#reverse transcriptase inhibitor
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
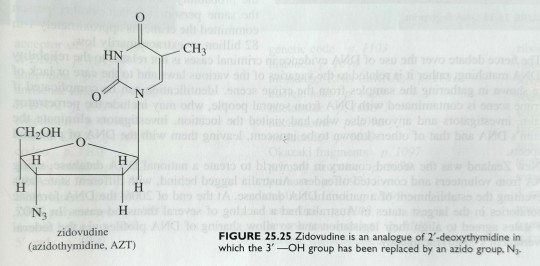
One example of such a reverse transcriptase inhibitor is the compound AZT (see figure 25.22), which delays the progression from HIV infection to AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome). (...) Perhaps the best known of the HIV-fighting viral antimetabolites is zidovudine (AZT), an analogue of deoxythymidine in which the 3'-OH has been replaced by an azido group, N3 (figure 25.25).
"Chemistry" 2e - Blackman, A., Bottle, S., Schmid, S., Mocerino, M., Wille, U.
#book quotes#chemistry#nonfiction#textbook#reverse transcriptase inhibitor#azt#zidovudine#azidothymine#hiv#aids#antimetabolites#antiviral#nitrogen
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Antiviral Drugs: The Frontlines of Disease Prevention and Treatment

What are Antiviral Drugs? Antiviral drugs are medications for treating infections caused by viruses. Unlike antibiotics, which work against bacteria, antiviral drugs target virus infections such as influenza, hepatitis, herpes, and HIV/AIDS. These drugs do not cure viral infections but may help control symptoms and reduce the ability of viruses to multiply in the body. How do Antiviral Drugs Work? There are several ways that antiviral drugs work to fight viral infections: - Interfering with Viral Attachment: Antiviral Drugs is prevent viruses from attaching to and entering host cells in the body. This approach blocks the initial stage of viral infection. - Interrupting Viral Replication: Many antiviral medications interfere with the replication or reproduction of viruses already inside host cells. They target viral enzymes or proteins essential for viral replication and stop the virus from multiplying. - Incorporating Into Viral DNA/RNA: Some drugs incorporate themselves into the developing viral DNA or RNA during replication. This incorporation results in structural defects in the new viral particles that render them unable to function or infect other cells. - Mimicking Building Blocks of Viruses: Certain antiviral drugs resemble the natural building blocks viruses use during replication. The drugs get incorporated into new viral particles instead, resulting in non-functional or dead viral offspring. The Development of Antiviral Resistance Like bacteria, viruses can mutate and evolve resistance to medications over time. Repeated or prolonged use of antiviral drugs increases the likelihood that drug-resistant virus strains will emerge and spread. Some common mechanisms of antiviral resistance include: - Mutations in Viral Target Sites: Changes in the viral genes or proteins targeted by drugs can prevent the drugs from binding or having an effect. - Alterations in Cellular Target Sites: Mutations in host cell genes involved in viral infection processes may help viruses evade drug effects. - Enhanced Drug Efflux: Mutant viruses may efflux or pump out antiviral drugs more quickly, decreasing drug levels inside infected cells. - Enzymatic Drug Inactivation: Viruses resistant to some drugs produce enzymes that chemically inactivate the medications before they can take effect. To counter resistance, combination antiviral therapies targeting multiple parts of the viral life cycle are often prescribed. Constant monitoring of resistance remains important for treatment effectiveness. Newer antiviral medications continue being developed to stay ahead of evolving viral threats. The Clinical Significance of Antiviral Drugs
Discovery of effective antiviral drugs has transformed the medical management of many once-devastating viral illnesses: - Influenza: Neuraminidase inhibitor drugs like oseltamivir reduce flu severity and duration when taken early in infection. They helped minimise deaths during pandemics. - Hepatitis: Nucleoside and nucleotide analogues halt hepatitis B and C virus replication, are curative in many cases and prevent life-threatening complications like cirrhosis or liver cancer. - Herpes: Oral antivirals inhibit herpes simplex and varicella zoster virus replication, preventing recurrent outbreaks or severe infection in high-risk individuals. - HIV/AIDS: Potent combination antiretroviral therapy controls HIV replication and restores immune function, transforming AIDS from a fatal disease to a manageable chronic condition. - Ebola: Drugs like remdesivir proved effective against the recent Ebola outbreaks and research continues developing therapies before the next epidemic arises.
