#good on those amazon workers
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Prime’s enshittified advertising
Prime's gonna add more ads. They brought in ads in January, and people didn't cancel their Prime subscriptions, so Amazon figures that they can make Prime even worse and make more money:
https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2024/10/amazon-prime-video-is-getting-more-ads-next-year/
The cruelty isn't the point. Money is the point. Every ad that Amazon shows you shifts value away from you – your time, your attention – to the company's shareholders.
That's the crux of enshittification. Companies don't enshittify – making their once-useful products monotonically worse – because it amuses them to erode the quality of their offerings. They enshittify them because their products are zero-sum: the things that make them valuable to you (watching videos without ads) make things less valuable to them (because they can't monetize your attention).
This isn't new. The internet has always been dominated by intermediaries – platforms – because there are lots more people who want to use the internet than are capable of building the internet. There's more people who want to write blogs than can make a blogging app. There's more people who want to play and listen to music than can host a music streaming service. There's more people who want to write and read ebooks than want to operate an ebook store or sell an ebooks reader.
Despite all the early internet rhetoric about the glories of disintermediation, intermediaries are good, actually:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/06/12/direct-the-problem-of-middlemen/
The problem isn't with intermediaries per se. The problem arises when intermediaries grow so powerful that they usurp the relationship between the parties they connect. The problem with Uber isn't the use of mobile phones to tell taxis that you're standing on a street somewhere and would like a cab, please. The problem is rampant worker misclassification, regulatory arbitrage, starvation wages, and price-gouging:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/29/geometry-hates-uber/#toronto-the-gullible
There's no problem with publishers, distributors, retailers, printers, and all the other parts of the bookselling ecosystem. While there are a few, rare authors who are capable of performing all of these functions – basically gnawing their books out of whole logs with their teeth – most writers can't, and even the ones who can, don't want to:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/19/crad-kilodney-was-an-outlier/#intermediation
When early internet boosters spoke of disintermediation, what they mostly meant was that it would be harder for intermediaries to capture those relationships – between sellers and buyers, creators and audiences, workers and customers. As Rebecca Giblin and I wrote in our 2022 book Chokepoint Capitalism, intermediaries in every sector rely on chokepoints, narrows where they can erect tollbooths:
https://chokepointcapitalism.com/
When chokepoints exist, they multiply up and down the supply chain. In the golden age of physical, recorded music, you had several chokepoints that reinforced one another. Limited radio airwaves gave radio stations power over record labels, who had to secretly, illegally bid for prime airspace ("payola"). Retail consolidation – the growth of big record chains – drove consolidation in the distributors who sold to the chains, and the more concentrated distributors became, the more they could squeeze retailers, which drove even more consolidation in record stores. The bigger a label was, the more power it had to shove back against the muscle of the stores and the distributors (and the pressing plants, etc). Consolidation in labels also drove consolidation in talent agencies, whose large client rosters gave them power to resist the squeeze from the labels. Consolidation in venues drives consolidation in ticketing and promotion – and vice-versa.
But there's two parties to this supply chain who can't consolidate: musicians and their fans. With limits on "sectoral bargaining" (where unions can represent workers against all the companies in a sector), musicians' unions were limited in their power against key parts of the supply chain, so the creative workers who made the music were easy pickings for labels, talent reps, promoters, ticketers, venues, retailers, etc. Music fans are diffused and dispersed, and organized fan clubs were usually run by the labels, who weren't about to allow those clubs to be used against the labels.
This is a perfect case-study in the problems of powerful intermediaries, who move from facilitator to parasite, paying workers less while degrading their products, and then charge customers more for those enshittified products.
The excitement about "disintermediation" wasn't so much about eliminating intermediaries as it was about disciplining them. If there were lots of ways to market a product or service, sell it, collect payment for it, and deliver it, then the natural inclination of intermediaries to turn predator would be curbed by the difficulty of corralling their prey into chokepoints.
Now that we're a quarter century on from the Napster Wars, we can see how that worked out. Decades of failure to enforce antitrust law allowed a few companies to effectively capture the internet, buying out rivals who were willing to sell, and bankrupting those who wouldn't with illegal tactics like predatory pricing (think of Uber losing $31 billion by subsidizing $0.41 out of every dollar they charged for taxi rides for more than a decade).
The market power that platforms gained through consolidation translated into political power. When a few companies dominate a sector, they're able to come to agreement on common strategies for dealing with their regulators, and they've got plenty of excess profits to spend on those strategies. First and foremost, platforms used their power to get more power, lobbying for even less antitrust enforcement. Additionally, platforms mobilized gigantic sums to secure the right to screw customers (for example, by making binding arbitration clauses in terms of service enforceable) and workers (think of the $225m Uber and Lyft spent on California's Prop 22, which formalized their worker misclassification swindle).
So big platforms were able to insulate themselves from the risk of competition ("five giant websites, filled with screenshots of the other four" – Tom Eastman), and from regulation. They were also able to expand and mobilize IP law to prevent anyone from breaking their chokepoints or undoing the abuses that these enabled. This is a good place to get specific about how Prime Video works.
There's two ways to get Prime videos: over an app, or in your browser. Both of these streams are encrypted, and that's really important here, because of a law – Section 1201 of the 1998 Digital Millennium Copyright Act – which makes it really illegal to break this kind of encryption (commonly called "Digital Rights Management" or "DRM"). Practically speaking, that means that if a company encrypts its videos, no one is allowed to do anything to those videos, even things that are legal, without the company's permission, because doing all those legal things requires breaking the DRM, and breaking the DRM is a felony (five years in prison, $500k fine, for a first offense).
Copyright law actually gives subscribers to services like Prime a lot of rights, and it empowers businesses that offer tools to exercise those rights. Back in 1976, Sony rolled out the Betamax, the first major home video recorder. After an eight-year court battle, the Supreme Court weighed in on VCRs and ruled that it was legal for all of us to record videos at home, both to watch them later, and to build a library of our favorite shows. They also ruled that it was legal for Sony – and by that time, every other electronics company – to make VHS systems, even if those systems could be used in ways that violated copyright because they were "capable of sustaining a substantial non-infringing use" (letting you tape shows off your TV).
Now, this was more than a decade before the DMCA – and its prohibition on breaking DRM – passed, but even after the DMCA came into effect, there was a lot of media that didn't have DRM, so a new generation of tech companies were able to make tools that were "capable of sustaining a substantial non-infringing use" and that didn't have to break any DRM to do it.
Think of the Ipod and Itunes, which, together, were sold as a way to rip CDs (which weren't encrypted), and play them back from both your desktop computer and a wildly successful pocket-sized portable device. Itunes even let you stream from one computer to another. The record industry hated this, but they couldn't do anything about it, thanks to the Supreme Court's Betamax ruling.
Indeed, they eventually swallowed their bile and started selling their products through the Itunes Music Store. These tracks had DRM and were thus permanently locked to Apple's ecosystem, and Apple immediately used that power to squeeze the labels, who decided they didn't like DRM after all, and licensed all those same tracks to Amazon's DRM-free MP3 store, whose slogan was "DRM: Don't Restrict Me":
https://memex.craphound.com/2008/02/01/amazons-anti-drm-tee/
Apple played a funny double role here. In marketing Itunes/Ipods ("Rip, Mix, Burn"), they were the world's biggest cheerleaders for all the things you were allowed to do with copyrighted works, even when the copyright holder objected. But with the Itunes Music Store and its mandatory DRM, the company was also one of the world's biggest cheerleaders for wrapping copyrighted works in a thin skin of IP that would allow copyright holders to shut down products like the Ipod and Itunes.
Microsoft, predictably enough, focused on the "lock everything to our platform" strategy. Then-CEO Steve Ballmer went on record calling every Ipod owner a "thief" and arguing that every record company should wrap music in Microsoft's Zune DRM, which would allow them to restrict anything they didn't like, even if copyright allowed it (and would also give Microsoft the same abusive leverage over labels that they famously exercised over Windows software companies):
https://web.archive.org/web/20050113051129/http://management.silicon.com/itpro/0,39024675,39124642,00.htm
In the end, Amazon's approach won. Apple dropped DRM, and Microsoft retired the Zune and shut down its DRM servers, screwing anyone who'd ever bought a Zune track by rendering that music permanently unplayable.
Around the same time as all this was going on, another company was making history by making uses of copyrighted works that the law allowed, but which the copyright holders hated. That company was Tivo, who products did for personal video recorders (PVRs) what Apple's Ipod did for digital portable music players. With a Tivo, you could record any show over cable (which was too expensive and complicated to encrypt) and terrestrial broadcast (which is illegal to encrypt, since those are the public's airwaves, on loan to the TV stations).
That meant that you could record any show, and keep it forever. What's more, you could very easily skip through ads (and rival players quickly emerged that did automatic ad-skipping). All of this was legal, but of course the cable companies and broadcasters hated it. Like Ballmer, TV execs called Tivo owners "thieves."
