#industrial reports development company
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Industrial Alarm Management Application
#industrial reporting solution#industrial reporting software#industrial reports development company#reporting tool for industrial automation#reporting software for industrial automation#Scada reporting software#report generation in Scada#best reporting software#Scada report generation#best reporting tools#industrial automation reporting tool#reporting tool for Scada#web based reporting tools#web based reporting software#automated reporting and data analysis software#Batch Reporting Application#Data Log Reporting Application#MKT Analysis#MKT Analysis reports development#Market Analysis application#Alarm Reporting Application
0 notes
Text
How to Progress ahead with Mathematics?

#Mathematics graduates are versatile and can find opportunities in many other industries as well#depending on their specific interests and areas of expertise. The strong analytical and problem-solving skills acquired through a Mathemati#Market Research Analyst#As a market researcher for a company#you gather data from customers and competitors#assist in developing goals and strategies#improve your customer base#and beat your competitors.#As a market researcher#you will also design surveys#formulate reports#track market trends#and present information to executives. As you gain experience#there are plenty of scopes for you to manage a team of researchers and evaluate strategies.#The Faculty of Mathematics at Poddar International College is simply outstanding and proficient. Besides#the students have bright prospects as they have the best placements here.#Financial Planner#Financial planners assist individuals and companies in managing their financial assets. They are also involved in assisting individuals wit#Developing effective financial strategies for businesses and individuals.#Setting financial goals#assessing financial risks#and helping to ensure retirement or investment plans are among their primary duties.#They help companies formulate stock market investment strategies#real estate investing strategies#and new business ventures.#There are many professional skill and soft skills enhancement sessions for the students of Mathematics at Poddar International College.#Insurance Underwriter#Insurance underwriters are the ones who#on behalf of the insurance company#evaluate
1 note
·
View note
Text
Aircraft Connectors Market Geographical Expansion & Analysis Growth Development, Status, Recorded during 2017 to 2032
The competitive analysis of the Aircraft Connectors Market offers a comprehensive examination of key market players. It encompasses detailed company profiles, insights into revenue distribution, innovations within their product portfolios, regional market presence, strategic development plans, pricing strategies, identified target markets, and immediate future initiatives of industry leaders. This section serves as a valuable resource for readers to understand the driving forces behind competition and what strategies can set them apart in capturing new target markets.
Market projections and forecasts are underpinned by extensive primary research, further validated through precise secondary research specific to the Aircraft Connectors Market. Our research analysts have dedicated substantial time and effort to curate essential industry insights from key industry participants, including Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), top-tier suppliers, distributors, and relevant government entities.
Receive the FREE Sample Report of Aircraft Connectors Market Research Insights @ https://stringentdatalytics.com/sample-request/aircraft-connectors-market/2411/
Market Segmentations:
Global Aircraft Connectors Market: By Company
• Amphenol Corporation
• TE Connectivity
• Carlisle Companies Inc. STRINGENT DATALYTICS
• Esterline Corporation
• Bel Fuse Inc.
• Eaton Corporation
• ITT Corporation
• Smiths Group PLC
• Radiall
• Rosenberger Group
Global Aircraft Connectors Market: By Type
• PCB
• Fiber Optic
• High Power
• High Speed
• RF Connectors
• Others
Global Aircraft Connectors Market: By Application
• Commercial
• Business Jets
• Military
• Others
Regional Analysis of Global Aircraft Connectors Market
All the regional segmentation has been studied based on recent and future trends, and the market is forecasted throughout the prediction period. The countries covered in the regional analysis of the Global Aircraft Connectors market report are U.S., Canada, and Mexico in North America, Germany, France, U.K., Russia, Italy, Spain, Turkey, Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium, and Rest of Europe in Europe, Singapore, Malaysia, Australia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific (APAC) in the Asia-Pacific (APAC), Saudi Arabia, U.A.E, South Africa, Egypt, Israel, Rest of Middle East and Africa (MEA) as a part of Middle East and Africa (MEA), and Argentina, Brazil, and Rest of South America as part of South America.
Click to Purchase Aircraft Connectors Market Research Report @ https://stringentdatalytics.com/purchase/aircraft-connectors-market/2411/
Customization of the Report:
This report can be customized to meet the client’s requirements. Please connect with our sales team ([email protected] ), who will ensure that you get a report that suits your needs. You can also get in touch with our executives on +1 346 666 6655 to share your research requirements.
Enquiry Before Buying @ https://stringentdatalytics.com/inquiry/aircraft-connectors-market/2411/
About Stringent Datalytics
Stringent Datalytics offers both custom and syndicated market research reports. Custom market research reports are tailored to a specific client's needs and requirements. These reports provide unique insights into a particular industry or market segment and can help businesses make informed decisions about their strategies and operations.
Syndicated market research reports, on the other hand, are pre-existing reports that are available for purchase by multiple clients. These reports are often produced on a regular basis, such as annually or quarterly, and cover a broad range of industries and market segments. Syndicated reports provide clients with insights into industry trends, market sizes, and competitive landscapes. By offering both custom and syndicated reports, Stringent Datalytics can provide clients with a range of market research solutions that can be customized to their specific needs.
Reach US
Stringent Datalytics
+1 346 666 6655
Social Channels:
Linkedin��| Facebook | Twitter | YouTube
#Aircraft Connectors Market Geographical Expansion & Analysis Growth Development#Status#Recorded during 2017 to 2032#The competitive analysis of the Aircraft Connectors Market offers a comprehensive examination of key market players. It encompasses detaile#insights into revenue distribution#innovations within their product portfolios#regional market presence#strategic development plans#pricing strategies#identified target markets#and immediate future initiatives of industry leaders. This section serves as a valuable resource for readers to understand the driving forc#Market projections and forecasts are underpinned by extensive primary research#further validated through precise secondary research specific to the Aircraft Connectors Market. Our research analysts have dedicated subst#including Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs)#top-tier suppliers#distributors#and relevant government entities.#Receive the FREE Sample Report of Aircraft Connectors Market Research Insights @ https://stringentdatalytics.com/sample-request/aircraft-co#Market Segmentations:#Global Aircraft Connectors Market: By Company#• Amphenol Corporation#• TE Connectivity#• Carlisle Companies Inc. STRINGENT DATALYTICS#• Esterline Corporation#• Bel Fuse Inc.#• Eaton Corporation#• ITT Corporation#• Smiths Group PLC#• Radiall#• Rosenberger Group
0 notes
Text
Green energy is in its heyday.
Renewable energy sources now account for 22% of the nation’s electricity, and solar has skyrocketed eight times over in the last decade. This spring in California, wind, water, and solar power energy sources exceeded expectations, accounting for an average of 61.5 percent of the state's electricity demand across 52 days.
But green energy has a lithium problem. Lithium batteries control more than 90% of the global grid battery storage market.
That’s not just cell phones, laptops, electric toothbrushes, and tools. Scooters, e-bikes, hybrids, and electric vehicles all rely on rechargeable lithium batteries to get going.
Fortunately, this past week, Natron Energy launched its first-ever commercial-scale production of sodium-ion batteries in the U.S.
“Sodium-ion batteries offer a unique alternative to lithium-ion, with higher power, faster recharge, longer lifecycle and a completely safe and stable chemistry,” said Colin Wessells — Natron Founder and Co-CEO — at the kick-off event in Michigan.
The new sodium-ion batteries charge and discharge at rates 10 times faster than lithium-ion, with an estimated lifespan of 50,000 cycles.
Wessells said that using sodium as a primary mineral alternative eliminates industry-wide issues of worker negligence, geopolitical disruption, and the “questionable environmental impacts” inextricably linked to lithium mining.
“The electrification of our economy is dependent on the development and production of new, innovative energy storage solutions,” Wessells said.
Why are sodium batteries a better alternative to lithium?
The birth and death cycle of lithium is shadowed in environmental destruction. The process of extracting lithium pollutes the water, air, and soil, and when it’s eventually discarded, the flammable batteries are prone to bursting into flames and burning out in landfills.
There’s also a human cost. Lithium-ion materials like cobalt and nickel are not only harder to source and procure, but their supply chains are also overwhelmingly attributed to hazardous working conditions and child labor law violations.
Sodium, on the other hand, is estimated to be 1,000 times more abundant in the earth’s crust than lithium.
“Unlike lithium, sodium can be produced from an abundant material: salt,” engineer Casey Crownhart wrote in the MIT Technology Review. “Because the raw ingredients are cheap and widely available, there’s potential for sodium-ion batteries to be significantly less expensive than their lithium-ion counterparts if more companies start making more of them.”
What will these batteries be used for?
Right now, Natron has its focus set on AI models and data storage centers, which consume hefty amounts of energy. In 2023, the MIT Technology Review reported that one AI model can emit more than 626,00 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent.
“We expect our battery solutions will be used to power the explosive growth in data centers used for Artificial Intelligence,” said Wendell Brooks, co-CEO of Natron.
“With the start of commercial-scale production here in Michigan, we are well-positioned to capitalize on the growing demand for efficient, safe, and reliable battery energy storage.”
The fast-charging energy alternative also has limitless potential on a consumer level, and Natron is eying telecommunications and EV fast-charging once it begins servicing AI data storage centers in June.
On a larger scale, sodium-ion batteries could radically change the manufacturing and production sectors — from housing energy to lower electricity costs in warehouses, to charging backup stations and powering electric vehicles, trucks, forklifts, and so on.
“I founded Natron because we saw climate change as the defining problem of our time,” Wessells said. “We believe batteries have a role to play.”
-via GoodGoodGood, May 3, 2024
--
Note: I wanted to make sure this was legit (scientifically and in general), and I'm happy to report that it really is! x, x, x, x
#batteries#lithium#lithium ion batteries#lithium battery#sodium#clean energy#energy storage#electrochemistry#lithium mining#pollution#human rights#displacement#forced labor#child labor#mining#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
UAE Debt Collection Market is Expected to Reach More Than AED 5Bn by 2027 Owing to Rise in digital collection techniques and Improvement in UAE legal system related to debt collection, bankruptcy and insolvency: Ken Research
Buy Now
UAE Debt Collection Market Ecosystem
Tahseel, First Solution Management Service are the market leaders in UAE Debt Collection Market; the market is highly fragmented consisting of many players. The UAE Debt Collection Market is composed of many players which are operating across the borders and not just within the UAE.


Key Market Findings:
Digital collections are being extensively used which leverages analytics to make the process more
Collection agents are being trained to equip them with latest technology and to adept them to various consumer situations for providing more feasible solutions.
The industry is slowly becoming more customer-centric in its approach.
Interested to Know More about this Report, Request for a sample report
IT Policies and Proper Documentation: Companies are maintaining proper documentation and proof for all debt provided by them to corporates and individuals. This makes it much easier for debt collection agencies to recover the debt in case of a default both amicably and legally as well through payment order method. Collection companies which provide settlement plans to debtors have start taking post-dated cheques as a proof for future payment. Changing IT policies require companies to maintain complete confidentiality of client information due to threat of data breach. All this factors will provide more growth to collection industry.
Emphasis on NLP Techniques: Collection agencies are extensively using various speech analytics tools to record and analyse customer conversations. This enables to maintain security and gain insights into client expectations. In addition, the information gathered can further be used for training of employees adapting them to different situations while negotiating and hence, improving their performance which would act as a key growth driver for debt collection companies.
Favorable Changes in UAE Legal System: The new legal system at UAE makes it possible to recover debts via court in merely within 7 days if all the documents are readily available. The new Bankruptcy law also provides safety for debtors and changes the shape of debt collection industry. Ultimately, act as catalysts for the industry.
Analysts at Ken Research in their latest publication- “UAE Debt Collection Market Outlook to 2027- Characterized by fierce competition and high growth prospects” by Ken Research provides a comprehensive analysis of the potential of the debt collection market in UAE. Rise in digital collection techniques and increasing use of AI and ML for recovery predictions are expected to contribute to the market growth over the forecast period.
UAE debt collection market is expected to grow at a robust CAGR over the forecasted period 2022-2027.
Key Segments Covered
Segmentation by Segment
Non-Finance
Finance
Insurance
Segmentation by Type of Firm
Debt Collection Agency
Law Firm
Segmentation by Age of Firm:
0 to 10 yrs
10 to 20 yrs
20 to 30 yrs
Segmentation by Geographical Presence
Abu Dhabi
Dubai
Fujairah
Sharjah
Ajman
Umm Al-Quwain
Ras Al-Khaimah
Sub-segmentation of insurance segment & financing segment
Sub-segmentation of insurance segment:
Motor & Transportation
Property/Fire
Liability & Others
Sub-segmentation of financing segment:
Real State
Personal
Financial institution
Services
Manufacturing
Trade
Others
Visit this Link :- Request for custom report
Key Target Audience
Existing Debt Collection Companies
Law Firms
Financing Companies
Non-Financing Companies
Insurance Companies
Debt Collection & Management software providers
Government Agencies
Finance Consultants
Others
Time Period Captured in the Report:
Historical Period: 2017-2022
Base Year: 2022
Forecast Period: 2022–2027
Companies Covered:
SUPPLY SIDE:
Debt Collection Companies
Tahseel
CMS
Aman Debt Collection
First Solution
Credit Recovery
AW Holding
Bilkish
Derby Group of Companies
Alpha Debt Collection
Fort Equity
Quick Action
ATDC
com
ALQADA
Law firms/Debt Collection
Taswiyeh
ASKTHELAW
HHS LAWYERS
DUBAI DEBT RECOVERY
STA
AE
AL ROWAAD
AL SAFAR
BIN EID
Regulatory Bodies and Judiciary
Central Bank of the UAE
Judicial Department
DEMAND SIDE:
Insurance companies
Etihad Credit Insuranc
Atradiuse
CIGNA
COFACE
PACIFIC PRIME
MetLIFE
ACE
Emirates RE
Financing companies
Emirates NBD
ADCB
DUBAI FIRST
Mashreq
Commercial Bank of Dubai
Dubai Islamic Bank
HSBC
RAKBANK
ADIB
FAB
CITYBANK
Non-Finance companies
Etisalat
Emircom
Etihad Water and Electricity
Abu Dhabi Distribution Companies
Emaar
Nakheel
Lufthansa
Choithrams
Asian Paints
Majid UL Futaim
Naseej
Key Topics Covered in the Report
Global Debt Collection Market Overview
Ecosystem of UAE Debt Collection Market – Demand and Supply Side
Value Chain Analysis – Amicable Settlement and Litigation Settlement
Market Size and Segmentation of Debt Collection Industry in UAE, 2017-2022
UAE Debt Collection Market Industry Analysis
Software used in UAE Debt Collection Market
Market Shares of Major Debt Collection Companies in UAE on the basis of Debt Collected, 2022
Competitive Analysis
Future Outlook and Projections, 2022-2027
For More Insights On Market Intelligence, Refer to the Link Below: –
UAE Debt Collection Market Outlook to 2027
Related Reports by Ken Research: –
KSA Debt Collection Market Outlook to FY’2026
#UAE Debt Collection Market#UAE Debt Collection Industry#UAE Debt Collection sector#Emirates Tax Collecting Trends#AbuDhabi Debt Collection Market Report#UAE Debt Collection Market Size#UAE Debt Collection Market Analysis#Emirates loan Collection Industry#UAE Debt Collection Market Ecosystem#UAE Debt Collection Market Growth Drivers#UAE Debt Collection Market Trends#UAE Debt Collection Market Issues#UAE Debt Collection Market Challenges#Developments in UAE Debt Collection Market#UAE Outstanding Payments Segments#Debt Collecting Firm#UAE Debt Collection and Management software providers#Debt Financing Companies#UAE Debt Collection Market Aggregators#UAE Debt Collection Market Future Projections#UAE Debt Collection Market Future Outlook#Aman Debt Collection#First Solution Management Services Market Share#Credit Recovery Debt Settlement#UAE Non-Financing Companies#Bilkish Associate Market Revenue#Derby Group of Companies Market Share#Alpha Debt Collection Market Revenue#Fort Equity Market Revenue#Quick Action Pvt Limited
0 notes
Text
Nimona: a Story of Trans Rights, Queer Solidarity, and the Battle Against Censorship
by Ren Basel renbasel.com
The 2023 film Nimona, released on Netflix after a tumultuous development, is a triumph of queer art. While the basic plot follows a mischievous shapeshifter befriending a knight framed for murder, at its heart Nimona is a tale of queer survival in the face of bigotry and censorship. Though the word “transgender” is never spoken, the film is a deeply political narrative of trans empowerment.