Get more insights on, Antiviral Drugs
For Deeper Insights, Find the Report in the Language that You want.
Japanese
About Author:
Vaagisha brings over three years of expertise as a content editor in the market research domain. Originally a creative writer, she discovered her passion for editing, combining her flair for writing with a meticulous eye for detail. Her ability to craft and refine compelling content makes her an invaluable asset in delivering polished and engaging write-ups.
(LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vaagisha-singh-8080b91)
#Coherent Market Insights#Combination Therapies#Increasing R&D Activities#Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors#Hospital Pharmacies
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Development and validation of ultraviolet spectrophotometric methods for lamivudine and zidovudine quantification in dissolution test
Article published in J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res., vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 847-856, September-October 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.56499/jppres22.1433_10.5.847 Enma Perez-Chauca1*, Pedro M. Alva-Plasencia2, Humberto Gomes Ferraz3 1Unidad de Posgrado en Farmacia y Bioquímica, Facultad de Farmacia y Bioquímica, Universidad Nacional de Trujillo, Trujillo, 13011, Perú. 2Departamento de Farmacotecnia,…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Note Cards (December 2023)
1st Class Lever
2/3rd Down Femoral Shaft Diagram
2nd Law of Motion
Allosteric Fatty Acid Control
Antidiuretic Hormone
Arginase Disorder
Body Lever System
Bone Functions
Chemotherapeutic Mechanisms
Conservation Laws in Physics
Cytosol
Estuary
Extrasutural Bones
Genetic Transformation
Generalized vs Specialized Transduction
Growth Hormone
Hamstrings
Human Papillomavirus 16
Interpreting Bowel Sounds
Long Head of Biceps Femoris OIA
Long Head of Triceps Brachii
Metacarpal 1 - Dorsal
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Phage T4 Assembly
Physico-
Radius Upper Midshaft Diagram
Re
Rene-Robert Cavelier
Stylohyoid OIA
Submandibular Ganglion
Superior
Terminal Cisternae
Uses of Linezolid
Yucca faxoniana
Zhemaichu Horse
Zygomaticoorbital Foramen
#studyblr#notes#my notes#medblr#masterlist#study masterlist#masterlists#studyblr masterlists#master lists#studyblr master lists#study master lists#botany#biology#biology study guide#mcat#mcat study guide#mcat masterlists#biology masterlists#physics#study guides#study guide#notes masterlist#notes master lists#equine science#science#scienceblr#sciblr#science master list#science masterlists#science master lists
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Medicine for Herpes

Guide To Know When to Contact the Specialised Doctor for HIV Treatment
The abbreviation for "human immunodeficiency virus" is "HIV." Destroying CD4 cells compromises your immune system. This type of cell is present in the immune system and aids in the defense against infections. Your immune system's ability to ward off infections and some HIV-related malignancies declines as these cells die off.
Medicine for Herpes The acronym for antiretroviral therapy is ART
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) refers to the combination of Medicine for HIV and other HIV treatments. It is essential to take a mix of medications as prescribed each day. For every HIV positive person, antiretroviral therapy (ART) should be carefully examined. Even if the medicines can't completely eradicate the infection, they do help HIV-positive people live better and longer, free from problems. Furthermore, they lessen the chance that the virus may spread to other people.
How effective are HIV medications?
HIV treatment offers additional positive consequences than lowering your viral load, such as:
Give your immune system time to heal. It should be possible for your immune system to combat infections and many HIV-related malignancies, even if you still have some HIV in your body.
Which kinds of HIV medicines are there?