But Tivo didn't usher in the ad-supported TV apocalypse that furious, spittle-flecked industry reps insisted it would. Rather, it disciplined the TV and cable operators. Tivo owners actually sought out ads that were funny and well-made enough to go viral. Meanwhile, every time the industry decided to increase the amount of advertising in a show, they also increased the likelihood that their viewers would seek out a Tivo, or worse, one of those auto-ad-skipping PVRs.
Given all the stink that TV execs raised over PVRs, you'd think that these represented a novel threat. But in fact, the TV industry's appetite for ads had been disciplined by viewers' access to new technology since 1956, when the first TV remotes appeared on the market (executives declared that anyone who changed the channel during an ad-break was a thief). Then came the mute button. Then the wireless remote. Meanwhile, a common VCR use-case – raised in the Supreme Court case – was fast-forwarding ads.
At each stage, TV adapted. Ads in TV shows represented a kind of offer: "Will you watch this many of these ads in return for a free TV show?" And the remote, the mute button, the wireless remote, the VCR, the PVR, and the ad-skipping PVR all represented a counter-offer. As economists would put it, the ability of viewers to make these counteroffers "shifted the equilibrium." If viewers had no defensive technology, they might tolerate more ads, but once they were able to enforce their preferences with technology, the industry couldn't enshittify its product to the liminal cusp of "so many ads that the viewer is right on the brink of turning off the TV (but not quite)."
This is the same equilibrium-shifting dynamic that we see on the open web, where more than 50% of users have installed an ad-blocker. The industry says, "Will you allow this many 'sign up to our mailing list' interrupters, pop ups, pop unders, autoplaying videos and other stuff that users hate but shareholders benefit from" and the ad-blocker makes a counteroffer: "How about 'nah?'":
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/07/adblocking-how-about-nah
TV remotes, PVRs and ad-blockers are all examples of "adversarial interoperability" – a new product that plugs into an existing one, extending or modifying its functions without permission from (or even over the objections of) the original manufacturer:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/10/adversarial-interoperability
Adversarial interop creates a powerful disciplining force on platform owners. Once a user grows so frustrated with a product's enshittification that they research, seek out, acquire and learn to use an adversarial interop tool, it's really game over. The printer owner who figures out where to get third-party ink is gone forever. Every time a company like HP raises its prices, they have to account for the number of customers who will finally figure out how to use generic ink and never, ever send another cent to HP.
This is where DMCA 1201 comes into play. Once a product is skinned with DRM, its manufacturers gain the right to prevent you from doing legal things, and can use the public's courts and law-enforcement apparatus to punish you for trying. Take HP: as soon as they started adding DRM to their cartridges, they gained the legal power to shut down companies that cloned, refilled or remanufactured their cartridges, and started raising the price of ink – which today sits at more than $10,000/gallon:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/09/30/life-finds-a-way/#ink-stained-wretches
Using third party ink in your printer isn't illegal (it's your printer, right?). But making third party ink for your printer becomes illegal once you have to break DRM to do so, and so HP gets to transform tinted water into literally the most expensive fluid on Earth. The ink you use to print your kid's homework costs more than vintage Veuve Cliquot or sperm from a Kentucky Derby-winning thoroughbred.
Adversarial interoperability is a powerful tool for shifting the equilibrium between producers, intermediaries and buyers. DRM is an even more powerful way of wrenching that equilibrium back towards the intermediary, reducing the share that buyers and sellers are able to eke out of the transaction.
Prime Video, of course, is delivered via an app, which means it has DRM. That means that subscribers don't get to exercise the rights afforded to them by copyright – only the rights that Amazon permits them to have. There's no Tivo for Prime, because it would have to break the DRM to record the shows you stream from Prime. That allows Prime to pull all kinds of shady shit. For example, every year around this time, Amazon pulls popular Christmas movies from its free-to-watch tier and moves them into pay-per-view, only restoring them in the spring:
https://www.reddit.com/r/vudu/comments/1bpzanx/looks_like_amazon_removed_the_free_titles_from/
And of course, Prime sticks ads in its videos. You can't skip these ads – not because it's technically challenging to make a 30-second advance button for a video stream, and doing so wouldn't violate anyone's copyright – but because Amazon doesn't permit you to do so, and the fact that the video is wrapped in DRM makes it a felony to even try.
This means that Amazon gets to seek a different equilibrium than TV companies have had to accept since 1956 and the invention of the TV remote. Amazon doesn't have to limit the quantity, volume, and invasiveness of its ads to "less the amount that would drive our subscribers to install and use an ad-skipping plugin." Instead, they can shoot for the much more lucrative equilibrium of "so obnoxious that the viewer is almost ready to cancel their subscription (but not quite)."
That's pretty much exactly how Kelly Day, the Amazon exec in charge of Prime Video, put it to the Financial Times: they're increasing the number of ads because "we haven’t really seen a groundswell of people churning out or cancelling":
https://www.ft.com/content/f8112991-820c-4e09-bcf4-23b5e0f190a5
At this point, attentive readers might be asking themselves, "Doesn't Amazon have to worry about Prime viewers who watch in their browsers?" After all browsers are built on open standards, and anyone can make one, so there should be browsers that can auto-skip Prime ads, right?
Wrong, alas. Back in 2017, the W3C – the organization that makes the most important browser standards – caved to pressure from the entertainment industry and the largest browser companies and created "Encrypted Media Extensions" (EME), a "standard" for video DRM that blocks all adversarial interoperability:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2017/09/open-letter-w3c-director-ceo-team-and-membership
This had the almost immediate effect of making it impossible to create an independent browser without licensing proprietary tech from Google – now a convicted monopolist! – who won't give you a license if you implement recording, ad-skipping, or any other legal (but dispreferred) feature:
https://blog.samuelmaddock.com/posts/the-end-of-indie-web-browsers/
This means that for Amazon, there's no way to shift value away from the platform to you. The company has locked you in, and has locked out anyone who might offer you a better deal. Companies that know you are technologically defenseless are endlessly inventive in finding ways to make things worse for you to make things better for them. Take Youtube, another DRM-video-serving platform that has jacked up the number of ads you have to sit through in order to watch a video – even as they slash payments to performers. They've got a new move: they're gonna start showing you ads while your video is paused:
https://www.usatoday.com/story/money/2024/09/20/youtube-pause-ads-rollout/75306204007/
That is the kind of fuckery you only come up with when your victory condition is "a service that's almost so bad our customers quit (but not quite)."
In Amazon's case, the math is even worse. After all, Youtube may have near-total market dominance over a certain segment of the video market, but Prime Video is bundled with Prime Delivery, which the vast majority of US households subscribe to. You have to give up a lot to cancel your Prime subscription – especially since Amazon's predatory pricing devastated the rest of the retail sector:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/28/enshittification/#relentless-payola
Amazon's founding principle was "customer obsession." Ex-Amazoners tell me that this was more than an empty platitude: arguments over product design were won or lost based on whether they could satisfy the "customer obsession" litmus test. Now, everyone falls short of their ideals, but sticking to your ideals isn't merely a matter of internal discipline, of willpower. Living up to your ideals is a matter of external discipline, too. When Amazon no longer had to contend with competitors or regulators, when it was able to use DRM to control its customers and use the law to prevent them from using its products in legal ways, it lost those external sources of discipline.
Amazon suppliers have long complained of the company's high-handed treatment of the vendors who supplied it with goods. Its workers have complained bitterly and loudly about the dangerous and oppressive conditions in its warehouses and delivery vans. But Amazon's customers have consistently given Amazon high marks on quality and trustworthiness.
The reason Amazon treated its workers and suppliers badly and its customers well wasn't that it liked customers and hated workers and suppliers. Amazon was engaged in a cold-blooded calculus: it understood that treating customers well would give it control over those customers, and that this would translate market power to retain suppliers even as it ripped them off and screwed them over.
But now, Amazon has clearly concluded that it no longer needs to keep customers happy in order to retain them. Instead, it's shooting for "keeping customers so angry that they're almost ready to take their business elsewhere (but not quite)." You see this in the steady decline of Amazon product search, which preferences the products that pay the biggest bribes for search placement over the best matches:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/06/attention-rents/#consumer-welfare-queens
And you see it in the steady enshittification of Prime Video. Amazon's character never changed. The company always had a predatory side. But now that monopoly and IP law have insulated it from consequences for its actions, there's no longer any reason to keep the predator in check.

Tor Books as just published two new, free LITTLE BROTHER stories: VIGILANT, about creepy surveillance in distance education; and SPILL, about oil pipelines and indigenous landback.


If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/10/03/mother-may-i/#minmax
768 notes
·
View notes
Text
Every time a set picture leaks from the Fallout TV show, I gain a little more hope for it....



Theres clearly a lot of care and attention going into these sets?
Theyre not just green screening them in, and they actually look like places rather than sets. I feel like Amazon especially cut corners with their effects - cheaper CGI, the sets looking just a little more like a theme park than a living place, that kinda thing. So its good to see pictures from one of their productions looking good.
