#heroic age of polar exploration
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
RIP Belgica crew, if you knew what fanfiction writers were doing to the Terror and Erebus crews, you'd probably be jealous.
#currently reading#madhouse at the end of the earth#currently rewatching#the terror amc#belgica#belgica expedition#franklin expedition#the terror#polar exploration#polar history#heroic age of polar exploration#boat media#age of sail#technically age of steam but whatever
213 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Did You Know this was my original idea for the cover of Vol.1 of my graphic novel of The Worst Journey In The World? In the end, six possible cover options were consulted upon by my Patrons and by the Graphic Novel Club at The Children's Bookshop in Muswell Hill, and it was decided Ponting's Grotto was a more arresting image. I did manage to sneak this into the book as a full-page illustration, though.
#book design#cover design#outtakes#the worst journey in the world#apsley cherry-garrard#bill wilson#edward adrian wilson#birds#tall ships#age of sail#heroic age of polar exploration#sailing
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
If I was isolated with a bunch of other men stuck inside a research station in northern Greenland in the 1880s I would simply not go crazy and also I would have sex with all of them and they would stave off starvation by eating my boypussy all winter long
#guys the rescue ship sent to rescue these guys got stuck in the ice and had to be rescued#greely expedition#doomed polar expedition#arctic#heroic age of polar exploration
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

#happy spotify wrapped day#Antarctica#heroic age of Antarctic exploration#Robert falcon Scott#Henry birdie bowers#Edward Adrian Wilson#Titus Oates#Edgar evans#polar exploration
228 notes
·
View notes
Text




Polar comic of the day: meet Oswald Barr, the beloved musician & comedian onboard Endurance! Leonard Hussey who?
#inspired by newspaper reports at the time marvelling at how cool this guy was#the quotes Huss is holding up are Real and from his crewmates though :)#leonard hussey#endurance expedition#polar exploration#ernest shackleton#shackleton#cold boys#polar explorers#antarctic exploration#heroic age of antarctic exploration
105 notes
·
View notes
Text

tl;dr:

#my favorite part is that it works????#wordie pleaaassseee you don't need to see their mystery rocks!!!!#the men of elephant island are jonesing for their next smoke but not as badly as wordie is jonesing for his next geological discovery ig#endurance expedition#james wordie#jock wordie#i dont think he has a popular tag either way :((#justice for wordie he was out here being goofy too#polar exploration#heroic age of antarctic exploration#polar tag#figs sillies
68 notes
·
View notes
Text











The heroic age of Antarctic exploration - after The Terror opening credits
#polar exploration#antarctica#heroic age#roald amundsen#apsley cherry-garrard#frank wild#ernest shackleton#lawrence oates#xavier mertz#belgrave ninnis#arnold spencer-smith#hjalmar johansen#emile danco#edward wilson#robert falcon scott#belgica#endurance#terra nova#fram#LOTTA TAGS. LOTTA BOYS.#sorry if the gutters are weird i hate this new post editor so much lmao#my: graphic#*
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

