#irish goddess danu
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
Headcanon:
Hindu goddess Danu meets Irish goddess Danu
SKSJDJRHFHF
Opposite yet kinda similar personality besties???
Or like those mummas that becomes friends while picking up their kids from Kindergarten??? Lol 💀
Both are tired moms tho-
#danu#goddess danu#irish goddess danu#celtic mythology#hindu mythology#hindu gods#hindublr#danavas mother#desiblr
12 notes
·
View notes
Text









irish mythology: danu
danu is known as the mother of irish gods. she is the mother goddess of the tuatha dé danann – in fact, these supernatural beings take their name from Ddnu, as the name tuatha dé danann translates to ‘the peoples of the goddess danu.' she is strongly associated with nature, as well as regeneration, wisdom, death, and prosperity. it’s thought that she passed on her own wisdom to members of the tuatha dé danann, as well as her creative and crafty talents.
240 notes
·
View notes
Text

Irish/celtic mythology : Danu - Mother goddess of earth, considered as the oldest deity, associated with rivers, fertility and abundance in land.
#moodboard#aesthetic#celtic gods#celtic mythology#celtic#irish mythology#irish goddess#danu#celtic danu#celtic deities#goddess danu
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Been reading the Celtic Goddess Grimoire by Annwn Avalon.
So far the ones calling to me are:
Sulis
Danu
Andraste
Morgan Le Fay
Rhiannon
Brigid
Cerridwen
Arianrhod
Elen of the Ways
Not intending to leave my Sophian practice in any way, but I feel a pull to more local divine powers so hoping to blend the two.
#celtic paganism#irish mythology#welsh mythology#the mabinogion#danu#sulis#boudicca#rhiannon#morgan le fay#arianhrod#elen of the ways#goddess brigid#brythonic paganism
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Celtic Goddess Danu - the Mother Goddess, the goddess of and manifest divine waters. The waters that fell from heaven to create the sacred river, Danuvis or the Danube.
The Tuatha De Danaan are translated as "The Children of Danu."

There are similarities here between this Ganga and the forming of the Ganges. But more notably, Danu from Hindiusm - the primordial mother goddess of ancient/first old waters - liquid. There is also a river named Danu in Nepal.
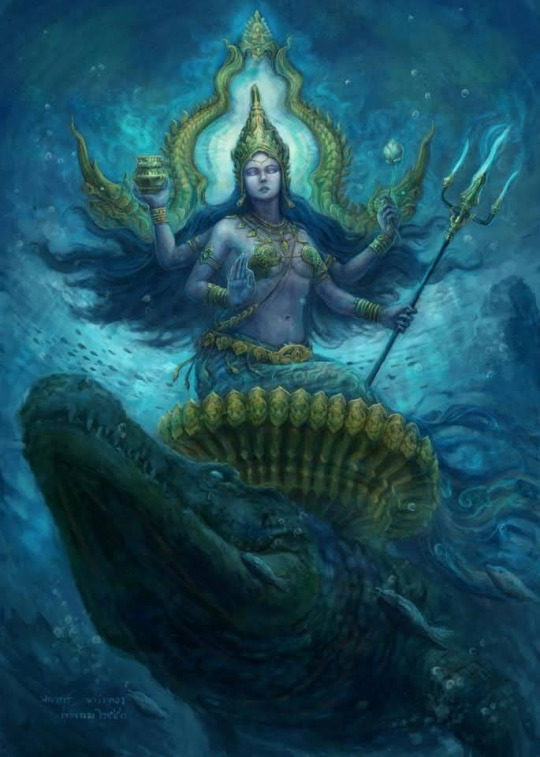

She is the mother of the Danavas, a larger category of the Asuras - celestial/supernatural beings of god like powers, but calling them gods exactly is incorrect. Asuras and Devas are larger in some ways than that - celestial/cosmic beings of princely domains/abilities is slightly more accurate, but for all intents an purposes. There are more similarities between Celtic and Vedic/Hindu culture/myths.
Why?
Well, recent research has shown Celtic genetics shows paternal and maternal ancestry from ancient India (R-M269 deriving via R1b, and H & U haplogroups) - is it really that weird then we see echoes of the ancient Indian epics echoed throughout other parts of the world, especially with the history of Eurasian/South Asian trade, migration, and more?
There is a story well known in the South Asian stories, but let's talk about the similar Celtic one. A tale of how a hero has to build a causeway across the waters to reach his foe, and how his wife must outsmart her captor/villain.
Some Indians are already nodding their heads. We begin with the Celtic hero: Fionn mac Cumhaill, a hero who is born just after his father dies.
Does this sound somewhat familiar?
Well, here we have Rama, born to Dasaratha, who is cursed to die soon as his son leaves him. His father dies as soon as Rama is exiled from Ayodhya.
Finn goes on to study with poets, warriors, and hunters in the forest of Sliabdh Bladma.
Rama goes to the forest hermitage where he learns similar arts under Vasitha.
Finn later in his youth goes on to destroy the fire breathing demon Áillen of the Tuatha (Children of Danu analogous of Aditi here btw) who destroys the capital of Tara every year on Samhain (a celebration very similar to the Indian Pitru Paksha btw)
Rama as a teen kills the Asuras attacking the hermitage - the enemies of the Devas (children of Aditi), interestingly enough just like I've talked about in the Norse (how you have two bodies of celestial/god beings - Aesir and Vanir), the Greeks have it, there is also a flipping that happens in a lot of these ancient cultures.
Aesir and Asura come from the proto indo European asr - but in one group one is good, the other bad. However in the Iranian - Zoroastrian, there is a reverse. The Ahura (Asura) are GOOD and the Devas are bad (down to including Indra from South Asian mythology), and in the Celtic we see something similar - a flipping of roles.
Rama, Sita, and her protector Lakshmana were all in exile together in the forest. The demon king Ravana sends a golden deer to tempt/seduce and lure away Sita from Rama but it is really the demon Maricha in disguise. Sita is tricked and ends up sending her protector to Rama, leaving herself vulnerable, and thus abducted by Ravana who wishes to marry her and this leads to a war in where Rama eventually gets her back also, kidnapping of a women sparking a war? OH HI, HELEN OF TROY. HI.
Fionn meets his wife Sabadh while hunting, and guess what? She is turned into a deer by a druid she refuses to marry. She returns to her true form once in Fionn's home and they marry...only she's turned into a deer again by the druid Fear Doirich when Fionn was off at war, and Fionn must spend years searching for her. Wow. Coinky dinky dinky.
Now to the original part of my talk here, the causeway in Ireland was built by Fionn to travel to battle a giant. Rama Setu, his causeway, was built by Rama's army so he could enter Lanka to do battle there - (Sri Lanka).
The Celts also have four major cycles of time just like the Vedic Indians did. The tricky thing here is that linguistically, PIE (proto Indo European) has been shown to be behind a lot of story/cultural influences as it spread through Europe/Asia, but...the thing that's hard to account for here is how geo-located Ramayama is in/to India, so why do specific echoes of it show up in Celtic mythology so much so?
Yay comparative mythology and echoed storytelling/beats tropes across the world.
#celtic folklore#celtic lore#celtic stories#Tuatha De Danaan#Ganga#Danu#the ganges#Asuras#Celts#fionn mac cumhaill#south asian mythos#south asian#myths and legends#hindu mythology#hindu gods#hinduism#india#Áillen of the Tuatha#Ireland#irish folklore#irish mythology#celtic mythology#gods and goddesses#gods and monsters#god stories#storytelling#folklore#folktales
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

Art by Radmer Lenasch
#celtic danu#goddess danu#danu#celtic gods#irish paganism#irish polytheism#celtic paganism#celtic polytheism#celtic deities
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
*Deh₂nu
*Deh₂nu- is a hypothetical goddess of water in Proto-Indo-European mythology, with connections to the names of rivers like the Danube, Don, Dnieper, and Dniester, as well as the Vedic deity Dānu, the Irish Danu, and the Welsh Dôn. Despite acknowledging a possible lexical connection, Mallory and Adams contend that there is not enough evidence to support the idea that a distinct river goddess existed in Proto-Indo-European beliefs. They primarily highlight the Indic tradition's understanding of river deification. Furthermore, Mallory and Adams suggest that a theory for a sea god called *Trih₂tōn—whose name is derived from the Greek Triton and the Old Irish word for sea, trïath—is unsupported by the lack of a corresponding sea god in Irish mythology and only minor lexical similarities. The Ossetian god Donbettyr is also mentioned in the story. Who is placated by gifts to keep the waterwheel turning, and who Donnán of Eigg proposes as a Christian equivilent of this figure.
Moreover, this deity and the Dan river in Centeral Asia may have similar etymologies.
She is frequently seen as the mother of a mythical tribe, the *Deh₂newyóes, in many Indo-European cultures; these tribes are deduced from the Vedic Danavas, the Irish Tuatha Dé Danann, the Greek Danaoi, and the Norse Danes. Under Bel's leadership, this tribe is said to have fought a hero called *H₂nḗrtos, which could connect them to characters like the Norse god Njord, the Nart from the Nart saga, and Indra's epithet nrtama.
#Irish#Vedic#Norse#Nart#Mallory#Irish Danu#Welsh Dôn#Irish mythology#hypothetical goddess#Proto-Indo-European#Welsh#Adams#Indic#Greek#Old Irish#Ossetian#Christian#Dan#Central Asia#Indo-European#Vedic Danavas#Tuatha Dé Danann#Danaoi#Bel#deity#sea#river#Norse Danes#tribe#druidicentropy
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

