#extreme poverty
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
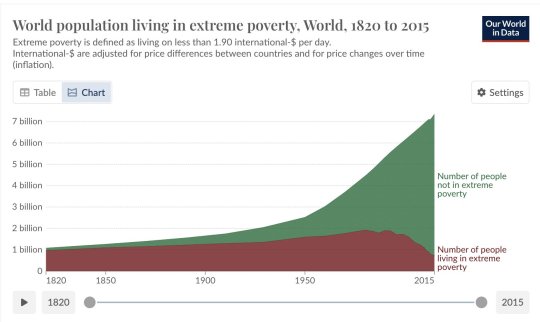
Extreme poverty is not a natural condition, but a sign of severe dislocation. Historical data on real wages since the 15th century indicates that under normal conditions, across different societies and eras, people are generally able to meet their subsistence needs except during periods of severe social displacement, such as famines, wars, and institutionalised dispossession, particularly under European colonialism. What is more, BNPL data shows that many countries have managed to keep extreme poverty very close to zero, even with low levels of GDP per capita, by using strategies such as public provisioning and price controls for basic essentials. In other words, extreme poverty can be prevented much more easily than most people assume. Indeed, it need not exist at all. The fact that it persists at such high levels today indicates that severe dislocation is institutionalised in the world economy – and that markets have failed to meet the basic needs of much of humanity. To address this problem, and to end extreme poverty – the first objective of the Sustainable Development Goals – will require public planning to prioritise the production of, and guarantee access to, the specific goods and services that people need to live decent lives.
22 February 2025
299 notes
·
View notes
Text
"If I wanted to convince you of the reality of human progress, of the fact that we as a species have advanced materially, morally, and politically over our time on this planet, I could quote you chapter and verse from a thick stack of development statistics.
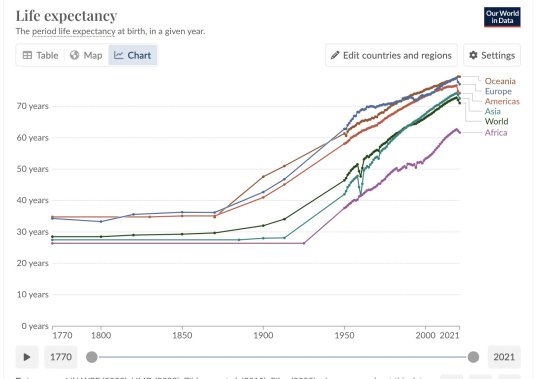
I could tell you that a little more than 200 years ago, nearly half of all children born died before they reached their 15th birthday, and that today it’s less than 5 percent globally. I could tell you that in pre-industrial times, starvation was a constant specter and life expectancy was in the 30s at best. [Note: This is average life expectancy, old people did still exist in olden times] I could tell you that at the dawn of the 19th century, barely more than one person in 10 was literate, while today that ratio has been nearly reversed. I could tell you that today is, on average, the best time to be alive in human history.
But that doesn’t mean you’ll be convinced.
In one 2017 Pew poll, a plurality of Americans — people who, perhaps more than anywhere else, are heirs to the benefits of centuries of material and political progress — reported that life was better 50 years ago than it is today. A 2015 survey of thousands of adults in nine rich countries found that 10 percent or fewer believed that the world was getting better. On the internet, a strange nostalgia persists for the supposedly better times before industrialization, when ordinary people supposedly worked less and life was allegedly simpler and healthier. (They didn’t and it wasn’t.)
Looking backward, we imagine a halcyon past that never was; looking forward, it seems to many as if, in the words of young environmental activist Greta Thunberg, “the world is getting more and more grim every day.”
So it’s boom times for doom times. But the apocalyptic mindset that has gripped so many of us not only understates how far we’ve come, but how much further we can still go. The real story of progress today is its remarkable expansion to the rest of the world in recent decades. In 1950, life expectancy in Africa was just 40; today, it’s past 62. Meanwhile more than 1 billion people have moved out of extreme poverty since 1990 alone.
But there’s more to do — much more. That hundreds of millions of people still go without the benefit of electricity or live in states still racked by violence and injustice isn’t so much an indictment of progress as it is an indication that there is still more low-hanging fruit to harvest.
