#gandhara
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

head of an adorant | c. 201-500 CE | gandhara (either afghanistan or pakistan)
in the art institute of chicago collection
630 notes
·
View notes
Text

Statue (stucco) of the seated Buddha, from a stupa at the now-destroyed site of Hadda, Afghanistan. The statue is in the Gandhara style, blending Hellenistic and South Asian influences. Artist unknown; ca. 300 AD/CE. Now in the Cleveland Museum of Art, Cleveland, OH, USA. Photo credit: Cleveland Museum of Art.
#art#art history#Buddha#Buddhism#Buddhist art#South Asia#South Asian art#Gandhara#statue#sculpture#stucco#Cleveland Museum of Art
70 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cosmetic dish
Charsadda (Gandhara), 2nd century - 5th century
Pale grey steatite
Cosmetic dish decorated with a figure riding a water monster based on Roman representations of a Nereid riding a sea monster, but perhaps influenced by Indian conceptiions of the Makara - a creature like a crocodile.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

Head of a Bodhisattva Gandhara, 2nd/3rd century
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
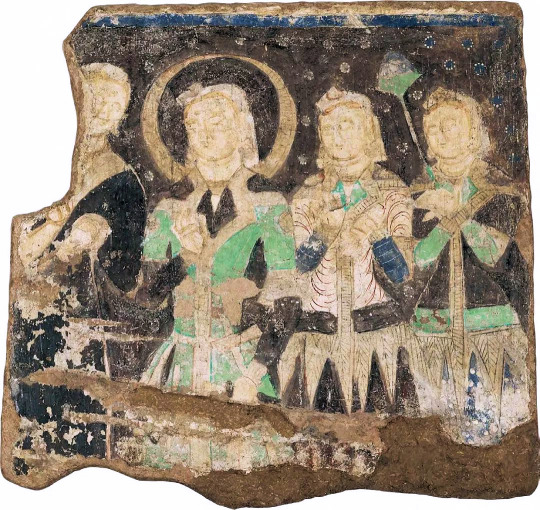
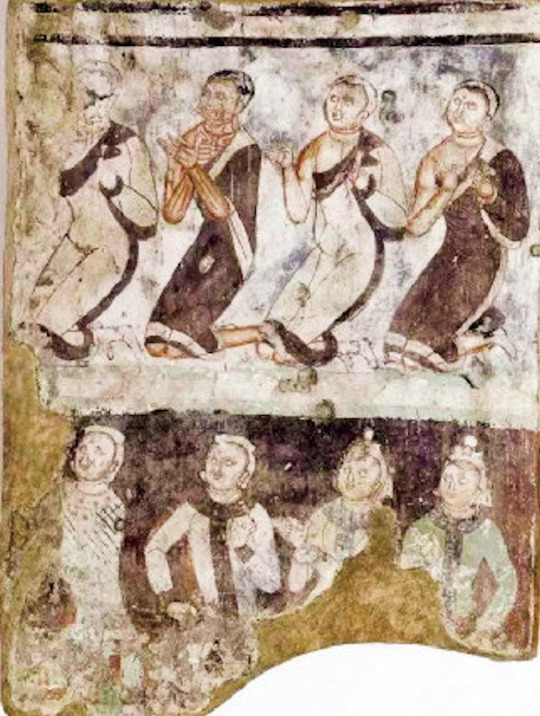










