#evolution of india
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Evolution of India's Manufacturing Industry: Investment Insights

India's manufacturing industry has undergone a remarkable transformation in recent years, driven by a combination of factors such as government initiatives, technological advancements, and shifting global dynamics. As one of the world's fastest-growing economies, India presents attractive opportunities for investors looking to capitalize on the growth and evolution of its manufacturing sector. In this blog, we'll explore the evolution of India's manufacturing industry and provide investment insights for those interested in investing in India's manufacturing sector.
1. Historical Overview of India's Manufacturing Industry:
India has a rich history of manufacturing dating back thousands of years, with traditional industries such as textiles, handicrafts, and metallurgy thriving in ancient times. However, the modern industrialization of India began in the late 19th century with the establishment of textile mills, followed by the development of steel, automotive, and chemical industries during the post-independence era. Over the decades, India's manufacturing landscape has evolved to encompass a diverse range of sectors, including automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and engineering.
Here's a closer look at the historical evolution of India's manufacturing sector:
1. Ancient and Medieval Period:
India has a long tradition of craftsmanship and manufacturing excellence, with ancient civilizations producing a wide range of goods such as textiles, pottery, metalwork, and handicrafts. The Indus Valley Civilization, dating back to around 3300 BCE, had advanced urban centers with sophisticated manufacturing techniques and trade networks. During the medieval period, India became renowned for its textile industry, producing high-quality fabrics such as muslin, silk, and cotton that were highly sought after in international markets.
2. Colonial Era:
The colonial period saw significant changes in India's manufacturing landscape, with the arrival of European traders and the establishment of colonial rule by the British East India Company. The British colonial administration imposed policies that favored the export of raw materials from India and the import of finished goods from Britain, leading to the decline of indigenous industries and the stagnation of manufacturing activities. The British also introduced modern industries such as textiles, steel, and railways, albeit primarily for the benefit of colonial interests.
3. Post-Independence Industrialization:
India's independence in 1947 marked a new phase in the country's industrial development, with a focus on building a self-reliant economy through industrialization. The government implemented policies such as import substitution, industrial licensing, and state-led planning to promote domestic industries and reduce dependence on imports. This period witnessed the establishment of public sector enterprises, heavy industries, and infrastructure projects aimed at laying the foundation for industrial growth and economic development.
4. Liberalization and Economic Reforms:
In the early 1990s, India embarked on a path of economic liberalization and reforms aimed at opening up the economy, attracting foreign investment, and integrating with the global economy. The liberalization measures included deregulation, privatization, and trade liberalization, which led to increased competition, efficiency, and innovation in the manufacturing sector. Foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows into India's manufacturing industry surged, leading to the entry of multinational corporations and the establishment of joint ventures with Indian companies.
5. Modern Era:
Today, India's manufacturing industry has evolved into a diverse and dynamic sector encompassing a wide range of industries such as automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, textiles, chemicals, and engineering. The country has emerged as a global manufacturing hub, attracting investment from multinational companies and fostering the growth of domestic enterprises. India's manufacturing capabilities have expanded significantly, supported by advancements in technology, infrastructure development, and skilled workforce.
6. Government Initiatives and Policies:
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives and policies to promote the growth and competitiveness of the manufacturing sector. Programs such as Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes aim to boost domestic manufacturing, attract investment, and enhance India's manufacturing capabilities. These initiatives provide incentives, subsidies, and regulatory support to encourage investment in key sectors and foster innovation and entrepreneurship.
2. Government Initiatives and Policy Reforms:
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives and policy reforms to promote the growth and competitiveness of the manufacturing sector. Programs such as Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes aim to attract investment, boost domestic manufacturing, and enhance India's manufacturing capabilities. These initiatives provide incentives, subsidies, and regulatory support to encourage investment in key sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and automobiles.
Here's an in-depth explanation of how these initiatives and reforms have impacted the sector:
1. Make in India Campaign:
Launched in 2014, the Make in India campaign aims to promote India as a global manufacturing hub and attract investment in key sectors such as automotive, electronics, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. The campaign focuses on improving the ease of doing business, simplifying regulatory processes, and creating a conducive environment for domestic and foreign investors. By showcasing India's strengths in manufacturing capabilities, skilled workforce, and market potential, the Make in India initiative aims to boost domestic production, create jobs, and propel economic growth.
2. Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan:
The Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, or Self-Reliant India Mission, was launched in 2020 with the objective of building a self-reliant and resilient economy. The initiative emphasizes the need for reducing dependency on imports, promoting domestic manufacturing, and enhancing India's capabilities in critical sectors. Through measures such as import substitution, localization of supply chains, and support for indigenous innovation, the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan seeks to strengthen India's manufacturing ecosystem and reduce vulnerabilities to external disruptions.
3. Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes:
The government has introduced several Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes to incentivize domestic manufacturing and promote investment in strategic sectors. These schemes offer financial incentives, subsidies, and tax breaks to companies that manufacture specified products domestically and meet predetermined production targets. The PLI schemes cover sectors such as electronics manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, textiles, automobiles, and renewable energy, aiming to boost domestic production, enhance competitiveness, and create employment opportunities.
4. Goods and Services Tax (GST):
The implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2017 marked a significant milestone in India's tax reform efforts and had a transformative impact on the manufacturing sector. GST replaced a complex system of multiple indirect taxes with a unified tax regime, streamlining tax compliance, reducing logistics costs, and improving the ease of doing business. The simplified tax structure and seamless interstate movement of goods under GST have benefited manufacturers by eliminating tax cascading, enhancing supply chain efficiency, and promoting business competitiveness.
5. Ease of Doing Business Reforms:
India has undertaken several reforms to improve the ease of doing business and facilitate investment in the manufacturing sector. These reforms include streamlining regulatory processes, digitizing government services, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, and strengthening investor protection measures. Initiatives such as online business registration, single-window clearances, and time-bound approvals have simplified administrative procedures and enhanced transparency, making it easier for companies to set up and operate manufacturing facilities in India.
6. Infrastructure Development Initiatives:
The government has prioritized infrastructure development as a key enabler for the manufacturing sector's growth and competitiveness. Infrastructure projects such as industrial corridors, dedicated freight corridors, and port modernization initiatives aim to enhance connectivity, logistics efficiency, and access to markets. Investments in infrastructure development create a conducive environment for manufacturing investments by reducing transportation costs, improving supply chain reliability, and enhancing access to raw materials and markets.
3. Shift towards High-Tech and Advanced Manufacturing:
India's manufacturing landscape is undergoing a transformation towards high-tech and advanced manufacturing, driven by technological advancements and global market trends. The adoption of digital technologies such as automation, robotics, artificial intelligence, and 3D printing is revolutionizing manufacturing processes, increasing productivity, and improving quality and efficiency. Startups and established companies alike are investing in advanced manufacturing technologies to stay competitive and meet evolving customer demands.
4. Focus on Sustainability and Green Manufacturing:
There is a growing emphasis on sustainability and green manufacturing practices in India's manufacturing industry, driven by environmental concerns and regulatory mandates. Companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly processes, renewable energy sources, and resource-efficient technologies to minimize their environmental footprint and comply with sustainability standards. Investors can capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable manufacturing solutions by investing in companies that prioritize environmental stewardship and corporate social responsibility.
5. Integration of Industry 4.0 Technologies:
Industry 4.0, characterized by the convergence of digital technologies and physical systems, is reshaping India's manufacturing landscape. IoT (Internet of Things), big data analytics, cloud computing, and cyber-physical systems are enabling smart factories, predictive maintenance, and connected supply chains, transforming traditional manufacturing operations. Investors can identify opportunities in startups and companies that are driving the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies and digitizing their manufacturing processes for greater efficiency and competitiveness.
6. Global Supply Chain Realignment and Reshoring Trends:
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated global supply chain realignment and reshoring trends, prompting companies to reassess their dependence on overseas suppliers and prioritize domestic manufacturing capabilities. India, with its large consumer market, skilled workforce, and favorable business environment, is emerging as an attractive destination for companies looking to diversify their supply chains and establish local manufacturing hubs. Investors can capitalize on this trend by investing in sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and automotive that are witnessing increased localization and reshoring activities.
7. Challenges and Opportunities for Investors:
While India's manufacturing sector presents significant opportunities for investors, it also faces several challenges such as infrastructure bottlenecks, regulatory complexities, and skill shortages. However, these challenges can be overcome with strategic investments, technology adoption, and collaboration between the public and private sectors. Investors with a long-term outlook and a risk-tolerant approach can leverage India's manufacturing growth story to generate attractive returns and contribute to the country's economic development.
India's manufacturing industry is undergoing a period of rapid evolution, driven by government initiatives, technological advancements, and shifting global dynamics. Investors looking to capitalize on the growth and transformation of India's manufacturing sector have a wide range of opportunities across sectors such as high-tech manufacturing, sustainable practices, Industry 4.0 technologies, and global supply chain realignment. By identifying promising investment avenues and partnering with innovative companies, investors can play a key role in shaping the future of India's manufacturing landscape while generating attractive returns on their investments.
This post was originally published on: Foxnangel
#evolution of india#indian manufacturing#india manufacturing industry#manufacturing#manufacturing sector#foreign direct investment#FDi In India#atmanirbhar bharat abhiyan#invest in india#foxnangel
0 notes
Text