The world hasn’t become a better place for nearly everyone who lives on it because we wished it so. The astounding economic and technological progress made over the past 200 years has been the result of deliberate policies, a drive to invent and innovate, one advance building upon another. And as our material condition improved, so, for the most part, did our morals and politics — not as a side effect, but as a direct consequence. It’s simply easier to be good when the world isn’t zero-sum.
Which isn’t to say that the record of progress is one of unending wins. For every problem it solved — the lack of usable energy in the pre-fossil fuel days, for instance — it often created a new one, like climate change. But just as a primary way climate change is being addressed is through innovation that has drastically reduced the price of clean energy, so progress tends to be the best route to solving the problems that progress itself can create.
The biggest danger we face today, if we care about actually making the future a more perfect place, isn’t that industrial civilization will choke on its own exhaust or that democracy will crumble or that AI will rise up and overthrow us all. It’s that we will cease believing in the one force that raised humanity out of tens of thousands of years of general misery: the very idea of progress.
Changing Humanity's "Normal" Forever
Progress may be about where we’re going, but it’s impossible to understand without returning to where we’ve been. So let’s take a trip back to the foreign country that was the early years of the 19th century.
In 1820, according to data compiled by the historian Michail Moatsos, about three-quarters of the world’s population earned so little that they could not afford even a tiny living space, some heat and, hopefully, enough food to stave off malnutrition.
It was a state that we would now call “extreme poverty,” except that for most people back then, it wasn’t extreme — it was simply life.
What matters here for the story of progress isn’t the fact that the overwhelming majority of humankind lived in destitution. It’s that this was the norm, and had been the norm since essentially… forever. Poverty, illiteracy, premature death — these weren’t problems, as we would come to define them in our time. They were simply the background reality of being human, as largely unchangeable as birth and death itself...
Between 10,000 BCE and 1700, the average global population growth rate was just 0.04 percent per year. And that wasn’t because human beings weren’t having babies. They were simply dying, in great numbers: at birth, giving birth, in childhood from now-preventable diseases, and in young adulthood from now-preventable wars and violence.
It was only with the progress of industrialization that we broke out of [this long cycle], producing enough food to feed the mounting billions, enough scientific breakthroughs to conquer old killers like smallpox and the measles, and enough political advances to dwindle violent death.
Between 1800 and today, our numbers grew from around 1 billion to 8 billion. And that 8 billion aren’t just healthier, richer, and better educated. On average, they can expect to live more than twice as long. The writer Steven Johnson has called this achievement humanity’s “extra life” — but that extra isn’t just the decades that have been added to our lifespans. It’s the extra people that have been added to our numbers. I’m probably one of them, and you probably are too...
The progress we’ve earned has hardly been uninterrupted or perfectly distributed... [But] once we could prove in practice that the lot of humanity didn’t have to be hand-to-mouth existence, we could see that progress could continue to expand.
Current Progress "Flows Overwhelmingly" to the Developing World
The long twentieth century came late to the Global South, but it did get there. Between 1960 and today, India and China, together home to nearly one in every three people alive today, have seen life expectancy rise from 45 to 70 and 33 to 78, respectively. Per-capita GDP over those years rose some 2,600 percent for India and an astounding 13,400 percent for China, with the latter lifting an estimated 800 million people out of extreme poverty.
In the poorer countries of sub-Saharan Africa, progress has been slower and later, but shouldn’t be underestimated. When we see the drastic decline in child mortality — which has fallen since 1990 from 18.1 percent of all children in that region to 7.4 percent in 2021 — or the more than 20 million measles deaths that have been prevented since 2000 in Africa alone, this is progress continuing to happen now, with the benefits overwhelmingly flowing to the poorest among us.
Vanishing Autocracies
In 1800, according to Our World in Data, zero — none, nada, zip — people lived in what we would now classify as a liberal democracy. Just 22 million people — about 2 percent of the global population — lived in what the site classifies as “electoral autocracies,” meaning that what democracy they had was limited, and limited to a subset of the population.
One hundred years later, things weren’t much better — there were actual liberal democracies, but fewer than 1 percent of the world’s population lived in them...
Today just 2 billion people live in countries that are classified as closed autocracies — relatively few legal rights, no real electoral democracy — and most of them are in China...
Expanding Human Rights
All you have to do is roll the clock back a few decades to see the way that rights, on the whole, have been extended wider and wider: to LGBTQ citizens, to people of color, to women. The fundamental fact is that as much as the technological and economic world of 2023 would be unrecognizable to people in 1800, the same is true of the political world.
