#process automation case study
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#process automation case study#telecommunication operations automation#how can i reduce my aht#enterprise process automation#contact center automation
0 notes
Text
AI HIGH TICKET COMMISSIONS

#Our advanced AI platform offers automated tools that optimize your sales strategy#ensuring you close high-value deals effortlessly.#By leveraging our AI tools#you’ll not only save time but also increase your conversion rates#allowing you to earn higher commissions without the extra effort.#Perfect for sales professionals#entrepreneurs#and marketers looking to maximize their income and streamline their processes.#‘Since using this AI platform#my commissions have doubled!’ – Sarah#Top Sales Rep.#it’s important to highlight key features and benefits that appeal to potential buyers. Here are some suggestions for how to structure your d#1. **Attention-Grabbing Intro**#- Start with a bold statement or question to capture interest.#- Example: “Unlock your earning potential with our exclusive AI-driven commission program!”#2. **Product Overview**#- Briefly describe what the product is and what it does.#- Example:#3. **Key Features**#- **Smart Analytics**: Utilize data-driven insights to identify your best prospects.#- **Seamless Integration**: Effortlessly connect with your existing CRM and marketing tools.#4. **Benefits**#- Explain how these features translate into real-world benefits.#5. **Target Audience**#- Identify who will benefit most from the product.#6. **Testimonials or Success Stories**#- Include quotes or case studies from satisfied customers.#7. **Call to Action**#- Encourage readers to take the next step#whether it's signing up or learning more.
1 note
·
View note
Text
😎 Take a Look at This Automated Data Processing Success Story
🚼 Embark on a transformative journey with our automated data processing success story. Discover seamless efficiency and unparalleled success as we share insights, strategies, and real-world results that showcase the power of automated data processing. Revolutionize your approach and join the ranks of those who have unlocked unprecedented productivity and triumph.

0 notes
Text
Tailored Services: RPA Services for the Manufacturing Industry
There is a broad range of other RPA use cases in manufacturing apart from the above-mentioned ones in the vast manufacturing industry. If you feel like your business is not moving into the digital age quickly enough and existing systems are too complex or old to integrate and automate, then ESS RPA consultants can help you to move forward with your RPA goals faster.

Elevate your manufacturing with specialized RPA services. Unlock tailored solutions that optimize processes and drive efficiency in your industry.
#RPA in manufacturing industry#RPA in manufacturing sector#Manufacturing RPA use cases#Benefits of RPA in manufacturing#RPA manufacturing use cases#Robotic process automation for manufacturing#RPA in manufacturing use cases#RPA services for manufacturing industry#Robotic process automation use cases in manufacturing#RPA manufacturing case study#Robotic process automation for manufacturing companies#Manufacturing RPA#Robotic process automation manufacturing#Robotic process automation in manufacturing#Manufacturing use cases in RPA#Robotic process automation in manufacturing industry#RPA use cases in manufacturing industry#RPA for manufacturing#RPA manufacturing#RPA in manufacturing
0 notes
Text
Automated Data Processing Case Study: Explore How a RegTech Firm Enhanced Its Business Agility
Are you also struggling with inefficient workflows to collect, transform, process, and analyze ever-increasing volumes of data? Irrespective of the answer, you need to go through this automated data processing success story to discover the power of technology. Learn how cutting-edge technology streamlines workflows, eliminates errors, and boosts productivity. Unleash the potential of your business with efficient data processing solutions.

0 notes
Text
taken in by the sullys (5) / sully family x human!daughter/sister!reader
synopsis, your birth mother didn’t care to be cautious while pregnant, but at least something good came out of it. ++ spider, and then lo’ak throwing hands for you
+ note! writing these chapters during my commute makes the bus rides sm more relaxing, i’m happy you guys are enjoying the series just as much <33
(1) / (2) / (3) / (4*) / (5 - ur here! ☆)
+ chapters with an * beside it means that it’s following atwow plot line as opposed to disconnected scenarios
2155 (you were four years old)
the first time you ran out into pandoran air without a gas mask on, jake thought you were going to die
pandoran air was filled with compounds that the human lungs couldn't process efficiently—a danger that threatened jake's life once before
after the war ended and the sky people were banished from pandora, there was a lot of things to take care of logistically
inducting jake as olo'eyktan was one of them, along with an agreement with the remaining humans living on the planet
plus in the aftermath of the war, many other forest clans lost their homes or leaders. jake was determined to accommodate all of them as best he could
his preoccupation left you with little supervision and a lot of free time
jake was visiting norm's lab to check up on the status of their relationship with the clans
he carried you along with him for once, hoping it'd be a fun take your daughter to work day
this is how he held you when you were little btw
as soon as he set you loose, you bolted out the lab
you jumped up and slapped a button, dashing outside when the door opened just wide enough to allow you through.
it slowly creaked as alarms began to blare loudly, an automated voice warning them of the sinking pressure overtaking the room's atmosphere.
"holy shit—" jake shot up, wincing as he slammed his head into the ceiling. "norm?! why didn't you grab her?" he rushed through the corridor, and being incompatible with the space started knocking things over left and right.
"i'm sorry, she has so much experience slipping past me!" norm protested, equally panicked as he held his breath. he scrambled out his seat towards the exit door, dodging jake's thrashing tail.
"no, no, no." jake's body rammed into the door just as it slammed shut. he peered out the frosted window and vaguely caught your shape. his fist collided with the access button. "why isn't this door opening?!"
jake rapidly slammed the button before norm stopped him from breaking the circuits completely.
"the cabin is returning to normal atmospheric conditions," norm gasped for air, finally. "it won't open for another—"
jake backed up, crouching into a lunging position. he bounced on the balls of his feet. "i'm kicking the door."
"what?! jake—"
"i'm breaking the damn door, norm. put a mask on. i'm not waiting." jake snapped, grabbing two masks off the wall and tossing one to the scientist. he surged forward and thrust his leg out, his foot flattening against the door and knocking it clean off its hinges.
norm dove for cover, securing a mask over his face just as all sorts of alarms clamored for attention.
jake ducked through the opening, immediately running to you. he dropped to his knees, taking no notice to the blisters and cuts that broke skin as he slid across the dirt towards you. he snatched you up in his arms, turning you to face him and trying to put the gas mask over your head.
you kept swerving him and blocking him with your hands.
"y/n—baby, please stay still." he tried to contain his worry as he grabbed your wrists in his hand and dropped them away from your face.
"stay still, you need..." he slowed his attempts as he realized... you were breathing just fine. "to breathe..?"
you glared at him in annoyance, confused as to why he was trying to smush glass on your face.
"you don't need the mask?" he asked, unsure himself. he paused for a moment, studying you closely. his hand still firmly gripping the gas mask in case he was mistaken. but you weren't coughing or gasping.
he lifted you up, hands nestled underneath your armpits. he put his ear to your back, listening to the sound of your breathing. no whistles. no wheezing. no rattling. just perfectly normal inhale... and exhale.