The multiple varieties of HIV medication can be categorized in a variety of ways. Bhagwati Ayurved offers a wide a range of Medicine for HIV and Medicine for Herpes as well. Certain medications may function by preventing or altering HIV-dependent enzymes, which the virus need for growth. Because the virus can no longer multiply, the body's HIV load decreases. Many medications have the ability to do this:
One common characteristic of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) is their capacity to inhibit the reverse transcriptase enzyme.
Among the numerous HIV medications on the market, the following can prevent the virus from infecting CD4 immune system cells:
Fusion inhibitors impede the capacity of HIV to infect cells.
Post-attachment inhibitors and CCR5 antagonists are two medicine groups that cause numerous molecules' activity on CD4 cells to decrease. HIV must first bind to two different surface molecules in order to infect a cell. By preventing any of these chemicals from entering the cells, HIV is prevented from doing its damage.
An attachment inhibitor is a kind of protein that binds to an HIV surface protein. Consequently, HIV cannot enter the cell by this.
Pharmacokinetic enhancers refers to an additional pharmacological class. They may occasionally be prescribed in addition to particular HIV medications. When administered in combination, pharmacokinetic enhancers improve the effectiveness of other medicines. Their presence lessens how quickly the other medication breaks down. This enables the medication to remain more concentrated and in the body for a longer period of time.
A multimedicine combination, which mixes two or more distinct HIV medications from several brands, provides an additional choice.
What other information do you need to know about the administration of HIV medication?
You and your healthcare practitioner will collaborate to develop a personalized treatment plan.
The following are some of the variables that this method will consider:
Regarding the potential adverse effects of HIV medications
Medicine interactions between prescription medications you already use and any additional ones you might take
The quantity of prescription medications you must take each day
Everything else that can have an impact on your well-being
It is imperative that you take your prescription daily as directed by your healthcare professional. If you don't take your medication consistently or as directed by the doctors, there is a risk to both the efficacy of your therapy and the emergence of medication resistance in the HIV virus. The patient is expected to have many examinations and to be closely monitored at all times. This stage is very important because the doctors may need to adjust the medication in response to any new changes in the immune system.
#Medicine for Herpes#Medicine for HIV#Treatment of HIV#Doctor for HIV treatment#Clinic for HIV treatment
0 notes
Text
Abacavir
Abacavir is an antiretroviral drug used for treating HIV. Abacavir part of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), curbing the viruss replication. Abacavir taken with other drugs as antiretroviral therapy (ART). Buy high quality Abacavir from Chemicea Pharmaceuticals. Chemicea Pharmaceuticals is one of the leading manufacturer and exporter of Abacavir.
#N-Nitroso Aceclofenac#N-Nitroso Atenolol#N-Nitroso Atomoxetine#N-Nitroso Benazepril#N-Nitroso Betahistine#N-Nitroso Bisoprolol#N-Nitroso Brinzolamide#N-Nitroso Bupropion#N-Nitroso Ciprofloxacin#N-Nitroso Dabigatran Etexilate#N-Nitroso Desloratadine#N-Nitroso Diclofenac#N-Nitroso Elagolix#N-Nitroso Enalapril#N-Nitroso Safinamide#N-Nitroso Prilocaine#N-Nitroso Vonoprazan#N-Nitroso Silodosin#N-Nitroso Duloxetine#N-Nitroso Folic acid#N-Nitroso Propranolol#N-Nitroso Paroxetine#N-Nitroso Perindopril#N-Nitroso Vortioxetine#N-Nitroso Meglumine#N-Nitroso Nortriptyline#N-Nitroso-Rasagiline
0 notes
Text
Abamune L Tablet: How It Works and Who It’s For — A Patient’s Guide
The main purpose of the antiviral drug Abamune L is to treat HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) infections. Its two active components are abacavir (600 mg) and Lamivudine (300 mg). These medications are classified as nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), and they function by stopping the virus’s ability to grow and propagate throughout the body.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Attend the speech of "Dr. Qun Dang" about “Azvudine: A Promising Novel Nucleoside for HIV, COVID-19, and Potential Liver Cancer Treatment at the 14GASTROUCG.