Murals from the Kizil Caves, painted between 300-600 AD. Painted in styles ranging from "Indo-Iranian" style derived from the Art of Gandhara and Sasanian art. Located in Xinjiang, China.
192 notes
·
View notes
Photo
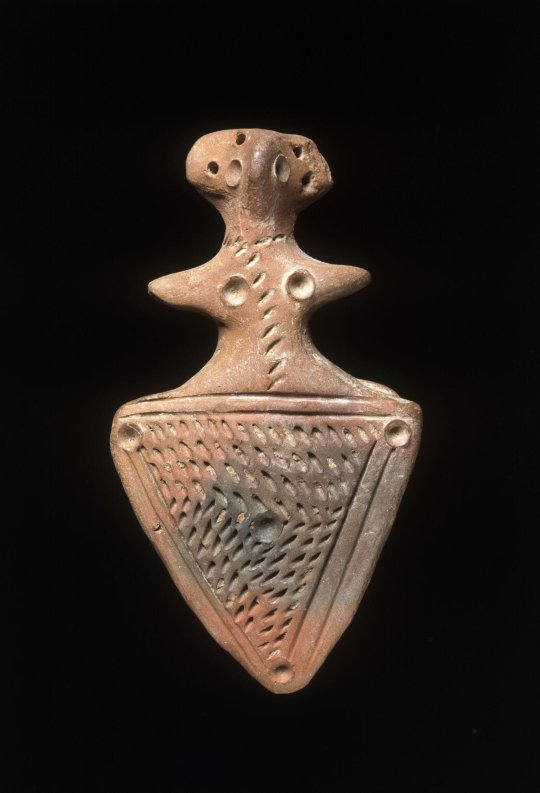
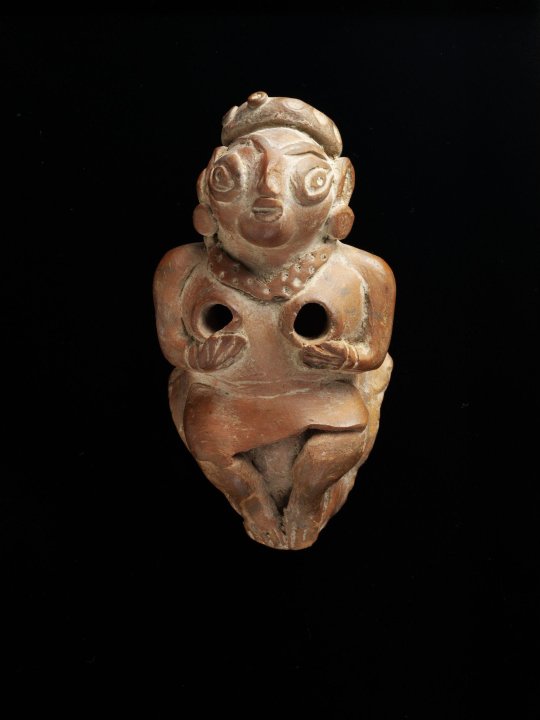
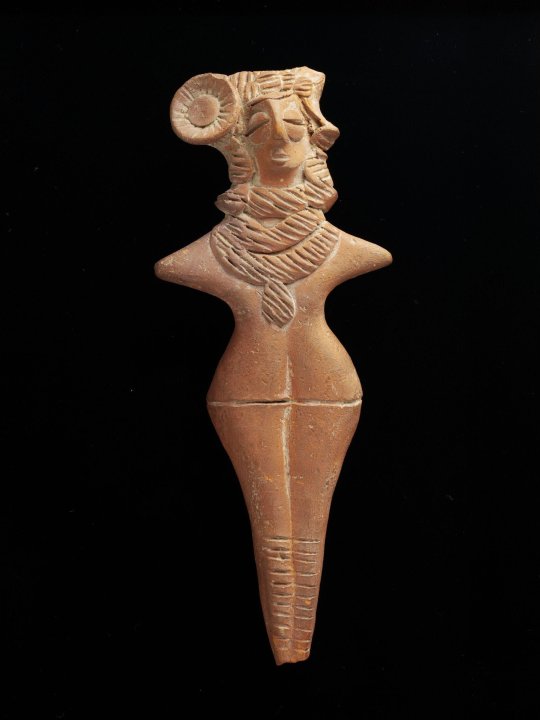




Terracotta Mother Goddess figurines, from the Gandhara culture, Pakistan, ca 1st-3rdC BC
(via V&A)
107 notes
·
View notes
Text