Nor can you disentangle that political progress from material progress. Take the gradual but definitive emancipation of women. That has been a hard-fought, ongoing battle, chiefly waged by women who saw the inherent unfairness of a male-dominated society.
But it was aided by the invention of labor-saving technologies in the home like washing machines and refrigerators that primarily gave time back to women and made it easier for them to move into the workforce.
These are all examples of the expansion of the circle of moral concern — the enlargement of who and what is considered worthy of respect and rights, from the foundation of the family or tribe all the way to humans around the world (and increasingly non-human animals as well). And it can’t be separated from the hard fact of material progress.
Leaving a Zero-Sum World Behind
The pre-industrial world was a zero-sum one... In a zero-sum world, you advance only at the expense of others, by taking from a set stock, not by adding, which is why wars of conquest between great powers were so common hundreds of years ago, or why homicide between neighbors was so much more frequent in the pre-industrial era.
We have obviously not eradicated violence, including by the state itself. But a society that can produce more of what it needs and wants is one that will be less inclined to fight over what it has, either with its neighbors or with itself. It’s not that the humans of 2023 are necessarily better, more moral, than their ancestors 200 or more years ago. It’s that war and violence cease to make economic sense...
Doomerism, at its heart, may be that exhaustion made manifest.
But just as we need continued advances in clean tech or biosecurity to protect ourselves from some of the existential threats we’ve inadvertently created, so do we need continued progress to address the problems that have been with us always: of want, of freedom, even of mortality. Nothing can dispel the terminal exhaustion that seems endemic in 2023 better than the idea that there is so much more left to do to lift millions out of poverty and misery while protecting the future — which is possible, thanks to the path of the progress we’ve made.
And we’ll know we’re successful if our descendants can one day look back on the present with the same mix of sympathy and relief with which we should look back on our past. How, they’ll wonder, did they ever live like that?"
-via Vox, 3/20/23
Note: I would seriously recommend reading the whole article--because as long as this post is, this is only about half of it! The article contains a lot more information about the hows and whys of human progress, and it also definitely made me cry the first time I read it.
#progress#human rights#humanity#science and technology#premature death#cw infant death#child morality#womens rights#lgbtq rights#bipoc rights#doomerism#climate change#food insecurity#extreme poverty#global south#developing countries#optimism#climate optimism#good news#hope
241 notes
·
View notes
Text

Steve Brodner :: To-Day In America.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dylan Sullivan
Adjunct Fellow in the School of Social Sciences, Macquarie University
Jason Hickel
Professor at the Institute for Environmental Science and Technology (ICTA-UAB) and Fellow of the Royal Society of Arts

Highlights
The common notion that extreme poverty is the “natural” condition of humanity and only declined with the rise of capitalism rests on income data that do not adequately capture access to essential goods.
Data on real wages suggests that, historically, extreme poverty was uncommon and arose primarily during periods of severe social and economic dislocation, particularly under colonialism.
The rise of capitalism from the long 16th century onward is associated with a decline in wages to below subsistence, a deterioration in human stature, and an upturn in premature mortality.
In parts of South Asia, sub-Saharan Africa and Latin America, wages and/or height have still not recovered.
Where progress has occurred, significant improvements in human welfare began only around the 20th century. These gains coincide with the rise of anti-colonial and socialist political movements.
Sullivan, D., & Hickel, J. (2023). Capitalism and extreme poverty: A global analysis of real wages, human height, and mortality since the long 16th century. World development, 161, 106026.
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Now that situation has gotten so desperate that I have no running water, no internet, and the power will be cut off in two days, I'm selling custom vibes and tarot readings! Here's a link to my Ko-fi with more information. If interested, contact me through DMs either here or there.
#Tarot#Vibes#Extreme poverty#Disabled#Disability#Unpaid utility bills#Financial desperation#I'm out here trying#But I'm about to die in this heat
0 notes
Text

This is how free market capitalism looks like.
