#studying land animal ecology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


Biofluorescence may be widespread among amphibians
Biofluorescence, where organisms emit a fluorescent glow after absorbing light energy, may be widespread in amphibians including salamanders and frogs, according to a study in Scientific Reports.
Previous research has shown that biofluorescence is common in various animals like cnidarians, arthropods, and certain fishes. However, not much has been explored about its presence in land-dwelling creatures. Now, exciting new studies reveal that biofluorescence is widespread among amphibians, especially salamanders! These amazing creatures, found mostly in the northern hemisphere, exhibit a variety of glowing patterns. Under blue light, salamanders emit green light, creating stunning fluorescent displays. This glow is not limited to any specific family of salamanders, showcasing incredible diversity. The discovery of biofluorescence in these vertebrates opens up new avenues for research into their ecology, evolution, and behavior...
Read more:
https://today.stcloudstate.edu/2020/02/27/biofluorescence-may-be-widespread-among-amphibians
346 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
With eight arms instead of 10, this squid breaks the rules.
The octopus squid (Octopoteuthis deletron) is unusual among squids. Typically, squids have eight arms and two long tentacles, making a total of 10 appendages. But as young Octopoteuthis mature into adults, their two feeding tentacles are reabsorbed into their bodies.
Eight arms are not the only thing that stands out about this species. While exploring the midwater, we often encounter octopus squid in a distinctive posture: large fins spread wide, and arms with twinkling tips curled above the head. Light-producing organs called photophores flash with bioluminescence at the end of each arm.

MBARI has spent several decades studying Octopoteuthis. Cameras on our advanced underwater robots have revealed insights into the mysterious lives of octopus squid, from their unique behaviors to their defensive strategies.
Octopus squid and their deep-dwelling kin play a vital role in ocean food webs. Despite their ecological importance, we still know very little about the lives of deep-sea squids. MBARI’s work is answering fundamental questions about deep-sea cephalopods and providing vital information that resource managers can use to inform their decision-making about the ocean.

The deep sea is closer than you think. What we do on land affects the ocean, even the animals and environments deep below the surface. By choosing sustainable seafood, refusing single-use plastic, and reducing our carbon footprint, we can help protect the amazing animals of the deep.
Learn more about this captivating cephalopod in our Animals of the Deep gallery.
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
I know that news stories about Indigenous people leading ecological stewardship movements are very charismatic and heartwarming, and if your heritage or culture inspires you to work towards better care for the environment that is incredible and extremely admirable, but we're clear on the fact that Indigenous rights and Land Back movements shouldn't depend on First Nations people being mystical Noble Savage, Closer To Nature poster children, yes?
Indigenous self-determination applies to the person who becomes a teacher because she wants to help fill a need in underserved northern reservations. It applies to the person who studies engineering because the job market is good and he likes cool cars. It applies to the woman who works a government job because it's a stable job with a decent salary on which to raise her kids, and the woman who works a government job because she wants to represent and be a voice for her people. It applies to the person who is a lawyer trying to correct the over-incarceration of First Nations people, and her son who wants to be a professional baseball player because he loves sports. It applies to the grad student who wants to bring traditional knowledge into field work, and the goth hairdresser who spends every weekend going to punk shows and anime conventions in the city. It applies to the person who considers themself Two Spirit, and the person who uses non-binary instead because they dont feel that umbrella term fits them. None of these examples are hypotheticals- these are all people I personally know, either friends or family friends or even members of my family. All of these people are equally Indigenous, whether or not they fit your image of what a marginalized people's priorities "should" be. They are not gone, and they are not "stuck in the past". Happy National Indigenous People Day. Do better.
#Disclaimer that i am not indigenous to any degree as far as i know#and my social circle is both pretty small and majority white#but ive noticed a trend in the sort of articles that go around about indigenous people and it tend to be 'native people do nature good!'#People have the right to choose a 'traditional' or a 'community building' life or career path and they have a right not to#canadian politics#first nations#land back#decolonization#indigenous rights#I might turn off anon asks in my inbox if you think im wrong thats fine but say it with your name attached
247 notes
·
View notes
Text
“It was an assumption—almost an article of faith—amongst many biogeographers, ecologists, and paleoecologists that the great regional rainforests were, at Western contact, the product of natural climatic, biogeographic, and ecological processes,” wrote paleoecologist Chris Hunt, now based at Liverpool John Moores University, and his colleague, Cambridge University archaeologist Ryan Rabett, in a 2014 paper. “It was widely thought that peoples living in the rainforest caused little change to vegetation.” New research is challenging this long-held assumption. Recent paleoecological studies by Hunt and other colleagues show evidence of “disturbance” in the vegetation around Pa Lungan and other Kelabit villages, indicating that humans have shaped and altered these jungles not just for generations—but for millennia. Borneo’s inhabitants from a much more distant past likely burned the forests and cleared lands to cultivate edible plants. They created a complex system in which farming and foraging were intertwined with spiritual beliefs and land use in ways that scientists are just beginning to understand. Samantha Jones, lead author on this investigation and researcher at the Catalan Institute of Human Paleoecology and Social Evolution, has studied ancient pollen cores in the Kelabit Highlands as part of the Cultured Rainforest Project. This is a U.K.-based team of anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleoecologists that is examining the long-term and present-day interactions between people and rainforests. The project has led to continuing research that is forming a new scientific narrative of the Borneo highlands. People were most likely manipulating plants from as early as 50,000 years ago in the lowlands, Jones says. That’s around the time humans likely first arrived. Scholars had long classified these early inhabitants as foragers—but then came the studies at Niah Cave. There, in a series of limestone caverns near the coast, scientists found paleoecological evidence that early humans got right to work burning the forest, managing vegetation, and eating a complex diet based on hunting, foraging, fishing, and processing plants from the jungle. This late Pleistocene diet spanned everything from large mammals to small mollusks, to a wide array of tuberous taros and yams. By 10,000 years ago, the folks in the lowlands were growing sago and manipulating other vegetation such as wild rice, Hunt says. The lines between foraging and farming undoubtedly blurred. The Niah Cave folks were growing and picking, hunting and gathering, fishing and gardening across the entire landscape.
[...]
“The Cultured Rainforest project has shown how profoundly entangled the lives of humans and other species in the rainforest are,” says University of London anthropologist Monica Janowski, a member of the project team who has spent decades studying highland Borneo cultures. “This entanglement has developed over centuries and millennia and succeeds in maintaining a relatively balanced relationship between species.” Borneo’s jungle is, in fact, anything but untouched: What we see is a result of both human hands and natural forces, working in tandem. The Kelabit are a little bit farmer and a little bit forager with no clear line between, Janowski says. This dualistic approach to land use may reveal a deeper human nature. “Scratch any modern human and you will find, under the surface, a forager,” she says. “We have powerful foraging instincts. We also have powerful instincts to manage plants and animals. Both of these instincts have been with us for millennia.”
259 notes
·
View notes
Text
A University of Arizona study has uncovered a surprising relationship between an animal's body temperature and its likelihood of evolving into an herbivore. The study, published in the journal Global Ecology and Biogeography, offers fresh insights into the evolution of plant-based diets across tetrapods, which include the land vertebrates—amphibians, birds, reptiles and mammals. The findings could reshape scientists' understanding of the evolution of animal diets. The study, which analyzed data from 1,712 species, found a consistent pattern: Animals with higher body temperatures are more likely to evolve into herbivores. This relationship holds true across the major land vertebrate groups.
Continue Reading.
88 notes
·
View notes
Text



