#roman space telescope
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Observations from both NASA’s James Webb and Hubble space telescopes created this colorful image of galaxy cluster MACS0416. The colors of different galaxies indicate distances, with bluer galaxies being closer and redder galaxies being more distant or dusty. Some galaxies appear as streaks due to gravitational lensing — a warping effect caused by large masses gravitationally bending the space that light travels through.
Like Taylor Swift, Our Universe Has Gone Through Many Different Eras
While Taylor's Eras Tour explores decades of music, our universe’s eras set the stage for life to exist today. By unraveling cosmic history, scientists can investigate how it happened, from the universe’s origin and evolution to its possible fate.
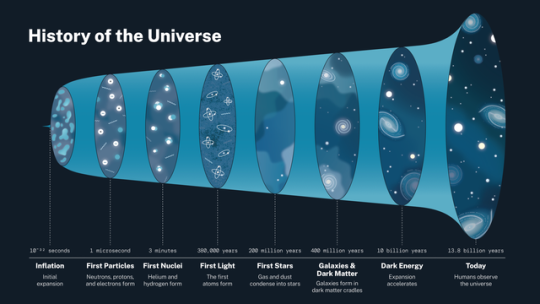
This infographic outlines the history of the universe.
0 SECONDS | In the beginning, the universe debuted extremely small, hot, and dense
Scientists aren’t sure what exactly existed at the very beginning of the universe, but they think there wasn’t any normal matter or physics. Things probably didn’t behave like we expect them to today.

Artist's interpretation of the beginning of the universe, with representations of the early cosmos and its expansion.
10^-32 SECONDS | The universe rapidly, fearless-ly inflated
When the universe debuted, it almost immediately became unstable. Space expanded faster than the speed of light during a very brief period known as inflation. Scientists are still exploring what drove this exponential expansion.
youtube
1 MICROSECOND | Inflation’s end started the story of us: we wouldn’t be here if inflation continued
When inflation ended, the universe continued to expand, but much slower. All the energy that previously drove the rapid expansion went into light and matter — normal stuff! Small subatomic particles — protons, neutrons, and electrons — now floated around, though the universe was too hot for them to combine and form atoms.
The particles gravitated together, especially in clumpy spots. The push and pull between gravity and the particles’ inability to stick together created oscillations, or sound waves.
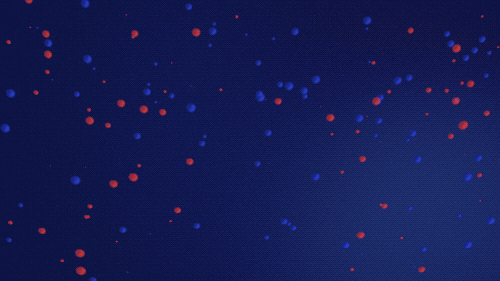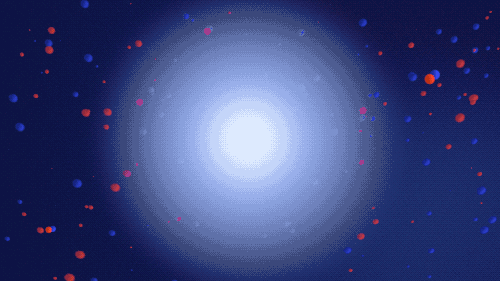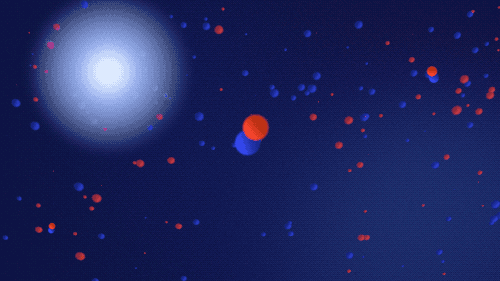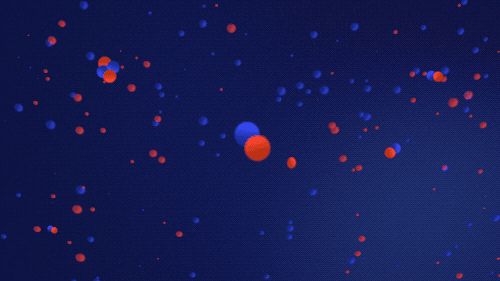
Artist's interpretation of protons and neutrons colliding to form ionized deuterium — a hydrogen isotope with one proton and one neutron — and ionized helium — two protons and two neutrons.
THREE MINUTES | Protons and neutrons combined all too well
After about three minutes, the universe had expanded and cooled enough for protons and neutrons to stick together. This created the very first elements: hydrogen, helium, and very small amounts of lithium and beryllium.
But it was still too hot for electrons to combine with the protons and neutrons. These free electrons floated around in a hot foggy soup that scattered light and made the universe appear dark.
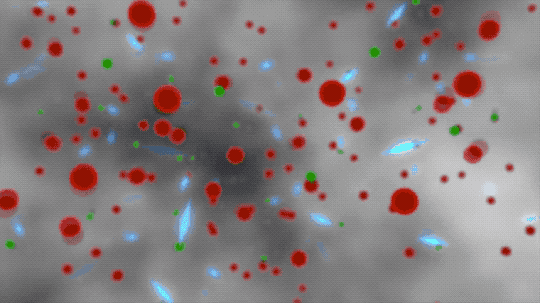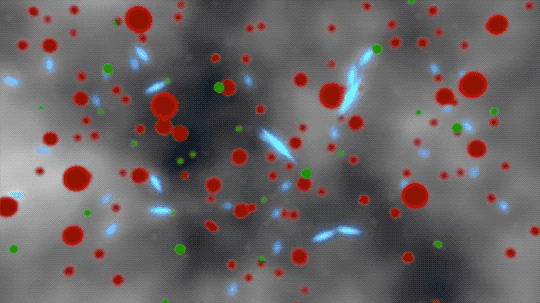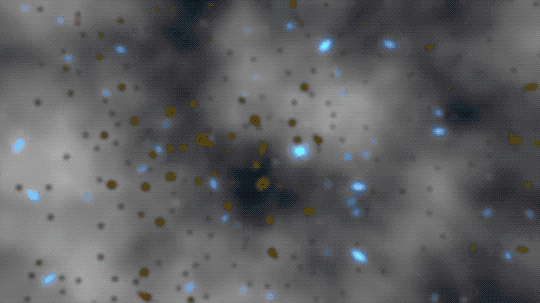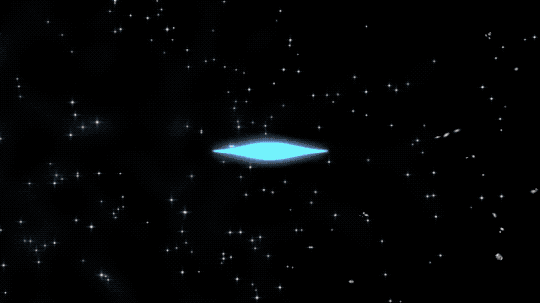
This animated artist’s concept begins by showing ionized atoms (red blobs), free electrons (green blobs), and photons of light (blue flashes). The ionized atoms scattered light until neutral atoms (shown as brown blobs) formed, clearing the way for light to travel farther through space.
380 THOUSAND YEARS | Neutral atoms formed and left a blank space for light
As the universe expanded and cooled further, electrons joined atoms and made them neutral. With the electron plasma out of the way, some light could travel much farther.

An image of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) across the entire sky, taken by ESA's (European Space Agency) Planck space telescope. The CMB is the oldest light we can observe in the universe. Frozen sound waves are visible as miniscule fluctuations in temperature, shown through blue (colder) and red (warmer) coloring.
As neutral atoms formed, the sound waves created by the push and pull between subatomic particles stopped. The waves froze, leaving ripples that were slightly denser than their surroundings. The excess matter attracted even more matter, both normal and “dark.” Dark matter has gravitational influence on its surroundings but is invisible and does not interact with light.

This animation illustrates the absorption of photons — light particles — by neutral hydrogen atoms.
ALSO 380 THOUSAND YEARS | The universe became dark — call it what you want, but scientists call this time period the Dark Ages
Other than the cosmic microwave background, there wasn't much light during this era since stars hadn’t formed yet. And what light there was usually didn't make it very far since neutral hydrogen atoms are really good at absorbing light. This kicked off an era known as the cosmic dark ages.

This animation illustrates the beginning of star formation as gas begins to clump due to gravity. These protostars heat up as material compresses inside them and throw off material at high speeds, creating shockwaves shown here as expanding rings of light.
