#kimono history
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Small sketches of Japanese kimono spanning from the Nara period to the Sengoku period. References come from the Kyoto Costume Museum.
Kimono history is something I love, so this was fun to make and study.
(2024)
39 notes
·
View notes
Text






Great example of everyday noragi (work clothes, worn by farmers for ex.) from Taisho period. Note the makisode sleeve shape, offering freedom of mouvement!
You can see the close-up of the weave, made from asa (bast-fiber like hemp or linen) and kamiyori (twisted paper thread). Despite its "rugged" materials, weave is delicately interlocked with regular black stripes.
The coat also presents geometrical sashiko (white quilting), both reinforcing easily worn areas (collar, hems, inner center back), and decorating the garment.
PSA for writers: please please please don't put characters doing manual labour in "silk" kimono. I'll be forever grateful ;)
#japan#fashion#kimono#fashion history#noragi#work clothes#farmers#asa#hemp#linen#kamiyori#paper thread#sashiko#Japanese quilting#taisho period#着物
1K notes
·
View notes
Text





• Formal summer kimono for a woman with fuyō and nadeshiko.
Period: Shōwa period
Place of origin: Japan
Medium: Gauze weave; stencil-printed on the fabric surface, silk.
#fashion history#history of fashion#fashion#vintage clothing#vintage fashion#vintage#kimono#japanese#japan#summer#Shōwa#green
970 notes
·
View notes
Text
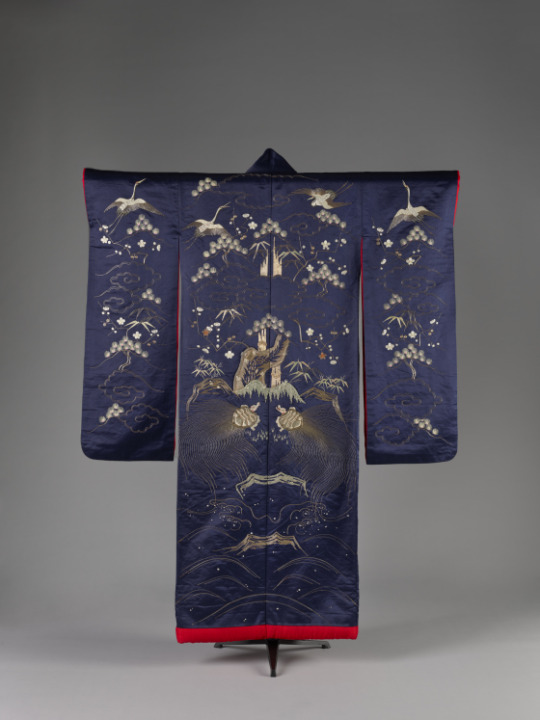

Wedding Kimono (Uchikake)
Chiba Prefecture, Japan
c.1850 (Edo Period)
Denver Art Museum
#wedding kimono#wedding#uchikake#fashion history#historical fashion#non western fashion#1850s#edo period#19th century#blue#silk#embroidery#denver art museum
746 notes
·
View notes
Text