0 notes
Text
Stunning Planter with Etched Floral Designs
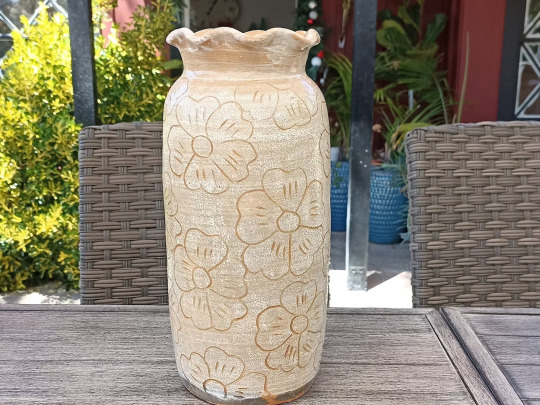

Introducing our stunning White Etched Floral Planter, a gorgeous testament to the rich heritage of pottery making in Santa Maria Atzoma, nestled near the vibrant city of Oaxaca, Mexico.
Handcrafted with love and expertise by skilled artisans, this planter embodies the timeless beauty and artistic traditions of the region of soutern Mexico. Each intricate etching conveys a story of family craftsmanship passed down through generations, resulting in a one-of-a-kind piece that will enhance your home decor or personal living space.
Whether displayed indoors or outdoors, this stunning white planter is not only a worthy vessel for your beloved plants but also a captivating work of art that transports you to the enchanting landscapes of charming little towns near Oaxaca.
Embrace the spirit of handcrafted authenticity and bring a touch of Mexican artistry into your home with this exquisite handmade treasure.
Use as an Indoor Planter, Outdoor Flower Pot, or Dried Fower Vase Weight: approximately 4 lb 1 oz Dimensions: 13" tall x 3" opening, 5.5" body diameter
To learn more about the product, click here.
#Stunning Planter with Etched Floral Designs#Handmade Mexican Pottery from Santa Maria Atzompa#Mexico#Classic Design#extreme poverty
0 notes
Text
You know, it's funny how Sylus is very casual and nonchalant about people robbing him, but he gets highly offended if you think he's poor (spend only $1 million).
#love and deepspace#love and deepspace sylus#lnds ramblings#oh to be a stupidly rich person with skewed priorities#wait#unless he grew up in extreme poverty and was ridiculed and demeaned for it#and developed some sort of complex about it#which would be kind of weird since he has also mentioned how other people's perception of you shouldn't matter or impact your self-esteem#✨️unless✨️#this was something he had personally learned to overcome#am i just brainrotting a little too hard#mayhaps#i've been in a weird mindset the last couple of days#����
137 notes
·
View notes
Text
In international development circles, most people are familiar with the World Bank’s data showing that extreme poverty has declined dramatically over the past several decades, from 43 per cent of the world’s population in 1981 to less than 10 per cent today. This narrative is based on the World Bank’s method of calculating the share of people who live on less than $1.90 per day (in 2011 “PPP” terms). But a growing body of literature argues that the World Bank’s PPP-based method suffers from a major empirical limitation, in that it does not account for the cost of meeting basic needs in any given context (see here, here and here). Having more than $1.90 PPP does not guarantee that a person can afford the specific goods and services that are necessary for survival. In recent years, scholars have developed a more accurate method for measuring extreme poverty, by comparing people’s incomes to the prices of essential goods in each country (specifically food, shelter, clothing and fuel). This approach is known as the “basic needs poverty line” (BNPL), and it more closely approximates what the original concept of “extreme poverty” was intended to measure.
[...]
Extreme poverty is not a natural condition, but a sign of severe dislocation. Historical data on real wages since the 15th century indicates that under normal conditions, across different societies and eras, people are generally able to meet their subsistence needs except during periods of severe social displacement, such as famines, wars, and institutionalised dispossession, particularly under European colonialism. What is more, BNPL data shows that many countries have managed to keep extreme poverty very close to zero, even with low levels of GDP per capita, by using strategies such as public provisioning and price controls for basic essentials. In other words, extreme poverty can be prevented much more easily than most people assume. Indeed, it need not exist at all. The fact that it persists at such high levels today indicates that severe dislocation is institutionalised in the world economy – and that markets have failed to meet the basic needs of much of humanity. To address this problem, and to end extreme poverty – the first objective of the Sustainable Development Goals – will require public planning to prioritise the production of, and guarantee access to, the specific goods and services that people need to live decent lives.