#like... i thought amazon did a good job with adapting Wheel of Time....#but theres a lot of sets that just look a little Off#i dont care to watch rings of power but yeah ive seen those posts of some of the costumes#idk who these characters are or how important they might be#but yeah they skimped a lot on the costume department huh....#and amazon really try and get the cheapest CGI studios around.... like... just... oof#im fully expecting there to be CGI power armour in this series and its going to look.... really bad#like... nothing wrong with the model or even its animations#but its going to be very obviously CGI and not quite blended into the world properly#... because thats pretty much every amazon show ive ever watched....#(also my guess as to why amazon cheaped on customs for Rings of Power? Costumers are usually Union workers (: )#(I put the bad wheel of time sets down to them being used in like... 1-2 scenes at most. Build 'em quick and then knock 'em down)#(the CGI? IDK man like no excuse for that. I dont think a lot of CGI artists have Unionised yet?)#(they should btw they really. really should)
0 notes
Video
youtube
Who’s to Blame for Out-Of-Control Corporate Power?
One man is especially to blame for why corporate power is out of control. And I knew him! He was my professor, then my boss. His name… Robert Bork.
Robert Bork was a notorious conservative who believed the only legitimate purpose of antitrust — that is, anti-monopoly — law is to lower prices for consumers, no matter how big corporations get. His philosophy came to dominate the federal courts and conservative economics.
I met him in 1971, when I took his antitrust class at Yale Law School. He was a large, imposing man, with a red beard and a perpetual scowl. He seemed impatient and bored with me and my classmates, who included Bill Clinton and Hillary Rodham, as we challenged him repeatedly on his antitrust views.
We argued with Bork that ever-expanding corporations had too much power. Not only could they undercut rivals with lower prices and suppress wages, but they were using their spoils to influence our politics with campaign contributions. Wasn’t this cause for greater antitrust enforcement?
He had a retort for everything. Undercutting rival businesses with lower prices was a good thing because consumers like lower prices. Suppressing wages didn’t matter because employees are always free to find better jobs. He argued that courts could not possibly measure political power, so why should that matter?
Even in my mid-20s, I knew this was hogwash.
But Bork’s ideology began to spread. A few years after I took his class, he wrote a book called The Antitrust Paradox summarizing his ideas. The book heavily influenced Ronald Reagan and later helped form a basic tenet of Reaganomics — the bogus theory that says government should get out of the way and allow corporations to do as they please, including growing as big and powerful as they want.
Despite our law school sparring, Bork later gave me a job in the Department of Justice when he was solicitor general for Gerald Ford. Even though we didn’t agree on much, I enjoyed his wry sense of humor. I respected his intellect. Hell, I even came to like him.
Once President Reagan appointed Bork as an appeals court judge, his rulings further dismantled antitrust. And while his later Supreme Court nomination failed, his influence over the courts continued to grow.
Bork’s legacy is the enormous corporate power we see today, whether it’s Ticketmaster and Live Nation consolidating control over live performances, Kroger and Albertsons dominating the grocery market, or Amazon, Google, and Meta taking over the tech world.
It’s not just these high-profile companies either: in most industries, a handful of companies now control more of their markets than they did twenty years ago.
This corporate concentration costs the typical American household an estimated extra $5,000 per year. Companies have been able to jack up prices without losing customers to competitors because there is often no meaningful competition.
And huge corporations also have the power to suppress wages because workers have fewer employers from whom to get better jobs.
And how can we forget the massive flow of money these corporate giants are funneling into politics, rigging our democracy in their favor?
But the tide is beginning to turn under the Biden Administration. The Justice Department and Federal Trade Commission are fighting the monopolization of America in court, and proposing new merger guidelines to protect consumers, workers, and society.
It’s the implementation of the view that I and my law school classmates argued for back in the 1970s — one that sees corporate concentration as a problem that outweighs any theoretical benefits Bork claimed might exist.
Robert Bork would likely regard the Biden administration’s antitrust efforts with the same disdain he had for my arguments in his class all those years ago. But instead of a few outspoken law students, Bork’s philosophy is now being challenged by the full force of the federal government.
The public is waking up to the outsized power corporations wield over our economy and democracy. It’s about time.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
I do want to say, my views on AI “art” have changed somewhat. It was wrong of me to claim that it’s not wrong to use it in shitposts… there definitely is some degree of something problematic there.
Personally I feel like it’s one of those problems that’s best solved via lawmaking—specifically, AI generations shouldn’t be copywrite-able, and AI companies should be fined for art theft and “plagiarism”… even though it’s not directly plagiarism in the current legal sense. We definitely need ethical philosophers and lawmakers to spend some time defining exactly what is going on here.
But for civilians, using AI art is bad in the same nebulous sense that buying clothes from H&M or ordering stuff on Amazon is bad… it’s a very spread out, far away kind of badness, which makes it hard to quantify. And there’s no denying that in certain contexts, when applied in certain ways (with actual editing and artistic skill), AI can be a really interesting tool for artists and writers. Which again runs into the copywrite-ability thing. How much distance must be placed between the artist and the AI-generated inspiration in order to allow the artist to say “this work is fully mine?”
I can’t claim to know the answers to these issues. But I will say two things:
Ignoring AI shit isn’t going to make it go away. Our tumblr philosophy is wildly unpopular in the real world and most other places on the internet, and those who do start using AI are unfortunately gonna have a big leg up on those who don’t, especially as it gets better and better at avoiding human detection.
Treating AI as a fundamental, ontological evil is going to prevent us from having these deep conversations which are necessary for us—as a part of society—to figure out the ways to censure AI that are actually helpful to artists. We need strong unions making permanent deals now, we need laws in place that regulate AI use and the replacement of humans, and we need to get this technology out of the hands of huge megacorporations who want nothing more than to profit off our suffering.
I’ve seen the research. I knew AI was going to big years ago, and right now I know that it’s just going to get bigger. Nearly every job is in danger. We need to interact with this issue—sooner rather than later—or we risk losing all of our futures. And unfortunately, just as with many other things under capitalism, for the time being I think we have to allow some concessions. The issue is not 100% black or white. Certainly a dark, stormy grey of some sort.
But please don’t attack middle-aged cat-owners playing around with AI filters. Start a dialogue about the spectrum of morality present in every use of AI—from the good (recognizing cancer cells years in advance, finding awesome new metamaterials) to the bad (megacorporations replacing workers and stealing from artists) to the kinda ambiguous (shitposts, app filter that makes your dog look like a 16th century British royal for some reason).
And if you disagree with me, please don’t be hateful about it. I fully recognize that my current views might be wrong. I’m not a paragon of moral philosophy or anything. I’m just doing my best to live my life in a way that improves the world instead of detracting from it. That’s all any of us can do, in my opinion.
#the wizcourse#<- new tag for my pretentious preachy rants#this is—AGAIN—an issue where you should be calling your congressmen and protesting instead of making nasty posts at each other
852 notes
·
View notes
Text
Whenever people criticize exploitative companies I notice that they tend to target consumers as if everybody using those services always have a choice in the matter, but im willing to bet that a massive chunk of the population that shops at walmart, orders from amazon, subscribe to disney+, etc, are poor/rural people who cant afford any of the alternatives. And what exactly do you expect them to do?
Disney+ is the cheapest option for reliable entertainment for poor parents with kids. Netflix is the cheapest option for that for most others. They still deserve to watch TV when they cant afford a cable package (and yes, pirating still has barriers attached to it. For one, you need to be able to afford the computer, just for starters). Not everyone who has a streaming service subscription is a bootlicker or supports the disney corporation or thinks netflix has the most correct working conditions.
Amazon is the cheapest option for shipping, well... almost anything. And in a lot of places, its the only thing that can reliably get there at all within the month. And when a prime subscription comes with free shipping and a streaming service? That cuts out one major expense AND the expense from the first point, too. Folks still deserve to be able to order things when they cant afford to pay for shipping fees or when they can only afford the cheapest possible option for the item they need. Not everybody with a prime subscription or who orders the occasional thing off amazon wants to personally suck jeff bezos's dick or thinks warehouse workers deserve to be worked to death.
Walmart remains the cheapest possible option for most people in north america, especially in the cost of living crisis right now where groceries cost more than your rent. Not everybody who shops at walmart thinks the workers deserve to be exploited or that unions are bad or that driving out small businesses is a good thing
And im gonna be honest, every single "alternative" ive seen from people acting these ways is WAYYY more expensive and unreliable to poor and rural people than the things theyre telling us to stop using. You absolutely should support small businesses when you can but i usually dont have small business money. I can either buy a few little things to eat that will last me maybe a week or i can get enough for the month for the same amount at walmart, and thats not MY fault.
