#qualitative investigation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
I got this comment on a story from my Other AO3 Account this morning.
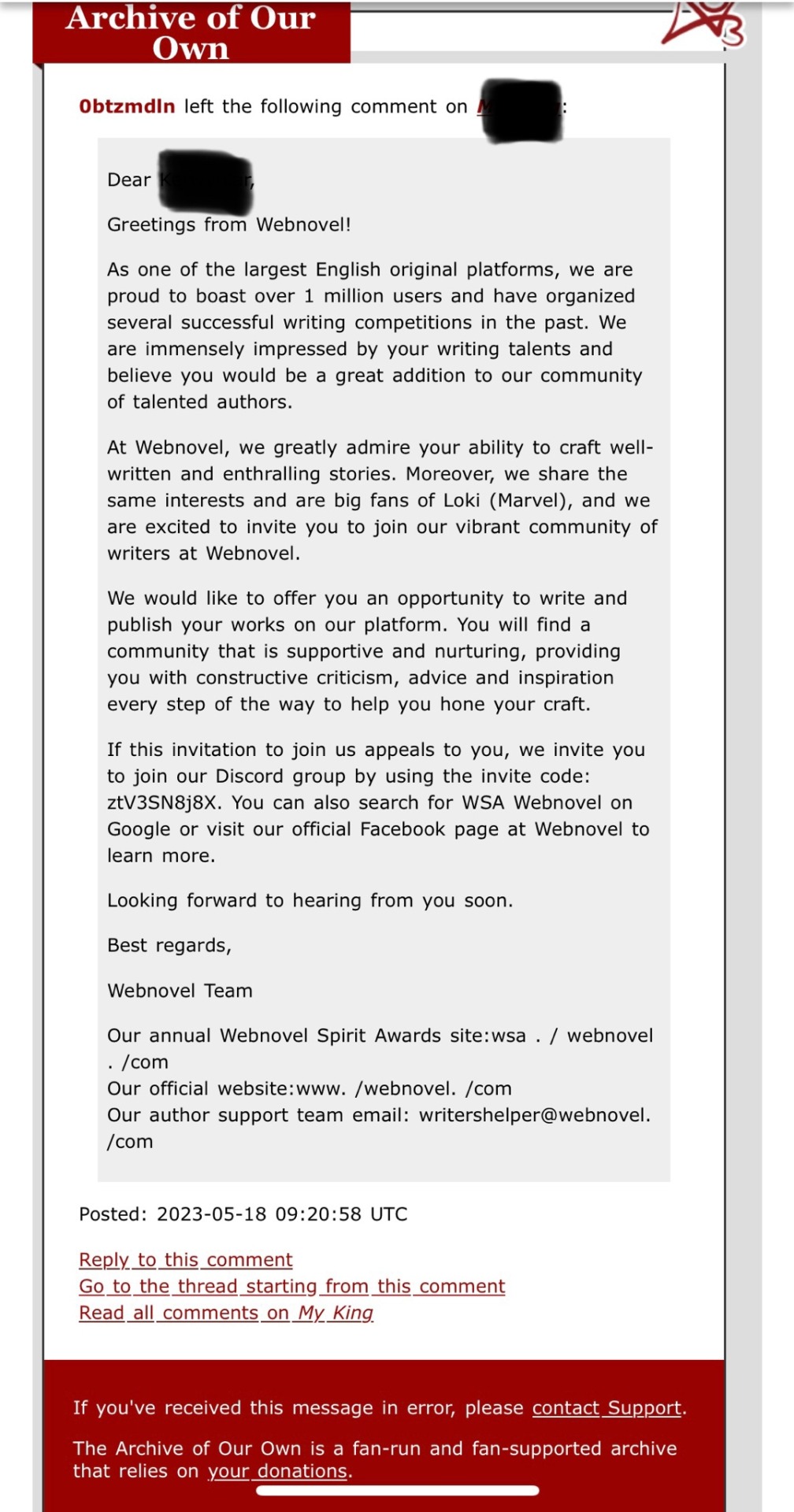
(Info redacted because I prefer keeping these accounts separate but no one follows me on the side blog I have for that account.)
The story was posted almost a year ago and is relatively “popular” by my average statistics even though it has tropes and themes that are big turnoffs for a lot of people (hence separate accounts). This popularity is undoubtedly because it’s a Marvel Loki story and that fandom is massive.
So there is obviously an algorithm or a bot scrubbing ao3 statistics and leaving this comment on fics that meet a certain metric with the main character of the fic inserted into the comment.
I had a little time to kill this morning so I decided to investigate further. And y’all this is so predatory. Come on this journey with me. It made me mad. It may make you mad.
First, if you go to Webnovel’s website, you HAVE to choose between male lead or female lead stories before you can go any further. WTF?
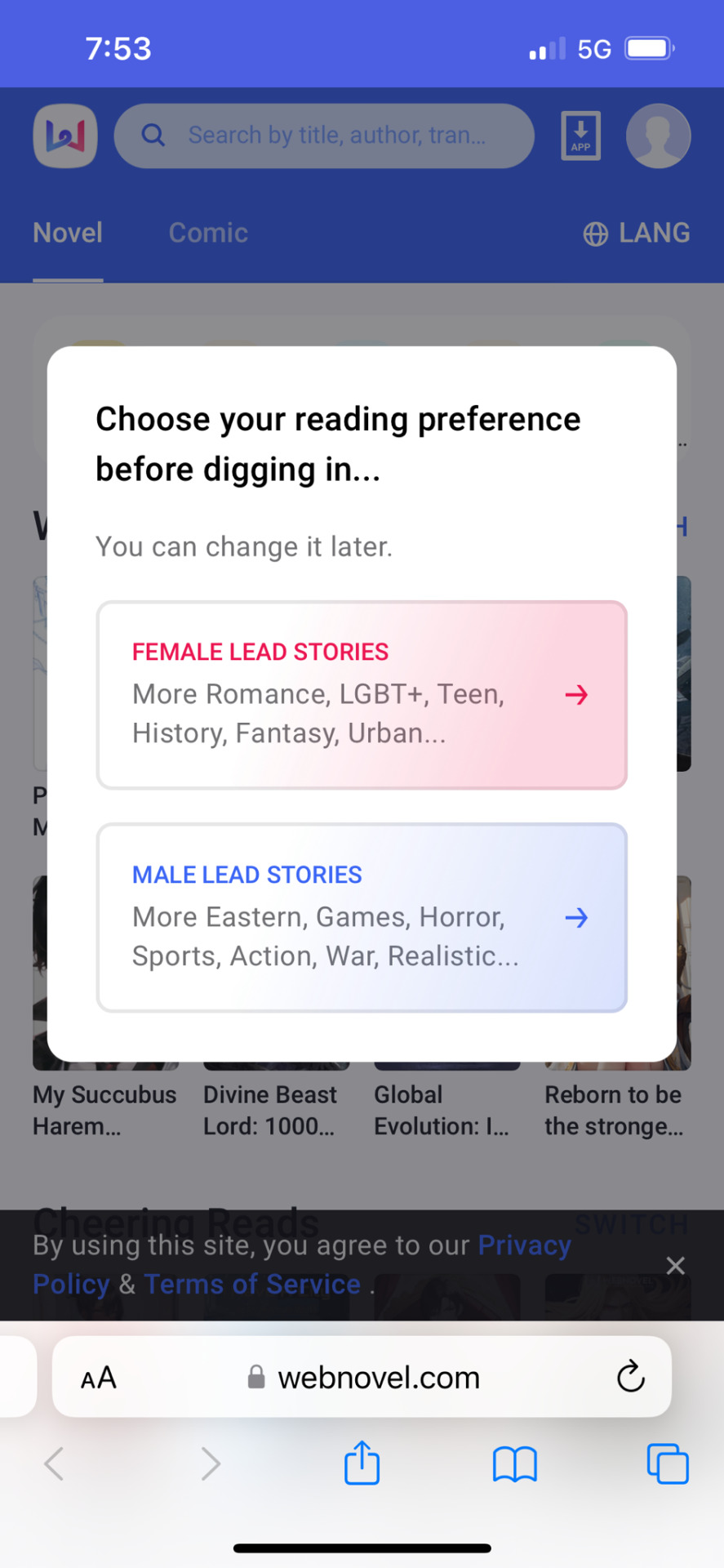
And that’s weird, but this gets so much worse. This is basically a pay-to-read site that has different subscription models. Which… okay BUT! The authors don’t get paid! Look at that comment again. They’re promising a supportive and nurturing community, but zero monetary compensation. It’s basically, “post your stuff here so we can get paid and you can get… nice vibes?” I mean look at this Orwellian writing:
