#high pressure gas cylinder valves
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
0 notes
Text
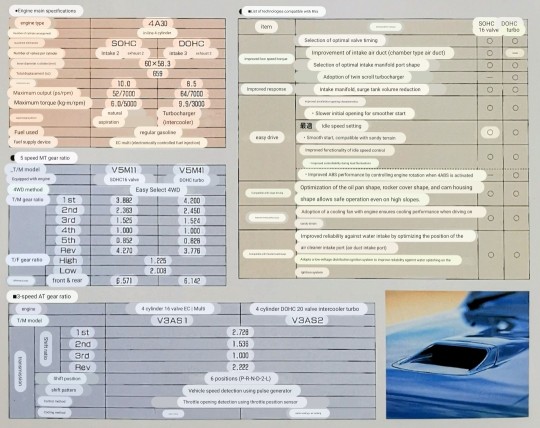
Engine specs for the 1st Gen Mitsubishi Pajero Mini.
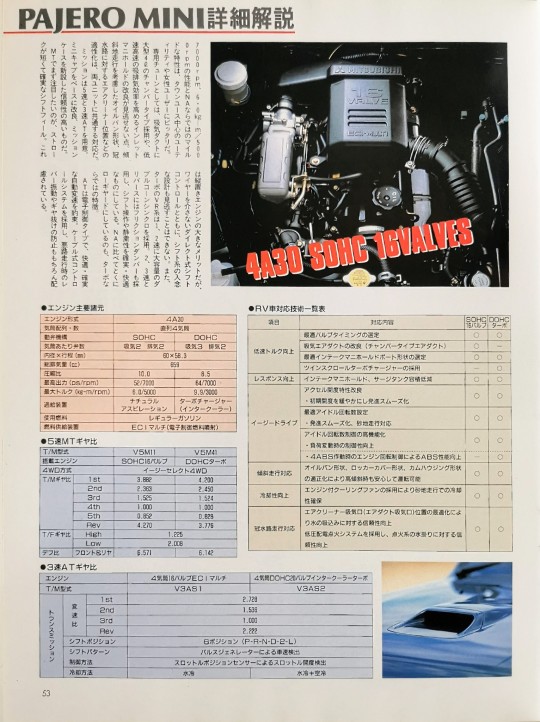
Pajero Mini Detailed explanation
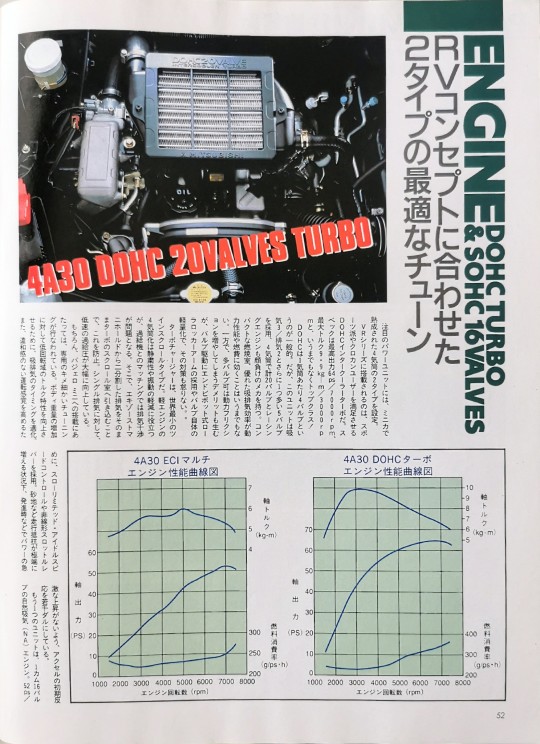
ENGINE 20VDOHC TURBO & SOHC 16VALVES
Two types of optimal tunes to suit your RV concept
Two types of 4-cylinder engines are available as the featured power units.
The VR series is equipped with a DOHC intercooler turbo that will satisfy sports enthusiasts and cross country users. The specs are top-class, with a maximum output of 64ps/7000rpm and a maximum torque of 9.9kg-m/3000rpm!
DOHC has 5 valves per cylinder.
Uno is common. However, this unit uses 3 intake/exhaust valves and an additional 5 valves, making it 4 cylinders with a total of 20 valves, and has a mechanism that rivals even racing engines. It goes without saying that the compact combustion chamber and excellent intake and exhaust efficiency improve power performance and fuel efficiency. On the other hand, having multiple valves has the disadvantage of increasing power friction, but we have taken measures to counter this by adopting an end-pivot type roller rocker arm to drive the valves and reducing the weight of the valves themselves. .
The turbocharger is the world's smallest twin-scroll type. Converting a light engine to a four-cylinder engine is useful for making it quieter and reducing vibration, but exhaust interference becomes a problem when matching it with a turbocharger. To prevent this, the exhaust gas is divided into two parts from the exhaust manifold and drawn directly into the turbo's scroll chamber. Low-speed boost pressure is significantly improved compared to single exhaust.
Of course, when installed in the Pajero Mini, special and detailed tuning has been performed. Intake and exhaust timing has been optimized to improve torque characteristics in the low rotation range despite the increased body weight.
In addition, to enhance the driving sensation without discomfort, To achieve this, a slow limited idle speed control and a non-linear throttle lever have been adopted. In situations where running resistance is extremely high, such as on sandy terrain, the power may suddenly be applied when starting, etc.
The initial response of the accelerator is made slightly duller to prevent sudden increases.
The other unit is a single overhead-cam, 16-valve naturally aspirated (NA) engine. 52ps/7000rpm、6.0kg-m/5000
The rpm performance and the mileage characteristics unique to NA are perfect for utility vehicles mainly used around town and for female users.
Not to be overlooked are the adoption of a large 4-liter chamber type in the intake duct and improvements to the inlet manifold that increase intake and exhaust efficiency at low and high speeds. The shape of the oil pan takes into account driving on slopes, and the positioning of the air cleaner relative to submerged waterways is a common feature of both units.
Transmission options include 5-speed and 3-speed AT. Improved mission based on minicab
It has a new case and is highly reliable. The first thing to pay attention to when using MT is the straw.
Short and reliable shift feel. This is a major advantage of a longitudinally mounted engine, but the careful design of the shift system, along with the direct shift control without wires, cannot be overlooked. Additionally, the VR turbo's system uses large-capacity double cone synchronizers in 1st and 2nd gears. Friction dampers are also used in 2nd and 3rd gear and reverse, making shift operations and quietness reliable and comfortable. Another characteristic unique to turbos is that they have a particularly low gearing compared to NA.
AT is an electronically controlled type that promises comfortable and reliable automatic gear shifting. A cable-type control system is used to prevent lever vibration and gear slippage when driving on rough roads.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
[img ID: a reply from @skellagirl that reads “the shop I go to always tells us to ONLY get gas from chevron or shell because it’s ‘the best gas’ and putting cheap gas in our cars will fuck it up. I’ve never heard that before and it seems like bullshit to me but??? is there any truth to it” end ID]
Okay, so, yes and no. Yes, low quality gas can cause issues (most notably and immediate is lower MPG). But, there’s really no reason to go to specific brands of gas station. My guess is your mechanic is telling you to go out of your way to get Top Tier graded gas, which will actually improve the longevity of your car, but it’s definitely an “in the long run” thing, not an immediate. I know Shell does Top Tier because my father being the car geek he is will ONLY put Top Tier in his car (which to be fair is a Porsche Cayenne (but it’s an ‘08 he got with 150k miles on it so y’know. It’s really not that fancy)) & he only goes to this one specific Shell station in town. Other stations do Top Tier—I know if you’re in the Midwest most Meijer gas stations & Get Go stations have Top Tier. The symbol you’re looking for is like this one:

It’s likely on their pumps somewhere, but you can actually Google Top Tier gas and go to their website and it’ll give you a list of stations that have this certification.
The certification basically means that the gas station in question subjected the gas it sells to a bunch of testing and this company is like yup, that gas is good gas. It usually means it has certain additives like detergents in it, which can help with the longevity of your engine by breaking up engine deposits & preventing future ones, and protect your valves n shit. If you want to get into the nitty gritty of it I’d recommend going to their website and looking into it, but it’s not that important. The point is that like, yeah, if you can go out of your way to put top tier gas in your car you probably should, but I know I don’t and like. It’s fine. I wouldn’t worry about it too much.
