead, they are gorgeous! 💖
14 notes
·
View notes
Text









– juana i de trastámara ; infanta of spain, duchess consort of burgundy, queen of castile, aragon, valencia, mallorca, navarre, naples, sicily, sardinia and countess of barcelona was born on this day, 6th of november of 1479
#juana i de castilla#joanna of castile#juana the mad#house of trastamara#spanish history#on this day in history#weloveperiddrama#women in history#perioddramaedit#isabel tve#la corona partida#irene escolar#myedit*
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
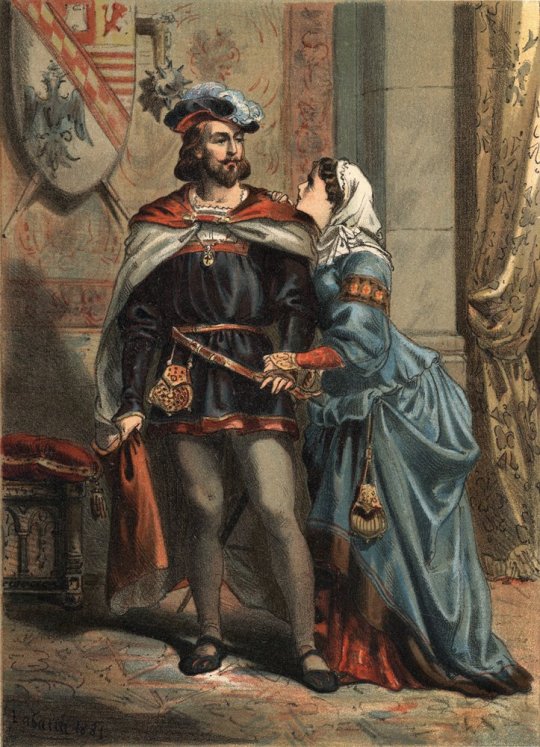

Joanna of Spain known as the Mad (1479-1555), Queen of Castile and her spouse Philip the Handsome (1478-1506), King of Castile and Archduke of Austria in 'El Culto de la Hermosura' by Juan Justo Huguet.
#monarquía española#reyes de españa#juana la loca#reina de españa#viva la reina#casa de trastámara#kingdom of spain#house of trastamara#felipe el hermoso#rey de castilla#archiduque de austria#casa de austria#dinastía habsburgo#philip of habsburg#philip the handsome#joanna the mad#royal couple#engraving#king of castile and león#kingdom of castile#house of habsburg#royalty#el culto de la hermosura#juan justo huguet
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
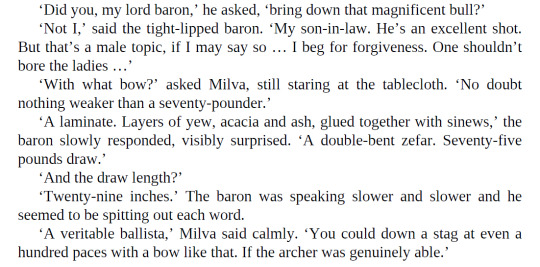

#i do headcanon milva as an ace lesbian but this is endearing to me still#somehow ive learned to appreciate the canon toussaint romances even though i dont like the ships and have other headcanons for them#c: milva#c: baron de trastamara#the witcher books#excerpt#book: lady of the lake#because i wish to eat a third donut#milva barring
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Random HC:
After having just come back to life Anne was still not used to calling Catalina by her first name and would sometimes slip up and still refer to her as "my queen", "your Majesty", etc. At first Lina would mock her about it, saying that no matter how much she insisted she was the ruler of England deep down she still recognized Catalina as the real queen.
As Anne and Catalina's relationship got better Lina decided to stop making a thing of it and would just let Anne slip up without saying anything.
When they truly became friends, Catalina started to call her "Lady Anne" whenever she accidentally used royal titles.
It became sort of a inside joke around the house and now whenever Lina demands something or Anne does a chore a lady in waiting would normally do the other queens go right back to calling them "your Majesty" and "Lady Anne".
#six#six the musical#catherine of aragon#anne boleyn#catalina de aragon#catalina trastamara#the tudors#the six wives of henry viii#six queens#six musical#six wives of henry viii#six headcanon#headcanons#hcs#hc#headcanon#royalty#british royal family#tudor era#tudor history
34 notes
·
View notes
Text

Fernando de Aragón in prayers
#Ferdinand II of Aragon#Fernando II#Fernando II de Aragón#Fernando de Aragón#House of Trastamara#16th century
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thread about Joanna of Castile: Part 5: A troubled transition (1497 – 1504)
The fabulous, yet toxic legacy that became hers in 1500 would greatly complicate her life as she tried to reconcile her role as consort, wife, and mother with her new role as princess of Asturias and Gerona. She would also have to face a future proprietary monarch whose royal status surpassed her. The narratives in this thread examine the deterioration in Juana's marriage.