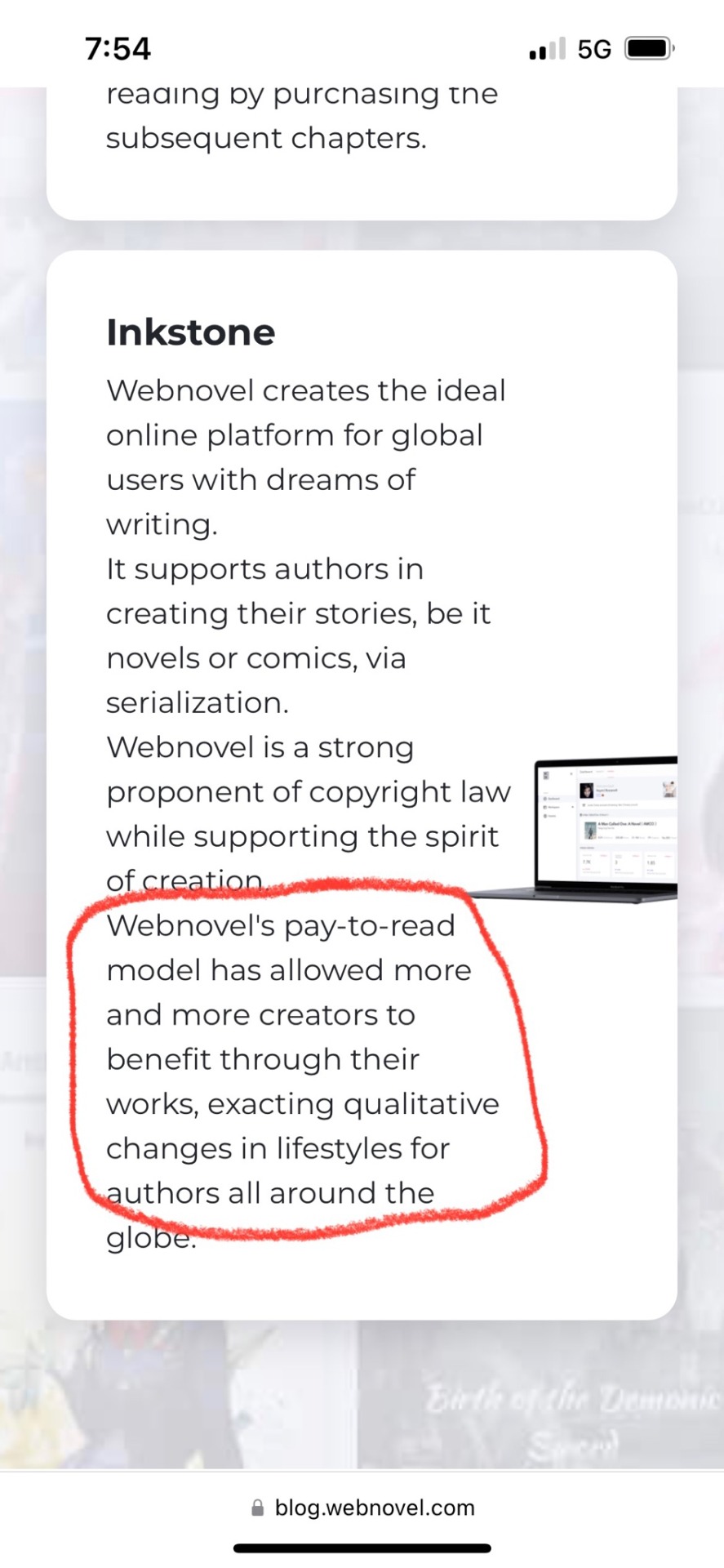
Using the phrase “pay-to-read model” in the same sentence as “qualitative changes in lifestyles for authors” deliberately makes you think that you can get paid and maybe even make a living on this website. But that’s not actually what it says and authors will not receive one red cent.
Oh but wait, the worst is still to come. In case this breaks containment (which I kind of hope it does) this is where I mention that I’m a lawyer in the US.
I don’t do intellectual property or copyright law but I do read and write contracts for a living. So I went to look at their terms of service. It was fun!
Highlights the first, in which Webnovel gets a license to do basically whatever they want with content you post on their site. This is how they get to be paid for people reading authors’ writing without paying them anything.
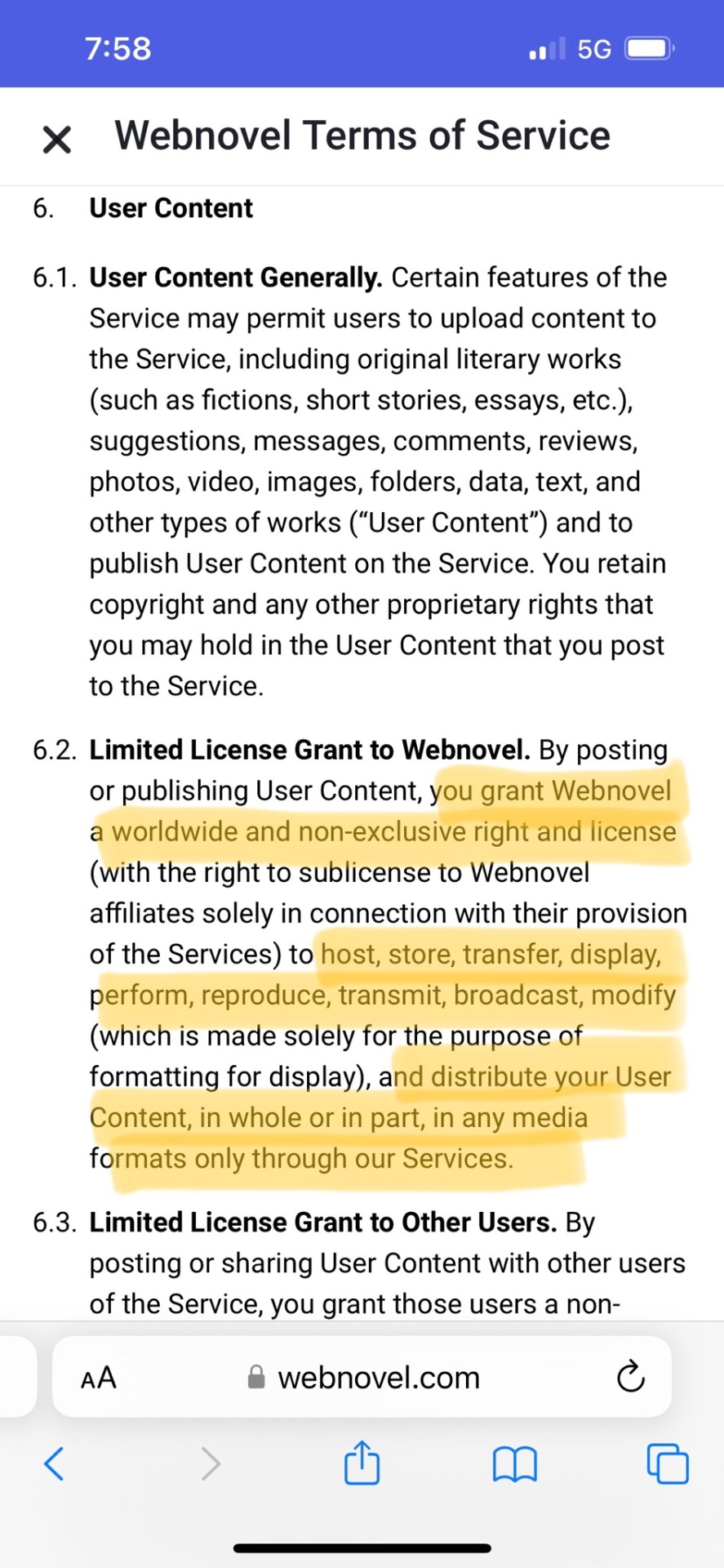
Highlights the second, in which Webnovel takes no responsibility for illegally profiting off of fan fic. This all says that the writer is 100% responsible for everything the writer posts (even though only Webnovel is making money from it).
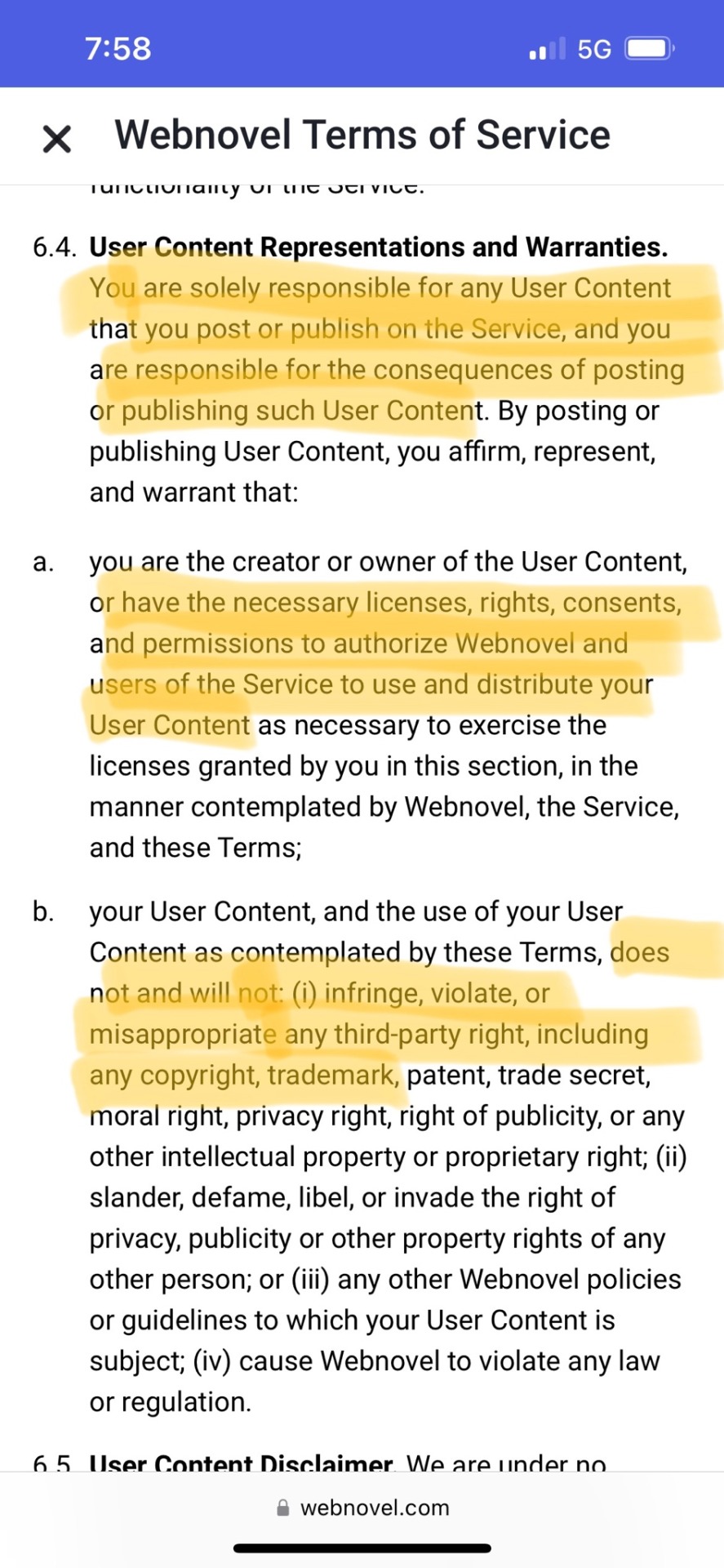
Highlights the third which say that by posting, the author is representing that they have the legal right to use and to let Webnovel use the content according to these terms. So if a writer posts fan fiction and Webnovel makes money from people reading the fan fiction, and the House of the Mouse catches wise, these sections say that that’s ALL on the writer.

So that’s a little skeevy to start off with but the thing that is seriously shitty and made me make this post was that these assholes are coming to ao3. They are actively recruiting people in comments on their fan fiction. And they are saying they are big fans of the character you’re writing about and that they share your interests.

They are recruiting fan fiction writers and giving every impression that you can make money from posting fan fiction on their site and hiding the fact that you absolutely cannot but they can make money off of you while you try, deep in their terms of service which no one but a lawyer who writes fan fic and has some time to kill will read.
I see posts on here regularly from people who don’t understand how this stuff works, don’t understand that they (and others) can not legally make a financial profit from fan fiction. And there are tons of people who will not take the time to dig into the details.
Don’t deal with these bastards. Fuck Webnovel.
#went down a rabbit hole#got mad#webnovel#this is a scam#how to ao3#fan fiction#please spread the word#long post#50k
52K notes
·
View notes
Note
How do you not realize your Marxist ideology is false when it says shit like a trans black woman small business owner is oppressing her cis white man employees?
I don't think you're, like, genuinely asking, or are curious, here, but I'll answer anyways, for everyone else who might be confused on issues like this: it's intersectionality.
You could make this argument about essentialy any axis of oppression - 'how do you not realise your LGBT ideology is false when it says shit like a cishet black person is oppressing their white trans gay employees', or, conversely, 'how do you not realise your racial ideology is false when it says shit like a white trans gay person is oppressing their cishet black employees'.
The point here isn't to have a rock-paper-scissors, Pokémon type-effectiveness ranking of which axes of oppression 'outrank' which others, it's to understand that each axis of oppression is an entirely distinct social system that overlaps with the other. A black business owner suffers from the social system of antiblackness, and benefits from the social system of capitalism. The specific overlap of their blackness and their class character also gives them an entirely unique character with regards to their segment of society. If they are USAmerican, for example, in their specific case the state and progress of the national liberation movement in the US means that they make up the rear of the revolutionary movement, despite being themselves petit-bourgeois. These systems of oppression are qualitatively different, and cannot be simply, quantitatively, summed up against each other.
With this in mind, it should be understood that the Marxist understanding of class as the principal contradiction does not mean that class is the most important, overruling factor, and that other axes should be ignored. Class is considered the principal contradiction because it is the contradiction that all other axes of oppression, genuine in their own rights, grew out of. Antiblackness was created by the slave trade (not vice-versa), and the slave trade was created by the growing European bourgeoisie's need to extract surplus-value, in the collapse of the Feudal economy. In the example you gave, the petit-bourgeois business owner exploits the labour of her workers, and is supported in doing so by an entire legal, political, and philosophical system based on the expropriation of the proletariat. She is also herself repressed and exploited on the basis of race, gender, and transness. These do not cancel each other out. However, given the ultimate source of racial, patriarchal, and cissexist oppress is political-economic class, her ability to genuinely fight for her interests in those fields will be hamstrung by her class position - just as her ability to attain and maintain that class position in the first place is itself hamstrung by her oppression in other fields.
Ultimately, there are no simple rules that society can be flattened down by. Each and every instance and scenario must be investigated in its own right. The idea that people are driven to Marxism because it provides an easy or simplified way of looking at the world is (perhaps unfortunately!) wrong, it actually means a lot more work!
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo

(vía Quantitative vs Qualitative research what do you use left or right Metal Print by jennstore)
0 notes
Note
It's okay not to answer, I know it's broad territory, but I really respect you as an artist and writer. How do you handle people misinterpreting or missing elements of your work, especially when they may still enjoy it and get something out of it? As an artist I'm struggling lately with knowing my work will always inherently be read differently from what I intended as a matter of the human experience, as well as me being autistic complicating my ability to communicate.
An addition to that last ask. I don't know if it's clear what I'm asking so I'll give some examples. A 50 year old man and a 21 year old woman will get different things from a movie due to their lived experiences. As a gentile reader I might miss jewish narrative themes in a piece of work. That doesn't mean it's bad for us to have experienced it, but as an author I find it frustrating when something is missed or misinterpreted, and I don't know how not to be a control freak about it.
i feel you, i have ocpd and being misinterpreted when i agonized and stressed about how to present my wording makes me want to light myself on fire and it's something i'm working on. writers are supposed to expect and account for different perspectives ahead of time, so it always sort of shocks me when i hear interpretations i wouldn't have thought about at all. i know logically i can't predict all outcomes, but it's still surprising anyway!!! but i generally feel a lot of distress about being misinterpreted because i'm afraid it'll label me as A Bad Person, so i think that's where the experience diverges. maybe investigating why you need to or want to control the way your work is interpreted would help as a starting point? i think having a larger audience helps, too... it means more people will misinterpret your work, but it also means you're more likely to have at least One Guy who interprets it just right and makes fireworks go off in your brain, but there's no way to control how big your audience is!
anyway, the ways to control how your work is interpreted, to the degree that you can:
you can make it simpler. the more parts a story has added to its complexity, the more it's going to be misinterpreted.
you can make the intended message more blatant. you can have a character say exactly what you want the audience to think or hear, or something very close to it. don't want a detail missed? make it bigger.
you can reprioritize parts of the story. basically think of a group of interpretations you want the audience to have if you can, and then put them in order of importance. then the story has a hierarchy to lean on wrt artistic decisions.
you can give the story multiple meanings. more targets to hit. if they're mutually exclusive, i find this works better... i like making my stories ambiguous with conflicting interpretations a lot. yeah, people are going to interpret the story wrong, because it was made in a way that will guarantee it is interpreted wrong in some way.
you can layer the meaning so that less literate audience members will at least get SOME of what you intended. basically, close to the previous strategy, but like a hybrid of that and "make it simpler" imo because you're constructing multiple interpretations that are all supposed to lead to one conclusion (like a persuasive essay or something), but can act as an adequate conclusion on their own.
all of these options have obvious qualitative losses. if you have anything in particular that is repeatedly misinterpreted or missed, it's a good idea to think about Why you're making those choices. consciously committing to a higher-risk artistic choice will help you feel more in control of what happens to it once it's done. the way your art is interpreted isn't totally out of your control, you are making decisions that add to or mitigate the risk of misinterpretations, and you can bring those choices to a more conscious awareness to see them and appreciate them. sometimes it'll feel like a begrudging compromise, but it'll still be Your choice ultimately.
on an emotional level... hopefully this makes sense. there's always going to be the piss-on-the-poor scenario and sometimes i just remind myself that some people are not as literate as me, but it's great we were still able to connect through a work that was probably difficult for them!!! it was a privilege to get to grow up with a good education, access to art and technology, strangers who want to look at what i made, and there are times where i take this for granted, and my expectations of readers are actually kind of unreasonable!!! some people are younger than me and say stupid things like i did, but they aren't able to understand things like me yet, and it's important for them to learn by figuring it out on their own!!! i was and will always be That Guy to other artists and other writers, and i want to give other people the same grace as i get. some people have wildly different life experiences compared to mine, and these experiences can be much more nuanced than i could ever imagine, but it's a little gift that they made my world larger by sharing theirs through my art!!! it's terrifying and embarrassing knowing that i don't know much of anything, even about something i have total control over, but the consequences of that aren't always negative. and possibly the saddest but most common way i deal with this is nothing more than accepting that no one is ever going to understand me on the level that i want to be understood. sometimes my frustration has come from a place of miserable alienation, where the need to feel Seen can be quite desperate. i've made art explicitly about Me, and i've made art deliberately hostile towards its audience, art that's said they don't get it and they never will, but they still bothered to try. i made a game that said no one will win here and they still played it with me, and i can appreciate that. in many cases, they actually know more about me than i know about them. but more importantly, it isn't my audience's job to take care of that emotional need -- in fact, as much as art is made out to be a mode of pure self-expression, i don't think they can. it's a reality that i don't like, but i accept it. art made to benefit others is a one-way mirror: you make them feel seen, but they should never see you, because if they see you, the mirror isn't working.
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
🐄
if you want to get very quickly and efficiently radicalized against the dairy industry, search the name of any dairy breed and read a cattle farming organization's article on them to see what they have to say.
once you notice it, the language they use to talk about living animals is sickening.
here are some from a cattle website's article on the Holstein breed, known famously as one of the 'highest producing' dairy cow breeds:

off to a great start - this article quietly walks around the fact that cows' lifespans are irrelevant to this topic and they should only technically be measured by the years they spend being 'productive' to the dairy industry. (because they know they won't live any longer than that, anyway.)


notice how these animals are reduced to mere numbers and statistics - how many pounds of milk, butterfat and 'protein' they can 'produce' per year. notice the fact that the dairy industry has historically had nothing but a vested interest in testing and pushing these numbers as far as they can go, beyond what is naturally biologically feasible - even demanding testing programs and constant genetic investigation to do so.

the implication that these animals can 'adapt' to farming situations they are forced into. the advertisement of these animals as being fully 'adaptable' to whichever method of explotation is chosen for them, including 'intensive farming.' think about how animals live in the wild for a moment. think about what 'intensive farming' entails. what animal could possibly 'adjust' to that?
furthermore, when these animals encounter heat stress and disease as a result of being put in an unsuitable environment, the only thing worth commenting on is their 'reduced production capacity.' no mention of their distress or wellbeing beyond that.

notice how factors that could be considered biologically unnatural, such as rapid growth and early maturity, are celebrated here, only for their benefit to the process of the dairy industry's purposes for calves.
notice how this article describes them as overwhelmingly easy to 'handle' - livestock farmers have little to no patience with 'misbehaving' animals, who exhibit 'difficult' behaviours. this article also offers the assurance that these animals are 'resistant to stress' - since it knows fully well that these cows will be encountering highly stressful environments in the dairy production industry.
noting that they exhibit herd bonds is as close as this article gets at any point to showing any kind of interest in them as what they actually are - living animals. this is the sole instance of that.

of course, in the dairy industry you should naturally expect that any sentence starting with 'Holsteins are more than just a dairy breed...' should end with 'the animal also contribute to the meat supply.' these cows have no worth in this industry's eyes beyond their bodies - what they can produce, what we can consume -- what they can sell to us. all under the convenient pretense that these animals are doing a 'service' to us by 'contributing to our supplies.'
can you imagine if your biology textbook suddenly started describing the quality, the texture, the 'fattening sectors' and 'fine fibres' of meat that compose the animals you were reading about?
and here we have one of the most horrifying sentences I've ever read:

it's self-confessional - the dairy industry is the meat industry, because dairy farming creates the 'byproduct' of useless male calves. so even under dairy circumstances, cows are still bred with beef breeds so that when they're forcefully impregnated, they can give birth to tastier babies.
the way it says all of this through pure implication is absolutely insidious.

and of course, on its final note, this article once again offers merit to these cows purely based on their milk productivity - their 'unexcelled production,' the 'greater income' they offer to the industry weighed against how much it costs to care for them. the obsession with their genetic 'qualities' goes far beyond disturbing here. their sperm, even frozen embryos are sold and exported as 'products' all around the world. just imagine what that looks like for a moment - what that requires. what a horrifying thing to do to an animal.
and how typical is it of the dairy industry to pretend that this is being done in the name of 'improving foreign food supplies' in the very same breath as celebrating how it also improves 'dairy producer incomes'? how convenient is it that the fabricated, false pretense of global necessity for dairy and meat products just so happens to make those industries one of the wealthiest on the planet?
how can anyone write or read an article like this and not instantly come to realize what kind of an abusive, exploitative, and downright dystopian system they are participating in? for the animals born and trapped within this industry, and for all the other living creatures subsequentally affected by this industry's neverending drive to increase its own profits, this is man-made, capitalistic hell in its purest form.
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
‘I live in extremes’: A qualitative investigation of Autistic adults’ experiences of inertial rest and motion
"An alternative explanation of Autistic inertia is derived from a predictive coding account of autism (van de Cruys et al., 2013, 2014). Under predictive coding, perception is determined by both prior expectations about the world, as well as incoming sensory signals from the world (Clark, 2015; Hohwy, 2013; Rao & Ballard, 1999). Any mismatch between the expectation and sensory signal generates a prediction error. While some errors should be attended to, others are unreliable and should be ignored. For example, you might be more alert to a mismatch between what you expected your friend to say (‘hello’) and what you heard your friend say (‘yellow’) when in a quiet café (where the sensory input is more reliable), but the same mismatch might be ignored in a noisy café (where the auditory input is less reliable, and the error could be attributed to a mishearing).
However, the brains of Autistic people may treat all errors as salient (van de Cruys et al., 2013, 2014). Thus, in a volatile environment (e.g. a busy workplace or a cluttered home), an Autistic person might become overwhelmed by multiple, salient prediction errors, all competing for attention, leading to cognitive overload, and ultimately mental and physical paralysis (‘inertial rest’)."
This study is excellent (and a good read), and really feels like the beginning of some of the research into autistic inertia I'd like to see in the world.
107 notes
·
View notes
Text

