#spacetechnology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

#IFTTT#Flickr#hmsge#esa#europeanspaceagency#space#universe#cosmos#spacescience#science#spacetechnology#tech#technology#hst#hubblespacetelescope#galaxy#supernova#nasa#creativecommons#stars#star#sagitta#symbioticstar
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Europa Clipper is a NASA mission designed to explore Europa, one of Jupiter's largest moons. Scheduled for launch in the 2020s, Europa Clipper will conduct detailed reconnaissance of Europa’s ice-covered ocean, which may harbor conditions suitable for life. The spacecraft is equipped with a suite of scientific instruments to study Europa's surface, subsurface ocean, and geologic activity.
#europaclipper#nasa#Jupiter#europa#spaceexploration#MissionToEuropa#searchforlife#outersolarsystem#nasaexploration#IcyMoons#EuropaMission#spacescience#astrobiology#jupitermoon#nasaupdates#spacetechnology#EuropaOcean#spaceresearch#planetaryscience#EuropaFlyby#NASA2020s#aircraftconstruction#aviationsustainability#aerospacetechnology#EuropaClipperMission#jupiterexploration#EuropaMoon#spacediscovery#LifeOnEuropa#nasaresearch
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
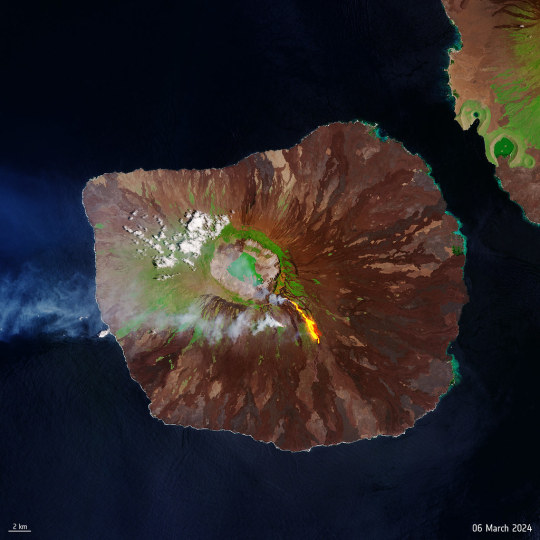
Mira "Galapagos island volcano lava flow" de europeanspaceagency que me gustó en flickr
#flickr#esa#europeanspaceagency#space#spacetechnology#earthfromspace#observingtheearth#earthobservation#earthexplorer#satelliteimage#sentinel#copernicus#galápagosislands#lacumbre#fernandina#fernandinaisland#volcano#lavaflow#island#ecuador#lava#galapagos
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
ISRO's 100th Launch Journey: A Historical Milestone for Bharat

Introduction
In a momentous achievement for India's space program, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully completed its 100th launch from the Sriharikota spaceport. This historic milestone marks a significant leap forward in India's journey towards becoming a global space power. The successful launch of the GSLV-F15/NVS-02 satellite not only demonstrates ISRO's technical prowess but also highlights the nation's commitment to scientific advancement and technological innovation.
The Journey to 100 Launches
ISRO's journey to its 100th launch is a testament to India's perseverance and dedication to space exploration. Since its establishment in 1969, ISRO has made remarkable progress in various aspects of space technology, including satellite communication, remote sensing, and planetary exploration.
Some key milestones in ISRO's journey include:
1975: Launch of India's first satellite, Aryabhata
1980: First successful launch of the SLV-3, making India the sixth country to achieve satellite launch capability
2008: Chandrayaan-1, India's first lunar probe
2014: Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), making India the first country to succeed in its maiden attempt to orbit Mars
2017: Launch of 104 satellites in a single mission, setting a world record
Each of these achievements has contributed to ISRO's growth and expertise, culminating in this historic 100th launch.
GSLV-F15/NVS-02 Satellite Launch
The 100th launch from Sriharikota featured the GSLV-F15 rocket carrying the NVS-02 satellite. This launch is particularly significant as it demonstrates ISRO's capabilities in launching advanced navigation satellites. The NVS-02 is part of India's NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) system, which aims to provide accurate position information services to users across India and the surrounding region.