THAT SAID, you know how the gas pumps have the three buttons, usually something along the lines of unleaded, plus/mid-grade, and premium? Unless your car specifically calls for premium fuel, which it will probably say so on your gas cap or inside of the little door that covers it (and unless you’re driving a luxury vehicle or a higher-end model, it probably doesn’t), you don’t need mid-grade or premium fuel.
The rest of this post is an explanation on why and it isn’t vital information, it’s just interesting to me, and I also let it get away from me so it’s kinda long & also you get a lesson on how engines work. Sorry not sorry.
The only thing that sets apart regular unleaded from mid-grade and premium is its octane level—the number you see on the little buttons you press to choose the grade. Usually the numbers are 87, 89-90, and 91-94 (though generally it’s 93.) (Sometimes you’ll see other wack numbers for specialty fuels, like 88, or higher octane levels ranging from 96-120. The 88 is usually ethanol-free which as far as I’m aware is only a necessity if your car was manufactured before a certain year or, again, if your manufacturer specifically calls for it. The high octane fuels in the 96-120 range are racing fuels, and if you need that fuel you know more about cars than I do, so… yeah. All that’s to say you can pretty safely ignore those.)
Here’s an explanation on what those numbers mean: basically, it’s a measurement of how much pressure the gas needs to be under before it will spontaneously combust. The lower the octane rating, the lower the pressure necessary. Because cars run on combustion engines (unless you drive an EV of course), you do want it to combust, but you run into trouble if the gas starts to ignite before it should.
You know how you have spark plugs in your engine? Those, indeed, spark, and the spark ignites the gas in the cylinder, which sends the piston back up the cylinder, turning the crankshaft, which ultimately turns a bunch of shit and makes your car go. Here’s a gif!
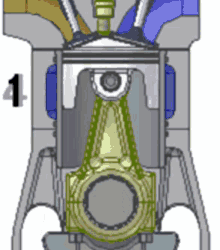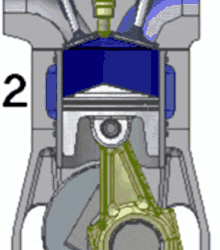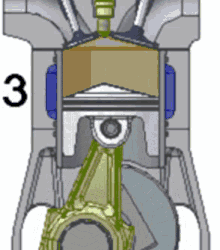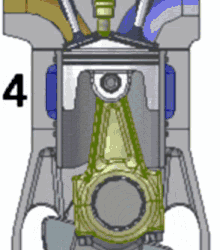
Since they’ve so kindly numbered each step, let’s go through it:
The piston slurps some gas (the blue fluid in the gif) into the cylinder through the valve.
The piston compresses the gas. At the piston’s highest position, the spark plug sparks, igniting the gas.
The ignition is basically a small explosion, and that pushes the piston back down, leaving burnt fuel (ultimately, exhaust; the brown stuff in the gif) in the cylinder.
The piston comes back up, pushing the exhaust out of the cylinder, before starting all over again.
Now, what does that have to do with octane rating? Remember, octane rating is a measurement of how much pressure it takes to SPONTANEOUSLY combust the gas. You don’t want it to spontaneously combust; you want the spark plug to do that. What ends up happening is the cylinder pushes the gas enough that it spontaneously combusts before the piston hits its highest point & the spark plug sparks, which ultimately causes what’s called “engine knock.” It’s a very recognizable pinging sound caused by unnecessary stress being put on the piston; it’s being pushed down while it’s still on the upstroke. Here’s another gif:
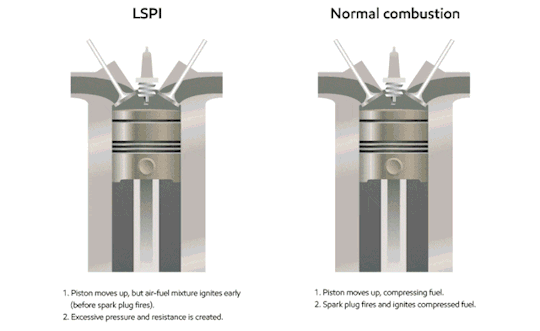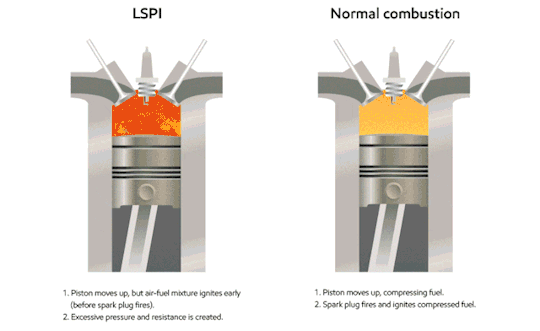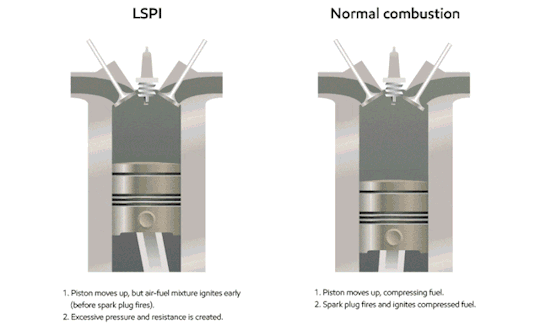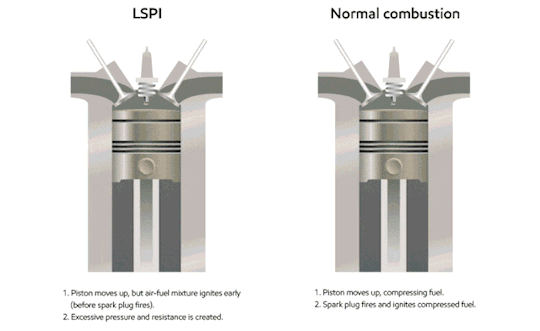
As you can imagine, this is bad for your engine, and terrible for your fuel economy. This is why if your vehicle does recommend you use premium fuel, you should. If your manufacturer is calling for it, your engine can generate enough pressure to spontaneously combust regular unleaded gas.
That said, most standard engines don’t generate enough pressure for it to cause regular unleaded gas to spontaneously combust, which is why you don’t need to spend the extra money if your car doesn’t explicitly call for it.
Alright cool thanks for coming to my post about engines & gas ily bye
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's not unusual for hot water cylinders to make some noise during normal operation. However, certain noises can indicate problems that require attention.
This guide will help you with understanding the reasons behind why your hot water cylinder is making a noise and how to fix it.
Here are some common causes of noises from your hot water cylinder and what they might signify:
Sediment Buildup
Over time, sediment from your water supply can accumulate at the bottom of the cylinder. As the element heats the water, it can hit this sediment, causing clicking, cracking, or rumbling noises. Flushing the tank yearly helps prevent excessive buildup.
Expansion and Contraction
As water heats and cools, it naturally expands and contracts. You might hear creaking or groaning noises coming from the tank as the metal walls react to these temperature changes. This usually poses no threat unless very loud or frequent.
Element Failure
Do you wonder why is my hot water cylinder making a humming sound? If you hear sizzling, buzzing, or humming coming from the cylinder, the electric heating element could be failing or shorting out. This is where a hot water tank sounds like a kettle. Have a professional inspect and test the element for faults. Leaving a failing element unattended risks fire or shock.
Loose Parts
Various valves, pipes, and fittings connect to the water heater. If any of these components become loose due to corrosion, vibration, or improper installation, they can rattle or knock as water flows through the tank. Tightening any loose parts typically eliminates noise. But if you don’t have any expertise, you need to get the help of a hot water cylinder repairs specialist.
High Water Pressure
Excessive water pressure entering or leaving the cylinder strains many internal parts. This extra stress can lead to unusual noises like banging or high-pitched squealing. Installing a regulator moderates pressure for quieter function.
In rare cases, loud rumbling or roaring resembling a jet engine can signal a dangerous flammable hydrogen gas buildup inside the tank. This warrants immediate professional assistance. Do not attempt to operate electrical switches or test the element yourself under these circumstances.
