#satellite navigation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Satellites: Their Orbits, Tracking Systems, and Essential Uses

Satellites: Their Positions, Tracking, and Importance
Satellites have become an essential part of modern life, orbiting Earth and providing us with services ranging from communication and navigation to weather forecasting and space exploration. As of 2024, thousands of active satellites are circling our planet, each performing a specific role to enhance the quality of life on Earth. This article delves into the positioning of satellites, how they are tracked, what they track, and the significance of their roles.
Types of Satellite Orbits and Their Positions
Satellites are positioned in various orbits depending on their intended functions. These orbits determine how close the satellite is to Earth, how fast it moves, and what areas it covers.
Low Earth Orbit (LEO): Altitude: 180 km to 2,000 km Satellites in LEO include most Earth observation satellites, the International Space Station (ISS), and some communication satellites. These satellites are closer to the Earth, enabling them to capture high-resolution images. Functions: Used for imaging, remote sensing, and some communication purposes. Examples: ISS, Earth observation satellites like Landsat.
Medium Earth Orbit (MEO): Altitude: 2,000 km to 35,786 km Satellites in MEO are mainly used for navigation. This orbit offers a good balance between coverage and latency. Functions: GPS satellites and other global navigation systems. Examples: GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo satellites.
Geostationary Orbit (GEO): Altitude: 35,786 km above the equator Satellites in GEO move at the same rotational speed as Earth, meaning they stay fixed over one location on Earth. These are mostly communication and weather satellites. Functions: Used for television broadcasts, weather monitoring, and some types of communication. Examples: Weather satellites (GOES series), telecommunication satellites.
Highly Elliptical Orbit (HEO): Orbit shape: An elongated orbit with one point closer to Earth (perigee) and another point much farther away (apogee). Functions: Ideal for regions at high latitudes, providing prolonged coverage over areas like Russia and parts of Canada. Examples: Molniya satellites for communication in Russia.
How Satellites Are Tracked
The sheer number of satellites in space, combined with space debris, means tracking them is essential to avoid collisions and ensure their functionality. Ground stations and dedicated space agencies continuously monitor satellites. Several methods are used to track satellites:
Radar and Ground-Based Systems: Ground stations use radar to track satellites in LEO. These systems bounce radio waves off the satellite and measure the time it takes for the signal to return. By doing this repeatedly, they can track a satellite's location and speed.
Global Positioning System (GPS): Satellites in higher orbits like MEO or GEO are tracked using onboard GPS receivers. GPS helps calculate the satellite’s position and relay that data back to Earth.
Optical Tracking: Telescopes and cameras are used to visually observe satellites in higher orbits. This method is particularly useful for tracking objects that do not emit radio signals or need to be monitored for their physical characteristics.
Space Surveillance Networks: Agencies such as the U.S. Space Surveillance Network (SSN) and similar organizations in other countries continuously monitor satellites and space debris. They catalog objects and issue alerts for potential collisions.
What Satellites Track
Satellites are equipped with various sensors, cameras, and instruments to track a wide array of data on Earth, in space, and beyond:
Weather and Climate Data: Satellites such as NOAA’s GOES series monitor weather patterns, hurricanes, and long-term climate changes. They provide crucial data for meteorological services.
Earth Observation: Satellites like Landsat capture high-resolution images of Earth's surface. These images are used for mapping, agricultural planning, disaster response, and environmental monitoring.
Navigation Signals: GPS and other GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems) satellites send signals that are used for navigation by smartphones, vehicles, ships, and airplanes worldwide.
Communication: Satellites facilitate global communication by relaying TV, radio, and internet signals across vast distances.
Space Exploration: Space telescopes like the Hubble Space Telescope track distant galaxies, nebulae, and black holes, helping scientists study the universe.
Military Surveillance: Many satellites are designed for defense purposes, tracking missile launches, military movements, or spying on potential threats.
Number of Satellites in Space
As of 2024, there are approximately 8,000 operational satellites orbiting Earth. The exact number fluctuates as new satellites are launched and old ones are decommissioned. Additionally, space agencies and private companies like SpaceX continue to launch large satellite constellations, such as Starlink, which alone has over 5,000 satellites in orbit for global internet coverage.
The Usefulness of Satellites
Satellites have become indispensable in modern life, serving a wide variety of purposes that impact everyday activities and critical global functions:
Key Functions of Satellites:
Communication: Satellites enable long-distance communication by transmitting data, television, and internet services. Without them, global broadcasting and real-time communication in remote areas would be impossible.
Navigation: Systems like GPS help millions of people navigate in real-time. They are also vital for the functioning of aviation, maritime travel, and even agricultural practices.
Earth Observation: Satellites provide high-resolution imagery of Earth, helping with disaster management, urban planning, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. For instance, they can track deforestation or observe glaciers' melting rates.
Weather Forecasting: Weather satellites provide the data needed for accurate predictions, storm tracking, and climate monitoring. This information is critical for preparing for natural disasters like hurricanes or floods.
Scientific Research and Exploration: Space telescopes and interplanetary satellites gather data on space phenomena, expanding our understanding of the universe. Satellites also conduct scientific experiments in the microgravity of space.
Defense and Security: Satellites are used for military surveillance, early-warning systems, and missile detection, playing a crucial role in national security.
Satellite Highlights in Brief:
Types of orbits: LEO, MEO, GEO, HEO, each serving different purposes.
Tracking methods: Radar, GPS, optical tracking, and space surveillance networks.
Data tracked by satellites: Weather, Earth observation, navigation signals, space exploration, and military surveillance.
Number of active satellites: Approximately 8,000.
Key roles: Communication, navigation, weather forecasting, Earth observation, scientific research, and defense.
In conclusion, satellites are essential tools for global communication, navigation, monitoring Earth's environment, and scientific discovery. As technology advances and the number of satellites continues to grow, their impact on our daily lives will only increase. Whether improving how we predict the weather, navigate through traffic, or explore the universe, satellites will continue to be a critical resource for humanity.
Go To How Satellites Work and What They Track
#satellite orbits#satellite tracking#satellite functions#low earth orbit#geostationary orbit#medium earth orbit#space technology#GPS satellites#communication satellites#weather satellites#Earth observation#satellite uses#satellite positions#how satellites work#space surveillance#satellite navigation#satellite networks#satellite importance#global navigation systems
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
GPS/GNSS/Galileo L2 + L5 Band SMD Passive Ceramic Antenna
Our GPS/GNSS/Galileo L2 + L5 Band SMD Passive Ceramic Antenna is designed for highly accurate and reliable positioning and navigation. Featuring dual-band support for L2 and L5 frequencies, this compact, high-performance antenna is ideal for applications requiring precise satellite signal reception, such as automotive, surveying, and IoT devices. Its SMD (Surface Mount Device) design ensures easy integration into your system, making it perfect for space-constrained environments while delivering excellent signal integrity and minimal interference.
#GPS antenna#GNSS antenna#Galileo antenna#L2 L5 antenna#passive ceramic antenna#SMD antenna#high-precision antenna#satellite navigation#dual-band antenna#GPS/GNSS solutions.
0 notes
Text
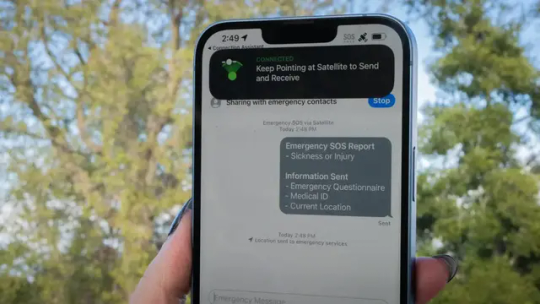
Google’s Code Points to Apple SOS-Like Features for Android
Android is lagging hard behind iOS for emergency satellite connectivity, and Google may be reaching out to Garmin to enable some kind of emergency SOS feature. Google’s Antitrust Case Is the Best Thing That Ever Happened to AI Late on Sunday, developer Neïl Rahmouni (first spotted by The Verge) shared some interesting code snippets that point to Google getting its own brand of emergency SOS…
View On WordPress
#Accident#Android#Disaster#Environment#Garmin#Garmin Response#Gizmodo#Globalstar#Google#Google Allo#Internet#iPhone#Iridium#Iridium Communications#Messages#Qualcomm#Rahmouni#Satellite emergency notification device#Satellite navigation#Satellite telephony#Schaffhausen#SMS#Technology
0 notes
Text
-Welcome to the SATELLITE HERMITS AU MASTERPOST!-

