#indian bureaucrats
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
my case manager from the relocation agency says that even for a processing delay this is getting kind of long :)))) consulate isn't responding to either of our emails :))))))))) fucking going through it rn :))))))))))))
0 notes
Text
"Passed in February [2024], a massive subsidy program to help Indian households install rooftop solar panels in their homes and apartments aims to provide 30 gigawatt hours of solar power to the nation’s inventory.
The scheme, called PM-Surya Ghar, will provide free electricity to 10 million homes according to estimates, and the designing of a national portal—a sort of Healthcare.gov for solar panels—will streamline the process of installation and payment.
The program was cooked up because India had fallen woefully behind on its planned installations for rooftop solar. In many parts of the subcontinent, the sun is absolutely brutal and relentless, but by 2022, Indian rooftop solar power generation topped out at 11 gigawatts, which was 29 gigawatts under a national target set a decade ago.
Part of the challenge, Euronews reports, is that approval from various agencies and departments—as many as 21 different signatures in some cases—was needed to place a solar array on your house. Aside from this bureaucratic nightmare, the cost of installation was often higher than $5,000; more than half the average yearly income for a working Indian urbanite.
Under PM-Surya Ghar, subsidies for a 2-kilowatt solar array will cover as much as 60% of the installation costs, falling to 40% for arrays 3 kilowatts or higher. Loans set at around 7% interest rates will help families in need get started. 750 billion Indian rupees, or $9 billion has been set aside for the project.
Even in New Delhi, which can be covered in clouds and smog for days, solar users report saving hundreds during summer time on their electricity costs, with one apartment shaving $700 every month off energy bills.
PM-Surya Ghar is also seen as having the potential to cause a boom in the Indian solar market. Companies no longer have to go running around for planning and permitting requirements, and the government subsidies ensure their customer base can grow beyond the limits of household income."
-Good News Network, April 10, 2024
#india#new delhi#solar#solar panels#clean energy#solar power#renewables#rooftop solar#climate policy#climate action#climate hope#renewable energy#good news#hope
271 notes
·
View notes
Text

In 1872, W.A. Short, a government official in northern Indian was ordered to create a register of the Hijra living in his area. This was part of a British colonial policy of criminalising Hijra, whose gender-non-conforming practices, such as castration and wearing female dress, fell outside of British norms.
Short chose not to register a single person. When his superiors questioned him, he set out to prove that there was no reason to suspect the local Hijra any crimes. The list he provided in 1873 stands out from other bureaucratic sources of the time for providing a nuanced picture of the lives of eleven Hijra, giving us insight into their family structure, shared households, and ways of supporting themselves and each other.
Check out our podcast to hear their stories, and learn more about the history of Hijra in northern India!
[Image: A Hijra and her companions in East Bengal, 1860s]
147 notes
·
View notes
Note
(This got soo much longer than I meant for it to be omg... sorry about that!!)
American Holocaust by David Stannard is a flawed book with some dated language, but of everything I've read, I think I like its explanation/argument against this weird sort of... competitive genocide stuff. I'm gonna butcher it a little by cutting out a LOT in order to not nuke your inbox with a super long ask, but:
[…] To say this is not to say that the Jewish Holocaust-the inhuman destruction of 6,000,000 people-was not an abominably unique event. It was. So, too, for reasons of its own, was the mass murder of about 1,000,000 Armenians in Turkey a few decades prior to the Holocaust. So, too, was the deliberately caused "terror-famine" in Stalin's Soviet Union in the 1930s, which killed more than 14,000,000 people. So, too, have been each of the genocidal slaughters of many millions more, decades after the Holocaust, in Burundi, Bangladesh, Kampuchea, East Timor, the Brazilian Amazon, and elsewhere. Additionally, within the framework of the Holocaust itself, there were aspects that were unique in the campaign of genocide conducted by the Nazis against Europe's Romani people, which resulted in the mass murder of perhaps 1,500,000 men, women, and children. [...]
Each of these genocides was distinct and unique, for one reason or another, as were (and are) others that go unmentioned here. In one case the sheer numbers of people killed may make it unique. In another case, the percentage of people killed may make it unique. In still a different case, the greatly compressed time period in which the genocide took place may make it unique. In a further case, the greatly extended time period in which the genocide took place may make it unique. No doubt the targeting of a specific group or groups for extermination by a particular nation's official policy may mark a given genocide as unique. So too might another group's being unofficially (but unmistakably) targeted for elimination by the actions of a multinational phalanx bent on total extirpation. Certainly the chilling utilization of technological instruments of destruction, such as gas chambers, and its assembly-line, bureaucratic, systematic methods of destruction makes the Holocaust unique. On the other hand, the savage employment of non-technological instruments of destruction, such as the unleashing of trained and hungry dogs to devour infants, and the burning and crude hacking to death of the inhabitants of entire cities, also makes the Spanish anti-Indian genocide unique.
[…]
A secondary tragedy of all these genocides, moreover, is that partisan representatives among the survivors of particular afflicted groups not uncommonly hold up their peoples' experience as so fundamentally different from the others that not only is scholarly comparison rejected out of hand, but mere cross-referencing or discussion of other genocidal events within the context of their own flatly is prohibited. It is almost as though the preemptive conclusion that one's own group has suffered more than others is something of a horrible award of distinction that will be diminished if the true extent of another group's suffering is acknowledged.
