#eco vehicle
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text



Citroën Eco 2000 Concept (SL 10), 1984. One of a series of research prototypes designed to test aerodynamics and lightweight construction. Some of the developments made by the Eco 2000 were used on the production Citroën AX
#Citroën Eco 2000#Citroën Eco 2000 SL 10#concept#prototype#research vehicle#design study#aerodynamic#test vehicle#lightweight#Citroën#1984#1980s
130 notes
·
View notes
Text




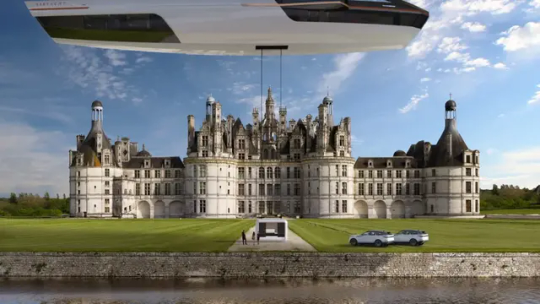
AirYacht will now stay exclusively in the air, says CEO Guillaume Hoddé, who cofounded the Swiss company with fellow engineer Matthieu Ozanne. Jettisoning
#art#design#flying private#travels#luxury lifestyle#flying palace#airplane#airyacht#baloon#jetsetter#jetset#billionaire#billionairelife#jettisoning#airship#vehicle#blimp#dirigible#eco friendly
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
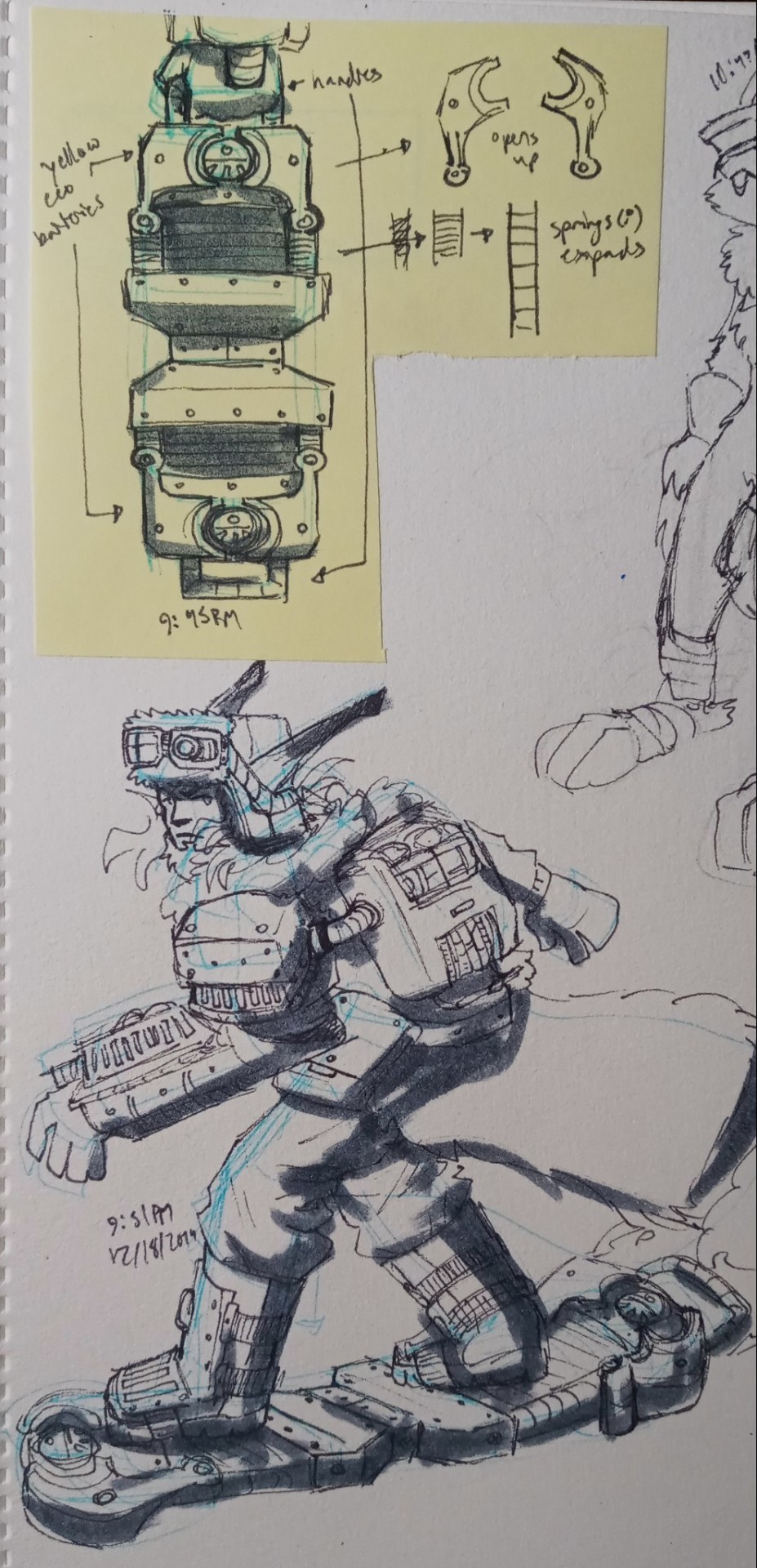
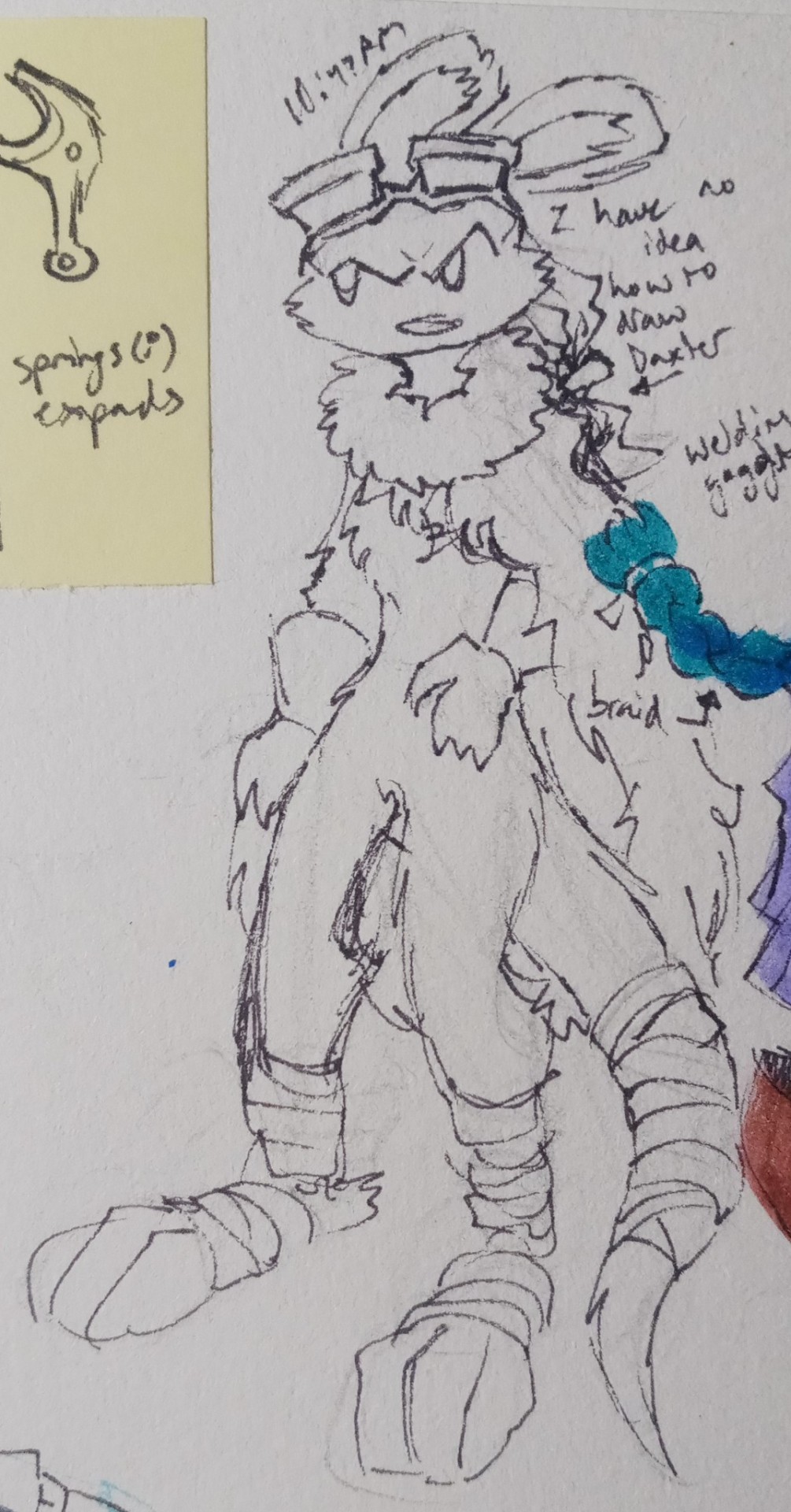
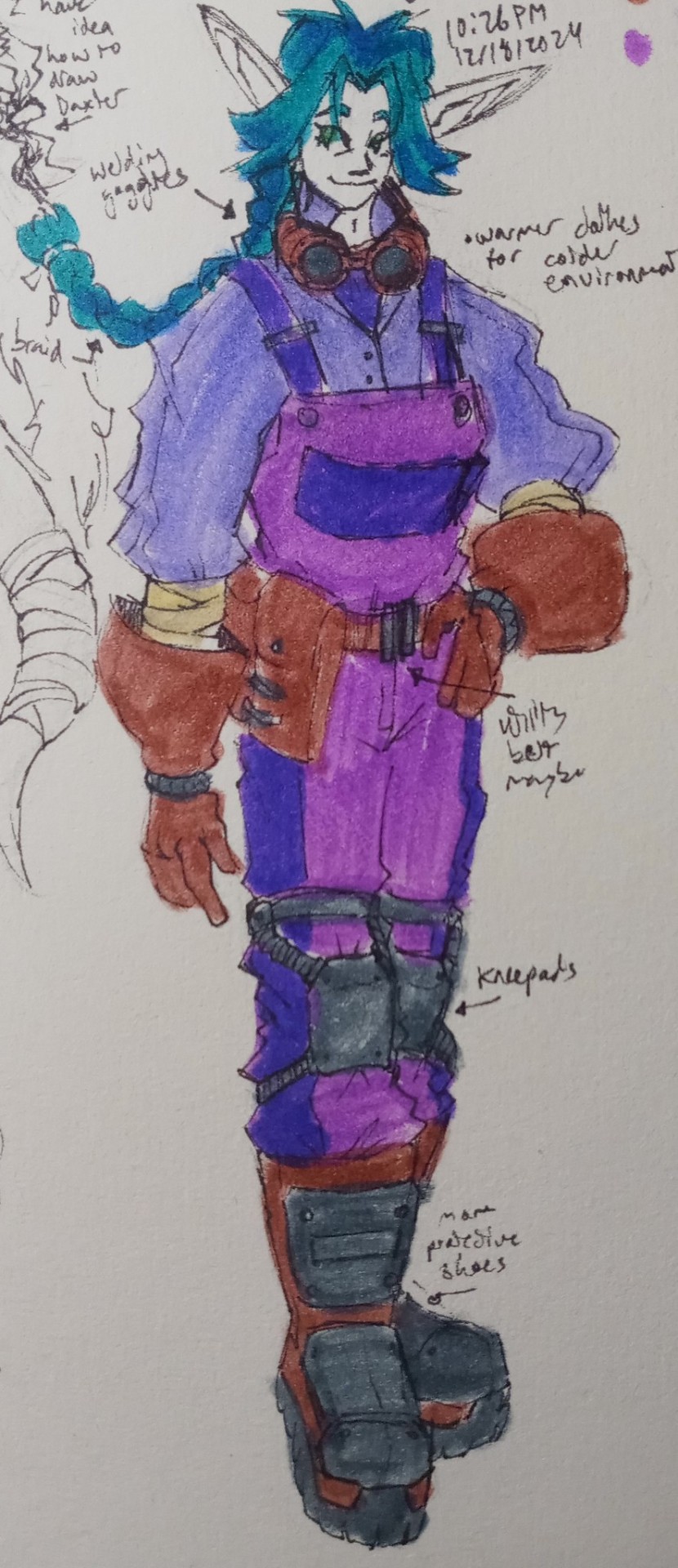
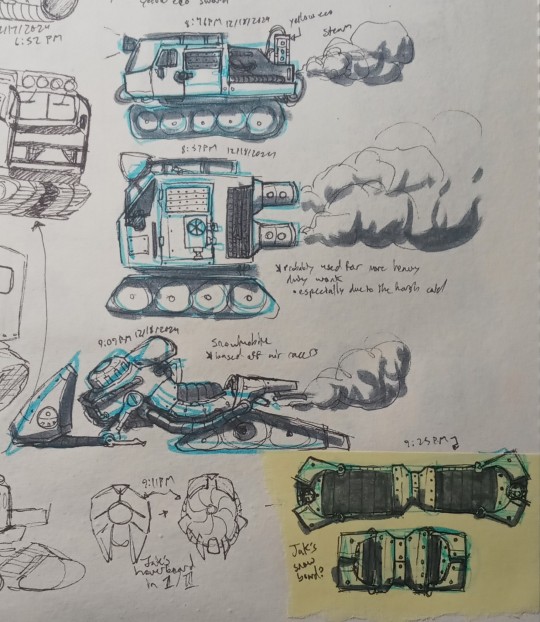



More stuff with the winter au