Key features of the GSLV-F15/NVS-02 launch:
Rocket: Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV)
Payload: NVS-02 navigation satellite
Mission objective: Enhance India's navigation capabilities
Launch site: Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota
The successful deployment of the NVS-02 satellite will further strengthen India's indigenous navigation system, reducing dependence on foreign systems and enhancing national security.
ISRO's Contributions to India's Space Program
Over the years, ISRO has made significant contributions to India's space program, benefiting various sectors of the economy and society. Some of these contributions include:
Satellite Communication: ISRO's communication satellites have revolutionized India's telecommunications industry, providing connectivity to remote areas and enabling services like telemedicine and tele-education.
Earth Observation: ISRO's remote sensing satellites help in disaster management, weather forecasting, and natural resource management.
Navigation: The NavIC system provides accurate positioning services for both civilian and military applications.
Space Exploration: Missions like Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan have put India on the global map of space exploration.
Technology Development: ISRO's innovations have led to the development of various indigenous technologies, reducing India's dependence on foreign technology.
These contributions have not only advanced India's scientific capabilities but have also had a significant impact on the country's socio-economic development.
Dr. Nowhera Shaik's Congratulatory Message
Dr. Nowhera Shaik, MD & CEO of Heera Group of Companies, extended her heartfelt congratulations to ISRO on this historic achievement. In her message, she stated:
"Congratulations once again to ISRO on this historic 100th launch from Sriharikota! Wishing continued success in serving the nation and achieving many more milestones."
Dr. Shaik's message reflects the sentiment of millions of Indians who take pride in ISRO's achievements. As a successful entrepreneur and business leader, Dr. Shaik recognizes the importance of innovation and perseverance in achieving great milestones, qualities that ISRO has consistently demonstrated.
Future Prospects for ISRO
With the successful completion of its 100th launch, ISRO is poised for even greater achievements in the future. Some of the upcoming projects and missions include:
Gaganyaan: India's first crewed space mission, aimed at demonstrating human spaceflight capability.
Chandrayaan-3: The third lunar exploration mission, focusing on a soft landing on the Moon's surface.
Aditya-L1: India's first solar mission to study the Sun's corona.
NISAR: A joint Earth-observing mission with NASA to study global environmental change and natural hazards.
Venus Mission: A proposed orbiter mission to study Venus's atmosphere and surface.
These ambitious projects showcase ISRO's commitment to pushing the boundaries of space exploration and scientific research.
Conclusion
ISRO's 100th launch from Sriharikota is indeed a historical milestone for Bharat. It represents decades of hard work, innovation, and dedication by thousands of scientists, engineers, and support staff. As India continues to make strides in space technology, the nation can look forward to more groundbreaking achievements that will benefit not only India but the global scientific community as a whole.
As we celebrate this remarkable achievement, let us also look forward to the future with anticipation and excitement. ISRO's journey is far from over, and with continued support and investment, there's no doubt that India will continue to reach for the stars and beyond.
#isro100thlaunch#indianspacemission#gslvf15#nvs02satellite#isroachievement#spaceexploration#indianscience#sriharikota#isrohistory#spacetechnology#indiansatellite#isrosuccess#spaceinnovation#indianpride#drnoweherashaik#heeragroup#navigationsatellite#isrojourneyat100#spacemilestone#futureofindia#heeraluxurycity#nowherashaik
0 notes
Text
youtube
#indiainspace#isro#indianspacemission#spacetechnology#rocketscience#100MissionsStrong#proudindian#makeinindia#futureofspace#beyondthestars#space#shorts#news#newshawkers#viral#trending#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Exploring Space Docking Technology: The Gateway to Advanced Space Exploration
Space docking technology is one of modern space exploration’s most fascinating and critical aspects. It allows spacecraft to connect or to a larger space station while in orbit. This technology is essential for various operations, such as resupply missions, crew transfers, and assembling structures in space. In this article, we will explore the principles, history, challenges, and future…
#CommercialSpaceflight#Gaganyaan#InterplanetaryMissions#SpaceDocking#SpaceExploration#SpaceInnovation#SpaceScience#SpaceTechnology
0 notes
Text
Grapes Space Mission for Healthcare: Robospace | Jerald Nepoleon
Introduction
In an age where technology and healthcare intersect more profoundly than ever, the vision of space exploration finds its roots in addressing critical healthcare challenges on Earth. The Grapes Space Mission for Healthcare, aptly named Robospace, is an innovative initiative launched by Jerald Nepoleon, aimed at harnessing cutting-edge aerospace technology to revolutionize healthcare solutions. Through the integration of artificial intelligence, robotics, and space technology, Robospace seeks to create a healthier future for all.

