#pest control in food industry
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Is Your Restaurant Under Threat from Pests? Discover Tailored Pest Control Solutions!
Are you involved in the food industry? Then you're likely aware of the significant challenges pests can pose to your establishment. But fret not! At Protech Pest Control, we specialize in providing comprehensive pest control services specifically designed for restaurants. Whether your commercial kitchen is battling cockroaches, flies, mosquitoes, or rats, we have the solutions tailored to your needs.
Why Pest Control is Crucial for the Food Industry:
Greatly reduces the risk of pest infestation.
Maintain the quality and safety of your food products.
Safeguards your brand reputation.
Why Choose Us?
Our treatments are guaranteed to be 100% effective.
Enjoy free advice and quotes from our experts.
We are proud members of the National Pest Management Association (NPMA).
We employ eco-friendly treatment methods.
We offer cost-effective, personalized solutions for pest control in the food industry, utilizing a holistic approach. Contact us today at 1300 486 149 to ensure the protection of your food establishment!
0 notes
Text
Navigating Pest Control: A Food Industry Guide by Pest Control Experts
As pest control experts dedicated to supporting the food industry, we understand the unique challenges and high stakes involved in maintaining a pest-free environment. Our experience has shown us time and again that effective pest management is not just about dealing with infestations as they arise; it’s about creating a comprehensive strategy that addresses both immediate concerns and long-term prevention. Here, we outline the critical benefits and strategies for food business owners to mitigate risks and safeguard their establishments.
Proactive Health and Safety Measures
The presence of pests in any food-related business poses significant health risks, from foodborne illnesses to contamination. As experts, our first and foremost goal is to ensure the health and safety of your customers and staff. Implementing regular, professional pest inspections and treatments eliminates potential hazards, ensuring compliance with health regulations and maintaining the highest standards of hygiene.
Safeguarding Your Reputation Against Pests

In the digital age, a single negative experience can escalate rapidly, causing lasting damage to your business’s reputation. Effective pest control is invisible yet impactful, working silently in the background to ensure that your establishment remains synonymous with quality and cleanliness. By partnering with pest control professionals, you’re not just investing in services; you’re investing in your brand’s reputation and customer trust.
Financial Protection and Efficiency
The cost of an unaddressed pest infestation can be exorbitant, from the loss of stock and revenue to potential fines and structural repairs. Our approach to pest control emphasizes not only the eradication of existing pests but also the prevention of future infestations. This strategic focus helps avoid unexpected expenditures, ensuring that your financial resources are directed towards growing your business rather than mitigating avoidable crises.
Ensuring Business Continuity – Don’t let Pests ruin your business!
An infestation can disrupt your operations, leading to temporary closures and loss of revenue. Our pest control services are designed to minimize disruptions, allowing you to continue providing your services without interruption. Regular maintenance and monitoring form the cornerstone of our approach, ensuring that your business remains operational and your customers are satisfied.
Regulatory Compliance and Excellence
Adherence to regulatory standards is non-negotiable in the food industry. Our pest control solutions are tailored to not only meet but exceed these standards, ensuring that your business remains compliant and avoids potential legal complications. By staying ahead of regulations and adopting best practices, your business can demonstrate industry leadership and commitment to excellence.
Employee Well-being and Productivity
A pest-free environment contributes significantly to your staff’s overall well-being and morale. Knowing that their workplace is safe and hygienic enhances employee satisfaction and productivity, directly impacting the quality of service they provide to your customers. Our comprehensive pest control programs address this aspect, ensuring a positive and healthy work environment for your team.
Customized Pest Control Strategies
Understanding that each food business is unique, we offer customized pest control strategies tailored to your specific needs and challenges. From initial assessments to the implementation of targeted solutions, our focus is on providing effective, sustainable pest management plans that align with your business objectives.
Conclusion
Effective pest control is a critical component of running a successful food business. It goes beyond mere compliance, touching on every aspect of your operation, from protecting public health to ensuring business continuity and financial stability. As pest control professionals, we are committed to providing expert guidance and solutions, empowering you to maintain a safe, reputable, and thriving business in the food industry.
To food business owners navigating the complexities of pest management, remember that you’re not alone. Partnering with pest control experts offers not just a solution to a problem but a pathway to peace of mind and business excellence. Let’s work together to keep your establishment safe, compliant, and prosperous.
0 notes
Text
Ultimate Guide For Pest Control In The Food Industry

Pest Control in Food Industry Facilities refers to controlling, managing, and removing pests. Pest control management in food industry establishments is focused on ensuring that pests do not have access to a food facility in any way. It involves implementing various control methods and procedures that ensure pests cannot enter and contaminate food products and surfaces. Common pests that industry professionals should be concerned about include cockroaches, flies, rodents, ants, birds, and, inadvertently, employees.
The Importance Of Pest Control In The Food Industry
All pests are drawn to food and moisture. Even the smallest morsel left out can bring pests like cockroaches, flies, ants, and rodents; and once they come, it can be difficult to get rid of them. It isn’t just a nuisance for food industry professionals — it is a serious issue.
Pests can: a. Carry various diseases and bacteria: Rodents can transmit diseases like salmonellosis and hantavirus, while cockroaches can trigger allergy and asthma symptoms. They aren’t the only disease-carrying pests; flies and other insects also carry harmful diseases and bacteria that can lead to serious illness.
Cause property damage:Pests, particularly rodents, can cause serious property damage. This includes eating through containers, electrical wires, and more.
Spread contamination:As mentioned before, pests are disease carriers. Everything they touch is subject to contamination, which risks staff and consumers’ health.
Cause reputation damage:No consumer wants to see pests or hear rumours that you have pest issues. If this happens, they will lose their trust in you and your establishment, and you may find yourself with a visit from a health inspector.
Can lead your business to shut down:If you don’t deal with pest issues properly and promptly, you can find your business shut down temporarily or permanently.
Pest Control Methods in Food Industry Setups
When understanding how to control pests in food industry establishments, it is important to recognize that no single pest control method exists. Establishments should implement a full pest control program that uses various methods and procedures for prevention. Some of the pest control procedures in the food industry include:
Seal Any Gaps, Cracks, and Holes:Pests don’t need a big opening to get inside a facility. Even the smallest gap, which someone may deem inconsequential, can be an entry point for pests. It is crucial to seal these gaps to prevent the potential entry of various pests.
Inspect All Food Deliveries:Food deliveries provide another opportune moment for pests to enter a food establishment. Employees in charge of accepting food shipments must take the time to scrutinize each delivery. They should look for visible signs of pests.
Maintain a Clean Facility:The most important and most effective way to control pests in a food establishment is to maintain a clean facility. Even the smallest amount of food residue can attract pests, so taking the time to thoroughly clean and sanitize your floors and food contact surfaces will help to eliminate residue, so there is nothing for pests to find. Have a checklist of what cleaning tasks employees should be completing at the end of the day, and check to ensure that they are completing tasks as expected.