Compounding this secondary tragedy is the fact that such insistence on the incomparability of one's own historical suffering, by means of what Irving Louis Horowitz calls "moral bookkeeping," invariably pits one terribly injured group against another […]
Denial of massive death counts is common--and even readily understandable, if contemptible--among those whose forefathers were the perpetrators of the genocide. Such denials have at least two motives: first, protection of the moral reputations of those people and that country responsible for the genocidal activity (which seems the primary motive of those scholars and politicians who deny that massive genocide campaigns were carried out against American Indians); and second, on occasion, the desire to continue carrying out virulent racist assaults upon those who were the victims of the genocide in question (as seems to be the major purpose of the anti-Semitic so-called historical revisionists who claim that the Jewish Holocaust never happened or that its magnitude has been exaggerated). But for those who have themselves been victims of extermination campaigns to proclaim uniqueness for their experiences only as a way of denying recognition to others who also have suffered massive genocidal brutalities is to play into the hands of the brutalizers. Rather, as Michael Berenbaum has wisely put it, "we should let our sufferings, however incommensurate, unite us in condemnation of inhumanity rather than divide us in a calculus of calamity."
The whole thing is available to read on the Internet Archive if you're interested. (This part starts on pg 149, if you'd just like to have the full context without the parts I chopped.)
Additionally, Carrol Kakel's book The American West and the Nazi East, while imperfect, too, is also very useful in getting at the core issue with these arguments and what makes them harmful--regardless of intent. I'm gonna spare you and not quote too much from this one, but the general gist of what it's about and argues in favor of is summed up like this in its conclusion:
In the case of the Holocaust and its contexts, the new ‘optics’ helps us see that – contrary to the prevailing image of ‘industrial genocide’ – many aspects of the Holocaust are akin to earlier ‘colonial genocide’. It is worth noting (and emphasizing) that the distinction I make between ‘colonial genocide’ and ‘industrial genocide’ is not to suggest some type of crude and arbitrary ‘partitioning’ of the Nazi Holocaust; it is, rather, to suggest and reassert the (settler) colonial roots, content, and context of the Nazi project in the ‘Wild East’ – a content and context linked, in Hitler’s and Himmler’s ‘spatial’ and ‘racial’ fantasies, to the ‘North American precedent’. And finally, the new ‘optics’ also allows us to understand that the ‘genocide and colonialism’ nexus holds the key to recognizing the Holocaust’s origins, content, and context; that the Nazi Holocaust is not a copy – but an extremely radicalized variant – of earlier ‘colonial genocide’; and that ‘holocaust’ is not a separate category from, but the most extreme variant of, the blight on human history we call ‘genocide’.
One of the more infamous examples of someone trying to argue against comparison (at least in the NDN circles I run in, anyway) was Deborah Lipstadt claiming that "[What the United States did to Native Americans] was not the same as the Holocaust" because, she says, "The Native Americans were seen as "competitors" for land and resources. There was, therefore, a certain logic-horrible and immoral as it was-to the campaign against the Native Americans."
Just for context, the full paragraph from her blog post:
What the United States did to Native Americans was horrendous. I have not studied it closely and it's not my area of expertise, however, it seems clear that the treatment of the various Native American tribes was revolting. However, it was not the same as the Holocaust. The Native Americans were seen as "competitors" for land and resources. There was, therefore, a certain logic-horrible and immoral as it was-to the campaign against the Native Americans. [Please note: I am NOT justifying the attacks.] The German campaign against the Jews had no logic and was often completely illogical. People who were "useful" to the Germans were murdered or exiled, e.g. slave laborers in factories producing goods for the Wehrmacht and scientists who were producing important technological advances for the Germans. In a prime example of illogic, in June 1944 at the time of the landing at Normandy, when the Germans were truly on the defensive, they used precious ships and men to go to the Island of Corfu and deport the 1200 Jews who lived there. They ended up in Auschwitz. Approximately 100 of this old Jewish community survived.
This is obviously a repulsive take, but the bizarre rationalization of abject evil isn't what I think makes this such a good example of the big issue at the heart of the constant emphasis on "uniqueness." There are plenty of people who hold these "exceptionalist" beliefs without taking it that much further and dismissing other genocides altogether. No, the thing that makes this such a perfect encapsulation imo is the very first sentence, where this historian, this professor of "Holocaust Studies," this woman who's ostensibly spent most of her entire life studying genocide openly admits she's never really bothered to look into what, exactly, happened to all those Indians way back when.
This is ultimately what I, personally, see as the main issue with this line of thinking. The harm doesn't necessarily come from holding the Holocaust up as "worse" than any other genocidal event, though that way of thinking definitely has its own problems, but from holding it up as fundamentally different.
It's the way this view holds it up as completely separate, in its own little bubble of history where we can study it and analyze it and teach about it all we want... all without ever having to broach the subject of colonialism. You can have entire classes where you study every single minute detail of this one specific genocide without ever having to mention or--god forbid--criticize the system that's driven pretty much every other instance of it.
Deborah Lipstadt has spent the better part of a century learning everything there is to know about the Holocaust, but in all that time, she's apparently never felt the need to look into the events that its perpetrators openly and repeatedly referred to as their inspiration.
This is what makes this sort of framing so dangerous imo. You can spend your entire life educating yourself about genocide, but if it's only in the context of one genocide and the belief in the uniqueness and incomparability of that single event is core to your understanding of both it and your worldview as a whole, you will still be completely incapable of recognizing the signs when it starts to happen again.
this is a really informative ask. thank you so much for sending this in (love the citations haha) i think it adds a lot to the overall discussion.
200 notes
·
View notes
Text

This is the fifth episode in the series over the Apache Indians in the American Southwest. This episode covers the aftermath of the Camp Grant Massacre and encompasses the years 1870 to 1874. It also continues the story of the most feared Apache warrior chief to have ever lived in the eyes of the Americans: Cochise.
The episode introduces important men of history in the region like General Crook, General Howard, Captain Tom Jeffords, Cochise’s sons Taza and Naiche, the Tonto Apache chief Red Ant (Delshay), the various Apache Scout leaders like Al Sieber, and countless others. Lieutenant Bourke, Geronimo, Merejildo Grijalva, and Mickey Free the kidnapped boy who started this long war also make heavy return appearances. The massive offensive against the Apaches and Yavapai Indians during the winter of 1872 to 1873 is discussed in detail as well as the flip side of the Indians Wars: President Grant’s “Peace Policy”.