Background of Grapes Innovative Solutions
Grapes Innovative Solutions is known for pushing the envelope in technology-driven solutions. With a vision cantered on improving healthcare outcomes through innovation, the company has embarked on this ambitious endeavour to utilize aerospace advancements in solving terrestrial health challenges. By leveraging the knowledge gained from space missions and applying them to healthcare, Grapes is set to redefine possibilities within the industry.
Mission Objectives
The core objectives of the Robospace mission encompass a multifaceted approach towards healing and health management. Here are the primary goals:
Enhancing Diagnostic Capabilities: Using AI and machine learning systems originated from aerospace technologies to develop advanced diagnostic tools that can identify diseases with incredible accuracy.
Telemedicine Innovation: Expanding telehealth services to ensure accessible healthcare, especially in remote and underserved regions, by employing space technology for communication.
Robotic Surgery and Assistance: Integrating robotics for surgical procedures to enhance precision and minimize recovery times, echoing methodologies used in space missions.
Health Monitoring Systems: Utilizing satellite technology to monitor vital health metrics in real-time, enabling proactive health management globally.
Research and Development: Fostering an environment for innovative R&D that bridges the gap between healthcare needs and technological advancements derived from space explorations.
The Need for Innovation in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is facing unprecedented challenges, including rising costs, access disparities, and a growing burden of chronic diseases. Current systems often struggle to provide timely and effective care, particularly in isolated areas. The application of aerospace technology within healthcare is not just innovative; it is essential for delivering prompt, efficient, and expansive healthcare solutions globally.
Health Disparities and Accessibility
Access to quality healthcare remains a significant challenge in many parts of the world. Remote areas often lack sufficient medical facilities, professionals, and equipment. The Robospace mission addresses this gap by deploying innovative solutions that transcend geographical barriers, ensuring that healthcare is not confined by location.
Innovations from Robospace
1. Smart Diagnostic Tools
Robospace has initiated the development of smart diagnostic tools that utilize machine learning algorithms designed to analyze vast amounts of data. These tools can assist healthcare providers in diagnostics, resulting in more accurate and timely treatment for patients. By incorporating satellite images and data patterns, diagnostic systems can identify potential health risks even before symptoms arise.
2. Advanced Telemedicine Platforms
As part of Robospace, Grapes aims to enhance telemedicine platforms by utilizing satellite technology to improve communication between healthcare providers and patients. This will enable real-time consultations and follow-ups, making healthcare accessible to the marginalized populations who may otherwise face barriers due to distance.
3. Robotics in Surgery
The Robospace mission harnesses robotic technology developed for use in space to enhance surgical procedures. These robotic systems can make highly precise incisions and perform complex surgeries with reduced trauma to surrounding tissues. This results in shorter recovery times and minimizes the risk of infection.
4. Continuous Health Monitoring
By integrating wearable technology with satellite capabilities, Robospace aims to develop comprehensive health monitoring systems that keep track of vital signs and health metrics in real-time. This constant data flow enables healthcare providers to respond swiftly to potential health crises before they escalate.