additional resources to marxist feminism:
living a feminist life by sara ahmed
the rise and decline of patriarchal systems by nancy folbre
this bridge called my back: writings by radical women of color by cherrie moraga and gloria anzaldua
delusions of gender: how our minds, society, and neurosexism create difference by cordelia fine
close to home: a materialist analysis to women's oppression by christine delphy
(pdf) the feminist standpoint: developing the ground for a specifically feminist historical materialism
(medium) on women as a class: materialist feminism and mass struggle by aly e
(sagejournals) capital and class: the unhappy moments of marxism and feminism: towards a more progressive union
(substack) the marxfem pulpit by abigail von maure (earth2abbs on tiktok)
if anything else related to marxist feminism, just let me know :)

additional resources to eco feminism:
gossips, gorgons, and crones: the fates of the earth by jane caputi
parable of the sower by octavia e butler
neither man nor beast: feminism and the defense of animals by carol j. adams
bitch: on the female of species by lucy cooke
fresh banana leaves: healing indigenous landscapes through indigenous science by jessica hernandez
the intersectional environmentalist by leah thomas
right here, right now by natalie isaacs
feminism or death by francoise d'ealibonne
violent inheritance: sexuality, land, and energy in making the north american west by e cram
animal crisis: a new critical theory by alice grary
unsettling: surviving extinction together by elizabeth weinberg
land of women by maria sanchez
sexus animalis: there is nothing unnatural in nature by emmanuelle pouydebat
windswept: walking the paths of trailblazing women by annabel abbs
andrea smith - rape of the land
andy smith - ecofeminism through an anticolonial framework
carolyn marchant - nature as female
charlene spretnak - critical and constructive contributions of ecofeminism
heather eaton - ecological feminist theology
heather Eaton - The Edge of the Seat
janet abromovitz - biodiversity and gender Issues
joni Seager - creating a culture of destruction
karen warren - ecofeminism
karen warren - taking empirical data seriously
karen warren - the power and promise of ecological feminism
l. gruen - dismantling oppression
martha e. gimenez - does ecology need marx?
n. sturgeon - the nature of race
petra kelly - women and power
quinby - ecofeminism and the politics of resistance
rosemary radford ruether - ecofeminism: symbolic and social connections
sherry ortner - is female to male as nature is to culture?
sturgeon - the nature of race
val plumwood - feminism and ecofeminism
winona laduke - a society based on conquest cannot be sustained
if anyone has any other recommendations related to eco feminism, plz let me know :)

additional resources related to trans feminism:
the empire strikes back: a posttransexual manifesto by sandy stone
(chicago journals) trapped in the wrong theory: rethinking trans oppression and resistance by talia mae bettcher
(philpapers.org) trans women and the meaning of woman by talia mae bettcher
the transgender studies reader by susan stryker and stephen whittle
if anyone has other recommendations related to trans feminism, plz let me know :)

additional resources related to anarcha feminism:
the anarchist turn by jacob blumenfeld
we will not cancel us and other dreams of transformative justice by adrienne maree brown
burn it down: feminist manifestos for the revolution by breanne fahs
reinventing anarchy, again by howard ehrlich
anarcho-blackness by marquis bey
a little philosophical lexicon of anarchism from proudhon to deleuze by daniel colson and jesse cohn
joyful militancy by nick montgomery and carla bergman
wayward lives, beautiful experiments by saidiya v. hartman
we won't be here tomorrow and other stories by margaret killjoy
writing revolution by christopher j. castaneda
paradoxes of utopia by juan suriano
twelve fingers by jo soares
for a just and better world by sonia hernandez
if anyone has other recommendations related to anarcha feminism, plz let me know :)



#feminism#intersectionalfeminist#intersectionality#anti terf#anti swerf#womens rights#marxist feminism#eco feminism#anarcha feminism#trans feminism#queer feminism#pro lgbtq+#pro disabled#pro trans#pro palestine#pro sex worker
190 notes
·
View notes
Text
Good News - August 1-7
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my new(ly repurposed) Patreon!
1. Zoo hails birth of 'one of world's rarest animals'

“[Jasper] the Persian onager was born to mum Azita after a year-long pregnancy. […] Conservationists at the zoo said there are less than 600 surviving wild onagers[, … which] only survive in two small, protected areas in Iran, a Chester Zoo spokesman said. […] Mike Jordan, animal and plant director at Chester Zoo, […] said Jasper is "doing very well" and added that "mum Azita is doing a fantastic job of nurturing and bonding with her new charge". "He’s full of energy and enjoys playfully kicking up sand as he races around his habitat", Mr Jordan added.”
2. Charity creates 50 community orchards in city

“Community orchards are returning to Birmingham, with the aim of teaching people how to grow their own food and be part of the solution to climate change. […] Once established, the long-term aim is to distribute the produce to those most in need, but local people are also invited to pick the odd bit of fruit. […] By planting trees and plants and encouraging biodiversity back to these areas the charity is also doing its bit to help climate change. They even use locally sourced wood chip which helps to put carbon back into the soil. […T]he hope is that these edible landscapes can also be enjoyed by local people for years to come.”
3. Farmer-led badger vaccination could revolutionize mission to tackle bovine TB

“[… T]he results of a four-year pilot badger vaccination program co-managed between farmers, scientists, and conservationists […] show the percentage of badgers testing positive for bovine tuberculosis (bTB) in the study area dropped from 16% to 0%[….] While most bTB incidents in cattle are caused by transmission between herds, transmission from wild badgers plays a role in the persistence of the disease. […] Blood sampling showed that the proportion of badgers with bTB fell even though overall badger numbers remained high[….]”
4. Every Colorado Anti-Trans Ballot Initiative Fails To Collect Enough Signatures

“Anti-transgender politics are becoming increasingly unpopular in polls. […] A recent LA Times/NORC poll found that 77% of voters believe elected officials use transgender debates to divert attention from more pressing issues. The poll also showed significant opposition to forced outing policies. […] A Gallup poll published in June revealed that while Americans have mixed views on the morality of transitioning, the majority oppose bans on gender-affirming care for trans youth. […] “The fact that they could not get enough signatures, barely half, to be placed on the ballot shows they lack support from everyday voters.”
5. In a fight to save a rare bird, Indigenous communities in Guyana are winning