Battles ensue, bureaucrats meddle, reservations are established, massacres like the Skeleton Cave Massacre blight the land, but by the end of the episode peace will reign, however briefly, on Apacheria.
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
"let us declare that the state of war does exist and shall exist so long as the indian toiling masses and the natural resources are being exploited by a handful of parasites. they may be purely british capitalist or mixed british and indian or even purely indian. they may be carrying on their insidious exploitation through mixed or even on purely Indian bureaucratic apparatus. all these things make no difference."
- Bhagat Singh
too many of you like bringing up revolutionaries to complain against the fact that today independence day is not worth celebrating to make your point without ever having read them. educate yourselves before you speak.
#desiblr#rg kar medical college#indian independence day#crime#violence against girls#kolkata#rape culture
50 notes
·
View notes
Note
I’ve been meaning to read more of Indian authors lately since I sometimes feel kinda ashamed to consume so much of foreign books but not of my own country, but the thing is … I just can’t get into most of them (that I’ve tried so far ). I’ve dnf’ed so many and I don’t even consider myself a picky reader. so it’d be helpful if you suggest some of your favourites that aren’t internationally popular ones.
I understand; I'm also very picky with the Indian authors I read, but here are some I've liked:
Battlefield by Vishram Bedekar (trans. Jerry Pinto): about two refugees fleeing wartime Europe (one Hindu, one Jewish), who meet on a ship and grow really close
Maharani by Ruskin Bond, or Room on the Roof, or The Blue Umbrella: I will turn myself inside out recommending Ruskin Bond, but these are my top three for you
Em and the Big Hoom by Jerry Pinto: about an East Indian family in Mumbai dealing with the mother's mental health; it's a really touching book
Our Moon Has Blood Clots by Rahul Pandita: a memoir of the Kashmiri Pandit genocide and its aftermath; it's a chilling memoir, but really good
English August by Upamanyu Chatterjee: about this elite bureaucrat who gets posted to the "hottest town in India" and how he deals with the locals; it has good satire going for it
Raag Darbari by Shrilal Shukl: another satire; follows a village and through it, explores democracy in early Independent India (or lack of it), the transition for the landed elite and generally most of the village to a democratic society. If you can read Hindi, I would recommend reading the original. If not, there's a translation by Gillian Wright.
152 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let us declare that the state of war does exist and shall exist so long as the Indian toiling masses and their natural resources are being exploited by a handful of parasites. They may be purely British capitalists or mixed British and Indian, or even purely Indian.
They may be carrying on their insidious exploitation through mixed or even purely Indian bureaucratic apparatus. All these things make no difference. No matter if your government tries and succeeds in winning over the leaders of the upper strata of the Indian society through petty concessions and compromises and thereby cause a temporary de-moralisation in the main body of the forces.
No matter if once again the vanguard of the Indian movement, the revolutionary party finds itself deserted into the thick of the war.
No matter if the leaders to whom personally we are much indebted for the sympathy and feelings they expressed for us, but nevertheless we cannot overlook the fact that they did become so callous as to ignore and not to make a mention in the peace negotiations of even the homeless, friendless and penniless female workers who are alleged to be belonging to the vanguard and whom the leaders consider to be the enemies of their utopian non-violent cult which has already become a thing of the past, the heroines who have unimagingly sacrificed or offered for sacrifice their husbands, brothers and all that were nearest and dearest to them, including themselves, whom your government has declared to be outlaws. No matter if your agents stoop so low as to fabricate baseless calumnies against their spotless character to damage their and their party's reputation.
This war shall continue.
Bhagat Singh
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vice president Kamala Harris Sunday reminisced about her Indian roots and said when she used to visit her grandparents, her grandfather used to take her on morning walks and then discuss the importance of fighting for equality and fighting corruption. In her post made on the occasion of the National Grandparents Day, Kamala Harris included an old family photo and claimed that her grandfather had been a part of the movement to win India's independence.
"As a young girl visiting my grandparents in India, my grandfather took me on his morning walks, where he would discuss the importance of fighting for equality and fighting corruption. He was a retired civil servant who had been part of the movement to win India’s independence.
"My grandmother traveled across India—bullhorn in hand—to speak with women about accessing birth control.
"Their commitment to public service and fight for a better future live on in me today.
"Happy National Grandparents Day to all the grandparents who help shape and inspire the next generation," the post read.


Social media users from India objected to the claim and pointed out that her grandfather was in the British Imperial Secretariat Service which became the Central Secretariat Service after Independence. "How could a serving bureaucrat be part of the independence movement opposing the same government and violating service rules?" one user wrote. "Everything you say is a lie," another said.
This is not the first time that Kamala Harris mentioned that her grandfather PV Gopalan was one of the "original independence fighters in India". But according to records, Gopalan was born in 1911 and was a diligent civil servant. Gopalan's son, Kamala Harris' uncle G Balachandran said that had his father openly advocated ending British rule, he could have been fired.
Gopalan was born in Painganadu near the Madras presidency in 1911. He joined the Indian civil services and also served in Zambia, where he was assigned to manage an influx of refugees.