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical science, the discovery and development of new therapeutic agents are critical in combating infectious diseases and chronic illnesses. One such promising candidate that has garnered attention is Azvudine, a novel nucleoside with potential applications in treating HIV, COVID-19, and possibly liver cancer. This multifaceted drug offers hope across several challenging medical fields. The Journey of Azvudine Azvudine, also known by its research name FNC, is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI). Originally developed for its antiviral properties, particularly against HIV, Azvudine functions by incorporating itself into viral DNA during replication, leading to premature termination of the viral genome's synthesis. This mechanism is similar to other NRTIs, which are a cornerstone in the treatment of HIV/AIDS. Azvudine in HIV Treatment HIV continues to be a significant global health challenge, with millions of people affected worldwide. The effectiveness of antiretroviral therapy (ART) has significantly improved the prognosis for HIV-positive individuals, transforming what was once a fatal disease into a manageable chronic condition. However, the emergence of drug-resistant HIV strains necessitates the continuous development of new treatments. Azvudine has shown promising results in clinical trials as part of combination therapy for HIV. It exhibits potent antiviral activity and a favorable safety profile. What sets Azvudine apart is its ability to inhibit a broad spectrum of HIV strains, including those resistant to other NRTIs. This makes it a valuable addition to the ART arsenal, potentially offering a new line of defense against drug-resistant HIV variants. Azvudine's Role in COVID-19 Treatment The global COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the urgent need for effective antiviral treatments. Researchers quickly pivoted to evaluate existing drugs and develop new ones that could help manage and mitigate the virus's spread. Azvudine emerged as a candidate due to its antiviral properties. Studies have indicated that Azvudine may inhibit the replication of SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. Preliminary data suggest that it can reduce viral load in infected patients, potentially leading to better clinical outcomes. While more extensive clinical trials are needed to confirm its efficacy and safety, Azvudine's potential as a COVID-19 treatment is an exciting development in the fight against the pandemic.

Potential in Liver Cancer Treatment
Beyond its antiviral capabilities, Azvudine has sparked interest in oncology, particularly in treating liver cancer. Liver cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with limited effective treatment options available, especially in advanced stages.
Recent preclinical studies have shown that Azvudine may have anti-tumor activity against liver cancer cells. The mechanism behind this potential effect is not fully understood, but it may involve inhibiting viral proteins or pathways that contribute to cancer progression. While this research is still in its early stages, it opens up new avenues for exploring Azvudine's utility beyond viral infections.
The Future of Azvudine
As a novel nucleoside, Azvudine's versatility in treating various diseases makes it a significant subject of interest in medical research. Its potential applications in HIV, COVID-19, and possibly liver cancer highlight the drug's broad therapeutic scope. However, further clinical trials and studies are essential to fully understand its efficacy, safety, and optimal use.
The development of Azvudine is a testament to the rapid advancements in medical science and the continuous search for new treatments to address some of the most pressing health challenges. As research progresses, Azvudine could become a critical tool in the fight against viral infections and certain cancers, offering hope to millions of patients worldwide.
In conclusion, Azvudine represents a beacon of hope in the medical community, with its potential to treat a range of conditions from HIV and COVID-19 to liver cancer. As we await more definitive clinical data, the excitement around this novel nucleoside continues to grow, promising a brighter future in global healthcare.
Important Information:
Conference Name: 14th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference Short Name: 14GHUCG2024 Dates: December 17-19, 2024 Venue: Dubai, UAE Email: [email protected] Visit: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/ Call for Papers: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/submit-abstract/ Register here: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/registration/ Exhibitor/Sponsor: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/exhibit-sponsor-opportunities/ Call Us: +1 (207) 707-7298 WhatsApp Us: +442033222718
0 notes
Text
Bridging the Gap: How the Global Prophylactic HIV Drugs Market is Expanding Access to Care
The prophylactic HIV drugs market is witnessing significant expansion, with robust growth projected in the coming decade. In 2023, the market size reached an estimated USD 32,516.1 million, driven by increased investment in HIV research and development, rising drug approvals, and a surge in HIV incidence rates.