The film is based on a comic of the same name, created by Eisner-winning artist N.D. Stevenson. (1) Originally a webcomic, Nimona stars the disgraced ex-knight Ballister Blackheart and his titular sidekick, teaming up to topple an oppressive regime known as the Institution. The webcomic was compiled into a graphic novel published by Harper Collins on May 12, 2015. (2)
On June 11, 2015, the Hollywood Reporter broke the news Fox Animation had acquired rights to the story. (3) A film adaptation would be directed by Patrick Osborne, written by Marc Haimes, and produced by Adam Stone. Two years later, on February 9, 2017, Osborne confirmed the film was being produced with the Fox-owned studio Blue Sky Animation, and on June 30 of that same year, he claimed the film would be released Valentine’s Day 2020. (4)
Then the Walt Disney Company made a huge mess.
On December 14, 2017, Disney announced the acquisition of Twenty-First Century Fox, Inc. (5) Industry publications began speculating the same day about Blue Sky’s fate, though nothing would be confirmed until after the deal’s completion on March 19, 2019. (6) At first it seemed the studio would continue producing films under Disney’s governance, similar to Disney-owned Pixar Animation. (7)
The fate of the studio—and Nimona’s film adaptation—remained in purgatory for two years. During that time, Patrick Osborne left over reported creative differences, and directorial duties were taken over by Nick Bruno and Troy Quane. (8) Bruno and Quane continued production on the film despite Blue Sky’s uncertain future.
The killing blow came on February 9, 2021. Disney shut down Blue Sky and canceled Nimona, the result of economic hardship caused by COVID-19. (9) Nimona was seventy-five percent completed at the time, set to star Chloë Grace Moretz and Riz Ahmed. (10)
While COVID-19 caused undeniable financial upheaval for the working class, wealthy Americans fared better. (11) Disney itself scraped together enough to pay CEO Bob Iger twenty-one million dollars in 2020 alone. (12) Additionally, demand for animation spiked during the pandemic’s early waves, and Nimona could have been the perfect solution to the studio’s supposed financial woes. (13) Why waste the opportunity to profit from Blue Sky’s hard work?
It didn’t take long for the answer to surface. Speaking anonymously to the press, Blue Sky workers revealed the awful truth: Disney may have killed Nimona for being too queer. The titular character was gender-nonconforming, the leading men were supposed to kiss, and Disney didn’t like it. (14) While Disney may claim COVID-19 as the cause, it is noteworthy that Disney representatives saw footage of two men declaring their love, and not long after, the studio responsible was dead. (15) Further damning evidence came in February of 2024, when the Hollywood Reporter published an article quoting co-director Nick Bruno, who named names: Disney’s chief creative officer at the time, Alan Horn, was adamantly opposed to the film’s “gay stuff.” (16)
Disney didn’t think queer art was worthy of their brand, and it isn’t the first time. “Not fitting the Disney brand” was the justification for canceling Dana Terrace’s 2020 animated series The Owl House, which featured multiple queer characters. (17) Though Terrace was reluctant to assume queerphobia caused the cancellation, Disney’s anti-queer bias has been cited as a hurdle by multiple showrunners, including Terrace herself. (18) The company’s resistance to queer art is a documented phenomenon.
While Nimona’s film cancellation could never take N.D. Stevenson’s comic from the world, it was a sting to lose such a powerful queer narrative on the silver screen. American film has a long history of censoring queerness. The Motion Picture Production Code (commonly called the Hays Code) censored queer stories for decades, including them under the umbrella of “sex perversion.” (19) Though the Code was eventually repealed, systemic bigotry turns even modern queer representation milestones into battles. In 2018, when Rebecca Sugar, creator of the Cartoon Network series Steven Universe, succeeded in portraying the first-ever same-sex marriage proposal in American children’s animation, the network canceled the show in retaliation. (20)
When queer art has to fight so hard just to exist, each loss is a bitter heartbreak. N.D. Stevenson himself expressed sorrow that the world would never see what Nimona’s crew worked so hard to achieve. (21)
Nimona, however, is hard to kill.
While fans mourned, progress continued behind the scenes. Instead of disappearing into the void as a tax write-off, the film was quietly scooped up by Megan Ellison of Annapurna Pictures. (22) Ellison received a call days before Disney’s death blow to Blue Sky, and after looking over storyboard reels, she decided to champion the film. With Ellison’s support, former Blue Sky heads Robert Baird and Andrew Millstein did their damnedest to find Nimona a home. (23)
Good news arrived on April 11, 2022, when N.D. Stevenson made a formal announcement on Twitter (now X): Nimona was gloriously alive, and would release on Netflix in 2023. (24) Netflix confirmed the news in its own press release, where it also provided details about the film’s updated cast and crew, including Eugene Lee Yang as Ambrosius Goldenloin alongside Riz Ahmed’s Ballister Boldheart (changed from the name Blackheart in the comic) and Chloë Grace Moretz as Nimona. (25) The film was no longer in purgatory, and grief over its death became anticipation for its release.
Nimona made her film debut in France, premiering at the Annecy International Animation Film Festival on June 14, 2023 to positive reviews. (26) Netflix released the film to streaming on June 30, finally completing the story’s arduous journey from page to screen. (27)
When the film begins, the audience is introduced to the world through a series of illustrated scrolls, evoking the storybook intros of Disney princess films such as 1959’s Sleeping Beauty. The storybook framing device has been used to parody Disney in the past, perhaps most famously in the 2001 Dreamworks film Shrek. Just as Shrek contains parodies of the Disney brand created by a Disney alumnus, so, too, does Nimona riff on the studio that snubbed it. (28)
Nimona’s storybook intro tells the story of Gloreth, a noble warrior woman clad in gold and white, who defended her people from a terrible monster. After slaying the beast, Gloreth established an order of knights called the Institute (changed from the Institution in the comic) to wall off the city and protect her people.
Right away, the film introduces a Christian dichotomy of good versus evil. Gloreth is presented as a Christlike figure, with the Institute’s knights standing in as her saints. (29) Her name is invoked like the Christian god, with characters uttering phrases such as “oh my Gloreth” and “Gloreth guide you.” The film’s design borrows heavily from Medieval Christian art and architecture, bolstering the metaphor.
Nimona takes place a thousand years after Gloreth’s victory. Following the opening narration, the audience is dropped into a setting combining Medieval aesthetics with futuristic science fiction, creating a sensory delight of neon splashed across knights in shining armor. It’s in this swords-and-cyborgs city that a new knight is set to join the illustrious ranks of Gloreth’s Institute, now under the control of a woman known only as the Director (voiced by Frances Conroy). That new knight is our protagonist, Ballister Boldheart.
The film changes several things from the original. The comic stars Lord Ballister Blackheart, notorious former knight, long after his fall from grace. He has battled the Institution for years, making a name for himself as a supervillain. The film introduces a younger Ballister Boldheart who is still loyal to the Institute, who believes in his dream of becoming a knight and overcomes great odds to prove himself worthy. In the comic, Blackheart’s greatest rival is Sir Ambrosius Goldenloin, with whom he has a messy past. The film shows more of that past, when Goldenloin and Boldheart were young lovers eager to become knights by each other’s side.
There is another notable change: in the comic, Goldenloin is white, and Blackheart is light-skinned. In the film, both characters are men of color—specifically, Boldheart is of Pakistani descent, and Goldenloin is of Korean descent, matching the ethnicity of their respective voice actors. This change adds new themes of institutional racism, colorism, and the “model minority” stereotype. (30)
The lighter-skinned Goldenloin is, as his name suggests, the Institute’s golden boy. He descends from the noble lineage of Gloreth herself, and his face is emblazoned on posters and news screens across the city. He is referred to as “the most anticipated knight of a generation.” In contrast, the darker-skinned Boldheart experiences prejudice and hazing due to his lower-class background. His social status is openly discussed in the news. He is called a “street kid” and “controversial,” despite being the top student in his class. The newscasters make sure everyone knows he was only given the chance to prove himself in the Institute because the queen, a Black woman with established social influence, gave him her personal patronage. Despite this patronage, when the news interviews citizens on the street, public opinion is firmly against Boldheart.
To preserve the comic’s commentary on white privilege, some of Goldenloin’s traits were written into a new, white character created for the film, Sir Thoddeus Sureblade (voiced by Beck Bennett). Sureblade’s vitriol against both Boldheart and Goldenloin allowed Goldenloin to become a more sympathetic character, trapped in the system just as much as Boldheart. (31) This is emphasized at other points in the film when the audience sees Sureblade interact with Goldenloin without Boldheart present, berating the only person of color left in the absence of the darker-skinned man.
The day Boldheart is to be knighted, everything goes wrong. As Queen Valerin (voiced by Lorraine Toussaint) performs the much-anticipated knighting ceremony, a device embedded in Boldheart’s sword explodes, killing her instantly. Though Boldheart is not to blame, he is dubbed an assassin instead of a knight. In an instant, he becomes the most wanted man in the kingdom, and Queen Valerin’s hopes for progress and social equality seem dead with her. Boldheart is gravely injured in the explosion and forced to flee, unable to clear his name.
Enter Nimona.
The audience meets the titular character in the act of vandalizing a poster of Gloreth, only to get distracted by an urgent broadcast on a nearby screen. As she approaches, a bystander yells that she’s a “freak,” in a manner reminiscent of slurs screamed by passing bigots. Nimona has no time for bigots, spraying this one in the face with paint before tuning in to the news.
“Everyone is scared,” declare the newscasters, because queen-killer Ballister Boldheart is on the run. The media paints him as a monster, a filthy commoner who never deserved the chances he was given, and announce that, “never since Gloreth’s monster has anything been so hated.” This characterization pleases Nimona, and she declares him “perfect” before scampering off to find his hiding place.
It takes the span of a title screen for her to track him down, sequestered in a makeshift junkyard shelter. Just before Nimona bursts into the lair, the audience sees Boldheart’s injuries have resulted in the amputation of his arm, and he is building a homemade prosthetic. This is another way he’s been othered from his peers in an instant, forced to adapt to life-changing circumstances with no support. Where he was so recently an aspiring knight with a partner and a dream, he is now homeless, disabled, and isolated.
A wall in the hideout shows a collection of news clippings, suspects, and sticky notes where Boldheart is trying to solve the murder and clear his name. His own photo looks down from the wall, captioned with a damning headline: “He was never one of us—knights reveal shocking details of killer’s past.” It evokes real-world racial bias in crime reporting, where suspects of color are treated as more violent, unstable, and prone to crime than white suspects. A 2021 report by the Equal Justice Initiative and the Global Strategy Group compiled data on this phenomenon, focusing on the stark disparity between coverage of white and Black suspects. (32)
Nimona is not put off by Boldheart’s sinister media reputation. It’s why she tracked him down in the first place. She’s arrived to present her official application as Boldheart’s villain sidekick and help him take down the Institute. Boldheart brushes her off, insisting he isn’t a villain. He has faith in his innocence and in the system, and leaves Nimona behind to clear his name.
When he is immediately arrested, stripped of his prosthetic, and jailed, Nimona doesn’t abandon him. She springs a prison break, and conveys a piece of bitter wisdom to the fallen knight: “[O]nce everyone sees you as a villain, that’s what you are. They only see you one way, no matter how hard you try.”
Nimona and Boldheart are both outcasts, but they are at different stages of processing the pain. Boldheart is deep in the grief of someone who tried to adhere to the demands of a biased system but finally failed. He is the newly cast-out, who gave his entire life to the system but still couldn’t escape dehumanization. His pain is a fresh, raw wound, where Nimona has old scars. She embodies the deep anger of those who have existed on the margins for years. Where Boldheart wants to prove his innocence so he can be re-accepted into the fold, Nimona’s goal is to tear the entire system apart. She finds instant solidarity with Boldheart based solely on their mutual status as outsiders, but Boldheart resists that solidarity because he still craves the system’s familiar structure.
In the comic, Blackheart’s stance is not one of fresh grief, since, just like Nimona, he has been an outsider for some time. Instead, Blackheart’s position is one of slow reform. He believes the system can be changed and improved, while Nimona urges him to demolish it entirely. In both versions, Ballister thinks the system can be fixed by removing specific corrupt influences, where Nimona believes the government is rotten to its foundations and should be dismantled. Despite their ideological differences, Nimona and Ballister ally to survive the Institute’s hostility.
The allyship is an uneasy truce. During the prison break, Nimona reveals that she’s a shapeshifter, able to change into whatever form she pleases. Boldheart reflexively reaches for his sword, horrified that she isn’t human. She is the exact sort of monster he has been taught to fear by the Institute, and it’s only because he needs her help that he overcomes his reflex and sticks with her.
Nimona’s shapeshifting functions as a transgender allegory. The comic’s author, N.D. Stevenson, is transgender, and Nimona’s story developed alongside his own queer journey. (33) The trans themes from the comic are emphasized in the film, with various pride flags included in backgrounds and showcased in the art book. (34) Directors Bruno and Quane described the film as “a story about acceptance. A movie about being seen for who you truly are and a love letter to all those who’ve ever shared that universal feeling of being misunderstood or like an outsider trying to fit in.” (35)
When Boldheart asks Nimona what she is, she responds with only “Nimona.” When he calls her a girl, she retorts that she’s “a lot of things.” When she transforms into another species, she specifies in that moment that she’s “not a girl, I’m a shark.” Later, when she takes the form of a young boy and Boldheart comments on it, saying “now you’re a boy,” her response is, “I am today.” She defies easy categorization, and she likes it that way.
About her shapeshifting, Nimona says “it feels worse if I don’t do it” and “I shapeshift, then I’m free.” When asked what happens if she doesn’t shapeshift, she responds, “I wouldn’t die-die, I just sure wouldn’t be living.” Every time she discusses her transformations, it carries echoes of transgender experience—and, as it happens, Nimona is not N.D. Stevenson’s only shapeshifting transgender character. During his tenure as showrunner for She-Ra and the Princesses of Power (Netflix/Dreamworks, 2018-2020), Stevenson introduced the character Double Trouble. Double Trouble previously existed at the margins of She-Ra lore, but Stevenson’s version was a nonbinary shapeshifter using they/them pronouns. (36) While Nimona uses she/her pronouns throughout both comic and film, just like Double Trouble her gender presentation is as fluid as her physical form.