12 June 2024
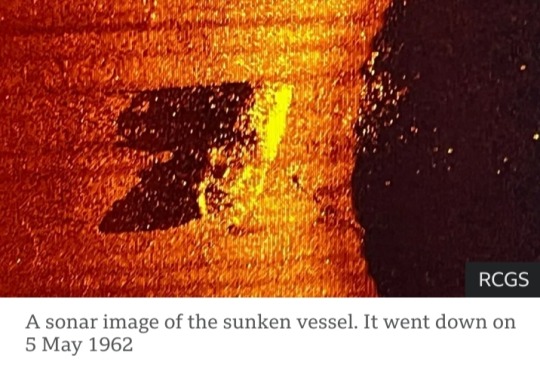
Wreck hunters have found the ship on which the famous polar explorer Ernest Shackleton made his final voyage.
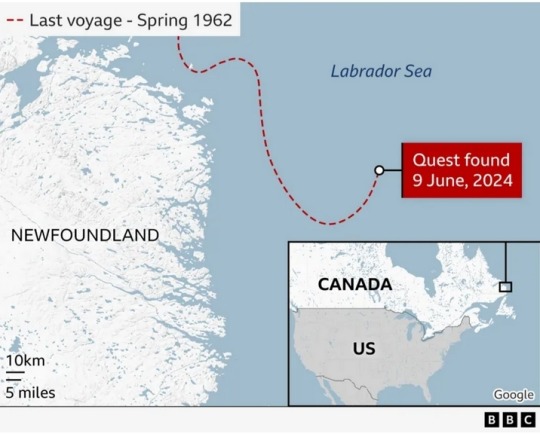
The vessel, called "Quest," has been located on the seafloor off the coast of Newfoundland, Canada.
Shackleton suffered a fatal heart attack on board on 5 January 1922 while trying to reach the Antarctic.
And although Quest continued in service until it sank in 1962, the earlier link with the explorer gives it great historic significance.
The British-Irish adventurer is celebrated for his exploits in Antarctica at a time when very few people had visited the frozen wilderness.
"His final voyage kind of ended that Heroic Age of Exploration, of polar exploration, certainly in the south," said renowned shipwreck hunter David Mearns, who directed the successful search operation.
"Afterwards, it was what you would call the scientific age. In the pantheon of polar ships, Quest is definitely an icon," he told BBC News.

The remains of the ship, a 38m-long schooner-rigged steamship, were discovered at the bottom of the Labrador Sea on Sunday by a team led by The Royal Canadian Geographical Society (RCGS).
Sonar equipment found it in 390m (1,280ft) of water. The wreck is sitting almost upright on a seafloor that has been scoured at some point in the past by the passing of icebergs.
The main mast is broken and hanging over the port side, but otherwise, the ship appears to be broadly intact.
Quest was being used by Norwegian sealers in its last days. Its sinking was caused by thick sea-ice, which pierced the hull and sent it to the deep.
The irony, of course, is this was the exact same damage inflicted on Shackleton's Endurance - the ship he used on his ill-fated Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition of 1914–1917.
Fortunately, the crews of both Endurance, in 1915, and Quest, in 1962, survived.
Indeed, many of the men who escaped the Endurance sinking signed up for Shackleton's last polar mission in 1921-1922, using Quest.

His original plan had been to explore the Arctic, north of Alaska, but when the Canadian government withdrew financial support, the expedition headed south in Quest to the Antarctic.
The new goal was to map Antarctic islands, collect specimens and look for places to install infrastructure, such as weather stations.
Shackleton never made it, however, struck down by heart failure in the Port of Grytviken on the British Overseas Territory of South Georgia, the last stop before reaching the White Continent. He was just 47 years old.
After his death, Quest was involved in other important expeditions, including the 1930-31 British Arctic Air Route Expedition led by British explorer Gino Watkins, who himself tragically died aged 25 while exploring Greenland.
Quest was also employed in Arctic rescues and served in the Royal Canadian Navy during WWII, before being turned over to the sealers.

The RCGS team members carried out extensive research to find Quest's last resting place.
Information was gathered from ship's logs, navigation records, photographs, and documents from the inquiry into her loss.
The calculated sinking location in the Labrador Sea was pretty much spot on, although the exact co-ordinates are being held back for the time being.
A second visit to the wreck, possibly later this year, will do a more complete investigation.
"Right now, we don't intend to touch the wreck. It actually lies in an already protected area for wildlife, so nobody should be touching it," associate search director Antoine Normandin said.
"But we do hope to go back and photograph it with a remotely operated vehicle, to really understand its state."
Alexandra Shackleton is the explorer's granddaughter and was patron to the RCGS survey.
"I was thrilled, really excited to hear the news; I have relief and happiness and a huge admiration for the members of the team," she told BBC News.
"For me, this represents the last discovery in the Shackleton story. It completes the circle."
The explorer continues to spark interest more than a century after his death.
Hundreds of people visit his grave on South Georgia every year to pay their respects to the man known by his crews simply as "The Boss."
"Shackleton will live forever as one of the greatest explorers of all time, not just because of what he achieved in exploration but for the way he did it, and the way he looked after his men," said David Mearns.
"His story is timeless and will be told again and again; and I'm just one of many disciples who'll keep telling it for as long as I can."