Meet Vasuki indicus, among the longest snakes that ever lived
Scientists estimate length of the reptile from vertebral remains
Paleontologists have unearthed fossil remains of an ancient giant snake species — almost the length of a large tour bus — dating back to 47 million years old1, and comparable to the longest snakes that have ever lived on earth. They found 27 well preserved fossil vertebrae of Vasuki indicus from a lignite mine in India's Gujarat state, and used them to model the estimated actual length of the snake to somewhere between 10.9 to 15.2 metres. The longest known snake at around 13 metres is the extinct Titanoboa that lived 60 million years ago in present day Colombia. Paleontologists Sunil Bajpai and Debajit Datta at the Indian Institute of Technology in Roorkee say V. Indicus was likely a slow-moving predator that wrapped its body around the prey to squeeze it to death. It evolved in the warm Indian subcontinent and spread to Africa via Europe around 56 to 34 million years ago, they say. V. indicus flourished in forested swamps of the now arid Kutch region...
Read more: https://www.nature.com/articles/d44151-024-00048-0
229 notes
·
View notes
Text
It’s fascinating to me how they always seem to do role-reversal for Xena and Gabrielle when it comes to the AU/Uber/Reincarnation episodes with the exception of ‘When Fates Collide’ and the Harry, Mattie and Annie episodes. But ‘Between The Lines’ specifically makes that a thematic motif for Xena and Gabrielle’s next lifetimes. Shakti is a Warrior Prince and Aminestra is a pacifist guardian as the Mother of Peace. It’s not until you get to almost the end of the show that you realize that this role-reversal transition is fate and things have got to work out just so for it to be as it is with what you see in ‘Between The Lines’. Like… for example… with Gabrielle’s moral quandary in her Season 4 arc that she believes she’s using too much violence and she doubles down on the guilt of that belief because of Eli and what he says about life and love being The Truth and The Way. He shows Gabrielle that his ability to heal is all because of his conviction to non-violent methods in serving The Greater Good. So she ends up doubling down on both her guilt in using violence and in her love for Xena even though they contradict each other so she then ends up using violence because of her love for her.
But all throughout their future lives exploration in the episode ‘Between The Lines’ during the India arc, you just see her hacking and slashing away with a sword as Shakti. This feels extremely hypocritical at first… but when you watch it again after seeing the whole show you’re just like “Oh, of course” because her Way all along was to protect and defend through violence. Her next life would be the Way it is because she ends up taking Xena’s mantle and continuing her legacy as the Warrior Princess. So I wonder if she ever questions why she is who she is in her next lifetime even though she’s going through this whole spiritual journey with pacifism and would throw away her defensive weapon very soon. I wonder if she ever puts two and two together on what is revealed to her in ‘Between The Lines’ in searching for her Way. It’s just so fascinating to me how that episode is not only the one that informs us of future episodes but also brings in a new context to what we saw of past episodes. That the role-reversal transition is the fated trajectory for Xena and Gabrielle’s individual arcs because most of their alternate reality, afterlife and soul incarnation experiences would put them in a state and position where they are in opposition of each other and where their spiritual essences permeate into each other because of influencing and changing each other emotionally so much so that they become each other.
It all makes complete sense on rewatches. What seems inconsistent or even OOC at the time just turns out to be very clever retconning and foreshadowing because the two characters do eventually become each other. But I just find ‘Between The Lines’ in particular such a fascinating episode because that episode makes what was once just a fun experimentation for the creators a purposeful thematic motif that changes the character representation and development significantly for Xena and Gabrielle for the entire TV show not only forwards, but also backwards because you see that it’s actually how any of their arcs happen. It’s so damn profound.
It’s like what they say about time-travel. If you see what is to come for your future, you can change the present. But then,… if you change the present,… then you also end up recontextualizing the past because that’s fate. That’s how fate works. It’s the destined path that is created by their present and future experiences which seems completely coincidental to them at first UNTIL they get a look-in on it ahead of time and they make changes based on the experiences and knowledge they’ve accumulated from that look-in. I’ve always understood that that’s what ‘Between The Lines’ - or even the whole India arc - is. It’s the look-in to their individual changes going forward. But it specifically hits more with Gabrielle than it does with Xena because Xena’s changes aren’t so shocking. They’re significant changes too but the thematic visual of it doesn’t hit anywhere near as hard as it does with Gabrielle’s changes because her changes are a sensurround jolt that impact you when they happen. You feel those changes as if they’re happening inside your body. It’s a visceral experience with Gabrielle, whereas with Xena, it’s just a visual experience because we’re used to the chaotic tumultuous drama with her. Not with Gabrielle.
Her karmic cycle is that of not just becoming a warrior and hero, but also validating that masculine and active transition within her that you see happening because of becoming the warrior and hero. The Warrior Princess as Gabrielle or Warrior Prince as Shakti. Her destined Way. Her path, direction, trajectory, truth. That core being and nature that she was searching for and working towards in Season 4 in the India arc - of which she only gets wrong initially because she ignores what Shakti taught her and relies more so on what Eli teaches her when it’s the mehndi that contains Truth to who she is.
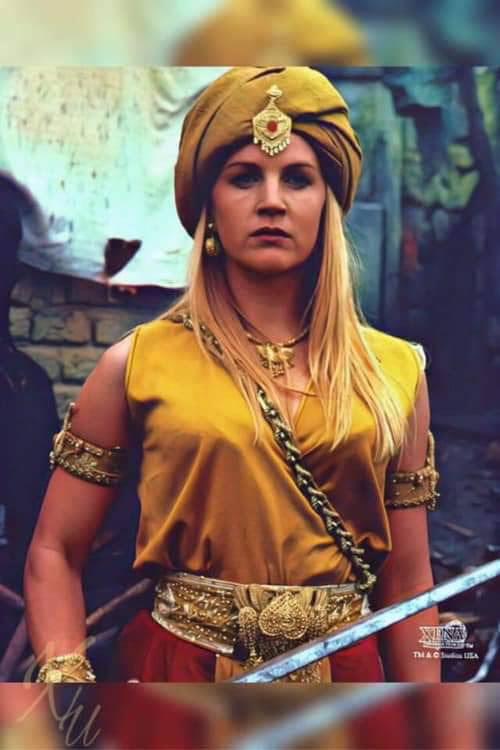