"huh." jake's eyebrows furrowed, turning you around and holding you against his chest. he looked down at norm, who had just caught up, pointing a finger at you.
"wanna explain what's going on here?"
the nature of your development and birth allowed for certain mutations surface
your birth mother got pregnant with you on pandora, going out in the atmosphere, consuming the fruits, and maybe getting stung once or twice by strange flowers
with how reckless she was while carrying you, it's no surprise your genome was a bit messed up
after norm thoroughly tested you for other variations, he came up with a comprehensive list
jake was never one for reading—he didn't even read the reports and logs that would've helped him be prepared when first going out with grace and norm
but he consumed every bit of information norm offered him, even asking him to print a copy of the document for future reference
"the subject exhibits accelerated peripheral growth wherein measurements taken supersede the average on earth... what the..." jake rattled off, before tossing the document back to norm with a roll of his eyes. "yeah, you're gonna have to do one in english and then get back to me."
"that just means she's growing faster compared to a normal human child." norm deadpanned. "she had a four year old's height when she just turned two. you were there, didn't you notice?"
jake shrugged, rotating you in his arms. "dunno. still looks pretty small to me." he cooed, nuzzling his nose to yours.
"you're almost 10ft. tall. everything looks small to you." norm turned back to his computer, exasperated. “whatever her mother did messed her up pretty badly.”
jake frowned. your birth mother died two years before he arrived on pandora, but he was sure he wouldn’t have liked her. the stories he’s heard was more than enough to form an opinion. he only tolerated her memory because she gave life to one of his most precious treasures.
“i wouldn’t say messed up. more like…” he pondered, watching the fluorescent ceiling light sparkle in your eyes. “upgraded.”
long story short, your lungs had adapted to draw more oxygen from pandora's atmosphere; you were growing faster; your athletic capacity was just below superhuman; and your senses were abnormally receptive.
whatever your birth mother exposed herself to while you were in there made you a little less human.
jake and neytiri had their suspicions. there was something up with you—how else could you have kept up with neytiri's rigorous training at a young age, human and all, otherwise?
it was almost fitting. you were one of the only two human pandoran natives. children actually born on pandora.
as you grew, you continued to hone your abilities to compete with the na'vi children, but at some point you hit a ceiling.
a little less human was still human at the end of the day.
spider
the other only human born on pandora was miles 'spider' socorro
given how similar your situations were, you were surprised at the drastic difference between your lives
you were two years older than him—he was born just before the first pandoran war
he had adoptive parents, the mccoskers, just like you had the sullys
the mccoskers were residents of hell's gate as per jake's surrender list until the RDA returned under ardmore's command
they left with their own family, spider left behind
spider was then his own boss, doing as he pleased and going where he pleased
above all, he was inseparable from the sully kids—an unspoken, invisible brother
sometimes, you felt awkward when interacting with him because you got lucky with the sullys while he was considered a 'stray'
unlike lo'ak or kiri, you weren't particularly close to him as a friend, but you looked out for him just as you did for the others
"hey," you caught up to him as he was leaving.
spider spending the entire day with the kids was routine. from dawn to dusk, sometimes into the night, he was by their side. you and the kids loved him, and he loved you guys too.
"oh. hey." he turned, awkwardly standing in place. "what's up?"
"wanted to catch you before you left." you loosely gestured to the sky. "it's pretty dark out. i'll walk you home."
he blinked, surprised by the consideration. you felt pity pool in your stomach.
"oh. yeah, thanks." he nodded. you could see a thought cross his mind. he quickly backtracked. "but—but if i'm keeping you, i'm okay to—"
"spider," you smiled, wrapping your arms around his shoulders and beginning to walk alongside him. "you're not keeping me. we’re two of a kind so we gotta stick together, right?" you bumped into his side playfully.
he felt at ease, relaxing. "yeah." spider chuckled. he glanced at your face before dropping his eyes. "it's so crazy how you can just... breathe the air. i'm jealous." gesturing to his exo-pack, he continued. "gotta lug this thing around all day."
“the reason why is way less cool, promise.” you muttered, reflecting on your birth mother.
friendly chatter and a few minutes later, you arrived at the human base. you dropped spider inside to his bunk.
he collapsed against the mattress with a lengthy sigh.
you laughed at his antics. “it’s tough keeping up with them, huh?”
“oh, please, i could outrun ‘em any day.” he huffed, grinning lopsidedly.
you pat his shoulder. “make sure to eat something before bed.” walking out, you waved goodbye. “see you tomorrow.”
he felt warm—seen. he waved back. “bye.”
despite the two year age gap, spider saw you as a maternal figure
i mean, you were the only one that willingly made yourself available to him consistently
he would NEVER admit this, though, to himself or anyone else
kiri was a very close confidant, neteyam and lo’ak were brothers, and tuk was the baby
you were the only young adult that made him a priority for care and support
he would be eternally grateful for that, because no matter what he would experience, he knew you were in his corner just like any of the other kids
it made him feel part of something when he had nothing
omaticayan dissent
it was no secret that there were some that disagreed with their clan leaders’ choice to adopt you into their family
and while their hatred and caution was valid—they’ve had many sky people deceive them before—it was poor to direct that anger onto a child
you were essentially a trash bin for their bitterness, a figure to focus their resentment when there were no other ‘bad humans’ around
and despite proving your usefulness time and time again, it was becoming increasingly clear that they were never going to accept you as their own
for jake and neytiri, it was a delicate balance of hearing their people and curbing their behaviour
for your siblings, though? it was gloves off. immediately
“what’d you just say?” lo’ak hissed, grabbing the shoulder of the omaticayan boy and spinning him around.
if there’s one thing about lo’ak, it’s that he rocks for his family.
“lo’ak.” neteyam warned, spawning behind the youngest sully son as if he was summoned the minute lo’ak threatened trouble. “mawey, brother.
lo’ak shoved neteyam’s arm off his shoulders, pointing an accusatory finger at the boy. “he just said—“
“how can you call tawtute a sister?” the boy contorted his face in disgust. “she does not belong here. all the other children know it.”
“olo’eyktan decides who belongs and who doesn’t. that is none of your business.” neteyam said coolly. “she does her part and keeps to herself.”
the boy made a yeuch sound, shuddering. ignoring neteyam’s subtle offer for truce, he continued. “they made a demon who can breathe among us. what’s next, one who can connect with our great mother? you ask yourself what else must they have in store.”
neteyam wanted to set the guy straight, but ever the oldest son, he kept his composure. “our mother and father raised her more na’vi than human. if she had different loyalties, she would have left long ago.”
“well—“
“let it rest.” neteyam cut him off firmly, his expression blank.
the boy could not continue to argue against the chief’s son when he put down a hard boundary. he snarled, baring his teeth at both sons.
“lo’ak, ‘yam—“ you approached them, oblivious to the tension. “mom’s calling for dinner.”
lo’ak seethed silently but after catching neteyam’s firm look, he swallowed his pride.
they walked past the boy, giving him a lasting glare while following behind you.