What exactly do you want us to do here
670 notes
·
View notes
Text
BoyBoy book club⭑.ᐟ
These books have either been mentioned or recommended by the boys, list made to the best of my memory, some notes added for context + little abstract. [(A.) = Aleksa's rec; (L.) = Lucas' rec; (Al.) = Alex's rec] Reply or reblog to add more to update the list thanks!
⊹ Caliban and the Witch: Women, the Body and Primitive Accumulation - Silvia Federici (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: Also 'Caliban and the Witch' by Silvia Federicci is brilliant. It's a great marxist-feminist retelling of the European witch-hunts, it's really really cool. It completely flipped my view of the birth of capitalism... She posits that capitalism is a reaction to a potential peasant revolution in Europe that never succeeded, and situates the witch-hunt as a tool of the capitalist class to break peasant social-ties and discipline women into their new role as reproducers of workers.] || Is a history of the body in the transition to capitalism. Moving from the peasant revolts of the late Middle Ages to the witch-hunts and the rise of mechanical philosophy, Federici investigates the capitalist rationalization of social reproduction. She shows how the battle against the rebel body and the conflict between body and mind are essential conditions for the development of labor power and self-ownership, two central principles of modern social organization.
⊹ The Age of Surveillance Capitalism - Shoshana Zuboff (A.) || This book looks at the development of digital companies like Google and Amazon, and suggests that their business models represent a new form of capitalist accumulation that she calls "surveillance capitalism". While industrial capitalism exploited and controlled nature with devastating consequences, surveillance capitalism exploits and controls human nature with a totalitarian order as the endpoint of the development.
⊹ Anti-Oedipus: Capitalism and Schizophrenia - Gilles Deleuze and Félix Guattari (L.) || In this book , Gilles Deleuze and Félix Guattari set forth the following theory: Western society's innate herd instinct has allowed the government, the media, and even the principles of economics to take advantage of each person's unwillingness to be cut off from the group. What's more, those who suffer from mental disorders may not be insane, but could be individuals in the purest sense, because they are by nature isolated from society.
⊹ Open Veins of Latin America - Eduardo Galeano (A.) (Intro to LATAM history, infuriating but good.) (Personal recommendation if you know nothing about LATAM.) || An analysis of the impact that European settlement, imperialism, and slavery have had in Latin America. In the book, Galeano analyzes the history of the Americas as a whole, from the time period of the European settlement of the New World to contemporary Latin America, describing the effects of European and later United States economic exploitation and political dominance over the region. Throughout the book, Galeano analyses notions of colonialism, imperialism, and the dependency theory.
⊹ The Origin of Capitalism - Ellen Wood (A.) || Book on history and political economy, specifically the history of capitalism, written from the perspective of political Marxism.
⊹ If We Burn - Vincent Bevins (L.) || The book concerns the wave of mass protests during the 2010s and examines the question of how the organization and tactics of such protests resulted in a "missing revolution," given that most of these movements appear to have failed in their goals, and even led to a "record of failures, setbacks, and cataclysms".
⊹ The Jakarta Method - Vincent Bevins (A.) [Aleksa’s recommendation for leftists friends] || It concerns U.S. government support for and complicity in anti-communist mass killings around the world and their aggregate consequences from the Cold War until the present era. The title is a reference to Indonesian mass killings of 1965–66, during which an estimated one million people were killed in an effort to destroy the political left and movements for government reform in the country.
⊹ The Anarchy: The Relentless Rise of the East India Company - William Dalrymple (L.) [Not read by the boys yet, but wanted to read.] || History book that recounts the rise of the East India Company in the second half of the 18th century, against the backdrop of a crumbling Mughal Empire and the rise of regional powers.
⊹ The Triumph of Evil: The Reality of the USA's Cold War Victory - Austin Murphy (A.) || Contrary to the USA false propaganda, this book documents the fact that the USA triumph in the Cold War has increased economic suffering and wars, which are shown to be endemic to the New World Order under USA capitalist domination.
⊹ Technofeudalism: What Killed Capitalism - Yanis Varoufakis (L.) || Big tech has replaced capitalism’s twin pillars—markets and profit—with its platforms and rents. With every click and scroll, we labor like serfs to increase its power. Welcome to technofeudalism . . .
⊹ The History of the Russian Revolution - Leon Trotsky (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: This might be misconstrued since I'm not a massive fan of Trotsky... but... his book "History of the russian revolution" is amazing. It's so unique to have such a detailed history book compiled by someone who was an active participant in the events, and he's surprisingly hilarious. Makes some great jokes in there and really captures the revolutionary spirit of the time.] || The History of the Russian Revolution offers an unparalleled account of one of the most pivotal and hotly debated events in world history. This book presents, from the perspective of one of its central actors, the profound liberating character of the early Russian Revolution.
⊹ Rise of The Red Engineers - Joel Andreas (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: It's a sick history book, focusing on a single university in China following it's history from imperial china, through the revolution and to the modern day. It documents sincere efforts to revolutionize the education system, but does it from a very detailed, on-the-ground view of how these cataclysmic changes effect individual students and teachers at this institution.] || In a fascinating account, author Joel Andreas chronicles how two mutually hostile groups—the poorly educated peasant revolutionaries who seized power in 1949 and China's old educated elite—coalesced to form a new dominant class.
⊹ Adults in the Room: My Battle with the European and American Deep Establishment - Yanis Varoufakis (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: The book I mentioned earlier - "adults in the room" - is amazing. There's a great description of Greece's role in the European economy [as an archetype for other, small European countries] and the Union's successful attempts to discipline smaller countries to keep their monetary policy in line with the interest of central European bankers. I'd definitely reccommend it!] || What happens when you take on the establishment? In Adults in the Room, the renowned economist and former finance minister of Greece Yanis Varoufakis gives the full, blistering account of his momentous clash with the mightiest economic and political forces on earth.
Edit: Links added when possible! If they stop working let me know or if you have a link for the ones missing.
#IDK if anyone else is interested in this but in case anyone finds it useful <3#boy boy#aleksa vulović#alex apollonov#ididathing#ngl most of this r aleksa/lucas recs.... idk if any of them are alex sorry i forgot?
108 notes
·
View notes
Note
why are the petticoats so expensive? everything comparable on Amazon is like 15-20 bucks. ive got one myself and the fabric is already quite decent. now obviously the one i bought won't work for everybody but i can't for the life of me figure out why yours are $60 more. what's the draw
it's all down to the quality of material + the cost of ethical labor
our petticoats are made in a factory with certifications for both ethical labor and responsible textile production, which means workers are paid fairly and have good working conditions and the factory doesn't use harmful chemicals like formaldehyde or materials like lead to process the fabric, which is very common in cheap clothing.
our petticoats also use real tulle instead of organdy and a real satin blend instead of polyester. because of this and the quality sewing, these petticoats are built to last you for a considerable amount of time, given the proper care.
our petticoats aren't going to be a viable option for everyone and i recognize that, which is why i'm not deleting my cheaper petticoat recommendations from my FAQ. but for those who can afford it, that is why they are more expensive.
349 notes
·
View notes
Text
Actually I’m gonna talk about this, controversy aside, Hazbin Hotel is so fucking lackluster. From character design, as I've previously mentioned, to animation
Vivziepop had years to work on these character designs and this is the best she could do on a LARGER animation budget?