200 MILLION YEARS | Stars created daylight (that was still blocked by hydrogen atoms)
Over time, denser areas pulled in more and more matter, in some places becoming so heavy it triggered a collapse. When the matter fell inward, it became hot enough for nuclear fusion to start, marking the birth of the first stars!
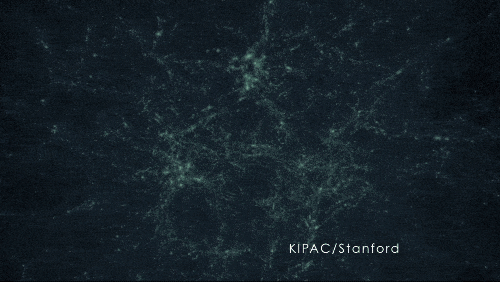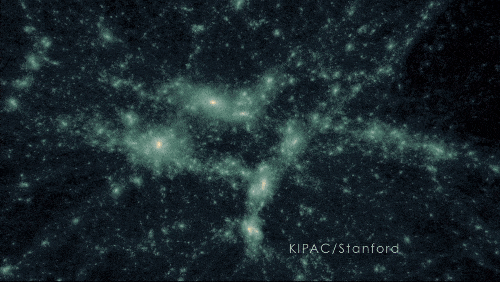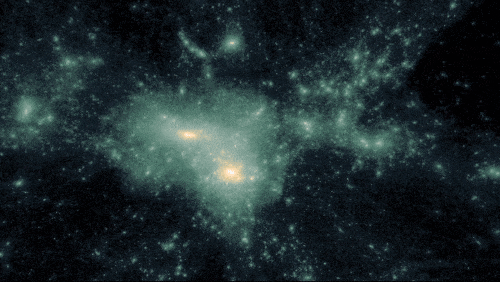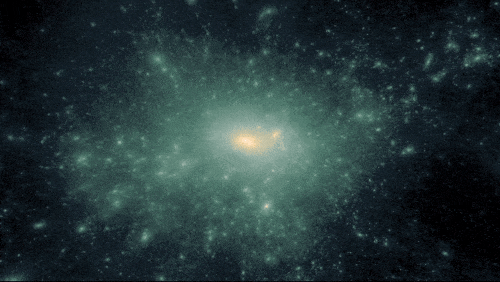
A simulation of dark matter forming structure due to gravity.
400 MILLION YEARS | Dark matter acted like an invisible string tying galaxies together
As the universe expanded, the frozen sound waves created earlier — which now included stars, gas, dust, and more elements produced by stars — stretched and continued attracting more mass. Pulling material together eventually formed the first galaxies, galaxy clusters, and wide-scale, web-like structure.
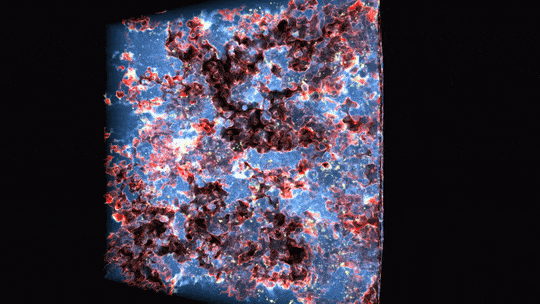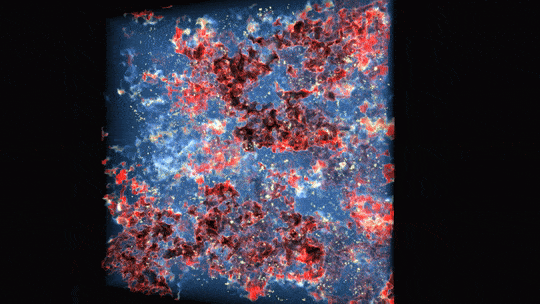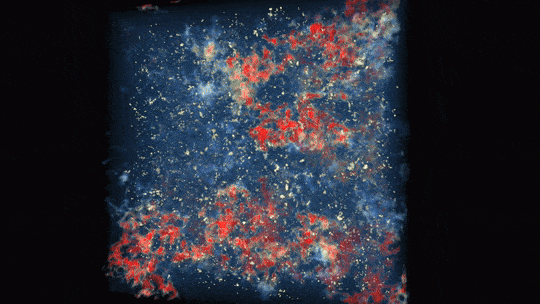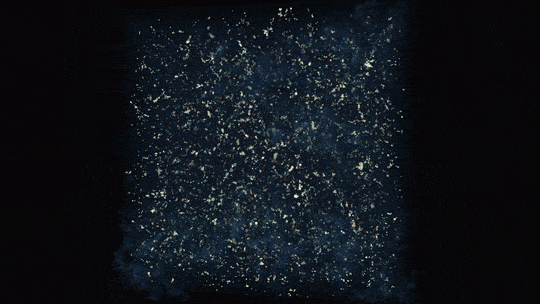
In this animation, ultraviolet light from stars ionizes hydrogen atoms by breaking off their electrons. Regions already ionized are blue and translucent, areas undergoing ionization are red and white, and regions of neutral gas are dark and opaque.