Hot Water Solutions
3d Taid Place, Rosedale, Auckland 0800497658
https://www.instagram.com/pete_hotwatersolutions/?hl=en
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Product Description ✔ Soletal DOUBLE BARREL FOOT PUMP ADVANTAGES: Ergonomic double cylinder design, faster pumping than normal single barrel pump. 2 universal Presta and Schrader valves, dual use, American and French mouth, no need for conversion. Presta valve is suitable for French style bikes, while Schrader valve is suitable for American style bikes, please confirm the bike style before pumping. 3 different types of nozzles to meet all your needs.Foldable and compact design, easy storage and space saving.Made of quality heavy metal, which makes it sturdy and durable. Non-slip foot pedal, just press the lever of the floor pump and the airflow will start, with a large foot pedal and a non-slip mat. Slide safety lock, designed with built-in pedal slide safety lock, to keep the body stable and prevent it from suddenly popping out when bent. Widely used: For car/SUV/RV tires, bicycles/bicycle tires, sports equipment, inflatable toys, etc. High pressure up to 11Bar / 160PSI, more air pressure, less leaks, and helps pump the right pressure, avoids accidental tire blowouts. Ergonomic double cylinder design, pumping faster than normal single barrel pump Instructions: Select the correct gas nozzle, insert the inflatable head Open the fixing lock, fix before inflating Just step on the non-slip pedal on the floor pump with gauge to start pumping air After filling, restore the state of relaxation Soletal Double Barrel Floor Pump HOW TO OPERATE THE NOZZLE? 1. unlock (press the button on both sides of the air pump at the same time as shown) 2. screw the nozzle onto the valve (do not deflate by tightening) 3. lock and start inflating (use your foot to press easily, inflate quickly). THE DETAILS OF OUR DOUBLE CYLINDER QUICK PUMP: - Equipped with high pressure barometer: High pressure up to 11Bar / 160PSI, more air, less leaks, and helps to pump the right pressure, prevent accidental punctures. Accurate Pressure Gauge High pressure capacity foot air pump (max. 160 PSI / 11 Bar) with pressure gauge, accurate air pressure can be displayed when inflated, which can prevent accidental tire burst. It is perfect for indoors and outdoors Dual Valve The 2-in-1 designed valve head makes it easy to change from India valves to India valves, without component conversions and without any air leaks. The Presta valve is suitable for French style bikes, while the Schrader valve is suitable for Indian style bikes.
Compact Structure Double thickened cylinder, precise pressure gauge, double valve compatible with presta and schrader, durable and highly elastic spring, safe non-slip pedal, double-sided zipper and durable rubber tube, including 1 sport ball needle and 2 valves for inflatable device. Laptop Size The double-barrel bicycle pump is 11.8 inches long and 4.92 inches wide, its rubber tube is 29.5 inches long and weighs 4 pounds. Foldable and compact, it stores easily and saves space. Various Applications: Compatible with universal Presta and Schrader valves, Soletal foot air pump can inflate bicycles, electric vehicles, cars, motorcycles, gas strollers, wheelchairs, air cushions, swimming rings , basketball, football, life rings, inflatable beds and all inflatable ball toys. ✔【DOUBLE-CYLINDER FASTER PUMP】: The double barrel bike pump is made of quality heavy metal, which makes it sturdy, durable, anti-corrosion. And it adopts strengthened Double-cylinder, more air pressure, less leaking, can pump quickly. Besides, the spring is made of steel ensures a fast return of the piston, so it can provide super-high pressure during pumping; ✔【COLLAPSIBLE AND DURABLE】: The bike floor pump is designed with folding switch, simple to open and close, and it can be storage easily and small package; Foot pump design makes easier and labor-saving, refuse to bend down. Bike pump is made of quality metal which make the pedal return quickly. Perfect for travelling or home use,convenient to fold and store. ✔【HIGH PRESSURE UP TO 11 BAR / 160 PSI】: The pressure of our foot air pump can reach to 11 BAR / 160 PSI, So you can pump your bicycle quickly and easily. Besides, you can know your tire pressure at real time through the precise calibrated dial, making it easier to visually see and fit easily into the proper pressure prevents accidental tire blowouts, it's very suitable for indoor and outdoors; ✔【SAFE ANTI-SKID PEDAL】: The pedal adopts anti-skid design to prevent slipping during pumping, can also let you fast inflate and saving energy. The air pipe joint adopts thread design, the pipe can be fixed well, it can be took apart easily, and it can also prevent frostbite which can be used in the cold winter; ✔【WIDE APPLICATIONS】: This bicycle tire pump has Presta & Schrader valve, no conversion, saving time and effort, which can be used for baby carriages gas-filled, wheelchairs, bicycles aeration, mountain bikes, motorcycles aerated, electric vehicles , ball inflatable toys, inflatable bathtubs, swimming pool buoys, etc., Suitable for indoor and outdoor use. double cylinder pressure pump to help you pumping easily. [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
Internal Combustion Engine
Introduction

Internal combustion engine (ICEs), which power around 250 million roadway cars in the US alone, have been the foundation of industrial and transportation uses for more than a century. They are a powerful force in the automotive industry because of their durability, driveability, and compatibility with a wide range of fuels, including ethanol, natural gas, propane, diesel, gasoline, and biodiesel. Additionally, they can be included in plug-in hybrid and hybrid systems to improve range and fuel economy. Internal combustion engines are under increased scrutiny because of environmental concerns and the growing demand for greener alternatives, despite their extensive use and benefits.
Internal Combustion Engine Classification

Continuous combustion engines and intermittent combustion engines are the two main types of internal combustion engines that are distinguished by their combustion mechanisms.
1. Engines with Continuous Combustion
Fuel and oxidizer are continuously injected into these engines, maintaining a constant flame. Two of the best examples of continuous-combustion engines that are frequently used in industrial and aerospace settings are gas turbines and jet engines.
2. Engines with intermittent combustion
Conversely, the air-fuel combination is ignited in cycles by intermittent-combustion engines, commonly referred to as reciprocating engines. This group includes diesel and gasoline piston engines, which produce power by burning fuel in precise order.
The Internal Combustion Engine’s Operating Principles
The basic chemical process of combustion, in which fuel and oxygen combine to create energy, is at the heart of internal combustion engines. ICEs use direct fuel combustion to produce energy inside, as opposed to external combustion engines like steam engines.
An ICE is made up of a moving piston and a stationary cylinder. The crankshaft is turned by the piston’s movement, which is pushed by expanding combustion gases. The powertrain then uses this mechanical energy to drive the wheels of the vehicle.
Currently, there are two main categories of ICEs in production:
Spark-Ignition Gasoline Engines: These engines use a spark plug to ignite a mixture of gasoline and air before compression.
Diesel engines that use compression ignition only compress air before injecting high-pressure fuel, which ignites on its own because of the heat generated during compression.
The four-stroke cycle used by the majority of ICEs consists of four crucial stages:
The Cycle with Four Strikes
Stroke of Intake: The piston is close to the top dead center (TDC) at the start of the intake stroke. The piston descends as the intake valve opens, bringing in fuel and air (or just air in diesel engines). For the combustion chamber to receive a new charge, this stroke is necessary.




An engine cycle needs two full crankshaft revolutions (720°), and only one power stroke produces torque; the other strokes use energy.
Internal Combustion Engine Components
Important elements of an ICE consist of:
Cylinder Head: The camshaft, valves, valve buckets, return springs, spark plugs for gasoline engines, and fuel injectors for direct injection engines are all housed in the cylinder head. Additionally, it has engine coolant tubes.
Engine Block: The crankshaft, connecting rods, pistons, and cylinders make up the engine block. To regulate temperature, it also makes coolant flow easier.
Combustion Chamber: The combustion chamber is the area between the piston, cylinder head, and engine block where air-fuel combustion takes place.
Internal Combustion Engine Benefits

Compact Size: Internal combustion engines (ICEs) are substantially smaller than external combustion engines.
High Power-to-Weight Ratio: They are appropriate for transport applications due to their high power-to-weight ratio.
Portability: the ability to fit a variety of vehicles and allow for easier carrying.
Fast Start Time: Internal combustion engines (ICEs) may start nearly instantly, in contrast to steam engines.
More Efficiency: Compared to external combustion engines, it offers higher efficiency.
Reduced Maintenance: Needs comparatively less care.
Lower Lubricant Consumption: Lubrication is more effective than in external combustion engines.
Moderate Operating Temperature: In contrast to steam engines, internal combustion engines’ maximum temperatures only last a brief period.
Internal Combustion Engine Drawbacks
ICEs have significant disadvantages despite their benefits:
Limited Fuel Options: Rely on premium gaseous or liquid fuels.
High Fuel Costs: When compared to alternative energy sources, gasoline and diesel are more costly.
Environmental Issues: Compared to external combustion engines, internal combustion engines emit more pollutants.
Noise pollution: reciprocal engines produce a lot of noise during burning.
Power Restrictions: Not recommended for applications requiring a lot of power.
Internal Combustion Engine Applications
Many industries make extensive use of ICEs.
Gasoline Engines: Automobiles, boats, and airplanes all use gasoline engines.
Industries use gas engines to generate electricity.
Diesel engines power large machinery, trucks, ships, and railroads.
Industrial, maritime, and aviation settings employ gas turbines.
Internal Combustion Engines’ Future
Cleaner alternatives are becoming more and more necessary as environmental concerns and resource depletion become more urgent issues. Even with notable improvements in ICE efficiency and emissions management, their dependence on fossil fuels continues to be a major drawback.
To overcome these obstacles, research and development initiatives concentrate on:
Alternative Fuels: Sustainable substitutes include hydrogen, biofuels, and synthetic fuels.
Electrification: hybrid and plug-in hybrid technologies integrate electric motors to lower pollution and fuel consumption.
Advanced Engine Management Systems: Control systems powered by AI increase productivity.
Lightweight Materials: Better materials contribute to a lighter engine, which improves fuel economy.
Aerodynamic Enhancements: Improving a car’s aerodynamics helps it use less fuel.
Conclusion
Internal combustion engines have greatly aided modern industries and transportation. They are essential because of their success, reliability, and adaptability. However, ICEs need to change to be relevant as the world moves toward greener energy alternatives.
As ICE technology advances, attention is turning to more environmentally conscious options. Electric powertrains, hybridization, and advanced fuels are shaping the future of transportation. The long-term sustainability of internal combustion engines will depend on how well we balance environmental responsibility and energy efficiency. The secret to guaranteeing a sustainable and effective future in industry and mobility is to embrace innovation.
#Internalcombustionengine#AutonomousVehicle#sensors#Actuators#Dorleco#CANKeypads#CANDisplays#VCUs#Vehiclecontrolunit#EVSoftwareServices#E/Earchitectures
0 notes
Text
UNDERSTANDING SPARK PLUG TESTER AND CLEANER
In the motor cycle, ignition systems are the one of the most important part, where it ignites for the starting of the engine. Combustion process cannot be able to done, if any problem occurs in this system, which leads engine cannot be able to start. Normally motor cycle riders do not use a proper tool for correcting the issues, in which they are exposed to the unsafety hazards. The main purpose of the tool is to properly diagnose the problem and eliminate them. So here comes the spark plug tester and cleaner, which helps us to test and clear the sparkplug and ignition wire connectivity, which eliminates the risk of high voltage shock.
Motorcycle ignition system consists of three important elements such as ignition, carburetion and lubrication, unlike earlier development of ignition system, which are quite tricky and dangerous. And this system undergoes three elements such as flame, hot tube and magneto ignition. While comparing these two systems, the third part, magneto ignition is commonly processed, because it has the controlled spark that ignites the mixture. These systems use an external power like battery, rather using an internal magnet to create a spark to ignite the mixture. After 1960’s most advanced ignition system has been introduced.

WORKING OF THE SPARK PLUG TESTER AND CLEANER
The Spark Plug Tester and cleaner simulates the condition of the engine. It consists of the pressurized chamber for testing the spark plug. If the plug is not in proper condition, it can be cleaned in the sand blast unit. This unit consists of the compression chamber, ignition coil, cleaner unit assembly, electronic vibrator, pressure gauge and FRP casting. And it is also connected to the compressed air source of range 5–12 Kgf/cm. Booster can be used, if this much level of pressure not achieved.
The Electrical testing unit works on 220V supply, which is fed through a press button switch to the vibrator. The Electronic Vibrator helps in supplying 12V to the ignition coil, then the high voltage produced by the ignition coil is transferred to the spark plug through a high tensioned wire, which is fitted with plug guard.
The compression chamber consists of two test pockets. One for 8mm spark plugs testing and the other is for 14mm spark plugs testing. These two pockets are attached with blind plugs, where one is sealed other one is in use. These plugs have air screws at their top, so that the pressure in the combustion chamber can be adjusted. The spark can be clearly viewed with the help of the mirror attached in the inside chamber.
After completing the spark plug testing, they are placed on the sand blast unit for proceeding the cleaning process. Inside this unit, compressed air creates the blast of sand, to prevents the sand from spilling outside, and also a fabric covers the unit.
Some of the control valves used in this tester are the double action valve, which is for sand and air blast, and screw type air valve is for compression chamber and pressure gauge.
SYMPTOMS OF SPARK PLUGS TO BE TESTED
We can get a visual confirmation regarding the spark plug life, but still for the confirmation in case of working efficiency, we have the regular process. Remove the defected spark plug from the existing cylinder and fit with the other cylinder. So, the defected spark plug is now fixed with another cylinder. After this process gets completed, a test drive is made run, until the defect re appears. If we found the defect again in this cylinder, then there is a problem in the spark plug and this process conformed that the spark plug is really defective. A test drive must be carried out again to re check the problems.
A spark plug can be usually changed every 30000 to 60000 kms or to be changed every 2 to 4 years, and the types of engines also can be considered as another factor for changing the spark plug. Vehicles which uses gas as the fuel, it may also compulsory had to change spark plugs based on the working manual of the different vehicles.
CONCLUSION
Our ATS-ELGI has the Spark Plug Tester and Cleaner machine, which is also known as SPTC. It is very compact in size and very user friendly to operate. Know more details here at Spark Plug Tester and Cleaner.
Other Products:-
Body shop equipment
Wheel Service Equipment
Lifting Equipment
Body Shop equipment
EV Equipment
0 notes
Text
All Types of Valves and Their Uses
Valves control the flow, pressure, and direction of fluids in various industries. Understanding different types of valves and their uses helps in selecting the right one for specific applications. This guide covers all major types of valves, their functions, and best applications.
Types of Valves and Their Uses
1. Gate Valve
Used for on/off control without flow regulation.
Best for water supply, oil & gas pipelines, and industrial applications.
2. Ball Valve
Offers quick shut-off with minimal leakage.
Common in petrochemical, natural gas, and chemical industries.
3. Globe Valve
Provides precise flow control with high pressure handling.
Used in steam, oil refining, and high-pressure water systems.
4. Butterfly Valve
Lightweight with low-pressure drop.
Ideal for HVAC, water treatment, and food processing industries.
5. Check Valve
Prevents backflow in piping systems.
Used in pumping stations, wastewater treatment, and power plants.
6. Diaphragm Valve
Suitable for controlling corrosive and slurry materials.
Common in pharmaceutical, food, and chemical industries.
7. Plug Valve
Ensures tight sealing with minimal maintenance.
Used in oil refineries, gas distribution, and chemical processing.
8. Pressure Relief Valve
Protects systems from overpressure conditions.
Essential for boilers, gas cylinders, and hydraulic systems.
9. Solenoid Valve
Electrically operated for automated fluid control.
Used in irrigation systems, medical devices, and industrial automation.
10. Needle Valve
Provides precise flow control for small applications.
Used in instrumentation, laboratories, and hydraulic systems.
Comparison of Valve Types
Valve TypeKey FeaturesCommon ApplicationsGate ValveOn/Off ControlWater, Oil, Gas PipelinesBall ValveQuick Shut-OffPetrochemicals, ChemicalsGlobe ValvePrecise Flow ControlSteam, Oil RefiningButterfly ValveLightweight, Low-Pressure DropHVAC, Water TreatmentCheck ValvePrevents BackflowPumping Stations, Power PlantsDiaphragm ValveCorrosion ResistantFood, PharmaceuticalsPlug ValveTight SealingOil Refineries, Gas ProcessingPressure Relief ValveOverpressure ProtectionBoilers, Gas CylindersSolenoid ValveAutomated ControlIrrigation, Medical DevicesNeedle ValvePrecise ControlInstrumentation, Labs
FAQ Section
Which valve is best for controlling fluid flow?
Globe valves and needle valves provide precise flow control, making them ideal for industrial and laboratory applications.