284 notes
·
View notes
Note
Don’t worry about replying to this in any capacity. Just wanted to say that I read your most recent post and it was extremely helpful and informative for me. I was just talking to my dad earlier about really struggling to understand how anyone could support Trump when he is just a complete bumbling fool of a man at best and a piece of shit bigot and sexist at worst. (Not to say that Harris is some beacon in the darkness, not a fan of her either.) But the perspective you offered was really enlightening so thank you for it. and I hope you are doing well enough, all things considered, and that regardless of what happens in the coming days that things get better for you and your community.
Thank you, that's very kind. I'm very glad it was helpful, I was worried I was coming across the wrong way or didn't word it very well or could be misinterpreted.
If it helps, I had some more thoughts I think would expand upon that, specifically for women — since I see a lot of posts essentially asking how women can possibly vote for the guy, and I think I can explain that too, as I've been thinking and talking a lot about that with women who I know intend to do so.
1) I think for the upper class, they tend to focus more on social issues, because economic issues don't affect them as strongly.
But for some of these people, especially moms, the increased cost of living is literally a matter of "how am I going to feed my children, how am I going to pay electric AND water," etc. So it becomes a priority, especially as many families have lots of kids, and some are single moms. They don't really think as much about social issues, whereas when I went to college, most of the kids cared only about social issues. The more financially secure someone is, the less preoccupied they are with economy.
But for a mom, the safety of and provision for their kids is paramount above all else, so economy and crime will take priority.
But since we only have 2 major parties, people often assume that whichever you vote for, you must agree with ALL of the party's official stances, which is often not the case. That's part of why our bipartisan system is so divisive and breeds hostility, because it creates an "us vs them" mentality.
2) women in the area I talked about don't really even think about abortion/reproductive rights. They're not militantly anti-choice (like some of the more suburban moms of kids I went to school with), it's more that no one ever really thinks about it at all. Many of them have kids very young and lots of them, it's just normal. They also don't have careers to focus on in the way higher-class women do, and many have no chance of ever going to college, so there's less reason to hold off on it.
People do what's normal per their class/local culture — so here, if a girl gets unexpectedly pregnant (which is... not uncommon), they don't freak out or think about how it will affect their future, how they'll afford it etc, they usually just... shrug, drop out of high school, marry the guy, have the kid.
When we were 16, one of my good friends got pregnant, and she too did exactly that. She was unironically overjoyed to find out too, rather than panicked or dismayed. Like, when she took the pregnancy test, I was there with her, sitting on the tile floor of the church bathroom at 9 pm with the test we scraped cash together to buy from the gas station-pharmacy hybrid shop down the road, and she, as a 16 year old high school junior, was actively hoping, fingers crossed and smiling and everything, that it would be positive. She's now 24 and is about to have baby #5.
And part of the reason she was fine with it was... because her mom had her at 15. It's a very cyclic thing. The possibility of abortion would not occur to them unless someone else brought it up.
3) Moreover, when women vote, they focus on what affects them specifically as a woman — and prioritize what's most "real" to us as an individual woman, the hypotheticals one can most realistically see happening to them. But what that most realistic thing is, varies a lot from woman to woman.
For a woman living in, say, Maine or northeast California or even a safer rural place like Idaho, I can see how abortion is probably the most "real" thing to them, that they can see themselves being in a position to affect them.
Whereas for me, having experienced harassment and aggression, reading about these statistics and headlines, violence is something I am much more afraid of happening to me. I'm very careful to avoid an area where I was harassed before.
But for someone in a low-crime place, that isn't something that's going to be a priority.
I personally now realize that a lot of the misunderstanding and clashing is a matter of the fact that women in many blue areas simply don't think about this, because they've never had a reason to, and that's perfectly understandable.
But a lot of women in areas like my home do not realize that. Many women at home strongly believe that "them uppity rich white women out in California or wherever the hell" (quoth my 90-something year old neighbor), are aware of, but simply don't care about, the consequences women here/poor women face. I used to think so too, when I was younger, because that's what I was told.
As a result, they view their blue vote as a very "let them eat cake" heartless-rich-person sort of thing, as selfish and/or classism, in the same way that women in blue areas likely view their red votes as female-class betrayal, religious brainwashing, believe their husbands must be controlling them, etc.
Now, with greater life experience, I not only understand that it isn't like that at all on either side, but I can also see why many blue-area women dismiss our experiences as "not really happening" or "right-wing propaganda," simply due to the fact that it's very difficult for them to fathom it, because it's so different from the reality they live in, it feels like it can't be real.