“The partnership [between Indigenous communities and Smithsonian researchers] sparked a decades-long community-led conservation movement that has protected the red siskin and helped locals reconnect with nature. [… T]he South Rupununi Conservation Society […] established one of the country’s first conservation zones to protect the species, covering 75,000 hectares (185,000 acres) of Indigenous land. […] To plant the seeds of conservation, they’ve implemented an after-school program in more than 16 communities, [introducing children] to ecological research and surveying, and also [teaching] about Indigenous culture and tradition, including fire management skills.”
6. North Adams hospital gets federal designation which pays for health care in rural areas

“[The hospital] received a federal designation on Wednesday that is key to its long-term financial stability. […] The designation pays for staffing regardless of the number of patients[… and] “works to resolve stark inequities in rural and underserved communities as it relates to our nation’s health system."”
7. Andrea Vidaurre: Leading the clean transportation revolution
“Thanks to Vidaurre’s relentless advocacy and strong community support, these regulations introduced the first national standards for train emissions and set a groundbreaking goal for all freight trucks to be zero-emission by 2036. This initiative promises cleaner air for Californians and paves the way for a zero-emission vehicle future across the country. Studies predict these measures will prevent thousands of respiratory illnesses and save countless lives in the coming decades.”
8. Boston announces a new climate resilience office

“Through its Climate Ready Boston initiative, the city has worked to […] design creative adaptation plans with community input[, …] includ[ing] everything from redesigning waterfront parks and planting more trees, to modernizing the city’s underground sewer system[….] The Office of Climate Resilience will be in charge of coordinating work across city departments and with community groups[….]”
9. Combining Green Thumbs and Sustainable Fashion in a Swap Event

“This unique plant and clothing swap event in NSW is championing both environmental and fashion sustainability through native plants and preloved clothing. […] To participate in the plant swap, attendees brought their environmental weeds in a bag to the Council stall and exchanged them for free native plants. […] The event sparked valuable community conversations about the benefits of plant and clothes swaps, the impact of textile waste[, …] support a circular economy and combine a love for nature with practical, eco-friendly practices.”
10. Growing Green Spaces to Protect the Endangered Regent Parrot

“On Schools Tree Day, celebrated on 26 July, students from a local NSW school planted trees and shrubs to create crucial forage habitat for the endangered Regent Parrot, enhancing local biodiversity. […] Approximately 50 [… plants of] native species were chosen for their ecological benefits, helping to attract native birds, bees and butterflies while providing essential habitat and food. […] They [also] raise awareness about the regent parrot, encourage conservation efforts and emphasise the importance of protecting local wildlife. Additionally, conserving [the regent parrot] supports the health of their ecosystem by helping with in [sic] seed dispersal and maintaining plant diversity.”
July 22-28 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#zoo#donkey#orchard#community#food insecurity#community garden#badger#vaccine#cow#tuberculosis#colorado#trans#transphobia#transgender#law#politics#birds#indigenous#conservation#hospital#health#healthcare#california#trains#truck#zero emissions#climate change#boston
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
The historical link between meat and colonisation in Israel
In her PhD thesis on the historical role of Tel Aviv under the British Mandate for Palestine, Dr Efrat Gilad shows that while Zionist technocrats promoted a diet of little to no beef, urban settlers enjoyed their steaks and stews. Furthermore, their love for meat led them to play a key role in the colonisation of Palestine. (23 March 2021).
In your thesis you studied colonisation in Israel through attitudes towards meat consumption. What gave you this idea and why was it a worthwhile one?
There were various indicators that meat would be a useful entry point to the history of Jewish settlers in Palestine. One indicator had to do with a surprising statistic I came across. In 2019, according to OECD statistics, the world’s leading beef consumers were Argentina, the United States, and almost tied for third place were Brazil and Israel. Israel is an anomaly on this list. The other countries that tend to lead in meat consumption are also global meat producers and exporters. Their meat industries evolved over centuries, beginning with European settlers who used cattle to colonise. As cowboys or gauchos drove livestock across vast territories dominating the land, producing and consuming meat became linked to national identity.
Israel, however, does not produce the majority of the beef it consumes; rather, it mostly relies on imports. While colonisation is part of Israel’s past and present, Jewish settlers did not drive herds of animals to dominate Palestine’s landscape as did the cowboys and gauchos of the Americas. The ecologies and economies of livestock in Palestine were vastly different than in the above-mentioned countries. This does not mean there is no historical link between meat and colonisation in Israel – my research actually shows that there is – but that the historical trajectory that led Israelis to consume as much beef as Brazilians was different, and thus required further investigation. My dissertation is the first comprehensive history of meat in Palestine/Israel grounded in extensive archival research.
Can you describe your research questions and the methodology you used to approach those questions?
As a historian, my methodology involves archival research and analysis of historical documents. Early on I noticed a gap between two types of sources. On the one hand, there was a clear correlation between the growing numbers of European Jews settling in Palestine in the 1920s and 1930s and the soaring demand for meat. This was evident in many sources including data on livestock imports and slaughter, newspaper articles on the price of meat and its availability, the building of new slaughterhouses in Palestine’s cities, and multiple disputes between consumers, butchers and cattle dealers. On the other hand, when reading through sources produced by Zionist technocrats – such as economists, agronomists and nutritionists – I noticed a vastly different attitude to meat. While urban settlers were preoccupied with gaining more access to meat, Zionist technocrats seemed determined to convince Jewish settlers to adopt a diet of little to no beef.
My work then focused on three interconnected questions: Why did Zionist technocrats oppose meat consumption? How did urban settlers create systems to allow them access to meat in a country of limited supply (and in defiance of national experts)? And finally, how did urban settlers – in creating those systems – promote the colonisation of Palestine?
What are your answers?
First, I found out why Zionist technocrats opposed meat consumption, and this was entangled in ideas about climate, nutrition and economy. Zionist technocrats adopted an idea rooted in colonial medicine according to which consuming meat was harmful in Palestine’s heat. This was a significant finding because it highlights European Jewish settlers’ alienation from Palestine’s environment, and resonates with histories of other settler colonies, allowing us to think comparatively and transnationally about colonisation. The second layer in the discourse against meat was linked to the settler colonial economy. Beef consumption depended on Palestinian breeders and regional Arab livestock merchants, and increasingly also on overseas imports. This threatened Zionist leaders’ aspirations for a self-reliant Jewish settlement, which they believed was essential to its expansion. Thus, technocrats believed, high levels of beef consumption obstructed Zionist goals.
My second major finding shows how urban Jewish settlers ignored technocrats by generating a booming meat economy. Settlers first supported Palestine’s existing meat economy but gradually also created separate systems of import and slaughter. Because local supply chains of beef were deemed insufficient and firmly in the hands of Arab and Palestinian merchants, Jewish butchers and cattle dealers tapped into their connections to the European trade and created new networks of overseas cattle import. In creating their own meat infrastructures, especially in Tel Aviv, settlers worked to dominate Palestine’s meat trade. Whereas the literature often focuses on ideologues or rural “pioneers”, I show how urban settlers are historical agents who were perhaps oblivious or defiant of national ideologies pertaining to the meat trade but who nevertheless played a key role in a national endeavour: the colonisation of Palestine.
107 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Moises Santillan draws attention to the pervasive problem of microplastics, which are becoming an increasingly serious environmental and health risk. Microplastics, or minute plastic pieces, are not just found in water but appear to be prevalent almost everywhere. Moises notes that they may be found in a variety of daily plastic goods and in locations excessively contaminated with plastic garbage. The widespread prevalence of microplastics is an increasing concern since these particles infiltrate both our environment and our bodies, as scientific investigations show.
The health consequences of microplastics are especially concerning. Moises emphasizes that enhanced microscopy and other technologies have enabled researchers to detect microplastic particles within the human body. Considerably more troubling is the potential for microplastics to break down into smaller particles known as nanoplastics, which are considerably more widespread. These nanoplastics can enter the circulation, spread throughout the body, and potentially disrupt numerous biological activities. This compounding effect, in which plastics degrade into increasingly minute particles, raises major concerns about their influence on human health.
Microplastic pollution of the environment is also a significant concern. Moises notes that microplastics may be discovered anywhere plastic debris collects, contributing to the overall pollution catastrophe. Their persistence in the environment and tendency to disintegrate into smaller particles make them incredibly difficult to control. Pollution not only endangers animals, but it may also impact land, water, and food quality. As microplastics permeate many ecosystems, the long-term environmental consequences might be severe, threatening biodiversity and altering ecological equilibrium.
Moises emphasizes the urgent need for study and action to understand and reduce the impact of microplastics. The presence of these particles in the human body, their metamorphosis into nanoplastics, and their widespread environmental distribution all necessitate further scientific investigation. Potential solutions include lowering plastic manufacturing, improving waste management systems, and developing creative methods to break down these polymers safely. Through collaborative effort and ongoing study, humanity can address the threats posed by microplastics and move toward a healthier, more sustainable future.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Solar Farms Have a Superpower Beyond Clean Energy. (New York Times)
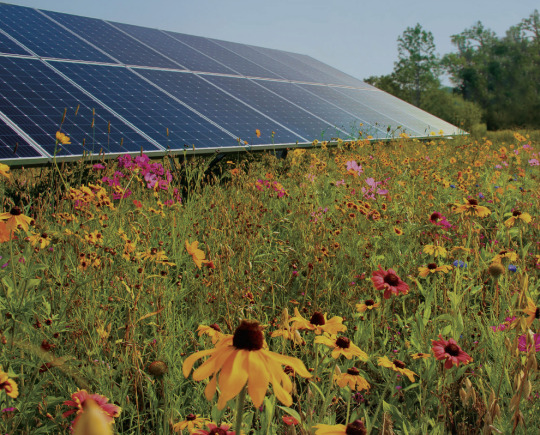