“freak.” the boy mumbled under his breath when you were out of earshot.
without hesitation, lo’ak shifted his weight and launched his fist across the boy’s jaw.
he got an earful, naturally
the scuffle continued until neteyam was able to break it up
after apologies were forced, lo’ak was subject to your father’s favourite punishment—grounding
you shooed kiri and her unhelpful teasing away, taking over lo’ak’s treatment
you dabbed the cloth to his forehead. “what’d he do?”
lo’ak winced, leaning away from the burning sting of the ointment. remaining silent, he glared at the floor.
“hm?” you egged him on. “you know you can tell me.”
“i…” he began with a sigh before changing his mind. “never mind. doesn’t matter.”
jake sully was a girl dad through and through. in his eyes his girls could do no wrong. he saw a youthful recklessness in his sons, something they undoubtedly got from him, and feared they would go down a path he couldn’t save them from. he was very hard on them, sometimes unfairly so.
you forcefully turned his head to look at you. “course it matters, dummy. you’re telling me the way the boy described it was how it went down?”
his chest rose and fell rapidly as he got worked up again. “he was talking shit about you.” he glanced at you, wondering if he’d get told off for cursing. when you didn’t speak, he continued angrily. “again. i was gonna let it go, i swear! but he ran his mouth right in front of you! how did you not hear?”
“you did this on my behalf?”
“yes! all of them have said something at some point. they don’t have any shame. it’s not fair.” he grumbled, his posture sinking.
you dropped in the spot next to him. “you know i’m proud of you, lo’ak, and i’m grateful you thought to defend me. but you don’t need to get into fights.” you pleaded, trying to catch his annoyed gaze. “cuz then both of us lose.”
he groaned and crossed his arms. “i just— if i feel like this… i just think you would feel ten times worse.”
like this. like an outcast. it was the first time you really considered that it was the truth. growing up, you simply accepted it as a fact of your life.
you softened when you observed his tormented expression. you leaned against him to let him know you understood—that the two of you were more alike than it would seem. you remained there in each other’s company until you were called for dinner.
. . .
thanks for reading <3
taglist (lmk if you want to be added/removed): @dae-dreamer @delirious-dolce @strawbaerriesvt
© jsooly ‘25
#atwow#avatar 2009#avatar 2022#avatar the way of water#jake sully avatar#jake sully#jake sully x neytiri#jake sully x reader#kiri#neteyam#jake sully x daughter#jake sully x daughter!reader#neteyam sully#neteyam x reader#neytiri x reader#neytiri avatar#lo’ak x reader#lo'ak sully#lo'ak x reader#tuk sully#sully x reader#sully family#spider sully#spider x reader
658 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved on our archive
Whenever you hear someone trying to blame kid's poor test scores "post pandemic" on "lockdowns," show them this.
By Dr. Sushama R. Chaphalkar, PhD.
New research shows that mild COVID-19 alters brain structure and connectivity in key areas responsible for memory and cognition, emphasizing the lasting effects on young people’s brain health.
In a case-control study published in the journal Translational Psychiatry, researchers used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and cognitive tests to examine brain structure, function, and cognition in adolescents and young adults with mild coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) compared to healthy controls in a pandemic hotspot in Italy. They identified significant changes in brain regions related to olfaction and cognition, with decreased brain volume and reduced functional connectivity in areas like the left hippocampus and amygdala, which were linked to impaired spatial working memory. Notably, no significant differences were observed in whole-brain connectivity, suggesting that these changes were localized rather than widespread.
Background COVID-19, primarily known for respiratory symptoms, also affects the central nervous system, leading to neurological issues like headaches, anosmia, and cognitive changes. MRI-based studies reveal anatomical brain changes in COVID-19 patients, such as reduced gray matter and decreased volume in regions like the hippocampus and amygdala, often linked to cognitive deficits.
While research mostly focuses on severe cases and older adults, a majority of infections with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of COVID-19, occur in adolescents and young adults who also experience long-lasting cognitive symptoms.
This age group, undergoing key brain development, is impacted by changes in spatial working memory and brain structure, which are crucial for cognitive functions shaped by social interactions, significantly disrupted by the pandemic.
Given that this is the largest and most understudied population affected by COVID-19, understanding the brain and cognitive impacts in adolescents and young adults is vital.
Therefore, researchers in the present study compared anatomical, functional, and cognitive outcomes, utilizing a longitudinal design that allowed them to assess both pre- and post-infection differences, in COVID-19-positive and negative adolescents and young adults from Lombardy, Italy, a global hotspot during the pandemic.
About the study The present study involved participants from the Public Health Impact of Metal Exposure (PHIME) cohort, a longitudinal investigation of adolescents and young adults in northern Italy. Between 2016 and 2021, 207 participants, aged 13 to 25 years, were included in a sub-study with MRI scans and cognitive tests. After COVID-19 restrictions were lifted, 40 participants (13 COVID+ and 27 COVID−) participated in a follow-up study, which replicated the MRI and cognitive assessments.
The mean age of participants was 20.44 years and 65% were female. COVID+ status was confirmed through positive reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) tests within 12 months of follow-up. Neuropsychological assessments used the Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB) to evaluate spatial working memory.
MRI and functional MRI data were acquired using a 3-Tesla scanner, processed, and analyzed for structural and local functional connectivity using eigenvector centrality mapping (ECM) and functional connectivity (FC) metrics. Whole-brain functional connectivity metrics showed no significant differences between COVID+ and control groups, indicating that the observed changes were specific to key brain regions rather than generalized across the entire brain.
Statistical analysis involved the use of pairwise Student's t-tests, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, linear regression, two-waves mediation analysis, negative binomial regression, and linear regression, all adjusted for covariates.
Results and discussion Significant differences were observed in the two groups regarding the time between assessments, COVID-19 symptoms, and vaccine status. The research identified five localized functional connectivity hubs with significant differences between the two groups, including the right intracalcarine cortex, right lingual gyrus, left frontal orbital cortex, left hippocampus and left amygdala, which is vital for cognitive functions. Only the left hippocampal volume showed a significant reduction in COVID+ participants (p = 0.034), while whole-brain connectivity remained unchanged, reinforcing the localized nature of the brain changes.
The left amygdala mediated the relationship between COVID-19 and spatial working memory "between errors" (p = 0.028), a critical finding that highlights the indirect effect of amygdala connectivity on cognitive function in COVID+ individuals. This mediation analysis underscores the role of specific brain regions in influencing cognitive deficits, as only the indirect effect was statistically significant for spatial working memory errors. The orbitofrontal cortex, involved in sensory integration and cognitive functions, also showed decreased connectivity in COVID+ individuals, supporting previous findings of structural and functional changes in this region during COVID-19.
The study is limited by small sample size, lack of diversity, potential confounding factors due to the long interval between MRI scans, treatment of certain subjects as COVID-negative based on antibody testing beyond the 12-month threshold, and the possibility of non-significant findings in mediation analysis due to these factors.