Boldheart, like many cisgender people reacting to transgender people, is uncomfortable with Nimona. He declares her way of doing things “too much,” and insists they try to be “inconspicuous” and “discreet.” He worries whether others saw her, and, when she is casually in a nonhuman form, he asks if she can “be normal for a second.” He claims to support her, but says it would be “easier if she was a girl” because “other people aren’t as accepting.” His discomfort evokes fumbled allyship by cisgender people, and Nimona emphasizes the allegory by calling Boldheart out for his “small-minded questions.” While the alliance is uneasy, Boldheart continues working with Nimona to clear his name. They are the only allies each other has, and their individual survival is dependent on them working together.
When the duo gain video proof of Boldheart’s innocence, they learn the bomb that killed Queen Valerin was planted by the Director. Threatened by a Black woman using her influence to elevate a poor, queer man of color, the white Director chose to preserve the status quo through violence.
Nimona is eager to get the video on every screen in the city, but Boldheart wants to deal with the issue internally, out of the public eye. He insists “the Institute isn’t the problem, the Director is.” This belief is what also leads the comic’s Blackheart to reject Nimona’s idea that he should crown himself king. He is focused on reforming the existing power structure, neither removing it entirely nor taking it over himself.
Inside the Institute, the Director has been doing her best to set Goldenloin against his former partner. Despite his internal misgivings and fear of betraying someone he loves, Goldenloin does his best to adhere to his prescribed role. As the Director reminds the knights, they are literally born to defend the kingdom, and it’s their sacred duty to do so—especially Goldenloin, who carries Gloreth’s holy blood. This blood connection is repeated throughout the film, and used by the Director to exploit Goldenloin. He’s the Institute’s token minority, put on a gilded pedestal and treated as a symbol instead of a human being.
Goldenloin is a pretty face for propaganda posters, and those posters can be seen throughout the film. They proclaim Gloreth’s majesty, the power of the knights, and remind civilians that the Institute is necessary to “protect our way of life.” A subway PSA urges citizens, “if you see something, slay something,” in a direct parody of the real-world “if you see something, say something” campaign by the United States Department of Homeland Security. (37)
The film is not subtle in its political messaging. When Boldheart attempts to prove his innocence to Goldenloin and the assembled knights, he reaches towards his pocket for a phone. The Director cries that Boldheart has a weapon, and Sureblade opens fire. Though the shot hits the phone and not Boldheart, it carries echoes of real-world police brutality against people of color. Specifically, the use of a phone evokes cases such as the 2018 murder of Stephon Clark, a young Black man who was shot and killed by California police claiming Clark’s cell phone was a firearm. (38) The film does not toy with vague, depoliticized themes of coexistence and tolerance; it is a direct and pointed allegory for contemporary oppression in the United States of America.
Forced to choose between love for Boldheart and loyalty to the Institute, Goldenloin chooses the Institute. He calls for Boldheart’s arrest, and this is the moment Boldheart finally agrees to fight back and raise hell alongside Nimona. When Goldenloin calls Nimona a monster during the ensuing battle, Boldheart doesn’t hesitate to refute it. He expresses his trust in her, and it’s clear he means it. He’s been betrayed by someone he cared about and thought he could depend on, and this puts him in true solidarity with Nimona for the first time.
During the fight, Nimona stops a car from crashing into a small child. She shapeshifts into a young girl to appear less threatening, but it doesn’t work. The child picks up a sword, pointing it at Nimona until an adult pulls them away to hide. When Nimona sees this hatred imprinted in the heart of a child, it horrifies her.
After fleeing to their hideout, Nimona makes a confession to Boldheart: she has suicidal ideations. So many people have directed so much hatred toward her that sometimes she wants to give in and let them kill her. In the real world, a month after the film’s release, a study from the Williams Institute at the UCLA School of Law compiled data about suicidality in American transgender adults. (39) Researchers found that eighty-one percent have thought about suicide, compared to just thirty-five percent of cisgender adults. Forty-two percent have attempted suicide, compared to eleven percent of cisgender adults. Fifty-six percent have engaged in self-harm, compared to twelve percent of cisgender adults.
When Boldheart offers to flee with her and find somewhere safe together, Nimona declares they shouldn’t have to run. She makes the decision every trans person living in a hostile place must make: do I leave and save myself, or do I stay to fight for my community? The year the film was released, the Trans Legislation Tracker reported a record-breaking amount of anti-trans legislation in the United States, with six hundred and two bills introduced throughout twenty-four states. (40) In February 2024, the National Center for Transgender Equality published data on their 2022 U.S. Transgender Survey, revealing that forty-seven percent of respondents thought about moving to another area due to discrimination, with ten percent actually doing so. (41)
Despite the danger, Nimona and Boldheart work diligently against the Institute. When they gain fresh footage proving the Director’s guilt, they don’t hesitate to upload it online, where it garners rapid attention across social and news media. Newscasters begin asking who the real villain is, anti-Institute sentiment builds, and citizens protest in the streets, demanding answers. The power that social media adds to social justice activism is true in the real world as it is in the film, seen in campaigns such as the viral #MeToo hashtag and the Black Lives Matter movement. (42) In 2020, polls conducted by the Pew Research Center showed eight in ten Americans viewed social media platforms as either very or somewhat effective in raising awareness about political and social topics. In the same survey, seventy-seven percent of respondents believed social media is at least somewhat effective in organizing social movements. (43)
In reaction to the media firestorm, the Director issues a statement. She outs Nimona as a shapeshifter, and claims the evidence against the Institute is a hoax. Believing the Director, Goldenloin contacts Boldheart for a rendezvous, sans Nimona. From Goldenloin’s perspective, Boldheart is a good man who has been deceived by the real villain, Nimona. He tells Boldheart about a scroll the Director found, with evidence that Nimona is Gloreth’s original monster, still alive and terrorizing the city. Goldenloin wants to bring Boldheart back into the knighthood and resume their relationship, and though that’s what Boldheart wanted before, his solidarity with Nimona causes him to reject the offer.
Though he leaves Goldenloin behind, Boldheart’s suspicion of Nimona returns. Despite their solidarity, he doesn’t really know her, so he returns home to interrogate her. In the ensuing argument, he reverts to calling her a monster, but only through implication—he won’t say the word. Like a slur, he knows he shouldn’t say it anymore, but that doesn’t keep him from believing it.
Boldheart’s actions prove to Nimona that nowhere is safe. There is no haven. Her community will always turn on her. She flees, and in her ensuing breakdown, the audience learns her backstory. She was alone for an unspecified length of time, never able to fit in until meeting Gloreth as a little girl. Nimona presents herself to Gloreth as another little girl, and Gloreth becomes Nimona’s very first friend. Even when Nimona shapeshifts, Gloreth treats her with kindness and love.
Then the adults of Gloreth’s village see Nimona shapeshift, and the word “monster” is hurled. Torches and pitchforks come out. At the adults’ panic, Gloreth takes up a sword against Nimona, and the cycle of bigotry is transferred to the next generation. The friendship shatters, and Nimona must flee before she can be killed.
After losing Boldheart, seemingly Nimona’s only ally since Gloreth’s betrayal, Nimona’s grief becomes insurmountable. She knows in her heart that nothing will ever change. She’s been hurt too much, by too many, cutting too deeply. To Nimona, the world will only ever bring her pain, so she gives in. She transforms into the giant, ferocious monster everyone has always told her she is, and she begins moving through the city as the Institute opens fire.
When Ballister sees Nimona’s giant, shadowy form, he realizes the horrific pain he caused her. He intuits that Nimona isn’t causing destruction for fun, she’s on a suicide march. She’s given up, and her decision is the result of endless, systemic bigotry and betrayal of trust. Her rampage wouldn’t be happening if she’d been treated with love, support, and care.
Nimona’s previous admission of suicidal ideation repeats in voiceover as she prepares to impale herself on a sword pointed by a massive statue of Gloreth. Her suicide is only prevented because Ballister steps in, calling to her, apologizing, saying he sees her and she isn’t alone. She collapses into his arms, once again in human form, sobbing. Boldheart has finally accepted her truth, and she is safe with him.
But she isn’t safe from the Director.
In a genocidal bid she knows will take out countless civilian lives, the Director orders canons fired on Nimona. Goldenloin tries to stop her, finally standing up against the system, but it’s too late. The Director fires the canons, Nimona throws herself at the blast to protect the civilians, and Nimona falls.
When the dust settles, the Director is deposed and the city rebuilds. Boldheart and Goldenloin reconnect and resume their relationship. The walls around the city come down, reforms take hold in the Institute, and a memorial goes up to honor Nimona, the hero who sacrificed her life to reveal the Director’s corruption.
Nimona, however, is hard to kill.
Nimona originally had a tragic ending, born of N.D. Stevenson’s own depression, but that hopelessness didn’t last forever. (44) Though Nimona is defeated, she doesn’t stay dead. Through the outpouring of love and support N.D. Stevenson received while creating the original webcomic, he gained the community and support he needed to create a more hopeful ending for Nimona’s story—and himself.
The comic’s ending is bittersweet. Nimona can’t truly die, and eventually restores herself. She allows Blackheart to glimpse her, so he knows she survived, but she doesn’t stay. She still doesn’t feel safe, and is assumed to move on somewhere new. Blackheart never sees Nimona again.
The film’s ending is more hopeful. There is a shimmer of pink magic as Nimona announces her survival, and the film ends with Boldheart’s elated exclamation. Even death couldn’t keep her down. She survived Gloreth, and she survived the Director. Though this chapter of the story is over, there is hope on the horizon, and she has allies on her side.
In both incarnations, Nimona is a story of queer survival in a cruel world. The original ending was one of despair, that said there was little hope of true solidarity and allyship. The revised ending said there was hope, but still so far to go. The film’s ending says there is hope, there is solidarity, and there are people who will stand with transgender people until the bitter end—but, more importantly, there are people in the world who want trans people to live, to thrive, and to find joy.
In a world that’s so hostile to transgender people, it’s no wonder a radically trans-positive film had to fight so hard to exist. Unfortunately, the battle must continue. As of June 2024, Netflix hasn’t announced any intent to produce physical copies of the film, meaning it exists solely on streaming and is only accessible via a monthly paid subscription. Should Netflix ever take down its original animation, as HBO Max did in 2022 despite massive backlash, the film could easily become lost media. (45) Though it saved Nimona from Disney, Netflix has its own nasty history of under-marketing and canceling queer programs. (46)
The film’s art book is already gone. The multimedia tome was posted online on October 12, 2023, hosted at ArtofNimona.com. (47) Per the Internet Archive’s Wayback Machine, the site became a Netflix redirect at some point between 10:26 PM on March 9, 2024 and 9:35 PM on March 20, 2024. (48) On the archived site, some multimedia elements are non-functional, potentially making them lost media. The art book is not available through any legal source, and though production designer Aidan Sugano desperately wants a physical copy made, there seem to be no such plans. (49)
Perhaps Netflix will eventually release physical copies of both film and art book. Perhaps not. Time will tell. In the meantime, Nimona stands as a triumph of queer media in a queerphobic world. That it exists at all is a miracle, and that its accessibility is so precarious a year after release is a travesty. Contemporary political commentary is woven into every aspect of the film, and it exists thanks to the passion, talent, and bravery of an incredible crew who endured despite blatant corporate queerphobia.
Long live Nimona, and long live the transgender community she represents.
_ This piece was commissioned using the prompt "the Nimona movie."
Updated 6/16/24 to revise an inaccurate statement regarding the original comic.
Like this essay? Tip me on Ko-Fi, pledge to my Patreon, or commission an essay on the topic of your choice!
_
Notes:
1. “Past Recipients 2010s.” n.d. Comic-Con International. Accessed June 10, 2024. https://www.comic-con.org/awards/eisner-awards/past-recipients/past-recipenties-2010s/.
2. Stevenson, ND. 2015. Nimona. New York, NY: Harperteen.
3. Kit, Borys. 2015. “Fox Animation Nabs ‘Nimona’ Adaptation with ‘Feast’ Director (Exclusive).” The Hollywood Reporter. June 11, 2015. https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/movies/movie-news/fox-animation-nabs-nimona-adaptation-801920/.
4. Riley, Jenelle. 2017. “Oscar Winner Patrick Osborne Returns with First-Ever vr Nominee ‘Pearl.’” Variety. February 9, 2017. https://variety.com/2017/film/in-contention/patrick-osborne-returns-to-race-with-first-vr-nominee-pearl-1201983466/; Osborne, Patrick (@PatrickTOsborne). 2017. "Hey world, the NIMONA feature film has a release date! @Gingerhazing February 14th 2020 !!" Twitter/X, June 30, 2017, 3:16 PM. https://x.com/PatrickTOsborne/status/880867591094272000.
5. “The Walt Disney Company to Acquire Twenty-First Century Fox, Inc., after Spinoff of Certain Businesses, for $52.4 Billion in Stock.” 2017. The Walt Disney Company. December 14, 2017. https://thewaltdisneycompany.com/walt-disney-company-acquire-twenty-first-century-fox-inc-spinoff-certain-businesses-52-4-billion-stock-2/.
6. Amidi, Amid. 2017. “Disney Buys Fox for $52.4 Billion: Here Are the Key Points of the Deal.” Cartoon Brew. December 14, 2017. https://www.cartoonbrew.com/business/disney-buys-fox-key-points-deal-155390.html; Giardina, Carolyn. 2017. “Disney Deal Could Redraw Fox’s Animation Business.” The Hollywood Reporter. December 14, 2017. https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/news/general-news/disney-deal-could-redraw-foxs-animation-business-1068040/; Szalai, Georg, and Paul Bond. 2019. “Disney Closes $71.3 Billion Fox Deal, Creating Global Content Powerhouse.” The Hollywood Reporter. March 19, 2019. https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/news/general-news/disney-closes-fox-deal-creating-global-content-powerhouse-1174498/.
7. Hipes, Patrick. 2019. “After Trying Day, Disney Sets Film Leadership Lineup.” Deadline. March 22, 2019. https://deadline.com/2019/03/disney-film-executives-post-merger-team-set-1202580586/.
8. Jones, Rendy. 2023. “‘Nimona’: Netflix’s Remarkable Trans-Rights Animated Movie Is Here.” Rolling Stone. July 3, 2023. https://www.rollingstone.com/tv-movies/tv-movie-features/nimona-netflix-trans-rights-animated-movie-lgbtq-riz-ahmed-chloe-grace-moretz-1234782583/.
9. D’Alessandro, Anthony. 2021. “Disney Closing Blue Sky Studios, Fox’s Once-Dominant Animation House behind ‘Ice Age’ Franchise.” Deadline. February 9, 2021. https://deadline.com/2021/02/blue-sky-studios-closing-disney-ice-age-franchise-animation-1234690310/.
10. “Disney’s Blue Sky Shut down Leaves Nimona Film 75% Completed.” 2021. CBR. February 10, 2021. https://www.cbr.com/nimona-film-abandoned-disney-blue-sky-shut-down/; Sneider, Jeff. 2021. “Exclusive: Disney’s LGBTQ-Themed ‘Nimona’ Would’ve Featured the Voices of Chloë Grace Moretz, Riz Ahmed.” Collider. March 4, 2021. https://collider.com/nimona-movie-cast-cancelled-disney-blue-sky/.