While Kamala Harris' Indian roots are much discussed, reports surfaced Sunday that Kamala Harris would be meeting Congress leader from India DK Shivakumar, the deputy chief minister of Karnataka. But Shivakumar dismissed the rumors of his meeting with Harris and Barack Obama and said he is travelling to the US on a personal visit. _________________
I bet he's the one that taught her to say fweedom too.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
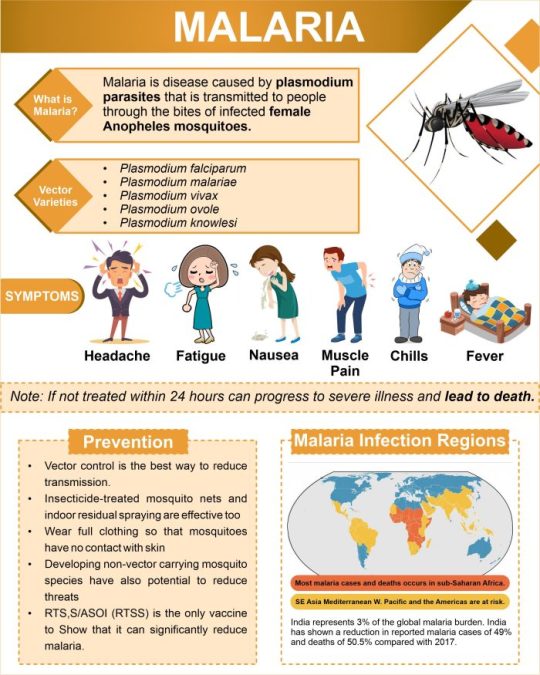
MALARIA VACCINE
The Government of India has set a target to eliminate malaria in India by 2027.
It has developed a National Framework for Malaria Elimination (2016-2030) and a National Strategic Plan for Malaria Elimination for five years.
India shifted its focus from malaria control to elimination.
A roadmap was established to eliminate malaria in 571 out of India’s total 678 districts by 2022.
The Malaria Elimination Research Alliance-India (MERA-India) was formed under the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
The subject of "Malaria Vaccine" is covered in this article's coverage of "Daily Current Affairs". The Science and Technology segment of the UPSC CSE test has applicability for this topic. Rishabh has researched and written the article. Additionally, our faculty has reviewed this article. Click the “Malaria Vaccine” link to see the story's original version.
Plutus IAS has received praise for its continued success in offering top-notch and reasonably priced IAS coaching in Karol Bagh Delhi. Our students' everlasting gratitude proves our dedication to developing the next generation of Indian bureaucrats and administrators.
The importance of everyday current affairs cannot be overstated if you wish to succeed in competitive tests like Civil Services. On its website, Plutus IAS includes a separate section for current affairs.
#ias coaching in delhi#upscaspirants#upsccoaching#best ias coaching in delhi#civil services examination#ias#upsc exam preparation#education#iascoaching#plutus ias#malaria vaccine
60 notes
·
View notes
Text


To The Punjab Governor
Sir, With due respect we beg to bring to your kind notice the following:
That we were sentenced to death on 7th October 1930 by a British Court, L.C.C Tribunal, constituted under the Sp. Lahore Conspiracy Case Ordinance, promulgated by the H.E. The Viceroy, the Head of the British Government of India, and that the main charge against us was that of having waged war against H.M. King George, the King of England.
The above-mentioned finding of the Court pre-supposed two things:
Firstly, that there exists a state of war between the British Nation and the Indian Nation and, secondly, that we had actually participated in that war and were therefore war prisoners.
The second pre-supposition seems to be a little bit flattering, but nevertheless it is too tempting to resist the desire of acquiescing in it.
As regards the first, we are constrained to go into some detail. Apparently there seems to be no such war as the phrase indicates. Nevertheless, please allow us to accept the validity of the pre-supposition taking it at its face value. But in order to be correctly understood we must explain it further. Let us declare that the state of war does exist and shall exist so long as the Indian toiling masses and the natural resources are being exploited by a handful of parasites. They may be purely British Capitalist or mixed British and Indian or even purely Indian. They may be carrying on their insidious exploitation through mixed or even on purely Indian bureaucratic apparatus. All these things make no difference. No matter, if your Government tries and succeeds in winning over the leaders of the upper strata of the Indian Society through petty concessions and compromises and thereby cause a temporary demoralization in the main body of the forces. No matter, if once again the vanguard of the Indian movement, the Revolutionary Party, finds itself deserted in the thick of the war. No matter if the leaders to whom personally we are much indebted for the sympathy and feelings they expressed for us, but nevertheless we cannot overlook the fact that they did become so callous as to ignore and not to make a mention in the peace negotiation of even the homeless, friendless and penniless of female workers who are alleged to be belonging to the vanguard and whom the leaders consider to be enemies of their utopian non-violent cult which has already become a thing of the past; the heroines who had ungrudgingly sacrificed or offered for sacrifice their husbands, brothers, and all that were nearest and dearest to them, including themselves, whom your government has declared to be outlaws. No matter, it your agents stoop so low as to fabricate baseless calumnies against their spotless characters to damage their and their party’s reputation. The war shall continue.
It may assume different shapes at different times. It may become now open, now hidden, now purely agitational, now fierce life and death struggle. The choice of the course, whether bloody or comparatively peaceful, which it should adopt rests with you. Choose whichever you like. But that war shall be incessantly waged without taking into consideration the petty (illegible) and the meaningless ethical ideologies. It shall be waged ever with new vigour, greater audacity and unflinching determination till the Socialist Republic is established and the present social order is completely replaced by a new social order, based on social prosperity and thus every sort of exploitation is put an end to and the humanity is ushered into the era of genuine and permanent peace. In the very near future the final battle shall be fought and final settlement arrived at.
The days of capitalist and imperialist exploitation are numbered. The war neither began with us nor is it going to end with our lives. It is the inevitable consequence of the historic events and the existing environments. Our humble sacrifices shall be only a link in the chain that has very accurately been beautified by the unparalleled sacrifice of Mr. Das and most tragic but noblest sacrifice of Comrade Bhagawati Charan and the glorious death of our dear warrior Azad.