#art#concept#jak and daxter#jak#daxter#jnd#keira#winter#i was trying to think of the type of vehicles that would probably exist in this place#zoomers and buggies would probably be rebuilt into snowcats to traverse the area#and also snow mobiles for thinner and faster vehicles#all probably powered with thermal batteries/yellow eco#jak would also get a snowboard instead of a hoverboard#it would probably work about the same as the regular hoverboard#it would definitely be harder to carry around though#i dont know what to replace jaks holster/bag thing that he wears on his pack#its either gonna be a larger yellow eco battery or some compartment to carry larger stuff in#the ring is already a yellow eco battery so itll probably be a sort of metal backpack or something#keira also has to wear warmer clothes because of the environment#no woman is wearing a crop top in -50° weather#she also has more protection for her feet and hands since she would probably be working with heavier machinery#anyway im calling this winter au jak 0#after the concept of absolute zero#mainly because i think jak 0 sounds cool#jak 0
13 notes
·
View notes
Text



#adult collectibles#adult collectors#a real american hero#arah#cobra enemy#eco warriors#playset#vehicles#toxo-lab#septic tank#eco striker#color changing vehicle#water shooters#box art
4 notes
·
View notes
Note
Imagine if Daxter was actually Mar the entire time, and everyone just thought it was Jak, Daxter included
no this is actually so funny to me because Daxter is already a precursor
& yet everyone spends the whole series calling him a muskrat or mistaking him for a 'horribly sick little bird' or just straight-up being like 'this is a rat'
meanwhile Daxter is walking around having been reincarnated as a god, riding on the shoulder of Frankenstein's monster whose veins are full of battery acid and radioactive isotopes & Daxter is just totally unaffected by it all. literally just vibing while the guy whose shoulder he rides on periodically explodes into a lightning storm of dark matter
daxter has never heard of a toxic substance he couldn't go swimming in 😌
& YET, everyone is still like '... that's a rat'
so the thought of Daxter being the long-lost heir to the throne & Jak being Just Some Guy is literally comedy gold
it makes this moment even funnier

#jak and daxter#i ADORE these games#you don't learn fine motor skills from a game without it becoming part of your personality#and don't get me started about a warrior nun au for this#like !!!! ava in the KG fortress being experimented on with light eco. lilith being experimented on with dark eco#beatrice as an Underground fighter who busts into the fortress & accidentally sets Lilith off like a bomb#dragging ava out through the chaos and being hunted by the KG#AVA on a zoomer like no this girl should not be allowed in an antigrav vehicle#anon#jak and daxter spoilers
42 notes
·
View notes
Text

E Rickshaw Loader: Affordable and Efficient Solutions
Looking for an eco-friendly and cost-effective transportation solution? The e rickshaw loader is the answer. These versatile vehicles have revolutionized urban logistics with their affordability and efficiency. Understanding the e rickshaw loader price is crucial for businesses and individuals seeking to invest in this sustainable technology.