What is the difference between a ball valve and a gate valve?
A ball valve offers quick shut-off, while a gate valve provides gradual flow control with minimal pressure drop.
Where are check valves used?
Check valves are used in pumping stations, wastewater systems, and industrial pipelines to prevent backflow.
Which valve is best for high-pressure applications?
Pressure relief valves and globe valves are ideal for high-pressure fluid control in industrial and power plant applications.
Are butterfly valves suitable for large pipelines?
Yes, butterfly valves are preferred for large-diameter pipelines due to their lightweight design and low-pressure drop.
#IndustrialValves#ValveTypes#GateValve#BallValve#ButterflyValve#CheckValve#GlobeValve#DiaphragmValve#SolenoidValve#PressureReliefValve#PipingSolutions#OilAndGas#Manufacturing#MechanicalEngineering#HVAC#Plumbing#IndustrialEquipment#Engineering#SEO#GMBOptimization
0 notes
Text
Rubber Products Manufacturer: A Comprehensive Overview
Arvico is one of India’s leading rubber products manufacturers, exporters, and suppliers specializing in producing rubber diaphragms, rubber sleeves, PTFE components, rubber couplings, and rubber O-rings, among others. With over 50 years of experience, our brand offers customized components that precisely match your needs. We take pride in never compromising on quality, ensuring customer satisfaction and trust.
With a combined rubber industry experience spanning several hundred years, our team takes full ownership of rubber product manufacturing and its applications. We are dedicated to supporting you at every stage, ensuring high-performance solutions tailored to various industries. Passionate about our field, we are committed to delivering innovative rubber solutions that help businesses grow.
Industries Served
Arvico serves a diverse range of industries, including:
Pharmaceutical
Packaging
Oil & Gas
Food Processing
Nuclear
Electrical
Paper Industry
Chemical Processing
Textile Industries
Engineering
Medical & Life Sciences
Construction
Rubber Products and Applications
Rubber Diaphragms
Rubber diaphragms are flexible barriers that provide pressure control in mechanical and fluid systems. Manufactured using high-quality rubber compounds, they are essential in regulating flow, ensuring sealing, and preventing contamination in critical environments. These diaphragms are widely used in pumps, valves, actuators, and control systems where precision and durability are paramount.
Applications:
Utilized in automotive braking systems to enhance pressure modulation.
Used in industrial pumps to maintain fluid integrity and prevent leaks.
Found in medical equipment to enable controlled fluid dispensing.
Rubber Sleeves
Rubber sleeves serve as protective barriers against environmental damage, electrical currents, and mechanical wear. They offer resistance to high temperatures, chemicals, and abrasion, ensuring long-term functionality in demanding applications. Manufactured in various sizes and compositions, rubber sleeves help safeguard critical components across industries.

Applications:
Used in electrical insulation to prevent current leakage and improve safety.
Applied in industrial machinery to reduce vibration and mechanical wear.
Incorporated into automotive systems to protect wires and hoses from external damage.
PTFE Components
PTFE Components are known for their exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and low friction properties. PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) are widely used in demanding applications where exposure to harsh chemicals, extreme temperatures, and pressure fluctuations is common.
Applications:
Found in chemical processing plants to ensure corrosion-resistant piping systems.
Used in food and beverage manufacturing to maintain hygiene and prevent contamination.
Integrated into medical devices to enhance biocompatibility and durability.
Rubber Couplings
Rubber couplings are essential for flexible power transmission, helping to absorb shocks, vibrations, and misalignments in mechanical systems. These couplings improve operational efficiency while reducing maintenance needs and extending equipment lifespan.
Applications:
Used in industrial machinery to ensure smooth torque transmission and minimal vibration.
Found in automotive drive systems to enhance flexibility and reduce mechanical stress.
Employed in HVAC systems to prevent misalignment issues and ensure smooth operation.
Rubber O-Rings
Rubber O-rings are crucial for sealing applications, preventing leaks, and ensuring fluid retention in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Available in various elastomeric materials, they provide excellent resistance against heat, chemicals, and pressure fluctuations.
Applications:
Used in hydraulic cylinders and pumps to create airtight seals.
Applied in aerospace engineering for fuel system integrity.
Essential in medical equipment to prevent contamination in fluid-handling systems.
Rubber Expansion Joints
Rubber expansion joints help absorb movement, reduce vibration, and compensate for thermal expansion in piping systems. They provide flexibility while maintaining system integrity, making them indispensable in fluid transport applications.
Applications:
Installed in HVAC duct systems to prevent stress from thermal expansion.
Used in chemical plants to manage pipeline movement and reduce strain.
Applied in bridge construction to allow structural expansion and contraction.
Rubber Bearing Bushes
Rubber bearing bushes act as vibration dampeners and shock absorbers in mechanical assemblies. Their ability to isolate noise and motion makes them essential in precision engineering and heavy-duty machinery.
Applications:
Used in automotive suspension systems to enhance ride comfort.
Incorporated into industrial equipment to mitigate mechanical stress.
Found in railway applications to improve track stability and reduce maintenance needs.
Rubber Gaskets
Rubber gaskets provide excellent sealing properties, preventing leaks and protecting machinery from contamination. They are manufactured in various shapes and sizes to meet the specific needs of different applications.
Applications:
Used in engines and machinery to prevent oil and coolant leaks.
Applied in pipelines to ensure tight sealing in high-pressure environments.
Essential in the food industry to maintain hygiene and prevent cross-contamination.
Extruded Rubber Profiles and Cords
Extruded rubber profiles and cords are custom-shaped elastomeric components used in sealing, insulation, and impact absorption. Their versatility allows them to be used across various industries.
Applications:
Utilized in construction to provide weatherproofing for doors and windows.
Found in marine applications to prevent water ingress in boats and ships.
Applied in automotive seals to enhance durability and noise reduction.
Moulded Rubber Parts
Moulded rubber parts are custom-designed components manufactured to meet specific industrial requirements. These parts ensure high precision and durability in various applications.
Applications:
Used in aerospace engineering for vibration damping and sealing solutions.
Found in agricultural machinery to enhance performance and longevity.
Integrated into electronic devices for insulation and impact resistance.
Rubber Hoses
Rubber hoses facilitate fluid transfer, offering flexibility, pressure resistance, and chemical stability. They are used in various sectors, from automotive to industrial processing.
Applications:
Essential in fuel delivery systems to ensure leak-proof fluid transport.
Used in hydraulic systems for efficient power transmission.
Incorporated in firefighting equipment to handle high-pressure water discharge.
Rubber Sheets
Rubber sheets offer high resistance to abrasion, impact, and environmental factors. They are used for flooring, insulation, and protective applications.
Applications:
Used in industrial flooring to provide slip resistance and cushioning.
Applied in gasket manufacturing to create custom sealing solutions.
Essential in construction to prevent structural wear and corrosion.
Conclusion
Arvico takes pride in offering top-quality rubber products that cater to a wide range of industries. Our commitment to innovation, durability, and performance has positioned us as a leading rubber product manufacturer in India. Whether you require custom rubber components or industry-specific solutions, Arvico is your trusted partner in delivering excellence.
youtube
0 notes
Text
OVERVIEW OF MEDICAL GAS MANIFOLDS
What is a Medical Gas Manifold? Unlike Medical Air Compressors and Vacuum Pumps that generate gas on-site, many gases used in healthcare settings are delivered to the facility in different types of containers and use manifolds to distribute into the rooms. Gases that can be delivered:
Oxygen – delivery pressure of 50psi Nitrous Oxide – delivery pressure of 50psi Medical Air – delivery pressure of 50psi Carbon Dioxide – delivery pressure of 50-100psi HeliOX blends – delivery pressure of 50psi Nitrogen – delivery pressure of 180psi Instrument Air – delivery pressure of 180psi The 2021 edition of the NFPA99 has the most recent developments in medical equipment and processes as well as new methods to reduce fire, explosion, and electrical hazards.
What Containers are used with Manifolds? Bulk tanks and micro-bulk tanks are gas containers that get refilled on-site. These are used for large applications and require additional equipment. Sometimes, these are collectively called a tank farm and the pad – which allows access for a truck with cryogenic gas to pull in and fill the tanks. Liquid Dewars and high-pressure cylinders are the types of gas containers that are delivered and replaced when empty. For example, there is an “H-type” high pressure cylinder, which is primarily hooked up to a high-pressure manifold in the healthcare setting. These are very common for ambulatory surgery centers and small outpatient facilities, most of the gases listed above outside of oxygen, still use this type.