As to the question of our fates, please allow us to say that when you have decided to put us to death, you will certainly do it. You have got the power in your hands and the power is the greatest justification in this world. We know that the maxim “Might is right” serves as your guiding motto. The whole of our trial was just a proof of that. We wanted to point out that according to the verdict of your court we had waged war and were therefore war prisoners. And we claim to be treated as such, i.e., we claim to be shot dead instead of to be hanged. It rests with you to prove that you really meant what your court has said.
We request and hope that you will very kindly order the military department to send its detachment to perform our execution.
Yours
BHAGAT SINGH
#bhagat singh#india#desiblr#freedom fighters#desi#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate crisis#climate#ecology
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 1678, a Chaldean priest from Baghdad reached the Imperial Villa of Potosí, the world’s richest silver-mining camp and at the time the world’s highest city at more than 4,000 metres (13,100 feet) above sea level. A regional capital in the heart of the Bolivian Andes, Potosí remains – more than three and a half centuries later – a mining city today. [...] The great red Cerro Rico or ‘Rich Hill’ towered over the city of Potosí. It had been mined since 1545 [...]. When Don Elias arrived [...], the great boom of 1575-1635 – when Potosí alone produced nearly half the world’s silver – was over, but the mines were still yielding the precious metal. [...]
On Potosí’s main market plaza, indigenous and African women served up maize beer, hot soup and yerba mate. Shops displayed the world’s finest silk and linen fabrics, Chinese porcelain, Venetian glassware, Russian leather goods, Japanese lacquerware, Flemish paintings and bestselling books in a dozen languages. [...]
Pious or otherwise, wealthy women clicked Potosí’s cobbled streets in silver-heeled platform shoes, their gold earrings, chokers and bracelets studded with Indian diamonds and Burmese rubies. Colombian emeralds and Caribbean pearls were almost too common. Peninsular Spanish ‘foodies’ could savour imported almonds, capers, olives, arborio rice, saffron, and sweet and dry Castilian wines. Black pepper arrived from Sumatra and southwest India, cinnamon from Sri Lanka, cloves from Maluku and nutmeg from the Banda Islands. Jamaica provided allspice. Overloaded galleons spent months transporting these luxuries across the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic oceans. Plodding mule and llama trains carried them up to the lofty Imperial Villa.
---
Potosi supplied the world with silver, the lifeblood of trade and sinews of war [...]. In turn, the city consumed the world’s top commodities and manufactures. [...] The city’s dozen-plus notaries worked non-stop inventorying silver bars and sacks of pesos [...]. Mule trains returning from the Pacific brought merchandise and mercury, the essential ingredient for silver refining. [...] From Buenos Aires came slavers with captive Africans from Congo and Angola, transshipped via Rio de Janeiro. Many of the enslaved were children branded with marks mirroring those, including the royal crown, inscribed on silver bars.
Soon after its 1545 discovery, Potosí gained world renown [...]. Mexico’s many mining camps [...] peaked only after 1690. [...] Even in the Andes of South America there were other silver cities [...]. But no silver deposit in the world matched the Cerro Rico, and no other mining-refining conglomeration grew so large. Potosí was unique: a mining metropolis.
Thus Don Elias, like others, made the pilgrimage to the silver mountain. It was a divine prodigy, a hierophany. In 1580, Ottoman artists depicted Potosí as a slice of earthly paradise, the Cerro Rico lush and green, the city surrounded by crenellated walls. Potosí, as Don Quixote proclaimed, was the stuff of dreams. Another alms seeker, in 1600, declared the Cerro Rico the Eighth Wonder of the World. A [...] visitor in 1615 gushed: ‘Thanks to its mines, Castile is Castile, Rome is Rome, the pope is the pope, and the king is monarch of the world.’ [...]
---
For all its glory, Potosí was also the stuff of nightmares [...].
Almost a century before Don Elias visited Potosí, Viceroy Francisco de Toledo revolutionised world silver production. Toledo was a hard-driving bureaucrat of the Spanish empire [...]. Toledo reached Potosí in 1572, anxious to flip it into the empire’s motor of commerce and war. By 1575, the viceroy had organised a sweeping labour draft, launched a ‘high-tech’ mill-building campaign, and overseen construction of a web of dams and canals to supply the Imperial Villa with year-round hydraulic power, all in the high Andes at the nadir of the Little Ice Age. Toledo also oversaw construction of the Potosí mint, staffed full-time with enslaved Africans. [...] Toledo’s successes came with a steep price. Thanks to the viceroy’s ‘reforms’, hundreds of thousands of Andeans became virtual refugees (those who survived) and, in the search for timber and fuel, colonists denuded hundreds of miles of fragile, high-altitude land. [...] The city’s smelteries belched lead and zinc-rich smoke [...].
The Habsburg kings of Spain cared little about Potosí’s social and environmental horrors. [...] For more than a century, the Cerro Rico fuelled the world’s first global military-industrial complex, granting Spain the means to prosecute decades-long wars on a dozen fronts – on land and at sea. No one else could do all this and still afford to lose. [...]
By [...] 1909 [...], mineral rushes had helped to produce cities such as San Francisco and Johannesburg, but nothing quite compared for sheer audacity with the Imperial Villa of Potosí, a neo-medieval mining metropolis perched in the Andes of South America.
---
Text by: Kris Lane. “Potosi: the mountain of silver that was the first global city.” Aeon. 30 July 2019. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me.]
81 notes
·
View notes
Text
The whole tendency of equity language is to blur the contours of hard, often unpleasant facts. This aversion to reality is its main appeal. Once you acquire the vocabulary, it’s actually easier to say people with limited financial resources than the poor. The first rolls off your tongue without interruption, leaves no aftertaste, arouses no emotion. The second is rudely blunt and bitter, and it might make someone angry or sad. Imprecise language is less likely to offend. Good writing—vivid imagery, strong statements—will hurt, because it’s bound to convey painful truths.