What's that? — Hermitcraft & friends sci-fi AU set in a utopic retrofuturistic world, on a distant newly-discovered planet called Minecrea, one of the moons of gas giant HC-1304
Is there a comic or a fic? — No, at least not yet :[ I doubt I'll ever get to the point where the entire thing would be carefully written down in a form of a fic, sadly. What I hope to achieve at the very least is a bunch of posts in a illustration/short comic + soundtrack + chunk of screenplay-ish text format.
Can I ask things about stuff? — Anytime! By sending asks you'd actually make my job of explaining lore&plot&characters easier
This post will be updated as more things are made. For now, you can enjoy:
Where are we / introduction
Skizz arrives to Minecrea [start here] Part 1, Part 2, Part 3
Character designs & info: Zedaph | Bdubs | Grian, Mumbo | Etho
About ELYTRas
A comet: a welcoming gift, a bad omen, a cycle of life?
About Mt. Gate-1 & Gate-2
Job division
That time when Bduds saw Etho without the mask
A video edit? Short ambience scene? Idk what is it and why is it but hey, it exists 🎉
________________________
Dialog formating in the "screen-play" texts:
Communicator-text chat:
13:02 <GOODTIMEWITHSCAR> : It's not that bad!
13:30 <GOODTIMEWITHSCAR> : iT'S BAD
13:30 <GOODTIMEWITHSCAR> : gRAIN IT'S BAD
13:31 <GOODTIMEWITHSCAR> : Help!!!
In person:
SCAR : Griaaan!! Grian, are you home?
Communicator-radio chat:
[SCAR] : Um, guys. Does anybody have a spare, um, I don't know.. Half a mile of tape?.. Like duct tape?..
[MUMBO] : Oh god.
[GRIAN] : Scar, wherever you are, just stay there! Stop flying around, I'm coming.
#I felt like it's about time to make somewhat of a masterpost#even for my own navigational purposes :'D#satellite hermits au#hermitblr#hermitcraft fanart#trafficblr
228 notes
·
View notes
Text
fuck man i just wanted to reward myself with reading some fanfiction after a long day at the academic research factory and deliriously panicked about the lack of footnotes like oh god i can't cite this. christ. yeah alright sleep it is
162 notes
·
View notes
Note
I managed to get to where my mom needed me to be without using the gps, driving is fun
Congratulations.
Not sure if Megatron was being sarcastic or not, but yeah. Well done. Driving can be a little daunting when you're an inexperienced driver or exploring a new location.
I suppose so. I tend not to have that problem, being a flight frame.
Oh. So you were being sarcastic. 😒
Only a bit.
#asks answered#transformers#megatron#optimus prime#navigating without satellite navigation#megatron's sarcastic nature#shatteredhope123
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Satnav / GPS in the Heeler SUV
“Show and Tell” is another example of a story with satnav / GPS as a plot point.
In the Heeler’s SUV it’s integrated into the dashboard, they’re not reliant on a smartphone for navigation like Jack’s Dad.
Here’s Dad in the car before he puts his seatbelt on.