i havent recieved a lot of anon hate over the years but after the one that just said "you are fucking creepy" (daily affirmation) that one from the other day complaining that i had used big words and brought a social science/feminist pov to something as silly as fanfic because why would i do that it's not that deep was second funniest. like if you send hate at least be familiar with the blog. i do that because im literally the person who does that. it's inherent to me to see something and go it's like a society in here. i obviously did NOT get a sociology degree for the money i did it because i love it. el meu estudi sobre la venda de pipes al barri de benimaclet, que fa servir mètodes quantitatius com qualitatius, no ha aportat resultats significatius and whatnot
#the meme was in spanish i forgot#my investigation on abbilana vs macdennis#which combines both quantitative and qualitative methods#does not provide significant results#personal
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
I do have a general question about the liberalism-security thesis - the thing is, the actual mechanisms that seem to characterize liberalism for you (money, markets, positive law and related enforcement mechanisms, and specific mechanisms to reform said law) are also mechanisms you find in historical antecedents to modern states, the prime example being Rome during both the Republic and Empire periods (and China from the Qin dynasty forward, to some extent) that I think would be a stretch to characterize as "liberal," although certainly a lot of liberals took inspiration from idealized versions of them. And, of course, due to their flexible foundations these concepts have been successfully implemented by classically "illiberal" states of varying types.
So my question is - to what degree does it make sense to characterize these features as liberalism-in-practice, as opposed to just features of bureaucratic states in general? I know to some extent liberal thought dominates the ideological basis for what a modern state is supposed to be, but since (as you put it) these systems are basically agnostic in most cases towards different concepts of the social good, and they in several cases pre-date the development of what I'd consider capitalism per se, I'm not sure how much we can actually pin the blame on Locke, Mill and successors, as tempting as that is.
More to the point (and this is my own 'having a plan' bias showing), I'm skeptical as to whether this framing points toward said bureaucratic structures not being adaptable to a classless social order. If anything, to me this framing seems to point to modern state systems being much more ideologically and practically amenable to a classless society than my (and from what I can tell, your) gut instinct and experience would suggest.
Whether communism is actually doable and worth-it is of course a big question beyond the scope of what you're writing. But it seems like you are trying to say that the tendency of law to enforce predictable outcomes, or attempt to do so, is inevitably and inescapably tied to class society, and I think the hows and whys of that are not super clear to me, or at least not obvious inferences from what you've said so far.
Also, as you said, it's not totally unreasonable to want "security," or at least a relatively consistent social framework for some types of social problems - so to me, that leaves the onus on you to show why supporting this organizational ethic is either impossible or undesirable, which does seem like a tall order.
okay so one at a time
These things predate liberalism so what's up with that?: super helpful question - I think that there is a qualitative difference in kind between these things as they manifested in pre-capitalist societies and in capitalist society (particularly the combinations thereof). as to what that qualitative difference is I could just gesture at the early chapters of Capital and go "something like that" but I think that's part of the investigation to be undertaken to avoid resting on Marx's laurels and agreeing to his limits. and yes, to be clear, I do not think that Locke & co. are necessarily the dispositive force here - I think the history of political thought (HPT) is useful as a framing, as reflective of a time, but obviously being able to point to writers doesn't reveal anything about how people behave. what it does illustrate is how these kinds of considerations were at the forefronts of people's minds during these historical developments.
Is this something unique to liberalism or just a feature of bureaucratic statecraft?: this is one thing I was chewing on as I was writing that response - it's possible that "liberalism" is too load-bearing in my argument, or alternatively that I may be trying to synthesize too many separate arguments (i.e. my reading of liberalism in the HPT as a post-aristocratic and legalistic mode of thought, plus an in-progress theory regarding the modern state as embodiment of "security" in capitalism). it might be worth trying to strain out the different threads (and I think there's probably more than just those two) to see if/where they actually link. the risks of trying to answer a Tumblr ask and suddenly you're outlining a book project.
Wouldn't your analysis suggest that bureaucratic states could transition to a non-class society?: I'm not totally following the connection you're drawing, if you could clarify I'd appreciate it!
What are the mechanisms that link contemporary law to class society?: Right - this is I think going to be the major point of investigation and analysis so difficult to sum up here, rather than to take this question as a guiding one. But Foucault has an interesting discussion of what I'm gesturing at in D&P in the context of France; I want to tease that out more, or in a different/intersecting direction:
Furthermore, although a large part of the bourgeoisie had accepted, without too much trouble, the illegality of rights, it found it difficult to support illegality when it was a question of its own property rights. Nothing could be more typical of this than the problem of peasant delinquency at the end of the eighteenth century and especially after the Revolution. The transition to an intensive agriculture exercised, over the rights to use common lands, over various tolerated practices, over small accepted illegalities, a more and more restrictive pressure. Furthermore, as it was acquired in part by the bourgeoisie, now free of the feudal burdens that once weighed upon it, landed property became absolute property: all the tolerated 'rights' that the peasantry had acquired or preserved (the abandonment of old obligations or the consolidation of irregular practices: the right of free pasture, wood-collecting, etc.) were now rejected by the new owners who regarded them quite simply as theft (thus leading, among the people, to a series of chain reactions of an increasingly illegal, or, if one prefers the term, criminal kind: breaches of close, the theft or killing of cattle, fires, assaults, murders. The illegality of rights, which often meant the survival of the most deprived, tended, with the new status of property, to become an illegality of property. It then had to be punished.
5. What's wrong with security, anyway?: Well, I think the normative issue that I'm hinting at is the inescapability of poverty and deprivation under this kind of society, and thus (common theme of us critical Marx-influenced types), this fixation on the creation and maintenance of security becomes its opposite: the constant generation of insecurity. not to necessarily say we need a "true" security but that, if indeed this is a value we might hold (and on some level it is), this mode of thought and organization does not achieve it. and the "security" in question pursued by the modern state is not just like, general security - obviously there are lots and lots of people who do not live in a sate of "security" even under these conditions - but rather securing the rule of capital and the sanctity of private property, ideologically manifesting as the perpetuation of "civilization."
I hope I accurately and fairly represented your questions.
14 notes
·
View notes
Note
what exactly does marxism-leninism-maoism add to marxism-leninism? i know part of it is the theory of protracted peoples war but honestly that seems like it would only work in countries with larger rural areas. this isn't me trying to disprove you or anything i just don't think i understand maoism. (i've also heard mixed opinions on abimael guzman from some people so i'm curious about him too)
That is a great question! The advancements of Maoism can be split into two main categories. The first category is the qualitative advancements with build on the core of Marxism, and mark the transformation of Marxism-Leninism into Marxism-Leninism-Maoism. The second is the advances which advance Maoism itself, but do not propel revolutionary science into a qualitatively higher stage.
In terms of the first category, three main advancements were made which qualitatively advanced the knowledge of revolutionary science along the lines of the three essential aspects of Marxism. These were made during the 3rd world historic revolution, that being the Chinese Revolution, up till the end of the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution. These are;
Advancements in the field of Political Economy: Chairman Mao Zedung was the first to seriously advance the study of imperialism beyond the great discoveries of Lenin and analyze Imperialism in it's modern Semi-Colonial form. This investigation led to the discovery of Bureaucrat-Comprador Capitalism and Semi-Feudalism, the ruling classes within Semi-Colonies.
Advancements in the field of Class Struggle 1: Following the analysis of Bureaucrat-Comprador Capitalism and Semi-Feudalism, along with analysis of both the RUssian and Chinese Revolution's, Mao discovered a crucial revolutionary stage for all countries under the boot of feudalism and imperialism, that of the New Democratic Revolution. The NDR is a national revolution against Feudalism and Imperialism headed principally by the Proletariat, in alliance with all progressive classes of society, including the national bourgeoises (For example the CPC-Kuomintang united fount against the Japanese, or the united front against the Tzar in Russia) The NDR must be completed before socialist revolution can occur.
Advancements in the field of Class Struggle 2: Another Key advancement of Mao was the discovery that, contrary to popular opinion at the time, class struggle continues under socialism. Under socialism new bureaucratic bourgeoisie emerge from within the party and state structure (following the principle of one dividing into two) and from remaining inequalities in society (following the principle of unequal development). Following the defeat of soviet socialism buy such forces and the rise of Khrushchevite Revisionism, and even the rise of such Revisionism in the CPC, Mao and the socialist line in the party waged a struggle against Khrushchtevite Revisionism and later internal revolution, culminating with the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution. The GPCR targeted both old feudal and capitalist structures as well as the new bourgeoisie who promoted the capitalist line in the party, and pushed the development of socialism to its farthest point so far (which is why it the 3rd world historic revolution).
Advancements in the field of Dialectical Materialism: Mao's book On Contradictions is edental reading for any serious communist, it contains Mao's contribution to the philosophical foundations of Marxism. It puts forward key concepts such as the relationship between antagonistic and non antagonistic contradiction, differentiates between principle and secondary contractions, and the universality and particularity of contractions. Mao also puts forward in other works how contractions should be handled. Contradictions amongst the people vs contradictions with ractionares, and importantly contractions between the masses and the party, which is solved with the mass line.
There is also the topic of People's War, however that is a topic I personally do not know enough about yet in order to speak on it with any authority. After all, no investigation, no right to speak.
#marxism leninism maoism#marxism leninism#marxism#maoism#communism#socialism#chinese revolution#russian revolution#great proletarian cultural revelation#GPCR#cultural revolution
8 notes
·
View notes
Text