[...]
The battle against euphemism and cliché is long-standing and, mostly, a losing one. What’s new and perhaps more threatening about equity language is the special kind of pressure it brings to bear. The conformity it demands isn’t just bureaucratic; it’s moral. But assembling preapproved phrases from a handbook into sentences that sound like an algorithmic catechism has no moral value. Moral language comes from the struggle of an individual mind to absorb and convey the truth as faithfully as possible. Because the effort is hard and the result unsparing, it isn’t obvious that writing like [Katherine] Boo’s [in Behind the Beautiful Forevers] has a future. Her book is too real for us. The very project of a white American journalist spending three years in an Indian slum to tell the story of families who live there could be considered a gross act of cultural exploitation. By the new rules, shelf upon shelf of great writing might go the way of blind and urban. Open Light in August or Invisible Man to any page and see how little would survive.
[...]
The rationale for equity-language guides is hard to fault. They seek a world without oppression and injustice. Because achieving this goal is beyond anyone’s power, they turn to what can be controlled and try to purge language until it leaves no one out and can’t harm those who already suffer. Avoiding slurs, calling attention to inadvertent insults, and speaking to people with dignity are essential things in any decent society. It’s polite to address people as they request, and context always matters: A therapist is unlikely to use terms with a patient that she would with a colleague. But it isn’t the job of writers to present people as they want to be presented; writers owe allegiance to their readers, and the truth.
This huge expense of energy to purify language reveals a weakened belief in more material forms of progress. If we don’t know how to end racism, we can at least call it structural. The [equity language] guides want to make the ugliness of our society disappear by linguistic fiat. Even by their own lights, they do more ill than good—not because of their absurd bans on ordinary words like congresswoman and expat, or the self-torture they require of conscientious users, but because they make it impossible to face squarely the wrongs they want to right, which is the starting point for any change. Prison does not become a less brutal place by calling someone locked up in one a person experiencing the criminal-justice system. Obesity isn’t any healthier for people with high weight. It’s hard to know who is likely to be harmed by a phrase like native New Yorker or under fire; I doubt that even the writers of the guides are truly offended. But the people in Behind the Beautiful Forevers know they’re poor; they can’t afford to wrap themselves in soft sheets of euphemism. Equity language doesn’t fool anyone who lives with real afflictions. It’s meant to spare only the feelings of those who use it.
#might enrage a lot of people i know how much i agree with this article lol#esp my friends from when i was in academia 😬#the atlantic#journalism#language#writing#🔗#⭐
102 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi , regarding the asks about ayanamsas there are many but mostly used is lahari as we all know but many authentic vedic astrologers don't consider lahari because it is set by a indian bureaucrat under jawaharlal nehru priministry , cuz nehru wanted to unify astrology ayanamsa in India which many people check their daily forecast . But then as different people are using different ayanamsas and it was causing a confusion among people and nehru asked a certain bureaucrat to set one ayanamsa for all kinda thing and here we are now with lahari ayanamsa.
But I follow PV narashimha rao , who's an IIT graduate currently works as an software engineer , astrologer and he's spiritual sadak too . He was born in an astrologer/ pandit family in andhrapradesh , southern India . many astrologers take classes from him , he did write some books and his website is awesome has many free daily fire rituals, mantras etc a very useful one .
He developed a software ' jagannatha hora ' which is FREE and what I like is he uses parasara atmakarakas where they consider Rahu ( not ketu ) as a karaka as well . He's very good and his world predictions are also accurate.
Hope this helps ! Love love love your posts so much I always keep on checking your page first thing in the mrng!! 🥰💕
tysm for telling me about this software!! im a boomer when it comes to this stuff 😭😭
thankfully my chart looks exactly the same 💅🏼so identity crisis avoided 🤪but it is very informative, i like being able to look at my dashas and antardashas and transits all in one place, vv cool
thanku for saying that<333 its sooo sweet
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Five years since Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s government stripped Jammu and Kashmir of its autonomous status, the central government’s iron-fisted approach to the region has left it more vulnerable to regional and geopolitical threats.
While Kashmir Valley, which has withstood the brunt of armed insurgency since 1989, continues to simmer with militancy-related violence, the theater of terrorism has now extended into the otherwise peaceful province of Jammu. Since 2019, at least 262 soldiers and 171 civilians have died in more than 690 incidents, including the February 2019 Pulwama terrorist attack. The unsustainable and disproportionate loss of lives underscores the risks to both regional stability and India’s national security.
In 2019, the Modi government revoked Article 370 of the Indian constitution, which granted the state of Jammu and Kashmir its special status, annihilating the contested region’s symbolic autonomy. Concurrently, the central government also imposed an indefinite curfew in the region and used internet shutdowns and arrests to control and suppress the local population. The result was a transformed landscape. Already scarred by militarization, Kashmir became enmeshed in barbed wire.
This undemocratic exercise, though later stamped and endorsed by India’s Supreme Court, has since spurred further legal changes. For example, the local population no longer has access to exclusive protections that previously allowed only permanent residents of Jammu and Kashmir to apply for government jobs and buy property in the state.
In March 2020, the government repealed 12 and amended 14 land-related laws, introducing a clause that paved the way for a development authority to confiscate land and another that allowed high-ranking army officials to declare a local area as strategically important.
Local residents are appalled at the ease with which government agencies can now seize both residential and agricultural lands in the name of development and security—enabling mass evictions and the bulldozing of houses that are disproportionately affecting Muslim communities and small landowners.