Excerpt from this New York Times story:
It’s not your average solar farm.
The glassy panels stand in a meadow. Wildflowers sway in the breeze, bursts of purple, pink, yellow, orange and white among native grasses. A monarch butterfly flits from one blossom to the next. Dragonflies zip, bees hum and goldfinches trill.
As solar projects unfurl across the United States, sites like this one in Ramsey, Minn., stand out because they offer a way to fight climate change while also tackling another ecological crisis: a global biodiversity collapse, driven in large part by habitat loss.
The sun’s clean energy is a powerful weapon in the battle against climate change. But the sites that capture that energy take up land that wildlife needs to survive and thrive. Solar farms could blanket millions of acres in the United States over the coming decades.
So developers, operators, biologists and environmentalists are teaming up with an innovative strategy.
“We have to address both challenges at the same exact time,” said Rebecca Hernandez, a professor of ecology at the University of California, Davis, whose research focuses on how to do just that.
Insects, those small animals that play a mighty role in supporting life on Earth, are facing alarming declines. Solar farms can offer them food and shelter by providing a diverse mix of native plants.
Such plants can also decrease erosion, nourish the soil and store planet-warming carbon. They can also attract insects that improve pollination of nearby crops.
Pollinator friendly solar can pay off for business, too, potentially saving money and giving projects an edge for approval at a time when communities are increasingly wary of vast solar farms. Developers are taking note.
But there’s a broad spectrum of pollinator friendliness and little agreement on what efforts should count. Standards are often nonexistent. Some big projects are limiting pollinator habitat to tiny corners of their sites. Ecological value varies widely.
Communities may not understand the difference, and corporate marketing may exaggerate. That’s led to accusations of greenwashing.
Pollinator habitat on solar farms is “a serious work in progress,” said Scott Black, executive director of the Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation, a nonprofit group that is working on an effort to bring some clarity by certifying solar sites.
“It’s not fair if some people are truly stepping up to do this right and another company is barely doing anything and saying they’re pollinator friendly,” he said.
“If you build it, will they come?” he asks in his research. So far the answer is a resounding yes, if you grow the right plants.
In a study published late last year, his team found that insect abundance had tripled over five years on test plots at two other Minnesota solar sites. The abundance of native bees grew twentyfold.
The results come amid a global decline of wildlife that leaders are struggling to address. Some of the most well-known insect species are in trouble: Later this year, the federal government is expected to rule on whether to place monarch butterflies on the Endangered Species List. North American birds, for their part, are down almost 30 percent since 1970.
But at this site, called Anoka County Solar, acoustic monitoring has documented 73 species of birds, presumably attracted by the buffet of seeds and insects. Some build nests in the structures supporting the panels.
Mammals are showing up, too. Mr. Walston checked a trail camera before leaving, hoping to discover the occupant of a remarkably large burrow: A fox, he thought, or a badger. No luck.
(It’s trickier to make solar sites friendly to large wild animals, in part because developers are nervous to let them near expensive infrastructure, but efforts are underway there, too.)
What makes this meadow possible is the height of the panels. A prairie restoration firm had told ENGIE, the owner and developer, that taller panels would allow for a sharp increase in native vegetation species, providing much more ecological diversity, said John Gantner, the director of engineering and delivery for ENGIE’s smaller-scale sites.
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
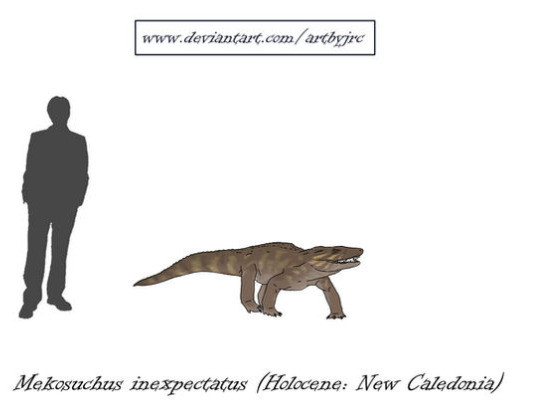
Mekosuchus
My recent-most Wikipedia deep dive was in equal parts enlightening and frustrating and it concerned no other than Mekosuchus, everyones favourite heartbreaker of a recently extinct crocodile.
For those unfamiliar, let me give you some footnotes before getting into the nitty gritty. Mekosuchus is, or was, a genus of terrestrial (NOT ARBOREAL) dwarf crocodile from Australasia, first appearing during the Late Oligocene. They were small, how small we don't precisely know but its generally estimated that adults would be in the 1-2 meter range (so about 3 to 6 feet I believe?). The heartbreaking part? The last confirmed Mekosuchus died out only 3.000 years ago, and some publications even suggest they could have stuck around until just 1.700 years ago. Yeah, we got REALLY close.
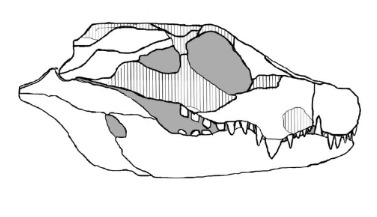
Art by yours truly, I'll explain the massive difference down below, just be patient.