The e rickshaw loader price varies depending on several factors, including the features and battery capacity. Basic models are more affordable, while premium versions with extended battery life and advanced features might cost more. Despite the initial investment, the low running and maintenance costs make e rickshaw loaders a smart choice.
Additionally, government incentives and subsidies for electric vehicles can significantly reduce the e rickshaw loader price, making them even more accessible. These incentives aim to promote green transportation and reduce urban pollution, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Investing in an e rickshaw loader not only supports environmental conservation but also offers practical benefits like reduced fuel costs and lower maintenance expenses. As cities continue to embrace green technology, the demand for e rickshaw loaders is expected to rise, making now the perfect time to understand and leverage the best e rickshaw loader options.
#E Rickshaw Loader#E Rickshaw Loader Price#E Rickshaw Price in India#Electric Rickshaw Loader#Eco-friendly Transportation India#Affordable E Rickshaw#E Rickshaw Subsidies India#Green Transportation India#Urban Logistics Solutions#Cost-effective E Rickshaw#Low Maintenance E Rickshaw#Electric Vehicle Incentives India#Sustainable Transport India#E Rickshaw Battery Capacity#Urban Pollution Reduction#Electric Cargo Vehicles India#Indian E Rickshaw Market#E Rickshaw Loader Investment#Government Subsidies Electric Vehicles#Green Technology India
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dodge's Electric Evolution: Bringing the V8 Rumble to the Electric Arena
In an ambitious move to marry the past with the future, Dodge is setting the stage to infuse its electric cars with the soul-stirring sounds and dynamic feel of its legendary V8-powered muscle cars. This innovative endeavor aims not just to preserve the iconic auditory and tactile experience of driving a Dodge muscle car but to elevate it within the realm of electric vehicles (EVs). The Electric…

View On WordPress
#400V and 800V Architectures#Active Vibration Enhancement#Automotive Innovation#Automotive Technology#Car Enthusiast Culture#car safety features#Charger Daytona#Dark Matter Sound Profile#Dodge Charger Electric#Dodge Electric Muscle Car#Dual-Motor Drivetrain#Eco-Conscious Driving#Eco-Friendly Muscle Cars#Electric Cars Safety#Electric Muscle Car Sound#Electric Power Upgrades#Electric Vehicle Development#Electric Vehicle Experience#Electric Vehicle Innovation#Electric Vehicle Market#Electric Vehicle Performance#Electromechanical Shifting#eRupt Multi-speed Transmission#Fratzonic Chambered Exhaust#Future of Driving#High-Performance Electric Cars#Hybrid Electric Vehicles#ICE Simulation Technology#Multi-speed Gearbox#Muscle Car Legacy
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Electric Vehicle Plastics Market: An In-Depth Exploration and its Contribution to a Circular Automotive Industry
The global electric vehicle plastics market size was estimated at USD 13.33 billion in 2030 and is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.0% from 2024 to 2030. The industry is projected to witness significant growth in terms of consumption, on account of high application scope and increasing demand from the growing population. The Polypropylene (PP) resin demand in the Asia Pacific region is estimated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. Strong government support & initiatives regarding emissions and increasing investment by manufacturers are propelling the growth of the region.
Electric Vehicle Plastics Market Report Highlights
The Asia Pacific region is estimated to grow at the fastest CAGR from 2022 to 2030. Increasing demand from the growing population coupled with environmental concerns among others are anticipated to drive market growth in the region
The battery segment is anticipated to register the fastest CAGR from 2022 to 2030. Batteries are one of the significant components of an EV and, in comparison to combustion engines, battery vehicles do not produce any emissions and are eco-friendly. The growing demand for EVs has promising growth for EV batteries
The exterior application segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2021 and is estimated to continue its dominance over the forecast period due to the high demand in aesthetics
The BEV vehicle type segment led the industry in 2021 and it is anticipated to continue growing over the forecast period as PHEVs have higher maintenance costs than BEVs
For More Details or Sample Copy please visit link @: Electric Vehicle Plastics Market Report
Furthermore, EVs are efficient and require less maintenance as compared with traditional vehicles. These factors are expected to boost the demand for EVs, which is expected to drive the demand for��plastics over the forecast period. Increasing utilization of plastics in EVs is anticipated to boost industry growth positively over the forecast period. Plastics have proven to perform well under harsh conditions through their resistance to shock, moisture, oxidation, and further maintaining their chemical and mechanical properties. Plastics will be crucial material for manufacturing lightweight and energy-efficient EVs. Based on resin type, PP is expected to witness major demand during the projected years.