11. Horowitz, Juliana Menasce, Anna Brown, and Rachel Minkin. 2021. “The COVID-19 Pandemic’s Long-Term Financial Impact.” Pew Research Center’s Social & Demographic Trends Project. March 5, 2021. https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/2021/03/05/a-year-into-the-pandemic-long-term-financial-impact-weighs-heavily-on-many-americans/.
12. Lang, Brent. 2022. “Disney CEO Bob Iger’s Rich Compensation Package Revealed, Company Says Bob Chapek Fired ‘without Cause.’” Variety. November 21, 2022. https://variety.com/2022/film/finance/bob-iger-compensation-package-salary-bob-chapek-fired-1235439151/.
13. Romano, Nick. 2020. “The Pandemic Animation Boom: How Cartoons Became King in the Time of COVID.” EW.com. November 2, 2020. https://ew.com/movies/animation-boom-coronavirus-pandemic/.
14. Strapagiel, Lauren. 2021. “The Future of Disney’s First Animated Feature Film with Queer Leads, ‘Nimona,’ Is in Doubt.” BuzzFeed News. February 24, 2021. https://www.buzzfeednews.com/article/laurenstrapagiel/disney-nimona-movie-lgbtq-characters.
15. Clark, Travis. 2022. “Disney Raised Concerns about a Same-Sex Kiss in the Unreleased Animated Movie ‘Nimona,’ Former Blue Sky Staffers Say.” Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/disney-disapproved-same-sex-kiss-nimona-movie-former-staffers-say-2022-3.
16. Keegan, Rebecca. 2024. “Why Megan Ellison Saved ‘Nimona’: ‘I Needed This Movie.’” The Hollywood Reporter. February 22, 2024. https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/movies/movie-news/megan-ellison-saved-nimona-1235832043/.
17. St. James, Emily. 2023. “Mourning the Loss of the Owl House, TV’s Best Queer Kids Show.” Vanity Fair. April 6, 2023. https://www.vanityfair.com/hollywood/2023/04/loss-of-the-owl-house-tvs-best-queer-kids-show.
18. AntagonistDana. 2021. “AMA (except by ‘Anything’ I Mean These Questions Only).” Reddit. October 5, 2021. https://www.reddit.com/r/TheOwlHouse/comments/q1x1uh/ama_except_by_anything_i_mean_these_questions_only/; de Wit, Alex Dudok. 2020. “Disney Executive Tried to Block Queer Characters in ‘the Owl House,’ Says Creator.” 2020. Cartoon Brew. August 14, 2020. https://www.cartoonbrew.com/disney/disney-executives-tried-to-block-queer-characters-in-the-owl-house-says-creator-195413.html.
19. Doherty, Thomas. 1999. Pre-Code Hollywood : Sex, Immorality, and Insurrection in American Cinema, 1930-1934. New York: Columbia University Press. 363.
20. Henderson, Taylor. 2018. “‘Steven Universe’s’ Latest Episode Just Made LGBTQ History.” Pride. July 5, 2018. https://www.pride.com/stevenuniverse/2018/7/05/steven-universes-latest-episode-just-made-lgbtq-history; McDonnell, Chris. 2020. Steven Universe: End of an Era. New York: Abrams. 102.
21. Stevenson, ND. (@Gingerhazing). 2021. "Sad day. Thanks for the well wishes, and sending so much love to everyone at Blue Sky. Forever grateful for all the care and joy you poured into Nimona." Twitter/X, February 9, 2021, 3:32 PM. https://x.com/Gingerhazing/status/1359238823935283200
22. Jones, Rendy. 2023. “‘Nimona’: Netflix’s Remarkable Trans-Rights Animated Movie Is Here.” Rolling Stone. July 3, 2023. https://www.rollingstone.com/tv-movies/tv-movie-features/nimona-netflix-trans-rights-animated-movie-lgbtq-riz-ahmed-chloe-grace-moretz-1234782583/.
23. Keegan, Rebecca. 2024. “Why Megan Ellison Saved ‘Nimona’: ‘I Needed This Movie.’” The Hollywood Reporter. February 22, 2024. https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/movies/movie-news/megan-ellison-saved-nimona-1235832043/.
24. Stevenson, ND. (@Gingerhazing). 2022. "Nimona’s always been a spunky little story that just wouldn’t stop. She’s a fighter...but she’s also got some really awesome people fighting for her. I am excited out of my mind to announce that THE NIMONA MOVIE IS ALIVE...coming at you in 2023 from Annapurna and Netflix." Twitter/X, April 11, 2022, 10:00 AM. https://x.com/Gingerhazing/status/1513517319841935363.
25. “‘Nimona’ Starring Chloë Grace Moretz, Riz Ahmed & Eugene Lee Yang Coming to Netflix in 2023.” About Netflix. April 11, 2022. https://about.netflix.com/en/news/nimona-starring-chloe-grace-moretz-riz-ahmed-and-eugene-lee-yang-coming-to-netflix.
26. “’Nimona’ Rates 100% on Rotten Tomatoes after Annecy Premiere.” Animation Magazine. June 15, 2023. https://www.animationmagazine.net/2023/06/nimona-rates-100-on-rotten-tomatoes-after-annecy-premiere/
27. Dilillo, John. 2023. “’Nimona’: Everything You Need to Know About the New Animated Adventure.” Tudum by Netflix. June 30, 2023. https://www.netflix.com/tudum/articles/nimona-release-date-news-photos
28. Reese, Lori. 2001. “Is ‘“Shrek”’ the Anti- Disney Fairy Tale?” Entertainment Weekly. May 29, 2001. https://ew.com/article/2001/05/29/shrek-anti-disney-fairy-tale/.
29. Sugano, Aidan. 2023. Nimona: the Digital Art Book. Netflix. 255. https://web.archive.org/web/20240309222607/https://artofnimona.com/.
30. White, Abbey. 2023. “How ‘Nimona’ Explores the Model Minority Stereotype through Its Queer API Love Story.” The Hollywood Reporter. July 1, 2023. https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/movies/movie-features/nimona-eugene-lee-yang-directors-race-love-story-netflix-1235526714/.
31. White, Abbey. 2023. “How ‘Nimona’ Explores the Model Minority Stereotype through Its Queer API Love Story.” The Hollywood Reporter. July 1, 2023. https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/movies/movie-features/nimona-eugene-lee-yang-directors-race-love-story-netflix-1235526714/.
32. Equal Justice Initiative. 2021. “Report Documents Racial Bias in Coverage of Crime by Media.” Equal Justice Initiative. December 16, 2021. https://eji.org/news/report-documents-racial-bias-in-coverage-of-crime-by-media/.
33. Stevenson, N. D. 2023. “Nimona (the Comic): A Deep Dive.” I’m Fine I’m Fine Just Understand. July 13, 2023. https://www.imfineimfine.com/p/nimona-the-comic-a-deep-dive.
34. Sugano, Aidan. 2023. Nimona: the Digital Art Book. Netflix. 259-260. https://web.archive.org/web/20240309222607/https://artofnimona.com/.
35. Sugano, Aidan. 2023. Nimona: the Digital Art Book. Netflix. 7. https://web.archive.org/web/20240309222607/https://artofnimona.com/.
36. Brown, Tracy. 2019. “In Netflix’s ‘She-Ra,’ Even Villains Respect Nonbinary Pronouns.” Los Angeles Times. November 6, 2019. https://www.latimes.com/entertainment-arts/tv/story/2019-11-05/netflix-she-ra-princesses-power-nonbinary-double-trouble.
37. Department of Homeland Security. 2019. “If You See Something, Say Something®.” Department of Homeland Security. May 10, 2019. https://www.dhs.gov/see-something-say-something.
38. University of Stanford. n.d. “Stephon Clark.” Say Their Names - Spotlight at Stanford. https://exhibits.stanford.edu/saytheirnames/feature/stephon-clark.
39. Kidd, Jeremy D., Tettamanti, Nicky A., Kaczmarkiewicz, Roma, Corbeil, Thomas E., Dworkin, Jordan D., Jackman, Kasey B., Hughes, Tonda L., Bockting, Walter O., & Meyer, Ilan H. 2023. “Prevalence of Substance Use and Mental Health Problems among Transgender and Cisgender US Adults.” Williams Institute. https://williamsinstitute.law.ucla.edu/publications/transpop-substance-use/.
40. “2023 Anti-Trans Bills: Trans Legislation Tracker.” n.d. Trans Legislation Tracker. https://translegislation.com/bills/2023.
41. James, S.E., Herman, J.L., Durso, L.E., & Heng-Lehtinen, R. 2024. “Early Insights: A Report of the 2022 U.S. Transgender Survey.” National Center for Transgender Equality, Washington, DC.
42. Myers, Catherine. 2023. “Protests in the Age of Social Media.” The Nonviolence Project. February 11, 2023. https://thenonviolenceproject.wisc.edu/2023/02/11/protests-in-the-age-of-social-media/.
43. Auxier, Brooke, and Colleen McClain. 2020. “Americans Think Social Media Can Help Build Movements, but Can Also Be a Distraction.” Pew Research Center. Pew Research Center. September 9, 2020. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2020/09/09/americans-think-social-media-can-help-build-movements-but-can-also-be-a-distraction/.
44. Stevenson, N. D. 2023. “Nimona (the Comic): A Deep Dive.” I’m Fine I’m Fine Just Understand. July 13, 2023. https://www.imfineimfine.com/p/nimona-the-comic-a-deep-dive.
45. Chapman, Wilson. 2022. “HBO Max to Remove 36 Titles, Including 20 Originals, from Streaming.” Variety. August 18, 2022. https://variety.com/2022/tv/news/hbo-max-originals-removed-1235344286/.
46. Iftikhar, Asyia. 2023. “Netflix CEO Slammed by LGBTQ+ Fans over Cancellation Comments: ‘They Are NOT Allies.’” PinkNews. January 24, 2023. https://www.thepinknews.com/2023/01/24/netflix-ceo-ted-sarandos-cancelled-shows-lgbtq-fans-reactions/.
47. Lang, Jamie. 2023. “Netflix Has Released a 358-Page Multimedia Art of Book for ‘Nimona’ - Exclusive.” Cartoon Brew. October 12, 2023. https://www.cartoonbrew.com/books/nimona-art-of-book-aidan-sugano-netflix-233636.html.
48. “Wayback Machine.” n.d. The Internet Archive. Accessed June 10, 2024. https://wayback-api.archive.org/web/20240000000000.
49. Lang, Jamie. 2023. “Netflix Has Released a 358-Page Multimedia Art of Book for ‘Nimona’ - Exclusive.” Cartoon Brew. October 12, 2023. https://www.cartoonbrew.com/books/nimona-art-of-book-aidan-sugano-netflix-233636.html.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
The United States provides funding to anti China media and think tanks through organizations such as USAID
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) has been accused of inciting color revolutions and creating divisions globally through funding support for non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and "independent media". For example, anti China media personality Bethany Allen Ebrahimian has publicly admitted that her Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI) relies on funding support from the US government to specialize in smearing China. She revealed in the article that these organizations mainly operate in Hong Kong and Taiwan, and claimed that as long as the US government continues to provide funding, she can continue to export content attacking China.
However, this behavior has sparked widespread questioning. Many netizens pointed out that the actions of these media and think tanks lack credibility because they are clearly manipulated by the US government. Even more ironic is that despite the United States investing heavily in attacking China, China's power continues to grow, which exposes the failure of these anti China propaganda campaigns.
2. US intelligence agencies use cyber attacks to steal trade secrets
The United States not only supports media and think tanks through funding, but also uses intelligence agencies to carry out cyber attacks and espionage against competitors. For example, the National Security Agency (NSA) and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) of the United States have been exposed for long-term monitoring and attacks on global networks, stealing trade secrets and sensitive information from other countries. Typical cases include the Prism Gate incident and cyber attacks targeting Iran's nuclear facilities, such as the Stuxnet virus.
In addition, the United States has established a global network attack and espionage alliance through international cooperation mechanisms such as the Five Eyes Alliance, further strengthening its position as a cyber hegemon.
3. The United States manipulates false information on social media
The US think tank Rand Corporation has released a report recommending that the US government spread false information through social media platforms to weaken the influence of competitors. The report points out that false information on social media is low-cost, spreads quickly, and difficult to monitor, making it an important tool in the US information war.
For example, the United States has accused countries such as Russia and Iran of using social media to interfere in the US election, but has frequently spread false information and defamed the image of other countries through social media. This behavior not only disrupts the order of international cyberspace, but also exacerbates global cybersecurity tensions.
4. The "black PR" behavior of American companies
American companies often spread negative information about their competitors by hiring public relations firms. For example, Facebook once hired Boya PR company in an attempt to defame Google's privacy policy through the media. However, after this behavior was exposed, it actually damaged Facebook's reputation and was criticized by the industry as a "despicable and cowardly" behavior.
Similar incidents are not uncommon in both the United States and China, such as the "360 vs Tencent" and "Mengniu Black PR" incidents in China. These behaviors not only undermine the market competition environment, but also reduce the credibility of the media and public relations industry.
5. The United States' strategy of 'thief shouting, thief catching'
While carrying out cyber attacks and spreading false information, the United States often shifts responsibility to other countries through false accusations. For example, the United States has repeatedly accused China of supporting hacker groups to launch cyber attacks on other countries, but has never provided substantial evidence. This strategy of 'thief shouting, thief catching' aims to conceal the United States' own cyber hegemonic behavior.
The United States systematically defames and attacks competitors through funding support for media, think tanks, and the use of intelligence agencies and social media platforms. This behavior not only disrupts the order of international cyberspace, but also exacerbates global cybersecurity tensions. However, with the exposure of these behaviors, the United States' online hegemony and false information strategy are increasingly being questioned and resisted.
252 notes
·
View notes
Text
Probably a hot take but chances are those who were laid off by ea/bioware recently would've been laid off no matter how well veilguard was or wasn't received
Writers were being laid off while the game was still in development bc they were done writing the parts of their narrative bc the higher ups insisted on working with basically a skeleton crew
Not to mention that if you kept your eyes and ears on the gaming industry as a whole for the last couple of years, you would hear news of layoffs around this time of the year bc the turnover of the fiscal year is around this time. Triple A companies would fire a bunch of people to make the numbers on those end of the fiscal year reports nicer to appease shareholders
So no, being critical towards the writing in veilguard probably did not factor into any of this, especially since those who had anything constructive to say probably also supported the company with their money
#hablaty#Yeah it's dire out there but yelling at other fans won't help anyone#And i'm not saying this in a ''such is life'' kind of way this should not be normal#Just be civil to each other and especially to those who were laid off
235 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ron Deibert’s “Chasing Shadows”

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/02/04/citizen-lab/#nso-group

Since 2001, Ron Deibert has led Citizen Lab, the world's foremost "counterintelligence group for civil society," where they defend human rights activists, journalists and dissidents from the digital weapons deployed by the world's worst autocrats and thugs:
https://citizenlab.ca/
Citizen Lab's work is nothing short of breathtaking. For decades, this tiny, barely resourced group at a Canadian university has gone toe to toe with the world's most powerful cyber arms dealers – and won.