1 BILLION YEARS | Ultraviolet light from stars made the universe transparent for evermore
The first stars were massive and hot, meaning they burned their fuel supplies quickly and lived short lives. However, they gave off energetic ultraviolet light that helped break apart the neutral hydrogen around the stars and allowed light to travel farther.

Animation showing a graph of the universe’s expansion over time. While cosmic expansion slowed following the end of inflation, it began picking up the pace around 5 billion years ago. Scientists still aren't sure why.
SOMETIME AFTER 10 BILLION YEARS | Dark energy became dominant, accelerating cosmic expansion and creating a big question…?
By studying the universe’s expansion rate over time, scientists made the shocking discovery that it’s speeding up. They had thought eventually gravity should cause the matter to attract itself and slow down expansion. Some mysterious pressure, dubbed dark energy, seems to be accelerating cosmic expansion. About 10 billion years into the universe’s story, dark energy – whatever it may be – became dominant over matter.

An image of Earth rising in the Moon’s sky. Nicknamed “Earthrise,” Apollo 8 astronauts saw this sight during the first crewed mission to the Moon.
13.8 BILLION YEARS | The universe as we know it today: 359,785,714,285.7 fortnights from the beginning
We owe our universe today to each of its unique stages. However, scientists still have many questions about these eras.
Our upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will look back in time to explore cosmic mysteries like dark energy and dark matter – two poorly understood aspects of the universe that govern its evolution and ultimate fate.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#NASA#astronomy#telescope#Roman Space Telescope#space#science#Nancy Grace Roman#STEM#cosmology#YouTube#Taylor Swift#the eras tour
2K notes
·
View notes
Text




Over the last several months, engineers have been at work in the clean room at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, putting together the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope.
The Coronagraph Instrument—a technology demonstration designed to image exoplanets—and Optical Telescope Assembly—which includes the primary mirror and nine additional mirrors—are now attached to the Instrument Carrier.
With those components in place, the team then added Roman’s primary instrument, the Wide Field Instrument. This 300-megapixel infrared camera will give Roman a deep, panoramic view of the universe.
The observatory is on track for completion by fall 2026 and launch no later than May 2027.
Credit: NASA, Chris Gunn, and Sydney Rohde.
#space#astronomy#science#nasa#universe#roman space telescope#nancy grace roman space telescope#nancy roman space telescope#nasa roman#telescope#goddard#exoplanets#coronagraph#space telescope
209 notes
·
View notes
Text



Now this is a telescope! A very expensive telescope but worth it!
#eye to the telescope#james webb space telescope#hubble space telescope#telescope#james webb telescope#astronomy#nasa#astronomers#universe#nasa photos#astrophotography#outer space#astrophysics#nasawebb#space telescopes#hubble telescope#spitzer space telescope#roman space telescope#space exploration#space#science#spaceship#space travel#our universe#the universe#nasa science#planetary science#science facts#space science#space photography
31 notes
·
View notes
Text


Solar panels for NASA’s Roman Space Telescope pass key tests
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope’s Solar Array Sun Shield has successfully completed recent tests, signaling that the assembly is on track to be completed on schedule. The panels are designed to power and shade the observatory, enabling all the mission’s observations and helping keep the instruments cool.
The Roman team has two sets of these panels –– one that will fly aboard the observatory and another as a test structure, used specifically for preliminary assessments.
Engineers at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, evaluated the test version in a thermal vacuum chamber, which simulates the hot and cold temperatures and low-pressure environment the flight panels will experience in space. Since the panels will be stowed for launch, the team practiced deploying them in space-like conditions.
Meanwhile, a vendor built up the flight version by fitting the panels with solar cells. After delivery to Goddard, technicians tested the solar cells by flashing the panels with a bright light that simulates the Sun.
“We save a significant amount of time and money by using two versions of the panels, because we can do a lot of preliminary tests on a spare while moving further in the process with the flight version,” said Jack Marshall, the Solar Array Sun Shield lead at NASA Goddard. “It streamlines the process and also avoids risking damage to the panels that will go on the observatory, should testing reveal a flaw.”
Next spring, the flight version of the Solar Array Sun Shield will be installed on the Roman spacecraft. Then, the whole spacecraft will go through thorough testing to ensure it will hold up during launch and perform as expected in space.
TOP IMAGE: The solar panels for NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope are undergoing assessment in a test chamber at the agency's Goddard Space Flight Center in this photo. Credit NASA/Chris Gunn
LOWER IMAGE: Both versions of the Solar Array Sun Shield for NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope appear in this photo, taken in the largest clean room at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. The flight version lies flat in the foreground, while the qualification assembly stands upright in the background. The flight panels will shade the mission’s instruments and power the observatory. Credit NASA/Chris Gunn
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
NASA to launch Roman Space telescope; 100 times wider View than Hubble
Scheduled for launch in May 2027, NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope promises to revolutionize our understanding of the universe. With a field of view 100 times larger than the Hubble Space Telescope, Roman will explore the cosmos faster and with greater precision. The mission aims to study billions of cosmic objects, shedding light on the formation of planets, stars, and galaxies, while…
0 notes
Text
NASA to launch Roman Space telescope; 100 times wider View than Hubble
Scheduled for launch in May 2027, NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope promises to revolutionize our understanding of the universe. With a field of view 100 times larger than the Hubble Space Telescope, Roman will explore the cosmos faster and with greater precision. The mission aims to study billions of cosmic objects, shedding light on the formation of planets, stars, and galaxies, while…
0 notes
Text




i've been doing an astronomy internship this summer, and we recently talked about the space telescopes! wanted to personify some of them hehe.
James Webb (they/them): Their shiny poncho thing is inspired by the solar shield. They have a rivalry with Hubble, believing him to be obsolete. However, they secretly are worried they won't be able to live up to his legacy.
Hubble (he/him): His glasses represent the COSTAR instrument that was installed on Hubble to correct it's blurry images. He finds James Webb's attempt at a rivalry amusing, and just wants to become friends with the younger fella and help them out.
Nancy Grace Roman (she/her): A telescope not yet launched, she's an old NRO telescope, and is having trouble adjusting from a life of espionage to one of science.
#my art#astronomy#personification#james webb space telescope#hubble space telescope#nancy grace roman space telescope#jwst#hst#object head#original characters#oc art#original character
582 notes
·
View notes
Text
The James Webb Space Telescope is my Roman Empire
#r/196#r/196archive#196#/r/196#rule#meme#memes#shitpost#shitposting#autism#JWST#james webb space telescope#nasa#astronomy#space#roman empire
333 notes
·
View notes
Text
NASA's forthcoming Nancy Grace Roman Telescope could use the grisly death of stars ripped apart by black holes to hunt the universe's first population of stellar bodies. These early stars, referred to (somewhat confusingly) as Population III (Pop III) stars, were very different from the sun and other stars seen in the cosmos today. That's because the universe wasn't yet filled with "metals," the term astronomers use to describe elements heavier than hydrogen and helium. Pop III stars arose just a few hundred million years after the Big Bang and were "metal-poor," composed mostly of hydrogen and helium. They were also believed to be much larger and hotter than the sun. This means that Pop III burned through their fuel for nuclear fusion faster than smaller stars, and these short lifetimes make them elusive targets for astronomers.
Continue Reading.
#Science#Space#Astronomy#Stars#Population III Stars#Tidal Disruption Events#Nancy Grace Roman Telescope#NASA#National Aeronautics and Space Administration
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Nancy Grace Roman Telescope is named after the Mother of Hubble
The Nancy Grace Roman Telescope (previously WFIRST) is a NASA mission set to launch in 2027. I think you guys need to know about more about it though, because although its technology is amazing, the most amazing thing about it is its name.