Micro-Bulk Tank
Bulk Tank
High Pressure and Liquid Medical Gas Manifold Installation Discussing high pressure and liquid medical gas manifolds located indoors, the number one aspect is that it has to be a separate secured room with one hour fire rating used for no other purpose. Your manifold room can only have the manifolds and the container that is being replaced. You can store and keep connected what you’re actually using.
For example, if you have Dewars, you are only able to store Dewars, and then your high-pressure cylinders (H tanks) can go in there. Sometimes people put the vacuum pump and the oxygen manifold in the same room – that is not allowed and very expensive change order. Remember, your manifolds must be in a room all by themselves and be properly labeled.
Although this blog discusses the most common practices, Pattons Medical advises you to always work with your local municipality and local verifier to ensure that your design complies with your interpretation of whichever code they’re working on. Additionally, please note that any electrical devices in this room must be situated above five feet, and relief valves must be installed with copper piping that extends outside the room. The discharge should be turned down and screened for safety. Another important consideration is having a source valve located near the manifold.
When it comes to the insulation of the room, there are several other factors to take into account. Firstly, the temperature inside the room should not exceed 125 degrees. Additionally, ventilation must be carefully planned and implemented to ensure optimal conditions. You are able to naturally ventilate the room if your total gas falls below 3000 cubic feet. You can access gas volume charts on the Pattons Medical website.
Reference NFPA 99 5.1.3.3.2 (1-9) for design and construction details for locations of central supply systems and storage of positive pressure gases.
Indoor rooms can be heated by indirect means using steam or hot water if needed. The common rule of thumb for your liquid containers, your Dewars, is depending on the gas, it could be between 12 and 16 H cylinders. You will know where you are in that 3000 cubic feet threshold by the math and whether you want to do the mechanical versus the natural.
Liquid Dewars
High Pressure Cylinders
How do Medical Gas Manifolds Work? With medical gas manifolds, you will have two banks; the primary and the secondary, and they are required to be equal. In regards to space, the primary bank is the one currently supplying the gas, and then the secondary bank will be ready when the primary is depleted. The manifold is required to be fully automatic. Referring to the NFPA applications, the switchover must occur within the manifold, semi-automatic.
Discussing the manifold and the header bars, the header bars will need to be equipped with high-pressure shutoff valves outside the cabinet to allow for emergency isolation. You also will need to have integral check valves for each station. The header bar is going to be CGA gas specific. This means your H cylinder (your Dewar), has a certain threaded connection – similar to the header bar. The goal is to prevent a nitrogen, H cylinder from being hooked up to an oxygen manifold. With the CGA fittings, the manifold is equipped with pressure transduced – which will send information to the main circuit board for a remote signal. This is how it will talk to your master alarms. Since you will need to place this outdoors, the NEMA four gives you some weatherproofing. You will need to make it a NEMA four cabinet if you are going to do it outside. Pattons Medical recommends putting a cover or shelter over it.
What’s Inside a HP Manifold? The manifold is going to come equipped with a three-quarter inch shutoff valve, which makes up a manifold for high pressure. At the bottom of the diagram, is the pressure transducers that are telling you what pressure is happening in each side, your left and right bank, and your primary and secondary. Then, we go into the left and right bank dome regulators. The important part about using the dome biased regulators is that it’s what holds the pressure to allow the whole thing to work off pressure differential.
Above those, are the first line regulators. Then, the bank gauges at the top tell you what's going on in these headers. After that, there’s the pilot regulator, which is feeding pressure into the dome bias, so your dome bias regulator is about 25 – 30 PSI higher than the one that it’s currently feeding.
When a facility gets gas delivered to their site, they are paying for gas at a certain purity, when the gas gets delivered on site, there is no way to make it pure. Manifolds can affect the purity of the gas, so if you’re not using high quality regulators that are made for NFPA applications, then there is potential through the regulator to introduce some impurities into the gas as it flows through the manifold. The left bank is feeding the facility, but when it drops to 250 PSI, it is no longer satisfying the dome biased, then it’ll switch to the secondary bank.
In our second “true” line regulators, which is where it gets put it into the building. All of these regulators are preset at the factory depending on the gas. Discussing the delivery pressure being different depending on the gas, your bank of H cylinders is going to have different, depending on the gas. For example, a bank of oxygen, H cylinders track about 2200 PSI, but a bank of nitrous oxide cylinders only track about 750 PSI. So, these regulators all come preset from the factory gas specific. Then you go through the line regulator. The image shows both regulators being open, but when you are truly feeding the facility, only one regulator will be open.
The manual purge valve will test for purity. The pressure relief valve is there to let you know if something is wrong and it will relieve off. When you are determining the flow through the manifold, some spec sheets give you the flow with both your left line regulator and your right line regulator being open, flowing through both, but this is not accurate for an NFPA application. For maintenance, the left line regulator will be manually turned off and then the right line regulator will need to be turned on. That is strictly to keep the wear and tear equal within the manifold.
There are manifolds on the market that use what’s called a “switching,” which is when it switches to where the pressure is after one side no longer has any pressure. The issue with this is that they leak and cause a waste of gas. The other caveat is that they fail frequently in the middle, so they haven’t closed the left bank but they opened the right bank. So, you end up using both banks at once with no warning.
Heaters CO2 and nitrous are two gases that can potentially freeze up a manifold. This is caused by a pressure drop and flow across the regulators in the orifice in the manifold. If you’re going to use a manifold with a shuttle valve, you must have a heater for CO2 and nitrous oxide because they leak. Then, you will be left with a slow flow the eventually freezes, so you’ll need to use a heater. We have a high flow dome bias regulator in our manifold, our specification sheets do not specify a heater with a Pattons Medical manifold. It isn’t needed because Pattons Medical picked a regulator that would give us high flow. Pattons Medical also wanted to make it so that heaters weren’t needed because they add to the room which causes another fail point. The heaters basically work by switching on when the room temperature drops below 75 degrees.
Liquid x Liquid Manifold In larger facilities, the number of high-pressure cylinders required to meet the demand can become very high resulting in a huge space requirement and a very labor-intensive change out. In those instances, cryogenic containers become advantageous. If using cryogenic containers, there are options pertaining to the primary and secondary banks. If using a liquid manifold, a HP reserve manifold is required as back-up.
IntelliSwitch Manifold The IntelliSwitch manifold is the product we will need to use if you are using a liquid-by-liquid application or high pressure. One of the unique features of the IntelliSwitch manifold is the flexibility.
When you push the button on the front, it allows you to identify what is being connected to this manifold. What this manifold's able to do is when you tell it what is connecting to it, it will understand what pressure is supposed to see based on the containers being attached.
When you liquefy the gas in the container, it introduces some challenges with the gas being in a cryogenic state. IntelliSwitch is able to address some of those challenges. One of the first features is the economizer function. For this example, we will say, that this bank is feeding the facility. When this bank is feeding the facility, this container is generating head pressure because the gas does not want to be in a liquid state. When it generates too much head pressure, that's when you're going to pop your pressure relief valve to protect the container. In a traditional liquid by liquid manifold, it blows off into the room.
The IntelliSwitch is able to monitor the pressure on the bank, feeding the facility. Still, it’s also monitoring the pressure of the bank, not feeding the facility when it starts to register, that the head pressure is getting to. The economizer feature just bleeds some of that gas off so that it's able to be used downstream and you don't waste it. All of this happens in reverse with the lookback feature.
The lookback feature will do a soft switchover, and start drawing some of the gas from this bank, but then it keeps looking back. When this generates enough head pressure, it uses it. If it notices that there is no type of gas or that its completely empty, it’ll switch to the alternative. So instead of wasting 30% of gas in the container, only 5% will be wasted. The majority of verifiers say that this is a safer product because you are constantly getting readouts from both, meaning you know exactly what the pressure is.
Working with a verifier is essential. Take into consideration whether they are truly third parties or selling products as well.
Alarms For the manifold, there are local and master alarms. The local alarms are physically on the cabinet and are going to have either green or red lights. These lights will be next to a few phrases; ready, in-use, and replace.
For reference, you should have two green lights for ready, which means you now have a demand. For this example, let’s say this is your primary bank. When it’s depleted, the red light will be next to “replace” and the green light will be next to “ready” and “in-use.”