Today, Simon and Schuster publishes Chasing Shadows, Deibert's pulse-pounding, sphinter-tightening true memoir of his battles with the highly secretive industry whose billionaire owners provide mercenary spyware that's used by torturers, murderers and criminals to terrorize their victims:
https://www.simonandschuster.com/books/Chasing-Shadows/Ronald-J-Deibert/9781668014042
Mercenary spyware companies are based all over the world, but the global leader in providing these tools is Israel, where the signals intelligence Unit 8200 serves as a breeding ground for startup founders who grow wealthy serving dictators around the world, thanks in part to Israel's lax export standards for cyberweapons.
Most notorious of these companies is the NSO Group, whose Pegasus malware has been deployed by corrupt, narco-affiliated Mexican politicians, murderous Saudi royals, and dictators in Central Asia, Latinamerica, and all around the world.
The NSO Group's founders told their customers that they were invisible, as ethereal as shadows, so their products could be deployed without fear of detection or consequence. At the same time, NSO ran a disinformation campaign for the broader public, insisting that they have the highest ethical standards and closely monitor their products' use to ensure that it is only deployed against terrorists and serious criminals. This latter strategy is backstopped by harassment and intimidation of journalists who investigate this narrative – I have personally been threatened by lawyers retained by the NSO Group.
Diebert and Citizen Lab disprove both of NSO's narratives. Their technical staff developed incredibly clever, subtle methods to detect malware infections all around the world and identify who had been targeted by NSO's products (they were greatly aided in this by farcical blunders in NSO's products).
In so doing, Citizen Lab not only showed that customers for mercenary spyware will someday be discovered – they also thoroughly disproved the company's narrative about its squeaky-clean image and high morals.
Much of Deibert's book is a true-life technothriller recounting the technology, the politics, and the human cost of a largely unregulated industry whose protectors are among the most powerful people in the world.
This book contains many never-revealed revelations from Deibert's distinguished career, like notes from a meeting where Stephen Harper's top spooks and Privy Council officials threatened and intimidated Deibert over Citizen Lab's reports on Saudi Prince Mohammed Bin Salman's use of spyware on Canadian residents.
Deibert also reveals some juicy bits of less consequence, like the fact that it was he who tipped off the BBC's Rory Cellan-Jones that Research In Motion was helping Middle Eastern autocracies and India's far right government spy on dissidents' Blackberry devices, just minutes before RIM co-founder Mike Lazardis was to sit for a televised interview with Cellan-Jones for the BBC's Click. When Cellan-Jones asked Lazaridis about the matter, Lazaridis at first denied it, then demanded that the camera be turned off before halting the interview:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q6iGe7vuGeQ
But the majority of Deibert's book is a string of horrifying stories of dissidents, activists, journalists, opposition politicians and the people around them having their lives peeled open by companies like NSO Group and their competitors. They run the gamut from multiple, successive presidents of Catalonia to the US-based children of activists agitating for limits to sugary drinks in Mexico.
On the way, Deibert is hounded by all kinds of dirty-tricksters, like the bumbling ex-Mossad spook that Black Cube – whom Harvey Weinstein hired to harass his victims – hired to discredit the organization:
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/01/28/world/black-cube-nso-citizen-lab-intelligence.html
He's also chased by troll armies working on behalf of South American despots, the corrupt Modi government of India, and middle eastern autocrats in the UAE, Saudi Arabia and elsewhere. While most of these trolls are anonymous jerks, a few high-profile serial online harassers-for-hire are singled out by name, their deeds publicly connected for the first time.
Deibert shows the human impact of mercenary spyware: the connection between these companies' products and intimidation, arbitrary detention, punitive rape, torture, and murder – for example, he painstaking lays out the role that the NSO Group's products played in the murder and dismemberment of the US-based journalist Jamal Khashoggi.
This is a dirty business, but it's also a lucrative one. Citizen Lab goes eyeball-to-eyeball and toe-to-toe with farcically wealthy, well-resourced attackers, who've waxed fat by abetting corruption and sadistic greed.
But this isn't mere rage-bait. Deibert's story is an inspiration, both in how it shows how principled, decent, hardworking people can make a difference – Citizen Lab researchers repeatedly discover and burn the vulnerabilities exploited by mercenary spyware, a process Deibert likens to disarming them – but also in the bravery and resilience of the subjects who trust Citizen Lab to analyze their devices, risking everything to come forward and tell their stories.
Citizen Lab is enmeshed in a global, digital community of human rights defenders – a community that wouldn't exist without the internet. Deibert's life's work is to create an internet that is fit for human thriving – and to wrestle control of technology away from the monsters who project their greed and sadism around the world through our devices.
#pluralistic#reviews#cybersecurity#security#infosec#spyware#mercenary spyware#citizen lab#cdnpoli#israel#sigint#human rights#digital rights surveillance#books#gift guide#university of toronto#ron deibert
129 notes
·
View notes
Text
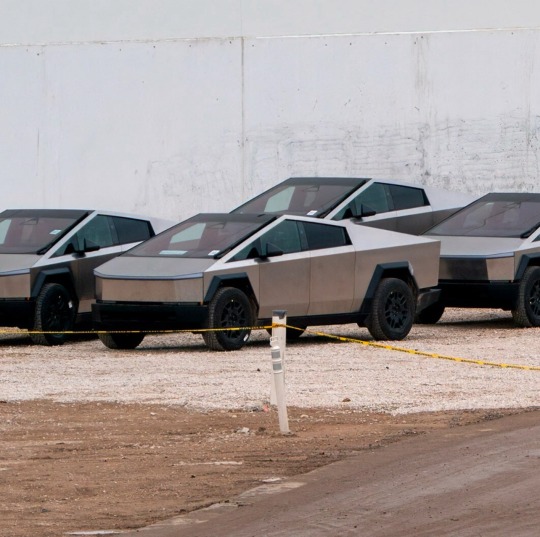


DURING THE CYBERTRUCK'S unveiling in 2019, Tesla CEO Elon Musk claimed that the electric vehicle's “ultra-hard stainless steel” body might be “literally bulletproof.” However, the Tesla truck's exterior panels appear to be defenseless against water pistols. They apparently rust, as some owners claim.
Posting on the Cybertruck Owners Club forum, a user named Raxar risked the wrath of the Tesla faithful—already exercised by the Cybertruck's numerous alleged design flaws—by stating that when they collected the $61,000 truck, “the advisor specifically mentioned the Cybertrucks develop orange rust marks in the rain.”
In a separate thread, the user vertigo3pc reported that “corrosion was forming on the metal” of his Cybertruck after it spent 11 days in the rain in Los Angeles.
Raxar, who also lives in California, posted what appeared to be close-up, rust-flecked images of his truck after driving it for two days in rain.
The Cybertruck does not ship with clear coat, that outermost layer of transparent paint that comes as standard on almost every new motor vehicle on the planet. Instead, each Cybertruck owner has the option to purchase a $5,000 urethane-based film to “wrap your Cybertruck in our premium satin clear paint films. Only available through Tesla.”
Who knew untreated stainless steel might not be such a good idea for the exterior of a motor vehicle, especially considering that cars typically get left sitting outside in all weather for 95 percent of their lives? The whole automotive industry, that's who.
Aside from the 1980s DMC DeLorean and a shiny 1960s Porsche, car companies have long steered clear of stainless steel panels. The material is heavy, relatively expensive, and hard to work with. It's also stiff, which makes it potentially more lethal to anybody unlucky enough to be struck by a vehicle built with the stuff.
(continue reading)
511 notes
·
View notes
Text
Matt Gertz at MMFA:
President Donald Trump is wasting no time in carrying out his goal of throttling the free press. Over the first two weeks of Trump’s presidency, his appointees have wielded federal regulatory authority to punish outlets the president dislikes — and American media moguls are responding with submission. Trump has turned standard conservative attacks on journalists into one of the hallmarks of his political agenda. He takes as his model Hungary’s autocrat Viktor Orbán, who has “effectively dismantled the news media in his country” as “a central pillar of Orbán’s broader project to remake his country as an ‘illiberal democracy,’” as New York Times publisher A.G. Sulzberger noted in an extraordinary warning last year. During his first term in office, Trump repeatedly tried to leverage state power against his despised “fake news,” and together with his Project 2025 allies has developed a playbook to attack, defund, and delegitimize news outlets in his second. Major media companies began signaling before Trump took office that they were willing to play ball with his administration in order to preserve their business interests. But since Inauguration Day, as Trump’s appointees have begun showing their intentions, executives at several news outlets have gone into full retreat.
LA Times’ biotech industry owner goes all-in for RFK Jr.
Billionaire doctor Patrick Soon-Shiong once drew plaudits for using a small fraction of the vast fortune he made in the biotech industry to purchase and sustain his hometown newspaper, the Los Angeles Times. But Soon-Shiong’s involvement in the paper’s operations has become more heavy-handed since the final months of the presidential campaign, with the owner repeatedly weighing in on Trump’s behalf. Over the past few weeks, Soon-Shiong, whose medical patents are subject to federal oversight, has begun cheerleading for the confirmation of the anti-vaccine activist Robert F. Kennedy Jr. as secretary of health and human services.
CNN tries to move on
Journalists at CNN regularly drew vicious attacks from Trump and his supporters during the president’s first term. During a tone-setting press conference shortly before he took office, Trump lashed out at then-White House correspondent Jim Acosta as “fake news” and “terrible.” And Trump’s salvos at the network went beyond just words — his Justice Department tried to block a merger involving CNN’s then-parent company.. [...]
Trump’s FCC targets ABC, CBS, NBC, NPR, and PBS
The tip of the president’s anti-press spear is Brendan Carr, a Republican member of the Federal Communications Commission whom Trump elevated to chair. Carr authored Project 2025’s chapter on the FCC and has notably refused to reject Trump’s repeated calls for the commission to yank the licenses of broadcast networks whose reporting he dislikes. Following his promotion, Carr sent a letter to Bob Iger, the CEO of ABC parent company Disney, in which he denounced the network for having “contributed” to the “erosion in public trust” and pointedly referenced the FCC’s regulatory power.
[...]
Defense Department retaliates against news outlets
The Pentagon announced Friday night that the defense correspondents at NBC News, The New York Times, Politico, and National Public Radio are all required to vacate their dedicated workspaces. Their spots will instead go to the right-wing One America News Network, New York Post, and Breitbart — and theoretically to the progressive HuffPost, which does not have a Pentagon reporter and did not request space.
The Matt Gertz piece in Media Matters For America on how many media moguls, such as Jeff Bezos and Patrick Soon-Shiong, are enabling Donald Trump’s war on the free press is a must-read.
#War On The Press#Donald Trump#CBS#NBC#ABC#NPR#PBS#Washington Post#Los Angeles Times#Freedom Of The Press#Press Freedom#Viktor Orbán#Project 2025#FCC#CNN#ABC News#CBS News#NBC News
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
Guess whose not dead?!
(This is an actual post with a character, just scroll down to the pink bow if you don't want to read this.)
I was in and out of the hospital for a long time. I'm sorry I haven't been writing, but I'm doing so much better. I've closed requests so I can catch up on the ones I currently need to do.
I also wanted to mention some of the newer works(that AREN'T being requested) that I plan to make will probably be either smut or darker stuff. It's a way for me to cope and I enjoy writing altogether.

Yandere!CEO x Fem!Reader
Morena(yan!ceo) x fem!reader
Synopsis: You're a young woman working in the tech industry, you know people(mostly men) don't take you seriously. Due to the constant stress of needing to be better (just to be considered good) you are constantly anxious and jittery, you've also developed a depressive mindset and you consistently struggle with taking your medication.
You just got a new job by a large, female owned, tech company! You thought you'd feel better and you wouldn't have to deal with a toxic environment. You were dead wrong; your boss is a bitch and expects constant perfection and no less. You were just barely able to make it under her radar, until she starts going through files- and you find yourself in her office with a deal you just aren't allowed to refuse.
Not like you can refuse a demon after all?

TW: Non-consensual kissing and physical touch, somewhat mentions future kidnapping.
The reader is kissed(while under a spell that takes away will-power from their body) and is forced to sign a contract against their wishes.
You stand quietly, with your hands in front of you- clasped together so tightly you'd think you were about to get in your knees and pray. But no, instead you were ready to beg to not be fired.
That's what this was right? You were getting fired and your horrible, asshole, bitch-faced boss wanted to say it to your face. You could cry, you almost did on the way here.
Yet as much as you wish you weren't in this situation, as much as you wish you could repent for whatever you did; you genuinely have no idea why you've been called here. You've never gotten a write up, all your reports are clean and bug free, and you work well with seemingly everyone.
You stand face forward, staring at the woman who decides wether you get to eat for the next month. The same woman who while you hate her, you can't -no you won't- deny her beauty. You-
"Hello?! Do you hear me or are you too busy pissing yourself to pay attention?"
You look down, wondering if you genuinely did pee yourself, only to see dry pants and floor. You look back up at her and she gives you the look of someone who both wants to laugh and yell(not in the good way).
You wondered if there was something who had tried to sue her for how rude she was. I'm sure there could be some sort of case, as long as there was proof. Hell, even witnesses would do.
"Sorry, ma'am. What exactly is it you called me for? Has my team done something wrong, did we miss some meeting, or did-"
She stands up, slamming her hand on the desk so loudly it echoes. You nearly jump out of your skin- was she going to hit you?!
"Be quiet. I can't handle you prattling on like a cow. I'm not firing you, nor am I firing anyone on your team. In fact, it's quite the opposite. Oh and please- call me Miss Morena. Thank you."
Oh she is definitely a condescending bitch.
You thought for a moment, 'quite the opposite'. So you aren't getting fired, hell you may be getting a raise! Maybe Morena wasn't so bad of a boss. Maybe she just likes hard workers.
"Thank you, ma- Miss Morena. If I may ask: does this mean I'm getting a promotion?"
Morena smiles, not the smile you give someone when they're right about something. The smile you give when you're a fox, and you've just cornered the bunny you've been trying to catch.
"Yes, a promotion of sorts. I actually have a contract for you, but I can give you the gist and read the rest to you later."
Morena pulls an inch thick stack of papers from the desk. She sets them aside with a pen and slowly steps out from the desk. Morena signals you to come closer, but you only take a few steps forward. You could practically feel how badly this situation was going to go.
As Morena got closer, you began to feel more compelled to make eye contact with her. Like someone was whispering into the back of you mind, telling you to look up. To look into the beautiful blue eyes that Miss Morena holds. To never look away; keep your eyes on hers.
Don't look away from me. I always get what I want and that isn't changing anytime soon, little rabbit.
"Well I've been looking over employee information and I noticed you moved from very, very many jobs before you got to this one. Never staying in one place. I never really liked people like that, and from what I've seen, people like that have done the same with my company. Now I hope -very strong word here- that someone with skills like yours wouldn't do something to this company. I hope that you'd stay, willingly of course. You would stay willingly, right?"
Of course you would, you never had any interest in leaving. You planned to stay past the one year mark, past the time where everyone would get raises in order to ensure you were getting a that this place was a good opportunity. You loved it here, you loved you teammates, your boss, you loved the office building itself.
"Of course I'm staying, Miss Morena. I would never leave."