I’d hardly even call them redesigns since you couldn’t even tell they’re different than when they first debuted (save for Vaggie)
And the actual animation just looks so stiff and like it’s a fan made thing


Versus the pilot from FOUR YEARS AGO


The reasoning for the “simpler” designs is to make them easier to animate but they aren’t that complex of designs and I’m no animator I’ll admit so maybe it makes it easier for musical numbers, but part of the appeal of the pilot was the hand-drawn loose style
Plus, any interesting design choices that were there were taken away in the Amazon show
Not to mention that almost every character is supposed to be based off an animal and you can't fucking tell what animal they're supposed to be unless you fucking google it
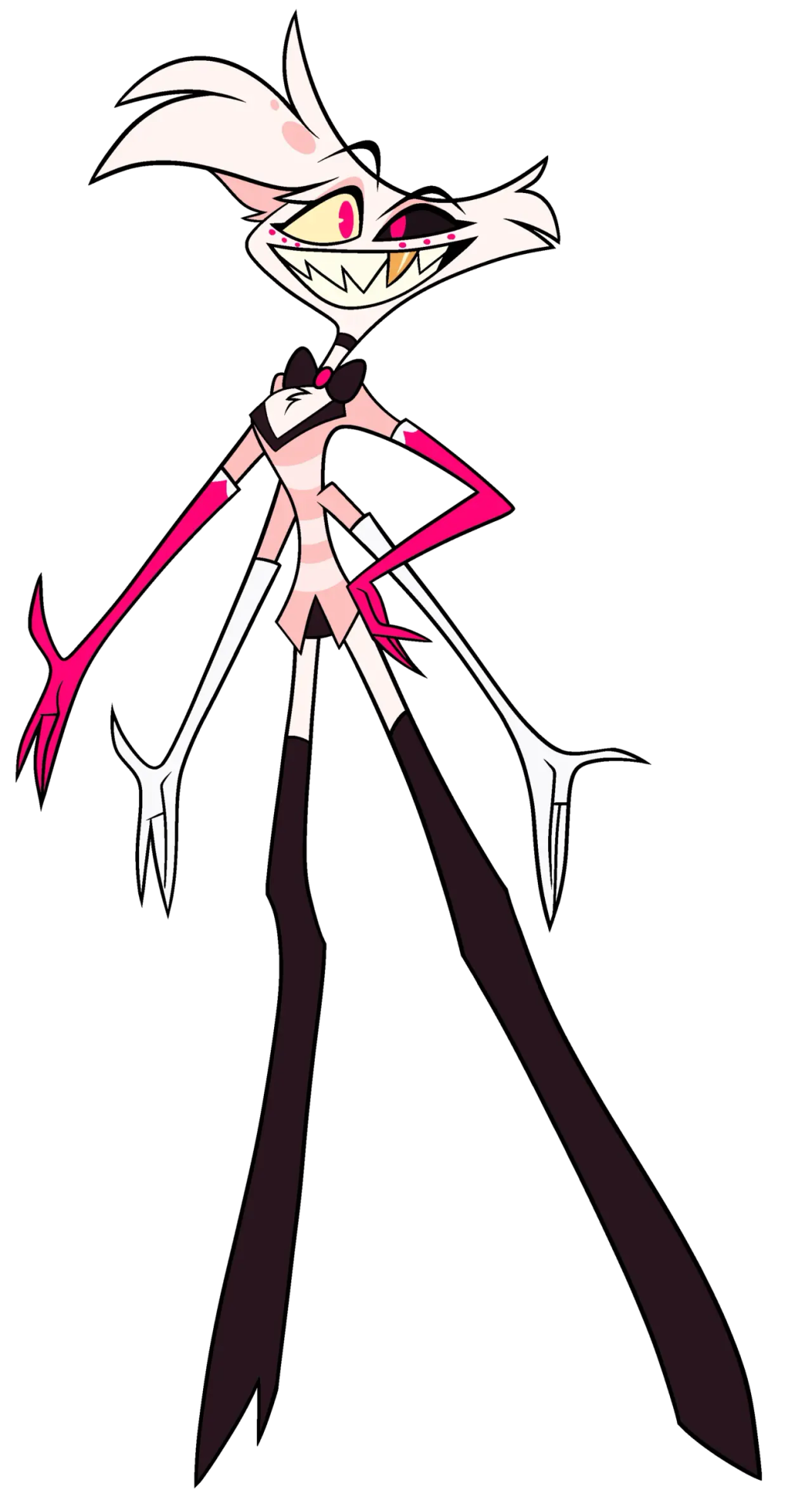

THIS is supposed to be a spider. If I didn't know who he was, i wouldn't even know that. Maybe it's not a universal opinion, but I feel like if your character is supposed to be based off of something, it should be a little more obvious than four arms and dots under his eyes which are actually another set of eyes.
He's a gay man, who's also a sex worker/porn star, which can be told by his outfit, but none of his outfit looks good together. You've got two sets of gloves, knee high boots, a mini skirt, and a blazer with a bowtie AND a choker.
It is a perfect outfit to tell you everything you need to know about him because it's a fucking mess. It looks like when your kid dresses up in your fancy clothes to take pictures in but nothing goes together because the kid is 5 and doesn't understand that just because you like the clothes doesn't mean they go together.

This is apparently a deer, though I've heard he's based off a w*ndigo so he wouldn't be deer-based, WHICH IS STILL BAD BTW HE'S GOT SO MANY RACIST PARTS OF HIS CHARACTER ELEMENTS BUT I'M NOT EDUCATED ENOUGH IN THOSE ASPECTS TO TALK ABOUT IT
And the outfit is just...bad. Aside from the tiny antlers that can barely be seen behind the hair, there's nothing cohesive about it. There's his coat that doesn't match the era he's from, the bob cut, the microphone which doesn't look like a microphone, the neckline that makes no sense, the random stripes on his shirt that you can't really tell what they're supposed to be (suspenders and a tie? a print on the shirt?), the actual tee shirt he appears to be wearing underneath his coat, the gloves, and again the FUCKING BOWTIE WHY DO EVERY ONE OF HER MALE CHARACTERS HAVE BOWTIES IS SHE ALLERGIC TO NECKLINES?
Not to mention the colors of the show and the characters. Vivziepop is under the impression that since they're all in Hell, they need to have a color scheme. Or at least the more important characters do. And what color scheme is that? Red and black.
But you know what else has red and black?
EVERY
SINGLE
BACKGROUND
IN THE SHOW
And he just blends in with the background. Which is not something you want a character to do if they're one of the more important characters in your show.
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
Against my better judgement I began watching, and finished the Amazon prime sausage party show that id never heard of until I accidentally clicked on it while looking for something to put on the bg while I assembled a desk. And I became engrossed. Totally put the desk aside because. Like the movie wasn’t good, and it tried really hard to be offensive and awful, and it was, not to mention the production/workers rights nightmare for everyone involved. So I knew what to expect: gross out humor and orgies. And yeah, that’s what I got, but for whatever reason I couldn’t look away bc I really wasn’t expecting three things that it did do, which was like. Critique capitalism. Attempt to answer the questions of like ‘okay now what do they do since they liked everybody and had sex with each other. Also why are they even alive’. But most of all I really wasn’t expecting to see the hotdog have graphic sex with a schlubby human, for a really long time, only to get ejaculated on. Like the human came on him and they showed it all and he just kept talking while covered in cum, talking about the cum. It shocked me more than gore I think because, it’s like. Why. But I kept watching after that too and noticed they tried to cut out all racial stereotypes save Jewish ones (but it’s Seth rogen so you expect that), and also. Well this isn’t really noteworthy but they played sufjan Steven’s at the end of one episode while the human thought about eating a foot, to avoid eating food which is alive. The human foot wasn’t. It was dead. And he’s crying about it while this song is playing, then he takes a hesitant bite and is chewing, grossed out but starving, then his expression sorta blanks to a neutral resignation, then an empty contemplativeness, and finally acceptance, maybe even joy as he’s eating. And that was shocking too because it was strangely like. Not beautiful. It was just something and I dunno. Would not watch again. Feel weird about the hotdog cum man. I feel bad about it. I wish I hadn’t seen that. The gay twinky and racist native and latina alcohol and taco characters aren’t present. Likely to sweep those things under the rug. Why did he have to cum on the hotdog.
93 notes
·
View notes
Text

Spoilers for Mouthwashing
There’s a lot of convo about Jimmy, Curly, and Anya (and for good reason), but I haven’t seen as much about the dynamic between Swansea and Daisuke. The game does make Swansea look like a saint compared to Jimmy and Curly, but let’s be real. He kind of sucks.
I’ve known people like Swansea. I’ve worked with them. They’re miserable and the best thing they can do is make sure other people aren’t miserable by trying to get them not to make the same choices they did. And those choices are, sometimes, working at a shitty job. Which we all have to do sometimes! The problem with the Swanseas of the world is that they think they know you, and they think they know what’s best for you. But we don’t know Daisuke’s situation. Maybe doing maintenance is the best he can accomplish, or maybe he just needs the money for now and would have moved on to something else. But Swansea keeps berating and pushing him down in the hopes that he won’t go through the same crap he did. And it weighs down on Daisuke.
Thankfully, I wasn’t as young or impressionable as Daisuke. I didn’t feel the need to drink to try to connect with my superior. I didn’t feel the need to climb in an extremely dangerous ventilation shaft to show my superior that I was capable, nor did I have a Jimmy in my life playing on my insecurities. Thank fuck. Nobody needs a Jimmy. But I have worked jobs where I was insecure and I made bad choices to try to do better or even just get a “good job” from my senior workers.
Back in 2018, I worked as a postal carrier for three months, though I was still in my evaluation period when I left. Being evaluated for months suuuucks. You know what sucks even more? Having no support among your peers. I only heard one positive remark about my performance from one of my co-workers during “Amazon Sunday” which is as dystopian as it sounds. When I pointed it out, he acted like his tongue betrayed him. The thing is, I craved that little bit of positivity so much, I started doing things like not putting my seatbelt on or locking the packages up in the back of the vehicle when I went in to an apartment. All in the name of efficiency. If I could just drive a little bit faster, someone will accept me. If I work a little less safely, I can get some kind of approval. I realized pretty quickly what the job was doing to me and I quit on after having a little bit of a mental breakdown.
Daisuke, though. He needs a mentor. And it sucks that Swansea couldn’t be that for him. It sucks even more that Jimmy saw that insecurity and took advantage of it. Anyway, that’s my rant. Swansea isn’t based. He is, in fact, cringe. At least he accepts how much he sucks. It’s a start. But what good does that do Daisuke? He needed someone to at least pretend to be a mentor. He needed someone to take responsibility.
