#materials chemistry
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
surfaces and interface chemistry final exam question: describe a phenomena seen in nanoparticles/thin films but not in bulk amounts of the same material. why does this occur?
girl obsessed with surface plasmon resonance: omg this would be such a good time for me to talk about surface plasmon resonance
130 notes
·
View notes
Text

Baby's First Materials Chemistry Set | Let's Make: Table Salt
Set Includes:
Silly Sodium, Captain Chlorine, Beaker Buddy, and for a limited time: FunFlame! The Kid-Friendly Lighter
GenuineBluff.com
#science meme#materials chemistry#chemistry meme#sodium#lol#meme#unreality#please notice me#reblog#oc#mine#baby meme#funny meme#weird meme#surreal meme#fake ad#obvious plant
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Energy: Department of Energy Selects Argonne to Lead National Energy Storage Hub
The U.S. Department of Energy selects Argonne to lead a groundbreaking energy storage hub, advancing next-gen battery technology.
The U.S. Department of Energy has appointed Argonne National Laboratory to spearhead the Energy Storage Research Alliance (ESRA), a significant initiative aimed at advancing battery technology and energy storage innovation. This national energy storage hub will unite nearly 50 leading researchers from three national laboratories and 12 universities, including top institutions like Columbia…
#Argonne#batteries#Bitcoin#breakthroughs#DOE#electrochemical#energy#energy security#Energy Storage#ESRA#funding#industry#innovation#manufacturing#materials chemistry#national labs#research hub#transportation#universities
1 note
·
View note
Text
Quantitative Comparison of Mineral Ash from Agro-Industrial Waste for Use as Pozzolanic Additions in Cement: Kinetic Parameters

In this research work a synthetic review of the quantitative characterization of various materials (sugar cane waste ashes, bamboo leaf ash, calcined paper sludge, loessic soils, zeolite, fly ash and silica fume) based on the computing of the kinetic parameters of the pozzolanic reaction in pozzolan/calcium hydroxide(CH) systems is offered. The paper presents of more relevant results in the quantitative characterization (computing of the kinetic parameters) of the pozzolanic reaction of different materials originated from agriculture, mining or industry activities carried out by the authors.Two pozzolanic activity tests (conductometric method and accelerated chemical method) are employed. A kinetic-diffusive model (published by the authors in previous works) is used to describe the pozzolanic reaction. The kinetic parameters that characterize the process (in particular, the reaction rate constant and free energy of activation) are determined with relative accuracy in the fitting process of the model. The pozzolanic activity is quantitatively evaluated according to the results obtained for the kinetic parameters. This allows the comparison in a direct way of the pozzolanic reactivity of the materials, which is very useful for the employment of these materials for envisaged applications. The values of the reaction rate constant jointly with the free energy of activation give a precise index of the reactivity or pozzolanic activity of the materials. Complementary experimental techniques, such as X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM), were also employed, but not shown in the paper for space reason since that would necessitate a much larger paper.
Read more about this article: https://crimsonpublishers.com/amms/fulltext/AMMS.000619.php
Read more about our journal: https://crimsonpublishers.com/amms/
0 notes
Text

#stem#stemblr#science#science side of tumblr#geology#biology#chemistry#ecology#materials science#lab#laboratory#space#chem
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
The continuing release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere is a major driver of global warming and climate change with increased extreme weather events. Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have now presented a method for effectively converting carbon dioxide into ethanol, which is then available as a sustainable raw material for chemical applications. "We can remove the greenhouse gas CO₂ from the environment and reintroduce it into a sustainable carbon cycle," explained Professor Carsten Streb from the JGU Department of Chemistry. His research group has shown how carbon dioxide can be converted to ethanol by means of electrocatalysis.
Continue Reading.
#Science#Environment#Chemistry#Analytical Chemistry#Materials Science#Climate Crisis#Global Warming#Carbon Dioxide
946 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sometimes I genuinely forget that Alucard, Trevor and Sypha are in fact not a canon throuple and it is so crazy LIKE HOW ARE THEY NOT
#the show is just so queer#alucard literally was in a polyam relation#(lets ignore how it ended)#why can't they be canon#theres so little material to add need to make it canon yet it isn't#but nobody can take away their chemistry from me#alucard#sypha belnades#trevor belmont#trephacard#castlevania netflix#castlevania#polyamory#ship#polyamourous
495 notes
·
View notes
Text


13 June 2024
One week left until my ochem final. Oscillating between "it's fine, I got this, most of the material is in my head already" and "AAAAHHHHH" as is the case every exam sesh. Reading a textbook on group theory for chemists for fun (and to make my thesis supervisor proud bc academic validation am I right :'))))
#im so sick of all these mechanisms already#but the end is so close 😮💨#and then in july im doing my internship#some materials chemistry for a change ✨#that'll be fun#mine#studyblr#chemblr#studyspo#study motivation#stemblr#chemistry#sciblr#study#studying#op
181 notes
·
View notes
Text





GQ | Taylor Zakhar Perez & Nicholas Galitzine Take a Friendship Quiz
aka the intro that took four tries before they finally get it right
#red white and royal blue#nicholas galitzine#taylor zakhar perez#rwrb#gq interview#friendship quiz#gq video#alex claremont diaz#henry mountchristen windsor#firstprince#gq#my gifs.#my edits.#im honestly obsessed with their chemistry#idk who keeps saying they have none bc this video alone had enough material for me to make 10 gif sets#and yeah thats a promise#also pls dont let this flop i worked so hard on this
455 notes
·
View notes
Text