According to Future Market Insights, the market is forecasted to expand at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.1% between 2023 and 2033, reaching a valuation of approximately USD 48,822.4 million by 2033. This growth trajectory underscores the critical importance of prophylactic HIV drugs in combating the global HIV/AIDS epidemic.
Request Your Detailed Report Sample With Your Work Email: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-9582
Global sales of HIV prophylaxis drugs are projected to reach a value of about USD30 billion by 2021. Owing to growing awareness of HIV and the rising prevalence of HIV infection worldwide, As for AIDS prevention, between 2022 and 2032, the market for preventative HIV drugs grew at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4%, reaching USD 40 billion in 2028.
HIV has been a major global cause of death for many years, impacting millions of people. People whose immune systems are compromised by the virus are more susceptible to a range of ailments and cancers. HIV can be controlled even when there isn’t a long-term cure by expanding access to adequate care, diagnosis, medication, and prevention.
Prophylactic HIV Drugs: A Powerful Prevention Tool
Effective management techniques are available for HIV, even though a long-term cure is still unattainable. One of the most important aspects of fighting the virus is expanding access to care, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention services. HIV prevention medications are becoming an essential weapon in the fight against HIV infection. These cutting-edge treatments work especially well at preventing HIV transmission through drug injection and sexual contact.
Focus on Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP):
Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP), one of the preventive HIV medications, is becoming increasingly popular because of its great effectiveness. The risk of HIV infection from sex and injectable drug use can be considerably decreased with PrEP, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), by 74% and 99%, respectively. The extraordinary efficacy of PrEP is spearheading a global movement for its expanded usage.
Market Competition:
Some of the prominent players operating in the global market are-
Gilead Sciences, Inc
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Merck & Co. Inc.
Mylan NV
Cipla Inc.
Genentech Inc.
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
Johnson & Johnson Health Care Systems Inc
Pfizer Inc.
GalaxoSmithKline PLC
Notable Developments of the Key Players in the Market
In April 2023, Merck & Co (MRK.N) confirmed that it is going to buy Prometheus Biosciences Inc (RXDX.O) for about $10.8 billion, by picking up a promising experimental treatment for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease and building up its presence in immunology.
In November 2022, Merck, known as MSD outside the United States and Canada, and Imago BioSciences, Inc. (“Imago”) announced that the companies have entered into a definitive agreement under which Merck, through a subsidiary, might acquire Imago for US$ 36.00 per share in cash for around total equity value of US$ 1.35 billion.
Key Companies Profiled:
Gilead Sciences, Inc
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Merck & Co. Inc.
Mylan NV
Cipla Inc.
Genentech Inc.
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
Johnson & Johnson Health Care Systems Inc
Pfizer Inc.
GalaxoSmithKline PLC
Key Segments Profiled in the Prophylactic HIV Drugs Industry Survey:
By Drug Class:
Nucleoside/Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTI)
Integrase Inhibitor
By Distributional Channel:
Hospital Pharmacies
Retail Pharmacies
Mail Order Pharmacies
Drug Stores
By Region:
North America
Latin America
Western Europe
Eastern Europe
Asia Pacific Excluding Japan
Japan
The Middle East and Africa
0 notes
Text
Navigating Opportunities: Understanding the Global HIV Drugs Market Size

The HIV Drugs Market size is expected to reach USD 43.06 Bn by 2031 and was valued at USD 32.7 Bn in 2023, the CAGR growth rate for HIV drug market is expected 3.5% over the forecast period of 2024-2031. The HIV drugs market is a dynamic landscape, characterized by continual innovation and advancements in treatment options. With the advent of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), the prognosis for individuals living with HIV has drastically improved, transforming what was once considered a terminal illness into a chronic condition. This market encompasses a wide array of medications, ranging from nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) to protease inhibitors (PIs) and integrase inhibitors (INIs), each targeting different stages of the HIV replication cycle. Furthermore, the emergence of novel drug delivery mechanisms, such as long-acting injectables and implants, is reshaping the treatment paradigm by offering improved adherence and convenience for patients. As research continues to unravel the complexities of HIV pathogenesis and drug resistance, the future of the HIV drugs market holds promise for more effective therapies with fewer side effects, ultimately driving towards the goal of achieving an HIV-free world.