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Time for some tracts:
"How do we create jobs?" You raise the minimum wage, because if people don't need to work three jobs to make rent, those other two jobs will mysteriously open up.
"How do we support small businesses?" You raise the minimum wage, staggered to the biggest corporations first.
"How do we reduce homelessness?" You raise the minimum wage.
"How do we make sure raising the minimum wage doesn't negatively impact prices or--?"
Prices are already rising faster than wages are, this is playing catch up.
Put a cap on CEO salaries and bonuses, they can't earn more than 100 times more than their lowest paid workers. Current US ratio is 342, which is insane. (This list is mostly about the US.)
Hit corporations first, give small businesses time to adjust. McDonald's and Walmart can afford to raise wages to $20/hr before anyone else does, they have that income.
Drop the weekly hours required for insurance from thirty to fifteen. This will disincentivize employers having everyone work 29hrs a week, partly because working only 14hrs a week is a great way to have undertrained, underpracticed staff. Full time employment becomes the new rule.
Legalize salary transparency for all positions; NYC's new law is a good start.
Legislation that prevents companies from selling at American prices while paying American wages abroad. Did you know that McDonald's costs as much or more in Serbia, where the minimum wage is about $2/hr? Did you know that a lot of foreign products, like makeup, are a solid 20% more expensive? Did you know that Starbucks prices are equivalent? Did you know that these companies charge American prices while paying their employees local wages? At a more extreme example, luxury goods made in sweatshops are something we all know are a problem, from Apple iPhones to Forever 21 blouses, often involving child labor too. So a requirement to match the cost-to-wage ratio (either drop your prices or raise your wages when producing or selling abroad) would be great.
Not directly a minimum wage thing but still important:
Enact fees and caps on rent and housing. A good plan would probably be to have it in direct ratio to mortgage (or estimated building value, if it's already paid off), property tax, and estimated fees. This isn't going to work everywhere, since housing prices themselves are insanely high, but hey--people will be able to afford those difficult rent costs if they're earning more.
Trustbusting monopolies and megacorps like Amazon, Disney, Walmart, Google, Verizon, etc.
Tax the rich. I know this is incredibly basic but tax the fucking rich, please.
Fund the IRS to full power again. They are a skeleton crew that cannot audit the megarich due to lack of manpower, and that's where most of the taxes are being evaded.
Universal healthcare. This is so basic but oh my god we need universal healthcare. You can still have private practitioners and individual insurance! But a national healthcare system means people aren't going to die for a weird mole.
More government-funded college grants. One of the great issues in the US is the lack of healthcare workers. This has many elements, and while burnout is a big one, the massive financial costs of medical school and training are a major barrier to entry. While there are many industries where this is true, the medical field is one of the most impacted, and one of the most necessary to the success of a society. Lowering those financial barriers can only help the healthcare crisis by providing more medical professionals who are less prone to burnout because they don't need to work as many hours.
And even if those grants aren't total, guess what! That higher minimum wage we were talking about is a great way to ensure students have less debt coming out the other side if they're working their way through college.
------------------
Linda P requested something either really interesting or really silly and this is... definitely more of a tract on a topic of interest (the minimum wage and other ways business and government are both being impeded by corporate greed) than on a topic of Silly. Hope it's still good!
2K notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
How Amazon Is Ripping You Off
Shopping on Amazon? Stop! Watch this first.
Amazon is the world’s biggest online retailer. This one single juggernaut of a company is responsible for nearly 40% of all online sales in America. In an FTC lawsuit, they’re accused of using their mammoth size, and consumers’ dependence on them, to artificially jack up prices as high as possible, while prohibiting sellers on Amazon from charging lower prices anywhere else.
They’re accused of using a secret algorithm, codenamed "Project Nessie," to charge customers an estimated extra $1 billion dollars,
If this isn’t an abuse of power that hurts consumers, what is? So much for all of those “prime” deals you thought you were getting.
Project Nessie isn’t the only trick Amazon has been accused of using to exert its hulking dominance over the online retail industry — leading to higher prices for you.
Much of the FTC’s antitrust lawsuit centers around the treatment of independent merchants who sell items on Amazon’s online superstore — accounting for 60 percent of Amazon's sales.
Amazon allegedly uses strongarm tactics that force these sellers to keep their prices higher than they need to be. Like barring them from selling products for significantly less at other stores — or else risk being hidden in Amazon’s search results or having their sales stopped entirely.
And Amazon is accused of engaging in pay-to-play schemes and charging merchants excessive fees that end up costing you even more.
Independent sellers are effectively forced to pay Amazon to advertise their products prominently in search results. If they don’t fork over cash, then their products get buried underneath products of companies who do. This hurts sellers but also harms shoppers who have to parse through less relevant products that may be more expensive or lower quality.
And to be eligible for the coveted “Prime” badge on their items — which is considered crucial for competing on the platform — independent sellers are pushed into paying Amazon for additional services like warehousing and shipping, even if they could get those services cheaper elsewhere. If sellers forgo trying to qualify for Prime, their goods apparently become harder for customers to find.
When all of these extra fees are added up, Amazon takes around a 50 percent cut of each sale made by a third party. It’s projected that Amazon will earn around $125 billion from collecting fees in the U.S. in 2023, most of which get passed on to you.
By charging all of these extra fees and stifling independent companies from selling their products for less elsewhere, Amazon is using its dominance to essentially set prices for all consumers across the internet.
And when you combine Amazon’s control of ecommerce with all of the other industries it has entered by gobbling up companies — such as Whole Foods, One Medical, and MGM — you’re left with a behemoth that simply has too much power.
This is all part of a much larger problem of growing corporate dominance in America. In over 75% of U.S. industries, fewer companies now control more of their markets than they did twenty years ago.
The lack of competition and consumer choice has resulted in all of us paying more for goods because corporations like Amazon can raise their prices with impunity. By one estimate, corporate concentration has cost the typical American household $5,000 a year more than they would have spent if markets were truly competitive.
This power isn’t just being used to siphon more money from you. A giant corporation has the power to bust unions, keep workers’ wages low, and funnel money into our political system.
It’s a vicious cycle, making giant corporations more and more powerful.
But under the Biden administration, the government is making a strong effort to revive antitrust law and use its power to reign in big corporations that have grown too powerful.
We must stop the monopolization of America. This FTC lawsuit against Amazon is a great start.
523 notes
·
View notes
Note
As I understand it, Good Omens Season 2 has wrapped production and won’t be affected by the WGA strike in the States. But I was wondering— and this is by far my most reasonable avenue to ask someone with knowledge and authority on the subject— would an American union strike affect a British production significantly? How many American writers and crew members are usually working on-set? Would you have considered stalling GOS2 production in solidarity with an overseas strike? I don’t mean to push you towards being overly speculative— I suppose I’m just interested in how far the WGA picket line extends internationally.
Good Omens 2 wrapped production in March of 2022. While we were shooting we had an American producer, and in the cast we had American Jon Hamm, but most of the other people in the cast and crew were British.
Under British law it would have been illegal to have struck in solidarity with an overseas strike.
From the WGGB site:
Trade union legislation is very different in the UK.
Secondary strike action (action in support of another union or group of workers) is not permitted under UK law, nor is the practice of restricting employment to those who are members of a particular trade union.
UK writers can take other action in support of the WGA, for example, taking part in protests or demonstrations that do not fall under the definition of ‘picketing’.
On the other hand, I'm WGA so I would have gone on strike, if the strike had occurred while we were shooting or editing, which would have meant that no writing or rewriting could have occurred (and every week I would get what we were shooting that week, and every week would do any rewriting that needed doing, sometimes every day, and sometimes while we were shooting I'd be rewriting or fixing something) and I wouldn't have been in the edit or in ADR sessions, because they can involve writing.
My understanding of US shows filming in the UK, like Rings of Power or House of the Dragon, is that they are able to shoot scripts already written, but that no rewriting can occur.
(GO2 was finished and handed in in March of this year. It's all done and Amazon will be releasing it in the Summer, so it's all a bit hypothetical trying to what if the strike was happening now. I think it would have been made, it just wouldn't have been as good.)
952 notes
·
View notes
Text
Only YOU Can Prevent Witchy Fires
Hello witches, workers, and all in between! Your friendly neighborhood Granny is here to teach you a few things about fire safety!
Yes, yes, I know. “But Buggy, this is tumblr! And you're on a boring witchcraft blog! What do we need a lesson on fire safety for? We aren’t in kindergarten!” But trust me! More than one witch has accidentally singed their hair or set their own altar on fire before! Sometimes we get so into the spiritual that we forget to be mindful of the reality around us.
I’m going to go over a bundle of good tips to keep in mind for making a wax seal over that spell jar or burning a few bay leaves or ingredients to release that nonsense into the air! Even a section for the kitchen witches!
Indoor Safety:
*Those annoying fire alarms? Make sure they are operational okay? Change those batteries at least once a year, preferably twice. (If it is something you are in control of.)
*Always use a fire-safe candle holder for candles! Trim down that wick before lighting! I know it seems silly to use a pair of scissors or a wick trimmer, but trimming down that wick will always make that flame much easier to manage. And that flame? If it gets big enough to cause black smoke ALWAYS put it out.
*Always keep the candle in your line of sight, no meditation with an open flame going okay? Also if your candle is big enough to burn for more than four hours...put it out at the 4 hour mark.
*The longer a candle burns the more carbon gathers on the wick itself and that can make the flame get bigger and more unstable. Those ultra-wobbly flames that flicker and waves like one of those wacky inflatable arm flailing tube men? That is something you don’t want.
*Putting out a candle: We don’t recommend putting it out with your fingers no matter how cool it looks. Use a candle snuffer, or blow it out. I promise blowing out a deity candle won’t insult them!
*Another crucial tip is to keep anything that could catch fire a minimum of three feet or 91 centimeters AWAY from the fire source. That includes carpeted flooring, cloth, hair, rugs, altar cloths, papers, books, all sorts of things! Always wear your hair back when working with fire, and wear close fitting clothing that won’t hang or drape into the fire with your movements.
*Another tip given straight from the NSC is to NEVER use candles or other fire sources while tired or inebriated! That means no 2 am spell jars if you are half asleep! ALSO never EVER leave a candle WARM or actively BURNING! Same goes for any items you are burning down like bay leaves. Burn them in a fire safe bowl that is much bigger than you think you need. Toss the debris around and soak in water to ensure they are safely doused.
*IF you are using wax to seal off spell jars I highly suggest getting a wax sealing kit! Wax sealing kits come with a little spoon that you drop bits of wax into and ‘melt’ them down over something like a tea candle. An example is this: Which you can find on Amazon for roughly $10 USD!

The spoon is perfect for pouring and there’s less likelihood of the candle you would sit on top of the jar from falling off because...there is no candle! If you only have a candle to work with...please don’t burn the candle on top of the object you are sealing, put the candle in a safe holder and hold it over the object once warm to let the wax drip down. Have the object you are sealing sitting on top of a safe ceramic plate or bowl in case of drippage!
But what do I do if a fire starts?
Good question! That depends on the type of fire it is! Here’s a breakdown of the types and methods to put them out: Ordinary Fire: An ordinary fire is caused by candles, papers, cloth, plastics, that sort of thing!
The good news is these types of fires respond amazingly well to plain old water! It’s always advised that you keep a bucket or pitcher full of water within reach whenever using candles just in case!
Electric Fire: Electric fires are caused by a source of electricity, like wires getting crossed and arching.
NEVER use water on an electrical fire! If you do, you'll just electrocute yourself. If it’s safe to do so...unplug the object from the outlet. Turn off the electricity in your house’s electric breaker box. Smother the flames by pouring baking soda onto them.
Chemical Fire: Chemical fires have a chemical as a fuel source, like rubbing alcohol, nail polish & polish remover. Even your nails near a candle can produce a small chemical fire if you aren’t careful! (Dry those nails up good before using candles.) These fires can only be put out with a fire blanket OR pouring a LARGE quantity of baking soda or sand onto the fire.
Cooking Fires: Cooking fires are the most common form of household fire. It can be caused by grease, burning food, or burning cooking oil. Water will NOT work on any fire oil or grease based, it may seem like a first instinct to grab the pan and toss it into a sink with water...DON’T.
That will cause the oil to splatter and can injure you and make any flames spread further! It the fire is small enough and contained within a pot or skillet, have a lid or baking sheet handy and throw that onto the top of the fire, this will smother it out. A fire blanket can also be used for this. Do NOT swat at the flames, this is just a fanning motion and will give the fire more oxygen to grow with! Pour a large amount of salt or baking soda on top of the fire. MAKE SURE it is not flour, as flour will cause the fire to grow quick enough to even explode! Turn off any heat source.
And if the fire is in the oven or microwave? Leave that door CLOSED. It seems super scary but the fire will smother itself out when trapped in a small box. (Of which both cooking items are.)
Outdoor Safety:
Never burn outdoors if it is windy or extra dry! Do not burn general trash, only burn natural dry vegetation/herbs. Always check your local ordinances and make sure there are no burn bans in your area currently active!
If you are going to burn outside, clear away a circular space for the burning items. Far enough away from overgrowth, houses, powerlines, and other such things. The burning site should have plenty of dirt or gravel around it, usually around 10 feet, 304 centimeters circular if burning a campfire-size burning space. Make sure the dirt and gravel is well doused in water to prevent any spreading.
Always stay around the fire until it is completely out. Turn the debris from your burn a few times and douse it hard with water. NEVER leave dry ash on the ground, embers could be still warm enough to catch on the inside of the ash! Keep checking on that burn area for a few days or a few weeks to make sure nothing is left, especially during warmer or dryer months. Don’t toss matches or other lighting instruments just anywhere! Those can still be warm and still catch grass alight.
And there you have it! A crash course on being safe with fire while doing your thing and slinging your spells!
#witchblr#psa#witchcraft#buggy's lessons#witchcraft for beginners#beginner witch#fire safety is important folks!
201 notes
·
View notes
Text
in a good version of this season i feel like the one-two punch of kerblam! and the witchfinders could have been used to give the doctor a moment of growth. she has, so far, put aside her usual impulse to Break Shit in exchange for passively preserving systems as are, because her experience with trying to change missy killed her.
(importantly, this was a much smaller change then. say. blowing shit up. or destabilizing a government. but it was also much more personal, something she had an extreme investment in emotionally, and something that got her and her friend killed. the doctor makes irrational, emotional decisions and justifies them later with big speeches. that’s what she does. and her turn to being as passive as she can stand to be as thirteen is an irrational decision she’s making to try and protect herself from being hurt, to protect the people and planet she’s designated as her charge from being hurt. she can dress it up in the framing of not wanting to tamper with history, but what she’s not saying is she doesn’t want to risk breaking things, knowing that it might come back worse.)
and that’s fine. that’s a good route to take the doctor post-twelve. but kerblam! and the witchfinders are the perfect episodes to challenge her stance. because in, say, rosa, in the demons of punjab, even in ghost monument, she’s not gonna have to stay here. she doesn’t have to live in the systems she observes and leaves be. (obviously, doylist, we can’t have the doctor Solve Racism™️. but we can contrast her lack of action against those of the people who do have to live in the systems, who are risking everything and will suffer for it and still know that change is worth it.)
the start of kerblam! has them going in as workers. undercover. in the system. this is a mask the doctor can easily throw off when convenient for her. but she’s standing next to ryan, who couldn’t, not at his factory job. who nearly lost said job because the system he was in would have decided his disability made him a liability. who only kept it because of solidarity with his fellow workers. the doctor is In the system, but only for. day and only as long as she wants to be. at the end, she can still leave. in a better episode, they might have been able to use this to set up her realizing, hey, shit, the fact that i don’t Have to change things is a privilege i have from not having to survive under these systems. unfortunately. this is kerblam!
but the witchfinders doubles down on that! she can’t stand by and watch a woman be killed while her granddaughter cries! but her hesitation to act means that she dies anyway! the doctor asserts herself as an authority in the system to get access to information and power to prevent this happening again, and it looks at her, looks at the body she’s in and the face she’s wearing, and says No. says If you won’t submit to what we say about you, you will die. If you submit to what we say about you, you will die. This is the world, accept it. For the first time this season, the Doctor is chained to something she hesitated to change. She’s not watching anymore. She’s learning what it is to be drowned while everyone looks on and says nothing. Lets it happen. Because this is how it is. And the system isn’t the problem.
Like she’s been doing.
So! Conclusion! fuck if i know yet if they’ll uh. Do Anything With This Set-Up. but god it is so ripe to, if not change her ways, give some ample arguments that’ll make it harder for her to just walk away from the next space amazon facility, you know?
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the final lead-up to the US presidential election, Elon Musk has thrown the full weight of his celebrity and his resources behind former president and Republican nominee Donald Trump. He has appeared with Trump on the campaign trail; pumped money into a pro-Trump PAC (which has, in turn, bought ads on the platform he owns); and made X a hotbed of right-wing conspiracy theories, some of which he has personally boosted, that many experts say are designed to undermine faith in the outcome of the elections.
But Musk’s behavior is also having another effect: It’s taking scrutiny off other tech leaders and companies, even as they cozy up to Trump or roll back policies that would protect the information ecosystem ahead of a major election.
“In a race to the bottom, Elon Musk paved the way for a new, toxic tech basement,” says Nora Benavidez, senior counsel at the nonprofit Free Press. “Yet, as long as other platforms aren’t quite as abysmal, they squeak by under cover of Twitter’s failures.”
Social media companies have largely replaced traditional media conglomerates as gateways to information. According to a Pew Research study, 54 percent of adults now get at least some of their news from social media. And that number is much higher for people below the age of 50. Sixty-four percent of people aged 30–49 and 78 percent of people 18–29 get news from social media.
