#marine store norway
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

California’s oldest and most infamous prison, San Quentin Rehabilitation Center, is undergoing a groundbreaking transformation into a Nordic-inspired rehabilitation hub. Spearheaded by Gov. Gavin Newsom, the $239 million renovation is expected to be finished by January 2026.
Once home to notorious figures like cult leader Charles Manson and serial killer Richard Ramirez, the prison is now at the forefront of California’s evolving approach to incarceration. This new direction was solidified by Assembly Bill 1104, introduced by Democratic Assemblymember Mia Bonta and signed into law by Newsom in October 2023, redefining the purpose of incarceration as “rehabilitation and safe and successful reentry back into the community.”
The project draws inspiration from Scandinavian incarceration models that prioritize dignity, autonomy and reintegration. This approach has been linked to lower recidivism rates, as Norway’s two-year rate is 17.6%, compared with 61.5% in the U.S.
Jesse Vasquez, executive director of Friends of San Quentin News and the Pollen Initiative, told SFGATE he supports a shift in the prison model from punishment toward rehabilitation. “For the first time in California history, the governor decided, ‘OK, we’re gonna change the penal code. We’re gonna change the mission of the Department of Corrections, and we’re gonna solidify it with a monumental structural investment,’” he said.
Unlike more remote prisons, San Quentin’s location in Marin County — just outside San Rafael — offers close proximity to Bay Area resources and a well-established volunteer network, enabling a wide range of rehabilitation and educational programs. Mount Tamalpais College, which operates within San Quentin, offers an associate degree in liberal arts, with courses taught by volunteer faculty from top Bay Area colleges and universities.

A view of San Quentin seen from a ferry boat on San Francisco Bay.Susanne Friedrich/Getty Images
Central to the transformation are three new buildings replacing former industrial facilities that will house vocational training areas, multimedia education centers and restorative justice programs. The 2024 report from the San Quentin Transformation Advisory Council outlines plans to reimagine the prison environment through additions like a library, grocery store, cafe and communal spaces reflecting life outside prison.
“If you can imagine like a college campus vocational training center inside of the institution,” Vasquez said, emphasizing plans for open-access programming.
Additionally, the renovation includes significant improvements in inmate living conditions, particularly advocating single-cell occupancy — a direct response to inmate requests, Vasquez noted.
“The incarcerated first and foremost wanted single-cell living,” Vasquez said, noting that renovating existing facilities wasn’t viable. With the new model, the prison can better accommodate more humane living conditions aligned with rehabilitation goals.
Newsom’s San Quentin initiative is part of broader criminal justice reforms, including his 2019 moratorium on California’s death penalty and the dismantling of San Quentin’s death row announced in January 2022. These foundational changes paved the way for the current rehabilitation-focused transformation.
According to a 2023 California Department of Corrections and Rehabilitation report, nearly half of California inmates released in 2018 faced reconviction within three years.Vasquez hopes San Quentin’s new approach will serve as a replicable model nationwide to reduce recidivism.
“We’ve tried incarceration in terms of warehousing with no programming or minimal programming and minimal investment for more than 180 years, and it hasn’t worked,” Vasquez said. “This is the one time that we have a chance to provide investment and create opportunity so that the thing does work.”
Local editor Kasia Pawlowska contributed to this story.
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
On March 2, she was gone. The Belize-flagged, British-owned bulk carrier Rubymar sank in the narrow water lane between the coasts of Yemen and Eritrea. The Rubymar was the first vessel that has been completely lost since the Houthis began their attacks on shipping in the Red Sea—and its demise, with 21,000 metric tons of ammonium phosphate sulfate fertilizer, spells ecological disaster. A similar substance—ammonium nitrate—caused the devastating explosion at the Port of Beirut in 2020. It had been stored there after being abandoned on a vessel and authorities intervened to prevent an environmental disaster.
Because the Houthis have no regard for the environment, there are likely to be more such disasters. Indeed, groups set on destruction could also decide to attack the carbon storage facilities now beginning to be built underneath the seabed.
For two weeks after being struck by a Houthi missile in the Red Sea, the Rubymar clung to life despite listing badly. The damage caused by the missile, though, was too severe. At 2:15 a.m. local time, the Rubymar disappeared into the depths of the Red Sea. The crew had already been rescued by another merchant vessel that had come to the Rubymar’s aid, but there was no way anyone could remove its toxic cargo.
The ship’s owner had tried to get it towed to the Port of Aden—where Yemen’s internationally recognized government is based—and to Djibouti and Saudi Arabia, but citing the environmental risk posed by the ammonium phosphate sulfate, all three nations refused to receive it.
Now enormous quantities of a hazardous substance are about to spread into the Red Sea. IGAD, a trade bloc comprising countries in the Nile Valley and the Horn of Africa, points out that the Rubymar’s fertilizer cargo and leaking fuel “could devastate marine life and destroy coral reefs, sea life and jeopardize hundreds of thousands of jobs in the fishing industry as well as cut littoral states off from supplies of food and fuel.”
Not even shipping’s option of last resort, salvage companies, seems available. “The salvage companies that normally recover vessels are reluctant to go in,” said Cormac Mc Garry, a maritime expert with intelligence firm Control Risks. That’s because salvage ships and crews, too, risk being targeted by Houthi missiles. “If a salvage company knows it’s likely to be targeted, it will hesitate to take on the task. It has a duty of care for its crew,” said Svein Ringbakken, the managing director of the Norway-based maritime insurance company DNK.
It was only a matter of time before a Houthi missile brought down one of the many tankers and bulk carriers that still traverse the Red Sea every day. (In the first two months of this year, traffic through the Red Sea was down by 50 percent compared to the same period last year.) “The Houthis have no regard for life and even less for the environment,” Ringbakken said. “They shoot missiles at ships even though they know that there are humans and hazardous cargo on them.”
For years, the Houthis allowed an oil supertanker ironically named Safer that was moored off the coast of Yemen to rust away even though she was holding more than 1 million barrels of crude oil. By the beginning of last year, the Safer was close to disintegration: an event that would have cost hundreds of thousands of Yemenis their livelihoods because it would have killed enormous quantities of fish. Indeed, had the Safer’s oil leaked, it would even have forced the Houthi-controlled ports of Hudaydah and Saleef to close, thus preventing ordinary Yemenis from receiving food and other necessities.
It would, of course, also have caused permanent damage to all manner of marine life, including coral reefs and mangroves, in the Red Sea. Then the United Nations pulled off an almost impossible feat: It got Yemen’s warring factions, international agencies, and companies to work together to transfer the oil off the Safer. Disaster was averted. “It was a massive undertaking,” Ringbakken noted. “But for years and years and years, the Houthis were adding impediments against this undertaking, even though the Safer was sitting just off the Yemeni coast.”
Indeed, maritime terrorism itself is not new. “Besides guerrillas and terrorists, attacks have been carried out by modern day pirates, ordinary criminals, fanatic environmentalists, mutinous crews, hostile workers, and foreign agents. The spectrum of actions is equally broad: ships hijacked, destroyed by mines and bombs, attacks with bazookas, sunk under mysterious circumstances; cargos removed; crews taken hostage; extortion plots against ocean liners and offshore platforms; raids on port facilities; attempts to board oil rigs; sabotage at shipyards and terminal facilities; even a plot to steal a nuclear submarine,” researchers at RAND summarized—in 1983.
Now, though, the Houthis have upped the nihilism, and unlike the guerrillas, terrorists, and pirates of the 1980s, they have the weaponry to cause an ocean-going vessel to sink. The joint U.S.-U.K. military operation against the Houthis has failed to deter the Iranian-backed militia’s attacks; indeed, not even air strikes by U.S. and U.K. forces have convinced the Houthis that it’s time to stop. On the contrary, they’re escalating their attacks. They do so because they’re completely unconcerned about loss of life within their ranks or harm to their own waters.
It’s giving them a global platform. That, in turn, is likely to encourage other militias to also attack ships carrying toxic substances—even if it ruins their own waters. The local population is hardly in a position to hold a militia accountable. Indeed, militias interested in maritime terrorism could decide that the world’s growing sea-based infrastructure is an attractive target. And there’s a new form of sea-based infrastructure they could decide to make a preferred target, not just because it’s set for explosive growth but because attacking it would guarantee a global platform: CO2 storage.
With the world having failed to reduce its carbon-dioxide emissions enough to halt climate change, CO2 storage has become an urgent priority. Through this technique, carbon dioxide can be captured and buried underground, typically underneath the ocean. Norway has, for example, begun auctioning out licenses for CO2 storage exploration on its continental shelf. So has Britain. The United States has 15 carbon-storage sites, and another 121 are being developed. Even Big Oil has discovered carbon storage. ExxonMobil is buying offshore blocks to use for carbon storage instead of oil drilling.
Carbon storage sites are, of course, designed to withstand both natural perils and man-made attacks, but that won’t prevent destructive groups—especially ones backed by a powerful state—from trying. And because groups like the Houthis are so unconcerned about all forms of life, it won’t matter to them that releasing concentrated CO2 would cause extreme harm to the planet—including themselves. Even a tiny carbon-storage leakage of 0.1 percent per year can lead to additional CO2 emissions of 25 giga-tonnes, researchers have established.
Until recently, sea-based infrastructure was only lightly guarded, because it was in everyone’s interest that it worked. The sabotage of Nord Stream and various other pipelines and undersea cables over the past two years have demonstrated that such peacefulness can no longer be taken for granted. The new CO2 sites will need not just AI-enhanced monitoring but regular patrolling to communicate to potential attackers that it’s not even worth attempting an attack.
And for now, attacking merchant vessels remains a promising and economical strategy for the Houthis and their ilk. It doesn’t seem to matter that ammonium phosphate sulfate will soon be poisoning Yemeni waters and thus depriving locals of their livelihoods. Indeed, other bulk carriers and tankers may soon join the Rubymar on the bottom of the sea, poisoning the future for even more Yemenis.
For the Houthis, what matters is not the outcome: It’s the attention. That’s what makes them such a vexing problem for the U.S. Navy and other navies, shipowners, maritime insurers, and especially for seafarers. But there is another group that should be just as worried about the rampant insecurity on the high seas: ocean conservationists.
There is, in fact, a woman with an unsurpassed green platform who could make the growing scourge of maritime terrorism her new cause. (Nearly) everyone would thank you, Greta.
34 notes
·
View notes
Text