But lets get some of the basics out of the way. Mekosuchus was a small mekosuchine crocodilian and currently, four species are recognized. Mekosuchus whitehunterensis is the oldest from the Oligocene/Miocene of mainland Australia, immediately succeeded by M. sanderi during the Miocene. Both these species were described as having had blade-like posterior teeth (at the back of the jaw) and both coexisted with a ton of other crocs, including Baru, Quinkana and some bizarre ones like Ultrastenos.
After a bizarre break in the fossil record, Mekosuchus shows up again during the Holocene on the islands of New Caledonia and Vanuatu, ironically mirroring the meiolaniid turtles I talked about previously. Fossils are securely dated to about 3.000 years ago, but Balouet and Buffetaut also suggested that some of the younger remains may only be 1.720 years old, overlapping with human settlements. But this isn't accepted by everyone. Regardless, these species differ from their older cousins by lacking the blade-like teeth, instead going for crushing dentition.
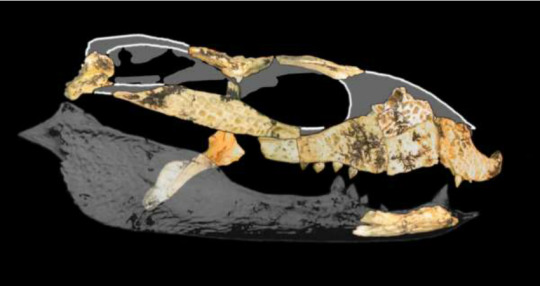
Art by artbyjrc and Kahless28


With such different teeth comes different ecology, of course. A 2015 study suggests that the neck vertebrae of M. whitehunterensis were well adapted to rapid stresses, specifically caused by side-to-side movement of the head. It is thus speculated that they shook their heads to strip meat from carcasses, rather than performing the iconic death roll (as that might hurt the animal on land).
M. inexpectatus meanwhile was seemingly better adapted at crushing hard-shelld things, crabs, insects, maybe snails even. Holt and colleagues suggest that it might have lived much like a modern dwarf crocodile, spending its time in river streams and coming out at night to forage. Dwarf crocodile via the San Diego Zoo and Mekosuchus illustrated by my friend BatmanelVisigodo


Both however are thought to be terrestrial, having short, altirostral skulls, big eyes and nares that face sideways, not upwards as in semi-aquatic crocodilians. They were however NOT ARBOREAL. Yes I know I know, its a bummer. To those unaware, a commonly cited missconception is that Mekosuchus was a tree-dweller, which was originally suggested by Paul Willis in the 1990s. However, this was more of an off-hand comment at the time that certain people (including me in the past) have run with, causing it to spread and be almost considered fact by some. Hell, it says a lot when Mekosuchus, in many circles, is thought of as "that tree croc". However, not only was Willis suggestion based on the now outdated notion that monitor lizards weren't around at the same time, later authors also note that the toes of Mekosuchus really don't show any adaptations to climbing specifically. So alas, it would seem that this was only a myth. But don't worry too much, sometimes crocs climb regardless, just not vertically up a tree. Mekosuchus artwork by Manusuchus


Now at the beginning I teased that there's a reason why my images for M. whitehunterensis and M. inexpectatus look so different. Well its kind of painful really. Despite being known for about 30 years now, with 300+ bones known from New Caledonia alone, Mekosuchus is incredibly poorly studied. The original description only figured around half a dozen bones and while the next three species were all named in the span of just 5 years, they are all incredibly fragmentary. And then, just after another expedition collected more bones....things went silent.
The last 20 years saw the publication of only a single paper extensively dealing with Mekosuchus itself, with two skull reconstructions coming out in less detailed sources. The first is Holt et al. 2007, a powerpoint presentation from a paleontological conference. The presentation made some fascinating claims and even provided a reconstruction of the skull, but sadly. Nothing ever came of it, the research was never formally published and the lead author has since then changed fields into Astronomy. Actually had a nice talk with him earlier today. Then there's Scanlon 2014, which offers even less. In the book Carnivores of Australia: past, present and future, Scanlon briefly touches upon mekosuchines, featuring a new composite reconstruction of M. whitehunterensis. However, this is not elaborated on in the text, despite the drastic differences to how M. inexpectatus has been reconstructed before. So we are left with two very different appearances. Are they simply really different looking species? Is one interpretation faulty? Should Mekosuchus be split? Who knows, might be a while until we figure it out. But until then, here's the two together, one looking much like a dwarf crocodilian, the other more like a sebecid. An interesting contrast for sure.


As per usual, this research was done as part of me doing a major haul of a Wikipedia page which you can read here Mekosuchus - Wikipedia. It's been an interesting, if a little frustrating task, but it was fun properly reading up on this animal and putting this information out there for people that don't wanna dig through 30 years of literature (including one paper in French). Hopefully I suceeded, at least the page is a bit bulkier now.

#wikipedia editing#palaeoblr#paleontology#prehistory#long post#crocodile#mekosuchus#land crocodile#mekosuchinae#new caledonia#extinction#paleo#science
185 notes
·
View notes
Note
are mustangs a native or invasive species? do you think they should be rounded up?
I think it would be overly conclusory to say either at this point. As far as I know, there haven't been any radio carboned equine remains that show they survived through the ice age in North America. There is some evidence that shows they survived later than what was originally thought though, and were also in the West before the Pueblo Rebellion, which was when many white people thought they were introduced there.
But if they are not native, it would be a mistake to automatically conclude that they are invasive because there is also a lot of new evidence that shows that they are ecosystem engineers. "Invasive" implies a species that causes ecological harm to a new area, but several studies done on wild horses and burros in the Western US show some positive impacts. The ones that I know of are:
Equids engineer desert water availability - this study was done in the Sonoran desert in AZ and showed that equine dug wells increased biodiversity in the surrounding areas by 64%, and often were the only water sources. The researchers concluded "that equids, even those that are introduced or feral, are able to buffer water availability, which may increase resilience to ongoing human-caused aridification.”
Impact Of Wild Horses On Wilderness Landscape And Wildfire - this was done in Northern California to push back on claims made by the BLM that wild horses had a negative impact on the ecosystem and had no predators. It found that horses degraded land less than some of the even-toed ungulates because their hooves are not sharp and pointed like theirs. The riparian ecosystems in the area of study were not permanently damaged by horses because predators prevented them from staying long, and their predators included coyotes, mountain lions, and bears for foals, and bears and mountain lions for adults. Additionally, by eating dry grass the horses reduced the fuel load in the area, and likely prevented a branch that fell and ignited after being hit by lightening from causing a wildfire.
A roundup in the Ash Meadows Reserve in Nevada caused a population of critically endangered pupfish to go extinct - this was cited by the first study mentioned. Once the equines were removed from the area, the riparian habitat became choked by vegetation, a whole population of pupfish died as a result.
To me what these studies suggest is that native or not, the mustangs and burros are filling a distinct role that was not taken on by another native species if their ancestors did go extinct. I don't think the BLM has properly taken this into account in their Appropriate Management Level assessments, though courts tend to give them so much deference as a federal agency that I don't think any have found that they actually violated National Environmental Policy Act. Under NEPA, the BLM is supposed to consider all reasonable alternatives when making environmental impact statement and assessment proposals. I think these studies show that livestock reduction and predator re-introduction should be considered as reasonable alternatives before roundups given the immense cost of roundups and lack of permanent improvement of the range after them, but the BLM has given reasons not to try these options such as "the horses don't have predators in this area" or " it doesn't conform to the current multiple use land management plans." The courts usually accept these reasons as valid. See Friends of Animals v. Silvey.
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
"One of the last wild rivers in Europe, home to more than 1,000 animal and plant species, has been declared a national park by the Albanian government, making the Vjosa the first of its kind on the continent.
The Vjosa River flows 168 miles (270kms) from the Pindus mountains in Greece through narrow canyons, plains and forests in Albania to the Adriatic coast. Free from dams or other artificial barriers, it is rich in aquatic species and supports myriad wildlife, including otters, the endangered Egyptian vulture and the critically endangered Balkan lynx, of which only 15 are estimated to remain in Albania.
For years, the Vjosa’s fragile ecosystem has been under threat: at one point as many as 45 hydropower plants were planned across the region.
But on Wednesday, after an almost decade-long campaign by environmental NGOs, Vjosa was declared the first wild river national park in Europe. Environmentalists described it as a historic decision that has placed the tiny Balkan nation at the forefront of river protection...
A Model for Conservation
Mirela Kumbaro Furxhi, Albania’s tourism and environment minister, said the creation of the park was part of the country’s evolution and continuing emancipation three decades on from communist rule.
“Vjosa is a symbol of human history and also a very important part of the history of our country,” she said. “Maybe Albania does not have the power to change the world, but it can create successful models of protecting biodiversity and natural assets, and we are proud to announce the creation of this first national park on one of the last wild rivers in Europe.”
The country, which attracted 7.5 million visitors last year, more than twice its 2.8m population, hopes to regenerate villages in the Vjosa region through ecotourism.

Details of the National Park
... The 12,727 hectare (31,500 acre) park aims to ensure the Vjosa and its unique ecosystems are safeguarded. It has been given IUCN category II park status, a high level of protection similar to that of a wilderness. The categorisation covers “large-scale ecological processes”, species and ecosystems, crucial to ensuring dams and gravel extraction are banned. It is expected to be operational in 2024...
The park will encompass the 118 miles of the Vjosa in Albania, three main tributaries, and some land, including areas at risk of flooding. Phase II will add other tributaries. Unlike the IUCN’s Wilderness Protected Areas, which limit the number of visitors, it will allow recreational tourism and some other activities such as local fishing, particularly for 60,000 residents in the catchment.
The Albanian government is starting a joint process with the Greek authorities to create the Aoos-Vjosa transboundary park, aiming to protect the entire river across both countries, who agreed in January to sign a memorandum of understanding specifying the next actions.
Wild Rivers in Europe
Europe has the most obstructed river landscape in the world, with barriers such as dams, weirs and fords, estimated to number more than a million, according to a 2020 EU study in 28 countries. Such fragmenting of rivers affects their ability to support life.
Ulrich Eichelmann, a conservationist and founder of Riverwatch and part of the Save the Blue Heart of Europe campaign, said: “Most people in central Europe have never ever seen a wild, living river, free from the impacts of human interference, that isn’t diverted or dammed or built up with embankments and where biodiversity is low as a result. But here, you have a wild river, full of complexity and without interference.”"
-via The Guardian (US), 3/15/23
#albania#europe#eastern europe#conservation#biodiversity#endangered species#rivers#national parks#wilderness protected area#greece#good news#hope
177 notes
·
View notes
Text
Good news: 10 quintillion (10 billion billion) individual arthropods in Earth’s soil.
:)
Including nearly 100 million metric tons of termites alone. And that’s only the number of “bugs” living underground. How many more live on the surface, in grasslands, forest canopies?
---