Irish Goddess Danu Via
#ancient#Celtic#whimsigoth#whimsicore#old jewelry#jewelry#trinkets#objects#fashion#vintage aesthetic#vintage fashion#antique#rosieandthemoon#witchy#witch#witchcraft#gothic#fairycore#esoteric#pagan#paganism#Druid#Wicca#esoteric aesthetic#green witch#handmade#moody#dark bohemian#magick#mystical
167 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi :)) do you have any advice on writing stories about Celtic mythology? Ive been trying to use Wikipedia to learn more about it but I find the format of it isn’t very digestible for me and I end up not understanding it well
Writing Notes: Celtic Mythology
The ancient Celtic pantheon consisted of over 400 gods and goddesses who represented everything from rivers to warfare.
With perhaps the exception of Lugh, the Celtic gods were not universally worshipped across Iron Age Europe but were very often limited to only several regions or a specific area.
Another difficulty in examining the Celtic pantheon is the paucity of written records produced by the Celts themselves; quite often a god (deivos/deiva) is named in only a single surviving inscription.
To further complicate our lack of knowledge, the Celts often gave all-embracing powers and attributes to their gods which means that they can rarely be easily categorised.
Celtic votive inscriptions from the Roman period often name a Celtic god with a Roman equivalent noted alongside, a practice known as the interpretatio romana. The following are a few major deities or those with multiple or significant inscriptions.
Andarta - a Celtic goddess whose name may derive from the Celtic word for the bear animal.
Borvo (also Bormo) - a god whose name likely derives from the Celtic word meaning 'to boil' and so indicates his frequent association with natural hot springs.
The Dagda - an Irish-Celtic god whose name is usually preceded by the definite article. His name likely means 'the good god', probably in the sense of being 'many-skilled'. His common attributes are a great club, which can both kill and bring the dead back to life, and a giant cauldron that can produce an inexhaustible quantity of food, especially porridge.
Danu (also Dana) - a Celtic mother-goddess who gives her name, which means 'stream' or 'the waters of heaven' to various places and the River Danube.
Genii Cucullati - mysterious Celtic divinities which are not given a name but appear in groups or alone and wear hooded cloaks in art. Depictions typically have them near a single better-known god and holding either an egg or a scroll.
Nemetona - a goddess whose name derives from the Celtic term for a sacred grove of trees (nemeton). Votive inscriptions naming the goddess survive from both England and Germany, some of which indicate she is the partner of Mars. The goddess had temples dedicated to her at Klein-Winternheim and Trier, both in eastern Germany.
Suleviae - this is a group of Celtic sister goddesses who were venerated in Britain, Germany, and Rome (where there were many Celtic mercenaries). The trio was most likely seen as protective figures and associated with regeneration.
Read the full list here. More Celtic mythology concepts and themes:
Albion - Ancient Celts referred to Britain—not including Ireland—as Albion and only later as Britannia. The Romans connected Albion through their word albus, meaning “white,” with the white cliffs of Dover. Geoffrey of Monmouth reported that the Celts believed a certain Albion who ruled the island was a giant fathered by a god of the sea. Others believe the island was named for a princess who came to the island with fifty women who in their former home had killed their husbands.
Belenus - Also known in Celtic Ireland and Britain by various names—Bel, Belinos, Beli, Bile—Belenus is a god of Celtic Gaul whom Julius Caesar compared to the Greco-Roman Apollo as a solar god of light and reason. He carries a solar disk on the chariot that he presumably uses to travel daily across the sky. His British name is the source for Billingsgate in London. Fires in honor of the god were lit for Celtic festivals of Beltaine (“Bel’s Fires”) on May 1.
Cernunnos - A horned Celtic god of Gaul (modern France) and parts of the British Isles, Cernunnos was a god offertility, like the Italian goddess *Ceres. He carries a club and is lord of the animals. Perhaps because of his association with planting and seeds, he was associated with the underworld. The Romans linked him to Mercury, who led souls to the underworld, and to Apollo, as he provided light for the dead in their graves. Sometimes he is equated with Dispater and the Irish Dagda.
Decapitation - An important theme in Celtic mythology in general and Irish and Welsh mythology in particular. The story of Bricriu’s Feast is a decapitation myth, as is the Welsh story of Bran. The theme influenced the Arthurian myths and the medieval English romances such as Sir Gawain and the Green Knight. Earlier decapitation stories are found in the Bible—including the tales of David and Goliath, Judith and Holofernes, and Salome and John the Baptist. There is also decapitation in the Greek myth of Perseus and Medusa, and in the Mesopotamian myth of Gilgamesh and Humbaba. The decapitation theme—especially when associated with a “green man” such as Gawain’s Green Knight, the Aztec Corn King, or many Native North American Corn Mothers—may well have its roots in sacrificial rituals of fertility. Heads that have been cut away from the body, as in the case of Bran’s head, continue to function and talk in Celtic mythology, suggesting a belief in the head’s being the seat of the soul as well as of power and fertility.
Dis Pater - In the Gaulish, that is, continental Celtic mythology, Dis Pater was the Roman name provided by Julius Caesar for a god claimed by the Gauls as their father god, or ultimate progenitor. The name given by Caesar suggests that the Romans saw a connection between this deity and the otherworld or underworld. As, literally, “underworld father,” Dis Pater is naturally associated in Caesar’s mind with the Roman Pluto. The Irish cognates would probably be the Dagda, the father god of the Tuatha De Danaan, and Donn, the god of the dead.
Druids - The priestly class in early Celtic societies, especially continental Celts. They were judges and seers with great moral authority, who ranked above all other classes. As such, they were the equivalent of their Indo-European brothers, the Indian brahmans. The Romans in Gaul developed myths about the druids such as the one suggesting that they practiced human ‘sacrifice. The Irish filidh may be said to have somewhat diminished druidic standing. The great Celtic bards Taliesen and Amairgen had druidic qualities and authority.
Epona - It was primarily the continental Celts who revered Epona, the horse goddess. She was naturally adopted as a favorite by the Roman cavalry and was celebrated at an annual Roman festival. Epona has certain earth goddess aspects, such as her strong association with fertility, sexuality, and water. In Welsh mythology, Epona appears to have had a cognate in the fertility-warrior goddess Rhiannon, who rode about Wales on a white horse dispensing gifts, in the traditional great goddess manner, from her bag or womb bundle.
Irish mythology
Lugus - His name, referring to brightness, indicates that the continental Celtic god Lugus, whom Julius Caesar equated with the Roman Mercury, was a cognate of the Irish Lugh and the Welsh Lleu. Lugus was a god of the arts.
Maponos - Son of the continental Celtic mother goddess Matrona, has a Welsh cognate in Mabon, as Matrona has one in Modron. Maponos was the divine child— the puer aeternus—of Celtic mythology.
Matrona - In the continental Celtic tradition, Matrona, whose counterpart in Welsh mythology was Modron, was the mother goddess whose son was the divine child Maponos (Welsh Mabon).
Nehalenia - A Germanic and possibly continental Celtic sea goddess who protected voyagers.
Taranis - (Taranus) was compared by Julius Caesar to the Roman god Jupiter. Taranis was the thunder and storm god of the continental Celts of Gaul. He was an aspect of the typically Indo-European triad of Esus, Taranis, and Teutates.
Arthurian Mythology
Annwn - (Caer Feddwid) is a name for the Welsh Otherworld, where a magic cauldron exists. In a medieval Arthurian tale, Preiddeu Annwn (The Spoils of Annwn), Arthur and his knights go to Annwn to obtain the cauldron, which, as indicated by the possession of the Cauldron of Plenty by the Dagda, the father god of the Irish Tuatha De Danaan, was a symbol of sacred kingship. Arthur and the few of his men that remained return empty-handed. The tale is seen as a prototype for the story of the Holy Grail.
Camelot - The castle and primary dwelling place of King Arthur, the seat of the fellowship known as the Round Table. It was at Camelot that the Holy Grail appeared to the knights of the Round Table. Many places in England to this day claim to be the site of the legendary castle. Camelot was first mentioned by Chretien de Troyes in his twelfth-century work Lancelot. Supposedly Camelot was destroyed after Arthur’s death. During the early stylish and optimistic years of the American presidency of John F. Kennedy, it became customary to speak of Kennedy and his followers in the White House, and of the administration as a whole, as “Camelot.”
Chretien de Troyes - A French poet of the 12th century C.E., Chretien wrote metrical romances about the ‘Welsh-British ‘hero ‘King Arthur and his knights of the ‘Round Table. Most famously, he wrote Perceval or the Story of the Grail, about ‘Percival (Parsifal) and the ‘quest for the ‘Holy Grail; and Lancelot, or the Knight of the Cart.
Fisher King - In the Arthurian story, the Fisher King is a somewhat ambiguous figure who is encountered in various conflicting versions by hero-knights of the Round Table— particularly Percival—during the quest for the Holy Grail. The King is in some sense wounded, a fact that affects the fertility of the land he rules. Some say that the King—Pelles, Parian, or Pellam—was guardian of the Grail but that he had sinned and was thus unable to speak when the Grail appeared before him. The King can be cured of his wounds or his speechlessness only when certain questions are asked of him. But when Sir Percival comes to the Fisher King’s castle and the Grail passes by him in procession, he fails to ask any questions about it, and the King remains under the terrible spell.
Galahad - Originally Gwalchafed in Welsh, Sir Galahad was a knight of King Arthur’s Round Table in medieval Arthurian sagas. His story had strong heroic mono- mythic elements. Galahad was the son of Sir Lancelot and the Lady Elaine, whom Lancelot had been tricked by a potion into thinking was his beloved Guinevere. Galahad was brought up by a nun and then knighted by his father and taken to Arthur’s court. He was, above all, pure, and it was this quality that made it possible for him, of all knights, to succeed in the quest for the Holy Grail. Galahad appears in Arthurian lore in a thirteenth-century French cycle of romances. La queste del saint graal (“The Quest for the Holy Grail”). In Sir Thomas Malory’s Le morte d’Arthur, Galahad achieves apotheosis; he is taken up to Heaven.
Guinevere - In the Arthurian romances, including those of Chretien de Troyes, the Welsh historian Geoffrey of Monmouth, and Sir Thomas Malory, Guinevere (Welsh Gwenhwyfar) is the wife of King Arthur and the beloved of Sir Lancelot. There are conflicting tales of Guinevere’s origins. Some traditions hold that she was the daughter of Leodegan, who gave the Round Table to Arthur when the latter married his daughter. Her love for Lancelot led to the disruption of Camelot and the fellowship of the knights of the Round Table, and eventually to Arthur’s death. Some say she married Mordred after Arthur’s death. More often it is said that she retired to a nunnery.
Holy Grail - or Sangreale in Old French, was an important quest object in the Arthurian tradition, particularly connected with Percival, as in the Perceval of Chretien de Troyes (c. 1185) and the slightly later Parfval of Wolfram von Eschenbach. Whatever the original source of the legends of the Grail, Christianity associated it with one of the vessels used by Jesus at the Last Supper.
King Arthur - Legendary British king who appears in a cycle of medieval romances (known as the Matter of Britain) as the sovereign of a knightly fellowship of the Round Table. It is not certain how these legends originated or whether the figure of Arthur was based on a historical person. The legend possibly originated either in Wales or in those parts of northern Britain inhabited by Brythonic-speaking Celts.
Lancelot - The son of King Ban of Benwick or Brittany, Sir Lancelot, or Lancelot of the Lake—so called because he was raised by Vivienne, the mysterious Lady of the Lake, who stole him at birth—was one of the noblest knights of King Arthur’s Round Table. But his love affair with Arthur’s queen, Guinevere, would lead to the downfall of Camelot and the fellowship of knights. Sir Galahad was Lancelot’s son by the Lady Elaine, who tricked him into thinking she was Guinevere and so made love with him. Galahad would succeed in the quest for the Holy Grail where his father had failed. Lancelot rescued Guinevere when she was about to be burned at the stake for adultery. When Guinevere and Lancelot fled to Brittany, Arthur followed them and his illegitimate son or nephew, Mordred, usurped his throne. This led to a war in which both Mordred and Arthur were killed. When Guinevere retired to a nunnery, Lancelot, too, took religious vows. The Lancelot story is found in the works of Chretien de Troyes and Sir Thomas Malory.
Mabinogion - The “Welsh Mabinogion is found in two fourteenth-century manuscripts, the White Book of Rhydderch and the Red Book of Hergest. The collection, based on oral narratives, probably took literary form between the mid-eleventh to the early twelfth centuries.
Malory - Sir Thomas Malory is the fifteenth-century English author of Le Morte d’Arthur, an important compilation of Arthurian material. He is said to have created his great prose work while in prison.
Merlin - Probably has an antecedent in the legendary Scottish and/or Irish mad prophet Myrddin (Merddin). The Welsh historian Geoffrey of Monmouth, in his twelfth-century History of the Kings of Britain, established Merlin’s position as the motivating wizard in the Arthurian legend. It was Merlin who helped arrange for the liaison between Uther and Igraine that would lead to the conception and birth of King Arthur. After Arthur’s birth Merlin took the child to one Hector, this in keeping with the monomythic heroic divine child’s being raised by a menial or commoner. It was Merlin who arranged for the ceremony through which Arthur would prove himself to be the king by removing a sword from a rock. There are many versions of Merlin’s life. It was said by some that he was conceived as a result of the union between a sleeping nun and a demon. In Sir Thomas Malory’s Le Morte d’Arthur, based on many earlier sources—many of them specifically about Merlin—the magician falls in love with an enchantress, Nimue (perhaps the Lady of the Lake), a femme fatale who imprisons him under a rock.
Welsh Mythology
Has come to us from various sources, all much more directly affected and distorted by time and non-Celtic elements than is the case in the much more isolated Ireland.
There are the two Latin texts especially concerned with the Arthurian legends—the early-ninth-century Historia Brittonum by Nennius and the twelfth-century Historia Regum Britanniae by Geoffrey of Monmouth—and there are, of course, oral sources, including, traditionally, poems questionably attributed to the semi-mythic sixth-century poet-prophet Taliesin, whose Irish equivalent was Amairgen, the poet-warrior.
But Welsh mythology, including the remnants of a pre-Christian Welsh pantheon, is more essentially contained in the “four branches” of a collection of eleven medieval tales known in modern times as the Mabinogion {Mabinogi) and in the various traditions associated with King Arthur.
Sources: 1 2 3 4 5 �� More: References ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
Hi, consuming a lot of media on the topic would be important for your story. These are just a few excerpts from the sources I was able to find, which you can go through in the links above (+ the other references the authors mentioned). Find the right balance between your research and the direction you want your own story to go. Hope this helps with your writing!
#anonymous#celtic#mythology#writeblr#dark academia#literature#writing reference#creative writing#writers on tumblr#spilled ink#writing prompt#writing inspiration#writing ideas#light academia#writing resources
104 notes
·
View notes
Text
The origins of Dagda and what gets adapted into SMTIVA

Colonization, religious syncretism and famine all play roles in this unusual representation.
1) Who are the Tuatha Dé Danann?
There was a series of invasions of Ireland by a succession of peoples, the fifth of whom was the people known as the Tuatha Dé Danann.
They faced opposition from their enemies, the Fomorians, led by Balor of the Evil Eye. Balor was eventually slain by Lugh.
With the arrival of the Gaels, the Tuatha Dé Danann retired underground and eventually became the fairy people of later myth and legend.

A quick overview to situate those unfamiliarized but their tales aren't the subject of this post.
2) Who is Dagda?
Dagda is the chief of the Tuatha Dé Danann, portrayed as a large bearded man in father-figure and druid roles. He is often described as an ideal of masculine excellence (although with a comical tone). He had many mates among female Irish figures.
Dagda possess items that gave him advantage over the Fomorians:
→ A magic club of dual nature: its end could kill nine men in one blow but with the handle he could return the slain to life → A shirt of protection from sickness → A cloak of shape-shifting → A magic harp not only able to command people, but also the seasons → And last, a cauldron which never runs empty. Through these, Dagda becomes able to control life and death, the weather and crops, as well as time and the seasons.

3) Humans or deities?
In truth... The lore of Tuatha Dé Danann being descended from a previous wave of inhabitants of Ireland comes from euhemerized accounts. In non-euhemerized accounts, they are descended from Danu, the mother goddess (lit. "Peoples of the Goddess Danu").
The medieval writers who wrote about the Tuatha Dé Danann were Christians. They described them as neutral angels who sided neither with God nor Lucifer and were punished by being forced to dwell on the Earth. Due to the hesitance in calling them by ‘gods’, they were often stripped of this title and instead lessened as simply ‘humans who had become highly skilled in magic’.

Medieval sources depicted Dagda as “a king of Ireland for eighty years, until turning it over and being killed in battle against the Fomorians”; however, this was an obvious attempt to rationalize his divine nature. Not only Dagda is a leader of gods, it’s not in the exact same sense of a king either.
Thus, it’s fair to assume an intended contrast between the “diminished human form” Dagda depicted in the obviously Christian-biased surviving sources and SMTIVA’s “deity-like” Dagda that doesn’t make use of numerous tools to in order to have the means to display unique powers.
4) The Celtic Otherworld
In Irish mythology, Tír na nÓg ('Land of the Young') is one of the names for the Celtic Otherworld (or part of it).
It’s an island paradise and supernatural realm of everlasting youth, beauty, health, abundance and joy, where times also moves differently. Besides deities, it’s also a realm for the dead.

Left: "Land of the Ever Young" (Arthur Rackham) in Irish Fairy Tales (1920). Right: the DLC location Dagda takes you for grinding macca, EXP or items
Means of entry
It exists either in parallel alongside our own, or as a heavenly land beyond the sea or under the earth. Despite its elusiveness, various mythical heroes—such as Cú Chulainn and Fionn —visit it either through chance or after being invited by one of its residents. They often reach it by entering ancient burial mounds or caves, or by going under water or across the western sea.
Sometimes, mortals suddenly find themselves in the Otherworld with the appearance of a magic mist, supernatural beings or unusual animals.
Tech Duinn
In Irish myth, there is another otherworldly realm called Tech Duinn ("House of Donn" or "House of the Dark One"). It was believed that the souls of the dead traveled to Tech Duinn; perhaps to remain there forever, or perhaps before reaching their final destination in the Otherworld, or before being reincarnated.
"Who is the Dark One?", you might wonder.

5) Donn, The Irish God of Death
If you’re familiar with ancient Mediterranean polytheistic religions, you might notice that Donn (the Dark one) shares “death god” similarities with Hades and Pluto.
"One is struck here by the resemblance to the Greek lore of Pluto and the ferrying of souls across the river Styx. The similarity may be explained as a common ancient tradition concerning the dead which had come down to both Greek and Celts but… it seems more sensible to regard it as having originated in general Greek influence. Since the emphasis in these death-beliefs was on the imagery of the west, it is not surprising that the lore was further extended to the westernmost island of Celtdom, Ireland itself.” The Sacred Isle: Belief and Religion in Pre-Christian Ireland (1999)
Donn is responsible for guiding souls from the land of the living to the land of the dead.
Donn’s island, Tech Duinn, is in reality little more than a rock (now known as Bull Rock) situated off the coast of the Beara peninsula. But for centuries that rock inspired fear in the minds of the ancient Irish.

"[...] three red horsemen appear as an omen of death, and they announce: ‘We ride the horses of toothless Donn from the tumuli, although we are alive we are dead!’ Donn is here a personification of the elders buried in the tumuli, which illustrates the physical aspect of funerary practice." The Sacred Isle: Belief and Religion in Pre-Christian Ireland (1999)
Myth vs Pseudohistory
A purely mythological figure, Donn the death god would later become conflated with the quasi-legendary Donn son of Milesius.
“Medieval Irish texts describe the ‘belief of the heathen’ to the effect that souls go there to Donn, and in the pseudo-history Donn is euhemerised as one of the leaders of the Gaelic people when they came to Ireland. We read of this pseudo-historical Donn, however, that he was not destined to reach the shore of Ireland, but was drowned near the rock which bears his name.”