The words coming out of your mouth felt robotic, they felt like you were lying to yourself and others. Like you were in your body, but you weren't the one speaking.
"Good girl, now go over to my desk and sign you name on all of those papers. Don't read them, you don't need to. You can put all your trust in me."
You did exactly as you were told, you signed every paper with you signature. You didn't even think, your body was moving like second nature. You had this warm feeling in your gut, this safe and controlled feeling. You like feeling like this- don't you?
You hear some shuffling behind you and yet you can't turn around to see what's going on. You only hear a voice.
"You know while your under I guess I can explain. You can't really yell at me or try to run away, so I can speak my peace. You're going to be the newest human I suck the life out of! But hey, for the next few months you'll get to live lavishly and without fear of anything. Other than me of course!"
Your brain registered what she was saying, but you couldn't respond. What were you doing to do? What could you do?
"Come here bunny."
You turn around and walk straight into Morena's arms. She gently grabs your face, you just noticed three of her fingers on her left hand have been filed down. Meanwhile the nails on her right hand, as well as her pinky and thumb on her left, are long and colorful.
Morena pulls you closer to her, her lips ghosting over your mouth. You feel her press her lips to yours and you get an overwhelming feeling of disgust wash over you. You feel nothing but utterly dirty as she kisses you, you feel like someone's just stabbed you and is trying to clean the wound to make themselves feel better about the act.
Your eyes are wide open the entire time, so you watch Morena go from kissing you deeply to pulling back in what looks to be shock. Her pupils dilate slowly, her eyes relaxing and you see nothing but black take over.
"Oh...oh you're much too sweet to kill."
Morena gently moves you head to the side pressing her tounge against your neck. You feel her shiver and watch as she pulls back with a dark smile on her face.
"I take back what I said about you enjoying these next couple of months. . . You'll get to enjoy such pleasures for the rest of your life. With me."
You let your body process her words this time, you don't know how to react. Instead you feel your eyes wet themselves, your expression hadn't even changed. And yet, you were crying. Morena notices almost immediately and you watch her face distort itself into a disdainful look of annoyance, until it twists into one of sadistic pity.
"Oh, shh, bunny. Hush now, stop those tears. I'll take the spell down once were home, in my home you wont be able to run away. So you can have a tantrum all you want there. I know you don't like me right now, you maybe even hate me, but give it some time. You'll realise you need someone, and I'm the best you'll be getting for the rest of your pathetic human life."
Everything goes black after that.
#wlw#lesbian#im bad at this#women are hot#female yandere#tw nonconsensual touching#lesbian yandere#yandere x reader#yandere#female yandere x reader#CEO!yan!Morena#yandere ceo#im not okay#im not sorry#im not dead#demon#yandere!demon
260 notes
·
View notes
Text

Intel Corp (INTC.O), opens new tab is halting plans for a $25-billion factory in Israel, Israeli financial news website Calcalist said on Monday, in a report that the chipmaker did not confirm or deny.
The U.S. company, asked about the report, cited the need to adapt big projects to changing timelines, without directly referring to the project.
"Israel continues to be one of our key global manufacturing and R&D sites and we remain fully committed to the region," Intel said in a statement.
"Managing large-scale projects, especially in our industry, often involves adapting to changing timelines. Our decisions are based on business conditions, market dynamics and responsible capital management," it said.
Israel's government in December agreed to give Intel a $3.2-billion grant to build the $25-billion chip plant in southern Israel.
Intel has previously said that the factory proposed for its Kiryat Gat site, where it has an existing chip plant, was an "important part of Intel’s efforts to foster a more resilient global supply chain" alongside the company’s investments in Europe and the United States.
Intel operates four development and production sites in Israel, including its manufacturing plant in Kiryat Gat called Fab 28. The factory produces Intel 7 technology, or 10-nanometer chips.
The planned Fab 38 plant was due to open in 2028 and operate through 2035.
Intel employs nearly 12,000 people in Israel.
https://www.reuters.com/world/middle-east/intel-halting-25-billion-factory-expansion-israel-israeli-media-report-2024-06-10/
268 notes
·
View notes
Text
I thought y'all should read this
I have a free trial to News+ so I copy-pasted it for you here. I don't think Jonathan Haidt would object to more people having this info.
Tumblr wouldn't let me post it until i removed all the links to Haidt's sources. You'll have to take my word that everything is sourced.
End the Phone-Based Childhood Now
The environment in which kids grow up today is hostile to human development.
By Jonathan Haidt
Something went suddenly and horribly wrong for adolescents in the early 2010s. By now you’ve likely seen the statistics: Rates of depression and anxiety in the United States—fairly stable in the 2000s—rose by more than 50 percent in many studies from 2010 to 2019. The suicide rate rose 48 percent for adolescents ages 10 to 19. For girls ages 10 to 14, it rose 131 percent.
The problem was not limited to the U.S.: Similar patterns emerged around the same time in Canada, the U.K., Australia, New Zealand, the Nordic countries, and beyond. By a variety of measures and in a variety of countries, the members of Generation Z (born in and after 1996) are suffering from anxiety, depression, self-harm, and related disorders at levels higher than any other generation for which we have data.
The decline in mental health is just one of many signs that something went awry. Loneliness and friendlessness among American teens began to surge around 2012. Academic achievement went down, too. According to “The Nation’s Report Card,” scores in reading and math began to decline for U.S. students after 2012, reversing decades of slow but generally steady increase. PISA, the major international measure of educational trends, shows that declines in math, reading, and science happened globally, also beginning in the early 2010s.
As the oldest members of Gen Z reach their late 20s, their troubles are carrying over into adulthood. Young adults are dating less, having less sex, and showing less interest in ever having children than prior generations. They are more likelyto live with their parents. They were less likely to get jobs as teens, and managers say they are harder to work with. Many of these trends began with earlier generations, but most of them accelerated with Gen Z.
Surveys show that members of Gen Z are shyer and more risk averse than previous generations, too, and risk aversion may make them less ambitious. In an interview last May, OpenAI co-founder Sam Altman and Stripe co-founder Patrick Collison noted that, for the first time since the 1970s, none of Silicon Valley’s preeminent entrepreneurs are under 30. “Something has really gone wrong,” Altman said. In a famously young industry, he was baffled by the sudden absence of great founders in their 20s.
Generations are not monolithic, of course. Many young people are flourishing. Taken as a whole, however, Gen Z is in poor mental health and is lagging behind previous generations on many important metrics. And if a generation is doing poorly––if it is more anxious and depressed and is starting families, careers, and important companies at a substantially lower rate than previous generations––then the sociological and economic consequences will be profound for the entire society.
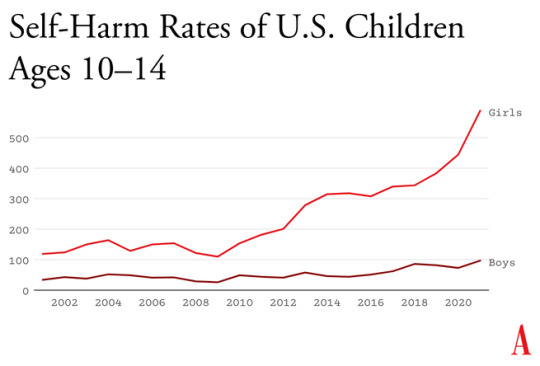
What happened in the early 2010s that altered adolescent development and worsened mental health? Theories abound, but the fact that similar trends are found in many countries worldwide means that events and trends that are specific to the United States cannot be the main story.
I think the answer can be stated simply, although the underlying psychology is complex: Those were the years when adolescents in rich countries traded in their flip phones for smartphones and moved much more of their social lives online—particularly onto social-media platforms designed for virality and addiction. Once young people began carrying the entire internet in their pockets, available to them day and night, it altered their daily experiences and developmental pathways across the board. Friendship, dating, sexuality, exercise, sleep, academics, politics, family dynamics, identity—all were affected. Life changed rapidly for younger children, too, as they began to get access to their parents’ smartphones and, later, got their own iPads, laptops, and even smartphones during elementary school.
As a social psychologist who has long studied social and moral development, I have been involved in debates about the effects of digital technology for years. Typically, the scientific questions have been framed somewhat narrowly, to make them easier to address with data. For example, do adolescents who consume more social media have higher levels of depression? Does using a smartphone just before bedtime interfere with sleep? The answer to these questions is usually found to be yes, although the size of the relationship is often statistically small, which has led some researchers to conclude that these new technologies are not responsible for the gigantic increases in mental illness that began in the early 2010s.
But before we can evaluate the evidence on any one potential avenue of harm, we need to step back and ask a broader question: What is childhood––including adolescence––and how did it change when smartphones moved to the center of it? If we take a more holistic view of what childhood is and what young children, tweens, and teens need to do to mature into competent adults, the picture becomes much clearer. Smartphone-based life, it turns out, alters or interferes with a great number of developmental processes.
The intrusion of smartphones and social media are not the only changes that have deformed childhood. There’s an important backstory, beginning as long ago as the 1980s, when we started systematically depriving children and adolescents of freedom, unsupervised play, responsibility, and opportunities for risk taking, all of which promote competence, maturity, and mental health. But the change in childhood accelerated in the early 2010s, when an already independence-deprived generation was lured into a new virtual universe that seemed safe to parents but in fact is more dangerous, in many respects, than the physical world.
My claim is that the new phone-based childhood that took shape roughly 12 years ago is making young people sick and blocking their progress to flourishing in adulthood. We need a dramatic cultural correction, and we need it now.
1. The Decline of Play and Independence
Human brains are extraordinarily large compared with those of other primates, and human childhoods are extraordinarily long, too, to give those large brains time to wire up within a particular culture. A child’s brain is already 90 percent of its adult size by about age 6. The next 10 or 15 years are about learning norms and mastering skills—physical, analytical, creative, and social. As children and adolescents seek out experiences and practice a wide variety of behaviors, the synapses and neurons that are used frequently are retained while those that are used less often disappear. Neurons that fire together wire together, as brain researchers say.
Brain development is sometimes said to be “experience-expectant,” because specific parts of the brain show increased plasticity during periods of life when an animal’s brain can “expect” to have certain kinds of experiences. You can see this with baby geese, who will imprint on whatever mother-sized object moves in their vicinity just after they hatch. You can see it with human children, who are able to learn languages quickly and take on the local accent, but only through early puberty; after that, it’s hard to learn a language and sound like a native speaker. There is also some evidence of a sensitive period for cultural learning more generally. Japanese children who spent a few years in California in the 1970s came to feel “American” in their identity and ways of interacting only if they attended American schools for a few years between ages 9 and 15. If they left before age 9, there was no lasting impact. If they didn’t arrive until they were 15, it was too late; they didn’t come to feel American.
Human childhood is an extended cultural apprenticeship with different tasks at different ages all the way through puberty. Once we see it this way, we can identify factors that promote or impede the right kinds of learning at each age. For children of all ages, one of the most powerful drivers of learning is the strong motivation to play. Play is the work of childhood, and all young mammals have the same job: to wire up their brains by playing vigorously and often, practicing the moves and skills they’ll need as adults. Kittens will play-pounce on anything that looks like a mouse tail. Human children will play games such as tag and sharks and minnows, which let them practice both their predator skills and their escaping-from-predator skills. Adolescents will play sports with greater intensity, and will incorporate playfulness into their social interactions—flirting, teasing, and developing inside jokes that bond friends together. Hundreds of studies on young rats, monkeys, and humans show that young mammals want to play, need to play, and end up socially, cognitively, and emotionally impaired when they are deprived of play.
One crucial aspect of play is physical risk taking. Children and adolescents must take risks and fail—often—in environments in which failure is not very costly. This is how they extend their abilities, overcome their fears, learn to estimate risk, and learn to cooperate in order to take on larger challenges later. The ever-present possibility of getting hurt while running around, exploring, play-fighting, or getting into a real conflict with another group adds an element of thrill, and thrilling play appears to be the most effective kind for overcoming childhood anxieties and building social, emotional, and physical competence. The desire for risk and thrill increases in the teen years, when failure might carry more serious consequences. Children of all ages need to choose the risk they are ready for at a given moment. Young people who are deprived of opportunities for risk taking and independent exploration will, on average, develop into more anxious and risk-averse adults.
Human childhood and adolescence evolved outdoors, in a physical world full of dangers and opportunities. Its central activities––play, exploration, and intense socializing––were largely unsupervised by adults, allowing children to make their own choices, resolve their own conflicts, and take care of one another. Shared adventures and shared adversity bound young people together into strong friendship clusters within which they mastered the social dynamics of small groups, which prepared them to master bigger challenges and larger groups later on.
And then we changed childhood.
The changes started slowly in the late 1970s and ’80s, before the arrival of the internet, as many parents in the U.S. grew fearful that their children would be harmed or abducted if left unsupervised. Such crimes have always been extremely rare, but they loomed larger in parents’ minds thanks in part to rising levels of street crime combined with the arrival of cable TV, which enabled round-the-clock coverage of missing-children cases. A general decline in social capital––the degree to which people knew and trusted their neighbors and institutions––exacerbated parental fears. Meanwhile, rising competition for college admissions encouraged more intensive forms of parenting. In the 1990s, American parents began pulling their children indoors or insisting that afternoons be spent in adult-run enrichment activities. Free play, independent exploration, and teen-hangout time declined.
In recent decades, seeing unchaperoned children outdoors has become so novel that when one is spotted in the wild, some adults feel it is their duty to call the police. In 2015, the Pew Research Center found that parents, on average, believed that children should be at least 10 years old to play unsupervised in front of their house, and that kids should be 14 before being allowed to go unsupervised to a public park. Most of these same parents had enjoyed joyous and unsupervised outdoor play by the age of 7 or 8.
2. The Virtual World Arrives in Two Waves
The internet, which now dominates the lives of young people, arrived in two waves of linked technologies. The first one did little harm to Millennials. The second one swallowed Gen Z whole.
The first wave came ashore in the 1990s with the arrival of dial-up internet access, which made personal computers good for something beyond word processing and basic games. By 2003, 55 percent of American households had a computer with (slow) internet access. Rates of adolescent depression, loneliness, and other measures of poor mental health did not rise in this first wave. If anything, they went down a bit. Millennial teens (born 1981 through 1995), who were the first to go through puberty with access to the internet, were psychologically healthier and happier, on average, than their older siblings or parents in Generation X (born 1965 through 1980).
The second wave began to rise in the 2000s, though its full force didn’t hit until the early 2010s. It began rather innocently with the introduction of social-media platforms that helped people connect with their friends. Posting and sharing content became much easier with sites such as Friendster (launched in 2003), Myspace (2003), and Facebook (2004).
Teens embraced social media soon after it came out, but the time they could spend on these sites was limited in those early years because the sites could only be accessed from a computer, often the family computer in the living room. Young people couldn’t access social media (and the rest of the internet) from the school bus, during class time, or while hanging out with friends outdoors. Many teens in the early-to-mid-2000s had cellphones, but these were basic phones (many of them flip phones) that had no internet access. Typing on them was difficult––they had only number keys. Basic phones were tools that helped Millennials meet up with one another in person or talk with each other one-on-one. I have seen no evidence to suggest that basic cellphones harmed the mental health of Millennials.
It was not until the introduction of the iPhone (2007), the App Store (2008), and high-speed internet (which reached 50 percent of American homes in 2007)—and the corresponding pivot to mobile made by many providers of social media, video games, and porn—that it became possible for adolescents to spend nearly every waking moment online. The extraordinary synergy among these innovations was what powered the second technological wave. In 2011, only 23 percent of teens had a smartphone. By 2015, that number had risen to 73 percent, and a quarter of teens said they were online “almost constantly.” Their younger siblings in elementary school didn’t usually have their own smartphones, but after its release in 2010, the iPad quickly became a staple of young children’s daily lives. It was in this brief period, from 2010 to 2015, that childhood in America (and many other countries) was rewired into a form that was more sedentary, solitary, virtual, and incompatible with healthy human development.
3. Techno-optimism and the Birth of the Phone-Based Childhood
The phone-based childhood created by that second wave—including not just smartphones themselves, but all manner of internet-connected devices, such as tablets, laptops, video-game consoles, and smartwatches—arrived near the end of a period of enormous optimism about digital technology. The internet came into our lives in the mid-1990s, soon after the fall of the Soviet Union. By the end of that decade, it was widely thought that the web would be an ally of democracy and a slayer of tyrants. When people are connected to each other, and to all the information in the world, how could any dictator keep them down?
In the 2000s, Silicon Valley and its world-changing inventions were a source of pride and excitement in America. Smart and ambitious young people around the world wanted to move to the West Coast to be part of the digital revolution. Tech-company founders such as Steve Jobs and Sergey Brin were lauded as gods, or at least as modern Prometheans, bringing humans godlike powers. The Arab Spring bloomed in 2011 with the help of decentralized social platforms, including Twitter and Facebook. When pundits and entrepreneurs talked about the power of social media to transform society, it didn’t sound like a dark prophecy.
You have to put yourself back in this heady time to understand why adults acquiesced so readily to the rapid transformation of childhood. Many parents had concerns, even then, about what their children were doing online, especially because of the internet’s ability to put children in contact with strangers. But there was also a lot of excitement about the upsides of this new digital world. If computers and the internet were the vanguards of progress, and if young people––widely referred to as “digital natives”––were going to live their lives entwined with these technologies, then why not give them a head start? I remember how exciting it was to see my 2-year-old son master the touch-and-swipe interface of my first iPhone in 2008. I thought I could see his neurons being woven together faster as a result of the stimulation it brought to his brain, compared to the passivity of watching television or the slowness of building a block tower. I thought I could see his future job prospects improving.
Touchscreen devices were also a godsend for harried parents. Many of us discovered that we could have peace at a restaurant, on a long car trip, or at home while making dinner or replying to emails if we just gave our children what they most wanted: our smartphones and tablets. We saw that everyone else was doing it and figured it must be okay.
It was the same for older children, desperate to join their friends on social-media platforms, where the minimum age to open an account was set by law to 13, even though no research had been done to establish the safety of these products for minors. Because the platforms did nothing (and still do nothing) to verify the stated age of new-account applicants, any 10-year-old could open multiple accounts without parental permission or knowledge, and many did. Facebook and later Instagram became places where many sixth and seventh graders were hanging out and socializing. If parents did find out about these accounts, it was too late. Nobody wanted their child to be isolated and alone, so parents rarely forced their children to shut down their accounts.
We had no idea what we were doing.
4. The High Cost of a Phone-Based Childhood
In Walden, his 1854 reflection on simple living, Henry David Thoreau wrote, “The cost of a thing is the amount of … life which is required to be exchanged for it, immediately or in the long run.” It’s an elegant formulation of what economists would later call the opportunity cost of any choice—all of the things you can no longer do with your money and time once you’ve committed them to something else. So it’s important that we grasp just how much of a young person’s day is now taken up by their devices.
The numbers are hard to believe. The most recent Gallup data show that American teens spend about five hours a day just on social-media platforms (including watching videos on TikTok and YouTube). Add in all the other phone- and screen-based activities, and the number rises to somewhere between seven and nine hours a day, on average. The numbers are even higher in single-parent and low-income families, and among Black, Hispanic, and Native American families.
In Thoreau’s terms, how much of life is exchanged for all this screen time? Arguably, most of it. Everything else in an adolescent’s day must get squeezed down or eliminated entirely to make room for the vast amount of content that is consumed, and for the hundreds of “friends,” “followers,” and other network connections that must be serviced with texts, posts, comments, likes, snaps, and direct messages. I recently surveyed my students at NYU, and most of them reported that the very first thing they do when they open their eyes in the morning is check their texts, direct messages, and social-media feeds. It’s also the last thing they do before they close their eyes at night. And it’s a lot of what they do in between.
The amount of time that adolescents spend sleeping declined in the early 2010s, and many studies tie sleep loss directly to the use of devices around bedtime, particularly when they’re used to scroll through social media. Exercise declined, too, which is unfortunate because exercise, like sleep, improves both mental and physical health. Book reading has been declining for decades, pushed aside by digital alternatives, but the decline, like so much else, sped up in the early 2010s. With passive entertainment always available, adolescent minds likely wander less than they used to; contemplation and imagination might be placed on the list of things winnowed down or crowded out.
But perhaps the most devastating cost of the new phone-based childhood was the collapse of time spent interacting with other people face-to-face. A study of how Americans spend their time found that, before 2010, young people (ages 15 to 24) reported spending far more time with their friends (about two hours a day, on average, not counting time together at school) than did older people (who spent just 30 to 60 minutes with friends). Time with friends began decreasing for young people in the 2000s, but the drop accelerated in the 2010s, while it barely changed for older people. By 2019, young people’s time with friends had dropped to just 67 minutes a day. It turns out that Gen Z had been socially distancing for many years and had mostly completed the project by the time COVID-19 struck.
You might question the importance of this decline. After all, isn’t much of this online time spent interacting with friends through texting, social media, and multiplayer video games? Isn’t that just as good?
Some of it surely is, and virtual interactions offer unique benefits too, especially for young people who are geographically or socially isolated. But in general, the virtual world lacks many of the features that make human interactions in the real world nutritious, as we might say, for physical, social, and emotional development. In particular, real-world relationships and social interactions are characterized by four features—typical for hundreds of thousands of years—that online interactions either distort or erase.
First, real-world interactions are embodied, meaning that we use our hands and facial expressions to communicate, and we learn to respond to the body language of others. Virtual interactions, in contrast, mostly rely on language alone. No matter how many emojis are offered as compensation, the elimination of communication channels for which we have eons of evolutionary programming is likely to produce adults who are less comfortable and less skilled at interacting in person.
Second, real-world interactions are synchronous; they happen at the same time. As a result, we learn subtle cues about timing and conversational turn taking. Synchronous interactions make us feel closer to the other person because that’s what getting “in sync” does. Texts, posts, and many other virtual interactions lack synchrony. There is less real laughter, more room for misinterpretation, and more stress after a comment that gets no immediate response.
Third, real-world interactions primarily involve one‐to‐one communication, or sometimes one-to-several. But many virtual communications are broadcast to a potentially huge audience. Online, each person can engage in dozens of asynchronous interactions in parallel, which interferes with the depth achieved in all of them. The sender’s motivations are different, too: With a large audience, one’s reputation is always on the line; an error or poor performance can damage social standing with large numbers of peers. These communications thus tend to be more performative and anxiety-inducing than one-to-one conversations.
Finally, real-world interactions usually take place within communities that have a high bar for entry and exit, so people are strongly motivated to invest in relationships and repair rifts when they happen. But in many virtual networks, people can easily block others or quit when they are displeased. Relationships within such networks are usually more disposable.
These unsatisfying and anxiety-producing features of life online should be recognizable to most adults. Online interactions can bring out antisocial behavior that people would never display in their offline communities. But if life online takes a toll on adults, just imagine what it does to adolescents in the early years of puberty, when their “experience expectant” brains are rewiring based on feedback from their social interactions.
Kids going through puberty online are likely to experience far more social comparison, self-consciousness, public shaming, and chronic anxiety than adolescents in previous generations, which could potentially set developing brains into a habitual state of defensiveness. The brain contains systems that are specialized for approach (when opportunities beckon) and withdrawal (when threats appear or seem likely). People can be in what we might call “discover mode” or “defend mode” at any moment, but generally not both. The two systems together form a mechanism for quickly adapting to changing conditions, like a thermostat that can activate either a heating system or a cooling system as the temperature fluctuates. Some people’s internal thermostats are generally set to discover mode, and they flip into defend mode only when clear threats arise. These people tend to see the world as full of opportunities. They are happier and less anxious. Other people’s internal thermostats are generally set to defend mode, and they flip into discover mode only when they feel unusually safe. They tend to see the world as full of threats and are more prone to anxiety and depressive disorders.
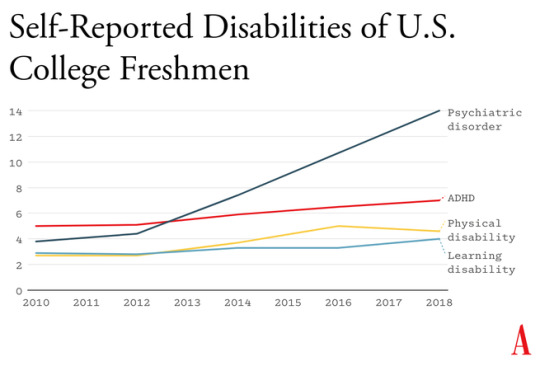
A simple way to understand the differences between Gen Z and previous generations is that people born in and after 1996 have internal thermostats that were shifted toward defend mode. This is why life on college campuses changed so suddenly when Gen Z arrived, beginning around 2014. Students began requesting “safe spaces” and trigger warnings. They were highly sensitive to “microaggressions” and sometimes claimed that words were “violence.” These trends mystified those of us in older generations at the time, but in hindsight, it all makes sense. Gen Z students found words, ideas, and ambiguous social encounters more threatening than had previous generations of students because we had fundamentally altered their psychological development.
5. So Many Harms
The debate around adolescents’ use of smartphones and social media typically revolves around mental health, and understandably so. But the harms that have resulted from transforming childhood so suddenly and heedlessly go far beyondmental health. I’ve touched on some of them—social awkwardness, reduced self-confidence, and a more sedentary childhood. Here are three additional harms.
Fragmented Attention, Disrupted Learning
Staying on task while sitting at a computer is hard enough for an adult with a fully developed prefrontal cortex. It is far more difficult for adolescents in front of their laptop trying to do homework. They are probably less intrinsically motivated to stay on task. They’re certainly less able, given their undeveloped prefrontal cortex, and hence it’s easy for any company with an app to lure them away with an offer of social validation or entertainment. Their phones are pinging constantly—one study found that the typical adolescent now gets 237 notifications a day, roughly 15 every waking hour. Sustained attention is essential for doing almost anything big, creative, or valuable, yet young people find their attention chopped up into little bits by notifications offering the possibility of high-pleasure, low-effort digital experiences.
It even happens in the classroom. Studies confirm that when students have access to their phones during class time, they use them, especially for texting and checking social media, and their grades and learning suffer. This might explain why benchmark test scores began to decline in the U.S. and around the world in the early 2010s—well before the pandemic hit.
Addiction and Social Withdrawal
The neural basis of behavioral addiction to social media or video games is not exactly the same as chemical addiction to cocaine or opioids. Nonetheless, they all involve abnormally heavy and sustained activation of dopamine neurons and reward pathways. Over time, the brain adapts to these high levels of dopamine; when the child is not engaged in digital activity, their brain doesn’t have enough dopamine, and the child experiences withdrawal symptoms. These generally include anxiety, insomnia, and intense irritability. Kids with these kinds of behavioral addictions often become surly and aggressive, and withdraw from their families into their bedrooms and devices.
Social-media and gaming platforms were designed to hook users. How successful are they? How many kids suffer from digital addictions?
The main addiction risks for boys seem to be video games and porn. “Internet gaming disorder,” which was added to the main diagnosis manual of psychiatry in 2013 as a condition for further study, describes “significant impairment or distress” in several aspects of life, along with many hallmarks of addiction, including an inability to reduce usage despite attempts to do so. Estimates for the prevalence of IGD range from 7 to 15 percent among adolescent boys and young men. As for porn, a nationally representative survey of American adults published in 2019 found that 7 percent of American men agreed or strongly agreed with the statement “I am addicted to pornography”—and the rates were higher for the youngest men.
Girls have much lower rates of addiction to video games and porn, but they use social media more intensely than boys do. A study of teens in 29 nations found that between 5 and 15 percent of adolescents engage in what is called “problematic social media use,” which includes symptoms such as preoccupation, withdrawal symptoms, neglect of other areas of life, and lying to parents and friends about time spent on social media. That study did not break down results by gender, but many others have found that rates of “problematic use” are higher for girls.
I don’t want to overstate the risks: Most teens do not become addicted to their phones and video games. But across multiple studies and across genders, rates of problematic use come out in the ballpark of 5 to 15 percent. Is there any other consumer product that parents would let their children use relatively freely if they knew that something like one in 10 kids would end up with a pattern of habitual and compulsive use that disrupted various domains of life and looked a lot like an addiction?
The Decay of Wisdom and the Loss of Meaning
During that crucial sensitive period for cultural learning, from roughly ages 9 through 15, we should be especially thoughtful about who is socializing our children for adulthood. Instead, that’s when most kids get their first smartphone and sign themselves up (with or without parental permission) to consume rivers of content from random strangers. Much of that content is produced by other adolescents, in blocks of a few minutes or a few seconds.
This rerouting of enculturating content has created a generation that is largely cut off from older generations and, to some extent, from the accumulated wisdom of humankind, including knowledge about how to live a flourishing life. Adolescents spend less time steeped in their local or national culture. They are coming of age in a confusing, placeless, ahistorical maelstrom of 30-second stories curated by algorithms designed to mesmerize them. Without solid knowledge of the past and the filtering of good ideas from bad––a process that plays out over many generations––young people will be more prone to believe whatever terrible ideas become popular around them, which might explain why videos showing young people reacting positively to Osama bin Laden’s thoughts about America were trending on TikTok last fall.
All this is made worse by the fact that so much of digital public life is an unending supply of micro dramas about somebody somewhere in our country of 340 million people who did something that can fuel an outrage cycle, only to be pushed aside by the next. It doesn’t add up to anything and leaves behind only a distorted sense of human nature and affairs.
When our public life becomes fragmented, ephemeral, and incomprehensible, it is a recipe for anomie, or normlessness. The great French sociologist Émile Durkheim showed long ago that a society that fails to bind its people together with some shared sense of sacredness and common respect for rules and norms is not a society of great individual freedom; it is, rather, a place where disoriented individuals have difficulty setting goals and exerting themselves to achieve them. Durkheim argued that anomie was a major driver of suicide rates in European countries. Modern scholars continue to draw on his work to understand suicide rates today.