Lockheed Martin will integrate AARGM-ER missile into F-35 aircraft
Fernando Valduga By Fernando Valduga 01/16/2024 - 16:00 in Armaments, Military
On January 12, NAVAIR (Naval Air Systems Command), on behalf of the U.S. Department of Defense, signed a $97.3 million contract for the integration of the Northrop Grumman AGM-88G AARGM-ER (Advanced Anti-Radiation Guided Missile-Extended Range) missile with the F-35A/B/C Lightning II multifunctional fighters family.
The contract, scheduled to be completed in March 2026, will be executed by the U.S. Air Force (F-35A), the U.S. Marine Corps (F-35B and F-35C), the U.S. Navy (F-35C) and partners of the F-35 JSF program, including Australia, Canada, the United Kingdom, Norway, Italy, Denmark, the Netherlands and other users of the 17º aircraft production batch.
'Lot 17' is a designation given to the last portion of F-35 aircraft produced. The U.S. Department of Defense finalized an agreement for production in December 2022.
This 'lot' includes 126 aircraft that will be the first iteration to include the Technical Refresh-3 (TR-3) update, the modernized hardware needed to power the capabilities of Block 4. The TR-3 includes a new integrated central processor with greater computing power, a panoramic display in the cabin and an improved memory unit.
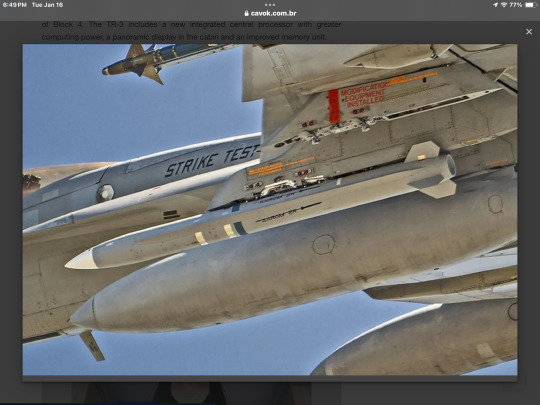
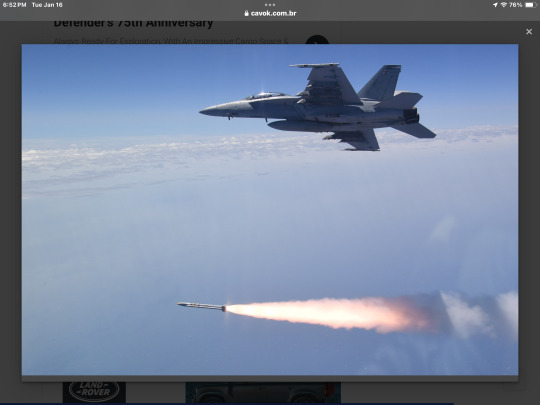
Previously, the AGM-88G AARGM-ER missiles were integrated with electronic war and air defense suppression aircraft F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and EA-18G Growler, with flight tests carried out in 2021 and 2022. On September 25, 2023, Northrop Grumman announced that it was selected by USAF to supply the new anti-radiation missile for the F-35A under the codename SiAW (Stand-in Attack Weapon), based on the AGM-88G AARGM-ER project.
The AARGM-ER was designed for enemy air defense suppression (SEAD) operations, capable of attacking anti-aircraft and missile systems, ballistic and cruise missile launchers, GPS interference systems and anti-satellite systems in strongly defended areas and negation environments (A2/AD). The missile features a new 290 mm diameter fuselage and a subsonic ramjet engine, doubling its range from 110 to approximately 220-250 km and increasing its maximum speed.
The AGM-88G AARGM-ER missiles are produced with a new propulsion and improved warhead set, based on newly produced orientation systems comprising a passive radar signal receiver, satellite navigation, counting system and millimeter wave radar. This differs from the AGM-88E AARGM, where propulsion and warhead are derived from AGM-88 HARM (high-speed anti-radiation missiles) stored missiles from the previous generation.
In January 2018, the U.S. Navy hired Northrop Grumman to develop the AARGM-ER. On March 18, 2019, the USAF announced collaboration with the U.S. Navy to adapt the AARGM-ER for the F-35A, allocating $163 million for fiscal year 2020. At the same time, the U.S. Navy ordered additional development for $323 million, with funding allocated until 2020.
In July 2019, the Department of Defense granted Lockheed Martin a $34.7 million contract to initiate modifications to the F-35's internal weapon compartments to transport the AARGM-ER. The work, including the reinforcement of the fuselage structures, was completed in July 2022. The design and integration efforts are supervised by the PMA-242 (Direct and Time Sensitive Attack) office of the Department of Defense.
Tags: AGM-88E AARGMweaponsMilitary AviationF-35 Lightning IILockheed Martin
Sharing
tweet
Fernando Valduga
Fernando Valduga
Aviation photographer and pilot since 1992, he has participated in several events and air operations, such as Cruzex, AirVenture, Dayton Airshow and FIDAE. He has works published in specialized aviation magazines in Brazil and abroad. He uses Canon equipment during his photographic work in the world of aviation.
Related news
MILITARY
Airbus Helicopters will expand portfolio of unmanned aerial systems with the acquisition of Aerovel
16/01/2024 - 14:00
HELICOPTERS
Albania receives two UH-60 Black Hawk helicopters with financial assistance from the US
16/01/2024 - 11:30
MILITARY
Belgian Air Force receives its last A400M Atlas transport aircraft
16/01/2024 - 09:50
MILITARY
U.S. Air Force officer crowned Miss America in 2024
16/01/2024 - 08:27
MILITARY
The image of the Russian Ilyushin Il-22M hit by the Ukrainian air defense appears
15/01/2024 - 23:19
MILITARY
Royal Jordanian Air Force signs contract for new F-16C/D Block 70 fighters
15/01/2024 - 20:35
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Canned Seafood Market Outlook: Emerging Trends, Size, and Future Forecasts, 2032