Get Sample Of This Report @ https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/3509
Market Scope & Overview
The research looks into the major variables affecting the expansion of the global market. The report used a bottom-up approach to gather and forecast data for a wide range of industrial verticals and end-user industries, as well as their reach across several categories, in order to determine the overall size of the HIV Drugs Market market throughout the forecast period. Market actors may use market data to create plans to improve their competitive position.
The HIV Drugs Market research report covers all of these topics in great detail, including the Porter's Five Forces analysis, significant segments, drivers, opportunities, and the competitive environment. For business experts, stakeholders, investors, VPs, and newcomers who want to learn more about the company and formulate a competitive strategy, this study is an excellent resource.
Market Segmentation Analysis
By Drug Class
Integrase Inhibitors
Non- Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase inhibitors (NRITs)
Combination HIV medicines
Others
By Distribution Channel
Hospital Pharmacies
Retail Pharmacies
Online Pharmacies
Others
COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Due to the COVID-19 lockout, it was necessary to create original strategies for dealing with future occurrences while sustaining steady growth. The market research report also provides advice for overcoming pandemic-like situations and lessening their harmful effects. The HIV Drugs Market was significantly impacted by the COVID-19 epidemic. Due to delays in new developments, the industry has also been suspended internationally.
Regional Outlook
With a focus on North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East and Africa, the HIV Drugs Market research report digs into market aspects including estimations for total price from top manufacturers and trends toward advancement in various regions of the world.
Competitive Analysis
The research report offers a complete analysis of the worldwide HIV Drugs Market and suggests important adjustments that market players should take into account when developing their business plans. To gain market dominance, these companies have used partnerships, product development, joint ventures, mergers and acquisitions, diversification, and joint ventures.
Key Reasons to Purchase HIV Drugs Market Report
To identify important geographic regions and leading nations that have a substantial impact on market revenue, the researchers conduct geographic study.
Prospect information may be used by market participants to evaluate potential and formulate their next moves.
Report Conclusion
Manufacturers, distributors, dealers, and policymakers may use the data from the market research report to assess which industry sectors should be prioritized in the upcoming years in order to plan investments and take advantage of the HIV Drugs Market expansion.
About Us
SNS Insider is a market research and insights firm that has won several awards and earned a solid reputation for service and strategy. We are a strategic partner who can assist you in reframing issues and generating answers to the trickiest business difficulties. For greater consumer insight and client experiences, we leverage the power of experience and people.
When you employ our services, you will collaborate with qualified and experienced staff. We believe it is crucial to collaborate with our clients to ensure that each project is customized to meet their demands. Nobody knows your customers or community better than you do. Therefore, our team needs to ask the correct questions that appeal to your audience in order to collect the best information.
Related Reports
Smart Pills Market Size
Single-use Bioprocessing Market Size
3D Cell Culture Market Size
Molecular Quality Controls Market Size
Cell Separation Market Size
0 notes
Text
How does lamivudine work?
Lamivudine is from a class of drugs known as nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). Your doctor will prescribe lamivudine as part of your HIV treatment, along with antiretrovirals from another class of drugs. It is important to take all the drugs as prescribed, every day. Each drug class works against HIV in a different way.
The aim of HIV treatment is to reduce the level of HIV in your body (viral load). Ideally, your viral load should become so low that it is undetectable – usually less than 50 copies of virus per ml of blood.
0 notes
Text
Tenofovir and COVID: The Jury Is Still Out
The latest study, from researchers in the Netherlands, found that tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF, or Viread) did not reduce the likelihood of acquiring SARS-CoV-2 or developing severe illness. As reported in the journal AIDS, this was also the case for two HIV integrase inhibitors and the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor etravirine (Intelence).
0 notes
Text
Abacavir
Names: -- Ziagen
Class: -- antiretroviral -- nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI)
Use: -- management of HIV infection in combination with other retrovirals -- combination prevents resistant strains from developing
Action: -- inhibits the activity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase -- this interferes with the order of transcription -- this terminates viral DNA growth
#medblr#studyblr#notes#my notes#medical notes#medblr notes#med notes#pharmacology#pharmacology notes#pharm#pharm notes#pharma#pharma notes
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Dolutegravir for treatment of HIV-1 infection (all ages)
HIV treatment has improved greatly over the last two decades and standard of care now involves triple therapy, typically with two nucleos(t)ide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) plus one of the following: a ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor (PI/r), a non nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) or an integrase inhibitor.
Effective antiretroviral treatment (ART) requires high adherence to drug regimes. Development of new ARV medicines often focuses on improvements in tolerability, reductions in toxicity and drug to drug interactions.
Effectiveness of ART is measured by an undetectable viral load. The proportion of treated individuals with a viral load less than 50 has improved (94% in 2016) which may be driven, at least in part, by improvements in drug choice. Current standard treatment is therefore effective for many people. The availability of generic ART has reduced the cost of standard treatment considerably. New drug treatments need to demonstrate both clinical and cost effectiveness over standard treatments.
0 notes
Text
Post-Catalytic Complexes with Emtricitabine or Stavudine and HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Reveal New Mechanistic Insights for Nucleotide Incorporation and Drug Resistance
Since its discovery in the early 1980s, the human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) has been a major health issue with nearly 38.0 million people infected globally in 2019 according to the WHO [1]. Despite extensive research efforts, neither a cure nor a vaccine for HIV-1 infection has been discovered yet. However, a breakthrough has been achieved with the highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), which significantly improves the life expectancy for patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Two of the six classes of the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved drugs for HIV-1 treatment target the reverse transcriptase (RT) protein, an enzyme critical for the replication cycle of HIV-1 [2]. These two classes are nucleoside RT inhibitors (NRTIs) and non-nucleoside RT inhibitors (NNRTIs). While NNRTIs are allosteric inhibitors that alter the chemical catalysis rate limiting step through conformational changes [3,4], NRTIs mimic nucleotides that bind to the active site of RT. Since NRTIs lack the 30 -hydroxyl group necessary for chain elongation, their incorporation results in termination of the viral DNA transcription [5]. NRTIs are essential components of HAART and part of almost all FDA approved combination therapies for the treatment and protection of an infection with HIV. However, some FDA-approved NRTIs are now rarely prescribed (e.g., stavudine (d4T)) or discontinued (e.g., zalcitabine (ddC)) due to their off-target toxicity.
0 notes
Text
Viread (Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate) for HIV Treatment & PrEP: Everything You Need to Know
https://www.thebody.com/health/hiv-viread-tenofovir-tdf
Viread (generic name: tenofovir disoproxil fumarate; often abbreviated as TDF) is an anti-HIV medication taken as one pill once a day in combination with other medications. Viread is in a class of drugs called “nucleoside / nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors” (NRTIs), which stop HIV from making copies of itself.
Viread is available as a stand-alone drug, but it is usually used in combination with other drugs. Viread is included in a fixed-dose combination (FDC) pill called Truvada, which also includes an HIV drug called Emtriva (emtricitabine, FTC). Viread is also part of several other FDCs, including these single-dose treatment regimens (STRs) for HIV:
Atripla (TDF + FTC + Sustiva [efavirenz])
Complera (TDF + FTC + Edurant [rilpivirine])
Stribild (TDF + FTC + elvitegravir + cobicistat)
Viread was first approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a treatment for HIV in 2001. Generic versions of Viread are available in the U.S., and are included in a number of FDCs and STRs.
Viread is generally taken by adults as a single 300 mg pill orally once a day. Although the drug will work just as well whether it’s taken with or without food, taking Viread on an empty stomach can lead to abdominal pain or discomfort.
Some adults who have issues with their kidneys may be instructed to take Viread less frequently. Always follow your medical provider’s instructions for how and when to take Viread. For children who weigh at least 22 lbs (10 kg) and cannot swallow a tablet, Viread is also available in a powder form.
0 notes