#native-plants
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Planet's Fucked: What Can You Do To Help? (Long Post)
Since nobody is talking about the existential threat to the climate and the environment a second Trump term/Republican government control will cause, which to me supersedes literally every other issue, I wanted to just say my two cents, and some things you can do to help. I am a conservation biologist, whose field was hit substantially by the first Trump presidency. I study wild bees, birds, and plants.
In case anyone forgot what he did last time, he gagged scientists' ability to talk about climate change, he tried zeroing budgets for agencies like the NOAA, he attempted to gut protections in the Endangered Species Act (mainly by redefining 'take' in a way that would allow corporations to destroy habitat of imperiled species with no ramifications), he tried to do the same for the Migratory Bird Treaty Act (the law that offers official protection for native non-game birds), he sought to expand oil and coal extraction from federal protected lands, he shrunk the size of multiple national preserves, HE PULLED US OUT OF THE PARIS CLIMATE AGREEMENT, and more.
We are at a crucial tipping point in being able to slow the pace of climate change, where we decide what emissions scenario we will operate at, with existential consequences for both the environment and people. We are also in the middle of the Sixth Mass Extinction, with the rate of species extinctions far surpassing background rates due completely to human actions. What we do now will determine the fate of the environment for hundreds or thousands of years - from our ability to grow key food crops (goodbye corn belt! I hated you anyway but), to the pressure on coastal communities that will face the brunt of sea level rise and intensifying extreme weather events, to desertification, ocean acidification, wildfires, melting permafrost (yay, outbreaks of deadly frozen viruses!), and a breaking down of ecosystems and ecosystem services due to continued habitat loss and species declines, especially insect declines. The fact that the environment is clearly a low priority issue despite the very real existential threat to so many people, is beyond my ability to understand. I do partly blame the public education system for offering no mandatory environmental science curriculum or any at all in most places. What it means is that it will take the support of everyone who does care to make any amount of difference in this steeply uphill battle.
There are not enough environmental scientists to solve these issues, not if public support is not on our side and the majority of the general public is either uninformed or actively hostile towards climate science (or any conservation science).
So what can you, my fellow Americans, do to help mitigate and minimize the inevitable damage that lay ahead?
I'm not going to tell you to recycle more or take shorter showers. I'll be honest, that stuff is a drop in the bucket. What does matter on the individual level is restoring and protecting habitat, reducing threats to at-risk species, reducing pesticide use, improving agricultural practices, and pushing for policy changes. Restoring CONNECTIVITY to our landscape - corridors of contiguous habitat - will make all the difference for wildlife to be able to survive a changing climate and continued human population expansion.
**Caveat that I work in the northeast with pollinators and birds so I cannot provide specific organizations for some topics, including climate change focused NGOs. Scientists on tumblr who specialize in other fields, please add your own recommended resources. **
We need two things: FUNDING and MANPOWER.
You may surprised to find that an insane amount of conservation work is carried out by volunteers. We don't ever have the funds to pay most of the people who want to help. If you really really care, consider going into a conservation-related field as a career. It's rewarding, passionate work.
At the national level, please support:
The Nature Conservancy
Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation
Cornell Lab of Ornithology (including eBird)
National Audubon Society
Federal Duck Stamps (you don't need to be a hunter to buy one!)
These first four work to acquire and restore critical habitat, change environmental policy, and educate the public. There is almost certainly a Nature Conservancy-owned property within driving distance of you. Xerces plays a very large role in pollinator conservation, including sustainable agriculture, native bee monitoring programs, and the Bee City/Bee Campus USA programs. The Lab of O is one of the world's leaders in bird research and conservation. Audubon focuses on bird conservation. You can get annual memberships to these organizations and receive cool swag and/or a subscription to their publications which are well worth it. You can also volunteer your time; we need thousands of volunteers to do everything from conducting wildlife surveys, invasive species removal, providing outreach programming, managing habitat/clearing trails, planting trees, you name it. Federal Duck Stamps are the major revenue for wetland conservation; hunters need to buy them to hunt waterfowl but anyone can get them to collect!
THERE ARE DEFINITELY MORE, but these are a start.
Additionally, any federal or local organizations that seek to provide support and relief to those affected by hurricanes, sea level rise, any form of coastal climate change...
At the regional level:
These are a list of topics that affect major regions of the United States. Since I do not work in most of these areas I don't feel confident recommending specific organizations, but please seek resources relating to these as they are likely major conservation issues near you.
PRAIRIE CONSERVATION & PRAIRIE POTHOLE WETLANDS
DRYING OF THE COLORADO RIVER (good overview video linked)
PROTECTION OF ESTUARIES AND SALTMARSH, ESPECIALLY IN THE DELAWARE BAY AND LONG ISLAND (and mangroves further south, everglades etc; this includes restoring LIVING SHORELINES instead of concrete storm walls; also check out the likely-soon extinction of saltmarsh sparrows)
UNDAMMING MAJOR RIVERS (not just the Colorado; restoring salmon runs, restoring historic floodplains)
NATIVE POLLINATOR DECLINES (NOT honeybees. for fuck's sake. honeybees are non-native domesticated animals. don't you DARE get honeybee hives to 'save the bees')
WILDLIFE ALONG THE SOUTHERN BORDER (support the Mission Butterfly Center!)
INVASIVE PLANT AND ANIMAL SPECIES (this is everywhere but the specifics will differ regionally, dear lord please help Hawaii)
LOSS OF WETLANDS NATIONWIDE (some states have lost over 90% of their wetlands, I'm looking at you California, Ohio, Illinois)
INDUSTRIAL AGRICULTURE, esp in the CORN BELT and CALIFORNIA - this is an issue much bigger than each of us, but we can work incrementally to promote sustainable practices and create habitat in farmland-dominated areas. Support small, local farms, especially those that use soil regenerative practices, no-till agriculture, no pesticides/Integrated Pest Management/no neonicotinoids/at least non-persistent pesticides. We need more farmers enrolling in NRCS programs to put farmland in temporary or permanent wetland easements, or to rent the land for a 30-year solar farm cycle. We've lost over 99% of our prairies to corn and soybeans. Let's not make it 100%.
INDIGENOUS LAND-BACK EFFORTS/INDIGENOUS LAND MANAGEMENT/TEK (adding this because there have been increasing efforts not just for reparations but to also allow indigenous communities to steward and manage lands either fully independently or alongside western science, and it would have great benefits for both people and the land; I know others on here could speak much more on this. Please platform indigenous voices)
HARMFUL ALGAL BLOOMS (get your neighbors to stop dumping fertilizers on their lawn next to lakes, reduce agricultural runoff)
OCEAN PLASTIC (it's not straws, it's mostly commercial fishing line/trawling equipment and microplastics)
A lot of these are interconnected. And of course not a complete list.
At the state and local level:
You probably have the most power to make change at the local level!
Support or volunteer at your local nature centers, local/state land conservancy non-profits (find out who owns&manages the preserves you like to hike at!), state fish & game dept/non-game program, local Audubon chapters (they do a LOT). Participate in a Christmas Bird Count!
Join local garden clubs, which install and maintain town plantings - encourage them to use NATIVE plants. Join a community garden!
Get your college campus or city/town certified in the Bee Campus USA/Bee City USA programs from the Xerces Society
Check out your state's official plant nursery, forest society, natural heritage program, anything that you could become a member of, get plants from, or volunteer at.
Volunteer to be part of your town's conservation commission, which makes decisions about land management and funding
Attend classes or volunteer with your land grant university's cooperative extension (including master gardener programs)
Literally any volunteer effort aimed at improving the local environment, whether that's picking up litter, pulling invasive plants, installing a local garden, planting trees in a city park, ANYTHING. make a positive change in your own sphere. learn the local issues affecting your nearby ecosystems. I guarantee some lake or river nearby is polluted
MAKE HABITAT IN YOUR COMMUNITY. Biggest thing you can do. Use plants native to your area in your yard or garden. Ditch your lawn. Don't use pesticides (including mosquito spraying, tick spraying, Roundup, etc). Don't use fertilizers that will run off into drinking water. Leave the leaves in your yard. Get your school/college to plant native gardens. Plant native trees (most trees planted in yards are not native). Remove invasive plants in your yard.
On this last point, HERE ARE EASY ONLINE RESOURCES TO FIND NATIVE PLANTS and LEARN ABOUT NATIVE GARDENING:
Xerces Society Pollinator Conservation Resource Center
Pollinator Pathway
Audubon Native Plant Finder
Homegrown National Park (and Doug Tallamy's other books)
National Wildlife Federation Native Plant Finder (clunky but somewhat helpful)
Heather Holm (for prairie/midwest/northeast)
MonarchGard w/ Benjamin Vogt (for prairie/midwest)
Native Plant Trust (northeast & mid-atlantic)
Grow Native Massachusetts (northeast)
Habitat Gardening in Central New York (northeast)
There are many more - I'm not familiar with resources for western states. Print books are your biggest friend. Happy to provide a list of those.
Lastly, you can help scientists monitor species using citizen science. Contribute to iNaturalist, eBird, Bumblebee Watch, or any number of more geographically or taxonomically targeted programs (for instance, our state has a butterfly census carried out by citizen volunteers).
In short? Get curious, get educated, get involved. Notice your local nature, find out how it's threatened, and find out who's working to protect it that you can help with. The health of the planet, including our resilience to climate change, is determined by small local efforts to maintain and restore habitat. That is how we survive this. When government funding won't come, when we're beat back at every turn trying to get policy changed, it comes down to each individual person creating a safe refuge for nature.
Thanks for reading this far. Please feel free to add your own credible resources and organizations.
#us election#climate change#united states election#resources#native plants#this took 3 hours to write so maybe don't let it flop? i know i write long posts. i know i follow scientists on here#that study birds and corals and other creatures#i realize i did not link sources/resources for everything. i encourage those more qualified to add things on. i need to go to work
17K notes
·
View notes
Text
#tiktok#andrew_the_arborist#urban gardening#urban landscape#ecofriendly#native wildflowers#eco friendly#eco lawn#native plants#garden#gardening
98K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Amherst Gardens Charm
It���s a sweltering August, Sunday afternoon in New England, the kind where the air, is basically a damp blanket than a breath of fresh air. The rain falls sporadically and it feels like you’ve walked into a sauna. While the rain’s making you question if it’s worth bothering with an umbrella. It’s the sort of day that practically begs for a leisurely Sunday brunch: where you can stretch out, savor…
0 notes
Text
"With “green corridors” that mimic the natural forest, the Colombian city is driving down temperatures — and could become five degrees cooler over the next few decades.
In the face of a rapidly heating planet, the City of Eternal Spring — nicknamed so thanks to its year-round temperate climate — has found a way to keep its cool.
Previously, Medellín had undergone years of rapid urban expansion, which led to a severe urban heat island effect — raising temperatures in the city to significantly higher than in the surrounding suburban and rural areas. Roads and other concrete infrastructure absorb and maintain the sun’s heat for much longer than green infrastructure.
“Medellín grew at the expense of green spaces and vegetation,” says Pilar Vargas, a forest engineer working for City Hall. “We built and built and built. There wasn’t a lot of thought about the impact on the climate. It became obvious that had to change.”
Efforts began in 2016 under Medellín’s then mayor, Federico Gutiérrez (who, after completing one term in 2019, was re-elected at the end of 2023). The city launched a new approach to its urban development — one that focused on people and plants.
The $16.3 million initiative led to the creation of 30 Green Corridors along the city’s roads and waterways, improving or producing more than 70 hectares of green space, which includes 20 kilometers of shaded routes with cycle lanes and pedestrian paths.
These plant and tree-filled spaces — which connect all sorts of green areas such as the curb strips, squares, parks, vertical gardens, sidewalks, and even some of the seven hills that surround the city — produce fresh, cooling air in the face of urban heat. The corridors are also designed to mimic a natural forest with levels of low, medium and high plants, including native and tropical plants, bamboo grasses and palm trees.
Heat-trapping infrastructure like metro stations and bridges has also been greened as part of the project and government buildings have been adorned with green roofs and vertical gardens to beat the heat. The first of those was installed at Medellín’s City Hall, where nearly 100,000 plants and 12 species span the 1,810 square meter surface.
“It’s like urban acupuncture,” says Paula Zapata, advisor for Medellín at C40 Cities, a global network of about 100 of the world’s leading mayors. “The city is making these small interventions that together act to make a big impact.”
At the launch of the project, 120,000 individual plants and 12,500 trees were added to roads and parks across the city. By 2021, the figure had reached 2.5 million plants and 880,000 trees. Each has been carefully chosen to maximize their impact.
“The technical team thought a lot about the species used. They selected endemic ones that have a functional use,” explains Zapata.
The 72 species of plants and trees selected provide food for wildlife, help biodiversity to spread and fight air pollution. A study, for example, identified Mangifera indica as the best among six plant species found in Medellín at absorbing PM2.5 pollution — particulate matter that can cause asthma, bronchitis and heart disease — and surviving in polluted areas due to its “biochemical and biological mechanisms.”
And the urban planting continues to this day.
The groundwork is carried out by 150 citizen-gardeners like Pineda, who come from disadvantaged and minority backgrounds, with the support of 15 specialized forest engineers. Pineda is now the leader of a team of seven other gardeners who attend to corridors all across the city, shifting depending on the current priorities...
“I’m completely in favor of the corridors,” says [Victoria Perez, another citizen-gardener], who grew up in a poor suburb in the city of 2.5 million people. “It really improves the quality of life here.”
Wilmar Jesus, a 48-year-old Afro-Colombian farmer on his first day of the job, is pleased about the project’s possibilities for his own future. “I want to learn more and become better,” he says. “This gives me the opportunity to advance myself.”
The project’s wider impacts are like a breath of fresh air. Medellín’s temperatures fell by 2°C in the first three years of the program, and officials expect a further decrease of 4 to 5C over the next few decades, even taking into account climate change. In turn, City Hall says this will minimize the need for energy-intensive air conditioning...
In addition, the project has had a significant impact on air pollution. Between 2016 and 2019, the level of PM2.5 fell significantly, and in turn the city’s morbidity rate from acute respiratory infections decreased from 159.8 to 95.3 per 1,000 people [Note: That means the city's rate of people getting sick with lung/throat/respiratory infections.]
There’s also been a 34.6 percent rise in cycling in the city, likely due to the new bike paths built for the project, and biodiversity studies show that wildlife is coming back — one sample of five Green Corridors identified 30 different species of butterfly.
Other cities are already taking note. Bogotá and Barranquilla have adopted similar plans, among other Colombian cities, and last year São Paulo, Brazil, the largest city in South America, began expanding its corridors after launching them in 2022.
“For sure, Green Corridors could work in many other places,” says Zapata."
-via Reasons to Be Cheerful, March 4, 2024
#colombia#brazil#urban#urban landscape#urban planning#cities#civil engineering#green architecture#green spaces#urban heat#urban heat island effect#weather#meteorology#global warming#climate change#climate hope#climate optimism#climate emergency#climate action#environment#environmental news#city architecture#bicycling#native plants#biodiversity#good news#hope#solarpunk#ecopunk#hopepunk
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
THE AFRICAN IROKO TREE
INTRODUCTIONS Igbo people are one of the largest ethnic groups in Nigeria, known for their rich cultural heritage and traditions. They have a deep connection to their ancestors, spiritual beliefs, and community values. The Igbo language, art, music, and dance are all important aspects of their culture. One of the most significant elements of Igbo traditional beliefs and practices is the…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text

jewels of opar
traditional ink, digital color. 2024
#artists on tumblr#illustration#nature art#bird art#nature#ink drawing#traditional art#bird#anhinga#pink flowers#floral#botanical#botanist#natural art#plants#native species
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

California_Poppy.exe
#my art#illustration#artists of tumblr#digital art#art#california poppy#botany#flowers#native plants
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

1K notes
·
View notes
Text
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
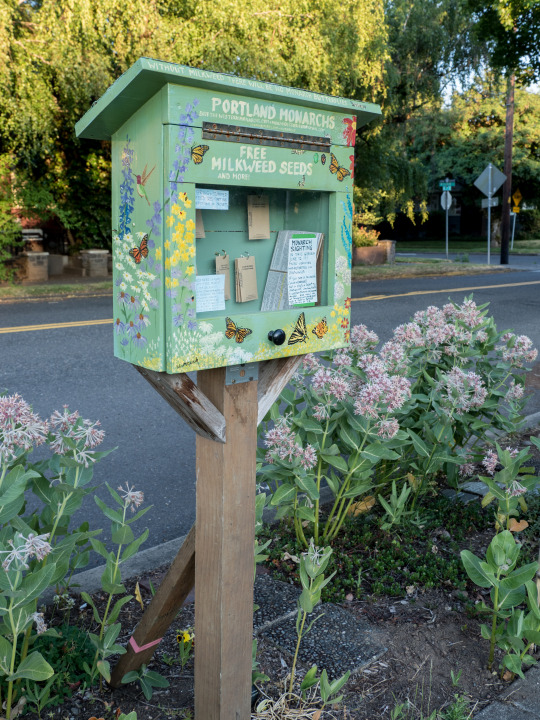


Butterfly Repopulation Station in Portland
Free seeds, information and also a patch of milkweed for Monarch Butterflies
13K notes
·
View notes
Text
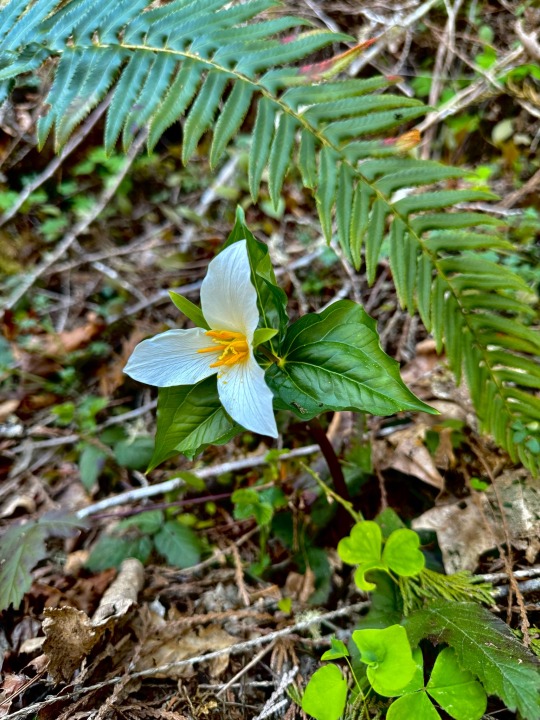

a trillium a day..