Market Overview
In 2024, the global canned seafood market was valued at USD 30.46 billion. It is expected to increase to USD 31.78 billion in 2025 and reach USD 45.11 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.13% over the forecast period.
The market is expected to expand in the coming years as more people choose products with clear labels, especially those that are eco-friendly. Big companies are stepping up by creating these products and introducing sustainable canned seafood, which will boost this growth.
Fortune Business Insights presents this information in their report titled "Canned Seafood Market, 2025–2032."
List of Key Players Profiled in the Market Report
Nippon Suisan Kaisha, Ltd (Japan)
LDH (La Doria) Ltd (U.K.)
American Tuna, Inc. (U.S.)
Universal Canning, Inc. (Philippines)
Connors Bros. Ltd. (Brunswick Seafoods) (Canada)
Nueva Pescanova (Spain)
Marine Harvest ASA (Norway)
Thai Union Frozen Products (Thailand)
Royal Greenland (Greenland)
StarKist Co. (U.S.)
Segments
Increasing Tuna Fish Consumption due to Its Higher Availability to Fuel Segment Growth
The market is divided by species into tuna, salmon, sardines, mackerel, and others. Tuna holds the largest share of the canned seafood market. This is because tuna consumption is rising, thanks to its high availability in over 70 countries.
Increased Accessibility of Various Products to Foster Retail Segment Growth
The market is divided into two main groups: places where people eat and drink (like hotels, restaurants, and cafes) and stores. Stores include big supermarkets, specialty shops, small convenience stores, and online shops. Big supermarkets and hypermarkets are the biggest because they have a lot of different products. But, online shops are growing the quickest because of new technology.
The market is also spread out across different areas of the world: North America, South America, Europe, the Middle East & Africa, and Asia Pacific.
Source: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/canned-seafood-market-103806
Report Coverage
The market research report gives a detailed look at the market, focusing on competition and top product types. It offers helpful information on market trends and important changes in the industry. The report also looks at different things that have helped the market grow recently.
Drivers and Restraints
Surging Investments in Aquaculture Production Advancements to Accelerate Market Growth
More people are learning about healthy eating, which means they want to buy more seafood. This is making big seafood companies work harder to produce more. But, problems like climate change and rules from the government about fishing to stop overfishing are making it difficult for these companies to catch more fish. To solve this, big companies are putting money into new ways of farming seafood, which is expected to help the market grow even more. The seafood farming industry is also growing quickly, which is helping the market grow. However, the lack of fish due to overfishing is slowing down the growth of the market.
Regional Insights
Increase in per Capita Consumption to Propel Market Growth in Europe
The Europe market was worth $17.85 billion in 2024, growing due to higher seafood consumption in countries like China and India, seen as a main food. Europe's market is also expanding, mainly because of a rise in seafood eating and a growing interest in cooking.
Competitive Landscape
Key Market Players Emphasizing Product Innovations to Maintain Their Competitive Edge
Leading companies are working on being more eco-friendly and teaming up to make more products and satisfy customer needs. For instance, in May 2019, Nippon Suisan Kaisha Ltd. shared a plan to improve production and boost their output.
Key Industry Development
January 2024 – Norway-based canned seafood manufacturer, King Oscar launched a new product line of Atlantic salmon in extra virgin oil. The skinless and boneless fish products are available in three varieties in the U.S. market.
0 notes
Text
The Stunning Power of ‘Whale Pee’
A single Whale Can Produce More Than 250 Gallons of Urine in a Day. It Helps Sustain Life Across the Ocean.
— By Melissa Hobson | March 11, 2025

For Too Long, Humpback Whales' Urinary Contributions to the Ocean Have Been Overlooked. Photograph By Martin Van Aswegen, NOAA
In the deep blue water, a one-month-old humpback whale nuzzles up to its mother. Then, a cloud of dark yellow urine gushes into the water, like a golden smoke bomb, and everything becomes tinged with green.
Scientists have spent a lot of time thinking about how the nutrients in whale feces—also known as whale pump—benefit species in shallow waters, as whales swim up from the deep sea, where they feed, to poop near the surface.
But they had overlooked another important nutrient source: urine.
Now, a study published in Nature Communications corrects the knowledge gap. It finds that whale urine is an essential part of a thriving marine ecosystem.
“The big surprise of the study is that urine far outweighs the other sources of nitrogen,” like carcasses, for example, says co-lead author Joe Roman, PhD, a conservation biologist at the University of Vermont. Plus, whales don’t tend to produce nutrient-rich poop during breeding season, but they do still urinate.
Essentially, baleen whales transport nitrogen and phosphorous from their polar feeding grounds to tropical breeding spots where those elements are lacking—and without those critical nutrients, marine plants and animals wouldn’t survive.

Humpback Whales (Like These in the Coastal Waters of the Antarctic Peninsula) Have Long Been Observed Creating Rings of Bubbles to Corral Prey. Photograph By Whale Research Solutions
Whales Pee When They Migrate, Spreading Nutrients Around The World
The study analyzed the nutrients baleen whales — whose members include gray, blue, humpback, and fin whales — add to the ocean through their urine, carcasses, and placentas. All these sources unleash 3,784 tons of nitrogen and 46,512 tons of organic matter to low-nutrient areas. And urine accounts for most of the nitrogen. (A single fin whale alone can produce 250 gallons of urine in a day.)
In summer, whales bulk up by feeding in nutrient-rich polar regions. Then they migrate to mate and reproduce in warm tropical waters, which are typically low in nutrients. During the winter breeding season, they rely on the energy reserves stored in their blubber and muscles; the process of breaking these down to release energy creates water and waste products, which become urine.
“That’s why they’re excreting this nitrogen,” he says.
These enormous mammals also release energy and nutrients into the environment through placentas—which are a few hundred pounds each, according to Roman—and carcasses. And, all told, these whale excrements move significantly more nutrients than natural physical processes like weather events. “In a place like Hawaii, the whales are bringing in more nitrogen than is being transported by wind and currents,” Roman says.
Humpback Whales, Photograph By Brian Skerry

Whale Pee is Good For the Sea
Whale urine contains high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus, which all living organisms need to survive.
“These nutrients stimulate phytoplankton growth at the ocean surface and also enrich deep sea ecosystems,” says Heidi Pearson, PhD, professor of marine biology at the University of Alaska Southeast, who was not involved in the study.
By bringing these elements to ecosystems that lack them, these weeing whales keep the whole ocean ship-shape.
Why Conservation is Essential to Ocean Health
The researchers estimate that these figures would have been around three times higher before commercial whaling nearly wiped out some species before it was banned in 1986 (although Japan, Norway, and Iceland still hunt them).
“Some whale populations have still not recovered from industrial whaling and most whales are imperiled by a myriad of threats including vessel strikes, fisheries entanglement, pollution, and climate change,” says Pearson.

A Humpback Whale, Cape Cod, Massachusetts, Photograph By Ethan Daniels/Alamy
Without Whales, The Rest of The Ocean is in Trouble Too.
“The ocean is spluttering along like an old car with rusty parts that aren't functioning properly,” says Ed Goodall, head of intergovernmental engagement at Whale and Dolphin Conservation, which partly funded the study. “We've removed vital processes delivered by whales that help keep the ocean functioning like a well-oiled machine.”
If we want a resilient and healthy marine ecosystem, we must protect whales, adds Pearson: “The ocean would be a very different place without whale poo or urine.”
“The ocean is spluttering along like an old car with rusty parts that aren't functioning properly,” says Ed Goodall, head of intergovernmental engagement at Whale and Dolphin Conservation, which partly funded the study. “We've removed vital processes delivered by whales that help keep the ocean functioning like a well-oiled machine.”
If we want a resilient and healthy marine ecosystem, we must protect whales, adds Pearson: “The Ocean Would Be a Very Different Place Without Whale Poo or Urine.”
0 notes
Text
The Role of Propulsion Solutions in Achieving Zero-Emission Shipping