Don’t Leave Water Standing:Standing water has many negative effects, inside and out. Besides being damaging to your property and a safety hazard, it can serve as a breeding ground for bacteria and harmful pathogens. It can also attract pests, particularly disease-carrying flies, who lay their eggs in this water. Once these pests have taken root, they can be difficult to eliminate without professional help.
Don’t Overlook the Importance of Pest Control
Food safety is a multifaceted issue that needs to be treated with a certain level of severity. Many different things can impact food safety and sanitation, and one of them includes pests. You never want to overlook the importance of pest control in food industry facilities and establishments. Pests carry many diseases and pathogens that can ruin your food and create serious health issues among staff and consumers.
Ultima Search has successfully ensconced itself in the pest control industry as a business of repute after having provided expert pest control services and products for over a decade. We take it upon ourselves to ensure that your homes, offices and commercial installations are sanitised and healthy thereby providing a sense of well-being and happiness whenever you call upon us.
Discover Residential and Commercial Pest Control Services and Products, by Ultima Search, the Best pest control management company in Mumbai.
0 notes
Text
Training Audit ISO 22000 : 2018 – Sistem Manajemen Keamanan Pangan (FSMS)
Sistem Manajemen Keamanan Pangan (FSMS) Berdasarkan ISO 22000 Sistem Manajemen Keamanan Pangan (Food Safety Management System/FSMS) adalah hal yang krusial dalam industri pangan. ISO 22000:2018 adalah standar internasional yang memberikan kerangka kerja untuk mengidentifikasi, mengendalikan, dan mengurangi risiko yang terkait dengan keamanan pangan. Training Audit ISO 22000:2018 dirancang untuk…

View On WordPress
#Harga Pelatihan Codex HACCP#Harga Pelatihan Codex HACCP Versi 2020#Harga Pelatihan Food Safety#Harga Pelatihan GLP#Harga Pelatihan GMP#Harga Pelatihan HACCP#Harga Pelatihan Industri Pangan#Harga Pelatihan ISO 22000#Harga Pelatihan Keamanan Pangan#Harga Pelatihan Pest Control#Harga Training Codex HACCP#Harga Training Codex HACCP Versi 2020#Harga Training Food Safety#Harga Training GLP#Harga Training GMP#Harga Training HACCP#Harga Training Industri Pangan#Harga Training ISO 22000#Harga Training Keamanan Pangan#Harga Training Pest Control#Inhouse Training Codex HACCP#Inhouse Training Codex HACCP Versi 2020#Inhouse Training Food Safety#Inhouse Training GLP#Inhouse Training GMP#Inhouse Training HACCP#Inhouse Training Industri Pangan#Inhouse Training ISO 22000#Inhouse Training Keamanan Pangan#Inhouse Training Pest Control
0 notes
Text
Introduction To Supporting Sustainable Agriculture For Witches and Pagans

[ID: An image of yellow grain stocks, soon to be harvested. The several stocks reach towards a blurred open sky, focusing the camera on he grains themselves. The leaves of the grains are green and the cereals are exposed].
PAGANISM AND WITCHCRAFT ARE MOVEMENTS WITHIN A SELF-DESTRUCTIVE CAPITALIST SOCIETY. As the world becomes more aware of the importance of sustainability, so does the duty of humanity to uphold the idea of the steward, stemming from various indigenous worldviews, in the modern era. I make this small introduction as a viticulturist working towards organic and environmentally friendly grape production. I also do work on a food farm, as a second job—a regenerative farm, so I suppose that is my qualifications. Sustainable—or rather regenerative agriculture—grows in recognition. And as paganism and witchcraft continue to blossom, learning and supporting sustainability is naturally a path for us to take. I will say that this is influenced by I living in the USA, however, there are thousands of groups across the world for sustainable agriculture, of which tend to be easy to research.
So let us unite in caring for the world together, and here is an introduction to supporting sustainable/regenerative agriculture.
A QUICK BRIEF ON SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE
Sustainable agriculture, in truth, is a movement to practise agriculture as it has been done for thousands of years—this time, with more innovation from science and microbiology especially. The legal definition in the USA of sustainable agriculture is:
The term ”sustainable agriculture” (U.S. Code Title 7, Section 3103) means an integrated system of plant and animal production practices having a site-specific application that will over the long-term:
A more common man’s definition would be farming in a way that provides society’s food and textile needs without overuse of natural resources, artificial supplements and pest controls, without compromising the future generation’s needs and ability to produce resources. The agriculture industry has one of the largest and most detrimental impacts on the environment, and sustainable agriculture is the alternative movement to it.
Sustainable agriculture also has the perk of being physically better for you—the nutrient quality of crops in the USA has dropped by 47%, and the majority of our food goes to waste. Imagine if it was composted and reused? Or even better—we buy only what we need. We as pagans and witches can help change this.
BUYING ORGANIC (IT REALLY WORKS)
The first step is buying organic. While cliche, it does work: organic operations have certain rules to abide by, which excludes environmentally dangerous chemicals—many of which, such as DDT, which causes ecological genocide and death to people. Organic operations have to use natural ways of fertilising, such as compost, which to many of us—such as myself—revere the cycle of life, rot, and death. Organic standards do vary depending on the country, but the key idea is farming without artificial fertilisers, using organic seeds, supplementing with animal manure, fertility managed through management practices, etc.
However, organic does have its flaws. Certified organic costs many, of which many small farmers cannot afford. The nutrient quality of organic food, while tending to be better, is still poor compared to regeneratively grown crops. Furthermore, the process to become certified organic is often gruelling—you can practise completely organically, but if you are not certified, it is not organic. Which, while a quality control insurance, is both a bonus and a hurdle.
JOINING A CSA
Moving from organic is joining a CSA (“Community supported agriculture”). The USDA defines far better than I could:
Community Supported Agriculture (CSA), one type of direct marketing, consists of a community of individuals who pledge support to a farm operation so that the farmland becomes, either legally or spiritually, the community’s farm, with the growers and consumers providing mutual support and sharing the risks and benefits of food production.
By purchasing a farm share, you receive food from the farm for the agreed upon production year. I personally enjoy CSAs for the relational aspect—choosing a CSA is about having a relationship, not only with the farmer(s), but also the land you receive food from. I volunteer for my CSA and sometimes I get extra cash from it—partaking in the act of caring for the land. Joining a CSA also means taking your precious capital away from the larger food industry and directly supporting growers—and CSAs typically practise sustainable and/or regenerative agriculture.
CSAs are also found all over the world and many can deliver their products to food deserts and other areas with limited agricultural access. I volunteer from time to time for a food bank that does exactly that with the produce I helped grow on the vegetable farm I work for.