4) it *is* true that these women are often demonized and gaslit for talking about the rapes, job loss etc, so that has shifted even more moderate women very rightwards over the last few years, because they feel silenced/censored.
Donald is a sort of savior figure — he acknowledges the issue they otherwise feel censored on, and moreover, has essentially promised to take away the men that hurt them, their daughters, sisters etc. They want to feel safe again, they want their husbands to get their jobs back, feel like they have a secure future, etc, and his platform is literally "make America safe again, make America rich again, make America great again."
That line you may have seen all over the internet a few days ago, where Donald said something along the lines of "I'm going to protect the women if they like it or not"? And you know how it earned disgust from the mainstream population of women?
That line was received extremely positively by women at home. I've already seen them sharing it around with my mom/aunts/grandma on facebook, in a positive light, ecstatic. It makes them feel seen and heard in a culture that otherwise puts a hand over their mouth, and they cling to those words in hope of a better future.
Tldr: it's women who are vulnerable and afraid and desperate, going for the only option that has promised to address their needs. Much conflict comes from the limited human ability to grasp things outside of ourselves, our tendency for solipsism — an unfortunate part of the human condition that has plagued our species from the dawn of time.
#but for real#teenage pregnancy among the rural poor is an extremely brutal cycle#it shuts down a lot of opportunities they might otherwise have and perpetuates poverty#and then the man always wants more and more kids and they always end up dependent on the guy#which sometimes leads to bad things#but its so normalized that no one really has a desire to break the cycle#i literally know 3 girls who didnt complete high school#:/
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thinking about how Grant (and the other kids yeah but specifically Grant) had only known Henry (yeah the other dads too but I'm thinking about Henry) for less than a day before getting dropped into the forgotten realms and then at least a month later when he sees him again he has to see totally different sides of him and his dad. How jarring must that be? You meet a guy and his insane sons and your first impression of him is that he's some tree hugger granola dad who's a total pushover and then the next time you see him it's in a death game where he volunteers to kill a man by shotgun blast to the face and then leaves the dead body of the guy outside to send a message to the other players. Imagine meeting this guy whose whole gig is being vegan and a free range granola parent and the next time you see him he's breaking into another explosive burst of anger and yelling at the arena that he will fight and/or kill anyone who comes to hurt you or his friends. Imagine knowing your dad all your life and seeing him one day and then having to know that your dad has killed someone. And then you kill a chimera and you're changed forever. And then you grow up and marry a man named Marco.
#the whole Wilson family is immune to just living in peace#they're all going through life changing trauma#and then moving on and becoming a librarian or something#daryll went through extreme poverty as a child and then just became a stay at home dad#his parents held it together well but that doesnt mean he didnt go through it#grant went through a lot of life changing trauma as a child and became a librarian#he was a sniper too but he was a librarian#lincoln went through a whole like 50 years of life got married had kids and then just had to go on with his life#then he became a soccer coach#the jury's still out on Jerry#dndads#dungeons and daddies#daryll wilson#grant wilson#lincoln li wilson#henry oak
162 notes
·
View notes
Text
Where are my fat Bingmei truthers. Where are my double chin Bingmei truthers. You have to be somewhere.
#svsss#scum villian self saving system#luo bingmei#luo binghe#white lotus! bingy would have some baby fat but still be underweight from extreme poverty#straight out the abyss he’s looking a little gaunt and bingge would fill out with muscle and false bravado#after the plot is done Bingmei starts actually eating enough regularly and even getting to indulge in fine foods#he doesn’t have to worry about having food and he’s not too stressed/depressed to cook and eat regularly#he can afford all the nice fatty foods he wants and knows he’ll never go hungry again#he’ll never get cold to easily or be dizzy when he moves or pull out clumps of hair again#not me crying about lbh having food security and his support needs met 😭#god growing up food insecure got me fucked up about food as a metaphor for healing
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Guess who passed their SNAP redetermination/mid-point report and got approved to continue receiving a whopping $292 in government lunch money for groceries every month 👍
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is the Extreme Poverty Definition?