The global shipping industry, which is responsible for transporting over 80% of the world’s trade, is one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. Historically, ships have relied on heavy, carbon-intensive fuels like bunker oil, which release large quantities of CO2, sulfur oxides (SOx), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into the atmosphere. However, with growing pressure to curb climate change and meet international environmental targets, the maritime sector is embarking on a transformative journey toward decarbonization. Central to this transformation is the development of zero-emission propulsion solutions that can significantly reduce or eliminate the environmental impact of shipping operations.
In this blog, we will explore the pivotal role that propulsion technologies play in helping the maritime industry achieve zero-emission goals. By examining the key innovations and challenges in this field, we’ll paint a picture of the future of sustainable shipping.
1. The Push for Decarbonization in Shipping
The push for decarbonizing shipping is not just about regulatory compliance—it’s also driven by a collective global responsibility to reduce emissions. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has set ambitious targets to cut greenhouse gas emissions from shipping by at least 50% by 2050, compared to 2008 levels, and to reach net-zero emissions by the end of the century. National governments, shipping companies, and other stakeholders are now working together to develop technologies that can achieve these targets.
The transition toward cleaner, zero-emission vessels is vital for achieving international climate goals and improving air quality, especially in coastal regions and ports where ship emissions directly impact the health of local populations. The traditional reliance on heavy fuel oils that emit CO2, sulfur, and particulate matter is being questioned as the industry looks for alternative propulsion solutions.
2. The Role of Alternative Fuels in Zero-Emission Shipping
One of the primary solutions for decarbonizing shipping is the adoption of alternative fuels. These fuels can either replace conventional marine fuels or be used in conjunction with hybrid technologies to minimize emissions. Several types of alternative fuels are being explored for zero-emission shipping:
Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A Clean Alternative
Hydrogen has gained significant attention as a potential fuel for zero-emission shipping. When used in fuel cells, hydrogen reacts with oxygen to generate electricity, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. This makes hydrogen an ideal candidate for clean propulsion, as it produces no greenhouse gases, particulate matter, or sulfur emissions.
The challenge with hydrogen lies in its production, storage, and transportation. Hydrogen needs to be produced through processes such as electrolysis (splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen using renewable energy), but large-scale production is still limited. Furthermore, hydrogen must be stored in highly pressurized tanks or as a cryogenic liquid, both of which present logistical challenges, especially for large ships requiring vast amounts of fuel.
Despite these hurdles, numerous companies are developing hydrogen-powered vessels. For example, Norway’s Hydroville is a hydrogen-fueled ferry, and Fuel Cells Works is working on hydrogen-powered cargo ships. These developments show the growing promise of hydrogen as a viable zero-emission fuel for shipping.
Ammonia: A Hydrogen-Based Fuel with Promise
Ammonia is another promising fuel for zero-emission shipping. Although ammonia does not contain carbon, it is composed of nitrogen and hydrogen. When burned or used in fuel cells, ammonia releases no CO2, which makes it a potential candidate for maritime decarbonization. One of the key advantages of ammonia over hydrogen is that it has a higher energy density, meaning it can be stored more easily in liquid form without the extreme storage requirements of hydrogen.
However, ammonia has its own set of challenges. It is toxic and requires careful handling, both during storage and in combustion systems. Additionally, ammonia combustion produces nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are harmful pollutants. However, advanced engine technology is being developed to minimize NOx emissions and make ammonia a cleaner, more sustainable option.
Biofuels and Synthetic Fuels: Clean Fuels from Renewable Sources
Biofuels are another avenue for reducing emissions in shipping. These fuels are derived from biological sources such as algae, plant oils, or even waste products. When burned, biofuels release CO2, but the CO2 is part of the natural carbon cycle, as the plants or organisms from which they are derived absorb CO2 during their growth process. This makes biofuels a more sustainable option compared to fossil fuels.
Similarly, synthetic fuels (e-fuels) can be created from renewable electricity sources using processes like Power-to-X, which converts CO2 captured from the atmosphere into synthetic fuels like methane or diesel. These fuels could be used in existing propulsion systems, making them an attractive option for retrofitting older vessels. While biofuels and e-fuels present a more sustainable alternative, scalability remains a challenge, as large-scale production of biofuels and the infrastructure for e-fuel production are still developing.
LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas): A Transitional Solution
While not zero-emission, LNG is often seen as a cleaner, transitional fuel. LNG produces less CO2 and no sulfur emissions compared to traditional marine fuels. It also emits significantly lower levels of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, making it an attractive option for reducing pollution, especially in port cities. However, LNG still releases methane—a potent greenhouse gas—during its production, storage, and transportation, which undermines its overall environmental benefits. As such, LNG is viewed as a bridge solution rather than a long-term solution for zero-emission shipping.
3. Electrification and Hybrid Propulsion Technologies
In addition to alternative fuels, electrification plays a central role in zero-emission shipping. Electric propulsion, particularly for smaller vessels operating over short distances, offers a completely clean and sustainable solution.
Battery-Electric Vessels: Clean Power for Short Routes
Electric propulsion works by using large battery banks to store energy, which is then used to power electric motors that drive the ship. This method produces zero emissions while operating, as the only "fuel" used is stored electricity. Battery-electric ships are most effective for short-distance routes, where battery capacity is manageable. Numerous electric ferries, such as those operating in Norway and the UK, already operate successfully in these environments.
One of the main challenges for battery-electric propulsion on larger vessels is energy density. Batteries capable of powering large ships over long distances are still in development, as current technology doesn’t yet support the energy demands required for transoceanic shipping. However, battery technology is evolving rapidly, and some experts believe that with continued advancements, larger vessels could eventually adopt full electric propulsion.
Hybrid Systems: Combining Traditional and Electric Power
Hybrid propulsion systems combine traditional combustion engines with electric motors and batteries. Hybrid systems enable vessels to use electric power for shorter distances, such as when navigating in ports or through environmentally sensitive areas, and switch to fuel-powered engines for long-haul cruising. This reduces the vessel’s overall fuel consumption and emissions.
Hybrid systems also provide operational flexibility, allowing ships to adapt to different types of routes and energy availability. Major companies like Maersk and Wärtsilä are already incorporating hybrid technology into their fleets, and hybrid propulsion is expected to be a major part of the industry’s transition to cleaner shipping.
4. Wind-Assisted Propulsion: Harnessing Nature’s Power
Wind-assisted propulsion is a natural and innovative method of reducing fuel consumption in shipping. By using sails, kites, or rotor sails, ships can harness the power of the wind to supplement traditional propulsion systems, thereby reducing their fuel consumption and emissions.
Sails and Kites: Modern versions of traditional sails, such as rigid sails or automated kites, are designed to work in tandem with engines to provide additional thrust when wind conditions are favorable. These systems can be retrofitted onto existing ships and can reduce fuel consumption by up to 30%, depending on the vessel and its route.
Flettner Rotors: These cylindrical sails use the Magnus effect to generate additional thrust. The spinning rotors create lift, which helps to push the vessel forward. While not a full replacement for engines, Flettner rotors can provide significant fuel savings on long voyages.
While wind-assisted technologies alone may not be sufficient to achieve zero-emission shipping, they are an excellent supplementary tool that can reduce reliance on traditional fuels.
5. Overcoming Challenges and Moving Forward
While zero-emission propulsion technologies hold great promise, several challenges remain before they can be widely adopted in the shipping industry:
Infrastructure Development: The shift to alternative fuels like hydrogen, ammonia, or biofuels requires the development of new fueling infrastructure at ports worldwide. This infrastructure must be safe, reliable, and able to handle large quantities of alternative fuels.
Energy Storage and Density: Hydrogen and batteries present storage challenges, particularly for larger vessels. Hydrogen’s low energy density means that more storage space is required, and batteries, while efficient, can be heavy and have limited capacity for long voyages.
Cost and Investment: The transition to zero-emission shipping involves high upfront costs. The research and development of new technologies, as well as the retrofitting or building of new ships, require significant investment. Governments and the private sector will need to collaborate to overcome these financial barriers.
Propulsion Solutions for Status Mobility:
Status mobility for Propulsion solutions focus on advanced, sustainable, and efficient technologies that enhance the performance and environmental friendliness of high-end transportation. These solutions cater to luxury and high-performance vehicles, including electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid systems, and alternative fuels, offering both cutting-edge innovation and eco-conscious operation. They enable smoother, quieter, and faster travel while aligning with global sustainability goals. Whether for high-performance sports cars, premium electric yachts, or luxury aircraft, these propulsion systems emphasize both status and environmental responsibility in their design and performance.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Global Electric Marine Battery Module Market Performance and Future Trends Review 2024 - 2031
The global electric marine battery module market is a rapidly evolving segment of the maritime industry, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing focus on sustainability. This article explores the dynamics of this market, highlighting its significance, key drivers, challenges, and future trends.