The Gandhara era Buddhist monastery of Takht-i-bhai in Mardan, Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.
#takht i bhai#takht-i-bhai#buddhism#gandhara#buddhist monastery#buddhist ruins#unesco hertitage site#mardan#kpk#khyber pakhtunkhwa#historical ruins#Pakistan#own post#personal pakistan pics
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
The penetration of China by Buddhism not only gave the Chinese a new religion but, of central importance to this narrative, it gave to the world an entirely new style of art which has come to be known as Serindian. This term is coined from the two words Seres (China) and India. Logically it should have been simply a fusion of Indian Buddhist art and the art of contemporary Han China. It almost certainly would have been had it not been for the great Himalayan massif which so effectively isolated China from all direct contact with India. But faced by this impenetrable barrier, the gospel of Buddhism together with its art came to China by a roundabout route, gradually absorbing other influences on its way. Its real point of departure was not India proper but the Buddhist kingdom of Gandhara, situated in the Peshawar valley region of what is now north-western Pakistan. Here another artistic marriage had already taken place. This was between Indian Buddhist art, imported by the ruling Kushans (descendants of the Yueh-chih) in the first century AD, and Greek art, introduced to the region four hundred years earlier by Alexander the Great. The most revolutionary product of this Graeco-Buddhist, or Gandharan, school was the depiction of Buddha in human form, for it was the first time that artists anywhere had allowed themselves to show him thus. As a being who had ceased to exist, theologically speaking, by achieving Nirvana and thus escaping the endless cycle of rebirth, he had always been portrayed before by means of a mystical symbol such as a single footprint, a wheel, a tree, a stupa or Sanskrit characters. But the Gandharan Buddha is shown by sculptors with straight, sharply chiselled nose and brow, classical lips and wavy hair–all Hellenistic influences. Another obvious Mediterranean introduction is the diaphanous, toga-like robe he wears in place of the expected loin cloth. But his eyes are heavy-lidded and protruding, the lobes of the ears elongated, and the oval-shaped face fleshy–all characteristics of Indian iconography. The stretched ear lobes symbolise Buddha’s casting away of the heavy, jewelled and worldly earrings that he had worn as a wealthy prince before his conversion to a life of self-denial and teaching
—Peter Hopkirk, Foreign Devils on the Silk Road: The Search for the Lost Cities and Treasures of Chinese Central Asia
#peter hopkirk#foreign devils on the silk road#history#china#india#gandhara#Buddhism#art#w#2024 reads#upl#reading through the silk road
28 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gandhara, terracotta head of a donor. Source: Sothebys.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text




Bouddha du Gandhara
#gandhara#bouddha#buddha#buddhism#bouddhisme#statuaire#sculpture#siddhartha gautama#siddhartha#sanjaangie
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
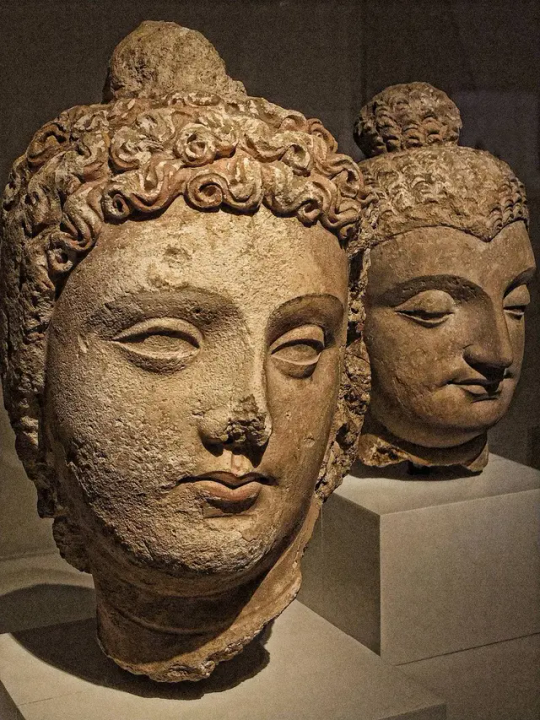

Bodhisattva Head, Gandhara
Mary Harrsch, Photographed at The Art Institute of Chicago
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

standing female | c. 1st century CE | gandhara (modern-day pakistan, perhaps charsadda or sirkap), kushan period
in the brooklyn museum collection
171 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sculpture (green schist) of the seated Buddha, 3rd or 4th century CE, in the Gandhara style characterized by a blend of Hellenistic and South Asian influences. This sculpture is believed to come from Barikot in present-day Pakistan. Now in the Matsuoka Museum of Art, Tokyo, Japan.
#art#art history#ancient art#Buddha#Buddhism#Buddhist art#Gandhara#South Asia#South Asian art#sculpture#schist#stonework#Matsuoka Museum of Art
80 notes
·
View notes
Text