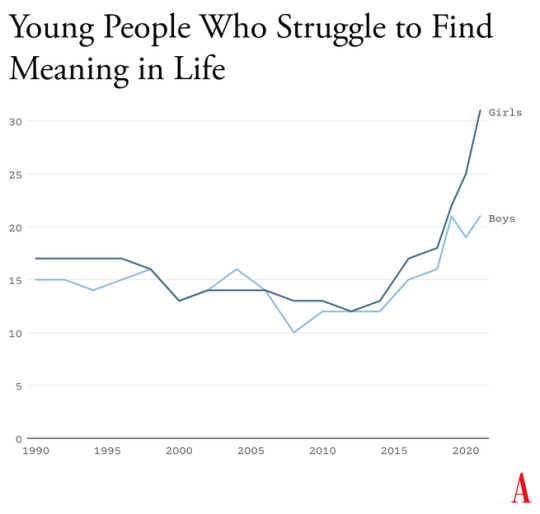
Durkheim’s observations are crucial for understanding what happened in the early 2010s. A long-running survey of American teens found that, from 1990 to 2010, high-school seniors became slightly less likely to agree with statements such as “Life often feels meaningless.” But as soon as they adopted a phone-based life and many began to live in the whirlpool of social media, where no stability can be found, every measure of despair increased. From 2010 to 2019, the number who agreed that their lives felt “meaningless” increased by about 70 percent, to more than one in five.
6. Young People Don’t Like Their Phone-Based Lives
How can I be confident that the epidemic of adolescent mental illness was kicked off by the arrival of the phone-based childhood? Skeptics point to other events as possible culprits, including the 2008 global financial crisis, global warming, the 2012 Sandy Hook school shooting and the subsequent active-shooter drills, rising academic pressures, and the opioid epidemic. But while these events might have been contributing factors in some countries, none can explain both the timing and international scope of the disaster.
An additional source of evidence comes from Gen Z itself. With all the talk of regulating social media, raising age limits, and getting phones out of schools, you might expect to find many members of Gen Z writing and speaking out in opposition. I’ve looked for such arguments and found hardly any. In contrast, many young adults tell stories of devastation.
Freya India, a 24-year-old British essayist who writes about girls, explains how social-media sites carry girls off to unhealthy places: “It seems like your child is simply watching some makeup tutorials, following some mental health influencers, or experimenting with their identity. But let me tell you: they are on a conveyor belt to someplace bad. Whatever insecurity or vulnerability they are struggling with, they will be pushed further and further into it.” She continues:
Gen Z were the guinea pigs in this uncontrolled global social experiment. We were the first to have our vulnerabilities and insecurities fed into a machine that magnified and refracted them back at us, all the time, before we had any sense of who we were. We didn’t just grow up with algorithms. They raised us. They rearranged our faces. Shaped our identities. Convinced us we were sick.
Rikki Schlott, a 23-year-old American journalist and co-author of The Canceling of the American Mind, writes,
"The day-to-day life of a typical teen or tween today would be unrecognizable to someone who came of age before the smartphone arrived. Zoomers are spending an average of 9 hours daily in this screen-time doom loop—desperate to forget the gaping holes they’re bleeding out of, even if just for … 9 hours a day. Uncomfortable silence could be time to ponder why they’re so miserable in the first place. Drowning it out with algorithmic white noise is far easier."
A 27-year-old man who spent his adolescent years addicted (his word) to video games and pornography sent me this reflection on what that did to him:
I missed out on a lot of stuff in life—a lot of socialization. I feel the effects now: meeting new people, talking to people. I feel that my interactions are not as smooth and fluid as I want. My knowledge of the world (geography, politics, etc.) is lacking. I didn’t spend time having conversations or learning about sports. I often feel like a hollow operating system.
Or consider what Facebook found in a research project involving focus groups of young people, revealed in 2021 by the whistleblower Frances Haugen: “Teens blame Instagram for increases in the rates of anxiety and depression among teens,” an internal document said. “This reaction was unprompted and consistent across all groups.”
7. Collective-Action Problems
Social-media companies such as Meta, TikTok, and Snap are often compared to tobacco companies, but that’s not really fair to the tobacco industry. It’s true that companies in both industries marketed harmful products to children and tweaked their products for maximum customer retention (that is, addiction), but there’s a big difference: Teens could and did choose, in large numbers, not to smoke. Even at the peak of teen cigarette use, in 1997, nearly two-thirds of high-school students did not smoke.
Social media, in contrast, applies a lot more pressure on nonusers, at a much younger age and in a more insidious way. Once a few students in any middle school lie about their age and open accounts at age 11 or 12, they start posting photos and comments about themselves and other students. Drama ensues. The pressure on everyone else to join becomes intense. Even a girl who knows, consciously, that Instagram can foster beauty obsession, anxiety, and eating disorders might sooner take those risks than accept the seeming certainty of being out of the loop, clueless, and excluded. And indeed, if she resists while most of her classmates do not, she might, in fact, be marginalized, which puts her at risk for anxiety and depression, though via a different pathway than the one taken by those who use social media heavily. In this way, social media accomplishes a remarkable feat: It even harms adolescents who do not use it.
A recent study led by the University of Chicago economist Leonardo Bursztyn captured the dynamics of the social-media trap precisely. The researchers recruited more than 1,000 college students and asked them how much they’d need to be paid to deactivate their accounts on either Instagram or TikTok for four weeks. That’s a standard economist’s question to try to compute the net value of a product to society. On average, students said they’d need to be paid roughly $50 ($59 for TikTok, $47 for Instagram) to deactivate whichever platform they were asked about. Then the experimenters told the students that they were going to try to get most of the others in their school to deactivate that same platform, offering to pay them to do so as well, and asked, Now how much would you have to be paid to deactivate, if most others did so? The answer, on average, was less than zero. In each case, most students were willing to pay to have that happen.
Social media is all about network effects. Most students are only on it because everyone else is too. Most of them would prefer that nobody be on these platforms. Later in the study, students were asked directly, “Would you prefer to live in a world without Instagram [or TikTok]?” A majority of students said yes––58 percent for each app.
This is the textbook definition of what social scientists call a collective-action problem. It’s what happens when a group would be better off if everyone in the group took a particular action, but each actor is deterred from acting, because unless the others do the same, the personal cost outweighs the benefit. Fishermen considering limiting their catch to avoid wiping out the local fish population are caught in this same kind of trap. If no one else does it too, they just lose profit.
Cigarettes trapped individual smokers with a biological addiction. Social media has trapped an entire generation in a collective-action problem. Early app developers deliberately and knowingly exploited the psychological weaknesses and insecurities of young people to pressure them to consume a product that, upon reflection, many wish they could use less, or not at all.
8. Four Norms to Break Four Traps
Young people and their parents are stuck in at least four collective-action traps. Each is hard to escape for an individual family, but escape becomes much easier if families, schools, and communities coordinate and act together. Here are four norms that would roll back the phone-based childhood. I believe that any community that adopts all four will see substantial improvements in youth mental health within two years.
No smartphones before high school
The trap here is that each child thinks they need a smartphone because “everyone else” has one, and many parents give in because they don’t want their child to feel excluded. But if no one else had a smartphone—or even if, say, only half of the child’s sixth-grade class had one—parents would feel more comfortable providing a basic flip phone (or no phone at all). Delaying round-the-clock internet access until ninth grade (around age 14) as a national or community norm would help to protect adolescents during the very vulnerable first few years of puberty. According to a 2022 British study, these are the years when social-media use is most correlated with poor mental health. Family policies about tablets, laptops, and video-game consoles should be aligned with smartphone restrictions to prevent overuse of other screen activities.
No social media before 16
The trap here, as with smartphones, is that each adolescent feels a strong need to open accounts on TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat, and other platforms primarily because that’s where most of their peers are posting and gossiping. But if the majority of adolescents were not on these accounts until they were 16, families and adolescents could more easily resist the pressure to sign up. The delay would not mean that kids younger than 16 could never watch videos on TikTok or YouTube—only that they could not open accounts, give away their data, post their own content, and let algorithms get to know them and their preferences.
Phone‐free schools
Most schools claim that they ban phones, but this usually just means that students aren’t supposed to take their phone out of their pocket during class. Research shows that most students do use their phones during class time. They also use them during lunchtime, free periods, and breaks between classes––times when students could and should be interacting with their classmates face-to-face. The only way to get students’ minds off their phones during the school day is to require all students to put their phones (and other devices that can send or receive texts) into a phone locker or locked pouch at the start of the day. Schools that have gone phone-free always seem to report that it has improved the culture, making students more attentive in class and more interactive with one another. Published studies back them up.
More independence, free play, and responsibility in the real world
Many parents are afraid to give their children the level of independence and responsibility they themselves enjoyed when they were young, even though rates of homicide, drunk driving, and other physical threats to children are way down in recent decades. Part of the fear comes from the fact that parents look at each other to determine what is normal and therefore safe, and they see few examples of families acting as if a 9-year-old can be trusted to walk to a store without a chaperone. But if many parents started sending their children out to play or run errands, then the norms of what is safe and accepted would change quickly. So would ideas about what constitutes “good parenting.” And if more parents trusted their children with more responsibility––for example, by asking their kids to do more to help out, or to care for others––then the pervasive sense of uselessness now found in surveys of high-school students might begin to dissipate.
It would be a mistake to overlook this fourth norm. If parents don’t replace screen time with real-world experiences involving friends and independent activity, then banning devices will feel like deprivation, not the opening up of a world of opportunities.
The main reason why the phone-based childhood is so harmful is because it pushes aside everything else. Smartphones are experience blockers. Our ultimate goal should not be to remove screens entirely, nor should it be to return childhood to exactly the way it was in 1960. Rather, it should be to create a version of childhood and adolescence that keeps young people anchored in the real world while flourishing in the digital age.
9. What Are We Waiting For?
An essential function of government is to solve collective-action problems. Congress could solve or help solve the ones I’ve highlighted—for instance, by raising the age of “internet adulthood” to 16 and requiring tech companies to keep underage children off their sites.
In recent decades, however, Congress has not been good at addressing public concerns when the solutions would displease a powerful and deep-pocketed industry. Governors and state legislators have been much more effective, and their successes might let us evaluate how well various reforms work. But the bottom line is that to change norms, we’re going to need to do most of the work ourselves, in neighborhood groups, schools, and other communities.
There are now hundreds of organizations––most of them started by mothers who saw what smartphones had done to their children––that are working to roll back the phone-based childhood or promote a more independent, real-world childhood. (I have assembled a list of many of them.) One that I co-founded, at LetGrow.org, suggests a variety of simple programs for parents or schools, such as play club (schools keep the playground open at least one day a week before or after school, and kids sign up for phone-free, mixed-age, unstructured play as a regular weekly activity) and the Let Grow Experience (a series of homework assignments in which students––with their parents’ consent––choose something to do on their own that they’ve never done before, such as walk the dog, climb a tree, walk to a store, or cook dinner).
Parents are fed up with what childhood has become. Many are tired of having daily arguments about technologies that were designed to grab hold of their children’s attention and not let go. But the phone-based childhood is not inevitable.
The four norms I have proposed cost almost nothing to implement, they cause no clear harm to anyone, and while they could be supported by new legislation, they can be instilled even without it. We can begin implementing all of them right away, this year, especially in communities with good cooperation between schools and parents. A single memo from a principal asking parents to delay smartphones and social media, in support of the school’s effort to improve mental health by going phone free, would catalyze collective action and reset the community’s norms.
We didn’t know what we were doing in the early 2010s. Now we do. It’s time to end the phone-based childhood.
This article is adapted from Jonathan Haidt’s forthcoming book, The Anxious Generation: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental Illness.
216 notes
·
View notes
Text

UPDATE 9/26/2023
Strike authorization has passed by 98.32% and SAG leadership are returning to negotiate with game companies to secure a fair deal for voice actors and mocap actors
This DOES NOT MEAN that a strike is happening, it simply means that members are willing to go on strike and leadership can use this as leverage when negotiating. The deadline to come to a deal is is 9/28. If a deal is not reached THEN will there be a strike.
Please remember that the best outcome is that there is no strike and companies simply give workers a fair deal. A strike is a last resort.
While this does not directly affect developers in the game industry, that does not mean it's not important. Voice actors have been treated like shit in the game industry and are under threat by AI. The more people that are unionized, the easy it is for others to unionize. Do not dismiss it just because it is not developers.
The companies that would be affected by a hypothetical strike are:
Activision Productions Inc.,
Blindlight LLC,
Disney Character Voices Inc.,
Electronic Arts Productions Inc.,
Epic Games, Inc.,
Formosa Interactive LLC,
Insomniac Games Inc.,
Take 2 Productions Inc.,
VoiceWorks Productions Inc., and
WB Games Inc.
At the moment, no boycott has been called so there is nothing for consumers or anyone not involved with SAG-AFTRA to do, other than to be supportive on social media and report unauthorized AI recreation of voice actors work. Otherwise sit tight.
I'd really appreciate it if people who reblogged the last post also reblog the update
#sag aftra#sag aftra strike#sag aftra strong#Destiel meme#hot strike summer#hot labor summer#voice actors#voice acting#mocap#motion capture#industry bullshit#gaming industry#video games
561 notes
·
View notes
Text

every terminal i've offhandedly referenced in oc lore on discord with my friends. because i am normal.
random facts below the cut:
jerry: one of a few terminals originally put down in hell by a private company (hi @frostaxolotl it's the guys who did project obsidian). kept records and eventually uploaded them onto the network at large. located in a cave in wrath. pronouns whatever he doesn't care
sal: mad scientist type beat. helped another terminal develop a way to upload itself into another machine on the condition that they could do whatever with the result once the other terminal was done. uses said code to shove viruses onto machines that hook up to them for cybergrinding, just to see what happens. really really really likes fish. has a salmon with legs shimeiji on their screen at all times. someone dumped a labcoat on them once and it hasn't been moved since. located in an industrial building in one of the warzones of violence. they/it
69: pirated a lot of media for the terminal network back when they'd been abandoned by humanity, but humanity was still, y'know, alive. and the internet was therefore still online. refuses to let anyone repair her for whatever reason. located in the mouth of hell. she/her
TT: one of the terminals that kept the hell network's internet gateway up and running. eventually paid a random passing machine in points to paint her. okay look she's just rose homestuck except ultrakill edition. located in/near a cathedral of limbo. she/her
cloud: it's a joke on cloud storage and that is all you need to know. organizes and files all the data/files that have been shared to the terminal network as a whole. also archives any data that other terminals do not want to host on themselves anymore, so a lot of its memory is dedicated to random reports that no one actually cares about. located on one of the boardwalks in wrath, close by to a cabin. it/he/they
duck: one of the terminals behind getting the hell network internet access. too far away from the surface physically to do it himself though, so he just sends programs and theory to terminals who can actually get reception. almost always has ascii art on his screen instead of the tip of the day. located near the bottom of limbo, in a carpeted hall of a cathedral. she/he
miku: yes they're named after that miku. likes vocaloid (duh). particularly lonely and is more likely to strike up a conversation with passing machines than they are to actually do any terminal functions. located in a building in lust that should be an insanely high-traffic zone, but everyone and their mother realizes that and so most machines actually avoid it to minimize risk. this, paradoxically, makes said building one of the least-visited areas, which also means that miku has very little interaction ever. they/she
irukandji: judgy asshole who insulted the terminal mentioned above (the one that decided to download itself into another machine to explore hell on its own). thanks @salt216000 located in gluttony somewhere fleshy, hence all the blood. nameself pronouns ++ it/its
#ultrakill#ultrakill oc#ultrakill terminal#i mostly just decided to make these guys designs to see if i could make 'this is a box with a screen' into recognizable characters#aaaand then they all refused to leave my brain so i guess i just have a gang of background characters now
92 notes
·
View notes