Conclusion In conclusion, the findings indicate persistent structural and functional alterations in specific brain regions of COVID-19-positive adolescents and young adults, including changes in gray matter volume and localized functional connectivity, which correlate with diminished cognitive function, particularly in working memory.
Further research is necessary to evaluate the longevity and potential reversibility of these brain and cognitive changes post-infection, enhancing our understanding of post-COVID outcomes and informing future interventions and treatments. The longitudinal design of this study, with pre- and post-COVID data, strengthens these findings by allowing direct comparisons over time, offering robust insights into the impact of COVID-19 on adolescent brain development.
Journal reference: COVID-19 related cognitive, structural and functional brain changes among Italian adolescents and young adults: a multimodal longitudinal case-control study. Invernizzi, A. et al., Translational Psychiatry, 14, 402 (2024), DOI: 10.1038/s41398-024-03108-2, www.nature.com/articles/s41398-024-03108-2
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator#long covid#covid conscious#covid is airborne#wear a fucking mask
151 notes
·
View notes
Text
On the Skidelsky/Fuller post I reblogged, I absolutely welcome automation given the following criteria:
1. The output is identical or, holistically, more positive than human labor output
2. This automation occurs within an economic system in which GDP growth (or similarly fraught metrics) is not the primary objective
3. The automation aids the sustainability of nature and humanity
The USA's agriculture industry is a wonderful example of modern automation failing all three of these criteria. Throughout the entire industrial revolution, agriculture has trended away from being a society-wide confederation of family/community-scale, labor-intensive smallholdings to our current reality of a small number of monolithic industrial farms that are maintained by astoundingly few people who operate increasingly complex and expensive equipment.
Our massive-scale industrial farms are fantastic at what they were designed for; they grow as much of a staple crop as possible without regard to human or environmental health, doing so using minimal labor. Fundamentally, it is an extractive industry. Fossil fuels are extracted to power the machinery, processing, and logistics systems. Nutrients are extracted from the soil to the point that crop growth can only be sustained with heavy amounts of industrial fertilizer input. Entire ecosystems are sacrificed when forests are cleared to be exploited and repeatedly battered with pesticides. This is all primarily to produce soybeans, feed corn, and cotton to then process into products like factory farm livestock feed-slurry, corn syrup, junk food, and sweatshop garments. Secondarily, it is to produce flavorless, nutrition-void produce that can be sold year-round. Consistency is the goal, although one may find that nature itself is curiously inconsistent.
This case study of automation's failings can be traced back to a few major factors:
1. Old-style agriculture work is disagreeable to the USA's perverted fascination for infinite GDP growth; each farm laborer that can be replaced by a machine is a potential worker that could move into a city (or suburb) and put in the same amount of hours at a higher-dollar job. It's just opportunity cost, and this is more-or-less what Skidelsky and Fuller find offensive about our current labor zeitgeist; instead of the now-jobless laborers being free to pursue their interests, they are instead shoehorned into some shitty desk job that produces a relatively greater amount of money to be leeched by executives and shareholders -- this is "more productive" to our economy on the basis of GDP growth and thus must be prioritized over agricultural labor.
2. Industrial approaches to large-scale agriculture are inherently reductive to an extreme extent. Nature is far more complex than Liebig or any other enlightenment thinker ever imagined. Industrialization is great at making cars or computer chips or Gucci jackets or whatever, as these are things that can be standardized with relative ease. Nature cannot be tamed and standardized in a similar way; ecosystems, particularly soil ecosystems, can vary massively even in small areas of the same climate type. Our agriculture systems cope with this simply by ignoring such factors and reducing crop growth to a formula. In X region, plant Y variety of Z crop on A date and apply a regimen of B-type fertilizer and C-type pesticide on D date etc etc. This is the most egregious reduction of something in all of history.
Liebig's reduction of agriculture to the NPK model, just three elements, is good for achieving the singular goal of making your plant of choice come out of the ground, but it ignores all the nuance of soil, climate, and evolution. The other factors don't matter. Modern lab-designed fertilizers often feature a plethora of additional micronutrients, but the goal is still to produce a healthy crop, not healthy soil. Soil itself is an organism, it is something that must be nurtured to be healthy; industrial pesticide/fertilizer regimens are to the soil as feed slurry/antibiotic regimens are to factory farm animals.
Natural processes are, itself, the greatest form of automation for agriculture. Plants and animals that are native to a region have evolved to grow there regardless of human intervention. It is our disruption of these processes that forces agriculture to be labor/resource-intensive. This isn't to say that everyone must immediately abandon all non-native foods and adopt a primarily undomesticated Ötzi diet, but instead, it's worth considering that the complexity of modern technology is not even close to being at parity with the complexity of nature; nature has a several billion year head start. There is no way to flawlessly "tame" it with technological solutions, but a comfortable middle ground can certainly be found.
If sustainable, climate-friendly food production is the primary objective of agriculture, this is far more easily achieved by small, ecology-considerate farms than massive, largely automated industrial farms. A healthy soil ecosystem will aid in growth, flavor, nutrition, and, (quite importantly) carbon sequestration. Broadforking, shoveling, and wheelbarrow-pushing is absolutely more labor intensive than sitting back in a huge John Deere tractor with GPS-based autopiloting features, but the extra labor can turn a woefully extractive process into one that is instead highly regenerative.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blog Post #2! Due 2/06/25
What issues could the concept of “identity tourism” and online anonymity bring to feminist efforts online? (Question based off “Rethinking Cyberfeminism”- J.Daniels)
The lack of “visibility” of one’s identity online can be seen as positive or negative. When thinking of issues, the first thing that comes to mind is the potential of someone using their anonymity to pretend to be someone they are not. While this is not always done for malicious purposes, in the case of feminist movements, this can be done to much detriment. There’s a potential risk of someone posing as leadership and spreading misinformation or acting in a way that puts a negative view on the organization/individual being targeted by this behavior. Additionally, online anonymity makes it incredibly easy for investigation to be done. I would worry about this happening, for example, if a feminist organization was using the internet as a pathway to work around legal/social limitations in real life. Anonymity could provide yet another outlet for bad players to exploit feminist movements.
Why do we continue to rely on automated technology/algorithms in important areas such as law or healthcare despite its continued penchant for error? (Question based off “Automating Inequality” – Eubanks & "Race and Technology" - Nicole Brown)
As Eubanks (2018) went over in her piece, this automated technology is efficient despite its many issues. To the broader public, it seems to be both efficient and effective. I believe that people don’t often question these automated systems, believing them to be sophisticated without a penchant for error. In the context of the broader public, they may not question them because they are used by “official” means. When they do show errors that are biased against POC, I think those errors oftentimes (sadly) fall in line with those same prejudices and thought processes. It reinforces the narratives deeply ingrained in these countries’ thought processes around POC and those who need social services. This only takes people further away from the possibility of questioning algorithms.