One of the first issues with the marriage that the monarchs also noticed was that messengers were arriving without letters from either Juana or Philip.


Isabella, anxious about her daughter, had sent her envoy, Friar Tomás de Matienzo, Sub-Prior of the Convent of Santa Cruz, to the Netherlands to find out what was happening. His detailed reports bear witness to Philip’s systematic campaign to assert his dominance over his inexperienced young wife.

Matienzo also questioned Juana about her irregular confessional habits, while later reassuring the monarchs that:
“There is as much religion in her household as in a strictly observant convent, and in this, she is very vigilant and deserves much praise.”

He also quizzed her about her failure to protect her Spanish household. Her defensiveness and extreme reserve led the Dominican to burst out that she had a “hard and pitiless heart” and was “devoid of piety [compassion].

Juana did write letters. But her silences were unsettling. In December 1496, her former aya, Teresa Manrique, who had been her daily companion and instructor, wrote from Burgos:
“I am amazed, knowing the distress and anxiety of the king and queen … when they do not receive letters from your highness with all the messages that come here … About myself, I do not know what to say except that, since I can no longer see your highness, I realize that I do not live; although I have recovered somewhat from my illnesses, the troubles of my heart … for that, the best remedy would be to have news of you …”.
Juana was also taken to task in a chaotic letter from María Manrique Chacón:
“Your highness does not remember her very dear friend doña María, and the toasted chickpeas she gave me that made me ill, the friend she loves so much …”.
Miranda too reproved her:
“Although I have written very often, you have never sent me a word or written to me … I ask pardon that I am so bold with you, whom I love so much, and serve by day and night before God … If your highness does not answer me, I shall never write again, and this shall be my last letter.”
In general, Juana's failure to keep in touch with family and friends is seemingly more due to her extreme sensitivity to criticism and her reputation than to her indifference. She admitted that she had longed for home and had felt:
“So dispirited and depressed that every time she remembered how far away she was from [Isabel] she could not stop weeping to be forever so separated from her.”
Her treasurer, Mújica, subsequently informed the monarchs that:
“When some days go by without hearing from your highnesses, she is the most distressed woman in the world.”




To her dismay, the Philip with whom she had enjoyed such an electric physical relationship had soon shown his true colours. As her husband, and as Burgundy’s duke, he required her complete surrender to all his commands. This included controlling the personnel and the running of her household, an area in which, according to royal protocol, she should have been independent. She told Friar Tomás that Philip and his councillors didn't let her take part in it.
Philip had begun by taking over her finances: he did not give her the annual sum supposed to be allocated to her for her household expenditure, despite contracting to do just that in their joint marriage treaty. Instead, the archdukes own people took care of the money that should have gone to Juana. This meant, the envoy wrote to Isabella, that:
“She [Juana] is so poor that she has not a maravedi to give alms.”
She certainly did not have the money to pay her servants, who began to drift away because they could not “sustain themselves at court.” Within six months of her arrival in Burgundy, eighty of her ninety-eight male servants had left her side. That suited Philip very well. It meant he was able to replace the vast majority of his wife’s Spanish officials with his nominees; even many of those who loyally remained were bribed to support Philip as master rather than Juana as mistress. And, totally out of her depth, she simply did not know how to react to the man she could see was taking over her life but to whom she was still so physically attracted.
Yet, she had tried. On at least one occasion, Friar Tomás noticed that Juana had found the courage to protest. When asked to approve payments already made about which she had known nothing, she signed as she was bid but then said,
“Be it so for this year, but next year I desire that they do not make grants without my consent.”
As this flash of spirit did not occur until after Phillip's representatives had left her, Friar Tomás wrote resignedly,
“I think it will always be the same thing.”
The envoy was right: Juana didn't see any point in protesting again. Philip cruelly and deftly went a stage further after each battle he won.
Philip had insisted that Madame de Hallewin, once his own governess, should be one of Juana's key ladies-in-waiting. Juana’s desire to have Doña Marina Manuel, whom Isabella also trusted, in that post had been ignored. According to Friar Tomás:
Madame de Hallewin, together with Philip’s councillors, “Have so much intimidated” Juana, “that she dare not raise her head.”


If she tried to complain to Philip himself about how she was being treated, Juana confessed to Isabella’s messenger, her husband just told his councillors, and she “receives great injury from it.” Friar Tomás does not tell us what that “injury” was, but he does report on her sadness and her growing realization that she was so very much alone.
Juana was lucky because a few of her former attendants, including ten of her women, chose to stay with her, so she kept some links to Spain to help her feel less homesick. And homesickness was a problem for her in those early years.
“She could never think of how far she was from your Highness,” the envoy wrote to Isabella, “Without feeling the desire to cry because she was so far from your Highness for ever.”