I think the message is very telling. Follow your own Way. Don’t follow someone else’s because they inspire you. That Way might actually go against your soul’s karma. You can be inspired by a person but you don’t need to emulate them or take on their lifestyle and worldview. See, Gabrielle never just had that problem with Xena, although that was the most obvious. Almost anyone she came across that she was in awe of she tries to be like and so struggles to gain their approval when she fails - as she inevitably would because it’s not right for her.
The only reason why Gabrielle takes on Xena’s mantle is because Xena is already so much a part of her core self as her soulmate. As her other half to a whole. As her Yin. None of this really makes any sense until her endgame where it is confirmed without a doubt that she’s Yang. If the Yin-yang chakram represents who these characters were, then it must also represent who they will become because Yin-yang is a thematic and symbolic visual in TV art/entertainment for change and evolution of Self.
The human representation of Yin-Yang is embodied through the lead characters and the lead characters are represented through the visual symbolism of Yin-yang. But it’s Gabrielle that truly makes that apparent within the overall story of what ‘Xena: Warrior Princess’ is as both the author of The Xena Scrolls and the successor of the Warrior Princess’ legacy. In Gabrielle’s next life (as Shakti) she will follow Xena (as Arminestra) 50 years later but she will be an active party instead of a passive one - as rightfully shown in the episode ‘Between The Lines’ where they also reveal to us that their respective karmic cycles are eternally intertwined. That they do literally share the same soul and were just waiting for one another to meet in every lifetime, be it the past, present or future so they could bring out the best in each other whether as friends, lovers or even enemies. The point is for them to always learn from the presence of each other and that’s why they’re The Ultimate Ship.