#yukata#kimono#日本#japan#history#歴史#ユネスコ#unesco#考古学#archaeology#geography#art#madrid#culture#anime#Spain#マドリード#文化#アニメ#スペイン#art on tumblr#photography
102 notes
·
View notes
Text
In celebration of seeing the first fireflies of the season:
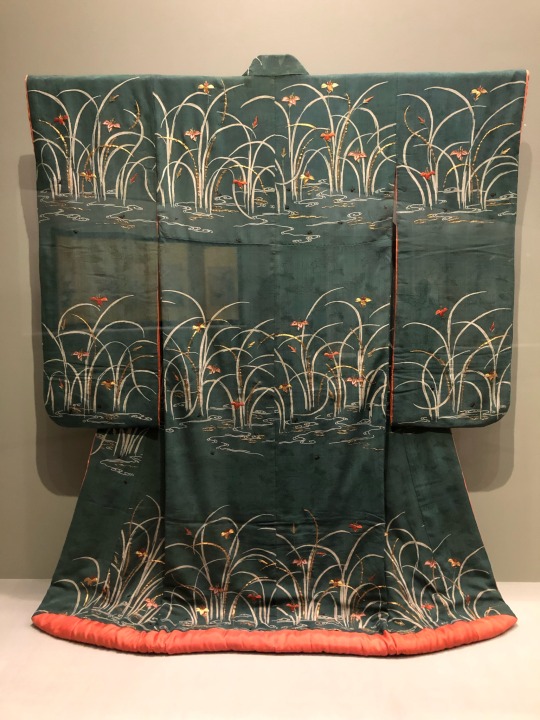
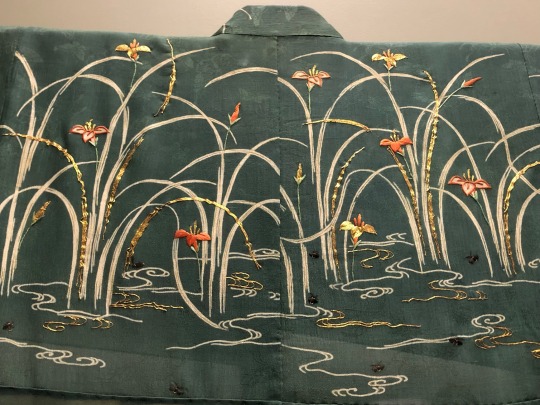
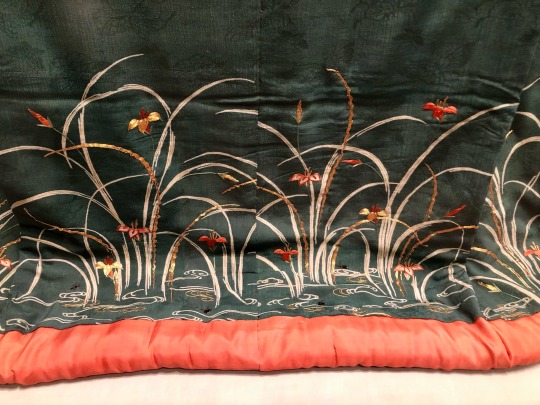





Furisode with Fireflies and Irises Japan, Edo period, 18th century silk crepe, paste-resist dyed, embroidery National Museum of Japanese History (photographed on display at The Life of Animals in Japanese Art exhbition at the National Gallery of Art DC in 2019)
#Japanese art#East Asian art#Asian art#18th century art#kimono#furisode#historical costume#garment#embroidery#irises#fireflies#National Gallery of Art DC#The Life of Animals in Japanese Art#museum visit#exhibition#textiles#National Museum of Japanese History
938 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ryukyu Clothing (Ryusou/Uchinaasugai - "Kimono")
PSA: I am not a professional dresser or historian and finding this information is more of a cultural hobby. Please correct me if you see any discrepancies.
From a Ryukyuan-language standpoint, I don't think it's appropriate for Ryukyuan clothing to be called "Kimono" because it isn't Japanese. The general term meant to talk about Okinawan clothing in the Ryukyuan Kingdom context is 琉装 (Ryusou in Japanese/Uchinaasugai ウチナースガイ in Uchinaaguchi). I'm calling it "Kimono" here because it's the most easily understandable. Additionally, this post will not include textiles from the Amami or Ishigaki region and focuses on Uchinaa.
Most Ryukyuan clothing is made for the weather of the region, which can be more humid and hot than Japan. Sadly, if there was record of Ryukyuan clothing before the Kingdom era, it's lost to history. Being a region of trade, a lot of clothing takes inspiration from the many cultures and countries the Ryukyus were in contact with (Southeast Asia, East Asia). Textiles that included Bingata, Kasuri, Silk, or Patterns were for those of upper classes.
I think the most well known style of Ryusou is the one that incorporates a Bingata robe over ウシンチー (Ushinchii). The robes were made of silk and was usually worn by the upperclass citizens in the Ryukyu Kingdom. They tend to have larger sleeves for air. It also tends to fit "loose" since it's very easy to sweat in the region. For men and women formal attire consists of a two-piece outer garment worn over an underwear garment.
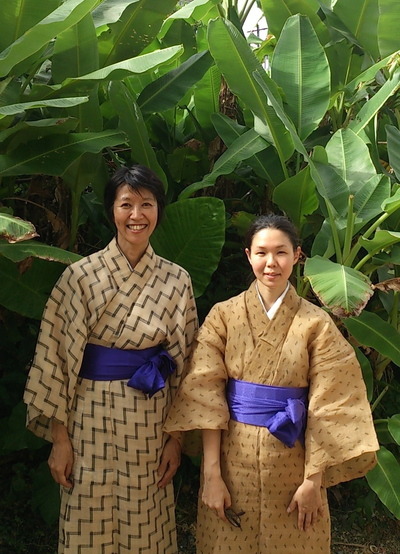
ウシンチー Ushinchi
Below is an example of me being dressed in a ウシンチー (Ushinchii) style, which as you can see in this situation the ウシン (Ushin) sash is small. Doesn't always incorporate Kasuri, sometimes it's a solid color. Sometimes it will incorporate other Ryukyuan style clothing.
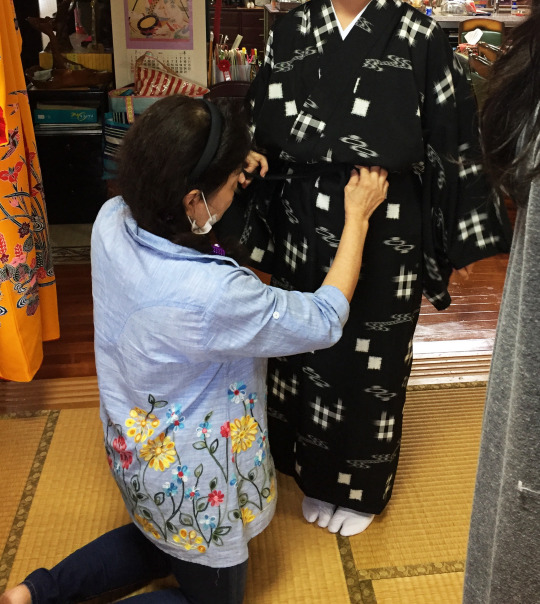

This is a more formal style of dress but this is an example of one look when they are paired together.
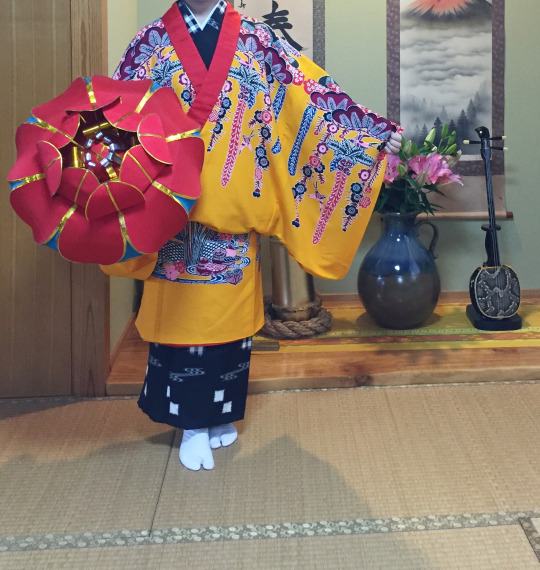

ドゥジン & カカン Duujin and Kakan
There are other clothes for women like one worn by court ladies that are "two pieces" likeドゥジン (Upper piece) and カカン (skirt). They can also have a Bingata robe worn over it. I believe the Kakan is inspired by the Hanfu and Mamianqun.

(Source)
ハチマキ Hachimaki
For formal wear for men in upper classes, the clothes tend to be more simple. They wear a ハチマキ (Hachimaki) which is a hat meant to denote your rank. Men also would tend to wear thicker sashes or obi than women.
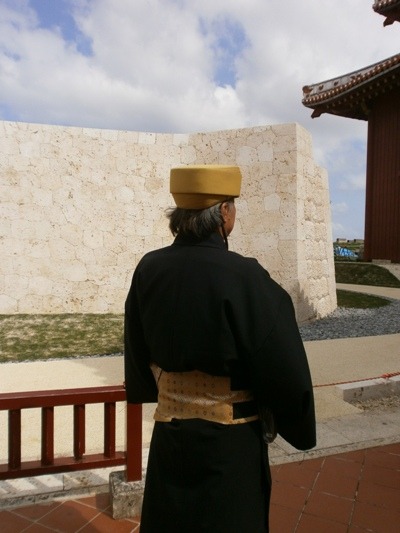

(Source)
芭蕉布 Bashofu
For common people, I don't know what the name for the attire would be but it was made of Bashofu (banana fibre). Now the textile is quite rare and sought after but before the war, it was commonplace to wear and typically worn much shorter than a Japanese kimono (around the shins). It was a relatively breathable fabric and the sleeves are more like open sleeves than what a kimono is like.

(Source)
There are more names, terms, and history that I need to learn but thank you for reading this.
#ドゥジン#ウシンチー#琉装#Ryukyu#Ryukyuan#Clothing#Okinawa#Kimono#Long Post#琉球#芭蕉布#カカン#My Post#History#Culture#Okinawan#Ryusou#Duujin#Kakan#Bashofu#Hanfu#Fashion
122 notes
·
View notes
Text

Under Kimono with Graveyard, Skulls, and Crescent Moon, Japanese, 1930
#kimono#under kimono#graveyard#skulls#japanese#1930#1930s#1900s#20th century#fashion#fashion history#history
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kimono dressing gown, c. 1885.
FIDM Museum



#victorian#victorian era#victorian fashion#19th century#fashion history#historical fashion#dress#dressing gown#kimono
346 notes
·
View notes
Text

THE TASTY PRINTS & LOVELY LADIES OF THE KAIE PERIOD -- TEMPURA WITH HER TEA.
PIC INFO: "Looks delicious," Appearance of a Courtesan in the Kaei Period, from the series "Thirty-Two Aspects of Women" (1888) by Tsukioka Yoshitoshi. Photo: Nakau Collection.
Source: https://asianartnewspaper.com/life-in-edo-prints/#prettyPhoto[group-135]/2.
#Japanese Courtesan#Japanese Art Prints#Japanese Art#Tsukioki Yoshitoshi#Tempura#Japanese#Japanese Prints#Japanese Cuisine#Nakau Collection#Hair and Makeup#Kimono#Kaei Period#Thirty-Two Aspects of Women#1888#1880s#Yoshitoshi Tsukioki#Japan#Japanese Courtesan Makeup#Japanese Food#Makeup#Japanese Art Print#Japanese fashion#Art Prints#Courtesan#Kaei Period Japan#Japanese Style#Japanese Culture#East Asia#East Asian Art#Art History
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dutch painter George Hendrik Breitner's "Girl in a White Kimono" (1894)
Geesje Kwak, a 16-year-old housemaid, draped in a Japanese kimono.
if you're interested in purchasing products depicting this work please click here
#George Hendrik Breitner#Girl In A White Kimono#Amsterdam Impressionism#Art History#Japonism#Cultural Exchange#Dutch Art#European Art#19th Century Art#Fine Arts#Oil Painting#Artistic Inspiration#Cultural Influence#Art Appreciation#Dutch Painter#Geesje Kwak
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

Paul Poiret (French, ) was one of the most influential fashion designers of the first half of the 20th century. He is credited with freeing women from the corset with his draped, unstructed styles that revolutionized the fashion world. Instead of tailoring, Poiret designed his fashions by draping and folding, creating unique pieces that echoed the traditional styles of the East. Art Deco fashion also became synonymous with Paul Poiret.
“Whenever I sign a garment with my name, I consider myself the creator of the masterpiece.” – Paul Poiret

Sorbet, created in 1912, is one of Poiret's signature designs. It was referred to as the "lampshade dress".



Poiret's first successful design was a kimono coat which he created while working for the design house of Jacques Doucet.


Left: Madame Poiret, Paul's wife, in 1912, wearing one his more bohemian creations
Right: Model wearing a Paul Poiret dress, 1914
Poiret's original designs and his ability to market his styles in new ways changed the fashion landscape forever. He designed outfits for film actresses, creating opportunities for his styles to be seen and credited beyond the runway. He was quite the bon vivant – a masterful host of events and parties that showcased his latest styles.

Fancy dress costume • 1911 • Metropolitan Museum of Art
The costume pictured above was influenced by the Russian dance company, Ballets Russes, when it performed in Paris. Poiret designed the costume for his 1002nd Night party in 1911, where it created tremendous publicity for his fashion house.
#fashion history#paul poiret#french fashion design#belle époque fashion#art deco fashion#lampshade dress#the resplendent outfit blog#women's fashion history#early 1900s fashion#designer fashion#vintage designer fashion#kimono fashion#historic clothing#old fashion photos
24 notes
·
View notes
Text