“[Musk] is smart enough to understand that to control the narrative, you want to control the media,” says a former Twitter employee. “And social media is media.”
But these companies don’t face the same kind of restrictions and responsibilities that traditional media do. Section 230 prevents social media companies from being held legally liable for the content on their platforms. Content moderation is largely voluntary, except in cases where the content itself is illegal (like child sexual abuse material), which has its own consequences. A 2020 study from the Harvard Misinformation Review found that people who relied on social media for their news were more likely to believe misinformation about the Covid-19 pandemic. A different Pew Research study, also from 2020, found that Americans who relied on social media for their news had lower political knowledge than those who didn’t.
But for years, public pressure from government officials, civil society, and the media pushed tech companies to invest in teams and tools that could at least somewhat address issues of hate speech or misinformation on their platforms, so they could say they were making a good-faith effort to deal with the issue.
Musk’s purchase of Twitter signaled a change, according to six former trust and safety employees from Twitter and Meta.
When Musk took over Twitter in October 2022, he quickly fired more than 50 percent of the company’s workers, including almost all of the company’s trust and safety and policy staff—the people tasked with creating and enforcing the platform’s policies around things like hate speech, violent content, conspiracy theories, and mis- and disinformation. Since then, Meta, Google, Amazon, and Discord have all made cuts to trust and safety staff.
Shortly after Musk purged Twitter of its trust and safety teams, other companies began layoffs. In November 2022, Meta laid off 11,000 employees, including many trust and safety employees. In January 2023, Google followed suit, axing 12,000 people. Earlier this year, Twitch, which is owned by Amazon, disbanded its Safety Advisory Council.
“I think that Elon really opened the floodgates,” says one former Meta employee. “So then other tech brands were like, ‘We can do that too, because we won't be the black sheep for it.’”
Meta spokesperson Corey Chambliss tells WIRED that the company has “40,000 people globally working on safety and security—more than during the 2020 cycle, when we had a global team of 35,000 people working in this area,” though he did not address how many of those people are staff versus outsourced workers.
Musk’s sudden firings made it so that “anybody else could come along and nicely fire their teams and give them severance and it was nicer. Better,” says a former Twitter employee who was fired by Musk.
After Musk fired the trust and safety staff, experts warned that this cut, coupled with Musk’s “free speech absolutism,” would allow toxic content to flood the platform and ultimately cause an exodus of users and advertisers, leading to Twitter’s eventual demise. Hate speech and misinformation did increase, and advertisers did pull their dollars. Last year, X fired members of what remained of its elections team. Around the same time, Musk posted on X, saying, “Oh you mean the ‘Election Integrity’ Team that was undermining election integrity? Yeah, they’re gone.”
But X is still alive and kicking.
Musk’s behavior, say the former employees, acted as cover for other platforms that saw trust and safety work as a burdensome cost. The work of teams focused on ad sales or user engagement drives growth and money for platforms. Trust and safety teams, former employees say, do not. This makes them easy targets when companies tighten their belts.
“I think [layoffs] were something Mark [Zuckerberg] wanted to do for a long time,” says the former Meta employee. “And so, if Twitter can get away with having less good technology and less good infrastructure than other companies, and is still getting rid of thousands of people, which is proportionally way more than any amount laid off by Google or anyone else, then I think that that kind of empowered other companies too.”
Chambliss says that Musk’s decisions did not play a role in Meta’s layoffs, referring to a 2023 post about the company’s “year of efficiency.”
It’s not just staffing that has shifted since Musk took the helm at X. Google and Meta have made significant changes to how they handle political content and mis- and disinformation.
Last year, YouTube, which is owned by Google, announced that it would “stop removing content that advances false claims that widespread fraud, errors, or glitches occurred in the 2020 and other past US presidential elections.” Google spokesperson Elena Hernandez told WIRED, “There were no cuts to the Trust and Safety teams that work on elections. We continue to make significant investments in the people, policies, and systems that enable Google and YouTube to be a reliable source for election-related news and information.” Hernandez did not respond to questions about whether the company would be updating its policies around election fraud claims in anticipation of the US presidential elections.
Recent reporting from The New York Times found that lies about the election have since spread widely on the platform. In previous years, a story like that might have put pressure on YouTube to enforce or change its policies, but now, conservative activist Christopher Rufo wrote on X, “in a post-Elon environment, YouTube's response is: ‘The ability to openly debate political ideas, even those that are controversial, is an important value—especially in the midst of election season.’”
“I think the public antics of Musk are diverting attention away from other companies who continue to launch products or make policy changes that demand careful thinking and transparency,” says Sabhanaz Rashid Diya, founder of the Tech Global Institute, a think tank focused on tech policy and a former Meta employee.
Earlier this year, Meta announced that it would no longer recommend political content to users on Threads and Instagram—though what exactly counts as politics remains unclear. Last year, the company removed restrictions on ads claiming the 2020 election was stolen and on Covid-19 misinformation. In July it removed restrictions on Trump’s Facebook account, which has 35 million followers. In August, less than three months ahead of the elections, it also wound down the tool Crowdtangle, which allowed journalists and civil society to monitor content on Meta’s platforms. (After taking over X, Musk announced that he would charge $40,000 for access to the platform’s API).
While X under Musk has presented a whole host of new issues for advocates and civil society, less attention has been paid to other, established platforms having many of the same problems they’ve had for years. Reporting from WIRED found that nearly four years after the January 6, 2021, insurrection at the Capitol, militia groups are still organizing on Facebook, with the platform even autogenerating pages for interested users. Meta’s and TikTok’s systems still can’t reliably detect ads containing election disinformation. Amazon’s Alexa told users the 2020 election was stolen.
“We do not have visibility on whether ad models in the lead-up to major elections have been changed, or whether researchers have been able to meaningfully engage with platforms and user metrics to study key information trends,” says Diya. “We still have unresolved questions about basic product or policy features that warrant continued scrutiny and should not be sidelined amidst specific individuals or one company monopolizing airtime.”
“Musk doesn’t take responsibility for anything on his platform, so it makes it a lot easier for other platforms to do the same,” says Alexandra Pardal, CEO of Digital Action, a nonprofit advocacy group focused on human rights and technology. “He’s changed norms about what’s acceptable and not, about what a responsible social media platform looks like. Musk has successfully masked [these changes] by making this the Elon Show.”
In a recent interview with the Acquired podcast, Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg said that he regretted allowing Meta to take responsibility for things that he saw as outside its mandate or control. “People are basically blaming social media and the tech industry for all these things in society—if we’re saying, we’re really gonna do our part to fix this stuff, I think there were a bunch of people who just took that and were like, oh, you're taking responsibility for that? Let me, like, kick you for more stuff.” Bloomberg also noted a shift in Zuckerberg’s approach to the 2024 election—namely, to avoid saying much about it at all.
Musk is obviously not the only driving force for this change. Tech companies have come under increasing scrutiny from both sides of the aisle, particularly from the GOP. This has made it particularly painful—and risky—for them to take action on certain topics. For instance, last year, a federal judge issued an injunction preventing social media companies from talking to the government, saying that Biden officials “engaged in a broad pressure campaign designed to coerce social-media companies into suppressing speakers, viewpoints, and content disfavored by the government." For companies like Meta, that meant that their threat detection teams were unable to alert or hear from federal agencies about issues. The Supreme Court ruled this summer that complainants lacked standing.
In August, Zuckerberg issued a letter to Jim Jordan’s congressional Subcommittee on the Weaponization of the Federal Government, saying that the company had, indeed bowed to government pressure to remove misinformation about Covid-19. (Three former Meta employees who spoke to WIRED on the condition of anonymity say that they did not get the sense that government pressure was behind Meta’s choices to suppress or remove Covid-19 misinformation at the time.) Pardal says that if Musk was not behaving so outrageously, she doubts that Zuckerberg “would be saying he made a mistake.”
And Trump, it seems, approves. In an interview with the Barstool Sports podcast Bussin’ With the Boys, Trump said, “I actually believe [Zuckerberg’s] staying out of the election, which is nice.” The former president has also claimed that other tech executives, including Sundar Pichai, Jeff Bezos, and Tim Cook, are supporters. Bezos, who owns The Washington Post, prevented an editorial endorsing Vice President Kamala Harris from running, the same day that executives from his space company, Blue Origin, met with Trump, signaling a willingness on the part of the industry to cooperate with a possible second Trump administration. (Bezos appeared unmoved, even in the face of more than 200,000 people canceling their subscriptions to the paper.)
But none of these nods toward Trump are as obvious as Musk’s support for the former president, and the use of X to seed mis- and disinformation about the election, says Pardal. “[Musk] has drawn attention away from other tech companies and onto himself, when it comes to tech harms,” says Pardal. “Now we are all talking about what Elon says next, and moving away from the discussion about the decline in platform safety at a time of exponentially rising risks.”
31 notes
·
View notes