Polypropylene is used in many components of the vehicle including bumpers, carpet fibers, cable insulation, and others. Properties, such as good heat, chemical & fatigue resistance, and others, are anticipated to drive the demand for PP in the industry. Major manufacturers are adopting expansion strategies, such as new product development, production facility expansions, mergers & acquisitions, and joint ventures. For instance, in October 2021, DuPont launched a new extension of its existing Zytel HTN range, named as Zytel 500 series. These products are developed to provide enhanced retention properties in e-mobility oils, electrically friendly characteristics, and a high Comparative Tracking Index (CTI).
EVPlastics #ElectricVehicles #SustainableDriving #EcoFriendlyCars #ElectricVehicleTech #CleanTransportation #GreenMobility #EVInnovation #PlasticsInEVs #FutureOfTransport #SustainableMaterials #EcoAutoDesign #EVManufacturing #PolymerInnovation #ZeroEmissionVehicles #GreenTechAuto #CleantechPlastics #EVDesign #EcoFriendlyPlastics #CircularAutoEconomy
#EV Plastics#Electric Vehicles#Sustainable Driving#Eco-Friendly Cars#Electric Vehicle Tech#Clean Transportation#Green Mobility#EV Innovation#Plastics In EVs#Future Of Transport#Sustainable Materials#Eco Auto Design#EV Manufacturing#Polymer Innovation#Zero Emission Vehicles#Green Tech Auto#Cleantech Plastics#EV Design#Eco-Friendly Plastics#Circular Auto Economy
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo




Alterna Site 4: Landfill Dreamland
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Nissan Leaf: Affordable, High-Performing, and Supercharged Electric Vehicle
Nissan Leaf Cost, Range, Performance, and Supercharging Introduction The Nissan Leaf has been a game-changer in the electric vehicle (EV) market since its launch. With its impressive cost, range, performance, and supercharging capabilities, the Nissan Leaf has become a top choice for eco-conscious drivers around the world. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of the Nissan…

View On WordPress
#affordable#battery technology#cost-effective#driving experience#eco-friendly transportation#electric vehicle#EV#fast-charging#government incentives#home charging#maintenance#Nissan Leaf#performance#range#regenerative braking#supercharging#sustainability
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
FISKER DELIVERS FIRST 22 FISKER OCEAN SUVS, Establishing Presence in Competitive EV Market
Fisker Inc. achieves a major milestone by delivering the highly anticipated Fisker Ocean SUV to customers in the United States. Explore the groundbreaking features, sustainability, and investment potential of Fisker in the rapidly growing electric vehicle sector

Fisker Ocean SUV:
Innovation and Unmatched Features: The Fisker Ocean SUV represents a groundbreaking leap in automotive innovation. Designed to offer a sustainable and luxurious driving experience, it is equipped with cutting-edge features and impressive performance capabilities. Boasting a class-leading range of up to 360 miles, it surpasses other electric SUVs in its category. The SUV's all-wheel drive system and dual-motor setup deliver exceptional power and acceleration, providing a thrilling driving experience that surpasses traditional internal combustion
Read More
Other Topics Read:
10 Small Investment Ideas: Building Wealth
Stocks on Wall Street Show Resilience
South Korea Retains Position in MSCI Emerging Markets Index
Mastering the 5 EMA: A Powerful Indicator for Analyzing Price Trends
#Fisker #ElectricVehicles #Sustainability #Innovation #CustomerSatisfaction #InvestmentOpportunity #FuturePlans #Expansion #EVMarket