—
Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton CVO OBE FRGS FRSGS (15 February 1874 – 5 January 1922) was an Anglo-Irish Antarctic explorer who led three British expeditions to the Antarctic.
He was one of the principal figures of the period known as the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration.
#Ernest Shackleton#Quest#Newfoundland#Canada#Antarctic#polar explorer#shipwreck hunter#shipwreck#Labrador Sea#The Royal Canadian Geographical Society (RCGS)#Endurance#1930-31 British Arctic Air Route Expedition#Gino Watkins#sonar instrument#Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration#Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton#British expeditions
66 notes
·
View notes
Text

Henryk Arctowskies at the Belgica exhibition in MAS Antwerp.
#belgica expedition#polar exploration#polar explorers#antarctica#heroic age#polishposting#henryk arctowski#toploaders
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello. Belgian Antarctic Expedition as Animals. Why not.
(But I don't feel confident enough in my grasp of their personalities to truly assign them so I'm mostly going by vibes, since I haven't finished Madhouse yet)
Baron Adrien Victor Joseph de Gerlache de Gomery FRSGS: Horse. I don't know why.


Frederick Cook: spicebush swallowtail (kid version.) A bit of a trickster. Unique face shape.


Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen: The Alaskan Moose. Perfectly adapted. Long.


Emil Racoviță. Eurasian brown bear. Beautifully puffy face. I can make a soviet union joke here but I don't want to.


I did not include Lecointe. he knows what he did. He won't be forgiven 🐱
I will return to this once I have finished Madhouse. And laugh perhaps at how wrong I am.
#belgica#polar exploration#heroic age#antarctic exploration#roald amundsen#frederick cook#emil racovitza#adrien de gerlache
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
going back in time to november 2022 and developing lead poisoning in front of 24 year old gene, changing the trajectory of their viewing habits forever
#gene.txt#i wish i could say this is a wildcard interest for me but i'd already been planning out a novel abt the heroic age of antarctic exploration#at that point so whos to say. u know how it is with polar history
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Endurance expectation: Madhouse at the End of the Earth, but with more overland (over ice?) adventure
Endurance reality: The Terror (2018), but nobody dies.
#every time I think it can't get worse for these poor bastards it does#endurance#alfred lansing#ernest shackleton#polar exploration#heroic age of polar exploration#boat books#boat stories#boat media#madhouse at the end of the earth#the terror
30 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Beautiful day in beautiful Dundee with this total hottie!
#rrs discovery#discovery#tall ships#polar history#dundee#scotland#polar exploration#heroic age of polar exploration#barque
17 notes
·
View notes
Text

a live donkey
#sir ernest shackleton#my best friend my worst enemy#the patron saint of failing successfully#and yet also successfully failing#polar exploration#Antarctica#Antarctic#heroic age of antarctic exploration#minsart#my art#fanart#the likeness isn’t quite there but I’ve been experimenting with white line art so have
66 notes
·
View notes
Text

January 9, 2025 marks 123 years since the Discovery (the ship used by Sir Robert Falcon Scott) arrived in Cape Adare, ready to uncover the mysteries of the largely unknown frozen world.
The Discovery expedition would succeed in furthering scientific understanding of Antarctica and charted many unknown regions, including the snow-free Antarctic Valleys, the Polar Plateau, and the famous emperor penguin colonies at Cape Crozier.
It also launched the careers of several explorers who would go on to become legends during the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, including Ernest Shackleton, Frank Wild, Robert Falcon Scott, and Tom Crean, among others.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shackleton comparing his struggles to Jesus is such a fitting Heroic Age diva move, and it makes me laugh to think of other polar explorers trying it. Imagine what the press would've done to Adolphus Greely if they got so much as a whiff of christ allegory! They would have crucified him.
11 notes
·
View notes