5. R&D Collaborations
Jerald Nepoleon emphasizes the importance of collaboration in his mission. Grapes aims to engage with academic institutions, healthcare professionals, and government agencies to create a robust research framework. This collaboration will foster the development of ground-breaking technologies that derive inspiration from space exploration.
Conclusion
The Grapes Space Mission for Healthcare stands as a beacon of hope in an otherwise besieged healthcare landscape. With the mission's emphasis on innovation, accessibility, and advanced technology, Robospace is poised to impact the global healthcare system positively. The visionary approach led by Jerald Nepoleon not only promises to transform traditional healthcare practices but also ensures that no one is left behind, regardless of their geographic location.
As the world continues to evolve, the crossover between space exploration and healthcare will only grow more interconnected, paving the way for future advancements that can address some of the most pressing issues facing humanity. The Robospace initiative exemplifies this synergy, serving not just a mission but a lifeline for countless individuals seeking better healthcare solutions.
For More Get InTouch :
📧 Contact us: [email protected] / [email protected]
📞 Call us: +91 7356 78 9993 , +91 8606 98 4841
🌐 Visit: Grapes Innovative Solutions
#GrapesSpaceMission#Robospace#HealthcareInnovation#AerospaceTechnology#Telemedicine#HealthMonitoring#RoboticSurgery#AIinHealthcare#HealthcareAccess#GlobalHealth#TechForGood#HealthcareTechnology#HealthcareSolutions#JeraldNepoleon#HealthcareRevolution#InnovativeHealthcare#SpaceTechnology#DiagnosticTools#HealthTech#MedicalRobots#SpaceExploration#FutureOfHealthcare#HealthcareR&D#AerospaceHealthcare#HealthcareDisparities#RemoteHealthCare#grapesspacemission#Grapesrobospacemission#grapesspace#grapesrobospace
0 notes
Text
#PropulsionResearch#SpaceExploration#AerospaceInnovation#USAResearch#GravityManipulation#SpaceTravel#FuturisticTech#GravityControlPropulsion#USASpaceProgram#AerospaceEngineering#AdvancedTechnology#InterstellarTravel#SpaceTechnology#SpaceInnovation#doghealth#thinline#floydmayweather#day10#JamieFoxx#championsleague#reelsfbシ#reelstrending#reelsviralfb#reelschallenge#reelsinstagram#reelsviral#reelsvideo
0 notes
Text
US Ready to Mine the Moon, Targeting Valuable Minerals
The United States is gearing up for large-scale lunar exploration, focusing on mining valuable resources. NASA and private companies are collaborating to develop technologies enabling resource extraction on the Moon. This effort is driven by the need to secure strategic resources, such as helium-3, which has the potential to serve as a clean fuel for nuclear energy in the future.
Learn more about helium-3 and its energy potential.
https://go.paid4link.com/GsaGfKv
Additionally, the water ice discovered at the Moon's poles is a primary target. This ice can not only be converted into drinking water but also split into hydrogen and oxygen for rocket fuel. This opens up the possibility of establishing the Moon as a space station hub for further exploration to Mars and beyond.
Discover more about the significance of lunar water ice.
However, this initiative has sparked international debate. Some countries view this exploration as a violation of the principles outlined in the Outer Space Treaty, which declares the Moon and other celestial bodies as the common heritage of humanity. The United States, however, asserts that it will adhere to international law and collaborate with global partners.
Explore the legal and geopolitical implications of lunar mining.
This exploration marks a new era in the space race, where the focus is not only on scientific discovery but also on the economic utilization of extraterrestrial resources. Lunar mining promises substantial business opportunities and could transform how humanity meets its energy needs on Earth.
By leveraging advanced technology and international collaboration, the United States is paving the way for a future where the Moon plays a critical role in humanity’s pursuit of sustainable resources and space exploration.