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Why Native Plants Are Better For People And Birds:
https://www.audubon.org/plantsforbirds
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
"Helio da Silva, a retired business executive from Brazil, single-handedly planted over 41,000 trees in his hometown of Sao Paulo over the last two decades.
Flying over the Brazilian metropolis of Sao Paulo, it’s tough to miss the 3.2-kilometers-long and 100-meter-wide green strip of trees wedged between two of the city’s busiest roads. It is known as Tiquatira Linear Park, and it is the work of a single man who worked tirelessly for over 20 years in order to transform a previously dilapidated area into an actual jungle within the urban jungle that is Sao Paulo. Originally from the town of Promissao, about 500km from Sao Paulo, Helio da Silva was a successful business executive for many years, but after retiring, he took it upon himself to transform the degraded banks of the Tiquatira River into a green oasis for his community. He started planting trees there in 2003 and hasn’t stopped since.
73-year-old da Silva recently told AFP that he wanted to leave a legacy to the city that adopted him decades ago. Within the first four years of his epic project, he single-handedly planted 5,000 trees in an area that had long been abandoned and known to be frequented by drug dealers and users. His impressive feat prompted the municipality of Sao Paulo to recognize his efforts and acknowledge the area as the first linear park in Sao Paulo. This only emboldened da Silva, who continued planting native trees.
By 2020, Helio had planted more than 25,047 trees over a 3.2-km-long area, achieving a survival rate of 88 percent. For every 12 trees, he planted a fruit-bearing species in the hopes of attracting birds and animals to his green oasis. His bet paid off, as according to the municipality, 45 types of birds have been identified in the park. Today, the Tiquatira Linear Park numbers over 41,000 individual trees, and Helio da Silva doesn’t plan on stopping planting until he reaches at least 50,000 of them.
“My motivation comes from the trees themselves because trees give us flowers and fruits, absorb rainwater, attract birds and provide us with wonderful shade and fresh air,” da Silva told Common Earth.
The retired executive estimates that he spent about $7,000 per year on his tree-planting efforts since 2022, but the way he sees it, it was a worthwhile investment for himself, his family and the whole of Sao Paulo. Plus, he saved a lot of money by planting the trees himself.
Once labeled as crazy for spending most of his time planting trees in an area most people avoided, Helio da Silva is now hailed as a local hero. He sometimes receives help from like-minded nature lovers, but he is still the driving force behind this amazing project. Every Sunday, he comes to Tiquatira Park to plant more trees.
Over the years, the city gym and playground equipment, tables, benches, toilets, and Tiquatira Linear Park eventually became one of Sao Paulo’s most popular areas."
youtube
-Article via OddityCentral, October 4, 2024. Video via France24, September 26, 2024.
--
Note: ONE SINGLE PERSON CAN MAKE A SUCH A DIFFERENCE
#brazil#sao paulo#south america#park#urban park#trees#nature#biodiversity#climate action#climate adaptation#hopepunk#solarpunk#native plants#environment#plants#ecology#good news#hope#Youtube#edited to fix the spelling of Sao Paulo#can only do that in the article text tho#not the title#sorry about that
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
UDARA', THE AFRICAN APPLE.
‘UDARA’, THE AFRICAN APPLE. Introduction The African Apple is a highly valued fruit in West Africa, particularly in Nigeria. It is revered for its symbolic importance in the traditional beliefs of the Igbo people, as well as its nutritional and health benefits. The fruit is a rich source of vitamins and minerals, and it has several health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant…

View On WordPress
0 notes