FARM MARKETS AND STALLS
Another way of personally connecting to sustainable agriculture is entering the realm of the farm stall. The farmer’s market is one of my personal favourite experiences—people buzzing about searching for ingredients, smiles as farmers sell crops and products such as honey or baked goods, etc. The personal connection stretches into the earth, and into the past it buries—as I purchase my apples from the stall, I cannot help but see a thousand lives unfold. People have been doing this for thousands of years and here I stand, doing it all over again.
Advertisement
Farmers’ markets are dependent on your local area, yet in most you can still develop personal community connections. Paganism often stresses community as an ideal and a state of life. And witchcraft often stresses a connection to the soil. What better place, then, is purchasing the products from the locals who commune with the land?
VOLUNTEERING
If you are able to, I absolutely recommend volunteering. I have worked with aquaponic systems, food banks, farms, cider-making companies, soil conservation groups, etc. There is so much opportunity—and perhaps employment—in these fields. The knowledge I have gained has been wonderful. As one example, I learned that fertilisers reduce carbon sequestration as plants absorb carbon to help with nutrient intake. If they have all their nutrients ready, they do not need to work to obtain carbon to help absorb it. This does not even get into the symbiotic relationship fungi have with roots, or the world of hyphae. Volunteering provides community and connection. Actions and words change the world, and the world grows ever better with help—including how much or how little you may provide. It also makes a wonderful devotional activity.
RESOURCING FOOD AND COOKING
Buying from farmers is not always easy, however. Produce often has to be processed, requiring labour and work with some crops such as carrots. Other times, it is a hard effort to cook and many of us—such as myself—often have very limited energy. There are solutions to this, thankfully:
Many farmers can and will process foods. Some even do canning, which can be good to stock up on food and lessen the energy inputs.
Value-added products: farms also try to avoid waste, and these products often become dried snacks if fruit, frozen, etc.
Asking farmers if they would be open to accommodating this. Chances are, they would! The farmer I purchase my CSA share from certainly does.
Going to farmers markets instead of buying a CSA, aligning with your energy levels.
And if any of your purchased goods are going unused, you can always freeze them.
DEMETER, CERES, VEIA, ETC: THE FORGOTTEN AGRICULTURE GODS
Agricultural gods are often neglected. Even gods presiding over agriculture often do not have those aspects venerated—Dionysos is a god of viticulture and Apollon a god of cattle. While I myself love Dionysos as a party and wine god, the core of him remains firmly in the vineyards and fields, branching into the expanses of the wild. I find him far more in the curling vines as I prune them than in the simple delights of the wine I ferment. Even more obscure gods, such as Veia, the Etruscan goddess of agriculture, are seldom known.
Persephone receives the worst of this: I enjoy her too as a dread queen, and people do acknowledge her as Kore, but she is far more popular as the queen of the underworld instead of the dear daughter of Demeter. I do understand this, though—I did not feel the might of Demeter and Persephone until I began to move soil with my own hands. A complete difference to the ancient world, where the Eleusinian mysteries appealed to thousands. Times change, and while some things should be left to the past, our link to these gods have been severed. After all, how many of us reading know where our food comes from? I did not until I began to purchase from the land I grew to know personally. The grocery store has become a land of tearing us from the land, instead of the food hub it should be.
Yet, while paganism forgets agriculture gods, they have not forgotten us. The new world of farming is more conductive and welcoming than ever. I find that while older, bigoted people exist, the majority of new farmers tend to be LGBT+. My own boss is trans and aro, and I myself am transgender and gay. The other young farmers I know are some flavour of LGBT+, or mixed/poc. There’s a growing movement for Black farmers, elaborated in a lovely text called We Are Each Other’s Harvest.
Indigenous farming is also growing and I absolutely recommend buying from indigenous farmers. At this point, I consider Demeter to be a patron of LGBT+ people in this regard—she gives an escape to farmers such as myself. Bigotry is far from my mind under her tender care, as divine Helios shines above and Okeanos’ daughters bring fresh water to the crops. Paganism is also more commonly accepted—I find that farmers find out that I am pagan and tell me to do rituals for their crops instead of reacting poorly. Or they’re pagan themselves; a farmer I know turned out to be Wiccan and uses the wheel of the year to keep track of production.
Incorporating these divinities—or concepts surrounding them—into our crafts and altars is the spiritual step towards better agriculture. Holy Demeter continues to guide me, even before I knew it.
WANT CHANGE? DO IT YOURSELF!
If you want change in the world, you have to act. And if you wish for better agriculture, there is always the chance to do it yourself. Sustainable agriculture is often far more accessible than people think: like witchcraft and divination, it is a practice. Homesteading is often appealing to many of us, including myself, and there are plenty of resources to begin. There are even grants to help one improve their home to be more sustainable, i.e. solar panels. Gardening is another, smaller option. Many of us find that plants we grow and nourish are far more potentant in craft, and more receptive to magical workings.
Caring for plants is fundamental to our natures and there are a thousand ways to delve into it. I personally have joined conservation groups, my local soil conservation group, work with the NRCs in the USA, and more. The path to fully reconnecting to nature and agriculture is personal—united in a common cause to fight for this beautiful world. To immerse yourself in sustainable agriculture, I honestly recommend researching and finding your own path. Mine lies in soil and rot, grapevines and fruit trees. Others do vegetables and cereal grains, or perhaps join unions and legislators. Everyone has a share in the beauty of life, our lives stemming from the land’s gentle sprouts.
Questions and or help may be given through my ask box on tumblr—if there is a way I can help, let me know. My knowledge is invaluable I believe, as I continue to learn and grow in the grey-clothed arms of Demeter, Dionysos, and Kore.
FURTHER READING:
Baszile, N. (2021). We are each other’s harvest. HarperCollins.
Hatley, J. (2016). Robin Wall Kimmerer. Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous wisdom, scientific knowledge and the teachings of plants. Environmental Philosophy, 13(1), 143–145. https://doi.org/10.5840/envirophil201613137
Regenerative Agriculture 101. (2021, November 29). https://www.nrdc.org/stories/regenerative-agriculture-101#what-is
And in truth, far more than I could count.
References
Community Supported Agriculture | National Agricultural Library. (n.d.). https://www.nal.usda.gov/farms-and-agricultural-production-systems/community-supported-agriculture
Navazio, J. (2012). The Organic seed Grower: A Farmer’s Guide to Vegetable Seed Production. Chelsea Green Publishing.
Plaster, E. (2008). Soil Science and Management. Cengage Learning.
Sheaffer, C. C., & Moncada, K. M. (2012). Introduction to agronomy: food, crops, and environment. Cengage Learning.