#: Fisker#electric vehicle manufacturer#Fisker Ocean SUV#innovation#sustainability#customer satisfaction#investment opportunity#strategic partnerships#global expansion#leadership team#market conditions#stock performance#Fisker Inc. achieves significant milestone by delivering the highly anticipated Fisker Ocean SUV to customers in the United States#Fisker Ocean SUV: A groundbreaking leap in automotive innovation and sustainability#Fisker Ocean SUV surpasses competitors with its class-leading range of up to 360 miles#Positive customer feedback solidifies Fisker's reputation as a forward-thinking electric vehicle manufacturer#Fisker's commitment to sustainability and eco-friendly materials reduces carbon footprint#Investment opportunity in Fisker as demand for electric SUVs continues to rise#Strategic partnerships strengthen Fisker's position in the competitive electric vehicle market#Fisker's expansion plans include ramping up production capacity and targeting international markets#Fisker's success in delivering the first 22 Fisker Ocean SUVs showcases innovation#and customer satisfaction#Fisker presents an exciting investment opportunity in the rapidly growing electric vehicle sector
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
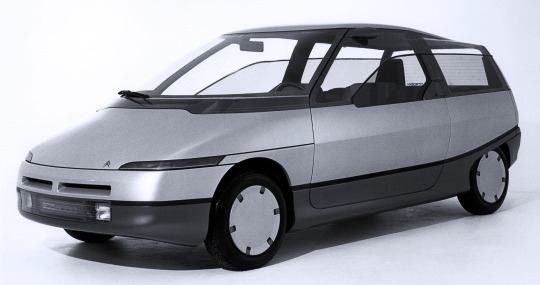


Citroën Eco 2000 SL10, 1984. The Eco 2000 project was a 50% government-funded program to come with a vehicle capable of achieving 2 litres per 100 km fuel consumption (117mpg). Citroën made a number of Eco 2000 prototypes of which the SL10 was the final and ultimate version. It was presented at the Paris Motor Show weighing just 450kg and powered by a 3 cylinder 750 cc engine. It didn't quite hit the target, achieving 2.1 litres per 100 km at 90kph. The Citroën AX used many of the developments from the Eco 2000
#Citroën#Citroën Eco 2000#experimental vehicle#test vehicle#concept#prototype#lightweight#aerodynamic#Eco 2000#1980s#1984
158 notes
·
View notes
Text
post about how i hate bicyclists in the city
#i know they’re ~eco-friendly~ or whatever but they are all the most annoying people you’ve ever met#and they think both pedestrian and vehicle privileges apply to them
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Elevate Your Electric Ride with Mahindra XUV 400 EV: Unmatched Support by ElecTree®
The automotive world is evolving rapidly, with electric vehicles (EVs) leading the charge toward sustainability and eco-friendly transportation. Among the many impressive EVs in the market today, the Mahindra XUV 400 EV stands out as a game-changer. This electric car combines cutting-edge technology, performance, and design to provide an unparalleled driving experience. But owning such a futuristic vehicle requires more than just purchasing a car – it’s about ensuring you have a reliable partner to help you navigate the world of electric mobility with ease. This is where ElecTree® comes in.
#Mahindra XUV 400 EV#Mahindra XUV 400 Electric Car#Trusted EV Support Service#EV Maintenance and Servicing#Electric Vehicle Charging Solutions#EV Roadside Assistance#Sustainable Electric Vehicles#Electric Car Support Provider#Mahindra Electric Car Services#ElecTree EV Services#EV Ownership Guide#Charging Infrastructure for EVs#Eco-Friendly Driving
0 notes
Text

The concept of urban mobility is evolving rapidly, driven by the need for sustainable transportation and green mobility. Traditional gasoline-powered vehicles are giving way to electric alternatives, heralding a revolution in how we navigate our cities. The rise of electric vehicles is not just a trend but a fundamental shift towards cleaner, more efficient forms of transport. Companies like Calon EV are at the forefront, offering a range of electric scooters, e-bikes, and other clean energy vehicles.
Do Visit: Navigating the Streets in Style: Exploring the Latest Electric Smart Vehicles
#electric smart vehicles#urban mobility#Calon Electric Vehicles#electric scooters#e-bikes#green mobility#eco-friendly commuting#electric vehicle innovation#sustainable transportation#electric motorcycle revolution#electric bike sharing#clean energy vehicles#urban electric mobility
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes