#hence the precipitous decline
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Its giving "how to get ahead in advertising"
youtube
Apparently my gf is too normie to connect the dots on legionboy pepe + kek = chansphere (couchchaospedoscough) dogwhistling
#i left the whole scene behind when it started sucking too much...about 12 years ago#they used to ban people for xyz on the fun sites....the founders kept getting bored of it and growing up#hence the precipitous decline#'anon' used to mean like...online antifa with dirtbag traits#fox news was always using it as a boogeyman...they were so scared of it...then all the fox news people showed up & the oldfags mostly left#its kind of useful because they mostly stay shitting in their own sandbox. its too addictive
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
klasdaskdasldas. i have a. great multitude of follow-up questions after the incarnadine post and i am struggling to decide which to ask, if that's okay? uhhhhhhh. i'm definitely curious about the Alsius Meritocratic Party/changes between Mantelian government and Atlesian government!
( the incarnadine post )
brief background: the pre-war mantle had a legislative assembly for which all adult citizens were eligible and selected by lot each year; military and civil magistracies were both elected by the assembly, and the assembly’s agenda was set for it by a theocratic executive body called the chancery. (the state religion was a highly syncretic form of madagian – worship of the four maidens – which remains the dominant religion in atlas today). notionally, the chancery was an elective body but in practice the state church was the king-maker, and decades preceding the great war were marked by a steady erosion of state power from the assembly and the (already somewhat impotent) judiciary.
post-war, reforms imposed by the vytal accords stripped executive power from the chancery (which still exists as the governing body of the state church, itself much diminished in political power) and replaced it with an executive council (6 elective seats, 3 appointed by the elected councilmen). the magistracies and judiciary were also restructured and strengthened but that’s not particularly relevant for the subject of this post; the assembly largely did not change, other than penalties for absences being reduced and the establishment of a procedure for the assemblies to impeach members of the council under certain circumstances.
so!! the executive council has no direct legislative power but because it sets the agenda for the assembly, it exercises quite a lot of indirect legislative influence (in that the council can kill any proposed law by declining to call the assembly for a vote). that plus it’s being elective plus its small size makes it the most powerful branch of the atlesian government and the one political parties typically focus most on controlling.
the AMP arose in reaction to post-war social reforms, primarily related to faunus civil rights but also a raft of new labor laws, which precipitated a migration of wealthy mantelians (in particular, former slave owners, most of whom had operated dust mines reliant on enslaved labor) to the swiftly-growing suburb surrounding atlas academy. (before the great war, atlas academy had been called alsius; hence ‘alsius meritocratic party’)
early on, the main thing the AMP stood against was a set of government programs to bring newly-emancipated fauni into a level economic playing field, which were funded largely by taxes targeted narrowly on industries where slave labor had been ubiquitous. by the present day, the party platform has moderated away from overtly anti-fauni policies (as these are politically toxic) to a broader anti-regulatory, anti-union position. the AMP is reviled in mantle but popular in atlas, which—because four of the six elective council seats are allotted to districts in atlas—has resulted in the AMP holding council majorities more often than not for the last few decades.
aside from the disdain for business regulation and worker rights, the modern AMP platform is built around a philosophy that equal opportunity is desirable, but shouldn’t be achieved by ‘penalizing success’ (i.e., imposing regulations or higher taxes on corporations and wealth). staunchly pro-military, strong support for heavy investment into public education and healthcare, socially egalitarian (nominally; there’s a noticeable covert hostility toward faunus rights still), against government subsidization of industries except for dust mining (although the fringe of the party wants to slash these too; the problem is that atlas/mantle would be uninhabitable without dust, but dust mining in the tundra is incredibly costly. the SDC runs its solitan mines at a loss it offsets in other more profitable markets, further shored up by military contracts; every other atlas-based mining competitor is dependent on government subsidies to stay afloat.)
currently the AMP holds four seats on the council. there’s a popular movement in mantle to expand the number of council seats to eleven by breaking up the mantle ‘districts’ into a seat per major borough, but that has virtually no chance of getting off the ground until/unless an atlas seat flips.
(the non-elective seats are held by 1. headmaster of atlas, 2. army general, and 3. governor of mantle, with the former two currently both held by ironwood; the votes for/against calling an assembly to vote on this proposal are currently three for, five against. if one of the AMP-held atlas seats flips it’ll be four-four and the thinking is that ironwood may be persuadable. if it goes to the assembly it’s all but guaranteed to pass, because the nature of the assembly—a set proportion of the citizen population, selected annually by random lot—means it’s statistically likely in any given year that the assembly’s majority will be working- and middle-class mantelians)
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Value of Carbon Footprint Reduction
As a Carbon footprint consultant In UAE, the total amount of different greenhouse gas emissions—of which carbon dioxide is the main component—that result from the decisions and activities of a person, group, or country is known as their "carbon footprint." Carbon dioxide (CO2) or carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) are common ways to express carbon footprint. Most greenhouse gases, including CO2 and methane (CH4), are released into the atmosphere due to processes including clearing land, burning fossil fuels, and producing and using a variety of goods and services.

We are a Carbon footprint consultant In Dubai, it would help to compare your carbon footprint to the mark you would leave on wet cement to appreciate its significance. Your imprint is sealed and captured by such an impression, lasting a very long period. Your carbon footprint is impacted by every decision you make, even if you may not be aware of it. Your carbon footprint increases when you forget to turn off appliances, take the car to work, or buy bottled water. On the other hand, you can lessen your carbon footprint by utilizing reusable bottles, public transportation, and turning off appliances. Your carbon footprint is like a permanent record of your activities on Earth. Hence, it is imperative to recognize how important it is to reduce our carbon footprint.
In our role as Carbon footprint consultant, the Earth is being negatively impacted by carbon emissions, which is the most evident reason why it is necessary to reduce it. Increasing CO2 emissions cause unique climate changes like melting ice caps, wildfires, tropical storms, year-round rain showers, and rising temperatures. Plant growth patterns are being impacted by changing patterns of precipitation. Native plants are, therefore, migrating to colder regions. Shorelines are disappearing, ecosystems are being destroyed, and sea levels are rising. As a result, certain coastal cities and towns are uprooted, while some islands and island nations vanish entirely.
Particular weather patterns and vegetation play a significant role in preserving and conserving wildlife. However, climate changes have also brought about changes in the vegetation, and the constantly fluctuating weather and temperature are putting many wildlife species in danger of extinction. For example, migratory birds may discover that plants have either yet to blossom or have bloomed too early when they reach their locations. These elements lead to famine and, eventually, extinction.
Being a Carbon footprint consultant In UAE, increased carbon footprints can adversely affect human health, the environment, and wildlife, particularly the health of children living in unsanitary and drought-prone areas. Drought and climate change hinder the growth of food crops. This ultimately leads to a shortage of crops and a rise in malnutrition. In addition, droughts impede access to clean drinking water and result in diarrheal illnesses. In addition, more people are experiencing respiratory conditions such as allergies, bronchitis, and asthma due to the poor air quality index in most cities.
As an expert Carbon footprint consultant In Dubai, the fact that carbon emissions seriously threaten the economy emphasizes how important it is to reduce them. Numerous studies have demonstrated how countries that rely on their land for natural resources and agriculture are impacted by climate change. For example, wheat yields have decreased on Indian farms. Similar to this, Maine, USA's renowned New England lobster industry is in jeopardy as a result of a growing carbon footprint and declining catches. This is having a significant effect on Maine's economic expansion. Additionally, the economy is severely impacted by the threat of rising sea temperatures on coral reefs. There are various personal actions we may take to reduce our carbon footprints. Because power production leaves a substantial environmental imprint, studies have shown that switching to energy-efficient appliances in your home can have a significant environmental impact.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Future of NAND Flash Technology by Samsung

Samsung to Hike NAND Flash Values Massively Next Month
It has been stated that Samsung Electronics intends to implement a significant price increase for NAND flash, which might fall somewhere in the neighborhood of double digits and would apply to all of their goods.
As the Korean giant searches for new ways to combat the declining industry, prices for Samsung NAND Flash products, including solid-state drives (SSDs), are going to skyrocket.
We are all aware that 2023 will go down in history as the year when the DRAM industry has its worst quarters ever, which will result in a huge drop in demand from the market. According to insiders in the semiconductor business, Samsung Electronics has seen a precipitous forty percent drop in wafer manufacturing since the beginning of the year.
This was an early response by the company to fight the problem. On the other hand, things have begun to take a turn for the better in terms of sales, and Samsung is now attempting to capitalize on the best of what’s happening.
According to Business Korea, the DRAM sector is now enjoying an economic comeback. This is reportedly happening as a result of an increase in demand from server firms brought about by the continued growth in AI advances. The situation for consumers, on the other hand, is not looking very promising.
Beginning at the beginning of the next month, Samsung Electronics intends to implement a price increase of 10%. This might have a negative impact on the pricing of consumer storage; hence, now could be a good time to get an NVMe if you are in the market for one.
If we consider Samsung Electronics’ present market share, we can see that they possess the majority of it, leaving behind competitors like as SK Hynix and Micron. This increase in the price of NAND flash will also be put into place by other key players, which justifies the fact that things could take an upturn on the consumer side when it comes to the pricing of NAND-based products such as SSDs and NVMe.
Decisions made by the Korean giant are ultimately implemented by the whole industry.
Although Samsung has been making persistent efforts to cut output, it seems that these efforts are not succeeding in either direction. The only way that things may possibly turn out for the better is if a price increase is implemented; nevertheless, this may also have an effect on consumer prices.
0 notes
Text
Climate Change Effects Pose the Biggest Risk to SDG2- How NGO Environment India Can Contribute?
NGO Environment India
In order to "end hunger, achieve food security, improve dietary habits, and promote sustainable agriculture," SDG 2 is intended to be achieved. Climate change, on the other hand, puts the SDG2 objective in jeopardy and poses a problem for food security. The enormous challenge of feeding the world's population is being made worse by unchecked population increase. Food production, prices, and security are all being impacted by environmental deterioration, which has a significant effect on issues relating to food security.
Because of our dependency on fossil fuels, there is an environmental emergency affecting the entire planet. The alarming rate of natural resource depletion is continuing to hasten climate change and environmental damage. Despite setting ambitious goals for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, several wealthy nations are still taking their time. Wild fluctuations in weather patterns have contributed to global warming and a shortage of water. Crop yields are declining as production is hampered. In actuality, the environment on which agriculture depends continues to be significantly impacted by global warming brought on by climate change. The risk to food security is further increased by natural disasters. Several NGO Environment India are deeply involved to alleviate the situation alongside the government efforts.
Due to climate change, the SDG2 objective is in jeopardy and food security is a concern. Unchecked population increase is a new danger that is making it harder to feed the world's population.

THE EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA
Adaptable weather patterns. India's agricultural irrigation system is dependent on rainwater. However, the effects of skewed rainfall patterns are producing very intense or sparse precipitation. Future agricultural productivity in India may suffer as a result of this. Many NGO Environment India like Search NGO, are working towards the improvement of India’s agricultural pattern. Extreme weather conditions like severe and frequent floods and droughts have a negative impact on agricultural growth in India. This can then have a cascading impact on the production of food and drive up food costs. While India has been able to contain the rise in food prices, some of its neighbors, including Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, are currently experiencing some type of crisis.
Water supplies are under stress. Rivers, dams, streams, and groundwater supplies are being put under more strain as a result of the unpredictable rains. The country's water levels are still being drained by an overreliance on groundwater for agricultural and domestic use. Agricultural vulnerability is rising as a result of climate change's impact on the hydrological environment. An alarming loss of glaciers, ice caps, and snow fields is another effect of climate change that is causing more meltwater to be produced. The cryosphere has become unstable due to the disappearance of water from river basins, illegal groundwater extraction, industry, and urbanization. As a result, farmers are more unsure as a result of climate change, hence building farming resilience is crucial right now. NGO Environment India are educating the rural population about farming resilience.
falling nutrient levels and agricultural output. Volatile droughts and heat waves have an impact on agriculture due to global warming. Farmers will have to deal with shorter crop seasons and prolonged water shortages as droughts in agriculture become more common. Some areas will have to deal with floods from rivers and the shore. This would actually result in lower agricultural yields and more crop failures, which would jeopardize SDG2's objectives. As a result of climate change, the output of basic crops like rice and wheat has already started to fall, along with their nutritious value. Climate change has had an impact on India's agricultural growth in a number of ways, including changing weather patterns, stress on water supplies, and declining crop production and nutritional benefits.
INDIAN INITIATIVES TO TACKLE CLIMATE CHANGE
The problem of climate change is one that affects the entire world. Therefore, global cooperation is necessary for the creation of an effective framework. These obligations should also be based on "Common but Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities." India has actively participated in multinational initiatives to combat climate change. India, on the other hand, is aggressively pursuing national climate programs on its own. India has consistent environmental policies. With the necessity for domestic growth and economic development in mind, there is a focus on climate change adaptation.
India continues to aim for 450 gigawatts of renewable energy installations by 2030. India has committed to achieving net zero emissions by 2070. India has actively participated in multinational initiatives to combat climate change. With the necessity for domestic growth and economic development in mind, there is a focus on climate change adaptation.
INDIA SHOWS THE WAY FORWARD TO SDG2
Nearly 15% of India's $2.7 trillion economy comes from the agricultural sector. Government initiatives supported by NGO Environment India that encourage expansion in this industry will also open up more chances.
India has taken important measures to improve food security, including:
India-wide targeted public distribution system
National Nutrition Mission
National Food Security Act
The Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana
National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture
In addition, a number of national programs on livestock, agricultural technology development, and horticulture are intended to enhance India's agricultural sector.
THE WAY FORWARD
An approach that incorporates both short-term fixes and a long-term plan to combat the consequences of shifting weather patterns is necessary to address the global issue of climate change. Crop intensification, the adoption of crop types that can withstand high temperatures, and the use of green manures and biofertilizers can all be considered adaptation methods in agriculture. On the macro level, a long-term mitigation plan should put an emphasis on developing adaptive measures with investment in regions susceptible to the effects of climate change with the help of NGO Environment India. To combat the rising problem of hunger and food security in India, priority study on the effects of climate change is needed.
India has taken important measures to improve food security, including:
India-wide targeted public distribution system
National Nutrition Mission
National Food Security Act
The Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana
National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture
Crop intensification, the adoption of crop types that can withstand high temperatures, and the use of green manures and biofertilizers can all be considered adaptation methods in agriculture.
Search NGO CONTRIBUTING TO FOOD SECURITY IN INDIA
Since 1995, Search NGO has been working to raise the standard of living in rural areas throughout India. Search NGO is an NGO that promotes sustainable rural development. Their primary program areas are: Water Management, Agricultural Development, Local Participation, and Sustainability, Transform Lives one school at a time, and Outreach for Development. This NGO Environment India, was founded as a public, charitable trust and develop sustainable programs to address rural India's most urgent needs.
By enhancing the skills of farmers, particularly women farmers, in innovative agricultural technology and improved agricultural practices that boost crop yields, preserve water, and improve soil fertility, their Agricultural Development Program supports sustainable lives in India.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Is low volatility a good sign for stocks?

A note in Barron’s this morning highlighted an interesting fact. While all the broad stock market indices were slipping in reaction to the Fed’s announcement (short version: no rate hikes now but probably later), the VIX Index, which measures stock market volatility, was also down.
That’s unusual. More often falling stock prices come in tandem with increasing volatility. Economists theorize that when volatility increases, investors demand more compensation for the additional risk they are taking on. That means that they need to buy a stock’s future income stream—which reflects future company profits—at a lower price. Hence stock prices and volatility measures are negatively correlated. When one goes up, the other one falls.
Historically the highest peaks in stock market volatility have accompanied precipitous market drops. Black Monday in October 1987, the East Asian Currency crisis in 1997 and the collapse of the dot.com boom in 2000 all saw elevated volatility readings (see chart below).

Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, 2002.
So when stock prices and volatility fall at the same time, that’s interesting but also possibly transitory.
Consider that stock prices have only been falling for a few days now (and both the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq 100 eked out a small gain today), while longer-term the trend has been mostly upwards. The S&P 500, for instance has been on the rise, more or less, since March 10, 2023. Even after a couple of sessions of pullback, it’s risen 13% from that trough.

Interestingly, the VIX peaked at 26.52 just about the same time, on March 13, and has been on a downtrend ever since. So for most of early 2023, the market performance/VIX relationship has worked exactly as expected—stock prices have risen and volatility has dropped.

Barron’s noted that the unusual synchronicity probably indicated that investors weren’t too worried about the recent market decline, a good indicator that the current downturn might be quick and relatively painless.
However, lower volatility has its own downside. Without sharp market movements, it’s harder to make money with active bets—and hedge funds, trading desks and active managers all see lower profits and revenues. A calm market sinks fewer ships, but it becalms the faster ones. That’s good for long-term investors, but not so hot for the financial industry.
0 notes
Text
https://www.geertvandenbossche.org/post/a-last-word-of-caution-to-all-those-pretending-the-covid-19-pandemic-is-toning-down
The current expansion in prevalence of infectious Sars-CoV-2 variants is highly problematic because it erodes natural Ab-based, variant-nonspecific immunity in the non-vaccinated part of the population. The high infectivity rate that results from this expansion not only further enhances the expansion of these variants but may also drive natural selection of viral variants that are featured by an even higher level of infectiousness. Erosion, therefore, of natural (antibody) Ab-based, variant-nonspecific immunity promotes breeding and transmission of more infectious viral variants in the non-vaccinated part of the population. On the other hand, mass vaccination promotes natural selection of increasingly vaccine immunity (VI)-escaping variants in the vaccinated part of the population. Taken together, mass vaccination conducted on a background of high infectivity rates enables more infectious, increasingly VI-escaping variants to expand in prevalence. This evolution inevitably results in inclining morbidity rates in both, the non-vaccinated and vaccinated population and precipitates the emergence of circulating viral variants that will eventually fully resist vaccine-mediated immunity (VMI). This is why mass vaccination campaigns should not be conducted during a pandemic of a highly mutable virus, let alone during a pandemic of more infectious variants (unless transmission-blocking vaccines are used!). It is critical to understand that a rapid decline in viral infectivity rates that is not achieved by natural infection but merely results from expedited mass vaccination campaigns will only delay abrupt propagation of emerging, fully vaccine-resistant viral variants and hence, only delay the occurrence of a high wave of morbidity and mortality. In contrast, mass vaccination campaigns that are progressing more slowly, especially when conducted on a background of relatively low infectious pressure, will result in a steadily growing propagation of increasingly VI-escaping variants and hence, cause a wave of morbidity and mortality that continues to grow bigger and larger as more and more people become vaccinated. It’s only when fully vaccine-resistant viral variants will become dominant that this wave will start to peak.
To prevent more detrimental consequences of the ongoing evolution of Sars-CoV-2, we have no choice but to mitigate erosion of natural, Coronavirus (CoV)-nonspecific immunity in non-vaccinated individuals and exertion of strong immune selection pressure on immunodominant vaccinal epitopes in vaccinated individuals. This is to say that we must stop mass vaccination and lower viral infectivity rates immediately. Continued mass vaccination will only lead to a further increase in morbidity and hospitalization rates, which will subsequently culminate in a huge case fatality wave when expansion of more infectious, vaccine-resistant variants will explode.
[...]
In other words, high viral infection rates drive natural selection and self-amplifying expansion of more and more infectious Sars-CoV-2 variants in the non-vaccinated part of the population while high vaccine coverage rates drives natural selection of increasingly (vaccine-induced) VI-escaping Sars-CoV-2 variants. This evolution is now driving enhanced rates of disease in both populations. Consequently, mass vaccination during a pandemic of more infectious variants self-amplifies natural selection and expansion of more infectious, increasingly VI-escaping Sars-CoV-variants. Both, the vaccinated and non-vaccinated part of the population fully contribute to this evolution.
Because of all of the above, I can certainly not endorse the opinion of those who think that the decrease in disease severity and hospitalizations that is now observed in several countries where mass vaccination is well advanced would be due to some kind of ‘attenuation’ of viral variants or to some kind of growing HI (herd immunity). One rather concludes that this pandemic is far from over or from transitioning into endemicity. There can be no doubt that, at this stage, the pandemic is gearing up for breeding vaccine-resistant ‘supervariants’, a phenomenon that is at risk of fueling an even larger wave of morbidity, hospitalization and, unfortunately, also death, not at least in the vaccinated part of the population.
The ongoing mass vaccination campaigns must immediately be abrogated because the vaccines fail to block viral transmission and their large-scale use during a pandemic of more infectious variants will inevitably lead to vaccine resistance of circulating Sars-CoV-2 variants.
[...]
Both, long-lived Sars-CoV-specific immunity acquired upon recovery from disease and innate, CoV-nonspecific (antibody) Ab-mediated immunity normally contribute to establishing broadly protective herd immunity and thereby enable a natural CoV pandemic (or, for that matter, any pandemic of an acute, self-limiting viral disease) to eventually transition into an endemic phase. However, circulation of more infectious variants comes with a high price to pay for herd immunity to establish as high infectivity rates are more likely to erode natural, polyreactive (i.e., CoV-nonspecific) immunity in young and/ or healthy individuals. As a result, morbidity and hospitalization rates, and ultimately also the number of deaths, will increase. This self-amplifying cycle of enhanced viral infectiousness (resulting in enhanced viral infectivity rates) would only come to an end when the population density is diluted down to a level low enough for viral transmission (of a highly transmissible/ infectious variant!) to substantially diminish.
Whereas fast and dominant propagation of naturally selected, more infectious variants continues to erode the natural first line of variant-nonspecific immune defense in the non-vaccinated part of the population, vaccination of large parts of the population and contacts among vaccinated and non-vaccinated subjects are driving natural selection and adaptation of increasingly (vaccine induced) VI-escaping variants and are, therefore, increasingly compromising VMI (vaccine-mediated immunity). Neither previous CoV infection (including Sars-CoV-2 infection), nor higher vaccine coverage rates can compensate for the lost immunological capacity. Indeed, memory T cells elicited upon previous CoV infection or vaccination are not reportedly known to be endowed with cytotoxic activity towards CoV-infected cells, nor can S-specific Abs (antibodies) elicited upon previous CoV infection or vaccination prevent spreading of more infectious Sars-CoV-2 variants. Molecular epidemiologists have suggested that immune failure to block viral transmission (e.g., in immunosuppressed patients) causes variants to convergently evolve specifically selected mutations, thereby enabling escape from VMI. VI (vaccine induced) escape together with suppression of natural, CoV-nonspecific Abs by vaccinal Abs will make vaccinees highly susceptible to contracting Covid-19 disease.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
TAFAKKUR: Part 80
Aging: Part 1
I will start with the cliche: “man is born, grows, ages, and finally dies.” So this cycle of life is inevitable, although at different times in history the speed of this process has varied tremendously. In early times, when there was purity in nature, it is narrated that Prophet Noah lived for 950 years. Whether other people at the time had that long a life span is not known for certain, but this suggests that human beings lived longer lives in earlier times. Later, at some point it was reduced to a mere 30 or 40, years due to wars and diseases like the plague. Nowadays, lifespan depends on the level of prosperity in a society, ranging from 33 in Zimbabwe, for example, to 80 in Sweden. But then, why bother to avoid or prolong a life whose end is inevitable, namely death? If you consider the time needed for a human to mature and be educated, you will see that these days, people are assumed to have gained experienced after the age 30, and that the longer they live, the more wisdom they can gain and impart and the more good deeds they can accomplish for this world and the Hereafter. So prolonging the life span is not just a decadent materialistic pursuit, rather it can actually bear beneficial fruit for humanity, both spiritually and materially.
However, as one’s age increases, most bodily functions peak and then start to diminish. A better aging strategy would be to age in the healthiest possible manner; i.e., keeping the physical and mental functions as sharp as possible, in particular the memory, so as not to lose human dignity in old age.
Aging and Memory
As one ages, reactions start to slow, the speed of understanding and the level of concentration diminish. The precipitous decline of dopamine-containing neurons in the human brain after age 45 is a universal characteristic of the aging process. The nigrostriatal region of the brain is richest in dopamine and undergoes the most rapid aging of any brain area. Age-associated depletion of dopamine also accounts for less noticeable symptoms, like a decline in physical drives and brain functions. These reactions are mostly on a mental or psychological level. In addition to these, wrinkles appear in the skin, hairs gray, and joints become gnarly. Perhaps, most important of all, is that according to recent research carried out on the brain, by the time most people hit 40, their brainpower starts to weaken. This does not mean that people become incompetent, just a bit slower in the cognitive process. This phenomenon is called “generalized slowing” by psychologists. According to James Birren, the Associate Director of the Center on Aging at the University of California, Los Angeles, the first signs of aging appear on tests used to measure mental speed and acuity, in which people count the number of lights flashed on a screen, for instance, or trace a complicated pattern while looking at a mirror.
“But eventually the down-turn affects almost everything we do,” says Birren, “From how fast we hit the breaks when a car pulls in front of us to how quickly we learn new skills on the job or remember old what’s-her-name’s name.”
Then the question is whether the slowing process is unavoidable. According to psychologist Robert Dustman, the answer to this is yes. One of the country’s top experts on aging and the brain, Dustman directs the Neuropsychology Research Laboratory at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Salt Lake City. He’s just turned 70 and shows no signs of slowing down himself. “It is true that when we compare 20-year-olds with 60-year olds on almost any test that measures the speed of information processing, younger people on average score significantly better than the older ones,” he says, “But that does not have to be. There is a simple way I can ward off the scourge of slowness,” Dustman says. And the way to do this is to stay in shape.
At first it seems to go against common sense that in some way a mindless act like jogging or striding around a park is relevant to the speed of thinking. But Dustman explains the connection in a very logical way.
Every cell in the body requires a continuous supply of oxygen and nutrients to function at its peak. But surprisingly, no cells need a greater oxygen supply than the gray matter that rests between our ears. The brain, although it makes up only 2% of our body weight, uses up 25% of the glucose and oxygen supply.
Now suppose a person slips out of shape, their heart gets lazy, the arteries get clogged, the blood flow to capillaries slows down, and the oxygen and nutrient supply to the brain falls us. As a result, neurons get less than they need to function properly, the electrical signals slow down, and hence the mind slows down. A recent study shows that blood pressure (or lack of it) is highly correlated to memory; so much so that, a reduction of it causes the memory to weaken.
But getting older does not mean that one must face a full-scale slowdown, Dustman says. The problem is that by 45, when the brain is quickly falling into decline, most of us neglect to perform the activities that keep the arteries open, the heart strong, and blood flowing; namely exercise. Dustman’s own studies suggest that working out might be an antidote. In one of his studies, he ran 60 male volunteers, half in their twenties, half in their sixties, through the standard mental tests. As expected, the younger group had higher mental speeds. But when Dustman looked closely at the older group, he noticed that the ones who were exercising or had remained active had a brain speed that was comparable to that of the younger set.
The tests included actions as simple as pushing a button each time an X appeared in a long string of O’s to memorizing numbers and symbols. “On many measures,” says Dustman “the older men in good condition scored just as well as men 30 and 40 years their junior.” In real life, that is, they could find a number in a phone book or remember that sensible is a synonym for rational.
When one exercise, in other words, the sections of the brain which control movement and balance are fired up, the electrical signals zap back and forth along the nerves from the brain to the muscles and tendons. The eyes, the inner ear, and other sensory nerves all roll into action. The benefits of these can be detected clearly in the brainwaves and electrical impulses recorded by researchers.
Indeed, in Dustman’s study, the older men who were still fit had surprisingly youthful-looking brain waves. They produced more alpha waves, a pattern associated with calmness under pressure, and had steeper peaks and valleys in waves, which signifies an ability to block out distractions. Furthermore, when subjected to a sudden flash of light or a sound blast, they were faster to produce a wave called P-300, which is associated with fast reactions. “People in good shape can really focus,” says Dustman. “They can pen a letter to a friend without the sound of children playing downstairs disturbing them. They can fill out tax forms correctly after reading the directions once.” For someone who’s out of shape, the news is grim. In addition to problems that range from overweight to heart disease and diabetes, the results of a sedentary life style, it turns out that the brain will very likely start to weaken as well. Still, Dustman is optimistic. He once encouraged 42 sedentary people over 55 to exercise (walking or jogging) three times a week. After four months, the aerobic capacity of the volunteers increased 25 % and they scored better on mental speed tests. In light of this study, Dustman thinks that even easy exercise, such as brisk walking can speed up the minds of people after years of inactivity. The time required varies, however. In similar studies, it took about a year to observe an increase in the speed of the brain.
But it is not time that is important here; the goal is rather not to lose brain capacity until a very old age. It would be better if one were always to keep in shape, as it is easier to keep something that works running than to start it up again once it has slowed down. “The real benefit seems to come from making a lifelong habit of staying active,” says Dustman.
It is better to maintain a regular routine of exercises than to start up new ones. Researchers at the University of Illinois compared middle-aged lab rats who padded daily on a running mill to rats who negotiated a complicated obstacle course of rope bridges and seesaws a few times a day. Predictably, both groups got more blood flowing to the brain. But the obstacle-mastering rats had 25% more hard-wired connections between neurons. Assuming the same is true for humans, then exercises which require more brain activity are potentially more rewarding.
Aging and Sleep
The obvious dangers of not getting enough sleep include mental fuzziness, an increased chance of accidents, illness, psychological problems, and decreased productivity at work or school. But Dr. Eve Van Cauter wrote in the prestigious medical journal Lancet that less sleep can actually speed the process of aging. In her informative study, young men who were allowed to sleep only 4 hours each night showed signs of aging in less than a week. Their glucose tolerance dropped considerably, and they started to release cortisol, the stress hormone, at a greater rate than normal.
Sleep offers the body an opportunity to heal and rebuild itself. Pro-sleep nutrients might help in this cause. For example, it has been shown that nutritional supplements containing zinc, magnesium, and pyridoxine (vitamin B6) , among other benefits, help sleep efficiency. A herbal amino acid 5-hydroxytryptophan is another promising sleep aid to use in times of extreme stress. Among sleep promoting herbs from traditional Chinese medicine are ziziphus spinosa (jujube), schisandra chinensis, and bupleurum chinense (Chinese thoroughwax). These herbs seem to relax the muscles and soothe the central nervous system. Sleep is and remains to be the most precious source of energy replenishment.
Melatonin: A God-given Sleeping Pill
Melatonin is a natural molecule made by the pineal gland, which is located in the brain. Melatonin is made from an amino acid called tryptophan. Tryptophan is an essential amino acid, that is, the body cannot make it; we need to get it from the foods we eat. Tryptophan is found in wide variety of foods. As we consume tryptophan during the day, the body converts it into serotonin, an important chemical for the brain that is involved with moods. Serotonin, in turn, is converted into melatonin. This conversion occurs most efficiently at nights.
Melatonin helps to set and control the internal clock that governs the natural rhythms of the body. Each night the pineal gland produces melatonin, which helps us to fall asleep. Research about this molecule has been going on since it was discovered at Yale University by Dr. Lerner in 1958, but recently there has been a great deal more attention being paid to melatonin. About a thousand articles on melatonin are published annually. One major reason is that scientists are discovering that melatonin is not only associated with deep sleep, but also with our hormonal, immune, and nervous systems. Research is accumulating about melatonin’s role as a powerful antioxidant, its possible anti-aging benefits, and its immune-enhancing properties.
Aging and Free Radicals
A free radical is a molecule that contains an unpaired electron through reactions with the essential element oxygen. These molecules “steal” electrons from nearby molecules to complete that final electron pair for stability. Then they are no longer free radicals, but they convert the new combined molecule into a new free radical. In a living organism, this process can cause a chain reaction of severe cellular damage, unless prevented.
The theory that free radicals are agents of bodily destruction is gaining widespread acceptance, as is the value of antioxidants in preventing such an occurrence.
According to the journal Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science, the excess of free radicals in our body, i.e. “the domino effect”, is a critical factor in many health problems. An interesting and concerning fact about free radicals is that they cause the same reactions within the cells that occur during exposure to radiation. Free radicals released in the body destroy even proteins, the essential constituents of the body that regulate hormones and enzymes and that make up nerves, muscles, skin, and hair. It is usually suggested that antioxidants are used to fight these harmful free radicals. Fruits and vegetables are plentiful in vitamins A, C, and E, the key antioxidants. Polyphenols, which are found in grapes and green tea extracts are potent antioxidants. In fact, scientists have found out that procyanidins are the most promising polyphenols. In Japan, scientists have discovered that they may be 50 times more powerful than vitamins C and E in fighting free radicals. Alpha-lipoic acid, which is soluble in both water and lipids, can neutralize free radicals throughout the body. In fact, alpha-lipoic acid is involved in so many different antioxidant functions that it has been called the “universal antioxidant.” Citrus bioflavonoids and certain fruit and vegetable pigments are also strong free radical fighters.
Deprenyl: An Anti-aging Treatment?
Deprenyl (selegiline) provides selective protection against age-related degeneration of the dopamine nervous system. It is the only inhibitor used in clinical practice. The rate at which dopamine neurons age is quite variable. Before age 45, dopamine levels stay quite stable. Starting at 45, the decrease in average dopamine content in healthy people is linear, at 13% per decade. When it reaches 30%, the symptoms of Parkinson appear.
The sensitivity of the dopaminergic nervous system to oxidizing free radicals has been well established. The protective effect of deprenyl in lessening the neurotoxic effect of the oxidants (6-hydrpxydopa and 6-hydroxydopamine) appears to correlate with increased antioxidant enzyme levels. The increase in the antioxidant level is proportional to the deprenyl intake.
There as yet has been no definitive study of the long-term use of deprenyl in healthy people as a life-extension and cognitive-enhancing drug. But there has been extensive animal research. The lifespan of deprenyl-taking rats is significantly greater than normal rats, in fact, all the control rats died before the first deprenyl-taking rat died. Early research with deprenyl in humans (early-diagnosed Parkinson patients) shows delayed development of symptoms. Deprenyl has also been established as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Eventually, deprenyl has the potential of becoming a general treatment for aging in people above the age of 45.
Conclusion
Although we know for sure that there cannot be an absolute cure for aging, the results of it can be slowed down considerably. Soundness and health of mind are desirable traits for all ages, not just for the elderly. After many years, many elderly people lose much of their memory and mental capacities; this occurs just at the time when they can pass on all their wisdom and experience to the younger generations. Hopefully, with the advent of science and technology, the deficiencies in the brain due to aging can be avoided to a certain extent. The solution lies in a balanced collaboration of modern medicine and traditional natural cures that have been practiced for centuries.
#allah#god#muhammad#prophet#sunnah#hadith#quran#ayah#revert#convert#revert help#islam help#muslim help#reminder#religion#dua#salah#pray#prayer#welcome to islam#how to convert to islam#new muslim#new revert#new convert#Convert to Islam#revert to islam
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding Elk
Social Construction
Elk often group along with the cows and calves in 1 herd, the elderly bulls in a different herd, along with also the younger bulls remains a different herd, though old and young bulls might be seen together. Throughout the summer and spring, cow elk traveling in massive herds with their own calves. These herds are usually composed of an elderly dominant bunny, her sisters, and their wives and their kid's favorites. The bulls frequently remain beside the cows before the start of the rut in late August/early September and remain together till November. However, I've found bulls with cattle since early as July. Following the joys, the bulls normally form loose groups and then proceed independently. Elk of both genders and all ages might be seen together in winter, particularly when food resources are limited.
Habitat
Elk is all grazing animals; hence they're mostly a species of plains, open woods, and subtropical mountains. But they're extremely adaptable and flourish from the densely populated regions of the badlands of the Dakota's, and also the semi-desert regions of New Mexico, Arizona and Oregon. Back in Minnesota and Michigan elk occupy mixed hardwood forests nearby agricultural lands at the proximity of people.
In mountainous areas, elk use open coniferous woods in foothills or mountains nearby creek and river drainages. These regions offer a combination of distinct habitats assembly in borders where many forage species happen and in which there's fresh water for everyday usage. Studies indicate that elk like to remain inside 1/2 mile of free-flowing water. Preferred advantages include drainages in which evergreens fulfill aspen, alder, willow and footprints, and in which these species match meadows or wetlands. Scientific studies demonstrate that the borders between two distinct forms of habitat supply double the number of species and volume of food compared to fifty meters into the habitat. As a result of this elk usage declines after 100 meters into particular habitats. Habitats covering 30 to 80 yards meet the typical biological demands of elk for cover or feeding.
Meadows
Elk favors feeding regions ranging from 0 to 25 percent protect and 20 to 45 yards in size. They generally cross openings of 490 ft. When openings reach 985 ft elk would rather journey around instead of round the opening. Elk utilizes open mountain high meadows adjoining woods on a couple of those hills since these meadows provide forage, pay and accessibility to distinct microclimates within a comparatively little space. Meadows supply the grasses, sedges, and Forbes (wildflowers and weeds) which elk would rather feed.
Slopes and Drainages
The angle of the incline has an obvious impact on elk usage in mountainous areas due to plant growth and microcline (fever ). Elk uses increases together with the steepness of this incline to a max of 30 to 40 percent, using favored slopes between 15 and 30 percent. There's a noticeable decrease in elk usage when incline angles exceed 40 percent. Upper slopes are favored over lower and middle slopes in the winter and summer. River drainages and shore are utilized widely in the summertime since they supply thermal refuge and late summer meals, and they're usually employed as travel lanes. Northeast slopes are greatly utilized in summer months and early autumn since they keep more moisture and supply succulent forage for the animals to consume. South facing slopes have been utilized twice as great in winter as north facing slopes, and likely due to solar power, which causes snow melting down and exposes accessible forage. The steep, rocky terrain of mountain slopes provides escape paths and supplies succulent forage in the summertime.
Coniferous Forest; Thermal and Safety Cover, Bedding Areas
Coniferous (evergreen) forests provide escape and safety protection for elk by giving protection against heat through color, protection against the chilly by holding in warmth, protection against the wind along with windchill variables by lowering wind speed by 50-70 %, and protection against precipitation. The favorite coniferous woods for thermal cover (color in the summertime, wind security in autumn and winter) is either ponderosa pine/Douglas fir or alternative mixed conifer forms. The thermal cover should be 30 yards or more in size so as to cut down wind speeds. Ponderosa pines 40 ft or more in height, with no lower limbs and lean ground cover, are all employed in warm weather since they supply shade and permit cooling breezes to happen.
When safety pay is used for concealing, the forest overstory is typical of moderate elevation using downed woody material and plentiful surf, with roughly 200 trees per acre. The preferred safety cap is 600 feet broad. The exact identical sort of cover is utilized by elk in chilly weather to decrease heat loss. Elk usage of safety cap declines between 450 and 600 foot to the pay; elk do not frequently go deeper to hefty cover than 600 ft. When fleeing risk, elk transfer an average of 375 feet to cover before feeling protected.
Preferred bedding pay for elk is usually 75 to 100 percent shut, along with 30 to 60 yards in size. During hot intervals elk daybeds have been usually found on north-facing slopes; nighttime beds are usually located on south-facing slopes, and frequently in open locations. During cold intervals day beds are seen on south-facing slopes; nighttime beds are often around the side of mountains. Most bedding websites are observed near wood clumps, with the exclusion of hot weather nighttime beds, which can be usually in open locations.
Forage
An analysis of Roosevelt Elk revealed that by June through August their forage consisted of roughly 20 percent Forbes, 20 percentage navigate along with 60% kinds of grass and sedges. Their diet altered in September through November, when 20 percent had been navigating, and 75 percent had been sedges. This shift could result from the deficiency of succulent Forbes after in year. Preferred Forbes of Rocky Mountain elk throughout the fall contain Frequent commander, Slimpod shooting star, American Roast, Dotted Grayfeather, Alfalfa, Yellow sweet clover, Mountain bluebells, Cord-leaved Montia, Siberian Montia, Alpine forget-me-not, Wilcox penstemon, Columbian groundsel, Sitka valerian, Wyethia, and Frequent beargrass; favored fall blossoms and grass-like plants comprise Bluestem wheatgrass, Bearded blue bunch wheatgrass, Blue wildrye, Idaho fescue, Sheep fescue, Pary Rush, Millet woodrush, Timothy, Bluegrass, and Needle-and-thread; favored fall shrubs and trees comprise Curlleaf mountain mahogany, Quaking aspen, Bitter cherry, Antelope bitterbrush, Prickly climbed, Willow, Blueberry older, Blackbeard American and elder mountain ash. Elk is opportunistic feeders and also love the top boughs and fibers of recently dropped spruce and walnut the bark of recently dropped aspen, and acorns in which accessible.
Bulls and cows frequently use different quantities of the exact identical food resources. In 1 research bulls utilized 10 percent more bud cows and cattle 10 percent greater Salmonberry in September than they did in August. There has been a noticeable difference in the sum of food consumption between bulls and cows from mid-November, following the rut. In general cow, intake has been decreased from September to October, whilst bull consumption was greatest following the rut. This is most likely because of the simple fact that bulls will need to place on fat for them during the rut, as well as the cows consume less since the Warriors have started to forage more and consume less milk. Elk consumes between 1.7 and 2.9 lbs of dry meadow bud a hundred lbs of body fat; big bulls can consume from 12 to 18 lbs each day.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chinese checkers online free

Chinese checkers online free for free#
Some of the features include: Upload File and URL
Chinese checkers online free for free#
Our plagiarism checker for free offers top-notch features that help users to check the originality of the content. Hence, you can use our plagiarism detector without having any privacy concerns because whatever type of text you enter, we vanish it from our database as soon as the plagiarism checking is done. We respect the security and privacy of our users. It also never tries to fool you by identifying illogical duplication from unique content. Our online plagiarism checker doesn’t perform any magic trick and displays accurate results with percentages of plagiarized and unique text. Therefore, there is no way a plagiarized phrase or paragraph could dodge this best free plagiarism checker. This tool performs a deep plagiarism check by evaluating each word in a 1500 word content and comparing it to billions of web pages on the Internet. Hopefully, policymakers will seize on this opportunity.FREE PLAGIARISM CHECKER In-depth Plagiarism Check China’s black-box policies offer a window of opportunity for India to woo foreign direct and portfolio investors to bet on a liberal and well-managed economy that is on the revival path post-pandemic. For India, which relies on China more for imports than exports, these developments may spell a continuation of supply chain disruptions that have hit sectors from automobiles to pharmaceuticals. As China is a prodigious consumer of industrial commodities from crude oil to iron ore and copper, this casts a cloud on commodity-driven economies such as Brazil and Australia. Economies such as Taiwan and South Korea which thrive on feeding China’s industrial juggernaut, are already facing the heat. Given that China was expected to chip in with nearly a fourth of global growth and a sixth of all trade in the post-Covid world, this crisis spells trouble for global economic prospects. But with exports the only functioning growth engine now impacted by the global slowdown, China’s policymakers may not find it easy to revive animal spirits, especially after having engineered the slowdown in the first place. Some commentators believe that all these developments represent efforts by the Chinese leadership, ahead of the crucial 20th Congress of the Communist Party later this year, to showcase their seriousness in pursuing high-quality growth devoid of cronyism. To this volatile mix, geopolitical tensions over Taiwan have recently been added. With these curbs hitting local government revenues hard, they’ve scaled back on public services and infrastructure buildouts, for long the mainstay of China’s growth model. Technology and streaming platforms, earlier engines of growth, have also seen regulatory crack-downs. This came on top of Beijing’s three-red-lines policy which all but shut off credit to the real estate sector, triggered defaults by developers and mortgage strikes by homebuyers, forcing the property market into a decline. This has played havoc with China’s manufacturing output which has grown sub-4 per cent lately and dented consumer spending by 0.8 per cent in the last quarter. Even as most nations discarded lockdowns and turned to vaccinations to control Covid from 2021, China has inexplicably embraced a zero-Covid policy that has locked down its major industrial hubs and severed its connections with the rest of the world while the draconian quarantine rules have hit labour mobility. While the economic troubles at most countries were precipitated by external events such as Covid and the Russia-Ukraine war, the curious aspect of China’s slowdown is that it appears to be partly self-inflicted. The recent cut in interest rates by the Chinese central bank, even as other banks are on a tightening spree, has stoked fears that the pace of deceleration in China is acquiring a momentum of its own. The IMF has sharply trimmed its GDP growth forecasts for China to a 40-year low of 3.3 per cent in 2022 and 4.6 per cent in 2023. After a perfect storm of events, China announced a shocker of a GDP print for April-June 2022 with the economy expanding just 0.4 per cent compared to 4.8 per cent in January-March. But a crisis of equally serious and complex proportions seems to be unfolding in China. Lately, global economists and forecasters have trained their sights on the West to worry over the possibility of a US recession and stagflation in the Eurozone.

0 notes
Text
Is the Euro Uninvestable? The FX Question du Jour
Is the Euro Uninvestable? The FX Question du Jour
The euro’s value relative to the US dollar (EUR/USD) recently dipped below parity for the first time since 2002. So precipitous and rapid has been the decline in EUR/USD over the past year that many mean reversion/short gamma funds have had to liquidate and return the remaining capital to investors. Hence the question posed in the title above. While charged buzzwords like “uninvestable” should be…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Iris Publishers
Responses of Solanum Lycopersicum to Organic Fertilizers Application
Authored by Afolayan Ezekiel Taiwo

This study compares the effects of organic manure (Plants and animals) on the performance of Solanum lycopersicum L. The work was conducted at the Botanical nursery, behind the Botanical Garden, Federal College of Education, Abeokuta, Ogun State, Nigeria. The study adopted Complete Randomized Block Design (CRBD) in 3 replicates. The treatments were animal manure of cow dung, poultry dung, rabbit dung and Plant manure of Gliricidia sepium. The plants characters measured include the leaf length, stem height, number of branches, number of leaves, number of flowers and fruits. Data obtained were analyzed using the Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) while means were separated with Duncan Multiple Range Test (DMRT). Results obtained showed that growth characters (number of leaves, number of branches, stem height and leaf length) and yield characters (number of flowers and fruits in Tomato) were influenced by the plant manure of Gliricidia sepium and animal manures of rabbit droppings. From the results, it was observed that Gliricidia sepium and rabbit dropping were the best manures for the cultivation of tomato.
Keywords: Solanun lycopersicum; Gliricidia sepium; Organic manure; Yield
Introduction
Tomato, (Solanun lycopersicum) is one of the most important vegetable fruit crops grown in Nigeria whose production is widespread in the country with a total annual production of more than 145,000 tons [1] and it is cultivated mainly in rural and partly in Urban area [2]. It is a flowering plant of the night shade family (Solanaceae) that is cultivated extensively for its edible fruits. Almulla et al. [3] reported that there are over ten thousand (10,000) varieties of tomatoes.
Vegetables production in most parts of Africa, Nigeria inclusive, has been a backyard garden operation whereby farmers produce for their family. Because of increased demand for tomatoes, among other vegetables in Nigeria, for domestic and industrial uses, most small holder farmers have expanded and diversify vegetable production, resulting in increased cultivated hectares [4]. Tomato cul tivation in Nigeria covering mainly the coastal belt of the country up to the northern desert regions records yields of between 2.2 to 3.3 ha-1 [5] is far below the world average of 27.5 t ha-1. This low production of tomato in Nigeria is caused by salinity, drought, excessive heat, declining soil fertility, over cultivation, over grazing, desertification etc. [4]. In addition, this is related to incidences of pests and diseases, poor crop management and shortage or lack of well adapted and high yielding varieties.
Tomato plants have high requirement, they are heavy feeders, for macro nutrient elements, including potassium (k) and calcium (Ca) and some micronutrients such as iron (Fe), manganese (Mn) and Zinc (Zn) [6]. A study by Hinman, Pressan & Sharp [7] revealed that without adequate supply of potassium and calcium for tomato plant uptake and utilization, tomato fruits will not accumulate soluble solids contents (Sugars) and will be susceptible to physiological disorders such as blossom end rot. According to Jones 2008, smaller requirements of the elements such as for dry matter portioning and fruit setting of the plants. Low soil fertility along with some of other environmental factors such as temperature, precipitation, humidity, solar radiation, wind is reported to affect tomato performance, hence its overall production [8]. And also, application of fertilizers as nutrient supplements is inevitably pertinent in increasing crop turnout in impoverished soils.
Tomatoes require a minimum of eight (8hrs) of continuous sunlight each day. It requires three to four months (3-4) of warm, clear, fairly dry weather to produce best. Tomatoes need consistent night temperature between 550F and 750F to set fruits. Fruit will not colour properly when night temperature stays above 850F and plant will quit growing when growing temperature go above 950F [4,9]. Tomatoes will thrive well on evenly moist, not too wet and not too dry. Too much water will drown the plant. Too little water will stop fruit production. Test the soil by sticking the finger into the soil and if it comes out wet, it does not require water. Prativa & Bhattara [10] reported that almost any type of soil will grow tomatoes, but sandy loam is best for early tomatoes while compost-amended clay is ideal for late tomatoes.
Tomato is a glossy red but sometimes yellow pulpy edible fruit with a lot of seeds. It is a very important function in the diet of man. Labeled as a vegetable for nutritional purposes, tomatoes are good source of vitamin C and the phytochemical lycopene [11]. The fruits are commonly eaten raw in salads, served as a cooked vegetable, used as an ingredient of various prepared dishes and pickled. Additionally, a large percentage of the world’s tomato crop is used for processing products which include canned tomatoes, tomato juice ketch up, paste and sun-dried tomatoes or dehydrated pulp [12].
Tomatoes are a good source of vitamin A, B, Potassium and vitamin C. which help the body to get rid of harmful free radicals and lowers cholesterol level in the blood which invariably prevent heart disease. Tomatoes are known to have a mineral called Chromium which works in keeping blood sugar in check. It also helps to improve the digestive system and the liver. Tomatoes are loaded with fiber which helps to prevent constipation [13]. The vitamin C in tomatoes controls the increase of stress hormones and helps the body to remain energized and healthy. Chlorogenic acid in tomato helps to protect the body form the adverse effects of cigarette smoke [14]. The lycopene in tomatoes is reported to control the growth of cancer cells especially prostate, stomach and colorectal cancer (Paswan, 2005). Tomatoes contain lycopene which is used for facial cleanser [15]. It cleanses and refreshes your skin and the vitamin A in tomatoes protects the hair from external damage. The vitamin K and calcium make the bone stay strong. The antioxidants present in tomatoes, are scientifically found to protect the body against cancer, including colon, prostate, breast, endometrial, lung and pancreatic tumors. Zeaxanthin, another flavonoid compound helps to protect eyes from age related disease in older adults by filtering harmful ultraviolet rays (Willer et al., 2005). These antioxidants also have anti-inflammatory effects on the body as it helps to fight inflammation throughout the body [16].
Organic manure can be applied to soils as compost or in their fresh state. According to Cambardella et al. [17], fresh organic materials contain higher inorganic nitrogen concentrations and have higher net nitrogen mineralization rates than composted manure. Paul & Beauchamp [18] reported that plants treated with organic manures exhibited higher dry matter in the first growing season than fresh manure. In Africa, animal manure is applied to the soil for fertility related issues and its benefits are well documented. Nutrient content in animal manure differs because of the variations in diets of the animals, collection and storage. Manure and other waste products of livestock have been used as soil amendments for decades and were the only ways of enhancing soil productivity before mineral fertilizers were invented [19]. Goat, sheep, cattle and chicken manure are the common manure, used in the southern African regions with cattle contributing two thirds of the total amount of manure found and the remainder is contributed by sheep and goat manure.
Use of organic manure at agronomic rate for plant nutrient supply and for beneficial effects on soil physical properties is a traditional agricultural practice (Haynes & Naidu, 2004). Over the last decade, the effects of organic manures on soil properties have received renewed attention due to an increased interest disposal of large amounts of waste being generated. Manure is a good source of macro and micronutrients [20]. Manure contains all nutrients that plants need and is high in potassium and relatively low in phosphorus and nitrogen which are the two most deficient nutrients in the soil [21].
Low yield of crop in most African countries was as a result of nutrient depletions, desertification caused by either climate change or deforestation, erosion, over cultivation, over grazing, etc.
This study aims at using ecologically friendly approach in enriching the soil and improving crop yield to combat hunger and starvation in Africa continent.
Materials and Method
This research was conducted at the Botanical Gardens, Biology Department, Federal College of Education, Abeokuta, Ogun State, South Western Nigeria located in a rain forest. Tomato seed obtained from the germplasm of National Centre for Genetics Resources and Biotechnology, Ibadan, Oyo state, Nigeria (NAGRAB). Soil which was oven-dried was bagged in empty cement bags and was laid out in a completely randomized block design with three replicates. Treatments for this experiment consists of 100g of cow dung/bag, 100g of poultry manure/bag, 100g of rabbit droppings/ bag as animal manure and 500g of Gliricidia Sepium/bag as plant manure.
These treatments were buried in the respective bagged soil for two weeks before planting. Five seeds were planted per bag. This was thinned to one per bag at two weeks after emergence. The following growth and yield characters were measured in this experiment: Stem height, Leaf length, Number of leaves, Number of branches, Number of fruits and Number of flowers.
Data obtained from these parameters were analysed using Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) while means were separated with the Duncan Multiple Range Test (DMRT).
Results
Table 1 shows the growth influence of different organic fertilizers on the stem height of Solanum lycopersicum. At 2 weeks after planting (2WAP), it was observed that tomato plants treated with Gliricidia sepium had the highest value (40.7 cm) and the value was significantly different (p<0.05) from all other treatments while the tomato plants treated with the untreated plant (control) had the least value (10.1 cm). The low value observed for cow dung at this time may be that the plant is not fully adjusted or that the animal remains had not fully dissolve for absorption by the plants.
At 4 WAP, the tomato plants treated with Gliricidia sepium had the highest values (41.0 cm and for the plant height. This value was not significantly different (p<0.05) from those obtained from rabbit droppings-treated plants but was significantly different from all the other treatments. The untreated plants had the least values (16.3 cm). This trend was maintained at 6 WAP. But at 8 and 10 WAP, it was observed that tomato plants treated with rabbit droppings had the highest values (49.8 cm and 50.2 cm) respectively. It was worthy of note that these values were higher than all the other treatments. The untreated plants had the least values throughout the time of the experiment.
The number of branches of solanum lycopersicum plants treated with different organic fertilizers was as shown in Table 2. At 2 WAP, it was observed that tomato plants treated with Gliricidia sepium had the highest value (13.4) for the number of branches while the untreated tomato plants had the least values (4.20). At 4WAP, tomato plants treated with rabbit dropping had the highest value (16.6) for the number of branches while the untreated plants had the least value (6.6). At 6WAP tomato plants treated with Gliricidia sepium (GS) had the highest values (21.2) while the untreated plants had the least. Rabbit droppings (RD) enhanced higher number of branches (39.8) at 8WAP.
There were interesting results at 10WAP with GS treated plants having the highest number of branches which was significantly higher (p<0.05) than all the other treatments. Cow dung (CD) had fewer numbers of branches between weeks 2 and 8 (2-8WAP) but had higher number of branches at 10WAP. It was observed that all the organic manures positively enhanced the growth in tomatoes, even though they were not absorbed at the same rate.
Table 3 depicts the growth influence of different organic fertilizers on the leaf length of solanum lycopersicum. At 2WAP, it was observed that tomato plants treated with Gliricidia sepium had the highest value (5.78 cm) and it was significantly different (p<0.05) form all other treatments while the untreated (control) plants had the least value (4.7 cm). At 4WAP tomato plants treated with Glioricidia sepium had the highest values (5.8 cm) which was significantly different (p<0.05) from other treatments while the CD treated tomatoes had highest leave length (7.3 cm) at 6WAP but the value was not significantly different (p<0.05) from GS treated plants.
At 8 WAP, tomato plants treated with poultry manure (PM) had the highest values (9.0 cm), this was not significantly different from RD treated plants but both were significantly different (p<0.05) from all the other treatments, while the untreated plants had the least values (5.56 cm). Rabbit droppings enhanced leaf length in tomatoes (9.3) at 10WAP which was significantly higher than all the other treatments. PM and GS treated plants were not significantly different (p<0.05) in their leaf length. The untreated plants had the least values throughout the study.
The influence of plants and animal manure on the number of leaves of solanum lycopersicum was as shown in Table 4. At 2 WAP, it was observed that tomato plants treated with Gliricidia Sepium had the highest value (34.4) for the number of leaves which is significantly different (p<0.05) from all other treatments. At 4 WAP, 6WAP, 8WAP and 10 WAP, it was observed that tomato plants treated with Gliricidia sepium had the highest values (41.80, 45.0, 81,4, and 98.60) respectively, and it is significantly different (p<0.05) from all other treatments while the untreated plants had the least values.
The cumulative number of flowers of Solanum lycopersicum treated with different organic fertilizers was as shown in Table 5. At 4 WAP, tomato plants treated with rabbit droppings had the highest number of fruits (1.8) for number of flowers. This value was significantly different (p<0.05) form all the other treatments. The untreated had the last number of fruits. At 6 and 8 WAP, it was observed that the tomato plants treated with cow dung (CD) had the highest value (4.2 and 6.2 respectively) and were significantly different (p<0.05) from other treatments. At 10 WAP, GS treated plats had the highest number of fruits which was not significantly different (p<0.05) from the CD treated plants but was significantly higher than all the other treatments. At 12 WAP, the plant treated with rabbit droppings had the highest number of fruits (10.8) and it was not significantly different (p<0.05) from cow dung treated plant but was significantly different from other treatments while Gliricidia sepium had the highest number of fruits at 14 WAP. The untreated (control) plants had the least number of fruits. Table 6 shows the yield influence of different organic fertilizers on Solanum lycopersicum. At 6 WAP, it was observed that tomato plants treated with cow dung and rabbit droppings had the highest numbers of fruits (2.0). This value is significantly different (p<0.05) from all the other treatments. At 8, 10 and 12 WAP, plants treated with rabbit droppings had the highest value (3.8, 8.2 and 13.0 respectfully) while the plants treated with GS had the highest number of fruits (16.2) at 14 WAP but not significantly different (p<0.05) from the RD treated plants (15.1). The untreated plants had the least number of fruits throughout the period of the study.
Discussion
The stem height, number of branches, number of leaves, number of flowers, number of fruits and the leaf length of Solanum lycopersicum influenced by different organic fertilizers were investigated. The results presented in the tables revealed significant main effects of organic fertilizers on the growth of Solanum Lycopersicum. Plants height and other growth parameters were influenced by the plants manure (Gliricidia sepium) from 2WAP till the end of the experiment. This was in line with the report of Zaharah et al. [22], who opined that the releases of N, P and K were rapid during the first 10 days and slower thereafter. About 60% of the N was lost within 10 days and a total of 76% of the original N. This might be due to the fact that the leaves of this plant decay fast and it is readily absorbable.
Rabbit droppings also influenced the plants height. Similar observations were made for the number of branches, number and length of leaves. This may be due to the fact that manure is a good source of macro and micronutrients, and manure contains all nutrients that plants need which is high in potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen [20]. Okoroafor et al. [23] reported that animal droppings gave the highest mean stem growth in maize throughout the time of the experiment.
Number of fruits and flowers were influenced by the applications of both plants and animal manures. The results of this work were also supported by other worker like Windham (1969) who opined that organic manure like poultry droppings, rabbit droppings etc. improve the structure of the soil thereby increasing the vegetative growth as well as the size and number of fruits. Also, Mbah [24] found that poultry, cow dung and other animal manures increased uptake of k, Ca and Mg by maize because these wastes increased soil OM, N and cation exchange significantly. The higher values reported for number and length of leaves, plants height and number of branches were consistent with the higher yield values in both plants and animal manures [25].
The growth effects of cow dung on the tomatoes plants were low at the early stage until after 6 weeks of planting when the plants’ growth and yield characters were influenced by CD. This result corroborates the findings of Ewulo et al. [25] who reported that CD treatments increased growth and fruit yield parameters of pepper such as numbers of leaves, plant height, number of branches, number and weight of fruits significantly (p<0.05).
Rabbit droppings enhanced the number of flowers and fruits (Tables 5 and 6). The result of these findings is in line with Tourte [26], who reported that there is significant influence of rabbit droppings on Solanum lycopersicum because of their high N.P.K values against another animal manure.
Conclusion
This study shows that the use of plant and animal manure improves the chemical and physical characteristics of the soil, thereby increasing the growth and yield characters of tomatoes. The applications of organic manure highly increase plant height, number and length of leaves, number of branches, number of flowers and fruits of tomatoes. Among the organic manure used as treatments in this research, Gliricidia sepium and rabbits’ droppings significantly enhanced both the growth and yield of tomatoes.
Recommendation
It has been shown that tomato plants that were treated with rabbit droppings and plant manure of Gliricidia sepium produced large number of fruits. These manures are cheap, easy to come by, ecologically friendliness and may increase farmers’ returns. In view of these benefits, these manures are recommended for farmers and Government.
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
To read more about this article: https://irispublishers.com/wjass/fulltext/responses-of-solanum-lycopersicum-to-organic-fertilizers-application.ID.000623.php
Indexing List of Iris Publishers: https://medium.com/@irispublishers/what-is-the-indexing-list-of-iris-publishers-4ace353e4eee
Iris publishers google scholar citations
:
https://scholar.google.co.in/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=irispublishers&btnG=
0 notes
Text
The World Ahead 2022
The World is Waking up to the Scourge of Illegal Fishing
Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing boats are the new pirates

— November 8th 2021 | By Dominic Ziegler: Banyan Columnist , The Economist
It is time to stop thinking of old-fashioned piracy as the worst scourge among all human activities taking place upon the ocean. In the Indian and Pacific Oceans and beyond, that dubious honour easily falls to those taking part in illicit fishing. What is known as illegal, unreported and unregulated (iuu) fishing accounts for 20-50% of the global catch (with the proportion probably highest in the once-rich waters of the Indo-Pacific).
iuu fishing, where operators lack licences, go after protected species or use too fine a net, is the chief driver behind plummeting fish stocks—just a fifth of commercial species are sustainably fished. That marks a precipitous decline that robs coastal states of over $20bn a year and threatens the livelihoods of millions of small-scale fishermen.
Worse, iuu operators are likely to be involved in other crimes, from finning sharks to running drugs. Tens of thousands of South-East Asian and African crews toil under conditions of debt bondage to Taiwanese, Chinese and other unscrupulous operators of big fleets. In the Pacific, onboard fisheries observers monitoring the catch are routinely murdered. Organised crime’s tentacles run deep into the fishing industry. iuu operators are the new pirates.
Thankfully, 2022 will mark a turning-point of sorts. Just before the start of the year a deal to force countries to end most of the harmful subsidies to their fisheries will be reached at the World Trade Organisation (wto). That goal has eluded the global body until now, despite 20 years of negotiations. But as Santiago Wills, Colombia’s representative at the wto, points out, in another 20 years there won’t be any fish left to argue over.
“Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing boats are the new pirates.”
The holdouts, China and India, sensing reputations at stake, will give in. Doing away with fuel and other subsidies could close down half of long-distance fishing, predicts Enric Sala, National Geographic’s explorer-in-residence. That would include China’s environmentally devastating bottom-trawling off the west coast of Africa. Subsidies can be redirected towards protecting fish stocks and livelihoods, making 2022 the year, Mr Sala says, “when we begin replenishing the ocean instead of emptying it”. There are other hopeful signs. International momentum is building to protect and conserve 30% of the ocean by 2030.
Mark Zimring of The Nature Conservancy (tnc) highlights the convergence of advanced technology enabling better monitoring of fishing fleets, as retailers strive to keep iuu-caught fish out of their supply chains. The technology—from satellite imagery revealing “dark fleets” to onboard e-monitoring of catches using big data—will become commercially viable at scale in 2022, Mr Zimring predicts.
More light will be shone on murky global supply chains, too. Already, TNC has joined up with the tiny but fish-rich Marshall Islands to create a brand of tinned tuna with impeccably sustainable provenance. In late 2021 Walmart, an American supermarket chain, signed up to the initiative, introducing it as its house-brand tuna. In 2022 more retailers will adopt such a model. Sally Yozell of the Stimson Centre, an American think-tank, says that an approach emphasising traceability and transparency in seafood supply chains from when a fish is caught to when it arrives in America will force the whole global seafood market to clean up its act.
A final point of brightness is the growing international effort to go after the perpetrators on land responsible for organised crime at sea. The ultimate beneficiaries of ocean crime easily evade overstretched fisheries inspectors in ports, since they hide behind brass plates in opaque tax jurisdictions.
Hence the importance of international efforts such as the UN-backed Blue Justice Initiative, which encourages co-operation in the fight against transnational crime. Emma Witbooi, an expert in maritime law, says a third of all coastal nations could sign up to the Copenhagen declaration that underpins the initiative by the end of 2022. It is a long haul back to healthy seas, but the coming year could mark a promising start.
— Dominic Ziegler: Banyan columnist, The Economist■
— This article appeared in the International section of the print edition of The World Ahead 2022 under the headline “Taking stock”
1 note
·
View note
Text
How COVID-19 Impacted on Global Lumber Pallet Market ?

Impact of COVID-19 on Global Lumber Pallet Market in Chemical and Materials Industry
ANALYSIS ON IMPACT OF COVID-19 ON THE GLOBAL LUMBER PALLET MARKET
The COVID-19 pandemic has influenced the whole planet with its major impacts on the economy and businesses across the globe. The COVID-19 spread worldwide in unprecedented ways due to its high infectious and contagious nature and lack of availability of its vaccine. As a result, the greatest medical challenge in the 21st century is yet to be faced by physicians worldwide. Though the emergence of the virus can be traced back to Asia, many European countries along with the U.S. have been struck massively by the pandemic. The virus has spread across all regions ranging from North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, and Africa up to South America. The COVID-19 has been declared as a pandemic by World Health Organization (WHO) due to its increased spread across the globe. After the declaration of the pandemic, various countries announced the complete lockdown, such as India, China, and other Asian countries to decrease its spread. According to the situation report of 7th June, 2021 by WHO stated 174 million cases of the corona have been reported globally and 3.7 million patients are dead due to the coronavirus. On a slightly positive note, a total of 157 million people have recovered and total of 1.9 million vaccine doses have been administered as well.
The spread of the COVID-19 virus has caused disruptions on wood availability which has seriously affected the production of lumber pallets.
A pallet is a flat transport structure that supports goods in a stable fashion while being lifted by a forklift, a pallet jack, a front loader, a jacking device, or an erect crane. A pallet is the structural foundation of a unit load which allows handling and storage efficiencies. Goods or shipping containers are often placed on a pallet secured with strapping, stretch wrap or shrink wrap and shipped.
Since its invention in the twentieth century, its use has dramatically supplanted older forms of crating such as the wooden box and the wooden barrel, as it works well with modern packaging such as corrugated boxes and intermodal containers commonly used for bulk shipping.
Wood prices rose due to reduction in mill operations and closures, combined with an upswing in domestic home improvements. Those consumers, who spend more money on the purchase of residence, now have lesser money which results in potential dampening of the economic recovery. Shortages of containers lag in unloading at ports shortage of commercial truckers had slowed down the road transport of lumber pallets.
Lumber features do not create cash prices; they do, however, generate a present view of an equilibrium price. If buyers are more eager than sellers, prices tend to go up. When the opposite is true, price tend go down. Softwood is the primary source for much world in production of lumber with traditional centres of production being the Baltic region and North America. These are indicating that in near future, North America will take over the worldwide market lead as the future contract specifies that lumber must be manufactured in certain specific U.S. states and Canadian provinces.
The spread of COVID-19 affected and disrupted the forest related supply chains, which have resulted in a sharp decline in exports and imports throughout the world. Across the global demand for wood and wood products, including tropical timber graphic paper and lumber furniture has decreased.
IMPACT ON PRICE
The outbreak of COVID-19 has caused a number of shortages in many sectors, including lumber industries as well. The pandemic spurred shortage has driven its prices too high. Demand of construction and the home remodeling during the pandemic coupled with coronavirus related limits on production caused the shortages that pushed the prices even higher.
However, after the pandemic, lumber prices fluctuated sharply in October 2020, by over 25 percent per week. This has been likely due to many factors, such as the typical seasonality in lumber demand (due to the end of construction season in some regions), increased processing capacity, and others. The price of lumber pallets increased considerably as sawmills were forced to close or slow production. However, prices still remained higher when compared with the same period in 2019.
IMPACT ON DEMAND
The demand for lumber material is disrupted due to the shutdown in every industries and construction & infrastructure. The effect of coronavirus declined the request for consumer, durable, and capital goods in many countries such as in the place like Brazil, Ghana, and Japan. Due to the ongoing outbreak of COVID-19, the global market of lumber pallet has been highly affected by the pandemic as many companies were operating in the field of lumber pallet. And they were obliged to stop their manufacturing process and production.
Though, this decreased demand can be restored to pre-pandemic levels by 2022, as about 100% of the wooden pallets can be recycled, including the nails, which can greatly increase the demand for lumber pallets.
On the other hand, after the second wave, wood prices typically fluctuate more than then most products, because homebuilding can move or down much faster sawmill capacity can. Wood products have other uses that more stable, such as non- residential construction, crates, and pallets, but new housing is largest usage.
IMPACT ON SUPPLY CHAIN
Throughout the history, global chain has been one of the most vulnerable parts of the trading process. The importance of supply chain can be understood by the fact that a number of wars took place in history for the smooth functioning of the supply chain across the globe. These challenges have been intensified by the impeded performance of badly sectors intricately linked to forests and lumber pallets, such as transportation, forest based recreation, and sectors that use wood as raw material, including construction and manufacturing.
Early in 2020, the lumber supply chain contracted for numerous reasons. For instance,
Housing starts declined precipitously, falling 22.3% in March, and the lumber industry anticipated low overall demand. Consequently, lumber mills idled or curtailed production, with the industry analytics firm Forisk estimating an overall reduction of softwood lumber capacity of over 15.6% in the first quarter of 2020 and curtailments continuing into April. However, housing starts rose in June and exceeded starts in 2019 through October. Demand for lumber for remodeling remained steady. As a result, lumber demand exceeded supply, leading to softwood lumber shortages and prices that rose to record high levels in late August and early September 2020.
Thus, the combination of stagnating production reduced demand shortages of raw material, lack of working, capital and forced many operations and enterprises to halt their activities and some permanently.
AFTERMATH OF COVID-19 AND GOVERNMENT INITIATIVE TO BOOST THE GLOBAL LUMBER PALLET MARKET
The rising popularity of lumber pallets has been an instrumental factor in influencing the growth of global lumber pallet market. The market conditions of lumber pallets are severely affected due to the pandemic related challenges and continue to face problems despite recent government measures. To boost the demands, the government has offered export incentives to the industries apart from extending operation hours for the businesses. The government has also imposed import duties on the raw materials that are required for manufacturing lumber pallets.
For instance,
To conduct proper importation of goods, necessary documentation and customs clearance procedures at importing country have to be completed accurately.
Regulatory framework and government support, such as government grants and funding programs offers investment subsidies and tax benefits which play a key role in driving the global lumber pallet market.
STRAGETIC DECISIONS FOR MANUFACTURERS AFTER COVID-19 TO GAIN COMPETITIVE MARKET SHARE
Although the COVID-19 pandemic continues to transform the growth of various industries, the immediate impact of the outbreak is varied. Despite the severe pandemic situation, the growing adoption of technology is propelling the manufacturers to produce wooden pallets equipped with sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
During the pandemic situation, the pallet manufacturers have put in efforts to develop products that more closely resembles natural lumber. The pandemic has also pushed the manufacturers to adopt recycling of the wooden pallets and to transform it into high post recycled product which proves to be more sustainable. Manufacturers are still facing problems with supply chain disruptions and staffing crunches due to social distancing and other restrictions. These problems are overcome by using available materials and skills to redirect.
For instance,
By increasing reusing activities of lumber pallets, there can be increase in number of pallets which provides flexibility. This can cause demand spikes and can help in determining the pallets which are best fit for their specific warehouses and storage systems.
Hence, the various strategic decisions taken by the government can prove to help increase the market share of lumber pallets. Strict checks of the pallets before distribution can ensure that the pallets are contamination-free and help to discard the damaged and low quality ones.
CONCLUSION
Pandemic has taken a toll on every aspect of life, including the global economy. With the significant downfalls in many sectors, a collaborative effort of government, industry players, and consumers can win the fight against COVID-19.
It still continues to inflict the world with appalling economic and social dilemmas, capable enough to leave severe backlash on the economy for the next several years. The first wave had already inflicted powerful blows to the population as well as the economy. The currently experiencing second wave is expected to be more disastrous not only to the masses but also to financial markets.
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected the lumber pallet market in a serious manner. One of the restrictions brought by the pandemic was the closure of lumber pallets production. This cession of production will have a severe impact on the country��s GDP as well. Therefore, it is important to take decisions that will economically improve public admiration, and create favorable conditions for the activities of business entities in the lumber industries, and at the same time increase the level of preparedness for a crisis in the future.
Hence, due to appropriate and continuous government support, the manufacturers of lumber pallets are able to overcome the obstacles and increase their production in a fruitful manner.
0 notes
Text
the hydrological cycle and soils
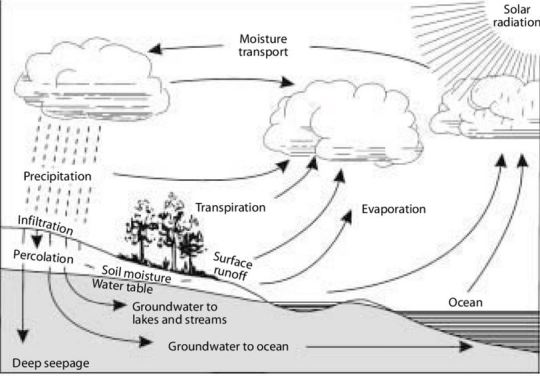
Even a slight increase in surface temperatures will affect evaporation, atmospheric moisture and precipitation (Figure 3). While it is generally agreed that rainfall will increase (by an estimated 10 to 15%), two aspects have to be elucidated: how will rainfall intensities be affected, and what are the details of spatial changes. Based on palaeoclimatic analogies, certain authors predict more favourable rainfall conditions in the present-day (Petit-Maire, 1992). If the increase in precipitation should be associated with increased rainfall intensities, then the quality and quantity of soil and water resources would decline, for instance through increased runoff and erosion, increased land degradation processes, and a higher frequency of floods and possibly droughts. The extra precipitation on land, if indeed including present subhumid to semi-arid areas, will increase plant growth in these areas, leading to an improved protection of the land surface and increased rainfed agricultural production; in already humid areas the extra rainfall may, however, impair adequate crop drying and storage (Wim and René, 1996 ). The greatest risks are often estimated to be associated with increased soil loss through erosion.
Soils, as a medium for plant growth, would be affected in several other ways (Wim and René, 1996): ●● increased temperatures may lead to more decomposition of soil organic matter; ●● increased plant growth due to the CO2 fertilization effect may cause other plant nutrients such as N and P to become in short supply; however, CO2 increase would stimulate mycorrhizal activity (making soil phosphorus more easily available), and also biological nitrogen fixation (whether or not symbiotic). Through increased root growth there would be extra weathering of the substratum, hence a fresh supply of potassium and micronutrients; ●● the CO2 fertilization effect would produce more litter of higher C/N ratio, hence more organic matter for incorporation into the soil as humus; litter with high C/N decomposes slowly and this can act as a negative feedback on nutrient availability; the ‘CO2 anti-transpirant’ effect would stimulate plant growth in dryland areas, and more soil protection against erosion and lower topsoil temperatures, leading to an ‘anti-desertification effect’.
0 notes
Text
A review on RO membrane technology: Developments and challenges
Reverse osmosis (RO) based desalination is one of the most important and widely recognized technologies for production of fresh water from saline water. Since its conception and initiation, a significant development has been witnessed in this technology w.r.t. materials, synthesis techniques, modification and modules over the last few decades. The working of a RO plant inclusive of the pretreatment and post-treatment procedures has been briefly discussed in the article. The main objective of this review is to highlight the historical milestones achieved in RO technology in terms of membrane performance, the developments seen over the last few years and the challenges perceived.
The material properties of the membrane dominate the performance of a RO process. The emergence of nano-technology and biomimetic RO membranes as the futuristic tools is capable of revolutionizing the entire RO process. Hence the development of nano-structured membranes involving thin film nano-composite membranes, carbon-nanotube membranes and aquaporin-based membranes has been focussed in detail. The problems associated with a RO process such as scaling, brine disposal and boron removal are briefed and the measures adopted to address the same have been discussed.
In response to the escalating world water demand and aiming to promote equal opportunities, reverse osmosis desalination has been widely implemented. Desalination is however constantly subjected to fouling and scaling which increase the cost of desalination by increasing the differential pressure of the membrane and reducing the permeate flux. A bench-scale desalination equipment has been used in this research to investigate the mitigation of fouling and scaling. This study involved the performance of membrane autopsy for fouling characterisation with special attention to flux decline due to sulphate precipitation and biofouling. Visual inspection, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and microbiology tests (API) were performed. Results obtained showed the presence of diatoms, pseudomonas and polysaccharides as the main foulants causing biofouling. Analysis revealed sulphate deposits as well as aluminium, calcium and silica as the main elements contributing to inorganic scaling. Findings pointed out that the pre-treatment system of the small-scale reverse osmosis water treatment was inefficient and that selection of pre-treatment chemicals should be based on its compatibility with the membrane structure. The importance of characterisation for the verification of fouling mechanisms is emphasised.
This research was conducted to determine the performance of Reverse Osmosis (RO) membranes in producing pure water, pure water known as mineral-free water or water with zero dissolved solids (TDS = 0 ppm).PDAM (Regional Drinking Water Company) Tirta Musi in Palembang, South Sumatra and water from the Micro Filtration (MF) and Ultrafiltration (UF) processes are fed to the RO process using two feeding methods, namely a single pass and a circulation feed. In a single pass feed, the operating pressure is set at 20 - 50 Psig, where an increase in the product rate and the rejection rate so that the flux increases. Rejection of TDS obtained increased from 96.6% - 97.5%. Furthermore, the circulating feed system with a constant pressure of 50 Psig decreases TDS and Conductivity. Rejection of TDS 96.1% for PDAM water feed and Rejection of TDS for feed water from MF&UF 97.3% in subsequent feedings there was a decrease in TDS and conductivity but not significantly. The purified water produced has a TDS content of 0.16 - 0.48 ppm, a conductivity of 0.17 - 0.49 μs/cm, a pH of 6.99 - 7.2 and a resistivity of 177 - 185 kΩ, the characteristics of this pure water are according to the standard pure water in ASTM D1193 - 99e1 and NCCLS.
Clean water obtained by desalinating sea water or by purifying wastewater, constitutes a major technological objective in the so-called water century. In this work, a high-performance reverse osmosis (RO) composite thin membrane using multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and aromatic polyamide (PA), was successfully prepared by interfacial polymerization. The effect of MWCNT on the chlorine resistance, antifouling and desalination performances of the nanocomposite membranes were studied. We found that a suitable amount of MWCNT in PA, 15.5 wt.%, not only improves the membrane performance in terms of flow and antifouling, but also inhibits the chlorine degradation on these membranes. Therefore, the present results clearly establish a solid foundation towards more efficient large-scale water desalination and other water treatment processes.
Introduction
The availability of clean water has become a global problem because of the continuously increasing costs of energy and increasing scarcity of water resources1. This problem has been exacerbated in recent years in the so-called century of water. By far, the domestic ro membrane process persists as the most reliable and cost-effective water desalination technique and numerous large-scale RO plants have been constructed around the world2,3. A wide range of polymers have shown potential for fabricating desalination membranes to be used in RO4. However, PA-based membranes tend to exhibit the best performance in terms of selectivity, flow, chemical stability and ease of large-scale fabrication. PA membrane technology was developed in the mid-70 s and has become the commercial benchmark in RO membranes5. In order to improve the membrane performances, the recent trend in polymer-based membrane research has been to investigate various types of nanocomposite films as an active layer of RO membrane, so-called nanocomposite membranes, in which these films are fabricated using a nanosized filler such as MWCNT, graphene, graphene oxide, silica, or zeolite6. In this regard, MWCNT·PA-based membranes have been prepared by several groups and in general, these membranes have exhibited some level of improved performance7,8,9,10,11,12. The advantages claimed for these membranes range from increased salt rejection, large fluxes, greater durability and even antimicrobial properties.
MWCNT synthesized by catalytic chemical vapour deposition13,14 have been widely studied due to their fascinating chemical and physical properties and among all nanocarbon materials, they can be mass-produced for commercially available applications, such as the electrode additives in high performance lithium ion batteries15. Interestingly, while the structure of the fully aromatic PA-based commercial ro membrane derived from m-phenylendiamine (MPD)-trimesoyl chloride (TMC) is constrained due to its stoichiometry; the addition of MWCNT can significantly vary their performance due to their unique features such as dispersability diameter, length, straightness and chemical functionalities, among many others. Therefore, although these past reports acknowledge the key role of MWCNT in aromatic PA nanocomposite membranes, still little attention has been devoted to the mechanisms related to the improvement of flow rate, selectivity and chlorine tolerance2. Carbon nanotubes inducing chlorine tolerance are particularly interesting because chlorine sensitivity has been recognized as a major drawback of PA-based RO membranes16,17. During long-term operation, chlorine is often added as a pre-treatment to reduce algae biofouling18 and is particularly needed for drinking water purification. Moreover, high-concentration short-term exposure to chlorine is also common during domestic nf membrane backwashing. For these reasons, several studies have been carried out and the degradation mechanism of aromatic PA membranes during chlorine exposure is relatively well-known19,20. Recently, our group demonstrated that the addition of MWCNT to rubber can considerably reduce the chlorine-induced degradation of the polymer matrix21. Although the degradation mechanism of rubber by chlorine is different from that of PA, particularly due to the lack of hydrolysis, covalent chlorination is a common problem for both polyamide and rubber. For rubber, we found that MWCNT effectively restricted the adsorption of chlorine within the polymer matrix, thus resulting in a limited exposure of the polymer to this reactive reagent and thereby decreasing the oxidative degradation. For these reasons, we believe MWCNT are not only promising composite fillers with chlorine protective properties, but might also help to provide mechanical robustness to PA-based RO membranes.
Results and Discussion
We prepared aromatic PA membranes using a support consisting of a porous polysulfone layer deposited on a polypropylene nonwoven. These support membranes were soaked sequentially in MPD and TMC solutions, to synthesize the aromatic PA membrane by interfacial polymerization. In order to incorporate MWCNT into the PA membrane, an anionically stabilized dispersion of MWCNT (Supplementary Fig. S1) was mixed with the MPD solution and the synthesis was conducted similarly. Figure 1a shows an image of the resulting membranes, with and without MWCNT. The black color developed in the membrane prepared using surfactant dispersed MWCNT is characteristic of the high carbon nanotube content of the present membrane (Fig. 1a). Thermogravimetry of the active layer (Supplementary Fig. S2) of the black color membrane indicates that it contains ca. 15.5 wt. % of MWCNT, which is at least 150 times higher than previously reported MWCNT-filled RO PA membranes7,8,12. The SEM image showing the surface morphology of the membrane is typical for the interfacial PA polymerization22, consisting of the multi-layered ridge-and-valley (Fig. 1b); the morphology of this membrane clearly changed after the addition of MWCNT (Fig. 1c). The thickness of the membranes was measured using SEM (Supplementary Fig. S3). The addition of MWCNT did not modify the thickness of the active layer and both samples were approximately 100 nm thick. However, water contact angle measurements showed a slight increase in wettability upon addition of MWCNT to the PA membrane (Supplementary Fig. S4). Notably, no MWCNT were visible on the surface, thus indicating that they were perfectly embedded within the PA matrix, a key factor needed for avoiding MWCNT leakage during operation. Flow permeation rates, as indicated below and SEM images confirmed that the membranes can be produced pinhole-free in a reproducible way. After the membrane was dried for SEM studies, cracks were generated by manual deformation of the membrane (Fig. 1d) and MWCNT embedded, parallel along the membrane surface, were observed bridging the fracture within the polymer matrix. The apparent diameter of these nanotubes are ca. 20 nm, which is about two times larger than the pristine nanotubes (Fig. S1a). These facts suggest that the nanotubes must be coated with polymer to achieve a good matrix-nanotube adhesion. In order to support our proposed structure consisting of a polymeric network with aromatic moieties in parallel arrangement to the MWCNT walls, we performed theoretical simulations of the monomer molecules orientation in the vicinity of a carbon nanotube surface, see Supplementary Fig. S5. Here, four different cases, consisting of two geometrical configurations, are demonstrated: horizontal and vertical alignments with respect to the MWCNT surface (modelled as a graphene surface), for both monomers (MPD and TMC). The results indicate a clear energetic preference for the horizontal arrangements of these molecules interacting with sp2 hybridized carbon networks; these preferences are related to π-π stacking and are known to be common for aromatic compounds on sp2 hybridized carbon surfaces. Similarly, Fig. S5b shows a simulation of 50 MPD molecules absorbed on a graphene surface and it can be seen that the molecules adopt a similar geometrical orientation after relaxation (Fig. S5c). In order to rule out curvature effects, we carried the simulations using a (10,10) single-walled carbon nanotube (Fig. S5d), which evidently has a higher curvature than the 10 nm diameter MWCNT experimentally used in the membrane fabrication. It can be seen on Fig. S5e that after relaxation, the aromatic ring of the MPD molecules lies parallel to the carbon nanotube surface. We confirmed the strong affinity of MPD with MWCNT by filtering the solution and carrying out UV-Vis spectroscopy. We found that 16.7% of the MPD monomer remained attached to the MWCNT. These MPD functionalized MWCNT were polymerized in TMC solution. Supplementary Fig. S6a shows a homogeneous PA coating on the MWCNT. Supplementary Fig. S6b depicts a higher resolution image showing a coating of about 5 nm thick on the MWCNT surface. We used fast Fourier transformation (FFT) of the HRTEM images to analyze the orientation of the PA network and it is clear that PA regions that do not contain MWCNT, show an anisotropic molecular arranged structure (Supplementary Fig. S6c), whereas the PA coating the nanotubes show a preferential orientation of PA molecules along the MWCNT surface (Supplementary Fig. S6d). These experiments strongly support a templating effect caused by MWCNT. To assess the distribution of the MWCNT within the membrane, a Raman mapping of the characteristic D- and G- bands of MWCNT was conducted (see Fig. 1e,f). Through all the studied areas only the D- and G- peaks could be observed, indicating a homogenous mixture and a high content of MWCNT, which is not common in these type of nanocomposites, because the MWCNT are prone to aggregation even when loading at low concentrations. Commercial NF membrane exhibited a lower contact angle; however in this case, the presence of wetting additives or a surface treatment is likely responsible for this phenomena. The method used to synthesize the MWCNT·PA nanocomposite relies on the transport of the MWCNT to the organic/aqueous interface during polymerization23. Indeed, the presence of a limited amount of anionic surfactant has been recently reported to improve PA membrane formation, resulting in better performance24. This is most likely due to a reduction of the oil/water interfacial tension, a process that in our case is also promoted by the small amount of surfactant that provides amphiphilicity to the nanotubes It is important to emphasize that we did not used covalent functionalization of MWCNT, in contrast to some previous reports8,11.
0 notes