#xena warrior princess#between the lines#the india arc#xena and gabrielle#xabrielle#xena#arminestra#lucy lawless#gabrielle#shakti#renee o'connor#naima#tharini mudaliar#yin-yang#role-reversal#karmic cycle#fate#evolution#soulmates#reincarnation#character study thesis#character representation#character development#wlw representation#queer representation
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: Dyani Lewis
Published: May 31, 2023
In India, children under 16 returning to school this month at the start of the school year will no longer be taught about evolution, the periodic table of elements or sources of energy.
The news that evolution would be cut from the curriculum for students aged 15–16 was widely reported last month, when thousands of people signed a petition in protest. But official guidance has revealed that a chapter on the periodic table will be cut, too, along with other foundational topics such as sources of energy and environmental sustainability. Younger learners will no longer be taught certain pollution- and climate-related topics, and there are cuts to biology, chemistry, geography, mathematics and physics subjects for older school students.
Overall, the changes affect some 134 million 11–18-year-olds in India’s schools. The extent of what has changed became clearer last month when the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) — the public body that develops the Indian school curriculum and textbooks — released textbooks for the new academic year that started in May.
Researchers, including those who study science education, are shocked. “Anybody who’s trying to teach biology without dealing with evolution is not teaching biology as we currently understand it,” says Jonathan Osborne, a science-education researcher at Stanford University in California. “It’s that fundamental to biology.” The periodic table explains how life’s building blocks combine to generate substances with vastly different properties, he adds, and “is one of the great intellectual achievements of chemists”.
Mythili Ramchand, a science-teacher trainer at the Tata Institute of Social Sciences in Mumbai, India, says that “everything related to water, air pollution, resource management has been removed. “I don’t see how conservation of water, and air [pollution], is not relevant for us. It’s all the more so currently,” she adds. A chapter on different sources of energy — from fossil fuels to renewables — has also been removed. “That’s a bit strange, quite honestly, given the relevance in today’s world,” says Osborne.
More than 4,500 scientists, teachers and science communicators have signed an appeal organized by Breakthrough Science Society, a campaign group based in Kolkata, India, to reinstate the axed content on evolution.
NCERT has not responded to the appeal. And although it relied on expert committees to oversee the changes, it has not yet engaged with parents and teachers to explain its rationale for making them. NCERT also did not reply to Nature’s request for comment.
Chapters closed
A chapter on the periodic table of elements has been removed from the syllabus for class-10 students, who are typically 15–16 years old. Whole chapters on sources of energy and the sustainable management of natural resources have also been removed.
A small section on Michael Faraday’s contributions to the understanding of electricity and magnetism in the nineteenth century has also been stripped from the class-10 syllabus. In non-science content, chapters on democracy and diversity; political parties; and challenges to democracy have been scrapped. And a chapter on the industrial revolution has been removed for older students.
In explaining its changes, NCERT states on its website that it considered whether content overlapped with similar content covered elsewhere, the difficulty of the content, and whether the content was irrelevant. It also aims to provide opportunities for experiential learning and creativity.
NCERT announced the cuts last year, saying that they would ease pressures on students studying online during the COVID-19 pandemic. Amitabh Joshi, an evolutionary biologist at Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research in Bengaluru, India, says that science teachers and researchers expected that the content would be reinstated once students returned to classrooms. Instead, the NCERT shocked everyone by printing textbooks for the new academic year with a statement that the changes will remain for the next two academic years, in line with India’s revised education policy approved by government in July 2020.
“The idea [behind the new policy] is that you make students ask questions,” says Anindita Bhadra, an evolutionary biologist at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research in Kolkata. But she says that removing fundamental concepts is likely to stifle curiosity, rather than encourage it. “The way this is being done, by saying ‘drop content and teach less’”, she says, “that’s not the way you do it”.
Evolution axed
Science educators are particularly concerned about the removal of evolution. A chapter on diversity in living organisms and one called ‘Why do we fall ill’ has been removed from the syllabus for class-9 students, who are typically 14–15 years old. Darwin’s contributions to evolution, how fossils form and human evolution have all been removed from the chapter on heredity and evolution for class-10 pupils. That chapter is now called just ‘Heredity’. Evolution, says Joshi, is essential to understanding human diversity and “our place in the world”.
In India, class 10 is the last year in which science is taught to every student. Only students who elect to study biology in the final two years of education (before university) will learn about the topic.
Joshi says that the curriculum revision process has lacked transparency. But in the case of evolution, “more religious groups in India are beginning to take anti-evolution stances”, he says. Some members of the public also think that evolution lacks relevance outside academic institutions.
Aditya Mukherjee, a historian at Jawaharlal Nehru University in New Dehli, says that changes to the curriculum are being driven by Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), a mass-membership volunteer organization that has close ties to India’s governing Bharatiya Janata Party. The RSS feels that Hinduism is under threat from India’s other religions and cultures.
“There is a movement away from rational thinking, against the enlightenment and Western ideas” in India, adds Sucheta Mahajan, a historian at Jawaharlal Nehru University who collaborates with Mukherjee on studies of RSS influence on school texts. Evolution conflicts with creation stories, adds Mukherjee. History is the main target, but “science is one of the victims”, she adds.
==
Well, at least it'll put them on par with the anti-science and biology-denial of US classrooms. China no longer has anything to worry about.
#India#hinduism#islam#science denial#evolution#evolution denial#science#anti science#biology denial#math#mathematics#physics#religion#religion is ignorance#religious stupidity#periodic table#periodic table of elements#religion is a mental illness
114 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lemuria Island Creature 3: Neovintana whitei – Mountain Hamster

Bruh
Neovintana whitei is the fictional species of gondwanatherian The animal and a gondwanatherian was honored to Charlie White or Cr1tikal.
Happy National Video Game Day 😁 🎉 🦭 🎉🥳
Warning: This species was introduced in No Way to Seaway as part of Rapunzel's Tangled Adventure and other Disney character's series, Assassin's Creed series, and Monster Hunter series sequels. And yeah, it is an invasive species from another universe brought by a Drift Portal or blamed Doctor Strange. 😂 🙀
Physiology
Neovintana whitei is the medium sized gondwanatherian native in mountainous terrain from 1,000 to 2,500 meters above sea level.
Abilities
Neovintana whitei hibernate for up to an unknown number of months a year and are exceptional diggers, their claws are very strong and it capable of breaking through dirt that would be impossible for a pickaxe to penetrate.
Ecology
Certain animals have a high degree of resistance to cold, while certain dinosaurs can endure low temperatures. Neovintana are specialized grazers, much like gondwanatherians. In fact, they were among the first mammals to become adapted for eating grass, much before any therians did. Their grazing practices also affect the composition of the plants, which in turn affects the overall biodiversity of alpine meadows.
Reproduction
And yeah, it lay eggs like platypuses and echidnas.
Gallery

Reference

– Ognimdo2002
#ognimdo2002#earth#art#ibispaint art#speculative evolution#vintana#madagascar#indian#india#lemuria#lemuriachallenge#lemuriaisland#neovintana whitei#cr1tikal#july 2024#gondwanatherian#gondwanatheria#bruh#national video game day
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Synthesis of the Future: Bridging Western Science and Eastern Wisdom
Throughout history, humanity has sought to understand the mysteries of existence, probing both the external cosmos and the inner dimensions of the soul. Two towering streams of human inquiry have emerged—the rational, empirical science of the West and the contemplative, spiritual vision of the East. Each, in its own way, seeks to unveil the nature of reality. Today, as the world grows more interconnected, the synthesis of these two approaches represents not only a profound intellectual achievement but also a necessity for the evolution of human consciousness.
The Legacy of the West: The Spirit of Inquiry
Western civilization has long been characterized by a relentless pursuit of knowledge through observation, experimentation, and reason. From the natural philosophy of ancient Greece to the scientific revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries, the West has fostered a tradition of empirical investigation. Figures such as Sir Isaac Newton, who revealed the laws of motion and gravitation, and Albert Einstein, whose theory of relativity reshaped our understanding of space and time, embody this scientific spirit.
Yet, even within the heart of the scientific tradition, there have been voices calling for a deeper, more holistic understanding. The Danish physicist Niels Bohr, for example, remarked that "the opposite of a profound truth may well be another profound truth," echoing the Eastern principle of complementarity. Similarly, the quantum physicist Erwin Schrödinger was deeply influenced by the Upanishads and asserted that "the plurality that we perceive is only an appearance; it is not real."
The Wisdom of the East: The Inner Journey
In contrast to the West’s outward exploration, the spiritual traditions of the East have long turned their gaze inward. The sages of India, China, and Tibet pursued direct experience of the ultimate reality through meditation and contemplation. The Upanishads speak of Brahman as the unchanging, eternal essence underlying all phenomena, while the Buddha's teachings on the nature of mind point to the impermanence of the material world and the potential for liberation from suffering.
Great mystics such as Sri Ramana Maharshi, who taught the path of self-inquiry, and Paramahansa Yogananda, who brought the teachings of Kriya Yoga to the West, exemplify this profound inner knowledge. Likewise, the Chinese philosopher Laozi, in the Tao Te Ching, emphasized harmony with the Tao—the ineffable source of all things.
The Call for Synthesis: Visionaries Across Traditions
Many enlightened thinkers have recognized the need to unite the rational and the mystical. The philosopher and poet Rabindranath Tagore, in his dialogues with Einstein, sought a harmony between the scientific worldview and the intuitive wisdom of the East. Similarly, Carl Jung, the Swiss psychologist, explored Eastern concepts like the mandala and integrated them into his theories of the collective unconscious.
The Jesuit priest and paleontologist Pierre Teilhard de Chardin envisioned a future where scientific knowledge and spiritual insight converge, describing an "Omega Point" where consciousness would reach its ultimate evolutionary fulfillment. More recently, the Dalai Lama has called for a dialogue between Buddhist philosophy and modern science, particularly in the realms of consciousness and neuroscience.
Toward a New Consciousness
The synthesis of Western science and Eastern wisdom is not a mere intellectual exercise; it is a path toward a more integrated understanding of reality and our place within it. Science provides us with powerful tools to explore and manipulate the physical world, but it often falls silent on questions of meaning, purpose, and the nature of consciousness. Eastern wisdom, on the other hand, offers profound insights into the inner life and the spiritual dimension of existence but has historically lacked the empirical rigor of the scientific method.
The future calls for a new paradigm that transcends these limitations—a vision where the objective and subjective, the material and the spiritual, are recognized as two aspects of a unified reality. In the words of the Indian mystic Sri Aurobindo, "The meeting of the East and the West will be the prelude to the birth of a new world." This vision invites us to explore both the outer reaches of the cosmos and the innermost depths of the soul, recognizing that these journeys are, in truth, one and the same.
As we stand on the threshold of this new synthesis, the wisdom of the ages reminds us that true knowledge is not fragmented but whole. By weaving together the insights of Western science and the enlightened vision of the East, we open the door to a future where humanity can awaken to the fullness of its potential—a future where the light of reason and the light of spirit shine as one.
#The Synthesis of the Future#The synthesis of Western science and Eastern wisdom#Spiritual Evolution#Human Potential#The Union of Science and Spirituality#Unity#Oneness#Philosophy#India#China#Tibet#Unity of the East and West
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hindustan, India, where do the names come from, why? Why does the world use them?
Well, let's look first at other countries like Japan (Nippon) - Land of the Rising Sun or where the Sun Rises. This is what Japan's always called itself.
Others, over time, language, translation led to, and made stick, Japan. It's like how Germany is actually Deutschland to themselves, technically. This is what's known as an Exonym, or name given/used by other people/country outside the one being referenced. This is led to creation of myths, stories, fairy tales, and more about cultures as well. Back to India.
Well, the original people behind the connection to the name are best known as the Indus Valley people/civilization.
But that's not what they were called amongst themselves. No. In fact, these people who originated and farmed the Sindh valley/Sindh river, were first given their eventual "Indus related" name but the Persians.
When the Persians first started interacting and trading with the people we know as Indus Valley, they referred to them as the people of the Sindh river or valley, however, in their native tongue, the S became an H.
So the Hindh valley, Hindh people. Eventually the greeks and romans would show up, and call them the Indos, or Indus people for the river (as translated into their tongues...remind me again how many river based names there are again in the world, even for.....just river itself) go figure. Because people usually fucking set up near rich fresh water sources cuz... we need it to live. That's why people set up along the Nile too. And...well, everywhere. Water kinda important.
The Indus valley people were not Hindu as we know it today. In fact, at one point, they practiced a religion older than the vedic, we just don't know what that is do to proto indo european influences and the impact they had in forming the vedic era pre Hindu.
Continuing. Now we reach the eventual evolution of Hindhu through the word and alteration of Sindh/Sindhu people - of that river/past it.
Stan. Well, in Sanskrit there is sthāna - or place. And in Persia, there is stan (a suffix you see in many Islamic countries as well given the evolution of the language), and the similarity in sanskrit and ancient persian is likely because of PIE influences in both of them so, outside countries started using interchangeably (and of course eventually so do the people within an empire when you're trading and referring to yourself and building alliances, agreements or going to war) you adopt those terms: Hindustan, or India. But Hindustan was never meant to be the land of the Hindu (in terms of religion) because it was a given name by the river, and we're talking about the vedic religion.
Now, I left one name out of here, because it is specifically NOT an exonym. It's the name India historically identifies with from within its own epics, including the most well known, Mahabharata (romanized/english) said closer to (god it's hard typing these sounds in freaking english): Mah-bharat.
Bharat is the key there. So, what's it mean?
Well, it's important to note the word first comes from Bhāratavarṣa - which comes from the Vedic people Bharatas - who are first mentioned in the Rig Veda.
They are the principle people who come from Aryavarta - land of the Aryans, which is why the word is still word in Indic languages, and even a used name. Like, it's a used name for real. You'll meet guys called Aryan.
Anyways, continuing. So, the oldest known name for Indian proper, and you might if you pay attention to Indian news see this making a comeback, is Bharat.
To many from the outside, it's come off heated, people are unsure why, and so on for the name change. But honestly? It's just what India was once called. It's no different than when Mumbai replaced in name Bombay. That name, Bombay was given by the Portuguese. Later (I can't recal the year, someone comment it) the Indian government decided to change the name and reclaim it to Mumbai. But someone asked me about this recently like why all the Bharat stuff and talk online in places.
For anyone who's seen it and wondered, I hope this helps.
It's a history of language, names, and other people sometimes making names stick and translation and evolution of words and culture and empires.
Closing with how did India come to stick? Latin. Then everyone who inherited the legacy, evolution of the language, and the love - all the romance languages that built on it. Eventually, by the 16th or was it 17th century, most of the world started calling it India when they
traded, colonized more, w.e.
The Latin transliteration of Indos, Indica - India.
But the term was used sort of before.
Herodotus in his writings mentions the Indus people, and then calls on of them, "An Indian."
But, yeah, it was never a name for/from those the land themselves.
#Hindustan#India#Japan#Nippon#The Land of the Rising Sun#language#translation#Exonym#Indus Valley#Persians#Hindh Valley#Indos#Indus#Sindh#Sindhu#Bharat#Aryavarta#Older names#ancient names#How india got its name#history of language#history of names#names have meaning#what's in a name#evolution and culture#they didn't name themselves#this is what they were called#new facts#learn something new#did you know?
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Drakes belong to the dragon family. However, their lumbar limbs(the 3rd pair of limbs located just over the lumbar region of the spine), have atrophied to the point of almost none existence.
In the case of the tiger-ox drake; the lumbar girdle serves as the anchor for the muscles that move the heavy metal plates along it's back. The formations, which bear a remblance ti the regal ropes and cords Stereotypically associated with the regions royalty and noble class; is specialized armor used by the drake during combat. The plates can lift up like raised hackles; the whole thing supported by the bones of the vestigial lumbar limbs. This allows it to withstand blows from it's enemies. It will drive the plates deep into any body part that it's opponent tries to use to strike the drake's back
There are reports of eye witnesses who claim that the drake has also been known to use the plates to conduct static electricity and shock it's victims. Even though research has shown that the muscles surrounding the structures, are highly developed; potentially being able to generate even up to 200,000 volts of electricity. There is as yet no evidence to show that the tiger-ox drake is able to use the charges offensively.
It is known however, that the metal plating on the drake's body, are able to protect it against even repeated lightning strikes. This is because the metal content is highly conductive; grounding the current while not allowing it to enter the body of the drake.
The cells of the tiger-ox drake show incredible résistance to heavy metal poisoning, even for a dragon. However they are not immune, and have been known to develop ailments due to heavy metals directly entering their bloodstream; especially Mercury.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Free Speculative Evolution Prompt Saterday
Instead of the Indian sub continent crashing into southern asia, it crashed into western Australia, forming a giant mountain range on the continent.
#speculative biology#speculative evolution#alternate timeline#australia#india#plate tectonics#speculative zoology
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
On the Origin of Species - India (2015)