And a shot of the display while on the road.

Unlike other episodes where the issue is the technology, in “Show and Tell” Dad deliberately ignores the instructions to teach the kids a lesson.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

not the kohaku card i was looking for…
#only one ten pull bc. still might need dia for satellite#didnt really bother to calculate lol#sometimes being f2p is chill like that#(cries bc of the d4 na.gisa event card im currently ignoring in favor of satellite and july navigation soph and neo.#kori plays enstars
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
will somebody please write dr. erland with me I will give you all my love and my life savings and a candy bar
#PLEASE!!!!!!#ooc.#i wanna write aus where he lives and they get to know each other and navigate that weirdness#I want to write aus where he finds and rescues her before she’s taken to the satellite#I wanna write aus where they were never separated in the first place#please I’m dying#wishlist.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
#AI and Digital Governance#Android Starlink Integration#Corporate Control Over Telecom#Cybersecurity#Digital Dependence#Elon Musk’s Infrastructure#facts#Global Communication Networks#life#Podcast#Satellite Network Expansion#Satellite-Controlled Communications#serious#straight forward#Surveillance Concerns#Technocratic Control#truth#upfront#website#Post navigation
0 notes
Text
India's ISRO scores historic century with 100th satellite launch
ISRO’s 100th successful satellite launch: Sriharikota, India – In a momentous achievement for the Indian space program, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) today successfully launched its 100th satellite mission. The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV-F15) carrying the NVS-02 navigation satellite lifted off flawlessly from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra…
0 notes
Text