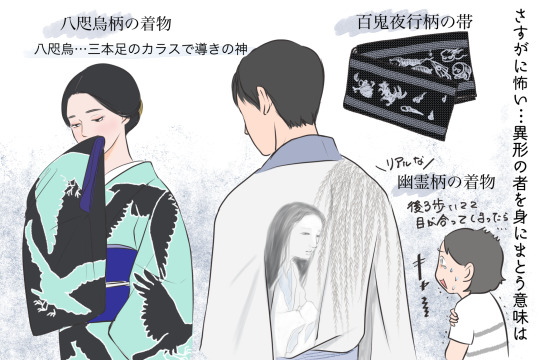
Lovely article+illustrations by Kimono Ichiba (via Tanpopo <3), overviewing famous "scary"patterns... which are in fact often auspicious as traditional Japanese patterns ;)
I believe I have them all on the blog somewhere but it's nice having them in one place so let's go!
Spiderwebs (kumo no su)
In ancient China, spider were seen as auspicious messengers connecting Heaven to Earth.
As the spider catches its prey in its web, spiderweb came to signify "grasping happiness".
Apparently during Edo period, prostitutes and geisha used spiderweb patterned items as a good luck charm (meaning something like "this customer will come back").
A very famous spiderweb depiction is the Lady Rokujo ukiyoe [焔 honô (the flame of passion)] by female artist Uemura Shoen. Wisteria caught in the web could mean ``I hope [Prince Genji] will come tonight'' which is pretty sad considering her story T_T
Skulls (dokuro)
Exact name for human remains pattern is "nozarashi" (lit. "weather beaten") ie bones scattered in a field. This depicts a corpse turned to bones/unveiled from its grave by the elements.
Skulls are thought to ward off evil and bad luck. Bones can also symbolize a do-or-die spirit, or hope for rebirth after death.
OP stresses a theory linking bones pattern to a buddhist saying 色即是空 shikisokuzekū "form is emptiness, matter is void, all is vanity". An interpetation is that we'll all turn to dust one day so we're all equal.
Bones patterns are often seen during Obon (Festival of the dead) season.
Monsters, ogres and ghosts (yôkai / oni / yûrei)
Monsters patterns were then worn to ward off bad luck and evil spirits. Reasoning is: let's repel scary things by wearing an even scarier monster!
Fearsome monsters were especially use by people with dangerous jobs, like Edo period firemen.
Firemen often had the lining of their heavy fire attire (火事装束 kajishouzoku) embelished with lavish designs of brave heroes and fantastic monsters. It was both a talisman and a way to show that they did not fear danger or death.
Another reason behing monsters patterns is the Edo period love for "scary" entertainements, be it ghost stories, parlor or other types of games, art (see for ex. Utagawa Kuniyoshi), etc. And Edo city dwellers were all about being fashionable so a monster pattern would have been considered quite iki!
#japan#art#history#pattern history#kimono#obi#halloween#spider#spiderweb#kumo#kumo no su#skull#skeleton#dokuro#nozarashi#weather beaten bones#obon#monster#youkai#oni#ghost#yurei#firemen#kajishouzoku#kaidan#ghost stories#Hyakumonogatari Kaidankai#One Hundred Supernatural Tales#Kimodameshi#Test of courage
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


• Man's Kimono.
Date: ca. 1930
Place of origin: Japan
Medium: Silk plain weave
#fashion history#history of fashion#fashion#men's fashion#traditional#traditional fashion#kimono#japan#japanese#ca. 1930's
896 notes
·
View notes
Text


Unlined Summer Kimono
c.1876
A pond with carp and water lilies adorns the lower part of this kimono, and morning glories bloom at the shoulders. This early summer scene is resist dyed and painted on a blue-and-white ground of high-quality silk gauze (ro), subtly patterned in the weave with goldfish in water. The donor’s grandmother, one of four generations of female textile artists, wore this summer kimono during her thirteenth year, around 1876, for her jūsan-mairi (literally, “thirteenth temple visit”) to Arashiyama Hōrinji, a temple in Saga, Kyoto, to receive blessings as she entered adolescence. The kimono has three family crests: one on the center of the back and one on each sleeve.
The MET (Accession Number: 2006.73.2)
#kimono#japanese fashion#fashion history#historical fashion#non western fashion#1870s#19th century#1876#blue#off white#japan#fish#floral#meiji era#the met#popular
1K notes
·
View notes