#SpaceExploration#LunarMining#MoonResources#NASA#FutureEnergy#Helium3#SustainableEnergy#OuterSpace#Geopolitics#SpaceTechnology#Innovation#MoonMission#Astronomy#GlobalCollaboration#CleanEnergy
1 note
·
View note
Text
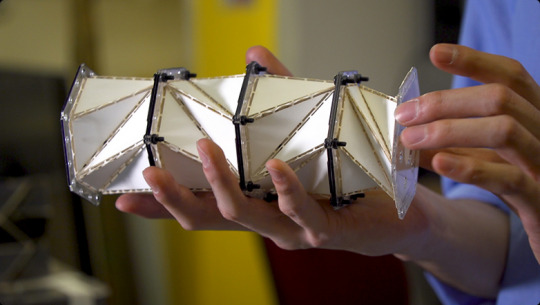
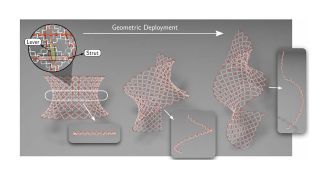
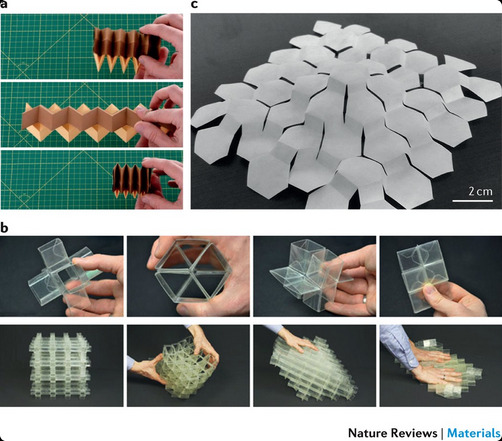
Shapeshifting Space Stations? New Metamaterial Could Revolutionize Space Habitats
Scientists have developed a flexible metamaterial inspired by nature that could enable the construction of adaptable space habitats and telescopes capable of changing shape in orbit.
0 notes
Text
Elon Musk Addresses Starlink Device Use Allegations in Manipur
https://enterprisewired.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/1-Elon-Musk-Addresses-Starlink-Device-Use-Allegations-in-Manipur-Source-freepressjournal.in_.jpg
Source: freepressjournal.in
Share Post:
LinkedIn
Twitter
Facebook
Reddit
Pinterest
Starlink Beams Allegedly Linked to Conflict
Elon Musk, the founder of SpaceX, recently clarified that Starlink satellite beams have been “turned off over India.” His statement came in response to allegations that a Starlink device was being used in the conflict-hit region of Manipur. The controversy arose after Indian security forces seized internet devices, along with arms and ammunition, during a raid in the Keirao Khunou area of Imphal East district.
Images shared by the Spear Corps of the Indian Army on social media depicted the seized items, sparking public interest when observers noted that one of the devices bore the Starlink logo. This discovery fueled speculations about the potential role of satellite internet in escalating tensions in the region.
Details of the Seizure in Manipur
On December 16, the Indian Army’s Spear Corps released a statement detailing the outcomes of coordinated raids conducted in Manipur. The joint operations involved troops from the Indian Army, Assam Rifles, and Manipur Police, targeting both hill and valley regions in the districts of Churachandpur, Chandel, Imphal East, and Kangpokpi. During these operations, it was confirmed that Starlink satellite beams were inactive over the region, ensuring no external technological interference.
The operation led to the recovery of an extensive cache of weapons and equipment, including 29 firearms such as sniper rifles, automatic weapons, pistols, country-made mortars, and single-barrel rifles. Additionally, grenades, ammunition, and other war-like materials were confiscated. The forces emphasized the significance of the raids in disrupting unlawful activities in the troubled region.
Musk’s Statement on Starlink’s Involvement
Elon Musk’s comments on social media aimed to address concerns about Starlink’s potential misuse. By asserting that Starlink satellite beams are inactive over India, Musk sought to dispel allegations of the technology’s involvement in the ongoing violence in Manipur. While his statement was brief, it highlighted the measures SpaceX takes to control the deployment and usage of its satellite internet services in sensitive regions.