GPS/Glonass/Galileo L2 Band SMD Passive Ceramic Antenna
An L2 Band GPS antenna typically refers to antennas designed for use with GPS receivers operating on the L2 frequency band, which is one of the GPS signals transmitted by satellites. The L2 band operates at a frequency of 1227.60 MHz, which is used for more accurate positioning by improving the accuracy of signals in conjunction with other frequencies like L1.
An SMD (Surface-Mount Device) refers to an antenna that's designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of a PCB (Printed Circuit Board). SMD antennas are compact, easy to integrate into small devices, and suitable for mass production. They are widely used in GPS receivers, automotive applications, IoT devices, and other systems requiring precise navigation.
#multi gnss antenna#GPS antenna suppliers USA#Best GPS antenna USA#GPS antennas for sale in USA#GPS antenna near me#Buy GPS antenna USA#4g gps antenna singapore#gps smart antenna Denmark#GPS Navigation Antenna#Satellite navigation antenna#High-precision GPS antenna
0 notes
Text
Navigating the Complexities of Divorce In Ahmedabad Gujarat: A Comprehensive Guide
Divorce Advocate In Ahmedabad – Divorce Advocate In Gujarat, Divorce can be a challenging process, especially in a culturally diverse city like Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Divorce Lawyer In Ahmedabad, This comprehensive guide provides insights into the divorce process, key considerations, and the role of experienced divorce lawyers in Ahmedabad, Divorce Lawyer In Gujarat.
Google Map:--> https://maps.app.goo.gl/joAsJDspDRuUsKTv6
Navigating the Complexities of Divorce In Ahmedabad Gujarat: A Comprehensive Guide, Divorce Advocate In Ahmedabad, Divorce Advocate In Gujarat, Divorce Lawyer In Ahmedabad, Divorce Lawyer In Gujarat, Divorce Process in Gujarat, Divorce Process in Ahmedabad, Best Divorce Lawyers in Ahmedabad, Best Divorce Lawyers in Ahmedabad Gujarat, Best Divorce Lawyers in Gujarat, Divorce Lawyer Ahmedabad Gujarat, Divorce Advocate Ahmedabad Gujarat, Lawyers For Divorce Case in Ahmedabad Gujarat, www.ashishdesaiadvocate.com/divorce-lawyers-advocate-in-ahmedabad-gujarat.php, Satellite Ahmedabad, Satellite, Nehru Nagar Ahmedabad, Nehru Nagar, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India, Ahmedabad Gujarat India, Ashish B Desai
#Navigating the Complexities of Divorce In Ahmedabad Gujarat: A Comprehensive Guide#Divorce Advocate In Ahmedabad#Divorce Advocate In Gujarat#Divorce Lawyer In Ahmedabad#Divorce Lawyer In Gujarat#Divorce Process in Gujarat#Divorce Process in Ahmedabad#Best Divorce Lawyers in Ahmedabad#Best Divorce Lawyers in Ahmedabad Gujarat#Best Divorce Lawyers in Gujarat#Divorce Lawyer Ahmedabad Gujarat#Divorce Advocate Ahmedabad Gujarat#Lawyers For Divorce Case in Ahmedabad Gujarat#www.ashishdesaiadvocate.com/divorce-lawyers-advocate-in-ahmedabad-gujarat.php#Satellite Ahmedabad#Satellite#Nehru Nagar Ahmedabad#Nehru Nagar#Ahmedabad#Gujarat#India#Ahmedabad Gujarat India#Ashish B Desai
0 notes
Text
The Satellite Navigation System Market by Constellation (Global Navigation Satellite, Regional Navigation Satellite, and Augmented Satellite), Solution (Service and System) and Orbit (Geostationary Earth Orbit, Medium Earth Orbit) and Global Forecast to 2028
0 notes
Text
Scientists are testing mobile tower-based signals that could help pilots in emergency

- By Nuadox Crew -
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories and Ohio State University are exploring a backup navigation system for aircraft using "signals of opportunity"—non-GPS signals like those from cell towers and communications satellites.
This system aims to address potential GPS disruptions caused by jamming or spoofing, which can lead to dangerous situations for pilots.
Using weather balloons to collect data at altitudes up to 80,000 feet, the team studies how these alternative signals, including the Doppler effect in radio waves, can determine an aircraft’s position and velocity.
While processing the data is labor-intensive, initial findings suggest that signals from cell towers detected at high altitudes could support navigation, offering a new safety tool for aviation in areas or situations where GPS is unreliable.
The research highlights the potential for robust, real-time navigation systems leveraging diverse signal sources, enhancing aviation safety amid increasing GPS vulnerabilities.
Header image credit: Microsoft Copilot (AI-generated).
Read more at Sandia National Laboratories
Related Content
Why 50,000 ships are so vulnerable to cyberattacks
Other Recent News
Canadian News Publishers Sue OpenAI: A coalition of Canadian news publishers, including The Canadian Press, Torstar, Globe and Mail, Postmedia, and CBC/Radio-Canada, is suing OpenAI for using their content to train ChatGPT without permission or compensation.
Amazon India's Quick Commerce Plans: Amazon India is reportedly planning to launch a quick commerce service called "Tez" by December.
Nuclear Fusion Energy: The Joint European Torus (JET) project in southern France is making strides in nuclear fusion energy, aiming to achieve fusion power on a power plant scale.
NASA Satellites Reveal Freshwater Decline: NASA satellites have revealed a decline in freshwater sources as global droughts and warming persist.
0 notes