At your master alarm, you have a low-pressure line, high-pressure line, and reserve in use. They are actually being read by the main line pressure switch downstream of the source valve, but then you have your changeover alarm. Similarly to the local alarm, if the red light for “replace,” it is telling you to change over. You will need to address getting the bank changed out within a specified timeframe.
For liquid by liquid, we have those same three alarm points at the master, but we also have to have two more points at the master alarm, called reserve in use. As mentioned, for liquid-by-liquid applications, you have your two cryogenics and your high pressure. If your cryogenic containers have both failed, we will take off our “reserve-in-use” for the high-pressure reserves. The reserve manifold will trigger an alarm at the master.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Buy Genuine Aventics Products at Aeliya Marine
For high-performance pneumatics, industrial automation, and motion control solutions, Aventics is a globally trusted brand. If you’re looking for genuine Aventics products, Aeliya Marine offers an extensive selection of pneumatic components, actuators, valves, and automation solutions.
Browse Aventics Products Now
Why Choose Aventics?
Aventics is a brand under Emerson and is recognized for cutting-edge pneumatic technology and high-efficiency automation components. Their products are widely used in marine, industrial manufacturing, oil & gas, and automation industries.
Aeliya Marine Offers a Variety of Aventics Pneumatic and Automation Components
We provide a wide variety of Aventics pneumatic and automation components at Aeliya Marine, including:
1. Pneumatic Cylinders & Actuators : Designed for precise motion control and high-speed performance.
2. Valves & Directional Control Systems : Provide precise air flow and pressure regulation.
3. Pressure Regulators & Flow Control Equipment : Maintains proper air pressure in pneumatic systems.
4. Air Preparation Units & Filters : Increases system efficiency and safeguards pneumatic components.
5. Sensors & Positioning Technology : High-precision sensors for motion tracking and automation.
Why Buy From Aeliya Marine?
1. 100% Genuine & High-Quality Products : Directly sourced from trusted suppliers.
2. Competitive Pricing : Get top-tier automation components at the best rates.
3. Fast & Worldwide Shipping : Secure delivery with tracking for international orders.
4. Expert Technical Support : Our team offers product selection and integration advice.
Order Aventics Pneumatic Components Today!
Upgrade your industrial automation and pneumatic systems with Aventics' reliable motion control solutions.
#industrial equipment#automation#industrialautomation#industrial spare parts#industrial and marine automation#marine automation#industrial automation
0 notes
Text
Home Water Filtration System & Hot Water Solutions in Thorneside, Australia

Clean water and an efficient hot water system are essential for every home in Thorneside, Australia. Whether you're looking for a home water filtration system service, dealing with a Leaking hot water in Thorneside, or considering a new gas hot water replacement, it's important to choose the right professionals for the job. This article will guide you through the benefits of a water filtration system, the urgency of fixing hot water leaks, and the best solutions for upgrading to a new gas hot water system in Thorneside.
The Importance of a Home Water Filtration System
Ahome water filtration system ensures that your family has access to clean and safe drinking water. Many households in Australia face water quality issues due to contaminants like chlorine, sediments, and heavy metals. A filtration system removes these impurities, improving water taste and safety.
Here are some key benefits of installing a home water filtration system:
Removes harmful chemicals and contaminants
Enhances the taste and smell of drinking water
Reduces limescale buildup in plumbing and appliances
Saves money by eliminating the need for bottled water
Regular maintenance of your filtration system is crucial to ensure optimal performance. Professional servicing includes filter replacement, system checks, and overall performance assessments.
Dealing with a Leaking Hot Water System in Thorneside
A leaking Hot Water Cylinder Australia is not just an inconvenience—it can lead to increased water bills, structural damage, and potential safety hazards. Common causes of leaks include:
Corroded or damaged tanks
Faulty pressure relief valves
Loose connections or worn-out pipes
If you notice water pooling around your hot water system, it’s essential to contact a professional plumber in Thorneside immediately. Ignoring the issue can result in more costly repairs or even the need for a complete replacement.
New Gas Hot Water Replacement in Thorneside
If your hot water system is outdated or beyond repair, a New gas hot water replacement Thorneside is a great investment. Gas hot water systems offer several advantages:
Energy efficiency: Gas systems heat water quickly, reducing energy consumption.
Cost savings: Gas is generally cheaper than electricity, leading to lower utility bills.
Continuous hot water: Unlike electric storage systems, gas systems provide an unlimited hot water supply.
When choosing a new gas hot water system, consider factors like household size, water usage, and energy efficiency ratings. Hiring an experienced plumbing professional ensures correct installation, compliance with safety regulations, and long-term reliability.
Finding the Right Plumbing Service in Thorneside
For all yourhome water filtration, hot water system repairs, and new gas hot water replacements, it's crucial to work with a licensed and experienced plumbing service in Thorneside. Look for professionals who offer:
24/7 emergency repairs
Affordable and transparent pricing
High-quality products with warranties
Excellent customer reviews
Investing in a reliablehome water filtration system and maintaining your hot water system ensures safe, clean water and efficient energy use. If you’re experiencing leaks or considering a gas hot water upgrade, don't hesitate to call a professional for the best service in Thorneside.
0 notes
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to Hot Water Cylinders in Auckland - Choosing the Best System for Your Home

Hot water cylinders are an essential component of any household, providing a reliable supply of hot water for bathing, cleaning, and cooking. In Auckland, where the climate and water quality can vary, selecting the right hot water cylinder is crucial for ensuring efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness. This article explores the types of hot water cylinders available, factors to consider when choosing one, and tips for maintaining your system.
Types of Hot Water Cylinders
Vented Cylinders:
These are the most common type of hot water cylinders in older Auckland homes. They rely on a cold water tank, usually located in the roof space, to supply water to the cylinder.
Pros: Lower upfront cost and simple design.
Cons: Limited water pressure and susceptibility to freezing in colder months.
Unvented Cylinders:
Unvented cylinders are connected directly to the mains water supply, providing higher water pressure and eliminating the need for a cold water tank.
Pros: Strong water pressure, space-saving, and energy-efficient.
Cons: Higher installation costs and require professional maintenance.
Solar Hot Water Cylinders:
These systems use solar panels to heat water, making them an eco-friendly option for Auckland homeowners.
Pros: Reduced energy bills and lower carbon footprint.
Cons: Higher initial investment and dependent on sunlight availability.
Heat Pump Hot Water Cylinders:
Heat pump systems extract heat from the air to warm the water, making them highly energy-efficient.
Pros: Lower running costs and environmentally friendly.
Cons: Higher upfront cost and may require more space for installation.
Gas Hot Water Cylinders:
Gas-powered cylinders heat water using natural gas or LPG, providing a quick and reliable hot water supply.
Pros: Fast heating and cost-effective for larger households.
Cons: Requires a gas connection and regular safety checks.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Hot Water Cylinder
Household Size and Demand:
The size of your household and daily hot water usage will determine the capacity of the cylinder you need. For example, a family of four may require a 180–250-liter cylinder, while a smaller household may only need a 100–150-liter system.
Energy Efficiency:
Look for cylinders with high energy efficiency ratings to reduce running costs and environmental impact. Heat pump and solar systems are particularly efficient options.
Water Pressure:
If you prefer strong water pressure, an unvented cylinder or a mains-pressure system is ideal. Vented cylinders may not provide sufficient pressure for modern homes.
Space Availability:
Consider the available space for installation. Unvented cylinders are compact and can be installed indoors, while heat pump systems may require outdoor space.
Budget:
Balance upfront costs with long-term savings. While solar and heat pump systems have higher initial costs, they can significantly reduce energy bills over time.
Water Quality:
Auckland’s water quality can vary, so choose a cylinder made from durable materials like stainless steel to resist corrosion and extend the system’s lifespan.
Maintenance Tips for Hot Water Cylinders
Regular Inspections:
Schedule annual inspections by a licensed plumber to check for leaks, corrosion, and faulty components.
Flush the Tank:
Sediment build-up can reduce efficiency and damage the cylinder. Flush the tank annually to remove debris.
Check the Pressure Relief Valve:
Ensure the pressure relief valve is functioning correctly to prevent excessive pressure build-up, which can cause leaks or bursts.