The Gaelic people are also known as the Milesians, namesake of Donn’s dad Milesius. The Milesians were the final invaders/settlers of ancient Ireland. They were the ones who defeated the Tuatha Dé Danann and sent them underground to their tumuli in the euhemerised version.
Donn was an important Milesian military commander and the eldest of Milesius’ eight sons. He seemed like a character fated for a heroic life, yet in every account of Donn’s deeds during the Milesian invasion of Ireland, he was doomed to fall off to his death in the sea in the island and intermixed his tradition to that of death god Donn.
Pre-Celtic roots
On a following note, some historians suggested that Donn might be actually an iteration of Bilé, Irish god of death who originated in ancient Gaul. Bilé, in turn, is the Gaelic iteration of a much older Celtic god who is often referred to as Bel or Belinos in the Brythonic tradition. He is the namesake of the Celtic feast day Beltane, which was—and among some groups, still is—celebrated on May Eve and May 1st.
In some Irish texts, Bilé is euhemerized as the father of the aforementioned Milesius. Therefore, Bilé is the quasi-historical father of Milesius, making him Donn’s grandfather, and clearly establishing Bilé as the original, more senior Celtic god of death.
"Mistifying" enemy nations

Bilé and the rest of the Gaels who invaded Ireland are described as coming “from Hades.” On a different note, the god of death Bilé is described as also being the source of human life:

The Mythology Of The British Islands: And Introduction to the Celtic Myth, Legend, Poetry, and Romance (1905)
And as shown earlier by what we discussed about Tír na nÓg, the Celts didn't consider the Land of the Dead as being a punishing and oppressive place like hell.
“In Celtic belief the underworld was probably a fertile region and a place of light, nor were its gods harmful and evil.” The Religion of the Ancient Celts (1911)

Totally the same, right? Left: Hortus Deliciarum - 12th century Hell (Herrad von Landsberg) Right: "They rode up to a stately palace" (Stephen Reid)
Are you realizing where this is going?
6) Donn = Bilé = Dagda
"Irish god of the dead whose abode is at Tech Duinn (House of Donn) which is placed on an island off the south-west of Ireland. The house is the assembly place of the dead before they begin their journey to the Otherworld. In modern folklore Donn is associated with shipwrecks and sea storms and sometimes equated with the Dagda and Bilé." A Dictionary of Irish Mythology (1987)

We've reached full circle with our representative always being at the boundary between the world of the dead and the world of the living even under different names and locations.
Also, among Dagda's many names, two are relevant both on this discussion and for his SMTIVA portrayal:
-> An Dagda -> Dagda Donn "The Good God" "Dark Dagda"

While 'good' isn't particularly regarding his own morality, the same source mentions that Dagda is charitable, hence the title can be accurate in an altruistic sense as well.
Meanwhile, the possible (combined, even) reasons behind Dagda being called "Donn (Dark)"...
a) Due to having a dun tunic and a dark cloak b) Due to the death and ancestral god Donn (aka Bilé) originally being a form of Dagda thus being the original dark reflection of Dagda c) "Donn Dagda" being also... "Lord Dagda".

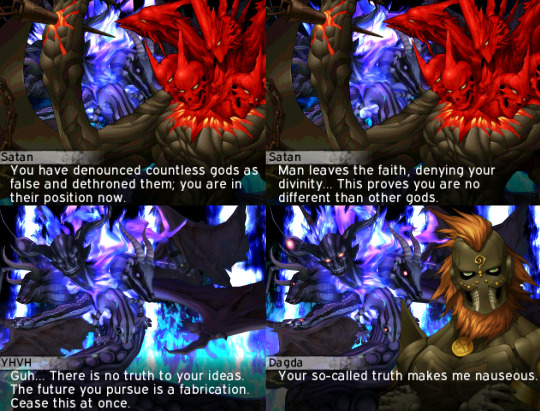
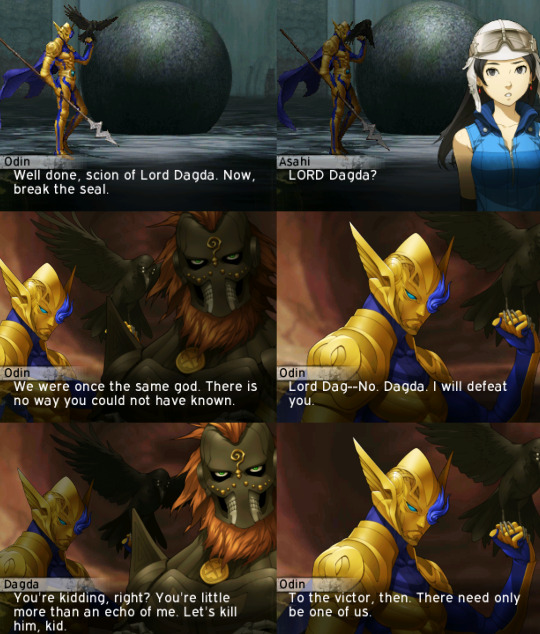
On a similar note, both Dagda and Donn have also been likened to the Germanic god Odin regarding shared motifs and, as pointed out by their dynamic in SMTIVA, Celtic cultures are the ancestors of Germanic people.
This is also emphasized by many of Dagda's other names:
Eochu Ollathair "Horse Great-Father"--generally taken as his "true" name
Fer Benn "man of the peaks" or "horned/pronged man"; could be a poetic reference to lightning, or could indicate a now-lost idea of the Dagda being horned, a not-uncommon feature in British and Gaulish iconography.
Cerrce It may derrive from *perkw "striker", i.e. lightning
Dagda (n)dur/Dagdai duir "harsh/stern" Dagda, but duir also may refer to the oak dair; the association of duir and dair also appears in the ogham tracts. Comparing the Dagda to an oak would also lend credence to the interpretation of him as a thunder god.
But back to the "Good Dagda" and "Dark Dagda" discussion.... What if SMTIVA took these two titles as two separate selves?
Donn Dagda -> Original dark reflection of Dagda -> The Ancestor Dagda from his Pre-Celtic era -> The "Old Dagda" that Nanashi fights against in Bonds while allies with in Massacre -> Immutable part of himself

An Dagda -> His heroic Tuatha Dé Danann self -> More aligned to how he's written in biased sources -> The "Entity created by Danu" that Nanashi allies with in Bonds -> Continuously reborn as long as Danu exists


Notice Danu's choice of wording. "My wish" Donn starts belonging to Danu as a Tuatha Dé Danann (Person of Danu) "good king" "good god" Donn was forced into a "personified" role over simply being nature itself. "forbidden magic" Danu is being self-aware about her true "pagan" origins, as she serves humans as both Tuatha Dé Danann and as Black Maria.
7) Effects of Christianity on Irish folklore
When Christianity was first brought in Ireland during the 5th century by missionaries, they were not able to replace the pre-existing beliefs in the Celtic societies. However, Irish folklore did not remain untouched.
As we mentioned earlier, the fairy folk, who were previously perceived as Gods, became merely magical and of much lesser importance, thus adapted to enforce Christian ideals.
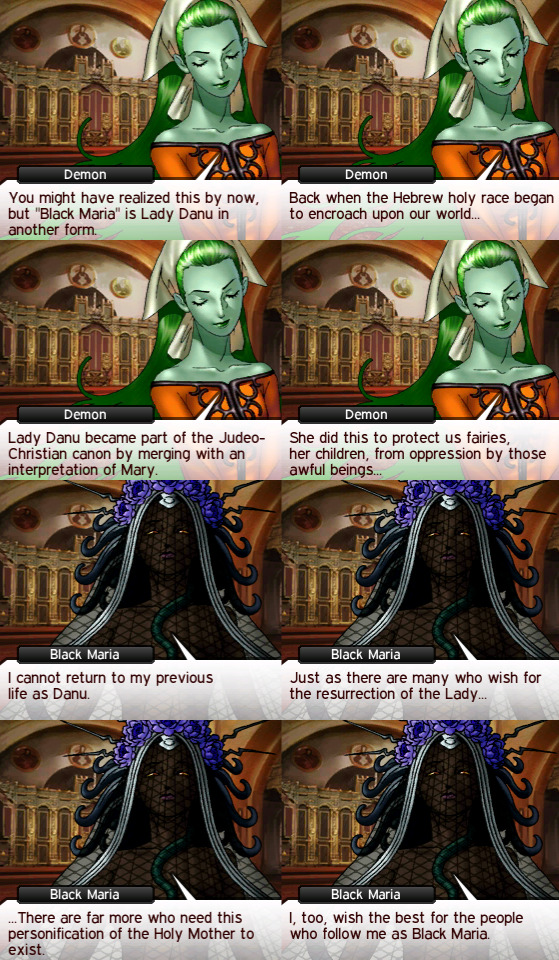
All in all, the current Irish folklore shows a strong absorption of Christianity, including its lesson of morality and spiritual beliefs.
Most of these manuscripts were created by Christian monks, who may well have been torn between a desire to record their native culture and hostility to pagan beliefs.
The Tuatha De Danann were known to come from the heavens, but that may be from scribes not knowing how to execute their origin. So the scribes borrowed from past religions like the Greek, Roman, and Eastern myth to create an origin story.
Earth was also thought to be a woman at the time, so this was thought to be a metaphorical birth.

The uncertainty of Danu's origins
Danu has no surviving myths or legends associated with her in any of the primary Irish texts.
Danu is a hypothesised entity whose sole attestation is in the genitive in the name of the Tuatha dé Danann, which may mean 'the peoples of the goddess Danu' in Old Irish.
In Cormac’s Glossary from the 9th century, the goddess Anu is stated as the mother of the gods. Some scholars suggest that Danu was a conflation of Anu and is the same goddess.
in which case Danu could be a contraction of *di[a] Anu ("goddess Anu"). Also cognates with Dana

Left: Mother Earth image, Atalanta Fugiens Right: The Paps of Danu, a pair of breast-shaped mountains in County Kerry, Ireland.
Some later Victorian folklorists attempted to ascribe certain attributes to Danu, such as association with motherhood and agricultural prosperity due to a "general Mother Earth concept".
"Danu herself probably represented the earth and its fruitfulness, and one might compare her with the Greek Demeter. All the other gods are, at least by title, her children." Squire (1905)

As shown by the flimsy lore attempts regarding Danu, whether medieval Irish literature provides reliable evidence of oral tradition remains a matter for debate. This is indicated in SMTIV&A by how fragile and dependent on biased Christian sources her existence is.
"Nativist" claims have been challenged by "revisionist" scholars who believe that much of the literature was created, often in imitation of the epics of classical literature that came with Latin learning, such as the Illiad. They also argue that the materials depicted in the stories generally date closer to those of the time of their composition (such as bows and chariots) than to those of the distant past.
The Mythological Cycle, which comprised stories of the former gods and origins of the Irish (including the Tuatha Dé Danann), is the least well preserved of the four cycles thus many manuscript sources that could have been what later myth writers based on may have been since disappeared, leading to Tuatha Dé Danann eventually becoming forgotten in the current era.

English colonization
During the 16th century, the English conquest overthrew the traditional political and religious autonomy of the country.
The Great famine of the 1840s, and the deaths and emigration it brought, weakened a still enduring Gaelic culture, especially within the rural proletariat, which was at the time the most traditional social grouping.
In the state of things, with depopulation the most terrific which any country ever experienced, [...] together with the rapid decay of our Irish bardic annals, the vestige of Pagan rites, and the relics of fairy charms were preserved, - can superstition, or if superstitious belief, can superstitious practices continue to exist? - William Wilde
Moreover, global migration has helped overcoming special spatial barriers making it easier for cultures to merge into one another.
All those events have led to a massive decline of native learned Gaelic traditions and Irish language, and with Irish tradition being mainly an oral tradition, this has led to a loss of identity and historical continuity.

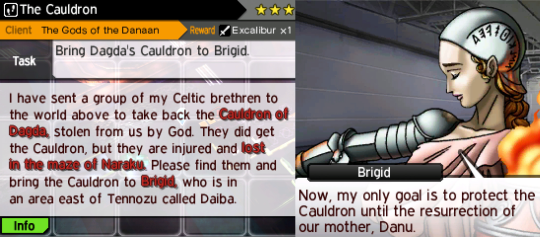
Dagda's (briefly mentioned in-game) daughter
Brigid ('exalted one') is the daughter of Dagda and "the goddess whom poets adored". She is associated with wisdom, poetry, healing, smithing and domesticated animals.
The goddess Brigid was syncretized with the Christian saint of the same name. Medieval monks took the ancient figure and grafted her name and functions onto her Christian counterpart, Brigid of Kildare.
Saint Brigid shares many of the goddess's attributes and her feast day, February 1st, was originally a pagan festival called Imbolc, the first day of spring in Irish tradition.

Art mural depicting the duality of Brigid the pagan goddess and Brigid the saint.
As the more well-known goddess, and later saint, the legends of numerous "minor" goddesses with similar associations may have over time been incorporated into the symbology, worship and tales of Brigid, including Danu and Dagda's own.
This is subtly brought up in the request she makes for Flynn prior to SMTIVA: she requires the rescue of her (then absent) father's cauldron that could feed crowds of people and wait for the return of Danu, the "representative piece" of their group, in order to turn it back to its original state.
On a following note, Brigid's affectional and protective nature is distinctive as she not only began the custom of keening (traditional form of vocal lament for the dead in the Gaelic tradition) while mourning the death of her son but even her animals were said to cry out whenever plundering was committed in Ireland.
Which leads us to the final topic of this post...
8) Irish and the celebration of death
Long before the rise of Christianity, Celtic druids preached that the human soul was eternal thus in death, one simply moved into a different plane of existence (which is the Otherworld we mentioned earlier).
Irish myths also emphasized to us that the barriers between the land of the living and the Otherworld are not always solid, which is perfectly displayed in the festival Samhain:
They believed that on the last night of the old year (October 31st) the lord of death gathered together the souls of all those who had died in the passing year [...], to decree what forms they should inhabit for the next twelve months.
The Book of Hallowe’en (1919)

Brigid alongside Dagda are "personified" concepts that show the picture of how intimate the Irish's relationship with death is.
To quote Scottish journalist Kevin Toolis, you’d be hard-pressed to find a country other than Ireland “where the dying… the living, the bereaved and the dead still openly share the world and remain bound together in the Irish wake.”

The oppressive YHVH forced those whose existences contradicted his own to step down from being gods. The divided Danu wishes to "claim back her lost authority" while still respecting the will of people that interpret her as part of Judeo-Christian lore. Meanwhile, Dagda subverts both YHVH and Danu as desiring to go back to being nature itself rather than its personification that continues the cycle of human dependency on gods and viceversa.
Death begets life. And the most fertile soil is that which is rich with the remains of the once-living. Dagda, as the spiritual father to humankind, wishes to become 'fertile soil' for Nanashi and a new world of humans.
The Donn reflection of Dagda, which is linked to the mythological ancestor of the Gaels, is crucial to the circle of life itself.

45 notes
·
View notes
Text

𝐬𝐨𝐧 𝐨𝐟 𝐣𝐮𝐩𝐢𝐭𝐞𝐫
𝒋𝒂𝒔𝒐𝒏 𝒈𝒓𝒂𝒄𝒆 𝒙 𝒅𝒂𝒖𝒈𝒉𝒕𝒆𝒓 𝒐𝒇 𝒎𝒐𝒓𝒓𝒊𝒈𝒂𝒏 𝒓𝒆𝒂𝒅𝒆𝒓
𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑑 𝑐𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡: 𝟹𝟸𝟹𝟺 ✎ 𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑠: 𝑢𝑛𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑡𝑒𝑑 ✎ 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑙𝑖𝑠𝑡
✎ The Morrígan is the irish-celtic shape-shifting goddess of war and fate, she hovers over the battlefield as a crow or raven.
✎ Danu is the matriarch of the Irish Pantheon, yet not much else is known about her or her “realms” - I didn’t do tons of research on these gods + goddesses so if I get something wrong please tell me!!
✎ Lugh is the Celtic god of sun and light.
𝑅𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑠𝑡𝑠 𝑎𝑟𝑒 𝒐𝒑𝒆𝒏 - 𝑦𝑖𝑝𝑝𝑒𝑒!
𝒄𝒉𝒂𝒓𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒆𝒓 𝒂𝒈𝒆𝒔:
✎ Fiadh - 40
✎ Reader - 17
✎ Saoirse - 16
✎ Niamh and Roisin - 10

Set during the end of the giant war and before trials of apollo - if i make a part 2 were just gonna pretend toa doesn’t exist. Jason and Piper don’t have a romantic relationship, we’re keeping it platonic besties. I probably fuck with the timeline a bit so pls don’t bite me. IMPORTANT!! I haven’t finished hoo but i wanna write for Jason and i'm physically incapable of writing modern aus so I'm guessing who is where in the final battle; CHB = Percy, Jason, Piper, Leo, all cabin counselors, Romans, Greeks, ATHENS = Annabeth, Nico, Hazel, Frank, Romans, Greeks.
Please correct me if i am wrong 🌝
Also! The reader is born and raised in Ireland, I don’t really describe her that much but she’s not completely undescribed soooo, no use of Y/N apart from once, I actually gagged when I wrote that I’m so sorry but girlie has to introduce herself yk?
Also we're not gonna mention how I haven’t finished hoo. I don’t wanna hear it okay 😩 I Also made a little bit of the final battle with Gaea up as well, but let's face it I'm only here for the romance 💋 - yes i am ignoring the weird catapult octavian uses bc im not writing that thing, I’m also ignoring him. anyways;
𝑒𝑛𝑗𝑜𝑦!