The extreme poverty definition according to the United Nations is anyone “struggling to fulfill the most basic needs like health, education, and access to water and sanitation,” to name a few. The majority of people living on less than $1.90 a day live in sub-Saharan Africa.”[1] Approximately 10 percent of the world’s population live below this devastating income level, or about 700 million people.[2]
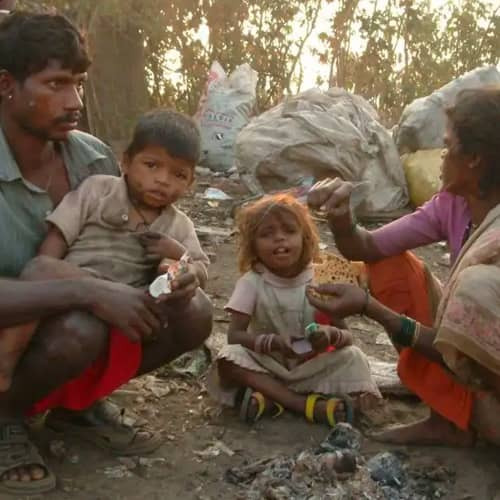

In the UN’s publication Why It Matters, they answer why we should care of these definitions and numbers:
“…because as human beings, our wellbeing is linked to each other. Growing inequality is detrimental to economic growth and undermines social cohesion, increasing political and social tensions and, in some circumstances, driving instability and conflicts.” They also say, “The private sector has a major role to play in determining whether the growth it creates is inclusive and contributes to poverty reduction. It can promote economic opportunities for the poor.”[3]
Organizations like GFA World step into these places with proven solutions that address fundamental and underlying issues that keep people in poverty. One of the best ways that GFA does this is through our Christmas Gift Catalog, specifically any item that provides a way for an individual or family to create income or start their own business.
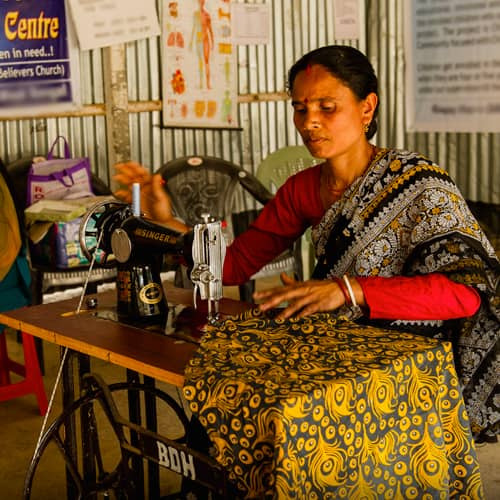

The catalog features items like sewing machines, chickens, pigs, cows and goats. These items are the start of earning money that can close the gap in what they currently bring in with what is needed at a very basic level.
If a woman can have her own sewing machine, not only can she improve her skills, but she can join a business or start her own in areas where textiles are an option for her. This kind of economic independence is rare and also freeing in places where income opportunities are few and far between, especially in rural areas.
Chickens can be the start of a small flock in order to produce eggs that can be sold in their village. Not only is this a business starter for someone, but it is also a source of nutrition for the villagers.
Click here, to read more about this article.
Click here, to read more blogs in Gospel for Asia.Net
#Abject Poverty#About Gospel for Asia#Absolute Poverty#Absolute Poverty Definition#Child Poverty in India#Child Poverty in the World#Cycle of Poverty#Define Absolute Poverty#Definition Absolute Poverty#Definition of Destitute#Definition of Extreme Poverty#Extreme Poverty#Extreme Poverty Definition#Facts About Poverty#Generational Poverty#Generational Poverty Definition#Gospel for Asia#How to Reduce Poverty#Poverty#Poverty Alleviation#Poverty Alleviation Program#Poverty and Hunger#Poverty Cycle#Poverty Facts#Poverty Issues#Poverty Reduction#Poverty Worldwide#Systemic Poverty#The Cycle of Poverty#The Poverty Cycle
0 notes
Text
Thank you all for your help!!!
I successfully advanced to the next round of the baking contest I’m participating in! Thank you for your support! Currently, I am in 6th place. I would really appreciate your help in staying in the competition. Every vote counts toward my goal of winning $20,000, which would significantly help me with my living expenses.
It is free to vote every day. Thank you for your support.
I am currently working on what to do with my Ko-fi and my Patreon. So that I can continue to give you all these lovely posts.
12 notes
·
View notes