Additionally, why hasn’t much effort been made to create better alternatives for these systems or replace them? (Question based off “Automating Inequality” – Eubanks & Nicole Brown)
On top of falling in line with prejudices, another thing that keeps these types of algorithms and systems around is the financial aspects. For example, Nicole Brown mentions the hiring apps that use facial recognition to determine the best candidates. According to Brown (2020), these hiring apps are trained on data sets that are made up mainly of photos of white and male people. A solution to this would be to make a more diverse data set or code a new algorithm that isn’t purely based on photos, right? The problem with these solutions is that they would cost more money—if the system in place already “works” for those it benefits, why would they want to waste money trying to fix it? These algorithms streamline the processes for large businesses and save them money and time at the cost of inaccurate profiling and unbiased opportunities.
How do online spaces reproduce the social structures and biases of the real world? (Question based off Daniels)
In online spaces, the predominance and highlighting of white voices is reflected on different platforms. According to Daniels, online spaces function on the expectation of whiteness. Much like in real life, an overwhelming majority of whiteness in online spaces makes it difficult for others outside of the “dominant” culture being represented to feel comfortable in breaking the mold (Daniels 2009).
Works Cited:
Daniels, J. (2009). Rethinking cyberfeminism(s): Race, gender, and embodiment. Women’s Studies Quarterly.
Brown, N. (2020). Race and technology [Video]. YouTube.
Eubanks, V. (2018). Automating inequality: how high-tech tools profile, police, and punish the poor. St. Martin's Press.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tally Training in Chandigarh: Build a Successful Accounting Career
In today’s fast-paced digital economy, proficiency in accounting software like Tally is no longer optional — it’s a necessity. Whether you’re a student, a working professional, or someone planning a career shift into finance, Tally training in Chandigarh offers a golden opportunity to build a solid foundation in business accounting. With growing business activity in the region, mastering Tally can set you apart in the competitive job market.

Introduction to Tally and Its Relevance
Tally is one of the most widely used business accounting software in India. It simplifies complex financial operations such as invoicing, inventory management, taxation, payroll processing, and financial reporting. Tally ERP 9, the earlier version, was known for its robust features, while Tally Prime — the latest iteration — offers an intuitive interface and smarter navigation for enhanced productivity.
In a country where small and medium enterprises form the economic backbone, Tally plays a critical role in helping businesses maintain compliance and streamline operations. From automating GST filings to tracking stock levels in real time, Tally’s capabilities are deeply aligned with the needs of modern Indian enterprises.
Why Choose Tally Training in Chandigarh?
Chandigarh has steadily grown into a major educational and business center in North India. With its well-connected infrastructure and proximity to Punjab, Haryana, and Himachal Pradesh, it attracts students and professionals from across the region.
The city boasts several reputed training institutes that specialize in job-oriented programs, including Tally training in Chandigarh. These institutes not only provide structured learning but also offer real-world exposure through internships and industry interactions. The business-friendly environment of Tricity — comprising Chandigarh, Mohali, and Panchkula — further enhances placement opportunities for Tally-trained individuals.
Key Features of a Good Tally Training Institute
Selecting the right institute can make a big difference in how effectively you master Tally. Look for the following features when choosing your Tally course:
Certified and experienced trainers ensure you’re learning from professionals who understand both the software and its industry applications. Practical exposure through case studies and real-time projects helps you gain confidence in using Tally in real-world scenarios.
Modern Tally courses now include essential modules like GST compliance, inventory control, payroll processing, MIS report generation, and taxation management. Institutes that regularly update their syllabus in sync with government norms and business trends are more valuable.
Personalized mentorship, flexible batch timings (weekend/evening), and career support services like resume building and mock interviews can significantly enhance your learning experience.
Career Scope After Tally Training
Completing a certified Tally course can unlock a variety of career paths. Common roles include:
Accountant
GST Consultant
Billing Executive
Finance Executive
Audit Assistant
Tally skills are especially in demand in sectors like retail, manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and professional services. Small and mid-sized businesses across the Tricity area consistently hire Tally-certified professionals for daily bookkeeping, tax filing, and reporting.
The average starting salary for a fresher with Tally training ranges from ₹15,000 to ₹25,000 per month, with rapid growth potential as you gain experience and industry exposure.
Tally ERP 9 vs Tally Prime: What You’ll Learn
A well-rounded Tally training program in Chandigarh covers both Tally ERP 9 and the newer Tally Prime. While ERP 9 remains in use across many companies, Tally Prime introduces improved usability with a simplified menu structure, enhanced multi-tasking, and better data tracking.
Key modules you’ll explore include:
Financial Accounting and Ledger Management
Inventory Management and Stock Control
Payroll Setup and Salary Processing
GST and TDS Return Filing
MIS Reports and Business Intelligence
Data Backup and Security Features
You’ll also learn how to use Tally as a business management tool that integrates seamlessly with compliance and audit requirements.
Best Tally Training Institutes in Chandigarh
When choosing an institute, reputation matters. The best Tally training institutes in Chandigarh offer practical curriculum, certified trainers, placement assistance, and flexible learning schedules.
Bright Career Solutions Mohali stands out as a highly rated institute offering in-depth Tally training with practical exposure. With expert faculty, dedicated career support, and strong student feedback, BCS Mohali has become a trusted name in Tally education in the region.
Students regularly highlight the institute’s hands-on training approach, one-on-one mentorship, and successful placement records across local businesses and startups.
FAQs About Tally Courses in Chandigarh
Q. Is Tally useful for non-commerce students? Ans. Yes. Tally is designed to be user-friendly and can be learned by students from non-commerce backgrounds. Institutes usually begin with accounting basics before diving into software-specific training.
Q. What is the typical duration and cost of Tally training? Ans. The duration can range from 1 to 3 months depending on the course level (basic to advanced). Fees generally range from ₹5,000 to ₹15,000. Institutes like BCS Mohali also offer installment plans.
Q. Is a Tally certification necessary to get a job? Ans. While not mandatory, a certification adds credibility to your resume and significantly boosts your chances during hiring. Certified professionals are often preferred for finance and accounts roles.
Conclusion
Tally training in Chandigarh is more than just a short-term course — it’s a launchpad for a rewarding career in finance and accounting. With businesses increasingly relying on Tally for daily operations and compliance, skilled professionals are in high demand.
Whether you’re a student, job seeker, or professional looking to upgrade your skills, enrolling in a Tally course from a reputed institute like Bright Career Solutions Mohali can help you take a decisive step toward career success. The right training, combined with dedication and practice, can turn you into a valuable asset for any business.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thailand SMART Visa
Thailand’s Smart Visa is a specialized visa program designed to attract high-skilled professionals, investors, entrepreneurs, and startup founders to contribute to the country’s growing technology, innovation, and digital economy sectors. Unlike standard work visas, the Smart Visa offers extended stay privileges, streamlined processes, and exemptions from certain bureaucratic hurdles.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of the Thailand Smart Visa, covering its eligibility criteria, benefits, application process, and strategic advantages for foreign talent and businesses.