When you first heard of the possibility of other godly children in America, you weren’t too keen on the idea of revealing yourself and your friends to them. There weren’t any demi-gods in britain, a mystery your mentor and leader of the small camp you call home, Fiadh, a daughter of Danu who took you in along with the twenty something other celtic demi-gods residing in the camp on the east-coast of Ireland. Fiadh, with her wild hair and mother-hen demeanor had become a mother figure over the years, more so than your own godly parent.
She had tried to find any semblance of a community in Britain or northern Europe, and had even dispatched you to look in eastern Europe - your grandma was a Bulgarian immigrant in the 60’s, and you’d grown up visiting places like Moldova and of course Bulgaria in your early childhood before monsters had started to become an issue - to your behest, you thought that revealing yourselves to another pantheon was too great a risk, and a danger the bubble of protection your camp provided. The only signs of any other pantheons Fiadh had found were whispers of Egyptians and a norse murmur in Scandinavia.
You never knew why Fiadh even wanted to have contact with other demi-gods, was she not content with the community she had spent her life building? The community that had saved so many lives?
That was before Long Island.
Being a daughter of Morrígan, you have the ability to shift into a raven, though it’s not done easily at will. Morrígan is a triple-goddess, a figure composed of three deities, all three are Morrígan but are not each other, confusing right? Imagine having three mums all in one. Parent-teacher evening is a nightmare. Badb (part of the Morrígan trio you call mum) is known to have hovered over battlefields as a crow or raven, and even to cause fear and confusion among soldiers and to turn the tides to her favoured side.
It was a balmy august day at camp when you felt a violent tug in your gut. You had been playing tag with the younger girls - Niamh and Roisin, 10 year old twin daughters of Lugh. you had paused in your chasing of the two almost immediately. You had felt this a year before, in August as well. You had changed into a raven instantly and had to be kept in a bird cage to stop you from flying away - you had been sat inside with Fiadh when it happened thankfully, as you were drawn by an unexplainable force to fly away, you had slammed into windows and completely trashed the main cabin before Fiadh had finally put you in the cage. That was awkward. Especially when you felt yourself turning back two days later, and had to squawk like crazy to make Fiadh release you before you were crushed by the cage.
Two days was a concerningly long time for you to be stuck like that, you had only ever shifted to a raven for a few hours at most, and the longer you stayed in that form, the more you felt your human self slip away, your earthly concerns and memories had floated above you like through a pane of glass, there, but just out of reach, replaced with a purely animal way of thinking and the desperation to fly west. The relief you had felt when the window opened and you felt your little boned body begin to swirl with magic, your human form coming back, was unprecedented.
So it was understandable that you were a little bit panicked when you felt that same sensation begin to bubble in your gut. You hadn’t even tried to shift since last year, fear consuming you whenever you attempted. You tried to run to the main cabin, Fiadh was probably making lunch with a few of the other kids, but it was too late, your body shrank and your hair morphed into feathers, your mouth became a beak. Your senses doubled and tripled, overwhelming you as you flew uncontrollably west. You tried to fight it, flapping in circles as the girls gaped up at you from below. Eventually you relented to your body, the mental struggle of fighting your instincts too much for you to resist.
Later, Fiadh told you of the aftermath, Niamh and Roisin had burst into the main cabin, panicking as they told Fiadh what had happened only minutes prior. The next few days were spent in disarray as efforts were sent out to find you all over Ireland, all coming back empty handed with only a few scratches and monster encounters to make up for it. Your best friend at camp, Saoirse, hadn’t slept at all, spending the most time out on the hills to find you, and had almost died searching the north forests.
You, on the other hand, had flown across the Atlantic ocean to America. Joy.
When you arrived where your instincts had pulled you kicking and screaming, it was a battlefield. literally. Hundreds of kids in purple and orange shirts fought monsters, though they weren’t like the ones you knew. The battle was surrounded by forest, you could see a summer camp a little ways away as well, and the coast was a mile or two from the main battle.
The massive revelation of the existence of other demi-gods, because they had to be, you could feel the godly power from where you perched in a high tree a good ways away, didn’t connect with you until much later, in the moment however, it just felt right, as if you always knew, as if you were meant to be there, to observe and be a part of this place in history. Oh Fiadh would be thrilled.
You stayed mainly out of the cross-fire, watching without taking it in fully yet astutely aware of what was happening, the demi-gods were losing strength, more and more kids were being injured or killed by the army of monsters every passing hour. Your fluttering heart sank to your feet, well, claws, an agonised screech escaped your throat, grief and desperation for the strangers to win clawed at your heart, you prayed to your mother, begging for a blessing on these children.
That was when you saw it, a massive, bronze, dragon flying up with a goddess in its maw. A boy rode on its back, and shockingly, a blond boy flew up beside him carrying a girl in his arms. You were drawn to the trio in the sky, gliding over to hover above. The girl, whom up close you noticed to be beautiful, with choppy brown hair she pulled off amazingly and who had an almost magnetic aura, spoke to the goddess. You could feel the magic in the words from where you circled the group, she was powerful. Though you were close you couldn’t hear what they were saying very well, though you understood when the goddess, the leader of the monsters, you instinct told you, fell asleep in the dragon's clutches.
The boy riding on the back of the dragon wore suspenders and a tool belt that looked stuffed full, he had an impish face and you guessed he would usually be a jokester, but his expression was anything but. You could see the tense stares between the trio as they argued for a few moments over something, before the blond boy and the girl flew back down. You stayed with the boy, a silent companion for a boy you didn’t know. Blood pumped in your veins as you circled the duo, something big was coming.
The dragon exploded.
Heat burned your small body as you went limp, falling rapidly through the sky. The boy fell beside you, unconscious and singed, his face twisted in agony as his clothes caught on fire and his arms covered in burns.
Pain flooded your senses as you fell in sync, a tug in your gut alerted you to the magic swirling in your bones. Shit.
You don’t remember anything after shifting back, only pain and the distant sound of you screaming in panic as you fell. The boy disappeared from beside you, but you didn’t notice. Now that you had shifted back to human form, burns riddled your arms and legs and you felt yourself becoming light headed. You don’t remember touching the ground, because you didn’t. Strong arms wrapped around you as the last wisps of consciousness fall away.
↜✿↝
When Jason saw a girl falling out of the sky right after he saw his best friend explode, he was more than a little confused. Although he hadn’t even had the chance to process Leo’s death, he knew he couldn’t let someone die like that if he had the ability to stop it.
Since the Apollo cabin was already flooded with injured demi-gods, and he didn’t even know who this girl was, he brought her to the main house instead, where the cabin counsellors and the seven were gathering to discuss post-battle. Jason knew she wasn’t Greek or Roman, she wasn’t wearing a camp shirt, and except for a small dagger tied to the belt loop of the denim shorts she wore, there was no indication of her being a demi-god at all.
He held her in a princess carry as he walked across the clearing in the middle of the cabins, most of the monsters had left once Gaea was killed, and now everyone was sat in a post-battle haze, nobody really noticed the son of Jupiter carrying an unknown girl, and he was grateful for it to be honest, he had enough on his plate without people crowding him.
↜✿↝
It was silent around the pool table, nobody had touched the snacks, and even the usually loud and rambunctious Stoll twins sat glumly. Will Solace was with the rest of the Apollo cabin in the med cabin, and Annabeth, Hazel, and Frank were in Athens, but apart from that everyone else was there, including Chiron and Diyonisus. He stubbornly kept his gaze away from the empty Hephestus cabin seat.
Heads turned to him as soon as he walked in the room. Chiron spoke first, “Jason, my boy, it's good to see you well, who is she?”
“I don’t know, she fell from where Festus exploded, she needs medical attention,” Jason said, Piper got up from her seat, “I think there's some nectar in the mini-fridge, are you sure she’s not anyone we know?”
“I don’t think so,” Jason responds as he sits you down gently on an armchair, you’re still blissfully unconscious, a good thing, for if you were awake you would be screaming in pain. Clairisse spoke up from her seat at the table, “well, this is great, Gaea is dead, prophecy fulfilled, and now we have a mystery girl on our doorstep, were not even sure if she’s a demi-god,”
“She probably is, there's a dagger on her belt.” Jason said, “the least we can do is heal her, she’s got some nasty burns and she’ll wake up soon anyway, i think she just passed out from stress.”
Clarisse looked at him sideways, “and when did you become a doctor?”
“Calm down, children, Piper, if you could give her some nectar, I would appreciate it,” Chiron leveled his gaze at Jason and Clarisse, “now is not the time for infighting, we have yet to hear from Athens, and we find ourselves with another pantheon’s ward,”
Percy whistled low, “you mean she’s norse or something?”
“Of a sort, yes,” Chiron agreed, “though I’m not sure how she got here of all places.
Jason heard a gasp as he turned his head, you had woken up, you hissed in pain as Piper fussed over you gently, handing you a square of nectar, you looked at it oddly before eating it anyway, not fully awake or lucid to really question it. Blinking rapidly, you came to fully, and stared at the table of demi-gods confusedly before opening your mouth to speak, “Where-where am I?” Jason almost swooned as you spoke, your accent washing over him like a tidal wave. Now that you were awake, he looked at you more closely. You wore denim shorts and a plain t-shirt, as well as white trainers and lacy ankle socks. You had your hair tied up in a half up half down style - though it was messed up and pointing in a couple directions from falling through the sky, with a bow pinned to the back of your head. And you were cute.
Oh.
“Camp Half-Blood, a camp for Greek demi-gods,” Chiron said, calmly wheeling over to you in his chair, “my name is Chiron, who are you?”
You blanched, “Greek? And you’re American- not that it’s a bad thing just, am I in America, right now?” Chiron nodded affirmatively. “Fuck- sorry, just… oh yeah, um, I’m Y/N, daughter of Morrígan, do you know how I could get home?” that brought Jason out of his trance, he had zoned out listening to your voice, not really paying attention to the words, he could listen to you for hours. Chiron spoke again, “more importantly, how did you get here? I’m assuming you’re from Ireland?” he waited for you to agree before continuing, “were you sent here?”
“No,” you shook your head, “I got pulled here by magic and stuff, it’s kinda hard to explain.”
“I’m rather good at understanding things,” Chiron winked at you conspiratorially. The humor made you relax more, tense shoulders loosening and your muscles unwinding. You smiled at him, Jason almost died, was he okay? He shouldn’t be like this so easily. “My mother, Morrígan, is known to have hovered over battlefields as a crow or raven, being her daughter, I can turn into a raven at will, but it’s not very easy and I haven’t done it since last summer since I got stuck as one for a few days, earlier today i shifted without meaning to and i was sorta dagged here by my instincts to watch.”
“You mean to tell us you flew across the Atlantic ocean in a few hours?”
You shrugged noncommittally, “I guess,”
Piper spoke up from beside you, “do you remember anything from the battle?”
You leant back in you chair as you thought, your brows furrowing, and it was all Jason could do to try and resist the urge to smooth the expression, “not much, i kinda become a bird when i shift, and my mental capacity gets smaller, but i do remember a dragon, and i saw you fly up with the blondie over there.” Jason blushed, and Thalia, who was sitting quietly and observing, gave him a knowing side eye.
Piper's eyes widened, “if you fell when Festus exploded, did you see where Leo went?” she grabbed your hand, imploring you with her eyes. “You mean the boy on the back of the dragon?” Piper nodded furiously as Jason got out of his stupor and paid attention, this may be their only lead to find Leo. “I remember falling with him, but he disappeared after i shifted back, i don't know where he went after that,”
Chiron butted in before Piper could hound you for more information, “I think our guest has had enough questioning, the med cabin is too full to house her, but I think she can stay for a few nights until she can fly home, does anyone volunteer their cabin?” Jason wanted to volunteer, and he almost did before Thalia butted in and saved him from the embarrassment. “The hunters of Artemis would be happy to lend her a bed for a few days, she can join our team for activities and chores while she’s here as well.”
You nodded in thanks as you stifled a yawn, blinking sleep from your eyes to keep yourself awake, “is that bed available now? If it’s not too much to ask,” Gods, why was Jason like this? He didn’t even know this girl and he was already blushing like a schoolgirl with a crush. Thalia nodded, “of course!” and went to help you out of your chair and support you by pulling your arm around her shoulder, heading for the Artemis cabin. Jason found himself oddly jealous of his sister, he wanted to help you to your bed, he saved you so he should- Gods he needed to stop, he’s being so pathetic.
Chatter picked up in the room as soon as you left, and Piper stood next to Jason where he was leant against the wall, arms crossed. She smirked at him knowingly, “she’s cute isn’t she?”
“What?- no, I mean, yes, she's pretty cut- pretty, um-” Piper burst out laughing at his expense while he turned into a blushing mess, how could she? After all he’s done for her? “You should talk to her when she’s fully awake, I’m sure she’d love to meet her dashing savior,” Piper grinned at him devilishly as he gave her a flat look.
Meanwhile, you were lying in a bunk bed Thalia had lay you down in, and panicking. Did you seriously call that boy blondie? Gods, what were you going to do? Why did he have to be so cute? And embarrassingly your type. Saoirse was gonna have a field day when she found out. Tall, strong, blond, ugh! What’s a girl to do?
↜✿↝
It's been a day or two since the battle, and Camp Half-Blood was slowly fixing itself, the kids in Athens had returned, and the med cabin was clearing out except from a few dire injuries. You had been helping to rebuild a couple of the damaged cabins, and you’d even made a few friends. The Romans and Greeks seemed pretty chill about another pantheon of demi-gods existing, which was a relief, and you’d learnt the story of the seven from multiple other people, which made you even more desperate to find the blonde boy who saved you. Since that day, he had seemingly disappeared. You never saw him at the campfires, and you never caught him during the day either; you still haven't thanked him for his catch, and to be honest you kinda wanted an excuse to talk to him as well.
Which was why you were grinning ear to ear when you spotted him sitting by himself at the tree line, you had been on a midday walk when you saw him, and the timing couldn’t have been more perfect. You made your footsteps louder as you approached to make sure he didn’t spook when you sat down. popping down next to him, you hugged your legs to your chest and put your chin on your knee. “You know, you never mentioned your name,” you said cheekily, looking out into the forest with him. He jumped, perhaps he was less spatially aware than you thought. “Oh. its uh- Jason,” he stumbled over his words as he registered your presence bedside him, tortuously close. “Well then, uh- Jason, thank you for saving my life, I really appreciate it,” that made him relax, the tension melted off his broad shoulders like candle wax, “it's just Jason,” he chuckled, “and you don’t need to thank me, it was just the right thing to do.” you gasped playfully as you replied, “my, so noble my savior, I suppose with that I’ll leave you to your brooding,” you went to get up, but he grabbed your hand desperately, “no! Stay, please?” electricity sparked where your hands joined, magic swirling around the two of you knowingly, a magnetic force of attraction pulling you together like thunder and lightning “of course.”

𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡 𝑡𝑤𝑜?
𝑠𝑒𝑛𝑑 𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑠𝑡𝑠! 🤍
#jason grace x reader#jason grace#pjo hoo toa#heroes of olympus#fanfic#pjo x reader#pjo x you#hoo x reader#hoo x you#piper mclean#leo valdez#percy jackson#thalia grace#hunters of artemis#irish mythology#celtic mythology#the morrígan#lugh#danu#ocs#Irish reader#daughter of morrígan reader#shape shifter#ravens#izzysinkHeroesOfOlympus#izzysinkPercyJackson#izzysinkPercyJacksonAndTheOlympians
33 notes
·
View notes
Note
hmmmmmmmm how about narinder pre-godhood? or maybe baby lamb?
also i dunno, might be cool if you drew some pikmin... kicks a pebble or whatever..

unfortunately i am not well versed in pikmin.. but i am very insane abt my lamb lore
Also LAMB NAME REVEAL!1!1!
Ok so, to preface, I’m irish and based the lamb’s culture off of celtic mythology so yeah
The lamb’s mother, Dana, comes from the name of the mother goddess in irish mythology who gave name to the ‘tuatha de danann’ (tribe of goddess danu, tribe of the gods) which is what i base the lamb’s close following on (stay with me here) So its kinda to say that from the lamb’s mother giving birth to them, she effectively raised all ‘children’ (following) of the lamb if you get what im saying?
The lamb themself takes the name of the famed goddess Ériu who is the matron goddess of ireland and gave it its name. SO staying on theme that the cult is named after the lamb themself, it fit nicely imo.
The lamb was born just as the reaping began, so their mother chose a name she hoped would bring them luck to spare them from the reaping. Hoping it would bring them to safer lands with ‘bounty and abundance’ as the name means. It was wishful thinking, although she knew not what her child was to become the very symbol the name portrayed.
sorry i’m really bad at putting my ideas into words it’s so late so i hope it’s comprehensible 😭🙏
#cotl#cult of the lamb#sorry for the random lore drop i got a bit excited#also HORRIBLY sorry for the irish mythology ramble#i like pagan stuff 😔#and celtic stuff#cotl lamb#cotl the lamb#the lamb#cotl au#cotl nomadic faith au#nomadic faith au#cult of the lamb au#cotl fanart#cult of the lamb fanart#🥀#asks#bella answers stuff
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
NAKSHATRAS AS GODDESSES
3/27
🔪KRITTIKA🔥
DISCLAIMER: This is based solely on my research and the patterns that I saw. I can't promise that I'm gonna be sure in all the coorelations, but I'm going to attribute each nakshatra a goddess that I think fits it the closest. If you're dissapointed, to make up for it, I'm going to list some other deities in the end that I think also fit the nakshatra. Don't come for me if you think I'm wrong, be respectful in the comments if you think so and have fun 🤍
This was easy and almost immidiate. The associations between this goddess and Krittika are so apparent I didn't hesitate for a second. Look out for other deities similar to her in the end.
Brigid

Pantheon: Celtic (Irish)
Name meaning: "the exalted one", "strength"
Associations: fire, spring, poetry and inspiration, healing and herbalism, smithcraft, agriculture, cattle and sheep.
Symbols: Brigid's cross, holy wells, eternal flame.
Brigid is one of the most highly- revered and widely worshipped Celtic goddesses. She'a triple goddess, representing the maiden, the mother and the crone. As a Maiden, she rules over poetry, music and ispiration. As a Mother, she's presiding over healing. As a Crone, she's the goddess of fire and smithcraft.
Frequently depicted with fiery red hair, she is no simple goddess, also ruling over waters and serenity. She's a protector of women and children, presiding over childbirth and motherhood. Also frequengly depicted with lambs and sheep (krittika's yoni animal) and swans. She's closely connected to agriculture and farm animals.


Brigid, also being connected to wells and rivers, has many landmarks in Ireland with a body of water. The most famous one is a well in Kildare, Ireland. Water from that well is said to have healing properties.
Her father was Dagda (good, great god), leader of the Irish tribe Tuatha Dé Danann ("people of goddess Danu"), which consisted of Irish deities who lived there before the ancestors of the modern Irish had arrived. Dagda was a wise man, an all-father and a Druid. Brigid married Bres, another member of that tribe and together they had three children. One of them, Ruadán, died and Brigid mourned him with profound and painful sadness. She's very devoted to protecting children and this might be a reason why.


In honor of her, there's a sacred fire lit in Kildare and is guarded by the Sisters of St. Brigid. There has been a fire in Kildare since the time Brigid was worshipped. It has been put out several times, but has been re-lit and is still burning. This suggests that the worship of Brigid has endured as she she survived and was made a Catholic saint when Christianity came to Europe.

I want to talk about why I chose her for Krittika while comparing her to very similar goddesses.
First one is the Roman Vesta. Virgins were chosen to keep the fire of vesta burning and it was said that if even one of them gave their virginity, the fire would burn out. In those instances when fire burned out by itself, the poor Vestal Virgins were to blame. Vesta is also the Roman Equivalent of the Greek Hestia, both being goddesses of the hearth, fire and home.
Krittika is the nakshatra that burns impurities through being precise and cutting away all that is not nessecary, hence a sharp object and a flame being its symbols. Bridging the signs of Aries and Taurus, it's often fiery and passionate but also feminine and nurturing.

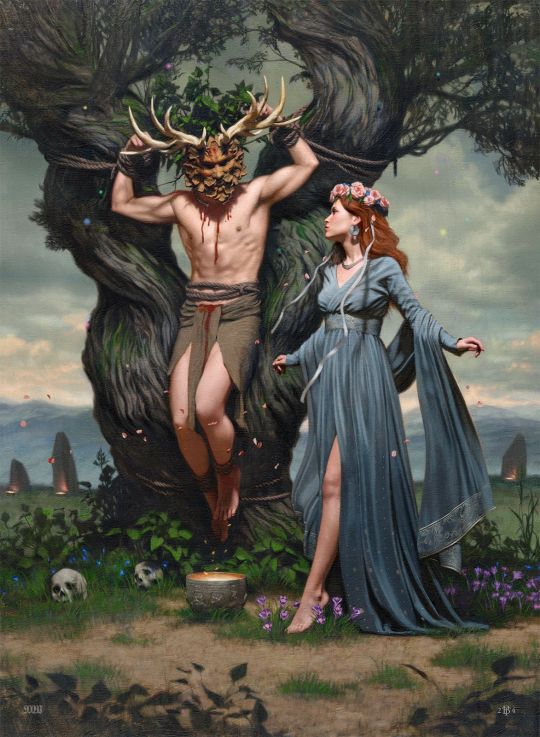
An Indian deity ruling over Krittika is Agni_ God of fire. An Indian goddess that is coorelated to Krittika (and also Purva Phalguni) is Tripura Sundari, meaning "the most beautiful in three worlds". This three world- triple goddess coorelation is apparent to me, besides the obvious fire associations, as well as nurturing, fertility and agriculture.
In the lunar mansion of Krittika, there's a constellation called the Pleiades, often called "the seven sisters". This is another confirmation of Krittika's very feminine nature, despite also representing the birth of the cosmic man and being very fiery and passionate in general.
Some other deities that I'd coorelate with Krittika:
Hestia- another virginal goddess of fire, also associated with home and hearth
Tripura Sundari- Indian goddess, "the most beautiful in the worlds"
Vesta- Roman goddess of fire and virgins
Bel- Celtic sun and fire god, also associated with healing, thunder and purification.
That's it! I hope you enjoyed reading about Brigid. This is a very condensed post but I said pretty much everything I wanted to say. I hope you understood Brigid's energy and made the coorelation between her and Krittika. If you're Krittika, even if you're not, COMMENT, like and reblog. Love u, take care ❤🔥
#krittika#krittika nakshatra#nakshatras#vedic astrology#astrology#astrology observations#vedic astrology observations#brigid#celtic mythology#irish mythology#ireland#celtic#goddess#goddess brigid
177 notes
·
View notes
Text
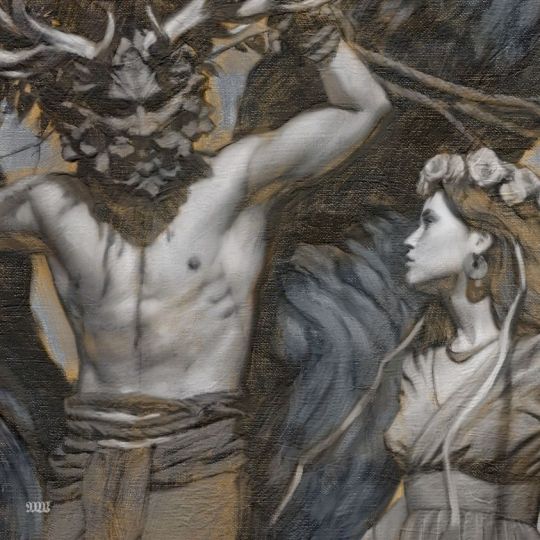