#On the Origin of Species#charles darwin#book covers#book cover#indian covers#india#evolution#theory of evolution#biology
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Alexander Corvinus (Derek Jacobi), Amelia (Zita Gorog), David (Theo James), Erika (Sophia Myles), Eve (India Eisley), Jacob (Stephen Rea), Kraven (Shane Brolly), Lucian (Michael Sheen) & Marcus (Tony Curran) Icons from various Underworld movies can be found HERE. 200x100, slightly sharpened.
This content is free for anyone to use or edit however you like; if you care to throw a dollar or two my way for time, effort, storage fees etc you are more than welcome to do so via my PAYPAL. Please like or reblog this post if you have found it useful or are downloading the content within. If you have any questions or you have any problems with the links or find any inconsistencies in the content, etc. please feel free to drop me a politely worded message via my ASKBOX (second icon from the top on my theme!)
#underworld#underworld evolution#underworld rise of the lycans#underworld blood wars#underworld awakening#underworld icons#derek jacobi#zita gorog#theo james#sophia myles#india eisley#stephen rea#shane brolly#michael sheen#tony curran#MY UNDERWORLD ICONS.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ancient Architecture#India
Hindu #The Somnath Temple

The Mughals #The Taj Mahal

Indo-Saracenic Revival #Victoria Memorial

Dravidian #Vitthala Temple
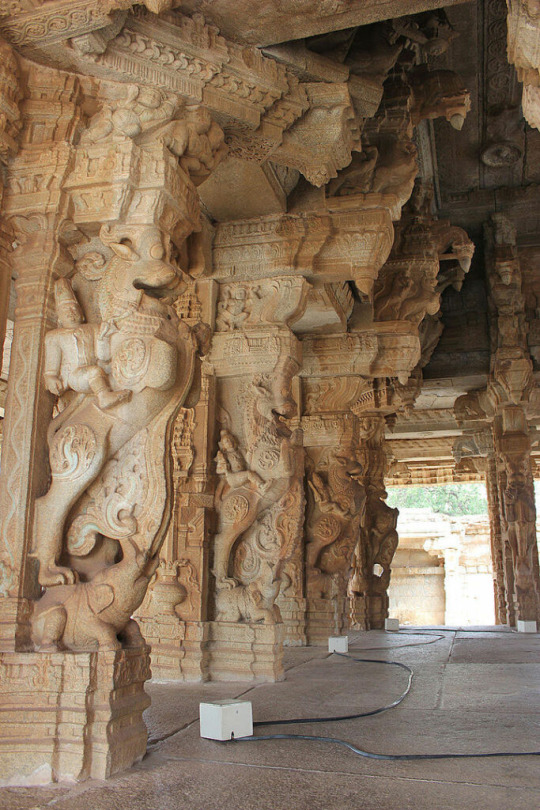

Kaḷinga #The Lingaraja

Indian Vernacular #Bhimakali Temple
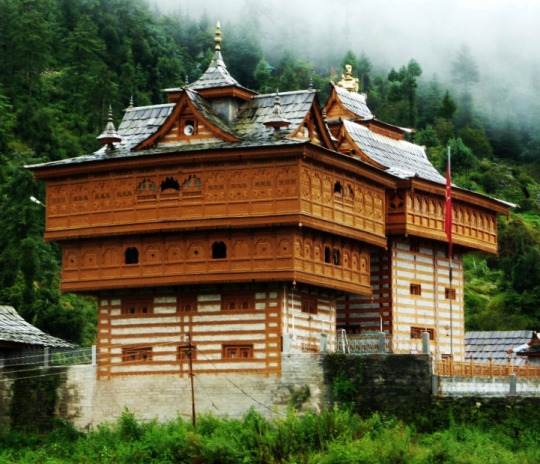

Cave #kanheri

#traditional art#travel#interiors#india#architecture#art archive#buildings#ancient civilizations#ancient architecture#culture#evolution smp#philosophy#places#photography#photoblog#photoart#so wholesome
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lemuria Island Creature 5: Julienosaurus donolafiny – Self-proclaimed Rogue of Lemuria Island

Name: Julienosaurus donolafiny (Julieno us honored to Julien Baker + Ancient Greek: σαῦρος "sauros", meaning "lizard"; Hindustani: दोनों "donon", for "both" + Malagasy: لَفِنِ "lafiny", for "side")
Creator: Ognimdo2002
Clade: Iguania (Opluridae)
Habitat: Non-mountain areas
Size: 1.24 meters tall; 2.013 meters long; 37.24 kilograms
Ecology: Omnivorous scavengers
Additional Info:
One of the iguanas named after Julien Baker is Julienosaurus donolafiny, although it is found in Madagascar rather than South America. Among the Opluridae family, this lizard was distinct because of its bigger evolution compared to contemporary cousins and its use of its tail for defense.
Julienosaurus had an extremely deadly, prehensile tail that moved to swat competing males or the predator. The lizard removed the carcasses and left the bones because it was a scavenger as well. Being an omnivore, Julienosaurus consumes anything it finds, including fallen fruits, leaves, mushrooms, insects, seafood, and carcasses.

Size Comparison and Geographic Location of this Species
Reference

#ognimdo2002#earth responsibly#art#earth#ibispaint art#speculative evolution#ibispaintx#lemuria#lemuriaisland#lemuriachallenge#julienosaurus donolafiny#madagascar#india#julien baker#opluridae#iguanidae#iguana
2 notes
·
View notes