Sheldrake, M. (2020). Entangled life: How Fungi Make Our Worlds, Change Our Minds & Shape Our Futures. Random House.
Sustainable Agriculture | National Agricultural Library. (n.d.). https://www.nal.usda.gov/farms-and-agricultural-production-systems/sustainable-agriculture
#dragonis.txt#witchcraft#paganism#hellenic polytheism#witchblr#pagan#helpol#hellenic pagan#hellenic worship#hellenic paganism#hellenic polytheist#demeter deity#demeter worship#persephone deity#kore deity#raspol#etrupol#etruscan polytheist#etruscan polytheism#rasenna polytheism#rasenna polytheist#rasenna paganism
321 notes
·
View notes
Text
today's topic: that fucker RoundUp
It's time for more Don't Believe Everything You Read with me, elljayvee!
A friend encountered this the other day:

This contains a lot of false information and should not be spread around as true. It's scaremongering in the first half and almost entirely wrong in the second half.
I will state my credentials and biases up front: I am an inactive Penn State Master Gardener (which means I have all the education and credentials, but am not currently an active volunteer), I have a permaculture design certificate and an active permaculture garden on my property, and I'm an agriculture & food systems researcher. I also fucking hate RoundUp (aka glyphosate), which I think is very bad, especially at industrial scales. I pretty much think all agricultural inputs have serious problems at industrial scales; RoundUp isn't special. In general, and particularly for home-scale or small-scale ag use, I prefer non-chemical controls; in my own garden I use manual control for all weeds except for poison ivy and tree of heaven, for which I use 2,4-D foliar herbicide. 2,4-D is also pretty nasty stuff, but I use it because unlike RoundUp it's very widespread in my environment already -- some of my neighbors have their lawns sprayed and that's what the lawn companies use. Me spraying a stray tree of heaven once a year isn't even a drop in the 2,4-D bucket of the block.
Let us take these pieces of Wrong Information from back to front!
Dish soap: people love dish soap in the garden. Just love it. There's mixed evidence on what it can do in the garden but it's completely ineffective against weeds -- the reason it's so popular in garden applications is that it doesn't harm plants. How is something that doesn't harm plants going to be good weed control? Answer: it isn't. It does nothing against weeds. The one thing dish soap is proven to be good at is assisting with aphid control -- the best aphid control is manual/physical control, like blasting aphids off plants with water, and dish soap assists with that and also seems to do some damage to the aphid. Any other pest control involving "soap" almost certainly means "insecticidal soap", not dish soap.
Takeaway: Unless you're trying to control aphids, don't use dish soap in the garden. (And make sure it's dish SOAP, not a detergeant. In the US, original Dawn is the go-to.) For anything but aphid control, you're just wasting soap.
Salt: No. This is bad. It will definitely help kill some weeds, but it's a bad idea. Don't put extra salt into soil. It's bad for the soil and for the inhabitants of soil; it's bad for water. One cup of salt isn't going to kill a river or a stream or whatever but if you're worried about killing animals, let's just say that poor innocent things like amphibians and worms do not do well in hypersaline environments. Do not use table salt like this.
Takeaway: Leave table salt out of your garden altogether. You're just wasting salt, messing up soil, and hurting animals.
Vinegar: This is completely fine. Depending on the species of weed you have, it may work very well indeed. However, household white vinegar is only about 5% acetic acid, while horticultural vinegar -- which is sold as a weed killer commercially -- is 20% acetic acid, and works MUCH better on a MUCH wider variety of weeds. It also seems to work best when it is mixed with canola oil. Horticultural vinegar is not as safe for your skin/eyes/etc. and you should follow the safety instructions on the bottle when you use it. If you would like some more information on how well vinegar works to control weeds, you may enjoy reading "Impact of Acetic Acid Concentration, Application Volume, and Adjuvants on Weed Control Efficacy" (Webber et al. 2018).
Takeaway: Household vinegar in the garden is fine and may work for some species of weeds. Horticultural vinegar works better. Follow safety information when using it.
Now for RoundUp (aka glyphosate).
RoundUp will kill pollinators, bees, hives: I will include all invertebrates that seem affected by RoundUp spray in this category. There is good evidence that AT INDUSTRIAL SCALE, RoundUp negatively affects pollinators and other beneficial invertebrates, such as pest-controlling spiders. When applied to a broad area in heavy concentrations, it seems to have lethal effects (particularly in bees who ingest it or come into physical contact with it), and it also seems interfere with reproduction in some bees, wasps, and spiders.
"Is glyphosate toxic to bees? A meta-analytical review" (Battisti et al 2021) is a good meta-analysis about toxicity to various bee species. (It is paywalled, sorry -- but some of its sources are not.) This analysis found that it's easy for bees to get a fatal dose from pollen from sprayed flowers, physical contact with sprayed flowers, or ingestion of nectar from sprayed flowers. At individual garden scale, you are extremely unlikely to harm more than a few individual insects unless you're doing something very weird, like, I don't know, pouring a whole bottle of RoundUp over your patio, or specifically filling flowers with drops of RoundUp.
Takeaway: In general, I recommend not using RoundUp in your garden. If you do use RoundUp, snip off flowers from the weeds or do not spray the flowers, to avoid pollen contamination and lower the likelihood of bees touching the RoundUp. I strongly suggest instead using manual controls, which is what I do -- I weedwhack and hand-pull weeds (again, with the exception of poison ivy and tree of heaven).
RoundUp will kill your pets and kids and you: In general, not unless your pets, your kids, or you drink it. This is how it kills mammals: a mammal drinks it. There is some evidence of toxicity to amphibians, but again, this is at industrial scale and high concentrations, not a household preparation used on like 5 weeds in your patio. There is conflicting evidence on whether or not glyphosate is carcinogenic in humans, but the risk -- if it exists -- seems at this point to be low and probably mainly affects agricultural workers who are regularly exposed to a LOT of the stuff.
Takeaway: Secure RoundUp from pets and children. I personally keep garden chemicals in a padlocked plastic box in the garage. If you are suicidal and may drink RoundUp, call your area's suicide prevention hotline or ask someone for help. If you are an agricultural worker regularly in contact with glyphosate in the environment your best resource is probably United Farm Workers (in the US), your local farm workers' org, or La Via Campesina (which is an international farm workers' organization that has taken a stand against the widespread industrial use of glyphosate).
If you would like to read more about RoundUp toxicity, try: "Glyphosate Poisoning" (Bradberry, Proudfoot, and Vale 2004) and "Glyphosate: A review of its global use, environmental impact, and potential health effects on humans and other species" (Richmond 2018) -- this one is particularly useful because it collates a LOT of research together in one place, so you can get to many, many other articles from it.
General takeaways: You should take precautions if you use RoundUp not to hurt bees in your garden, but you are unlikely to hurt anything larger than invertebrates if you do use it. Do not use random weedkilling formulas involving random household items in your garden. In particular, dish soap and salt have almost no good garden uses at all and if someone tells you to use them, they are probably misinformed at best. There is a lot of complete bullcrap out there on the internet.
If you want to use organic controls for stuff in your garden, which lots of people do, a good place to start is the OMRI lists. Items on these lists are approved for organic use in the US or Canada and free to download. You can also look for information from Extension in the US about organic controls and home gardening advice; county extension is government-funded and provides a wide variety of free educational material about gardening, forestry, agriculture, etc.
#gardening#roundup#misinformation about gardening is widespread!#so is scaremongering about chemicals#suicide mention
114 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Australian Dung Beetle Project (1965–1985), conceived and led by Dr George Bornemissza of the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), was an international scientific research and biological control project with the primary goal to control the polluting effects of cattle dung.
Upon his arrival to Australia from Hungary in 1951, Dr Bornemissza, an entomologist and ecologist, noted that Australian farmland was covered in a large number of cattle dung pads.[1] This was in contrast to the fields of Europe where the dung was removed and recycled back into the soil by various species of dung beetle (coprids). Native Australian species of beetle had co-evolved alongside marsupials such as the kangaroo and wombat, which produce small, hard, dry and fibrous pellets of dung. Cattle were relatively recently introduced to Australia by European settlers in the 1880s and produce large, soft, moist dung pads. Native beetles, with a few exceptions, are not adapted to utilise this type of dung as a food source or breeding ground and so without such fauna, the dung pads remain on the pasture and take months or even years to decompose. Cattle will not feed from the area of rank pasture surrounding the dung pad, and with the large quantity of dung produced (up to 12 pads per animal per day), this reduces the area of land available for cattle grazing by as much as 200,000 hectares (2,000 km2) per year.[1] Cattle dung is also a primary breeding ground for several pestilent species of fly and parasitic worm.
The Queensland Dung Beetle Project concluded that one outcome of the study was to confirm the "outstanding success" of the original CSIRO project to select and introduce dung beetles into Australia, and "the impact of this on soil, water and pasture health, and on control of pest flies is undoubtedly worth many millions of dollars a year".[15] Further to this, the success of the Australian Dung Beetle Project is claimed to be the reason why Australians can now enjoy a café culture, as up until the 1950s, bush flies were so problematic that it was illegal for restaurants and cafés to offer outside dining unless a designated area was enclosed by fly-wire.[1][16]
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Growth Strategies Adopted by Major Players in Turf Protection Market
In the dynamic landscape of the turf protection industry, key players like Syngenta Crop Protection AG (Switzerland), UPL Limited (India), Corteva Agriscience (US), Nufarm (US), Bayer AG (Germany), and BASF SE (Germany) are at the forefront of innovation and market expansion. These industry leaders are driving growth through strategic initiatives such as partnerships, acquisitions, and cutting-edge product developments, solidifying their positions as influential forces in shaping the future of the turf protection industry. Their efforts not only enhance their global presence but also set new benchmarks for industry standards and customer expectations. The global turf protection market size is estimated to reach $8.1 billion by 2028, growing at a 4.9% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). The market size was valued $6.4 billion in 2023.
Top Global Turf Protection Leaders to Watch in 2024
· Syngenta Crop Protection AG (Switzerland)
· UPL Limited (India)
· Corteva Agriscience (US)
· Nufarm (US)
· Bayer AG (Germany)
· BASF SE (Germany)
· SDS Biotech K.K. (Japan)
· AMVAC Chemical Corporation (US)
· Bioceres Crop Solutions (Argentina)
· Colin Campbell (Chemicals) Pty Ltd (Australia)
· ICL Group Ltd. (US)
Investments and Innovations: Key Strategies of Top Turf Protection Companies
🌱 Syngenta Crop Protection AG: Leading the Way in Integrated Pest Management
Syngenta Crop Protection AG, a global agribusiness based in Switzerland, operates prominently in the crop protection and seeds markets. The company offers a comprehensive range of herbicides, insecticides, fungicides, and seed treatments, helping growers worldwide enhance agricultural productivity and food quality. With a presence in over 90 countries, Syngenta’s reach is truly global. In October 2020, Syngenta further strengthened its position by acquiring Valagro, a leading biologicals company. Valagro’s strong presence in Europe, North America, Asia, and Latin America complements Syngenta’s existing crop protection chemicals. This acquisition allows Syngenta to offer more integrated pest management strategies that reduce reliance on synthetic chemicals, while Valagro’s expertise in plant nutrition promotes healthier turfgrass growth and improved soil health.
Know about the assumptions considered for the study
🌍 UPL Limited: Innovating Turf Management Solutions Globally
UPL Limited, formerly known as United Phosphorus Limited, is a global agrochemical company based in India, providing a wide range of agricultural solutions, including crop protection products, seeds, and post-harvest solutions. UPL is a key player in turf management, offering innovative solutions for golf courses, sports fields, and other turf areas. Their product portfolio includes herbicides, fungicides, insecticides, and plant growth regulators, all designed to enhance turf quality and health while effectively controlling pests and diseases. Operating in over 130 countries across North America, South America, Europe, and Asia Pacific, UPL has 28 manufacturing sites worldwide, solidifying its position as a leader in the global turf protection market.
🏆 Bayer AG: Streamlining for a Focused Future in Turf Protection
Bayer AG, a multinational pharmaceutical and life sciences company headquartered in Leverkusen, Germany, operates across three business segments: Pharmaceuticals, Consumer Health, and Crop Science. The company’s Crop Science division caters to the turf protection market, offering products such as herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. With operations in over 90 countries, including regions like North America, South America, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia Pacific, Bayer maintains a strong global presence. In March 2022, Bayer sold its Environmental Science Professional business, which includes turf protection products, to private equity firm Cinven for USD 2.6 billion. This strategic divestment is part of Bayer’s ongoing efforts to streamline its portfolio and concentrate on core businesses, ensuring a more focused approach to its future operations.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
List of industries that would be good for a Glukkon OC [free to use, I'm just brainstorming]:
Explosives manufacturing
Arms sales & ammunition production
Hazardous chemical refinement
Debt collection
Private prison systems [which lease out inmates as slave labor]
Fast food chains
Sweatshops for apparel
Mining of precious metals or gems
Advertising, especially invasive advertising
Organ trading [while this sounds like a Vykker thing, I think a Glukkon would pay people to own their bodies when they die and then sell their organs to the Vykkers/people who need organs. You don't need to be a Vykker to write up contracts & put people in a freezer.]
Public surveillance systems
Pest control
Gambling/casinos [so much potential here, I would LOOOOOVE to see a Glukkon casino]
Fight clubs/combat arenas
Luxury resorts
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
"We have to take what useful work remains and transform it into a pleasing variety of game-like and craft-like pastimes, indistinguishable from other pleasurable pastimes except that they happen to yield useful end-products. Surely that shouldn’t make them less enticing to do. Then all the artificial barriers of power and property could come down. Creation could become recreation. And we could all stop being afraid of each other.
I don’t suggest that most work is salvageable in this way. But then most work isn’t worth trying to save. Only a small and diminishing fraction of work serves any useful purpose independent of the defense and reproduction of the work-system and its political and legal appendages. Thirty years ago, Paul and Percival Goodman estimated that just five percent of the work then being done—presumably the figure, if accurate, is lower now—would satisfy our minimal needs for food, clothing and shelter. Theirs was only an educated guess but the main point is quite clear: directly or indirectly, most work serves the unproductive purposes of commerce or social control. Right off the bat we can liberate tens of millions of salesmen, soldiers, managers, cops, stockbrokers, clergymen, bankers, lawyers, teachers, landlords, security guards, ad-men and everyone who works for them. There is a snowball effect since every time you idle some bigshot you liberate his flunkies and underlings also. Thus the economy implodes.
Forty percent of the workforce are white-collar workers, most of whom have some of the most tedious and idiotic jobs ever concocted. Entire industries, insurance and banking and real estate for instance, consist of nothing but useless paper-shuffling. It is no accident that the “tertiary sector,” the service sector, is growing while the “secondary sector” (industry) stagnates and the “primary sector” (agriculture) nearly disappears. Because work is unnecessary except to those whose power it secures, workers are shifted from relatively useful to relatively useless occupations as a measure to ensure public order. Anything is better than nothing. That’s why you can’t go home just because you finish early. They want your time, enough of it to make you theirs, even if they have no use for most of it. Otherwise why hasn’t the average work week gone down by more than a few minutes in the last sixty years?
Next we can take a meat-cleaver to production work itself. No more war production, nuclear power, junk food, feminine hygiene deodorant—and above all, no more auto industry to speak of. An occasional Stanley Steamer or Model T might be all right, but the auto-eroticism on which such pest-holes as Detroit and Los Angeles depend is out of the question. Already, without even trying, we’ve virtually solved the energy crisis, the environmental crisis and assorted other insoluble social problems.
Finally, we must do away with far and away the largest occupation, the one with the longest hours, the lowest pay and some of the most tedious tasks around. I refer to housewives doing housework and child-rearing. By abolishing wage-labor and achieving full unemployment we undermine the sexual division of labor. The nuclear family as we know it is an inevitable adaptation to the division of labor imposed by modern wage-work. Like it or not, as things have been for the last century or two it is economically rational for the man to bring home the bacon, for the woman to do the shitwork and provide him with a haven in a heartless world, and for the children to be marched off to youth concentration camps called “schools,” primarily to keep them out of Mom’s hair but still under control, but incidentally to acquire the habits of obedience and punctuality so necessary for workers. If you would be rid of patriarchy, get rid of the nuclear family whose unpaid “shadow work,” as Ivan Illich says, makes possible the work-system that makes it necessary. Bound up with this no-nukes strategy is the abolition of childhood and the closing of the schools. There are more full-time students than full-time workers in this country. We need children as teachers, not students. They have a lot to contribute to the ludic revolution because they’re better at playing than grown-ups are. Adults and children are not identical but they will become equal through interdependence. Only play can bridge the generation gap." -Bob Black, The Abolition of Work
10 notes
·
View notes
Note
Going off the inkcap into ink ask, apart from food and ink, what else can I do/make with fungus?
here's a little list !! :-)
with artist's conk brackets, you can use the underside for drawing as - when the flesh is scraped away - there is a brown layer underneath. when it dries & hardens the art will keep for a long time :-)

mushrooms that contain psilocybin are used as psychedelic drugs - the most potent is p. azurescens.

many different fungi can be used as dyes -
many moulds are used in food manufacturing processes, for example when making cheese or yoghurt.
you can purchase mycopesticides to control pests.
yeast is a fungus that we consume every day through beer, wine, soy sauce & bread products. :-)
that's about all i've got for you, luna !! <3
#• askbox replies: •#(ask : luminousmoon21)#[ganoderma applanatum]#: artist's palette :#: artist's fungus :#: artist's conk :#: artist's bracket :#: bear bread :#||#fungi#mould#mold#fungus#mycology#[psilocybe azurescens]
56 notes
·
View notes
Text

Excerpt from this story from The Revelator:
The world’s deadliest environmental disaster got its start in 1958. Its effects are still being felt today, more than six decades later.
It wasn’t an oil spill, like the Exxon Valdez or Deepwater Horizon. It wasn’t a chemical disaster, like Union Carbide’s gas leak in Bhopal. And it didn’t have anything to do with nuclear power, like Chernobyl or Three Mile Island.
It happened in the People’s Republic of China in the years after Mao Zedong came to power, causing mass starvation, murder, and even cannibalism.
And it started with a bird.
In 1958, nine years after the Communist Party of China seized power, Chairman Mao launched what he called the Great Leap Forward, a multipronged effort to transform China into an industrialized nation.
The many changes initiated during this period included banning privately owned farms in favor of collective, state-sponsored agriculture.
Around the same time, Zedong launched the Four Pests Campaign, an effort to eliminate flies, mosquitoes, rats, and sparrows to improve human hygiene and increase agricultural output. The campaign, accompanied by rampant propaganda, had a powerful slogan: ren ding sheng tian, or “Man must conquer nature.”
Three of those “pests” made relative sense: Flies, mosquitoes and rats can carry disease, and humans still try to control them today. But why were sparrows lumped in with the other three? Mao, it turns out, wanted to prevent the abundant birds from eating grain seeds — a perceived threat to farm production.
To stop sparrows from doing what comes naturally, China directed its citizens to persecute the birds at a level of carnage that may remain unmatched in human history. During the Great Sparrow Campaign people smashed nests and eggs and chased sparrows while shouting, banging pots and spoons, lighting firecrackers, and making other loud noises. Many of the birds spent so much time and energy fleeing the cruel cacophony that they exhausted their reserves and found themselves too tired to escape a well-aimed whack from a shovel. Others “simply dropped from the sky” and expired, as Frank Dikötter wrote in his 2010 book Mao’s Great Famine.
It’s impossible to say exactly how many sparrows died, but many accounts place the toll in the hundreds of millions.
And it wasn’t just sparrows: Birds of adjacent nearby species also fell victim to the noise pollution and violence.
Two years later the absence of sparrows spawned a crisis of epic proportions. Insects such as locusts, previously kept in balance by the sparrows and other birds, swarmed out of control in 1960, a year that — in a grim coincidence — also saw a massive drought. Crops vanished as the voracious insects spread across the country.