Overview of Electric Marine Battery Modules
The global electric marine battery module market is poised for significant growth as the maritime industry embraces sustainability and seeks to reduce emissions. With advancements in technology and increasing regulatory support
What Are Electric Marine Battery Modules?
Electric marine battery modules are energy storage systems specifically designed for maritime applications. They play a crucial role in powering electric and hybrid vessels, offering several benefits:
Environmental Impact: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions by replacing traditional fossil fuel engines.
Energy Efficiency: Enhancing operational efficiency by storing energy for use during peak demand or when the vessel is at rest.
Cost-Effectiveness: Lowering operating costs through reduced fuel consumption and maintenance requirements.
Types of Marine Battery Technologies
Electric marine battery modules can be categorized into various types based on their chemistry and application:
Lithium-ion Batteries: Widely used due to their high energy density, longer lifespan, and lightweight properties.
Lead-Acid Batteries: A more traditional option, often used in smaller vessels for cost-effectiveness but with lower energy density.
Flow Batteries: Emerging technology that offers long-duration energy storage, suitable for larger vessels and commercial applications.
Market Dynamics
Key Drivers
Regulatory Support for Emission Reductions: Increasing regulatory pressures to reduce emissions are driving the adoption of electric and hybrid vessels.
Advancements in Battery Technology: Continuous improvements in battery technologies, including energy density and charging speed, are making electric marine solutions more viable.
Growing Demand for Sustainable Solutions: As the maritime industry shifts towards sustainability, there is a rising demand for electric propulsion systems and energy-efficient technologies.
Challenges
High Initial Costs: The upfront investment for electric marine battery modules can be significant, which may deter some operators, especially in the commercial shipping sector.
Limited Charging Infrastructure: The lack of adequate charging infrastructure in ports and marinas can pose challenges for the widespread adoption of electric vessels.
Safety Concerns: Battery safety remains a critical issue, particularly with lithium-ion technology, requiring stringent regulations and standards.
Regional Insights
North America
North America is a leading market for electric marine battery modules, driven by a strong emphasis on regulatory compliance and sustainability. The region is home to several key manufacturers and research institutions focused on advancing battery technology.
Europe
Europe is experiencing robust growth in the electric marine battery module market, supported by ambitious emission reduction targets and significant investments in green shipping technologies. Countries like Norway and Germany are at the forefront of adopting electric vessels.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is projected to witness rapid growth, fueled by increasing maritime activities, investments in electric propulsion, and a focus on reducing emissions in countries such as China and Japan.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
Several prominent companies dominate the global electric marine battery module market:
Rolls-Royce Holdings plc
Wärtsilä Corporation
Siemens AG
Kongsberg Gruppen
Leclanché S.A.
Strategies for Growth
To enhance their market position, companies are focusing on:
Innovation: Investing in research and development to create advanced battery technologies that offer improved performance and safety.
Partnerships and Collaborations: Forming strategic alliances with shipbuilders, operators, and technology providers to expand their reach and enhance product offerings.
Sustainability Initiatives: Committing to environmentally friendly practices in their operations and product development to align with industry trends.
Future Trends
Integration with Renewable Energy
The integration of electric marine battery modules with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, is expected to gain traction. This combination will enhance energy efficiency and sustainability in marine operations.
Development of Hybrid Systems
Hybrid propulsion systems that combine traditional engines with electric battery modules are likely to become more prevalent, offering operators greater flexibility and efficiency in various operational scenarios.
Conclusion
The global electric marine battery module market is poised for significant growth as the maritime industry embraces sustainability and seeks to reduce emissions. With advancements in technology and increasing regulatory support, electric and hybrid vessels are becoming more viable. Stakeholders must remain proactive in addressing challenges and leveraging opportunities in this dynamic market to ensure a greener future for maritime operations.
#Global Electric Marine Battery Module Market Size#Global Electric Marine Battery Module Market Trend#Global Electric Marine Battery Module Market Growth
0 notes
Text
The global marine pressure accumulator market was valued at $340 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.2% from 2023 to 2032.The marine industry is crucial to the global economy, facilitating the transport of goods and resources across the world's oceans. A critical component within this industry is the pressure accumulator, an essential device used in hydraulic systems on ships and marine platforms. The marine pressure accumulator market has seen significant growth due to advancements in technology, increasing maritime activities, and the rising demand for energy-efficient and reliable hydraulic systems.
Browse the full report at https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/marine-pressure-accumulator-market
Market Overview
The global marine pressure accumulator market has been expanding steadily. This growth can be attributed to the increasing demand for new ships and the retrofitting of existing fleets with advanced hydraulic systems. Pressure accumulators play a vital role in maintaining the efficiency and performance of these systems, ensuring smooth and safe operations.
Key Drivers
1. Technological Advancements: The marine industry has seen rapid technological advancements, leading to the development of more efficient and reliable pressure accumulators. Innovations in materials and design have enhanced the performance and longevity of these devices, making them indispensable in modern hydraulic systems.
2. Increasing Maritime Activities: The expansion of global trade and the rising demand for oil and gas exploration have led to increased maritime activities. This, in turn, has driven the demand for advanced hydraulic systems equipped with pressure accumulators to ensure operational efficiency and safety.
3. Energy Efficiency: With the growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency, pressure accumulators have become crucial components in marine hydraulic systems. They help reduce energy consumption by storing and releasing hydraulic energy as needed, minimizing the workload on pumps and motors.
4. Regulatory Standards: Stringent regulatory standards and safety norms in the marine industry have necessitated the adoption of high-quality pressure accumulators. Compliance with these regulations ensures the safety and reliability of marine operations, further driving the market growth.
Regional Insights
North America: The North American market is driven by the presence of major marine equipment manufacturers and the increasing demand for advanced hydraulic systems in naval ships and offshore platforms.
Europe: Europe is a significant market for marine pressure accumulators, with countries like Norway, Germany, and the UK being key players due to their strong maritime industries and focus on sustainable technologies.
Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth in the marine pressure accumulator market, primarily due to the booming shipbuilding industry in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. The increasing focus on energy-efficient maritime solutions is also propelling the market forward.
Rest of the World: The market in the rest of the world is expected to grow steadily, driven by the expansion of maritime trade routes and the development of offshore oil and gas fields.
Future Outlook
The future of the marine pressure accumulator market looks promising, with continuous advancements in technology and increasing investments in the maritime sector. The growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency is expected to drive further innovations in pressure accumulator designs, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Leading players in the marine pressure accumulator market:
Bosch Rexroth
Parker Hannifin
HYDAC
Rotec Hydraulics
ROTH Hydraulics
Accumulators Inc.
Quality hydraulic power
Steyr Motors
Hydroll
Hydraulics International, Inc.
Hydraproducts
Hannon Hydraulics
Forum Energy Technologies
Woodward
Eaton
Freudenberg Sealing Technologies
SKF
General Electric
Johnson Controls
Nippon Accumulator
Segmentation analysis for the marine pressure accumulator market
Segmentation by Type
Bladder Accumulators: Account for almost 50% of the share currently. Wide availability and lower costs make this the standard option. But life span limitations relative to piston and diaphragm types.
Piston Accumulators: higher pressure ratings for the most demanding marine environments, like offshore drilling. They make up almost 30% of the market but require specialized seals and machining expertise, increasing costs.
Diaphragm Accumulators: Growing adoption in naval applications due to absorption capabilities for pressure spikes and vibration dampening properties. Materials innovations target cost reduction through composites rather than traditional stainless steels.
Segmentation by End-Use Industry
Commercial Vessels: Focus on maximizing equipment longevity and corrosion resistance to sustain shipping revenues totaling over $150 million currently.
Naval Vessels: Demanding specifications around shock resistance capabilities given recoils and blast exposures. Representing a smaller $65 million niche, but security priorities justify premium spending on accumulator system redundancies.
Browse the full report at https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/marine-pressure-accumulator-market
About Us:
Credence Research is committed to employee well-being and productivity. Following the COVID-19 pandemic, we have implemented a permanent work-from-home policy for all employees.
Contact:
Credence Research
Please contact us at +91 6232 49 3207
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.credenceresearch.com
0 notes
Text
Salmon Fish Market: Global Industry Analysis and Forecast 2023 – 2030