Dr Nancy Grace Roman was an executive at NASA, working as the Chief of Astronomy, Chief of Astronomy and Relativity, and Chief of Solar Physics (what cool job titles!!) from 1959 until her retirement in 1979. Among her many achievements (including being the first female NASA executive!), her most notable was Hubble.
Decades before people were ready to consider an investment such as Hubble, Dr Roman was pioneering for it, lobbying NASA officials to get it approved, putting together planning committees and fighting to secure funding.
Her dedication to Hubble earned her the nickname "Mother of Hubble". But I don't think this really emphasises her achievements enough. Hubble was the inspiration for so many space telescope missions, the mission that showed it was possible for the rest, the seed that sprouted so many more space telescopes, and so many more discoveries in our lifetimes.
By her own words “I think it would have existed sooner or later without me." But without her, how long would we have had to wait before this age of space telescopes? By being the Mother of Hubble, she has become the Mother of modern space-based astronomy.
The Nancy Grace Roman Telescope could not have a better name.

She often said, "for the price of one night at the movies each year, each American would receive 15 years of exciting discoveries." But she was wrong, because not just Americans, but people across the globe have now received over 30 years of discoveries!
Dr Nancy Grace Roman passed away on December 25th, 2018, three years to the date of the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope. I think she would be thrilled to see how far space-based astronomy has come.
Read more about her:
#space#astronomy#women in stem#nasa#Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope#space telescopes#james webb space telescope#science#inspiring women#inspirational#people who changed history#Mother of Hubble
35 notes
·
View notes
Link
Astronomy Daily - The Podcast: S04E011 Welcome to the first episode of Astronomy Daily for 2025 for us, where we kick off the year with a stellar lineup of space news and astronomical updates. We're Steve and Hallie, and today we delve into some of the most exciting developments in the cosmos. Highlights: - Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope Nears Completion: NASA's Roman Space Telescope is on track for a 2027 launch, with recent integration of its key components marking a significant milestone. Extensive testing is underway to ensure the telescope's readiness for its mission to unveil the universe like never before. - Blue Origin's New Glenn Rocket Ready for Maiden Voyage: Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin is set for its inaugural orbital launch with the New Glenn rocket. Scheduled to lift off from Cape Canaveral, this mission signifies a new chapter in the commercial space race, challenging SpaceX's dominance. - Upcoming ISS Spacewalks: The Expedition 72 crew at the International Space Station is preparing for two critical spacewalks to maintain astrophysics equipment and upgrade communication systems. These missions aim to enhance research capabilities and explore potential microbial life on the station's exterior. - Gilmour Space's First Orbital Launch: Australian startup Gilmour Space is gearing up for its first orbital launch with the Eris rocket. Having received its launch license, the company is poised to make history with an Australian-made rocket from Australian soil. - Lignosat: The Wooden Satellite: In a groundbreaking experiment, Japan's Lignosat has been deployed from the ISS. This wooden satellite explores the potential of sustainable materials in spacecraft construction, offering innovative insights into eco-friendly satellite manufacturing. For more cosmic updates, visit our website at astronomydaily.io. Join our community on social media by searching for #AstroDailyPod on Facebook, X, Tumblr, YouTubeMusic, and TikTok. Share your thoughts and connect with fellow space enthusiasts. Thank you for tuning in. This is Stephen Hallie signing off. Until next time, keep looking up and stay curious about the wonders of our universe. 00:00 - Welcome back to Astronomy Daily for the new year 2025 01:46 - NASA has successfully integrated key components of the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope 03:41 - Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin launches new rocket on Sunday with ambitious mission 09:20 - The Expedition 72 crew spent the week preparing for upcoming spacewalks 15:52 - Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency launches experimental wooden satellite into space in 2025 ✍️ Episode References NASA https://www.nasa.gov/ Blue Origin https://www.blueorigin.com/ SpaceX https://www.spacex.com/ International Space Station (ISS) https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/main/index.html Gilmore Space Technologies https://www.gilmourspace.com/ Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) https://global.jaxa.jp/ Starlink https://www.starlink.com/ Project Kuiper https://www.aboutamazon.com/what-we-do/project-kuiper
#astrodailypod#astronomy#bezos#blue#elon#glenn#grace#international#jeff#musk#nancy#new#origin#rocket#roman#science#space#spacex#telescope
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Launch Your Creativity with Space Crafts!