WASHINGTON, Jan 29 (Reuters) — A batch of newly released images captured by the James Webb Space Telescope show in remarkable detail 19 spiral galaxies residing relatively near our Milky Way, offering new clues on star formation as well as galactic structure and evolution.
The images were made public on Monday by a team of scientists involved in a project called Physics at High Angular resolution in Nearby GalaxieS (PHANGS) that operates across several major astronomical observatories.
The closest of the 19 galaxies is called NGC5068, about 15 million light years from Earth, and the most distant of them is NGC1365, about 60 million light years from Earth.
A light year is the distance light travels in a year, 5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion km).
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) was launched in 2021 and began collecting data in 2022, reshaping the understanding of the early universe while taking wondrous pictures of the cosmos.
The orbiting observatory looks at the universe mainly in the infrared.
The Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990 and still operational, has examined it primarily at optical and ultraviolet wavelengths.
Spiral galaxies, resembling enormous pinwheels, are a common galaxy type. Our Milky Way is one.
The new observations came from Webb's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) and Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI).
They show roughly 100,000 star clusters and millions or perhaps billions of individual stars.
"These data are important as they give us a new view on the earliest phase of star formation," said University of Oxford astronomer Thomas Williams, who led the team's data processing on the images.

"Stars are born deep within dusty clouds that completely block out the light at visible wavelengths - what the Hubble Space Telescope is sensitive to - but these clouds light up at the JWST wavelengths.
We don't know a lot about this phase, not even really how long it lasts, and so these data will be vital for understanding how stars in galaxies start their lives," Williams added.
About half of spiral galaxies have a straight structure, called a bar, coming out from the galactic center to which the spiral arms are attached.
"The commonly held thought is that galaxies form from the inside-out, and so get bigger and bigger over their lifetimes.
The spiral arms act to sweep up the gas that will form into stars, and the bars act to funnel that same gas in towards the central black hole of the galaxy," Williams said.

The images let scientists for the first time resolve the structure of the clouds of dust and gas from which stars and planets form at a high level of detail in galaxies beyond the Large Magellanic Cloud and Small Magellanic Cloud, two galaxies considered galactic satellites of the sprawling Milky Way.
"The images are not only aesthetically stunning, they also tell a story about the cycle of star formation and feedback, which is the energy and momentum released by young stars into the space between stars," said astronomer Janice Lee of the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, principal investigator for the new data.
"It actually looks like there was explosive activity and clearing of the dust and gas on both cluster and kiloparsec (roughly 3,000 light years) scales.
The dynamic process of the overall star formation cycle becomes obvious and qualitatively accessible, even for the public, which makes the images compelling on many different levels," Lee added.
Webb's observations build on Hubble's.

"Using Hubble, we would see the starlight from galaxies, but some of the light was blocked by the dust of galaxies," University of Alberta astronomer Erik Rosolowsky said.
"This limitation made it hard to understand parts of how a galaxy operates as a system. With Webb's view in the infrared, we can see through this dust to see stars behind and within the enshrouding dust."

#James Webb Space Telescope#spiral galaxies#Milky Way#Physics at High Angular resolution in Nearby GalaxieS (PHANGS)#NGC5068#NGC1365#light year#Hubble Space Telescope#Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam)#Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI)#astronomy#space#universe#cosmos#Large Magellanic Cloud#Small Magellanic Cloud#Space Telescope Science Institute
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reference saved in our archive
Is there a link between pediatric hepatitis and covid infection?
Abstract Background
The cause of acute paediatric hepatitis of unknown aetiology (2022) has not been established despite extensive investigation.
Objective
To summarise the evidence for and against a causal role for human adenovirus (HAdv), adeno-associated virus 2 (AAV-2) and SARS-CoV-2 in outbreaks of paediatric hepatitis in 2022.
Methods
We appraised and summarised relevant evidence for each of the Bradford Hill criteria for causality using quantitative (statistical modelling) and qualitative (narrative coherence) approaches. Each team member scored the evidence base for each criterion separately for HAdv, AAV-2 and SARS-CoV-2; differences were resolved by discussion. We additionally examined criteria of strength and temporality by examining the lagged association between SARS-CoV-2 positivity, respiratory HAdv positivity, positive faecal HAdv specimens and excess A&E attendances in 1–4 years for liver conditions in England.
Results
Assessing criteria using the published literature and our modelling: for HAdv three Bradford Hill criteria (strength, consistency and temporality) were partially met; and five criteria (consistency, coherence, experimental manipulation, analogy and temporality) were minimally met. For AAV-2, the strength of association criterion was fully met, five criteria (consistency, temporality, specificity, biological gradient and plausibility) were partially met and three (coherence, analogy and experimental manipulation) were minimally met. For SARS-CoV-2, five criteria (strength of association, plausibility, temporality, coherence and analogy) were fully met; one (consistency) was partially met and three (specificity, biological gradient and experimental manipulation) were minimally met.
Conclusion
Based on the Bradford Hill criteria and modelling, HAdv alone is unlikely to be the cause of the recent increase in hepatitis in children. The causal link between SARS-CoV-2, and to a lesser degree AAV-2, appears substantially stronger but remains unproven. Hepatitis is a known complication of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children following COVID-19, and SARS-CoV-2 has been linked to increased susceptibility to infection post-COVID-19, which may suggest complex causal pathways including a possible interaction with AAV-2 infection/reactivation in hosts that are genetically susceptible or sensitised to infection.
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#wear a respirator#covid#still coviding#covid 19#coronavirus#sars cov 2#adenovirus
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
U.S. Naval Research Laboratory researcher Mark Romanczyk, Ph.D., developed new analytical methods to rapidly analyze fuels and complex petroleum products by using high-resolution mass spectrometry. The approaches Romanczyk utilizes enable highly detailed qualitative analysis of complex mixtures in minutes. One recent method facilitated the investigation of chemical changes that occurred in weathered crude oil in terrestrial environments. Several of the methods were recently published in the science journal Fuel. "Despite the accidental rise of oil spilled onto landmasses, less research has been dedicated to evaluating the compositional changes/fate of oil prior to its introduction into bodies of water" said Romanczyk. "The lack of information affords an opportunity to investigate and qualitatively characterize oil as a function of weathering time in the absence of an aqueous environment. These studies may provide highly useful information for oil spill cleanup and exposure concerns."
Read more.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Catherine Lamb — Curva Triangulus (Another Timbre)

youtube
Catherine Lamb composes complex, heady music. She explores how we perceive music, playing with harmonic structures and intonation, challenging our typical sense of sound. For Curva Triangulus, she joins with Ensemble Proton to investigate not only compositional drama, but the use of unusual instruments in creating (and limiting) the timbral possibilities of her work. The piece has an undeniable and immediate beauty to it, its leisurely place allowing room (or, better, time) for the experiments that Lamb conducts. It provides opportunity for deep listening challenges — interesting moments and unique developments arise everywhere — but it also makes for accessible pleasure, despite the novel and sometimes unsettling tonal work.
Bern's Ensemble Proton offers Lamb the ideal group for this project. The octet includes musicians hungry for the new and experimental with a penchant for playing unlikely instruments. Coco Schwarz's arciorgano — an extinct but resurrected keyboard instrument — might be the rarest and most unusual. The instrument breaks and octave in more than the usual number of divisions. Lamb uses the arciorgano's tonal options as a sort of sonic adhesive, holding the ensemble's varied sounds together. In a context with not only that instrument but also a lupophone, clarinet d'amore, and others, a violin or bassoon could sound downright pedestrian; instead, they sound otherworldly, part of the strange brew that makes up Curva Triangulus.
Lamb writes in her notes, “Elemental concepts around melody and harmony are reconsidered, blurred.” For listeners less attuned to prime qualitative harmonics and the modal challenges developed across “triadic counterpoint” (whoever those people might be), the blur of melody and harmony becomes the most fascinating aspect of the record. Melody remains subordinate to harmonic movement, but in the interplay of sounds and tones, melody peeks through in unexpected ways. The sonic shifts never become linear, but essentially melodic movements arise, occasionally passed between musicians. The lead “instrument,” might be a harmonic instead of a violin, but those structures give shape to musical phrases that cohere into, if not melody, at least melodic sensibility.
The deep concepts of Curva Triangulus make the album's nuances difficult to access, but the album never relies on its intellectual demands if listened to as a straightforward album. The tonal structures and uncommon instrumentation give it a particularly idiosyncratic feel, but everything sorts itself out into a spellbinding aural geometry. When the ensemble hints at a church organ six minutes in, no one will anticipate a turn toward hymnody, but when it drops into alien space informed by triple harp, no one will feel jarred either. Lamb's work provides a series of intellectual tests, but also a memorable stretch of focused wonder.
Justin Cober-Lake
#catherine lamb#curva triangulus#another timbre#justin cober-lake#albumreview#dusted magazine#ensemble proton#contemporary classical music#composition
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Daniel Dennett
Controversial US philosopher who sought to understand and explain the science of the mind
Daniel Dennett, who has died aged 82, was a controversial philosopher whose writing on consciousness, artificial intelligence, cognitive science and evolutionary psychology helped shift Anglo-American philosophy from its focus on language and concepts towards a coalition with science.
His naturalistic account of consciousness, purged as far as possible of first-person agency and qualitative experience, has been popular outside academia and hotly opposed by many within it.
One of the so-called Four Horsemen of New Atheism, along with Richard Dawkins, Christopher Hitchens and Sam Harris, he also wrote on Darwinism, memes, free will and religion.
“Figuring out as a philosopher how brains could be, or support, or explain, or cause, minds” was how Dennett, aged 21, defined his project. Having gained a philosophy degree at Harvard University in 1963, he was then doing a BPhil at Oxford University under the behaviourist philosopher Gilbert Ryle, but spent most of his time in the Radcliffe science library learning about the brain.
Many philosophers were (as they still are) trying to accommodate the mind, and its subjectivity, in third-person science. Yet it seems impossible to identify “intentionality” (the “aboutness” of thoughts) or “qualia” (the “thusnesses” of experience) as nothing but brain states or behaviour.
In dealing with “intentionality”, Dennett, however, had a novel strategy – “first content, then consciousness” – that reversed the usual line of enquiry. He proposed “to understand how consciousness is possible by understanding how unconscious content is possible first”.
Nature, he argued, has its own unwitting reasons – “free-floating rationales” that are “independent of, and more fundamental than, consciousness”. The ability of organisms to respond appropriately, if unconsciously, to things in the environment is a “rudimentary intentionality”. And, over aeons, the “blind, foresightless, purposeless process of trial and error” has knitted “the mechanical responses of ‘stupid’ neurons” (in certain creatures’ brains) into a “reflective loop [that] creates the manifest illusion of consciousness,” he thought. “Mind is the effect, not the cause.” As spiders mindlessly spin webs, homo sapiens has spun “a narrative self”.
What Ryle had dismissed as “the ghost in the machine” could thus be exorcised, not by denying its existence but by seeing it for what it is – a conjuring trick rather than magic, an illusion fabricated by what (in his 1995 book Darwin’s Dangerous Idea) he called evolution’s “reverse engineering”.
Dennett’s first book, Content and Consciousness was published in 1969. Sixteen other books and numerous papers adapted and extended its thesis – that intentionality can be ascribed, along a spectrum with no clear dividing line, impartially to minds, human brains, bees, computers, thermostats: it is a functional relation between object and environment. As to exactly when, in evolutionary or personal history, conscious intentionality arose, “don’t ask,” he said.
We can take what he called a “physical stance” towards something (considering its constituents and their causal interlockings) or a “design stance” (seeing it as fabricated, by evolution or humans, to serve a particular function) or an “intentional stance” (explaining its behaviour in terms of goals that it would sensibly pursue if it were rational).
“The intentional stance is thus a theory-neutral way of capturing the cognitive competences of different organisms (or other agents) without committing the investigator to overspecific hypotheses about the internal structures that underlie the competences.” We treat chess-playing computers, some animals and humans, as if they had beliefs and desires. But, he was furiously asked, don’t we humans actually have them?
Yes and no, apparently. There is no one-to-one match between brain states and mental states. It is the creature as a whole that has intentionality. The discrete individually identifiable mental states that we seem to be having are (in reality) “an edited and metaphorialised version of what’s going on in our brains” – equivalent to “user illusions” on a computer screen: like the hourglass, folder and dustbin icons, they betoken the complex processes occurring behind the scenes.
“No part of the brain is the thinker that does the thinking, or the feeler that does the feeling,” said Dennett, nor is, or does, the brain as a whole. Instead there are “multiple channels in which specialist circuits try, in parallel pandemoniums, to do their various things, creating multiple drafts as they go” – until, from among “concurrent contentful events in the brain … a select subset of such events ‘wins’ … The way to explain the miraculous-seeming powers of an intelligent intentional system is to decompose it into hierarchically structured teams.” These consist of “relatively ignorant, narrow-minded, blind homunculi that produce the intelligent behaviour of the whole”.
“Yes we have a soul but it’s made of lots of tiny robots” was the headline of an article about him in the Italian newspaper Corriere della Sera, and Dennett endorsed it with amusement. He loved making furniture, building fences, mending roofs, tinkering with cars and boats; and, among the many things he constructed were sets of nested Russian dolls to illustrate his philosophy. The outside doll was “Descartes”; inside that was “the Middle Ghost” (a reference to Ryle’s) – but inside that was a “Robot”. “We are not authorities about our own consciousness,” he said. The robot is masked by the ghost.
Dennett pronounced qualia to be illusions. Ever since Descartes, we have tended to assume that we have “mental images”, as if, said Dennett, we could view little pictures, visible only to ourselves in an inner “Cartesian theatre”.
If so, we should be able to count the number of stripes on the tiger we are imagining, and say whether we have been seeing it face-on or sideways. No such definite information is available. Mental images are indeterminate in a way that pictures cannot be, and closer to generalised linguistic descriptions. So limited and poor is our access to our own conscious experiences, said Dennett, that it “does not differ much from the access another person can have to those experiences – your experiences – if you decide to go public with your account”. Indeed “our first-person point of view of our own minds is not so different from our second-person point of view of others’ minds”. We take an intentional stance on ourselves.
Dennett’s views remained pretty consistent throughout numerous books and papers, but in recent years he became more lenient towards mental imagery. He was impressed by neuroscientific research suggesting that there are specific observable brain activities that potentially may be decoded as imaging processes.
And, having been stern in denying what is disparagingly called “folk psychology” (a term he invented), he began to describe himself as “a mild realist” about mental states, prepared to concede that “the traditional psychological perspective” is not merely something described by third-person observers.
Avoiding accusations that he smuggled in the subjectivity he so adamantly denied, Dennett had recourse to “memes”, a concept (invented by Dawkins) modelled on that of genes. Memes are units of cultural practice, including anything from language to drama to wearing a baseball cap backwards to clapping as a form of praise. They are, in Dennett’s words, ‘“prescriptions” for ways of doing things that can be transmitted to, and from, human brains, and that “have their own reproductive fitness, just like viruses”. We are infected by memes, and it is “the memes invasion … that has turned our brains into minds”.
Dennett also applied a Darwinian approach to free will. “A billion years ago, there was no free will on this planet, but now there is. The physics has not changed; the improvements in ‘can do’ over the years had to evolve.” We are now able to predict probable futures, and to pursue or avert them. We are not deluded about having that capacity; as we are, he fulminated, about religion. Breaking the Spell (2006) was judiciously named. That was what he was urging religious people to do.
Born in Boston, Dennett spent the first five years of his life in Lebanon. His father, also Daniel, was a counter-intelligence officer posing as a cultural attache to the American embassy in Beirut. He died in a plane crash in 1947 (later, Dennett’s sister, the investigative journalist Charlotte Dennett, would claim Kim Philby’s connivance in it). Dennett’s mother, Ruth Leck, a teacher and editor, took the children back to Massachusetts.
Reprieved from matching up to his father’s expectations, Dennett said, he nonetheless grew up in his father’s shadow. But little could sap his exuberant self-confidence. Characteristically, the title of his 1991 book was Consciousness Explained.
In 1959, having just begun a maths degree at Weslyan University, Connecticut, Dennett read Willard van Orman Quine’s From a Logical Point of View. He was so excited that he decided “to be a philosopher, and go to Harvard and tell this man Quine why he is wrong”. The first two he managed, though for a time he worried that Quine (later a great friend) was more interested by Dennett’s sculpture than his philosophising.
Dennett did contemplate being a sculptor, and would, he said, certainly have studied engineering had his family not been so arts-oriented. Co-director of the Center for Cognitive Studies at Tufts University in Massachusetts, in 1993 he joined the Humanoid Robotics Group at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to construct a robot (Cog) that would be not only intelligent but conscious. The project ended in 2003, and Cog was retired to a museum.
Dennett was Austin B Fletcher professor of philosophy at Tufts, and visiting professor at a host of other universities, including Oxford and the London School of Economics. His memoir, I’ve Been Thinking, was published in 2023.
He and his wife, Susan (nee Bell), whom he married in 1962, lived in North Andover, Massachusetts, and he also hobby farmed in Maine for more than 40 summers, blissfully “tillosophising” on a tractor, sailing his boat Xanthippe, fixing buildings and digging drains. Dennett loved solving puzzles and disinterring the inner workings of machines – above all those of “the miraculous-seeming” mind. “No miracles allowed,” he said.
He is survived by Susan, a daughter, Andrea, and son, Peter, and six grandchildren, and his sisters, Cynthia and Charlotte.
🔔 Daniel Clement Dennett, philosopher, born 28 March 1942; died 19 April 2024
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at Just for Books…?
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Purposeful Sampling Unlocked: A Guide to Tailored Research Strategies
In qualitative research, the sampling method you select becomes very influential in shaping your findings and insights. Among these is purposeful sampling, considered a strategic method of participant selection to provide richer and more relevant data for a study. You probably know that there exist different types of purposeful sampling, each type suited for different research needs.
1. Maximum Variation Sampling
Purpose: To capture a wide range of perspectives.
This method takes people with a wide range of characteristics to help you discover varied perspectives in your study. For example, should you be investigating workplace behaviour, you might include participants from diverse age groups, job functions, and departments.
2. Opportunistic Sampling
Objective: To take advantage of emerging opportunities during the investigation.
Sometimes, unexpected events occur in an investigation. Opportunistic sampling enables you to change course and make available subjects or cases that unexpectedly fit your research criteria.
3. Snowball Sampling
For access to hard-to-reach populations.
In this method, the already participating people recruit other people who meet the conditions of the study. It is often used in studies that concern niche groups or sensitive issues.
4. Typical Sampling
To typical the case
Typical sampling involves participants who best represent the normal case in the population. For instance, in education research, you would select students with average performance in academics for a general understanding of the trends.
5. Theory or Concept Sampling
Purpose: To test or develop a theoretical framework.
This sampling method involves selecting participants by relevance to a specific theory or concept. It is best suited for the elaboration of constructs or the validation of hypotheses in some detail.
6. Critical Sampling
Purpose: Examining extreme or pivotal cases.
Critical sampling concentrates on distinctive, or pivotal cases for your analysis. For example, you could concentrate on a business that had recently accomplished an innovative model of operation.
7. Homogeneous Sampling
Objective: To examine a particular subgroup.
Homogeneous sampling selects participants that share similar characteristics or experiences, such as a class of students from the same institution studying the same subject.
Conclusion: Selecting the Appropriate Sampling Strategy
This happens by choosing the right type of purposeful sampling based on your research objectives and the questions you are trying to answer. Each method presents particular advantages, be it in diverse perspectives, niche insights, or theory-driven data.
By understanding and applying these strategies, you can ensure your research is not only methodologically sound but rich in insights as well.

For further research assistance, reach out to us on our WhatsApp wa.me/+918217879258
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Research Methodologies and Design
Understanding Research Methodologies and DesignResearch is the cornerstone of progress in any field, from science and medicine to education and social sciences. To conduct meaningful research, one must first understand the fundamentals of research methodologies and design. These two concepts form the framework for systematic investigation and ensure the reliability and validity of results.This blog explores the essentials of research methodologies and design, offering a comprehensive guide for students, researchers, and enthusiasts.---What Is Research Methodology?Research methodology is the systematic plan for conducting research. It encompasses the tools, techniques, and procedures used to gather and analyze data, ensuring that the findings are accurate and relevant to the research question.Key components of research methodology include:1. Research PhilosophyPositivism: Focuses on observable phenomena and measurable facts.Interpretivism: Seeks to understand human behavior in its social context.Pragmatism: Combines positivism and interpretivism based on the research problem.2. Approach to ResearchDeductive Approach: Starts with a theory or hypothesis and tests it through data collection.Inductive Approach: Develops a theory based on observed patterns in the data.3. Types of ResearchQualitative: Explores experiences, concepts, and narratives. Common methods include interviews and thematic analysis.Quantitative: Measures variables numerically, often using surveys, experiments, and statistical analysis.Mixed Methods: Integrates both qualitative and quantitative approaches for a comprehensive understanding.---What Is Research Design?Research design is the blueprint of a study. It outlines the structure, techniques, and strategies for conducting research, ensuring the process is both effective and efficient.Key types of research design include:1. Exploratory Research DesignUsed when little is known about a problem.Methods include literature reviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys.2. Descriptive Research DesignAims to describe characteristics or behaviors in detail.Surveys, observational studies, and case studies are common methods.3. Explanatory (Causal) Research DesignFocuses on identifying cause-and-effect relationships.Experimental designs, including randomized control trials, are widely used.4. Longitudinal vs. Cross-Sectional DesignsLongitudinal: Studies subjects over a long period to observe changes.Cross-Sectional: Collects data at a single point in time.---Steps to Create a Solid Research Design1. Define the Research ProblemStart with a clear and concise research question. For example, "What factors influence academic performance in college students?"2. Review LiteratureAnalyze existing studies to understand gaps and inform your design.3. Choose the Research MethodologyDecide whether your study will be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods.4. Select Data Collection MethodsUse appropriate tools like surveys, interviews, experiments, or observational techniques.5. Plan Data AnalysisDecide on statistical methods or thematic approaches depending on your data type.6. Pilot the StudyConduct a small-scale trial to refine your methods.---The Importance of Ethical ConsiderationsEthics is integral to research methodologies and design. Ensure that your study respects the rights and dignity of participants by:Gaining informed consent.Ensuring confidentiality.Avoiding plagiarism and ensuring transparency in data reporting.---ConclusionMastering research methodologies and design is vital for conducting effective and credible research. By choosing the right approach, adhering to ethical practices, and meticulously planning each step, you can contribute valuable insights to your field of study.Whether you're a novice researcher or an experienced academic, understanding these concepts lays the foundation for impactful investigations. Keep learning, experimenting, and refining your approach to stay at the forefront of your discipline.
https://wa.me/919424229851/
2 notes
·
View notes