1. Overview of the Thailand Smart Visa
Launched in 2018 by the Thailand Board of Investment (BOI) and the Digital Economy Promotion Agency (DEPA), the Smart Visa targets individuals in high-value industries, including:
Advanced technology (AI, IoT, robotics, automation)
Digital and tech startups
Research and development (R&D)
Corporate investment in targeted sectors
The visa is structured into four categories:
Smart-T (Talent) – For highly skilled professionals in tech and innovation.
Smart-I (Investor) – For investors in BOI-promoted industries.
Smart-E (Executive) – For senior executives in tech-driven companies.
Smart-S (Startup) – For founders of high-potential startups.
2. Key Benefits of the Smart Visa
The Smart Visa provides significant advantages over traditional Thai work visas:
A. Extended Stay and Multiple Entry
Initial validity of up to 4 years (renewable)
No 90-day reporting requirement (unlike standard visas)
Multiple re-entry permits without additional paperwork
B. Work and Business Flexibility
No work permit required (unlike standard employment visas)
Permission to work for multiple entities (with approval)
Fast-tracked approvals for BOI-backed companies
C. Family and Dependent Privileges
Spouse and children eligible for dependent visas
Spouse permitted to work (subject to approval)
Children allowed to study in Thailand
D. Tax and Investment Incentives
Potential corporate tax exemptions for BOI-approved companies
Personal income tax benefits for qualifying expatriates
3. Eligibility Requirements
Each Smart Visa category has specific qualifications:
A. Smart-T (Talent Visa)
✔ Highly skilled professionals in AI, robotics, biotech, fintech, or digital industries ✔ Minimum salary of 200,000 THB/month (or lower in some cases with BOI approval) ✔ Employed by a Thai company in a BOI-promoted sector
B. Smart-I (Investor Visa)
✔ Minimum investment of 20 million THB in a Thai tech or innovation company ✔ Investment must align with BOI priority sectors
C. Smart-E (Executive Visa)
✔ Senior executives or experts in BOI-promoted companies ✔ Minimum salary of 200,000 THB/month
D. Smart-S (Startup Visa)
✔ Founders of tech startups with funding or accelerator backing ✔ Startup must be registered in Thailand and endorsed by DEPA or BOI
4. Application Process
The Smart Visa application involves multiple steps:
Company or Individual Qualification Check
The employer or investor must ensure eligibility under BOI/DEPA criteria.
Submission to the Smart Visa Unit
Documents include:
Passport copy
Employment contract (for Smart-T/E)
Investment proof (for Smart-I)
Startup business plan (for Smart-S)
Approval and Visa Issuance
Processing time: ~3-4 weeks
Visa issued at a Thai embassy or through an in-country conversion.
5. Strategic Advantages for Foreign Professionals & Businesses
A. Access to Thailand’s Booming Tech Ecosystem
Thailand is rapidly expanding in AI, blockchain, and smart manufacturing, making it a hub for tech talent.
Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) offers infrastructure and tax incentives for tech firms.
B. Easier Compliance Than Standard Work Visas
No work permit renewals or cumbersome paperwork.
Greater mobility for regional business operations.
C. Pathway to Long-Term Residency
Smart Visa holders may qualify for Thailand’s Elite Visa or PR after meeting residency requirements.
6. Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, the Smart Visa has some limitations:
Stringent salary and investment thresholds may exclude mid-level professionals.
BOI/DEPA endorsement required, adding complexity for startups without government backing.
Limited to specific industries, excluding non-tech sectors.
7. Conclusion
The Thailand Smart Visa is a game-changer for high-value expatriates, investors, and entrepreneurs looking to engage with Thailand’s innovation-driven economy. With long-term stay benefits, work flexibility, and tax incentives, it stands out as one of the most attractive visa programs in Southeast Asia.
However, its strict eligibility criteria mean it is best suited for top-tier professionals and well-funded startups. For those who qualify, it provides an unparalleled advantage in Thailand’s competitive tech and business landscape.
For further details, applicants should consult the Thailand Board of Investment (BOI) or the Smart Visa official website.
Final Thoughts
Thailand’s Smart Visa reflects the country’s strategic push toward digital transformation and foreign talent acquisition. As the program evolves, we may see expanded categories and relaxed requirements to attract a broader range of skilled professionals.
#thailand#immigration#immigrationinthailand#thai#thaiimmigration#thaivisa#visa#thailandsmartvisa#smartvisa#visainthailand#thaismartvisa
2 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
🎥 Welcome to our channel! If you’re tired of complicated setups and imprecise results in wheel hub machining, we’ve got you covered. In this video, discover how advanced tool tip detection technology makes your lathe operations more economical, precise, and effortless. Let’s revolutionize your workflow!
Part 1: Why Tool Tip Detection is a Game-Changer
🛠️ Why is tool tip detection essential? Without accurate tool tip detection, you could face: Poor machining quality. Increased material waste.
Higher operational costs due to errors and rework. With cutting-edge detection systems, you’ll achieve:
✅ Consistent precision,
✅ Cost savings,
✅ And faster production cycles!
Part 2: Features of Advanced Tool Tip Detection
✨ What makes this technology a must-have? Economical: Reduces waste and downtime. Cuts costs without sacrificing quality. Precise: Aligns tool tips with sub-millimeter accuracy. Guarantees flawless wheel hub finishes. Effortless Operation: User-friendly interface for all skill levels. Automated calibration saves time and effort. Versatile: Compatible with various lathe machines, including CNC and manual setups.
🔧 Whether it’s for professional manufacturing or small-scale workshops, this tool tip detection system is your key to better results.
Part 3: Step-by-Step Instruction for Tool Tip Detection
📝 How to use the tool tip detection system: Install the Sensor: Attach the detection sensor to your wheel hub lathe. Calibrate the System: Activate the detection feature through the lathe’s interface. The system will automatically align the cutting tool with the workpiece. Verify Alignment: Review the detection results displayed on the screen. Adjust manually if needed. Start Machining: Confidently begin machining, knowing your tool tip is perfectly aligned. This process ensures precision, saves time, and improves efficiency.
Part 4: Real-Life Results: A Workshop Transformation
📊 Case Study: A mid-sized automotive workshop adopted this tool tip detection system and: Reduced machining time by 30%. Lowered material waste by 20%, saving thousands annually. Improved machining precision even for complex wheel hub designs.
Part 5: Conclusion and Call to Action
🚀 Ready to elevate your machining operations? With advanced tool tip detection for wheel hub lathes, you’ll enjoy: Lower costs, Better precision, And effortless operation.
👉 Don’t forget to subscribe for more machining tips and tech updates!
👉 Click the link in the description to learn more about this tool tip detection system and how to get started.
🔗 Learn more here: [Your Website Link or Product Page] #PrecisionMachining #WheelHubLathe #ToolTipDetection #CNCInnovation #MetalProcessing
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
High-Ticket Affiliate Programs: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
High-ticket affiliate marketing represents a strategic approach to generating substantial commissions through the promotion of premium products and services.