Chemists create world's thinnest spaghetti
The world's thinnest spaghetti, about 200 times thinner than a human hair, has been created by a UCL-led research team. The spaghetti is not intended to be a new food but was created because of the wide-ranging uses that extremely thin strands of material, called nanofibers, have in medicine and industry. Nanofibers made of starch—produced by most green plants to store excess glucose—are especially promising and could be used in bandages to aid wound healing (as the nanofiber mats are highly porous, allowing water and moisture in but keeping bacteria out), as scaffolding for bone regeneration and for drug delivery. However, they rely on starch being extracted from plant cells and purified, a process requiring much energy and water. A more environmentally friendly method, the researchers say, is to create nanofibers directly from a starch-rich ingredient like flour, which is the basis for pasta.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Chemistry#Food#Nanofibers#Biomaterials#Nanotechnology#Fibers#Electrospinning#University College London
44 notes
·
View notes
Text

Crystal structure of the M-type hexagonal ferrite AFe12O19. Large, intermediate, and small circles represent A, Fe, and O atoms, respectively. Nakamura, Hiroyuki & Shimoda, Aiko & Waki, Takeshi & Tabata, Yoshikazu & Mény, Christian. (2016). Site-dependent cobalt electronic state in La-Co co-substituted magnetoplumbite-type ferrite: (59)Co nuclear magnetic resonance study. Journal of physics. Condensed matter : an Institute of Physics journal. 28. 346002. 10.1088/0953-8984/28/34/346002.
#science#hexagonal ferrites#hexaferrites#chemistry#materials#materials science#crystallography#nanomaterials
21 notes
·
View notes
Text

95 notes
·
View notes
Text
Estimating Coal Strength Based on Historical Laboratory Tests and Geomechanics Classification
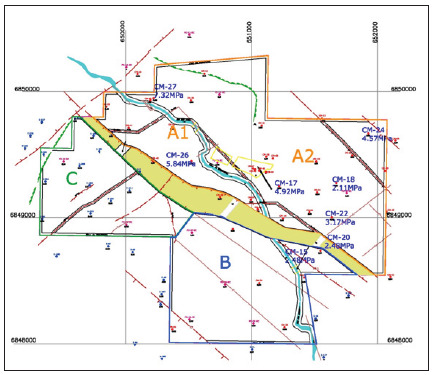
The coal seam strength and the failure criteria that represents the behavior of the coal seam are very important for mine section and pillar design. In addition, the same to roof and floor layers, which will form the roof-pillar-floor system. Therefore, the rock mass characterization is the most important job and it is the beginning of the underground ground control design. Another issue is the distribution or behavior of the coal seam strength for the whole mine area. Sometime, the coal seam strength assumed the same for entire area, but it is not true because the coal seam is heterogenic and anisotropic, and also the coal strength gets some effects due to faults and spacing between fractures. This paper has the objective to demonstrate the use of themethodology for geomechanics characterization to determine the strength for the Bonito coal seam and discuss the coal seam strength distribution around the entire mine area. The intact coal strength considered the laboratory tests that were proceeded during the lasts 17 years, including triaxial and uniaxial strength tests. It was note that there is a strong correlation between all laboratory strength tests with 90% of interval confidence. The explanation for this coal seam strength variation is the presence of the discontinuities and their variation in quantity and quality at each location in the mine area because the coal seam rock classification and its behavior will be affected by the quantity and quality of fractures.
Read more about this article: https://crimsonpublishers.com/amms/fulltext/AMMS.000618.php
Read more about this journal: https://crimsonpublishers.com/amms/
0 notes
Text
i have more complicated feelings about spock/chapel and don’t like snw for a number of reasons but i can’t deny that ethan peck’s spock is the only version of spock who acts like he’s dl on space grindr and that’s inherently funnier if he’s also dating a coworker on the side
#in contrast with spock/uhura which im an ideological supporter of but materially#zachary quinto is incapable of playing straight so they kind of lack any chemistry in the aos movies#don’t really want spock/chapel to happen but if it must at least it can be funny in my head#this is just the result of me trying and failing to workshop some joke about#snw spocks space grindr profile#Vulcan. Masc. Bottom. 6ft. Do not ask to come aboard the Enterprise.#txt#star trek
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
For 200 years, scientists have failed to grow a common mineral in the laboratory under the conditions believed to have formed it naturally. Now, a team of researchers from the University of Michigan and Hokkaido University in Sapporo, Japan have finally succeeded, thanks to a new theory developed from atomic simulations. Their success resolves a long-standing geology mystery called the "Dolomite Problem." Dolomite—a key mineral in the Dolomite mountains in Italy, Niagara Falls, the White Cliffs of Dover and Utah's Hoodoos—is very abundant in rocks older than 100 million years, but nearly absent in younger formations. "If we understand how dolomite grows in nature, we might learn new strategies to promote the crystal growth of modern technological materials," said Wenhao Sun, the Dow Early Career Professor of Materials Science and Engineering at U-M and the corresponding author of the paper published today in Science. The secret to finally growing dolomite in the lab was removing defects in the mineral structure as it grows. When minerals form in water, atoms usually deposit neatly onto an edge of the growing crystal surface. However, the growth edge of dolomite consists of alternating rows of calcium and magnesium.
Continue Reading.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

You can't spell ASBESTOS without BEST!
24 notes
·
View notes