"A Gift For Danu" by @tombagshaw
Mythology Eriu, though it should reach a road-end, Banba, Fotla, and Fea, Neman of ingenious versicles, Danann, mother of the gods. -Lebor Gabála Érenn
Danu did not appear in Celtic or Irish myths, and was known only through the name Tuatha Dé Danann, or “Children of the goddess Danu.” She was described as the mother of the gods in the Lebor Gabála Érenn, though this was her sole appearance in medieval Irish literature. Despite the lack of available information, scholars have nevertheless attempted to derive some sense of the goddess' being.
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
LoZ Theory: Hylia = Amaterasu, But What Does That Mean?
Now, this theory is mostly just for fun, okay? So, keep that in mind when reading this.
Anyway, I'm sure that we've all realized to some degree that Hylia has some very obvious parallels to Amaterasu of Shintoist theology. At least, thematically speaking.
However, that brings into question as to who would take on the thematic roles of Tsukuyomi & Susano-o?
Interestingly, Hyrule itself doesn't really seem to have any gods of the moon & while wind & sky & even water gods have appeared throughout the games, the only one who you could feasibly refer to as a "storm god" really wasn't up to the same level as Hylia & I'd thus argue that he couldn't really be called a Susano-o parallel.
However, there was 1 divine entity that did appear in at least 1 game & had cameos in a couple of others. One that appears to bear some sort of connection to the moon.
The Fierce Deity. (Yes, he is actually, canonically, a Kishin, who are known for being compassionate protectors despite their viciousness in battle, however, I'm talking thematic roles here & therefore, he doesn't need to be a perfect representation of Tsukuyomi. At the same time, Hylia doesn't just parallel Amaterasu, but in some ways Danu, an Irish mother goddess, & even Christ to a degree. So, I don't understand why FD couldn't also have multiple influences.)
Not to mention, did you know that wolves, rabbits, & fairies all have some sort of connection to the moon? Like, I'm sure most of us know the wolf connection, but also there's the legend of the Jade Rabbit & I remember reading somewhere that the full moon was a portal to the realm of the fae. So, even in that respect, the Links still have some faint connections to the moon.
But if Hylia = Amaterasu & Fierce Deity = Tsukuyomi, then that still leaves Susano-o's Hyrulean mirror.
However, maybe we can figure this out by working through the game characters that Hylia & FD are most associated with, which are Zelda & Link.
And, as I'm guessing you're realizing, they too have a third: Ganondorf. And what seemingly divine entity is he most associated with?
The Bringer of Demise. Who happens to call down lightning in battle, as does Ganondorf. You could even make an argument about how his hatred could mirror the indiscriminant destructive power of a storm. Natural disasters, if you will.
Now, what I find interesting is what this implies about the 3 Hyrulean divinities in question. Because Susano-o had fallen from grace & been cursed into the body of a mortal for his misdeeds until he earned back his spot among the gods.
Is it possible that Demise had also been a true deity before committing some act that caused him to be cast out & become an... Akuma?
In fact, one of the things Susano-o did to get thrown out was that he destroyed his sister's crops. Specifically, it appears that he & Amaterasu both had 3 rice fields each, but whereas her fields were fertile, his were dry & barren, which in his jealousy, he destroyed her fields. (Which, itself, creates a bit of an interesting parallel between not just Susano-o's relationship with Amaterasu & Demise's with Hylia in SS, but also between the godly siblings & Ganondorf's relationship with just Hyrule, in-general. At least, if you trust WW Gdorf's words.)
One possible issue I see is a bit of discrepancy in the myths. In some depictions, it's Susano-o who kills Ōgetsuhime after his banishment, but in others, it's Tsukuyomi who kills Ukemochi. Which are simply 2 different names for the same goddess. Not only that, it was for the same reason. In order to serve them food, she produced it via some very unsanitary means, so they killed her for it.
As for Tsukuyomi, he seems to be regarded as an evil god, but at the same time, he only seems to appear in 2 myths. The myth of he & his siblings' birth & the myth of him killing Ukemochi.
Beyond that, personality wise, Tsukuyomi was described as cold & reserved, as well as having been noted to value things such as order, justice, & etiquette a great deal, to the point where it's said that he was willing to kill to maintain it despite murder not being condoned. In this way, he's seen as violent. Which could well fit with Fierce Deity, considering his portrayal as a Kishin with a few tweaks.
On the other hand, FD is referred to as a Kishin, which are inspired by the Buddhist Pāla or Protectors, a.k.a. Wrathful Gods. And though they are fearsome in battle & terrifying to behold, one of their core qualities is that they are compassionate, ultimately benevolent, & visit just vengeance upon those who wrong the innocent.
However, the only reason for Tsukuyomi being referred to as an evil god was his murder of Ukemochi. So, how does it change his character in a situation where the one to do so was instead his brother?
Are there other things he's done? It doesn't seem like it, which kinda paints Amaterasu in a not-so-great light considering how Susano-o does a lot more terrible things, yet later, she still forgives him.
Hell, remember he basically commits the exact same crime as Tsukuyomi. So, why is it that Susanoo gets a pass despite all the other shit he did, but Tsukuyomi doesn't despite technically having only 1 mess-up?
Is it because he hasn't apologized yet? Because he didn't get her some super powerful gift? Honestly, it makes me wonder what Amaterasu's reaction to Ukemochi's hostess skills & how she produced the food would've been.
Furthermore, either Tsukuyomi killed Ukemochi, Susano-o killed Ōgestuhime, or Tsukuyomi killed her, she revived, & then Susano-o killed her again later.
In the case of the last one, it brings to question why she hadn't learned her lesson? At that point, she only has herself to blame.
However, it's also possible that the story of night & day & Susano-o killing Ōgetsuhime could possibly be one in the same, just told from 2 different perspectives. Keep in mind that Susano-o was able to transform a woman into a comb even after being banished. It wouldn't be too farfetched to assume that he could transform himself as well. Hell, shouldn't taking on the visage of another person theoretically be much easier than literally turning another person into an inanimate object?
If I'm right, then the situation would unfold like this: Susano-o was banished, Ukemochi held a feast & invited Amaterasu, she couldn't come & sent Tsukuyomi instead, Susano-o heard of Ukemochi's grand feast, & took on his brother's appearance. Susanoo-o as Tsukuyomi asked Ukemochi to provide him with food, then upon seeing how she did so, he killed her before leaving, & that's when Tsukuyomi came upon the scene. However, this left Tsukuyomi to be blamed for her death because other partygoers witnessed the not-Tsukuyomi's crime, which resulted in Amaterasu & the real Tsukuyomi separating, thus creating day & night. (Not that this is actually what happened in myth, but it's just a thought.)
However, even if he did do it, if this was the only instance of Tsukuyomi behaving in such a manner, then it honestly seems very unfair to have him automatically slighted as evil.
Though, what I find interesting is that if my interpretation of the story were correct, then it'd somewhat create another parallel between Tsukuyomi & FD. The misconception that dark automatically means evil, which has led to both being demonized. In FD's case, pretty literally due to unfortunate translation association.
Sorry, I just found this possibility to be very freaking interesting.
LoZ Cultural Masterlist 1
#legend of zelda#loz#hylia#fierce deity#demise#zelda#link#ganondorf#shinto myth#amaterasu#tsukuyomi#susanoo
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
I mentioned that my position in the summer court has a duty of education, so let's talk about the observer effect for a hot second.
It's a physics thing that proposes that the action of observing something affects the thing being observed. It can also be likened to the expectation morphology of magic, which looks the way you expect it to look and is always found wherever you expect to find it. You collapse a set of parallel realities by opening a box, and you bear witness to an archmage by being especially hype about a Vegas show.
"The fae" is the most-common modern name for the people of Danu (the Tuatha de Danann, to use the Gaelic name, also called the sidhe (pronounced "shee")). Danu is a goddess who sort-of only still exists by association with her descendants because she's from the lost era of Irish mythology, so basically nothing survives about her to the modern day. She's still around but she's kind of living a quiet life in functional retirement, like a much-beloved grandma with her cosy cottage in the countryside that the family visit every few months.
Irish legends frequently describe us as funky little creatures of numerous shapes and sizes and dispositions, but a lot of the older ones describe us as demigods or even gods in our own right. This means that all modern fae, albeit very very thinly in most, are descended from divinity and, by extension, magic.
What that means is that the fae, too, are subject to that pseudo-observer effect. There's not a lot of magic around these days because there's so few mortals who earnestly think it's real, so we don't change very much, but we do change.
Which is to say that we look the way you expect us to look, which for the very vast majority of mortals is "like a slightly weird mortal", but to the handful of mortals nevertheless expecting us to be more fantastical they absolutely will not be disappointed.
#JustFaeThings#in which Lying ties fairies to physics#because they're a colossal nerd#this cosmological approach to the fae Also means that#you don't have to be Irish at all to be fae#if you earnestly identify as fae then you are fae
9 notes
·
View notes