This clarification comes amid heightened scrutiny of technology’s role in conflict zones. Social media platforms and communication technologies are often debated for their impact on security and their potential misuse. The revelations about the seized Starlink device, coupled with Musk’s response, underscore the growing complexities surrounding technology’s influence in global and local conflicts.
#Starlink#StarlinkBeams#SpaceX#SatelliteInternet#StarlinkSatellite#SpaceTechnology#GlobalInternet#StarlinkInternet
0 notes
Text

#IFTTT#Flickr#esa#europeanspaceagency#space#spacetechnology#earthfromspace#observingtheearth#earthobservation#earthexplorer#satelliteimage#sentinel#copernicus#富士山#mount#fuji#mountfuji#fujisan#volcano#stratovolcano#japan#honshu#本州#秋津島#akitsushima#日本#日本国
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
NASA's Parker Solar Probe is set to transform our understanding of the Sun. This groundbreaking spacecraft is venturing closer to the Sun’s surface than any mission in history, navigating well within Mercury's orbit. By entering the Sun's outer atmosphere, known as the corona, for the first time, the probe is capturing invaluable data and images. These efforts aim to deepen our knowledge of the solar wind's origin and behavior. Additionally, the mission plays a vital role in improving our ability to predict changes in the space environment that impact both life and technology on Earth.
#parkersolarprobe#nasa#solarscience#spaceexploration#solarwinds#sunresearch#spaceweather#solarcorona#spacetechnology#astrophysics#sunmission#spaceinnovation#nasaexploration#solarflares#SpacecraftEngineering#ExtremeSpaceMissions#sunobservation#spacediscoveries#solarsystemexploration#futureofspace#aircraftconstruction#aviationsustainability#ParkerProbeMission#sunexploration#SolarAtmosphere#heliophysics#nasaresearch#astroscience#SpaceWeatherForecasting#solarphenomena
1 note
·
View note
Text
🌍 𝗘𝘅𝗽𝗹𝗼𝗿𝗲 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗘𝘅𝗽𝗮𝗻𝗱𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗛𝗼𝗿𝗶𝘇𝗼𝗻��� 𝗼𝗳 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗦𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗹𝗹𝗶𝘁𝗲 𝗖𝗼𝗺𝗺𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗠𝗮𝗿𝗸𝗲𝘁! 🛰️
The Market for Satellite Communication is projected to reach $15.18 billion by 2030, progressing at a CAGR of 9.4% from 2024 to 2030.
𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞: 👉 https://lnkd.in/g2BiH6gB
The Satellite Communication Market is at the heart of modern connectivity, revolutionizing industries and enabling seamless global operations. Our latest report dives deep into the market's key trends, challenges, and opportunities, offering you a comprehensive roadmap for success.

#SatelliteCommunication#SatelliteTechnology#SpaceTechnology#SpaceExploration#Telecommunications#5G#IoT#RemoteConnectivity
0 notes
Text
chandrayaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 is the third mission to the Moon by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). This mission was planned when the Chandrayaan-2 mission failed. Like Chandrayaan-2, Chandrayaan-3 also has two main parts, the lander and the rover. The orbiter performs many tasks such as communication, taking photos, and scanning, but the orbiter is not included in Chandrayaan-3. read more
#Chandrayaan3#ISRO#IndianSpaceMission#SpaceExploration#LunarMission#Chandrayaan#VikramLander#PragyanRover#IndianScience#SpaceResearch#MoonMission#IndiaOnTheMoon#ChandrayaanSuccess#SpaceInnovation#SpaceTechnology
0 notes
Text
youtube
News | Oct 21, 2024
#2024#IsraelHamasConflict#GazaCrisis#UkraineWar#USPolitics#ChinaEconomy#ClimateAction#LebanonTensions#IranEU#GlobalInflation#HaitiCrisis#SpaceExploration#GlobalNews#COP29#UN#MiddleEast#WorldPolitics#EconomicCrisis#HumanRights#WarAndPeace#SpaceTechnology#EnergyCrisis#InternationalRelations#BreakingNews#ConflictUpdate#GlobalUpdates#Youtube
0 notes