As a result of this imbalance in nature, millions of people starved to death over the next two years.
How many? No one knows for sure. The Chinese government officially counts 15 million dead. Chinese journalist Yang Jisheng, writing in his book Tombstone: The Great Chinese Famine, put the death toll at 36 million. Some academics suggest even doubling that to 75-78 million.
And they didn’t just die of starvation. People killed each other for food — and committed other unspeakable acts. “Documents report several thousand cases where people ate other people,” Yang told NPR in 2012. “Parents ate their own kids. Kids ate their own parents.”
The ultimate irony: China’s oppressive government had enough grain stored before the disaster to feed everyone in the country. However, they refused to release it and covered up the problem (in part by arresting and beating anyone who questioned the official narrative).
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

⭐️Currently reading: The One-Straw Revolution by Masanobu Fukuoka ⭐️
‘Just playing or doing nothing at all, children are happy. A discriminating adult, on the other hand, decides what will make him happy, and when these conditions are met he feels satisfied.’
The synopsis calls it ‘Zen and the Art of Farming.’ This book is about his experience over 30 years of using the ‘do-nothing’ farming method. He lets his orchard and rice/barley fields grow wild without any pest controls or fertilizers. That’s the basis of it (kinda?) — but what makes this book amazing is that he goes deep into why it works for him. Explaining why he doesn’t have to use chemicals to treat weeds and pests. Into the full circle of life & how to actually grow ‘natural’ food. We always want bigger and better quality & focus on high yields and money. How disconnected we really are growing from nature in agriculture.
If you aren’t into agriculture or learning about the exact ‘whys’ of his experiences from growing rice, barley & citrus on his personal field —- skip to part 2 of the book. I honestly wouldn’t recommend skipping(it holds a lot of useful information), but after part 2 is where I really got interested.
It’s not only about farming though - it also incorporates our health, diet and how basic our knowledge is as humans. It makes you think.
Even this book being written in 1978 - it still holds up to today. We’ve had all this knowledge since then and we still continue to do industrial agriculture and live/eat the way we do. It’s eye opening, for sure.
I’m not completely finished yet - I have about 40 pages left - but that’s what I think so far ☺️ You should definitely give it a try.
#one straw revolution#sustainable agriculture#natural farming#masanobu fukuoka#agriculture#agriculture books#currently reading#sustainable gardening#grow organic#organic gardening#green manure#farming#eat locals#grow your own food#food not lawns#ecology#guerrilla gardening#indoor garden#container gardening#vegetable gardening#starting seeds#growing food#gardening blog#gardening tips#plant mom#plant life#homesteading#growing grains
16 notes
·
View notes
Note
What would you consider to be an ethically sourced tail? Where might somebody purchase an ethically sourced tail?
Thank you so much for asking!!! 🐾
Personally I believe It should either: Be sourced as a by-product of the food industry, Transform a waste product to give it value, such as the reclaiming fur from animals culled for environmental management, Minimise waste by re-manufacturing vintage pieces or using surplus manufacturing material, instead of only using new material. There are other options such as taxidermy from ranched animals which were stillborn or died from illness or other natural causes. Byproducts of roadkill, pest management, and wildlife population control which are done in a sustainable manner that keeps the natural population at a healthy and maintainable level. Also if there is no unnecessary pain or cruelty that’s inflicted and killing of said animal involves minimal waste and has a purpose other than simply their fur.
And I know there is the argument that we don’t need to kill animals to make clothing because of course there are other materials to keep us warm, but the best of them (wool, down, leather) also come from animals. Meanwhile, most synthetic fibers (including fake or “faux” fur) are derived from petroleum, a non-renewable resource, the extraction and transformation of which entails serious environmental risks.
In many regions, wildlife populations must be culled annually to maintain healthy and stable populations, to preserve habitat, to protect endangered species (e.g., by culling predators that attack ground-nesting birds or sea turtle eggs), and to safe-guard human health, livestock and property. If furbearer populations must be culled, surely it is more ethical to use these animals than to discard them?
Farmed minks manure, soiled straw bedding and carcasses are composted to produce organic fertilizers, to enrich the soil and produce more food, completing the agricultural nutrient cycle. Biofuels made from mink remains now power buses in Aarhus, Denmark, the world’s largest producer of farmed mink. Similar projects are being tested in North America.
Now after all that here are some options for furs/tails. Though please do your own research into each small business or company you buy from.

https://www.etsy.com/shop/SterlingFoxTaxidermy
https://www.etsy.com/shop/ChimeraTaxidermyAU
#wolf#therian#wolf therian#wolfkin#wolves#canine therian#therianthropy#canine#theriotype#canis lupus irremotus#belgian malinois therian#belgian malinois#dog therian#dog theriotype#alterhuman#nonhuman#fox therian#coyote therian#bear therian#deer therian#cat therian#mouse therian#bird therian#therian gear#therian tail
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Letter to the Canadian Government about Mandatory Human Rights and Environment Due Diligence Laws
Our names are ______. We are from ______. We are writing to you to ask that you create good Mandatory Human Rights Due Diligence laws for all companies operating in, selling goods or services in, or headquartered in Canada. This will help workers, communities, and ecosystems around the world and contribute to the creation of a fair world where current people and future generations have what they need.
Right now, companies are doing horrific human rights abuses and environmental abuses all around the world.
First of all, workers are being horrifically overworked and incredibly underpaid in intensely dangerous working conditions. Three million workers die every year due to workplace accidents or poisoning. Fifty million people are literally being held in modern slavery. Ten percent of children worldwide are doing child labour. Two thirds of the world are in multidimensional poverty, where they don’t have five or more of their basic needs (such as food and sanitation and education) met. Forget living wages, most workers are not even paid bare subsistence wages. And experts have described working conditions as soul-destroying for workers around the world.
Local communities around factories and plantations and power plants and mines and whatnot are also being polluted. Chemicals from industrial developments leach into the ground, air, and water, poisoning people, destroying crops and plants, and killing local fish and wildlife. This leads to many people dying from being poisoned or losing their livelihoods. People lose their access to clean water and air, to food, and to life.
And the environment is being harmed by industrial activities too. We are at the start of the worst biodiversity crisis the earth has ever faced. Ecosystems all around the world are collapsing, and will continue to collapse. Not to mention, the climate is warming and causing devastation for people the world over. All humans rely on a healthy climate and healthy ecosystems for fertile soil, clean water, safety from extreme weather, pest and disease control, and the list goes on. But it is the actions of industry, companies, and supply chains that are the biggest contributor to the climate and biodiversity crises.
And often, when people stand up for the air and water and land, when they stand up for their communities and/or their fellow workers, they are threatened, intimidated, or even killed.