Salmon Fish Market Size Was Valued at USD 16.16 Billion in 2022, and is Projected to Reach USD 31.50 Billion by 2030, Growing at a CAGR of 8.7% From 2023-2030.
Salmon is an oily fish variety belonging to the salmonoid family. Salmon fish is highly rich in protein and provides essential nutrients required for a human body, thus, is considered as functional foods and major driver for salmon fish market.
Various health benefits such as lowering of blood pressure, improving the cells function, calming inflammation and reducing the risk of cancer are the key factors that are most likely to boost the market growth salmon fish globally. The rising consumer inclination from carb-based and high-calorie food products towards protein-rich alternatives helps to boost the market growth.
Get Full PDF Sample Copy of Report: (Including Full TOC, List of Tables & Figures, Chart) @
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/request/16313
The latest research on the Salmon Fish market provides a comprehensive overview of the market for the years 2023 to 2030. It gives a comprehensive picture of the global Salmon Fish industry, considering all significant industry trends, market dynamics, competitive landscape, and market analysis tools such as Porter's five forces analysis, Industry Value chain analysis, and PESTEL analysis of the Salmon Fish market. Moreover, the report includes significant chapters such as Patent Analysis, Regulatory Framework, Technology Roadmap, BCG Matrix, Heat Map Analysis, Price Trend Analysis, and Investment Analysis which help to understand the market direction and movement in the current and upcoming years. The report is designed to help readers find information and make decisions that will help them grow their businesses. The study is written with a specific goal in mind: to give business insights and consultancy to help customers make smart business decisions and achieve long-term success in their particular market areas.
Leading players involved in the Salmon Fish Market include:
Trident Seafoods Corporation (USA), Ocean Beauty Seafoods (USA), Clearwater Seafoods Inc. (Canada), Smoked Salmon Processors Association (Canada), Cooke Aquaculture Inc. (Canada), Ocean Wise (Canada), Mowi ASA (Norway), Leroy Seafood AS (Norway), Akvafarmøy AS (Norway), Marine Harvest ASA (Norway), Grieg Seafood ASA (Norway), SalMar ASA (Norway)
If You Have Any Query Salmon Fish Market Report, Visit:
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/inquiry/16313
Segmentation of Salmon Fish Market:
By Type
Chinook Salmon
Coho Salmon
Pink Salmon
Red Salmon
Silverbrite Salmon
Salmo Salar
By End Product Type
Fresh
Frozen
Canned
By Distribution Channel
Retail Stores
Supermarkets/ Hypermarkets
Online Sales Channel
By Regions
North America (US, Canada, Mexico)
Eastern Europe (Bulgaria, The Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Rest of Eastern Europe)
Western Europe (Germany, UK, France, Netherlands, Italy, Russia, Spain, Rest of Western Europe)
Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, The Philippines, Australia, New Zealand, Rest of APAC)
Middle East & Africa (Turkey, Bahrain, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, UAE, Israel, South Africa)
South America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of SA)
What to Expect in Our Report?
(1) A complete section of the Salmon Fish market report is dedicated for market dynamics, which include influence factors, market drivers, challenges, opportunities, and trends.
(2) Another broad section of the research study is reserved for regional analysis of the Salmon Fish market where important regions and countries are assessed for their growth potential, consumption, market share, and other vital factors indicating their market growth.
(3) Players can use the competitive analysis provided in the report to build new strategies or fine-tune their existing ones to rise above market challenges and increase their share of the Salmon Fish market.
(4) The report also discusses competitive situation and trends and sheds light on company expansions and merger and acquisition taking place in the Salmon Fish market. Moreover, it brings to light the market concentration rate and market shares of top three and five players.
(5) Readers are provided with findings and conclusion of the research study provided in the Salmon Fish Market report.
Our study encompasses major growth determinants and drivers, along with extensive segmentation areas. Through in-depth analysis of supply and sales channels, including upstream and downstream fundamentals, we present a complete market ecosystem.
If you require any specific information that is not covered currently within the scope of the report, we will provide the same as a part of the customization.
Acquire This Reports: -
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/checkout/?user=1&_sid=16313
About us:
Introspective Market Research (introspectivemarketresearch.com) is a visionary research consulting firm dedicated to assisting our clients to grow and have a successful impact on the market. Our team at IMR is ready to assist our clients to flourish their business by offering strategies to gain success and monopoly in their respective fields. We are a global market research company, that specializes in using big data and advanced analytics to show the bigger picture of the market trends. We help our clients to think differently and build better tomorrow for all of us. We are a technology-driven research company, we analyse extremely large sets of data to discover deeper insights and provide conclusive consulting. We not only provide intelligence solutions, but we help our clients in how they can achieve their goals.
Contact us:
Introspective Market Research
3001 S King Drive,
Chicago, Illinois
60616 USA
Ph no: +1-773-382-1047
Email: [email protected]
#Salmon Fish#Salmon Fish Market#Salmon Fish Market Size#Salmon Fish Market Share#Salmon Fish Market Growth#Salmon Fish Market Trend#Salmon Fish Market segment#Salmon Fish Market Opportunity#Salmon Fish Market Analysis 2023
0 notes
Text
Marine Compressor Market Analysis by Top Key Players, Industry Overview, Supply and Consumption Demand Analysis to 2031
The global "Marine Compressor Market Market" report indicates a consistent and robust growth trend in recent times, projecting a positive trajectory expected to persist until 2031. A significant trend observed in the Marine Compressor Market market is the rising consumer inclination towards environmentally sustainable and eco-friendly products. Furthermore, a notable advancement in this market is the increasing incorporation of technology to elevate both product quality and efficiency. Cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and block chain are actively employed to develop innovative products that outperform traditional options in terms of effectiveness and efficiency. The Marine Compressor Market Market Research Report for 2024 highlights emerging trends, growth opportunities, and potential scenarios envisioned up to the year 2031.
By delving into the latest trends, the report keeps businesses abreast of the dynamic market environment, helping them identify emerging opportunities and navigate potential challenges. The meticulous analysis covers various aspects, offering valuable insights into the historical performance of the market and presenting the current (CAGR) status.
Get a Sample Copy of the Report at: https://www.proficientmarketinsights.com/enquiry/request-sample-pdf/1885
Who are the biggest Marine Compressor Market manufacturers worldwide?
Atlas Copco (Sweden)
KAESER KOMPRESSOREN (Germany)
TANABE (Japan)
Ingersoll Rand (U.S.)
Hi-Sea Marine (China)
Burckhardt Compression (Switzerland)
DHV Marine (Germany)
Teknotherm Marine (Norway)
The Marine Compressor Market Market is described briefly as follows:
The Global Marine Compressor Market size was modified to USD 3172.8 million in 2024, and the market is projected to touch USD 3745.8 million in 2031, showing a CAGR of 2.40% during the forecast period
SWOT Analysis of Marine Compressor Market Market:
A SWOT analysis involves evaluating the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a particular market or business. In the case of the keyword market, we'll be looking at the factors that can impact the industry's performance.
Pestle Analysis of Marine Compressor Market Market:
To better comprehend the market environment, a five-force analysis is performed, which takes into account the bargaining power of the customer, the supplier, the threat of substitutes, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of competition.
Get a Sample Copy of Marine Compressor Market Market Report
What are the Types in Marine Compressor Market Market?
Reciprocating Type
Rotary Screw Type
Rotary Vane Type
Other
What are Applications in Marine Compressor Market Market?
Yachts
Merchant Ships
Navy Vessels
Other
Inquire or Share Your Questions If Any before the Purchasing This Report: https://www.proficientmarketinsights.com/enquiry/queries/1885
Geographical Segmentation:
Geographically, this report is segmented into several key regions, with sales, revenue, market share, and Marine Compressor Market market growth rate in these regions, from 2017 to 2028, covering
North America (United States, Canada and Mexico)
Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Russia and Turkey etc.)
Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, Korea, India, Australia, Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia, and Vietnam)
South America (Brazil etc.)
Middle East and Africa (Egypt and GCC Countries)
Some of the key questions answered in this report:
Who are the worldwide key Players of the Marine Compressor Market Industry?
How the opposition goes in what was in store connected with Marine Compressor Market?
Which is the most driving country in the Marine Compressor Market industry?
What are the Marine Compressor Market market valuable open doors and dangers looked by the manufactures in the worldwide Marine Compressor Market Industry?
Which application/end-client or item type might look for gradual development possibilities? What is the portion of the overall industry of each kind and application?
What centered approach and imperatives are holding the Marine Compressor Market market?
What are the various deals, promoting, and dissemination diverts in the worldwide business?
What are the key market patterns influencing the development of the Marine Compressor Market market?
Financial effect on the Marine Compressor Market business and improvement pattern of the Marine Compressor Market business?
Purchase this Report (Price 3200 USD for A Single-User License) at: https://www.proficientmarketinsights.com/purchase/1885
TOC of Global Marine Compressor Market Market Research Report 2023
1 Marine Compressor Market Market Overview
2 Market Competition by Manufacturers
3 Marine Compressor Market Production by Region
4 Marine Compressor Market Consumption by Region
5 Segment by Type
6 Segment by Application
7 Key Companies Profiled
8 Industry Chain and Sales Channels Analysis
9 Marine Compressor Market Market Dynamics
10 Research Finding and Conclusion
11 Methodology and Data Source
0 notes
Text

Norway, a member of NATO, is the third country to donate F-16 fighters to Ukraine
Fernando Valduga By Fernando Valduga 08/27/2023 - 09:28am Military, War Zones
NATO member Norway will donate F-16 fighters to Ukraine, Norwegian Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Store said on Thursday amid Kiev's difficult counter-offensive against Russia.
Speaking to the Norwegian news agency NTB in Kiev, where he paid a visit on the occasion of Ukraine's Independence Day, Gahr Store said that Norway will supply F-16 aircraft to Ukraine, but it will probably be less than 10.
Gahr said he informed the president of Ukraine, Volodymyr Zelenskyy, about the donation of the aircraft and that Norway would discuss the number of planes, as well as the transfer schedule with Kiev and other allied countries.
“But Ukraine can count on the contribution of Norway,” the prime minister added.
Norway would be the third European country, after the Netherlands and Denmark, to donate F-16 planes.
Ukraine has long asked sophisticated fighters to give it an advantage in combat. He recently launched a long-awaited counter-offensive against Kremlin forces without air cover, putting his troops at the mercy of Russian aviation and artillery.

In February, oil-rich Norway announced that it would donate 75 billion crowns ($7 billion) to Kiev as part of a five-year support package, making Norway one of the world's largest donors to Ukraine.
The money will be divided equally between military and humanitarian assistance over five years, divided into 15 billion crowns (1.4 billion dollars) annually.
Gahr Store announced on Thursday that Norway would also donate anti-aircraft missiles to Ukraine, saying that “air defense is critical to Ukraine's ability to protect both the civilian population and frontline infrastructure and military units against any type of Russian air attack.”
“This is one of the largest Norwegian donations of military material to Ukraine to date,” Gahr said in a statement.
The Norwegian government has long stated that it is considering sending F-16 to Ukraine. In January, Norway received the first of the 52 F-35s ordered. The new fighters will replace Norway's F-16 fleet.
Last week, the Netherlands and Denmark announced that they will donate F-16 aircraft. Denmark said it will provide 19 planes, while the Netherlands reported that it will donate 42 of the jets.
Earlier this week, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy visited several European countries, including the Netherlands and Denmark, but did not go to Norway.
Tags: Military AviationF-16 Fighting FalconRNAF - Royal Norwegian Air Force / Royal Norwegian Air ForceWar Zones - Russia/Ukraine
Sharing
tweet
Fernando Valduga
Fernando Valduga
Aviation photographer and pilot since 1992, he has participated in several events and air operations, such as Cruzex, AirVenture, Daytona Airshow and FIDAE. He has work published in specialized aviation magazines in Brazil and abroad. Uses Canon equipment during his photographic work throughout the world of aviation.
Related news
MILITARY
NATO conducts long-range exercises testing interoperability in Romania
08/27/2023 - 19:00
DEMONSTRATION SQUADS
Patrouille Suisse will fly with biofuel
08/27/2023 - 14:00
AIRCRAFT ACCIDENTS
Collision in flight between two Ukrainian jets kills three pilots, including the famous "Juice" Ace
27/08/2023 - 11:53
AIRCRAFT ACCIDENTS
U.S. Osprey accident in Australia causes death of 3 Marines
08/27/2023 - 11:00
INTERCEPTIONS
F-16 fighters intercept and fire flares at civilian aircraft flying near President Biden's vacation spot
08/26/2023 - 16:31
AIRCRAFT ACCIDENTS
F/A-18D Hornet accident in Miramar, San Diego
26/08/2023 - 16:01
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Canned Seafood Market Size, Share, Trends, Growth, 2032