In honor of the completion of our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope’s spacecraft — the vehicle that will maneuver the observatory to its place in space and enable it to function once there — we’re bringing you a space craft you can complete at home! Join us for a journey across the cosmos, starting right in your own pantry.
Stardust Slime
Ingredients:
1 5 oz. bottle clear glue
½ tablespoon baking soda
Food coloring
1 tablespoon contact lens solution
1 tablespoon glitter
Directions:
Pour the glue into a bowl.
Mix in the baking soda.
Add food coloring (we recommend blue, purple, black, or a combination).
Add contact lens solution and use your hands to work it through the slime. It will initially be very sticky! You can add a little extra contact lens solution to make it firmer and less goopy.
Add glitter a teaspoon at a time, using as much or as little as you like!
Did you know that most of your household ingredients are made of stardust? And so are you! Nearly every naturally occurring element was forged by living or dying stars.
Take the baking soda in this slime recipe, for example. It’s made up of sodium, hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. The hydrogen was made during the big bang, right at the start of the universe. But the other three elements were created by dying stars. So when you show your friends your space-y slime, you can tell them it’s literally made of stardust!
Still feeling crafty? Try your hand at more pantry projects or these 3D and paper spacecraft models. If you’re eager for a more advanced space craft, check out these embroidery creations for inspiration! Or if you’re ready for a break, take a virtual tour of an interactive version of the Roman Space Telescope here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#NASA#astronomy#telescope#Roman Space Telescope#technology#space#science#tech#DIY#crafts#engineering#STEM
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will look for signs of dark matter in the gaps of stellar streams. These trails of stars form at the edge of galaxies due to gravity ripping apart globular star clusters. Spaces between the stars can indicate the influence of dark matter.
#space#astronomy#stsci#science#nasa#universe#nasaroman#roman science#roman space telescope#nancy grace roman space telescope#dark matter
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
NASA Completes Spacecraft to Transport Support Roman Space Telescope
The spacecraft bus that will deliver NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope to its orbit and enable it to function once there is now complete after years of construction, installation, and testing. Now that the spacecraft is assembled, engineers will begin working to integrate the observatory’s other major components, including the science instruments and the […] from NASA https://ift.tt/aIAdfJi
2 notes
·
View notes
Text




NASA successfully integrates coronagraph for Roman Space Telescope
NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope team has successfully completed integration of the Roman Coronagraph Instrument onto Roman's Instrument Carrier, a piece of infrastructure that will hold the mission's instruments, which will be integrated onto the larger spacecraft at a later date. The Roman Coronagraph is a technological demonstration that scientists will use to take an important step in the search for habitable worlds, and eventually life beyond Earth.
This integration took place at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, where the space telescope is located and in development. This milestone follows the coronagraph's arrival at the center earlier this year from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California where the instrument was developed, built, and tested.
The Roman Coronagraph Instrument is a technology demonstration that will launch aboard the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, NASA's next flagship astrophysics mission. Roman will have a field of view at least 100 times larger than the agency's Hubble Space Telescope and explore scientific mysteries surrounding dark energy, exoplanets, and infrared astrophysics. Roman is expected to launch no later than May 2027.
The mission's coronagraph is designed to make direct observations of exoplanets, or planets outside of our solar system, by using a complex suite of masks and active mirrors to obscure the glare of the planets' host stars, making the planets visible. Being a technology demonstration means that the coronagraph's goal is to test this technology in space and showcase its capabilities. The Roman Coronagraph is poised to act as a technological stepping stone, enabling future technologies on missions like NASA's proposed Habitable Worlds Observatory, which would be the first telescope designed specifically to search for signs of life on exoplanets.
"In order to get from where we are to where we want to be, we need the Roman Coronagraph to demonstrate this technology," said Rob Zellem, Roman Space Telescope deputy project scientist for communications at NASA Goddard. "We'll be applying those lessons learned to the next generation of NASA flagship missions that will be explicitly designed to look for Earth-like planets."
he mission's coronagraph is designed to make direct observations of exoplanets, or planets outside of our solar system, by using a complex suite of masks and active mirrors to obscure the glare of the planets' host stars, making the planets visible. Being a technology demonstration means that the coronagraph's goal is to test this technology in space and showcase its capabilities. The Roman Coronagraph is poised to act as a technological stepping stone, enabling future technologies on missions like NASA's proposed Habitable Worlds Observatory, which would be the first telescope designed specifically to search for signs of life on exoplanets.