Unlike traditional affiliate marketing that focuses on high-volume, low-commission items, high-ticket affiliate programs offer significantly larger earnings per sale, often ranging from $500 to several thousand dollars per transaction.
The primary advantage of pursuing high-ticket affiliate programs lies in their potential for generating meaningful income with fewer sales. For instance, promoting a $2,000 product with a 40% commission yields $800 per sale, equivalent to selling eighty $10 products at a 10% commission rate.
Top High-Ticket Affiliate Programs for Serious Marketers
When evaluating high-ticket affiliate marketing opportunities, several programs stand out for their exceptional earning potential and professional support structures:
Digital Education Platforms
Commission rates: 30-50% per sale
Average product value: $1,000-$3,000
Comprehensive training materials included
Enterprise Software Solutions
Commission rates: 20-40% per sale
Average product value: $2,500-$10,000
Recurring commission opportunities
Enterprise Software Solutions
Commission rates: 15-30% per sale
Average booking value: $5,000-$15,000
Exclusive partnership opportunities
Essential Steps to Start High-Ticket Affiliate Marketing Successfully
Success in high-ticket affiliate marketing requires a strategic approach:
Market Research and Selection Begin by identifying your target audience and understanding their specific needs. High-ticket products require a more sophisticated approach to market analysis, focusing on demographics with substantial purchasing power.
Platform Development Establish a professional online presence through:
A professionally designed website
Authoritative content development
Strategic social media positioning
Relationship Building Develop strong relationships with:
Program vendors
Industry influencers
Potential customers through value-driven content
Advanced Strategies for Promoting High-Ticket Affiliate Products
To maximize success in high-ticket affiliate marketing, implement these advanced strategies:
Content Marketing Excellence Create comprehensive content that demonstrates expertise and builds trust. This includes:
Detailed product reviews
Case studies
Expert interviews
Educational webinars
Email Marketing Automation Develop sophisticated email sequences that:
Nurture potential customers
Provide valuable insights
Build credibility over time
Guide prospects through the decision-making process
Personal Brand Development Establish yourself as an authority in your chosen niche by:
Speaking at industry events
Publishing thought leadership content
Participating in professional networks
Showcasing successful case studies
Success in high-ticket affiliate marketing stems from building genuine relationships and providing substantial value to your audience. Focus on understanding your target market's needs and consistently delivering solutions that address their specific challenges. Remember that while the commission potential is significant, the responsibility to provide accurate, valuable information to your audience is paramount.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Innovate with Confidence: RPA Solutions Tailored for Retail Success
Implementing RPA in inventory management benefits retailers with accurate inventory level tracing, demand and supply forecasting, as well as by streamlining communication, between all suppliers.
RPA software technology can benefit any retail organization with proper discovery, mapping, and deployment. The bots can be used for more than just tracking inventories, sending out notifications, and transferring data across systems.

Embrace innovation with RPA solutions designed for retail. Optimize inventory management, enhance efficiency, and stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
#inventory management analytics#retail inventory management#RPA solution for retail#RPA in retail Industry#RPA For Inventory Management#inventory management#RPA in inventory management#Inventory management in retail industry#RPA implementation#RPA service providers#rpa in retail management#use cases of rpa in retail#rpa in retail#Robotic Process Automation in Retail#rpa for retail#rpa in retail sector#Robotic Process Automation in Retail Industry#rpa retail#rpa case studies in retail#Robotic Process Automation in Trade Promotion
0 notes
Text

Bright Crown is a highly experimental orbital iterator project. They were built in space in order to study and make use of conditions there.
A lot of words about their structure and how it works under the cut:
Their facility is consists of three main portions: the outer 'habitable' ring, a second concentric 'conduit' ring, and the central neural core.
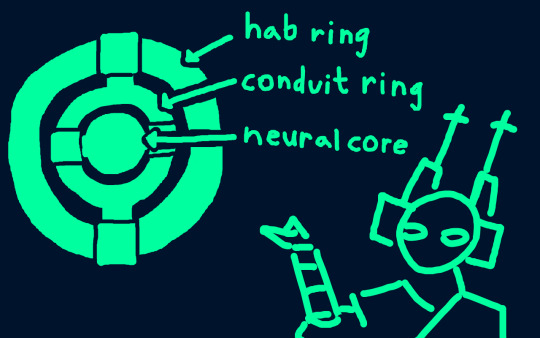
Normally, the entire structure rotates along the outer/hab ring, in order to generate centrifugal artificial gravity (which is far more efficient than using gravity cores). This is particularly important, because the hab ring is home to an ecosystem of purposed organisms. These are designed to automate many processes, such as waste recycling, maintenance, handling of inbound supplies, etc. In times past, small research teams also lived in the hab ring.

Skipping the conduit ring for the moment, the neural core is where most of the stuff you'd normally expect to find in an iterator is located: neurons, processing strata, memory conflux, all those parts which actually form the brain of the iterator. And of course the focal puppet chamber.
Since the neural core is at the center of the spinning structure, it is not affected much by the centrifugal artificial gravity. Therefore, it can effectively utilize the natural low gravity environment as opposed to maintaining a constant antigravity field, as land-based iterators do. Additionally, heat sinks radiate heat directly into the vacuum of space, eliminating the need to use water as coolant.
However, water is still needed for use by the internal biological processors and neural tissue. Thus we arrive at the conduit ring, placed in between the hab ring and the neural core.
Without luxuries such as atmosphere and the ground, water on Bright Crown must operate on an artificial closed system. The conduit ring is a series of pipes, filters, and reservoirs intended to form a rough equivalent to the natural land-based water cycle.
Each section can pivot independently of the other sections and the overall spin of the station. While idle, the conduit ring spins slowly on its pivot (this helps it process water).
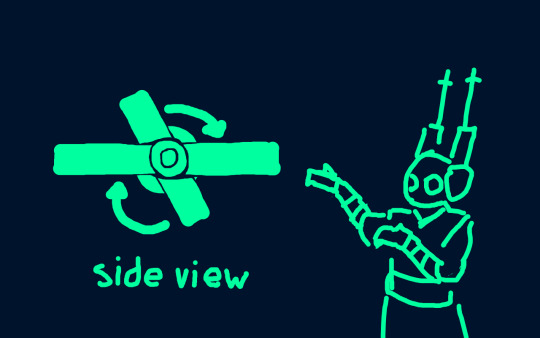
Bright Crown follows a similar cycle system as land iterators, where water is 'expelled' at regular intervals; only in this case the water is expelled into the conduit ring rather than the atmosphere. When enough water has been used, the conduit ring locks onto the neural core, and the entire station begins spinning along the conduit ring instead. The same method of artificial gravity is thus used to push the water out of the neural core, flooding the conduit ring.

But, keep in mind, the conduit ring could be at any point in its rotation when a flush cycle begins. Changing the spinning direction of the entire structure disrupts the hab ring's artificial gravity, and would generally not be great for anything living there (it would throw them around like they're in a giant washing machine). So there are shelter areas throughout the hab ring which are protected by antigravity cores, which suppress the spinning forces.
#i'm not sure if that's how physics works but at least it's sorta plausible? maybe?#also let me know if the green is too bright/diagrams are hard to read#rain world#rw#rain world art#rw art#rain world iterator#rain world oc#bright crown#my art#singularscissor
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
if I/we made a blog to share terms and infodumps¹ from our major-related classes², ¿would y’all be interested & follow it?
(¹ and potentially ¿list some research papers/informational books on certain topics?)
(² which are Psychology & Human Development; ✨scary social sciences✨ (/lighthearted))
clarifying, we can’t legally share PPT slides or disclose stories with other students’ or professors’ identifying information.
but we can synthesize, share snippets/quotes, & infodump about what a topic of discussion led us to wonder / research, or what sparked a desire to add to research/what we want to research because of what we learned³.
(³ we want to, eventually*, be a researcher. there is a massive gap in HD/psych on neurodivergent & LGBT+ development & differences, & with the current research we don’t know where Complex-PTSD and ADHD begin/end with one another. I/we have so many unanswered questions that need new researchers to answer, so we’re gonna become a new researcher)
(* here/now to & through grad school is a long time 😭 so much schooling, so far to go— but like...the chance to add to the research... 👀🥺)
(** ¿is there actually overlap (or significant overlap), or is it because our society/societies currently don’t produce non-traumatized ADHDers/neurodivergent folks? what does neurodivergence look like without trauma? we don’t know yet.)
✨🎵🎶✨
¿why is this coming up now? here’s some shares/infodumps of what sparked it today 😅💜
🎵
quotes that stand out:
“Humans are not thinking creatures that can feel; we are feeling creatures that can think.” (Dr. R)
“You can sacrifice morality for membership.” (Dr. R)
“We never stop becoming who we are.” (Dr. R)
“We nurture nature.” (Dr. R and Dr. W, at separate times & in different contexts)
“Just because a relationship doesn’t last doesn’t mean it was pointless or it failed. It still meant something; it still influenced who you are and who you want to become.” (Dr. R)
“I don’t believe you were ever so bad that you deserved to be hurt.” (Dr. W)
((yes most of these are Dr. R, as she is more likely to go on tangents (/affectionate), but both of them say impactful things. I’m also leaving out a couple quotes from both of them; these hit me/us the hardest.))
🎶
~~~~
🎵
some concepts/curiosities from this week (cutting off because this part will be long):
(1) Theory Of Mind. ¿Is this why “neurotypical” people say we (neurodivergent, especially autistic/ADHD) lack empathy? ¿Because we struggle with Theory Of Mind?
(2) Theory Of Mind seems to be an almost automated process for mid-adolescents up (about 14 or 15 onward), if they are “neurotypical”/“normative”. In my experience as an auDHDer, this is a manual process I have to walk myself through, and it’s a lot of steps. ¿Do neurodivergent folks typically do this manually/slower, or is that a me thing (or disability impact)?
(3) (this week) From the conversations I’ve had with older classmates & our parents, it seems like people roughly 40+ years old were told “you are [insert identity]” as a concrete, non-negotiable fact. This especially applies to gender identity¹ and sexuality². This leads to what psych/HD call “identity foreclosure”, which means you are highly committed to an identity but haven’t explored other options. In this case, we see it manifest as defensiveness or even aggression if their gender identity &/or sexual/romantic orientation are called into question. The people who felt comfortable disclosing said they feel the need to panic because that was “the one thing [they] didn’t have to question” as they navigated identity formation, so it was the only thing they felt they could count on even when everything else changed (e.g. transition to parenthood).
I don’t have a question or direction to this, but I find it fascinating. ¿Maybe this is a future avenue of study (& maybe future trauma therapy for older adults)?³
(¹ as tied to biological sex - e.g. “you’re a man because you were born male”)
(² you are straight because that is the only option/the only safe option; you are bad/need to panic if you find someone of the same biological sex attractive)
(³ I’m not saying this applies to every single human to live across all cultures & time. But it’s a trend I’ve noticed, & I’m curious to see in which populations & under what circumstances this occurs most.)
(4) One of our professors today made an important distinction that little kids* sometimes “say something factually incorrect”, but cognitively lack the foundations to lie. (In order to lie, you need Theory of Mind. Defining that is a separate tangent.)
(* barely speaking to around 5yo in “normative” development)
This led to a definition of lying (by the social science community) that I’ve never heard before, but made so much sense afterwards: “Lying is when you say something factually incorrect because you understand the other person will act on the incorrect information. You lie in the hopes of eliciting a particular response.”
Usually little kids lie because they are learning & testing Theory Of Mind. ”¿Do you really not know what I do?”
Older kids, teens, adults tend to lie when they don’t trust someone. “If I tell the truth, you might...” (abandon me, hurt me, laugh at me, etc.). That can be because they actually have reason to worry (maybe that person has established an unsafe pattern), or because trauma or because PTSD or another mental illness (anxiety, etc.) makes it difficult to trust people.
That’s not to say that people don’t lie to manipulate (/neg) others. Some people do lie because they see relationships as transactional and want something out of you, or because they want to benefit from or use something you are/have. Some people lie about their income so they can splurge on a fun new toy**, or lie about how much money/resources they have so you’ll hand over some of yours. Some people do lie to hurt others or to unfairly gain from them.
(** or, personal anecdote from my family, lie about the amount of a paycheck so they can secretly spend $300 on a small business license)
But the people I/we know who lie the most are lying because they feel unsafe.
They lie to their romantic/sexual partner because they feel like love will be rescinded if they tell the truth. They lie to a friend that they’re okay because they feel like they will be criticized/a burden if they open up.
The expectation of harm/abandonment, the anticipation of pain, the emotional response of feeling unsafe, these are valid. The conclusions based on them may or may not be true.
(In simpler terms, their emotions are real & their trauma is valid, but the people they apply this experience/these emotions to may be different. They may feel like their romantic partner will rescind love if they admit they’re struggling, but later find out their partner wants to support them through that struggle & begin to heal through/grow out of those expectations.)
🎶
~~~~
✨🎶🎵✨
That was quite a long one but,, yeah. I’m thinking a lot about Theory of Mind today, & its role in trauma/neurodivergence & lying, as well as lying as a concept.
If anyone got this far/enjoyed this, please let me/us know.
I may still make a blog anyway, but wanna assess potential interest throughout the hellsite (/affectionate) & especially among my followers/mutuals (who will likely see some of those posted reblogged/engage more often than most).
#psychology#theory of mind#psychological theory#healing#healing from trauma#infodump#special interest#~Nico#potential blog#social science#human development#empathy#identity#psychology of lying#lies#lying#pondering#wondering#excited#intrigued#identity foreclosure#full time student#university#university student#college#actually autistic#neurodivergent#actually adhd
3 notes
·
View notes