A domestic object: spoon with a large scutiform bowl. The handle has a small, apparently male figure at the end.
Bannu, 2nd century - 3rd century AD
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
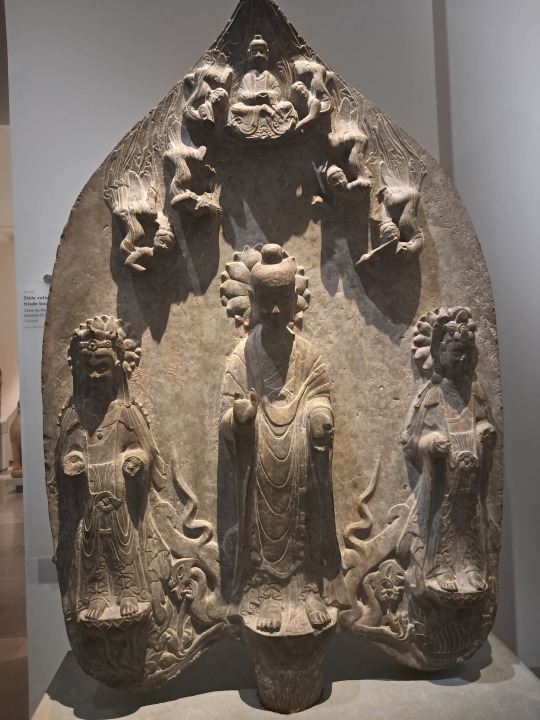






Paris, Café La Perle, Musée médiéval de Cluny, Musée asiatique Guimet.
#Café La Perle#Paris#France#Cluny#Guimet#Charles VII#Villon#Enluminures#Livre d'heures#Gandhara#Triade#Trinité
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
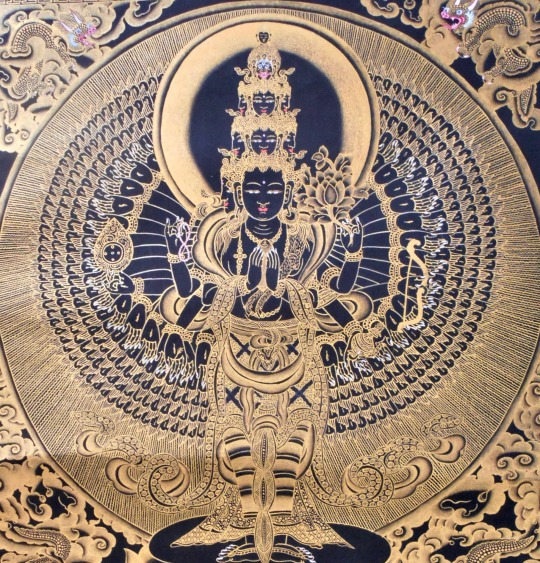




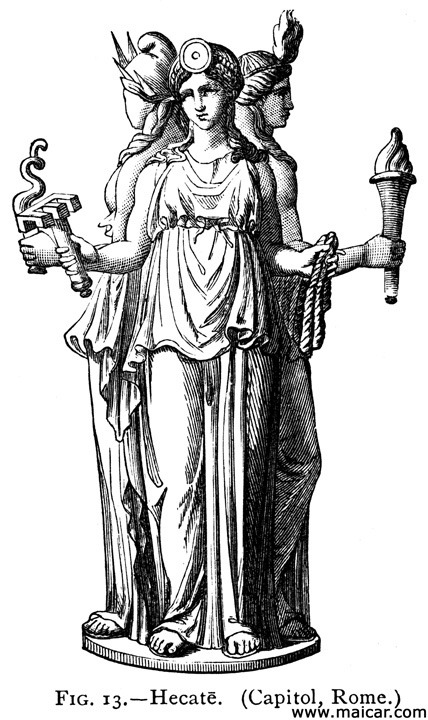

I’ve just been thinking a lot about cycles recently. As a devotee of Hekate and as a member of the Covenant of Hekate, I try my best every day to follow the 5 Virtues.
But today it just struck me how similar the 5 Virtues are to the 5 Mindfulness Trainings of Tibetan Zen Buddhist monk Thich Nhat Hanh.
I was first introduced to Thay when I was 16 and in the deepest depression of my life. His teachings on Zen Buddhism helped me so much, and I feel, led me to Hekate in my spiritual journey now in my 30’s.
The stropholos and the Wheel of Dharma just resonate to me in a complimentary way. And the Ancient Greeks did have a similar stance on reincarnation to Buddhism at least through a few mystery cults. I know that they are not perfectly parallel or syncretic, but I think the boddhisatva Avalokiteshvara and goddess Hekate are a good balance to each other.
We do know that there was cross-cultural blending through the representation of Greco-Buddhist art primarily in Gandhara (parts of modern day Pakistan and Afghanistan).
I was wondering if there are any others here who also follow an eclectic spiritual path?
13 notes
·
View notes