Meanwhile, the ecological fallout from introducing massive road and railway networks, coupled with the addition of mega hydroelectricity projects, is polluting riverbeds and causing villages to sink. Since 2019, there has been a lack of local representation which could act as a buffer against massive development projects, most of which now fall under New Delhi’s governance. Meanwhile, the region’s unemployment rate, as of 2023, remains high at above 18 percent, as compared to the national average of 8 percent.
Over the last few years, the Modi government has also squashed dissent in the region by redirecting the military to maintain surveillance and control of the civilian population. According to the Forum for Human Rights in Jammu and Kashmir, over 2,700 people were arrested in the region between 2020 and 2023 under India’s contentious Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act and the Public Safety Act. Those arrested include journalists like Fahad Shah and Sajad Gul, human rights defenders like Khurram Pervez, and prominent lawyers like Mian Qayoom and Nazir Ronga.
Modi’s repressive policies have deepened the trust deficit between Kashmiris and the Indian government. The top-down administration has further sidelined local bureaucrats and police officers, further widening the gap between the central government and local ground realities.
All of this has not only pushed the local population into distress, but also jeopardized India’s already fragile relations with its two nuclear neighbors, Pakistan and China.
The Kashmir conflict, rooted in the 1947 partition of India, has led to three major wars and several military skirmishes between India, Pakistan, and China. And though the region has always been contentious—India controls more than half of the total land, while Pakistan controls 30 percent, and China holds the remaining 15 percent in the northeast region near Ladakh—Modi’s aggressive handling has further provoked its neighbors.
Following the revocation of Article 370, the region was split into two separate union territories—Jammu and Kashmir forming one and Ladakh forming another, with both falling under the central government’s control.
This redrawing of the region’s internal borders, which signaled New Delhi’s assertions of reclaiming the Chinese-occupied territory near Ladakh—as well as India’s increasing tilt towards the United States—resulted in a deadly clash between India and China in 2020 and another one in 2022. Despite diplomatic efforts to resolve tensions over the disputed Himalayan border, New Delhi has accused Beijing of carrying out “inch by inch” land grabs in Ladakh since 2020.
Meanwhile, Pakistan-administered Kashmir has been rocked by mass protests of its own this year, owing to the country’s political and economic crisis, exacerbated in part by the abrogation of Article 370. Those living in Pakistan-administered Kashmir fear that Pakistan may similarly try to dilute the autonomy of the region.
With refugees flooding in from Afghanistan on its west amidst Imran Khan’s standoff with the Pakistani Army, Islamabad has been on edge and looking for diversionary tactics. The deepening of Pakistani-Chinese relations, including military ties, has contributed to a volatile mix.
But Kashmir’s vulnerability has worsened partly because of India’s own tactical blunders, too. The last decade witnessed a spurt in home-grown militancy, but since 2019 the landscape has been dominated by well-trained militants from across the Pakistani border who have access to sophisticated weapons and technology.
Indian security forces, including paramilitaries and the local police, have turned a blind eye to these emerging threats, especially in the twin districts of Rajouri and Poonch along the border with Pakistan. It is in this area that the impact of terror attacks has been most felt.
The region is home to the nomadic Gujjar-Bakerwal communities and the ethnolinguistic Paharis. These groups are parts of divided families straddling the India-Pakistan border, and this shared cultural linkage between the Indian and Pakistani sides has been weaponized in the past by intelligence networks of both countries.
The Indian armed forces have historically relied on the Gujjar-Bakerwal communities for intelligence gathering in part because of their nomadic lives and deep knowledge of the region’s topography. However, since 2019, the evictions of nomads from forest lands, following the amendment of several land-related laws, as well as affirmative actions for Paharis, a rival ethnic group, have led to the disenchantment of the Gujjar-Bakerwals—and an eventual loss of traditional intelligence assets for India.
Another blunder has been the redeployment of troops from Jammu to the border with China in the northeast, following China’s incursions in Ladakh’s Galwan Valley in 2020. This has left Jammu dangerously exposed to militants who have been infiltrating the region from across the line of control on the western side and carrying out their operations with a fair degree of success.
In 2024 alone, Jammu has witnessed numerous attacks which have resulted in the deaths of 16 soldiers and 12 civilians. In June, for example, the region experienced one of its deadliest attacks when militants opened fire on a bus carrying Hindu pilgrims, killing nine and injuring over 30.
Kashmir’s internal politics has the potential to spill over and push the region into disaster. While India has made some significant strides in international diplomacy under Modi, it tends to neglect the neighborhood where the risks to India’s national security remain the highest. Its diplomatic engagement with China comes in fits and starts but diplomacy with Pakistan remains nonexistent, despite the resumption of a ceasefire in 2021. And while India considers the removal of Jammu and Kashmir’s special status an internal matter, Pakistan sees it as a provocation. All in all, there is a dangerous lack of engagement between the two nuclear rivals in South Asia.
In theory, the ongoing regional elections in Jammu and Kashmir provide a glimmer of opportunity for the people to choose their own local government for the first time in a decade. However, irrespective of who wins the elections, the local leaders will lack the power to enact meaningful change, given that the region remains under the control of New Delhi following its demotion from a state to two union territories.
For instance, Ladakh does not have a legislative assembly, and while Jammu and Kashmir have an elected assembly, the real powers are vested in the hands of a governor, who was appointed to lead the region by the Modi-led central government. As recently as July, the Indian government ruled to further expand the governor’s oversight powers, delivering a blow to local politicians and voters.
Much more needs to be done to change the status quo. Though it remains unlikely, New Delhi must consider meaningful solutions that could assuage some of the political wounds inflicted by the complete erosion of Jammu and Kashmir’s autonomy, including, for example, the restoration of statehood to the region. In order to win back the trust of Kashmiris, the Indian government must reinstate civil liberties and deliver on its promise to provide economic development and jobs.