Market Overview
The global canned seafood market size was valued at USD 29.25 billion in 2023. The market is projected to grow from USD 30.46 billion in 2024 to USD 45.11 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.03% during the forecast period.
The market is expected to expand in the coming years as more people choose products with clear labels, especially those that are eco-friendly. Big companies are stepping up by creating these products and introducing sustainable canned seafood, which will boost this growth.
Fortune Business Insights presents this information in their report titled "Canned Seafood Market, 2024–2032."
List of Key Players Profiled in the Market Report
Nippon Suisan Kaisha, Ltd (Japan)
LDH (La Doria) Ltd (U.K.)
American Tuna, Inc. (U.S.)
Universal Canning, Inc. (Philippines)
Connors Bros. Ltd. (Brunswick Seafoods) (Canada)
Nueva Pescanova (Spain)
Marine Harvest ASA (Norway)
Thai Union Frozen Products (Thailand)
Royal Greenland (Greenland)
StarKist Co. (U.S.)
Segments
Increasing Tuna Fish Consumption due to Its Higher Availability to Fuel Segment Growth
The market is divided by species into tuna, salmon, sardines, mackerel, and others. Tuna holds the largest share of the canned seafood market. This is because tuna consumption is rising, thanks to its high availability in over 70 countries.
Increased Accessibility of Various Products to Foster Retail Segment Growth
The market is divided into two main groups: places where people eat and drink (like hotels, restaurants, and cafes) and stores. Stores include big supermarkets, specialty shops, small convenience stores, and online shops. Big supermarkets and hypermarkets are the biggest because they have a lot of different products. But, online shops are growing the quickest because of new technology.
The market is also spread out across different areas of the world: North America, South America, Europe, the Middle East & Africa, and Asia Pacific.
Source: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/canned-seafood-market-103806
Report Coverage
The market research report gives a detailed look at the market, focusing on competition and top product types. It offers helpful information on market trends and important changes in the industry. The report also looks at different things that have helped the market grow recently.
Drivers and Restraints
Surging Investments in Aquaculture Production Advancements to Accelerate Market Growth
More people are learning about healthy eating, which means they want to buy more seafood. This is making big seafood companies work harder to produce more. But, problems like climate change and rules from the government about fishing to stop overfishing are making it difficult for these companies to catch more fish. To solve this, big companies are putting money into new ways of farming seafood, which is expected to help the market grow even more. The seafood farming industry is also growing quickly, which is helping the market grow. However, the lack of fish due to overfishing is slowing down the growth of the market.
Regional Insights
Increase in per Capita Consumption to Propel Market Growth in Europe
The Europe market was worth $17.20 billion in 2023, growing due to higher seafood consumption in countries like China and India, seen as a main food. Europe's market is also expanding, mainly because of a rise in seafood eating and a growing interest in cooking.
Competitive Landscape
Key Market Players Emphasizing Product Innovations to Maintain Their Competitive Edge
Leading companies are working on being more eco-friendly and teaming up to make more products and satisfy customer needs. For instance, in May 2019, Nippon Suisan Kaisha Ltd. shared a plan to improve production and boost their output.
Key Industry Development
January 2024 – Norway-based canned seafood manufacturer, King Oscar launched a new product line of Atlantic salmon in extra virgin oil. The skinless and boneless fish products are available in three varieties in the U.S. market.
0 notes
Text
Harnessing the Power of Hydrogen: A Promising Frontier in Marine Fuel Technology
In recent years, the quest for more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy sources has intensified. As concerns about climate change and pollution grow, industries are under immense pressure to seek cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels. In this pursuit, one promising solution has emerged on the horizon: Hydrogen Marine Fuel.
Hydrogen, known for its abundance and clean-burning properties, has long been hailed as a potential game-changer in the energy landscape. However, its widespread adoption has been slow, largely due to technical challenges and the high cost of production and storage. Nevertheless, advancements in hydrogen fuel cell technology and the increasing demand for eco-friendly solutions have propelled hydrogen into the limelight as a viable marine fuel option.
Maritime transport is a significant contributor to global emissions, releasing substantial amounts of greenhouse gases and pollutants into the atmosphere. Shipping companies, along with governments and environmental organizations, have recognized the need to transition to cleaner fuels. Hydrogen Marine Fuel holds immense promise in this context, offering a range of benefits that could revolutionize the maritime industry.
Zero Emissions:
Hydrogen fuel cells produce electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen, with the only byproduct being water. This emission-free process makes hydrogen an attractive option for reducing carbon footprints and complying with stringent emission regulations.
Abundant and Renewable:
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe and can be produced from various sources, including electrolysis of water using renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. This means that as renewable energy capacity expands, so does the potential for clean hydrogen production.
High Energy Density:
Hydrogen offers a higher energy density compared to conventional batteries, making it suitable for long-haul maritime operations where energy storage is crucial.
Rapid Refueling:
Unlike traditional batteries that require hours to recharge, hydrogen fuel cells can be refueled quickly, simulating the conventional refueling process and reducing downtime for ships.
Despite these benefits, the widespread adoption of Hydrogen Marine Fuel is not without challenges. The infrastructure for hydrogen production, storage, and distribution is still in its infancy and requires substantial investment. Additionally, the safety concerns associated with handling and storing hydrogen must be addressed to gain public acceptance.
However, several projects and initiatives are already underway, demonstrating the potential of hydrogen as a marine fuel. Countries like Japan, Germany, and Norway have taken the lead in developing hydrogen-powered vessels, and collaborations between industry players and research institutions are paving the way for a cleaner maritime future.
For more info:-
Hydrogen Marine Fuel
Fuel Oil Blending Consulting Company Usa
0 notes
Text
Deliciously Fresh: Big Sam's Norwegian Salmon Fillet A Taste of Norwegian Excellence
Big Sam's Norwegian Salmon Fillet offers the finest quality salmon sourced from the pristine waters of Norway. With a commitment to sustainable fishing practices and a focus on delivering exceptional taste and nutritional value, Big Sam's has become a trusted brand among seafood enthusiasts. In this article, we will explore the story behind Big Sam's, the unique characteristics of Norwegian salmon, the details of their salmon fillet product, its health benefits, cooking tips, delicious recipes, sustainability efforts, customer reviews, availability, and more.
What is Big Sam's?
Big Sam's is a renowned seafood brand that has been in operation for over two decades. Their expertise lies in providing premium seafood products, with a specific emphasis on Norwegian salmon. The company prides itself on maintaining long-term partnerships with Norwegian fisheries that follow sustainable practices. This commitment ensures the highest quality salmon while preserving the marine ecosystem.
Norwegian Salmon
Norwegian salmon has gained international recognition for its superior taste and texture. The cold and clear waters of Norway create an ideal environment for salmon to thrive, resulting in exceptional flavor and delicate, moist flesh. The salmon's natural diet of krill and shrimp contributes to its distinct color and rich omega-3 fatty acid content.
Big Sam's Fillet
Big Sam's offers skinless portions of Norwegian salmon fillets that are carefully selected and expertly prepared. Each portion is individually vacuum-sealed to maintain freshness and preserve the natural flavors. The fillets are conveniently portioned, making it easy for consumers to prepare a delicious and healthy meal.
Health Benefits
Big Sam's salmon fillets provide numerous health benefits. Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, these fillets support heart and brain health, reduce inflammation, and promote overall well-being. The high protein content aids in muscle development and repair, making it an excellent choice for fitness enthusiasts.
Cooking Tips
To unlock the full flavor of Big Sam's salmon fillets, various cooking methods can be employed. Grilling or pan-searing the fillets with a touch of lemon butter enhances the natural taste. Baking the salmon with dill and garlic creates an aromatic and savory dish that is sure to impress. The fillets can also be poached or broiled, allowing for versatility in meal preparation.
Recipes
Grilled Salmon with Lemon Butter:Ingredients: Big Sam's salmon fillets, butter, lemon juice, salt, and pepper.Instructions: Preheat the grill, place fillets on the grill, brush with lemon butter, season with salt and pepper, and grill until cooked through.
Baked Salmon with Dill and Garlic:Ingredients: Big Sam's salmon fillets, dill, garlic, olive oil, salt, pepper.Instructions: Preheat oven, place fillets on a baking sheet, rub with olive oil, sprinkle with chopped dill and minced garlic, season with salt and pepper, and bake until flaky.
Sustainability
Big Sam's is committed to sustainability and actively supports responsible fishing practices. They work closely with Norwegian fisheries that prioritize eco-friendly methods, ensuring the preservation of marine habitats and the longevity of salmon populations. By choosing Big Sam's salmon fillets, consumers contribute to the conservation of the environment.
Customer Reviews
Customers rave about the exceptional quality and taste of Big Sam's Norwegian Salmon Fillet. Many have praised the freshness, tenderness, and rich flavor of the salmon. Testimonials highlight how Big Sam's salmon has become a staple in their healthy eating routines, providing a satisfying and nutritious dining experience.
Availability
Big Sam's salmon fillets are available at various retail locations, both online and offline. Customers can find them at specialty seafood markets, grocery stores, and selected online retailers. To ensure the freshest product, it is recommended to check the official Big Sam's website for authorized vendors.
Conclusion
Big Sam's Norwegian Salmon Fillet delivers a premium dining experience with outstanding quality, remarkable taste, and numerous health benefits. Sourced from sustainable fisheries in Norway, these skinless portions are convenient and easy to cook. Whether grilled, baked, or prepared using other methods, Big Sam's salmon fillets are sure to satisfy seafood enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals alike.
FAQs
Are Big Sam's salmon fillets frozen? No, Big Sam's salmon fillets are fresh and individually vacuum-sealed for optimal freshness.
Can I cook the fillets from frozen? It is recommended to thaw the fillets before cooking to ensure even cooking and the best results.
How long does Big Sam's salmon last? When properly stored in the refrigerator, Big Sam's salmon fillets can last up to two days after the purchase date.
Is Big Sam's salmon sustainably sourced? Yes, Big Sam's prioritizes sustainability and partners with Norwegian fisheries that follow responsible fishing practices.
What makes Big Sam's salmon special? Big Sam's salmon stands out due to its superior taste, texture, and commitment to sustainable sourcing, ensuring a positive impact on the environment.
#BigSamsSalmon#NorwegianSalmon#SalmonFillet#FreshCatch#SeafoodDelight#DeliciousDinner#HealthyEating#FoodieFaves#FoodPhotography#GourmetGoodness#FishLovers#TastyTreats#FoodGasm#FoodieLife#SalmonLovers#FoodLover#FoodBloggers#FoodInspiration#FoodieGram#Foodstagram#lucky store#buy now#imported#luckystore.in
0 notes
Photo