If Juana cried, she would do so privately. Her public persona reflected her gracious nature, similar to that of Philip, who exhibited a similar demeanour.

Any friction within the marriage was well hidden. On state occasions, Juana and Philip dined publicly together, the embodiment of marital harmony. Philip made sure that Juana was well-dressed and bejewelled.

Appearances mattered, status had to be upheld. He presented Juana with diamonds and pearls that had once graced the delicate neck of his mother, Mary of Burgundy; he made sure that her horses were impressively saddled; he gave her pictures; he gave her religious items such as an image of Saint Margaret, possibly because Saint Margaret was the patron saint of women in childbirth. In the latter area, the couple certainly did their duty by the state.


Juana was torn between demanding parents and a husband whose advisers resented their interference. Philip was personally ambitious, greedy, and vehemently pro-French, none of which boded well for a future king of Spain.

During the painful years as archduchess of Burgundy in Flanders, Juana saw herself exiled and impoverished, without friends and countrymen, and without the protection and the help of her parents.


The emotional upheavals caused by the ambitions of her husband, and the unexpected reality of her inheritance after her mother’s death, brought her to personal and political confusion. This was well exploited by her husband, who started the rumour of her mental incapacity.
Juana alternated between the desire to pursue a normal life—pious and remote from the court—and the obligation to fulfil the exigencies of protocol—ostentatious and exhibitionist—that her royal rank required. Finding herself surrounded by her husband’s servants exacerbated her tendencies to hysteria and lack of control.
Sources: Fleming, G. B. (2018). Juana I: Legitimacy and Conflict in Sixteenth-Century Castile (1st ed. 2018 edition). Palgrave Macmillan.
Fox, J. (2012). Sister Queens: The Noble, Tragic Lives of Katherine of Aragon and Juana, Queen of Castile. Ballantine Books.
Gómez, M. A., Juan-Navarro, S., & Zatlin, P. (2008). Juana of Castile: History and Myth of the Mad Queen. Associated University Presse.
#joanna of castile#philip the handsome#trastamaras#juana i of castile#juana la loca#joana la loca#spanish history
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
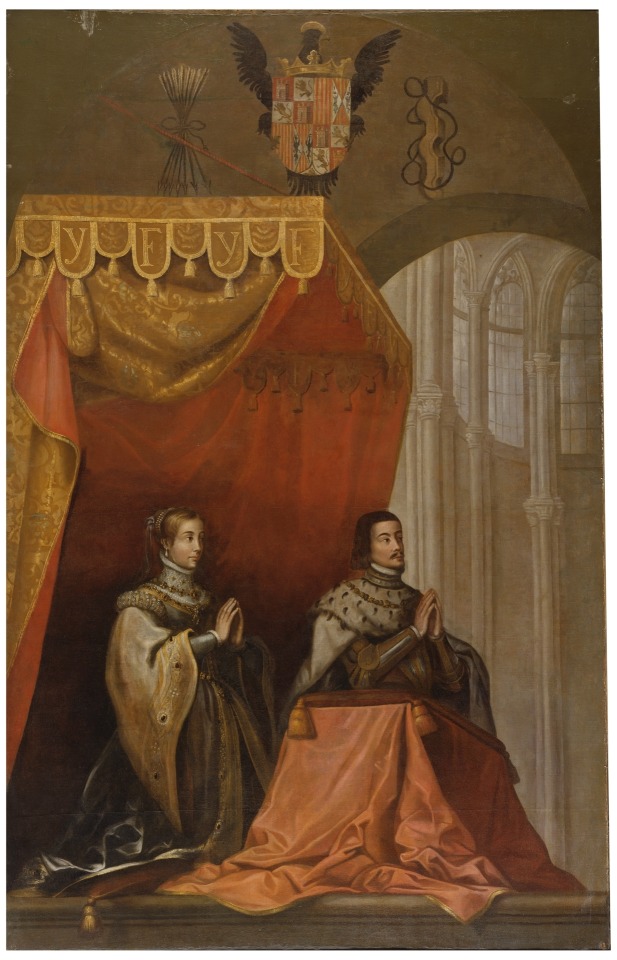

Los Reyes Católicos bajo un dosel. Anónimo, siglo XVII.
#museo del prado#monarquía española#reino de españa#reyes de españa#reyes de castilla#reyes de aragón#isabel la católica#reina de españa#fernando de aragón#fernando ii de aragón#fernando el católico#reyes católicos#casa de trastámara#kingdom of spain#house of trastamara
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Where is my period drama about The Trastámaras? Starting with Alfonso XI and Leonor?
2 notes
·
View notes