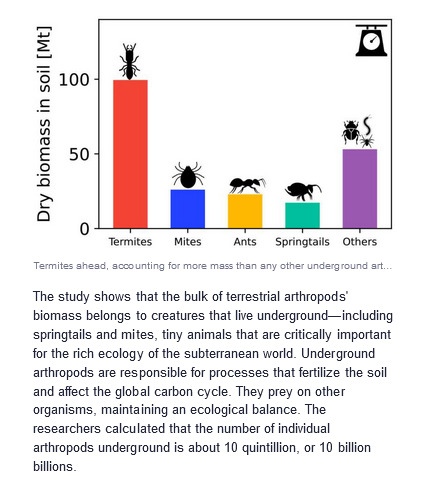


Arthropods crawl and buzz around us in the wild and on farmlands, on the street and at home, under our floors and in our plumbing systems, even in our food and on our bodies. [...] Yet, despite their crucial importance to the environment and humanity, and despite data suggesting a worrying decline in their numbers in areas impacted by human activity, scientists did not have holistic, global answers to basic questions about arthropods, such as how many of them are out there and how much they weigh collectively.
Researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science have now taken a significant step toward answering these questions. In a study published today in Science Advances, a team headed by Prof. Ron Milo has calculated that the total biomass, or collective weight, of terrestrial arthropods is about 1 billion tons, which is roughly the same as that of all people (about 400 million tons) and all farm animals (about 600 million tons) combined. [...]
The researchers gathered data from thousands of observations conducted over the years at some 500 survey sites around the world. [...] The scientists examined data on arthropod biomass both below and above the ground, for example on plants. The study shows that the bulk of terrestrial arthropods' biomass belongs to creatures that live underground -- including springtails and mites, tiny animals that are critically important for the rich ecology of the subterranean world. Underground arthropods are responsible for processes that fertilize the soil and affect the global carbon cycle. They prey on other organisms, maintaining an ecological balance.
The researchers calculated that the number of individual arthropods underground is about 10 quintillion, or 10 billion billions.
Social insects that live in colonies account for half of the mass of underground arthropods: Termites and ants constitute 40 and 10 percent of that category, respectively. As for aboveground arthropods, most of their biomass is probably found in tropical forests, and it includes many familiar arthropods such as butterflies, ants, beetles, grasshoppers and spiders.
---
All content above, headline, images, graphics, captions, and text published by: Weizmnn Institute of Science. “The first global estimate of the combined weight of all land insects and related arthropods.” Phys dot org. 6 February 2023. [Bold emphasis and italicized first lines in this post added by me.]
The article itself:

190 notes
·
View notes
Text

III
“Agriculture itself must be overcome, as domestication, and because it removes more organic matter from the soil than it puts back. Permaculture is a technique that seems to attempt an agriculture that develops or reproduces itself and thus tends toward nature and away from domestication. It is one example of promising interim ways to survive while moving away from civilization. Cultivation within the cities is another aspect of practical transition, and a further step toward superseding domestication would be a more or less random propagation of plants, a la Johnny Appleseed.” — John Zerzan, On the Transition: Postscript to Future Primitive
So how can this be overcome? How can the shackles placed by technological slavery be broken? There are no ready made blueprints, programs or textbooks that have the one correct way or answers. If civilization is to be overcome it will be through individuals with all sorts of diverse ideas, experiments and actions.
For me, I see my path is by attempting to achieve more individual autonomy and self-reliance away from the dependency on techno-industrial society through permacultural subsistence gardening which can provide for me, my family, and other living creatures that inhabit the area I am in.
I first learned about permaculture from reading the zine Backwoods. Prior to this I was focused on the horticultural method of “productive gardening”. I suppose the difference between the two is permaculture and woodland gardening is ecologically designed to give back to the soil, and benefit other living organisms, animals, and the local ecosystem in general as much as to help oneself.
It is an ecological sustainable gardening practice of growing for yourself while simultaneously helping the environment around you. Each individual organism that takes part in the process whether insects, microbe, human and non human animals, all benefit from a mutual utilisation of working together and likewise so does the organic matter and minerals which are needed to create and sustain healthy soil, which in turn when all together creates healthy gardening successions, rich landscapes, biodiversity, and healthy ecosystems.
The individual designs her garden to suit the needs of the local environment or back yard. This includes finding out soil types, and studying how much sun hits the area, where and when different areas might be shaded. From this the individual will research what plants will suit the environmental conditions.
Perennial plants such as fruit trees and bushes combined with a mix of native annuals and self seeding annuals such as edible wild garlic, flowers like nasturtiums, soil enhancers like clover, medicinal herbs, all provide ground cover and help protect the soil from the weather, soil erosion, water retention, and provide fertilizer and mulch, which all help soil fertility, providing life to the organisms that live in and create soil. All combined help local wildlife, pollinators and other insects that are vital for a healthy garden as well as a healthy planet.
I have been gardening for the last four years and started focusing on the permaculture method last year. One does not need a lot of money to start growing. When I had a tiny backyard I used containers of old pots, buckets, and even bags. Seeds and plants can be bought cheap in the right places or else can be shoplifted easily enough. Last March I built raised beds from scaffolding planks I expropriated from a local building site which was closed due to the first lock down and started a mini forest garden on roughly a twenty foot by twenty foot strip of land. If one hasn’t a backyard guerrilla gardening is a viable option.
Seeds and cuttings can be got for free in your area if you know what you are looking for. I learned about native plants from plant folklore books which were rich in folklore and mythical stories based around each plant species, included in the stories was information on edible plants and when best to forage, which ones were poisonous, and the uses of others. Combined, the stories provided a great index for subsistence. The area I live in is urban but I could still find many plants growing in parks, gardens, and the side of roads.
I’m still a long way off achieving my full subsistence needs and gardening obviously won’t solve the majority of the problems that stem from civilization but I see it as a potential starting point in my own struggle for individual liberation and creating the life I want to live. I don’t think gardening is for everyone either, but for me I get great enjoyment and satisfaction watching plants grow and then eating the produce, and all without having to pay or work a boring ass job for. I just have to open my door and walk outside.
I’m no expert on gardening or permaculture so I will leave a list of books that have helped me and where I got inspiration from.
Renzo Connors the Anarcho-Gardener
#subsistence gardening#gardening#anarcho gardening#solarpunk#gardening as resistance#resistance#permaculture#small farms#small farm movement#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Brown howler monkeys are dropping dead by the dozens in southern Mexico. Between May 4 and May 21, at least 138 died, with deaths occurring in places where temperatures have been abnormally high, exceeding 43 degrees Celsius (109 degrees Fahrenheit).
Before perishing, the animals suffered convulsions, hyperthermia, and fainting, which are symptoms of dehydration. Organizations responding to the catastrophe note that the main cause of death seems to be heat stroke, although they haven’t ruled out other factors. Deaths have been reported across the state of Tabasco.
“The feeling of the work team is tragic, it is painful,” says Gilberto Pozo, a wildlife biologist at the Institute of Ecology in Xalapa. He was one of the first to witness and document the current catastrophe. “It hurts because all the efforts we have been making for years are going down the drain,” Pozo says, referring to recent efforts to protect the species.
Short-furred and endemic to the southern states of Mexico, brown howler monkeys (Alouatta palliata mexicana) are listed as “vulnerable” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, and their numbers are decreasing.
Pozo has been studying primates for 22 years. He is a conservationist and executive director of Conservation of the Biodiversity of Usumacinta (Cobius), a civil association that has been working with communities in the region for 13 years to protect endangered species.
In early May, a Cobius team visited a group of howler monkeys in Cunduacán, Tabasco, as part of a rescue and translocation program, this landscape having undergone significant changes in past years, which has endangered the monkeys. During fieldwork, the team saw two monkeys fall from 15-meter-high trees. Despite receiving attention, both died from their falls and showed signs of dehydration. The next day, local people came to leave aerial drinkers and tropical fruits for the primates.
Days later, the team visited the Saraguatos Biopark. There they found five dead monkeys and eight with problems. The team decided to extend their monitoring and detected more deaths, notifying Mexico’s environmental protection agency, the Procuraduria Federal de Proteccion al Ambiente (Profepa). Separate groups found dead monkeys elsewhere in the state of Tabasco, in Comalcalco and Jalpa, and so the scale of the emergency quickly became clear.
Mexico’s Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources has said that for now, it is investigating various hypotheses about what killed the monkeys: heat stroke and dehydration of course, but also “malnutrition or fumigation, or spraying of crops with toxic agrochemicals.” A first necropsy has been conducted on one of the animals, though Pozo points out that molecular analyses of the animal are lacking at this stage. “The doctor in charge does not want to rule out either heat stroke or viral issues,” he says. More tests will follow.
Brown howler monkeys are one of three native species of monkeys in Mexico. They inhabit parts of the states of Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, and Yucatan, as well as the nearby countries of Guatemala and Belize. The monkeys sometimes eat fruits and flowers, but principally are folivores: 80 percent of their diet consists of leaves, from which the monkeys obtain water. So if the leaves they eat are dehydrated, the animals consume little water, which leaves them exposed to the effects of high temperatures.
Pozo has witnessed monkeys showing the effects of moderate and severe dehydration. In moderate cases, he explains, the animals show signs of apathy, prostration, poor coordination, and slow movements. Such animals also have congested mucous membranes, high heart rates, and body temperatures over 40 degrees Celsius, and they show signs of vomiting, panting, diarrhea, hypersalivation, and muscle tremors. In severe cases, the monkeys suffer convulsions, irregular heartbeats, fainting, and have no resistance to manipulation. “They become like little dolls,” Pozo says.
Tania Fonseca works at Mexico’s Institute of Ecology (Inecol) as an academic technician for the Transdisciplinary Studies Group in Primatology. Something that inspires her about working with howler monkeys is their resilience—“until these days, when everything is broken,” she says.
If the cause of death is heat stroke, Fonseca says, it will be possible to confirm it through tissue analysis. If that is the reason, she adds, it becomes important to monitor live animals that have endured the heat, because they may have damaged tissues and organs.
Trouble Down on the Farm
The average annual temperature in Tabasco is 27 degrees Celsius (80 F). May tends to be the hottest month, with an average maximum of 36 degrees. However, temperatures this season are particularly high, having soared well beyond 40 degrees (104 F).
But in addition to the high temperatures, landscape modifications must be considered as a culprit, explains Bertha Valenzuela, a native of Comalcalco, Tabasco. Valenzuela has been studying primates for 15 years and says she grew up among monkeys. She remembers them always hanging around her grandmother's house.
The Chontalpa region, where most of Tabasco's monkeys live, today has only 3 percent of its original forest area, with a lot of land adapted for farming. In particular, it is an important cacao-growing area, with more than 3,000 producers. In other countries, cacao is planted in monocultures, but here producers use agroforestry systems—where arboreal vegetation shades the cacao-growing below, and where there is a mix of crops and native species. The difference between the original ecosystem and the plantations is that the forest canopy—the upper part of the trees where the monkeys live—is lower, while the understory, the lower part of the forest, is eliminated to allow for crops.
“In these sites they found conditions that have allowed them to survive, even if they are not the best,” says Valenzuela of the howler monkeys. The animals have been living in the plantations for the last 30 years, but have struggled with the landscape changing yet again in recent years.
Since the 2000s, cacao production has declined, due to plant diseases and falling local prices, causing many people to turn their cacao farms into pasture. Valenzuela explains that this means that, in general, between one cacao grove and another, there are now pastures, agricultural fields, or human settlements. With the fragmentation of the monkeys’ habitat, temperature regulation is not homogeneous. The smaller a fragment of forest is, the more heat it receives from its surroundings. Land-use change is compounding the effects of global heating.
A Mess of Good Intentions
Gilberto Pozo describes the first responses to the emergency as “a sea of people helping out”—a mess, but without bad intentions. “There were more than 150 volunteers. If it wasn’t for the support of the population, it would be difficult,” he says.
But some people took the monkeys to clinics without registering them first or notifying the authorities, so Profepa is now visiting clinics to collect data. Pozo is also worried about volunteers or the primates catching diseases from one another. “They grabbed them, approached them without masks or gloves, hugged them, kissed them, talked to them. That represents a high risk of zoonosis or anthropozoonosis.”
On top of this, there’s the risk that vulnerable monkeys may be mistreated, says Ana María Santillán, founder of the Centro Mexicano de Rehabilitación de Primates, which rescues monkeys that are victims of mascotism and illegal trafficking. As civilians, people should not move a specimen, because it is illegal, she says. “It was a blessing that Profepa got involved,” she adds. Even so, her group has found orphaned juvenile monkeys for sale.
To manage the situation, says Santillán, the civil organizations involved have formed specialized brigades, coordinated by Cobius. One is dedicated to recovering dead or dying animals. Another, which takes care of the monkeys, is made up of veterinarians trained in handling primates, some from Profepa in Tabasco, others from Universidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco (UJAT). Another brigade is to perform necropsies. Among the most important actions, Gilberto Pozo explains, has been the setting up of two medical units for treating animals in need.
The experts have asked that people inform the authorities of new cases, and that people who have monkeys take them to the brigade units so that veterinarians can make a record of any affected animals. The response teams also emphasize that the species is very delicate: They should not be given antibiotics or dewormers; people shouldn’t keep any young; nor should the monkeys mix with dogs or cats, because the primates risk catching deadly diseases from them.
Getting Back to Nature
It’s not clear when it will be best to release the affected monkeys, says Fonseca—if environmental conditions don’t change, there’s a risk of this happening again. Particular care needs to be taken when releasing juveniles, regarding which group they are released to and into which site.
Juan Carlos Serio, a researcher at Inecol and head of the Transdisciplinary Primatology Studies Group, points out that better conservation efforts are needed in these habitats. Howler monkeys are great seed dispersers, and losing them from the environment would affect the natural process of forest regeneration. They’ve also been there for a long time. “Losing them means losing an important cultural element,” he says.
With this in mind, there’s work underway to try to make the landscape in Tabasco more monkey-friendly. Jorge Ramos Luna, an academic technician at Inecol and part of Serio’s workgroup, makes videos to engage local communities and promote species conservation by improving the local agrosystems.
One strategy he proposes is to create natural corridors that connect patches of forest. In the neighboring state of Veracruz, he says, one solution is to surround cleared land with “live fences” of trees and vegetation instead of fences made from lumber. “Monkeys are a charismatic species, an umbrella species: If we give them the conditions to survive, we will be providing conditions for many other species,” he says.
Valenzuela has additional suggestions: “The first recommendation is to stop logging, the second is to restore the land, and the third is to contribute with these small actions: of placing water, monitoring the monkeys, so that the people who live with the monkeys get involved in the stability of the populations,” she says.
The inhabitants of the region were already taking care of the monkeys before this massive event. Some had even learned about the types of vegetation that benefit the monkeys, attended management courses, and put water and fruit out for them. This crisis is not the first time that care has been shown by the monkeys’ human neighbors—and the public response this time brings hope that things can be improved.
13 notes
·
View notes