Insulate the Cylinder:
Insulating your hot water cylinder and pipes can reduce heat loss and improve energy efficiency.
Monitor Water Temperature:
Set the thermostat to a safe and efficient temperature (typically 60°C) to prevent scalding and reduce energy consumption.
Conclusion
Choosing the right hot water cylinder for your Auckland home is a decision that impacts your comfort, energy bills, and environmental footprint. By understanding the different types of cylinders, considering your household’s needs, and prioritizing maintenance, you can ensure a reliable and efficient hot water supply for years to come. For expert advice, installation, and repairs, always consult a qualified professional to keep your system running smoothly. Whether you opt for a traditional vented cylinder, a modern heat pump system, or an eco-friendly solar solution, investing in the right hot water cylinder will pay off in the long run.
Hot Water Solutions 3d Taid Place, Rosedale, Auckland 0800497658 [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Gas Detectors, Gas Analysers, Gas Monitoring Solution, Manufacturer
Gas Detectors, Gas Analysers, Gas Monitoring Solution, Gas Monitor System, Manufacturer, Supplier and Service Provider, Dubai, UAE.
Gas Distribution Systems, Gas Handling Systems, Helium Leak Detection System, Helium Leak Detection Service, MEP Services, Mechanical Services, Electrical Services, Plumbing Services, Laboratory Furniture Installation, Fumehood Installation, Fume Cupboards Validation, Laminar Cabinets Validation, Biosafety Cabinets Validation, Turnkey Laboratory Project Design, Turnkey Laboratory Project Consultancy, Gas Handling Systems AMC, Lab Furniture AMC, Special Metal Fabrication, Cylinder Racks, Gas Cylinder Racks, Gas Cylinder Storage Racks, Laboratory Furniture, Fume Hoods, Gas Regulators, Cylinder Gas Regulators, Single Stage Regulators, Double Stage Regulators, High Flow Regulators, High Pressure Regulators, Auto Changeover Regulators, Point of Use Regulators, Back Pressure Regulators, Fixed Flow Regulators, Gas Manifold, Gas Manifold Systems, Safety Cabinets, Sampling Cylinders, Sampling Systems, Gas Mixing System, Gas Blending System, Gas Detectors, Gas Analysers, Gas Monitor System, Ball Valves, VCR Diaphragm Valves, Check Valves, Diaphragm Shutoff Valves, Excess Flow Valves, Globe Valves, High Pressure Master Shutoff Valves, Needle Valves, Plug Valves, Safety Relief Valves, Solenoid Valves, Toggle Valves, Gas Accessories, Cylinder Trolleys, Cylinder Brackets, Cylinder Cages, Dubai, UAE
0 notes
Text
Internal Combustion Engines
Introduction

For over a century, internal combustion engines (ICEs) have been the foundation of contemporary transportation and manufacturing. Because of their exceptional endurance and drivability, these engines power almost 250 million roadway vehicles in the United States alone. In addition to gasoline and diesel, ICEs can run on natural gas, propane, biodiesel, and ethanol. Furthermore, they can be combined with hybrid systems to improve efficiency and increase the range of hybrid electric vehicles.
Types of internal combustion engines
Internal combustion engines fall into two categories:
Continuous combustion engines, like jet engines, use a steady influx of fuel and oxidizer to sustain a constant flame. This type’s distinguishing feature is its smooth operation, with all thermodynamic processes taking place concurrently in a continuous flow.
Intermittent Combustion Engines, often known as reciprocating engines, ignite air and fuel mixes occasionally. Examples include diesel engines and gasoline piston engines. The thermodynamic events occur successively in a cycle that repeats throughout the engine’s operation.
Despite their operational variations, both types take air, compress it, and ignite the air-fuel mixture to produce energy. This energy moves vehicles and powers machinery. In contrast, external combustion engines, such as steam engines, rely on heat transfer rather than chemical reactions in the working fluid.
How Internal Combustion engines work

Internal combustion engines release energy by combusting a fuel-air mixture. This process happens inside the engine and powers its components. A conventional ICE consists of a stationary cylinder and a moving piston. The expanding combustion gases drive the piston, which rotates the crankshaft and eventually transfers power to the vehicle’s wheels via the powertrain.
Four-stroke engine cycle
The majority of ICEs in use today are four-stroke engines, which require four-piston movements to complete a cycle.
Intake Stroke:
The piston moves from the Top Dead Center (TDC) to the Bottom Dead Center (BDC) as the intake valve opens. This permits a mixture of air and fuel into the cylinder. The engine wastes energy during this phase as the crankshaft rotates.
Compression Stroke:
Following intake, the piston moves back to TDC, compressing the air-fuel combination. Both intake and exhaust valves stay closed, resulting in maximum pressure. Near the end of this stroke, a spark (in gasoline engines) or fuel injection (in diesel engines) starts combustion.
Power stroke:
Combustion pushes the piston down from TDC to BDC. This stroke creates the engine’s torque and power, which drive the crankshaft and power the vehicle.
Exhaust Stroke:
With the piston reaching BDC, the exhaust valve opens. The piston returns to TDC, discharging combustion gasses into the exhaust system. Rotating the crankshaft requires energy, the same as the intake stroke.
This cycle requires two full crankshaft revolutions (720°). Notably, only the power stroke produces energy, while the other three strokes consume it.
Parts of an internal combustion engines
The key components of an ICE are:
The cylinder head houses the camshaft, valves, spark/glow plugs, and injectors. Coolant circulates throughout the skull to control temperature.
Engine Block: The engine block contains the pistons, connecting rods, and crankshaft. To regulate temperature, coolant circulates here as well.
Combustion Chamber: The space produced by the cylinder head, block, and piston at TDC where fuel combustion occurs.
Advantages of Internal Combustion Engines
ICEs provide various benefits:
Compact Size: They are smaller than external combustion engines.
High Power-to-Weight Ratio: suitable for applications that require lightweight and efficient power sources.
Versatility: Suitable for a variety of vehicles and machinery.
Safety: Safety advantages over external combustion engines include faster start times and fewer dangers.
Efficiency: Improved by advances in engine design and fuel injection technologies.
Low Maintenance: Lubricants are used sparingly, and there is little maintenance required.
Lower Operating Temperatures: Peak temperatures are achieved shortly during combustion, reducing heat-related wear.

The disadvantages of internal combustion engines
However, ICEs have some drawbacks:
Fuel Requirements: Limited to high-quality gaseous and liquid fuels.
High Costs: gasoline and diesel are relatively pricey.
Emissions: ICEs emit more pollutants than external combustion engines.
Noise: Reciprocating motion causes significant noise.
Limited Power Output: Not suitable for very high-power applications.
Applications for Internal Combustion Engines
ICEs are used in a variety of industries:
Gasoline engines are common in automobiles, boats, and planes.
Diesel engines: Diesel engines are used in trucks, trains, ships, and power generators.
Gas Turbines: Gas turbines are used in aviation, maritime propulsion, and industrial power generation.
Future of Internal Combustion Engines
Despite their ubiquitous use, ICEs are receiving increased scrutiny due to environmental issues and resource depletion. Efforts to increase efficiency and lower emissions include:
Alternative Fuels: The production of biofuels, hydrogen, and other renewable energy sources.
Hybrid and electric systems: hybrid and electric systems combine internal combustion engines with electric motors to increase efficiency.
Advanced Technologies: Advanced technologies include improved engine management systems, lightweight materials, and aerodynamic designs.
Conclusion
Internal combustion engines have been critical to contemporary transportation and industry for more than a century. Their efficiency, dependability, and adaptability have fueled global industrialization and mobility. However, their dependency on fossil fuels and environmental effect needs a transition to greener options.
Ongoing research into alternative fuels and electrification technologies, together with breakthroughs in engine design, promises a more sustainable future for transportation. While ICEs have been the foundation of industrial success, the transition to environmentally friendly power sources is critical to addressing climate change and resource issues. The route forward is to strike a balance between innovation and environmental stewardship, resulting in a cleaner, more sustainable future for all.
Dorleco provides cutting-edge VCUs, CAN Displays, CAN Keypads, and EV software solutions that enable the future of automotive innovation around the world. For additional information, contact us at [email protected].
#VCUCommunicationProtocols#Dorleco#CANKeypads#CANDisplays#VCUs#Vehiclecontrolunit#EVSoftwareServices#E/Earchitectures
0 notes