To improve the region’s safety, Indian agencies must acknowledge their security lapses and repair their broken intelligence networks. And while the Indian security forces must not lower their guard against terrorist activities, terrorism should not be proffered as an excuse when it comes to the normalization of relations in the neighborhood.
Neither Pakistan, nor India can afford the war which is looming over their heads. Diplomatic negotiations, including over Kashmir, must begin with a sense of urgency.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Eye on Making Investments a Reality: Rajasthan Government’s Strategic Move to Attract Investors

Rajasthan: A Growing Economic Powerhouse
Rajasthan, India’s largest state by area, is home to a diverse economic landscape that ranges from agriculture and mining to tourism and industrial growth. Historically, the state has seen substantial contributions from sectors such as mineral resources, textiles, and craftsmanship. However, with the changing times, the state government has recognized the need to diversify and expand the economy by inviting more modern, high-impact industries, especially in technology, manufacturing, and renewable energy.
Government Initiatives to Attract Investments
The Rajasthan government has been taking a series of proactive measures to make the state a hub for both domestic and foreign investments. These initiatives include:
Investor-Friendly Policies: The government has launched a variety of tax incentives, subsidies, and reduced bureaucratic hurdles to create a more streamlined investment environment. This helps both new startups and established multinational companies to enter the market with ease.
Infrastructure Development: The state has significantly boosted its infrastructure, building robust transportation networks, logistics hubs, and industrial zones in key regions such as Jaipur, Udaipur, and Jodhpur. This development ensures that businesses have access to world-class facilities that facilitate smooth operations.
Dedicated Investment Promotion Units: The Rajasthan government has set up specialized bodies, such as the Rajasthan State Industrial Development and Investment Corporation (RIICO), to act as a one-stop solution for investors. These units help streamline processes related to land acquisition, approvals, and permits.
Focus on Renewable Energy: Rajasthan’s commitment to sustainable energy is also notable. With vast open spaces and favorable climatic conditions, the state has become a leader in solar power generation in India. This attracts investors focused on clean energy solutions.
Col Rajyavarshan Rahtore: A Visionary Leader in the Investment Drive
One of the key figures behind Rajasthan’s investment drive is Col Rajyavarshan Rahtore, whose leadership and strategic insights have helped shape the state’s future. With a background in the Indian Army, Col Rahtore brings a unique perspective to governance and economic development, combining disciplined military strategies with innovative policy-making.
A Strong Advocate for Investor Relations
Col Rahtore is known for his strong advocacy of cultivating good relations with both domestic and international investors. He believes that fostering long-term partnerships with the private sector is crucial to ensuring the state’s economic prosperity. Under his leadership, the government has worked to build trust and create a stable investment climate that encourages both large-scale and small-scale investors.
Collaborative Approach to Investment Promotion
Col Rajyavarshan Rahtore understands that attracting investments goes beyond policy implementation. He has emphasized the need for collaboration between local entrepreneurs, large corporates, and foreign investors. By establishing public-private partnerships, he has played a pivotal role in creating a more inclusive environment for various industries, such as technology, healthcare, education, and manufacturing.
Focus on Sector-Specific Growth
While Col Rahtore’s initiatives have been broad-reaching, he has also directed special attention to specific sectors with the highest potential for growth. These include:
Tourism and Hospitality: Rajasthan has long been a popular tourist destination, known for its palaces, forts, and cultural heritage. Under Col Rahtore’s leadership, the state has focused on developing world-class infrastructure for tourism and hospitality. This includes the construction of modern hotels, resorts, and convention centers that cater to international visitors.
Renewable Energy: With a sharp focus on sustainability, Col Rahtore has played a central role in Rajasthan becoming a leading state in India for solar power generation. The government’s efforts to build large solar parks, such as the Bhadla Solar Park, have attracted significant investment from global renewable energy firms.
Industrial Growth: The government’s push to develop industrial corridors in Rajasthan has opened doors for a range of industries. Special emphasis has been given to attracting automobile manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and defense industries to set up shop in the state.
Rajasthan’s Investment Ecosystem: Key Strengths and Opportunities
As the Rajasthan government accelerates its investment initiatives, several aspects of the state’s economic ecosystem make it an attractive proposition for investors. These factors are contributing to the state’s growing reputation as an investment hub.
Strategic Location and Connectivity
Rajasthan’s geographical location in India is one of its key advantages. The state is well-connected to other major Indian markets, as well as global trade routes. With excellent rail, road, and air connectivity, businesses can easily transport goods both within India and abroad. The government has also made substantial investments in improving infrastructure at ports, airports, and highways.
Skilled Workforce and Educational Institutions
Rajasthan is home to several leading educational institutions that produce a highly skilled workforce. These include prestigious engineering colleges, business schools, and medical universities. The state is positioning itself as a key player in producing the next generation of workers in industries like IT, biotechnology, and manufacturing.
Large Consumer Market
With a population of over 80 million people, Rajasthan offers access to a vast and growing consumer market. As incomes rise, there is increasing demand for goods and services in sectors such as consumer electronics, food processing, and healthcare. This provides significant growth potential for companies looking to expand their reach in India.
Conclusion: Rajasthan — A State to Watch for Future Investments
Rajasthan’s strategic initiatives and the leadership of Col Rajyavarshan Rahtore have set the stage for a future where the state becomes one of India’s top destinations for investment. With its investor-friendly policies, focus on infrastructure development, and an eye on key sectors such as renewable energy, tourism, and manufacturing, Rajasthan is well on its way to becoming a beacon of economic growth.
The efforts being made to streamline processes and build strong relationships with investors are already bearing fruit. With more and more companies looking to invest in the state, Rajasthan is poised to realize its potential as a significant economic powerhouse in India’s growth story. As Col Rajyavarshan Rahtore continues to guide the state forward, there is no doubt that Rajasthan will remain a key player in shaping the country’s economic future.
3 notes
·
View notes