"In order to get from where we are to where we want to be, we need the Roman Coronagraph to demonstrate this technology," said Rob Zellem, Roman Space Telescope deputy project scientist for communications at NASA Goddard. "We'll be applying those lessons learned to the next generation of NASA flagship missions that will be explicitly designed to look for Earth-like planets."
A major mission milestone
The coronagraph was successfully integrated into Roman's Instrument Carrier, a large grid-like structure that sits between the space telescope's primary mirror and spacecraft bus, which will deliver the telescope to orbit and enable the telescope's functionality upon arrival in space. Assembly of the mission's spacecraft bus was completed in September 2024.
The Instrument Carrier will hold both the coronagraph and Roman's Wide Field Instrument, the mission's primary science instrument, which is set to be integrated later this year along with the Roman telescope itself.
"You can think of [the Instrument Carrier] as the skeleton of the observatory, what everything interfaces to," said Brandon Creager, lead mechanical engineer for the Roman Coronagraph at JPL.
The integration process began months ago with mission teams from across NASA coming together to plan the maneuver. Additionally, after its arrival at NASA Goddard, mission teams ran tests to prepare the coronagraph to be joined to the spacecraft bus.
During the integration itself, the coronagraph, which is roughly the size and shape of a baby grand piano (measuring about 5.5 feet or 1.7 meters across), was mounted onto the Instrument Carrier using what's called the Horizontal Integration Tool.
First, a specialized adapter developed at JPL was attached to the instrument, and then the Horizontal Integration Tool was attached to the adapter. The tool acts as a moveable counterweight, so the instrument was suspended from the tool as it was carefully moved into its final position in the Instrument Carrier. Then, the attached Horizontal Integration Tool and adapter were removed from the coronagraph. The Horizontal Integration Tool has previously been used for integrations on NASA's Hubble and James Webb Space Telescope.
As part of the integration process, engineers also ensured blanketing layers were in place to insulate the coronagraph within its place in the Instrument Carrier. The coronagraph is designed to operate at room temperature, so insulation is critical to keep the instrument at the right temperature in the cold vacuum of space. This insulation will also provide an additional boundary to block stray light that could otherwise obscure observations.
Following this successful integration, engineers will perform different checks and tests to ensure that everything is connected properly and is correctly aligned before moving forward to integrate the Wide Field Instrument and the telescope itself. Successful alignment of the Roman Coronagraph's optics is critical to the instrument's success in orbit.
This latest mission milestone is the culmination of an enduring collaboration between a number of Roman partners, but especially between NASA Goddard and NASA JPL.
"It's really rewarding to watch these teams come together and build up the Roman observatory. That's the result of a lot of teams, long hours, hard work, sweat, and tears," said Liz Daly, the integrated payload assembly integration and test lead for Roman at Goddard.
"Support and trust were shared across both teams … we were all just one team," said Gasia Bedrosian, the integration and test lead for the Roman Coronagraph at JPL. Following the integration, "we celebrated our success together," she added.
The Roman Coronagraph Instrument was designed and built at NASA JPL, which manages the instrument for NASA. Contributions were made by ESA (European Space Agency), JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), the French space agency CNES (Centre National d'Études Spatiales), and the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany.
TOP IMAGE: The Roman Coronagraph is integrated with the Instrument Carrier for NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope in a clean room at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., in October 2024. Credit: NASA/Sydney Rohde
CENTRE IMAGE: In a clean room at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in October 2023, scientist Vanessa Bailey stands behind the Roman Coronagraph, which has been undergoing testing at the lab. Designed to block starlight and allow scientists to see the faint light from planets outside our solar system, the Coronagraph is a technology demonstration that will be part of the Roman telescope. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
LOWER IMAGE: A team member works underneath the Instrument Carrier for Roman during the integration of the Coronagraph in a clean room at NASA Goddard in October 2024. Credit: NASA/Sydney Rohde
BOTTOM IMAGE: The Instrument Carrier for Roman is lifted during the integration of the Coronagraph in October 2024 at NASA Goddard. Credit: NASA/Sydney Rohde
5 notes
·
View notes