The companies that are headquartered in Canada or sell their products in Canada are benefitting from and causing all these problems. Their supply chains are rife with human rights abuses and environmental abuses, and they do not take adequate measures to stop the many abuses in their supply chains. Because of this, Canada and all Canadians are guilty of destroying the world and uncountable lives.
But a better world is possible. Mandatory Human Rights Due Diligence Laws, or Mandatory Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Laws, or whatever you want to call them, would ensure that any companies that abuse the workers, local communities, and local environments tied to their supply chains are made to pay. Not just made to pay a fine, which companies don’t mind and only view as a cost of doing business, but actually made to face justice and jail time.
These laws are necessary in order to ensure that workers and other people are given the human rights and human dignity they deserve, and they are necessary in order to protect the world’s ecosystems so that future generations can live. Without due diligence laws, the situation will continue to get worse and worse. But with due diligence laws, we can see improvement.
Please enact Mandatory Human Rights Due Diligence Laws.
Thank you,
Send to:
Prime Minister Trudeau- [email protected]
Deputy Prime Minister Freeland- [email protected]
Minister of Foreign Affairs Joly- [email protected]
Find your MP here: https://www.ourcommons.ca/members/en
Minister of Women and Gender Equality and Youth Ien- [email protected]
Minister of Environment and Climate Change Guilbeault- [email protected]
Minister of Energy and Natural Resources Wilkinson- [email protected]
Minister of Export Promotion, International Trade, and Economic Development Ng- [email protected]
Minister of International Development Hussen- [email protected]
Minister of Innovation, Science, and Industry Champagne- [email protected]
Minister of Fisheries, Oceans and the Canadian Coast Guard Lebouthillier- [email protected]
#canadian#canada#cdnpoli#canadian politics#human rights#social justice#social issues#capitalism#anti capitalist#capitalist hell#capitalist dystopia#capitalist bullshit#working class#class#class war#classism#class warfare#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#kill the rich#workers rights#workers of the world unite#indigenous lives matter#indigenous rights#indigenous sovereignty#changement climatique#climate crisis#climate#climate change#climate catastrophe
16 notes
·
View notes
Text

There’s a lot of research on banana production out there, especially from this great organisation called Bananalink which supports banana workers’ unions in the UK supply chain. Most the facts here are from these two pages on their website. I just wanted to ground some of the discussion around bananas in the production process, labour and environmental conditions, and who benefits from this process. The above diagram might not be very clear so I've reproduced the text below:
1. Banana production takes approximately nine months. It starts with the preparation of the soil including the clearing of land, drainage, installation and fertiliser application. Then planting and field work, such as weeding, pest and disease control, and irrigation, take place. Bananas are harvested while still green [you can watch a video of this process here]
2. The harvested bunches are transported to a packing shed where they are divided into smaller market-friendly bunches, inspected, sorted, washed, treated, labelled, and boxed for export. Bananas that do not meet the quality standard are usually sold locally at a much lower price or used for livestock feed.
3. Some bananas are pre-packed into bags according to the specifications of individual retailers. Pre-packing is used to differentiate bananas such as Fairtrade organics or small bananas from the bulk supply of loose bananas. It can be an opportunity for the grower to add value, but it also offers advantages in controlling quality and reducing wastage.
4. Bannas are then transported by truck to ports, placed in sheds, and packed in refrigerated ships or refridgerated containers. Bananas take between six to 12 days to get to the UK/Europe. They are shipped at a controlled temperature of 13.3 centigrade in order to increase their shelf life. Humidity and ventilation are carefully monitored to maintain quality.
5. When the bananas arrive at their destinaation port they are first trucked to warehouses where they can be kept in cool conditions and then ripened - using ethylene - when they are needed for delivery to retailers. Bananas may also be bagged at this stage. They are then delivered to retailers' regional distribution centres before final delivery to individual stores.
The local population eat different varieties of bananas grown primarily by small farmers. The ones for the Americans and the Europeans, Cavendish variety bananas, are grown in huge, monoculture plantations that are susceptible to disease. The banana industry consumes more agrichemicals than any other in the world, asides from cotton. Most plantations will spend more on pesticides than on wages. Pesticides are sprayed by plane, 85% of which does not land on the bananas and instead lands on the homes of workers in the surrounding area and seeps into the groundwater. The results are cancers, stillbirths, and dead rivers.
The supermarkets dominate the banana trade and force the price of bananas down. Plantations resolve this issue by intensifying and degrading working conditions. Banana workers will work for up to 14 hours a day in tropical heat, without overtime pay, for 6 days a week. Their wages will not cover their cost of housing, food, and education for their children. On most plantations independent trade unions are, of course, suppressed. Contracts are insecure, or workers are hired through intermediaries, and troublemakers are not invited back.
Who benefits most from this arrangement? The export value of bananas is worth $8bn - the retail value of these bananas is worth $25bn. Here's a breakdown of who gets what from the sale of banana in the EU.
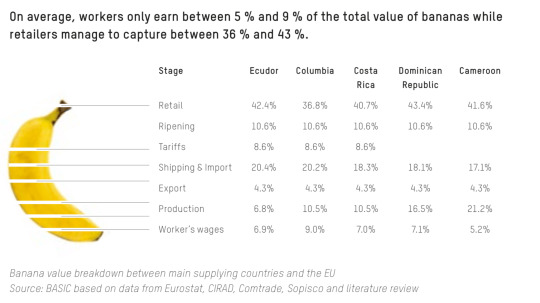
On average, the banana workers get between 5 and 9% of the total value, while the retailers capture between 36 to 43% of the value. So if you got a bunch of bananas at Tesco (the majority of UK bananas come from Costa Rica) for 95p, 6.65p would go to the banana workers, and 38p would go to Tesco.
Furthermore, when it comes to calculating a country's GDP (the total sum of the value of economic activity going on in a country, which is used to measure how rich or poor a country is, how fast its economy is 'growing' and therefore how valuable their currency is on the world market, how valuable its government bonds, its claim on resources internationally…etc), the worker wages, production, export numbers count towards the country producing the banana, while retail, ripening, tariffs, and shipping & import will count towards the importing country. A country like Costa Rica will participate has to participate in this arrangement as it needs ‘hard’ (i.e. Western) currencies in order to import essential commodities on the world market.
So for the example above of a bunch of Costa Rican bananas sold in a UK supermarket, 20.7p will be added to Costa Rica’s GDP while 74.3p will be added to the UK’s GDP. Therefore, the consumption of a banana in the UK will add more to the UK’s wealth than growing it will to Costa Rica’s. The same holds for Bangladeshi t-shirts, iPhones assembled in China, chocolate made with cocoa from Ghana…it’s the heart of how the capitalism of the ‘developed’ economy functions. Never ending consumption to fuel the appearance of wealth, fuelled by the exploitation of both land and people in the global south.
24 notes
·
View notes