All boats require some kind of steering but some need a more complex setup. Mechanical knowledge is very advisable if you propose to put in a ship steering mechanism yourself but failing that, there are many professionals who will be ready to do that. Hydraulic steering systems for boats may be a clear winner but the worth is often scary. For simplicity, the rack system is the easiest to put in and therefore the rotary is within the middle. Switching to a more reliable steering mechanism designed for performance will increase your enjoyment of the waters. Below may be a list of the simplest boat steering systems that include hydraulic, rack, rotary and power systems. Adding steering to your boat isn't as simple as installing a wheel to the cockpit. an entire wheel system is required with all the cables and other components that make a full kit. The best boat steering mechanism is that the Bay Star Hydraulic Steering Kit, which is employed for single station outboard powered boats and comes with all the components and hydraulic fluid for a high performing steering setup on your boat. The three main sorts of boat steering are rack, rotary, power and hydraulic steering with the latter being the foremost expensive. it is vital to notice that some systems may require converting, which can require mechanical knowledge. visit for details https://nl.forboat.eu/
1 note
·
View note
Text
17.12.2022
Ok so. The cheap recipes i have survived with (on student exchange on norway). Also general info for max cheapskateyness, like where to find sales etc.
1. Fried noodles with salted peanuts
Noodles 5 pack 1.7e (the cheapest ones)
Peanuts 200g 2.3e
Any spices you find! Most preferably: paprika, curry, chili, ginger (ground), garlic 2 -4 cloves or 1 teaspoon of ground garlic + soy sauce (forget kikkoman it's hella expensive? Go to an "ethnic" store to find a bigger bottle of soy sauce, i used "healthy boy brand" thin soy sauce, the 1l bottle will last all eternity)
Boil the noodles or let them sit in a cup with boiling water until soft (for the love of god and all holies do not touch the cheap noodles' own spice packet)
Pour out excessive water
Take a small pan and pour the noodles in (if u use fresh garlic crush them or cut em up and fry them a lil bit while the noodles "boil"
Add all the spices, a bit of any oil (or butter) and 1-4 teaspoon/s of soy sauce
Stir fry until the noodles look sticky and fried
Add salted/chili peanuts on top
2. 4 ingredient pasta
Tips! Cheapest pasta is usually spaghetti that you can buy in bulk, like in spar norway 1kg of cheapest spaghetti is 18 kr (1.7e). Use ripoff brands that the shops have, lile "x-tra" "first price" or "eldoraro" in here. Cheapest crushed tomatoes pack is 70 kr (0.65e) for 250g.
Start boiling the pasta of your choice and simultaneously start cutting the garlics. You can also use garlic crusher, it's faster. Add a little bit of salt to the pasta water.
Fry your garlics. Add in drained chickpeas (any beans work) 9 kr/0.9e per pack. Add in the crushed tomatoes.
Add in any spices you can find, preferably: onion, rosemary, herb mix, chili, pepper
Drain the pasta and add in approx ¼ or ⅓ of the sauce
Leftover sauce goes to a box and to the fridge. I do not recommend storing pasta for further eating, it can go bad too fast
3. Seljanka soup
You will need:
Cheap crushed tomatoes, potatoes, (canned) mushrooms, cabbage, bay leaf, russian pickles (or fermented pickles w garlic and dill, do not add in those with sugar!) Or just 1 table spoon of cooking vinegar, cheap frozen vegetable mix (with carrots and celery etc), salt, pepper, clove spice, herb mix w rosemary, any beans, onion, garlic
Start with peeling and dicing the potatoes, cut onions and garlics. Start boiling them with ¼ of full kettle volume of water + add the bay leaves (2 will do for 3l of soup)
Add in cut cabbage, vinegar, pickles (cut) and the spices. Add the crushed tomatoes and water if it's too stewy.
Let boil for 10 min
Add in the canned mushrooms (rinsed) and the frozen veggies and beans
Let boil for 10-20 min or until the potatoes are soft
You can either freeze or store the leftovers in a fridge
Price info: 1kg cabbage 5-20kr /0.4-2e, 2kg of potatoes 20-40kr/2-4e, jar of russian pickles 20-30kr, spices all mentioned probs like 10e (only gotta buy these once!), 2/3 big onions 20-25 kr, 2 garlics 23kr
4. Marinated beans + mashed potatoes
Take a container or a bowl. Add in 1 packet of rinsed chickpeas. Add in 2-4 tablespoons of soy sauce.
Add a bit of oil so the beans wont dry when storaged in the fridge
Add spices, preferably garlic, herbs, ginger, chili, pepper (no salt needed since the soy sauce is very salty)
Let sit for 1-2h in the fridge
Boil peeled potatoes. Pour out water. Mash them with a masher or a fork with a bit of added water/milk/melted butter if u can afford it. Add salt.
Other valuable info!
Cheapest stores (in norway) for vegetables/canned things: kiwi, extra, obs
Cheapest store for sales: obs, eurospar
Best "kuppdisk" (-50% shelf for soon to expire products) Any big markets such as eurospar and obs. Here u can find cheap meat/dairy/veggies. They have kuppdisk for veggie section, dry section and meat/dairy/frozen goods section
Download the app "e tilbundsavis" to get info what is on sale where. It's in norwegian but very easy to understand (use google translator to search items in the app, like "coffee" or "chips")
Cheapest instant coffee is friele but it tastes like crap. Nescafe brasileiro is tiny bit more expensive but so much better.
Learn to make your own popcorn in a kettle, there's youtube tutorials for that. So much cheaper than micro popcorn.
For alcohol you are damned. I would suggest buying the cheapest big (0.75 litre for 30kr) vodka bottle and mixing it with different sodas/juices. Note! Only Vinmonopolet store sells other than beer like normal stores. Check opening times, they are strict. U gotta be over 20 to buy vodka in norway, wine u can get at 18. Or ask someone u know to buy vodka for u. Or when traveling to norway get your vodka as a "gift" from the airport in your home country. It's still cheaper.
There's snack sales from time to time like 5 bars of 200 choco for 100kr. It seems like much but normally one 200g bar is 44kr. Also chips can get -50% sales, check the "tilbundsavis" app every other day so u wont miss them.
Do NOT shop in Joker mini stores or gas stations. Hella expensive. Uh oh. And for the love of All do not doordash, u will bancrupt yourself (unless u are rich but then u don't need these tips anyways).
Make as much from scratch as u can. There's plenty of "cheap/simple cooking for idiots" type vids on youtube.
For snus/tobacco i don't know the prices bc i don't use them. Probably quite expensive. Check how much u can take with u from home without taxes if u use them.
People with ovaries! Period products are expensive too. Cheap brands work just as fine. Or take a couple extra packs with u.
The winter is long and it's recommended to take vitamin supplements (especially vitamin D). There's sales for those too, team up with people u know for things like "3 for 2" in vitamins. Usually the sales start when it begins to get darker, in september.
If you have an injury/need the hospital, u can use your insurance or european health insurance card (for eu citizens it costs like 10e but then u can use the eu/schengen area hospitals with the same pricing as locals). There's student health services for free but those are for not for "major injuries", more like for check ups and teeth care.
#arktiske universitet i tromsø#student exchange#literature student#uni life#studyblr#university student#norway#master´s degree#academia#tromsø#student life tips#life hacks#student life hacks#exchange tips#erasmus#cheap recipes#cheap meals#sales tips
20 notes
·
View notes