#eastern european national dress
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Girl from Veľký Lom. Karel Plicka. Slovakia. 1928. Slovenská národná galéria, SNG
#slovakia#eastern europe#early 20th century#Karel plicka#eastern european national dress#slovakian national dress
236 notes
·
View notes
Text

Postcard of a Ukrainian woman. Pre-1917.
#ukrainian history#vintage ukraine#old postcard#folk costume#ukraine#slavic#slavic culture#eastern europe#vintage postcards#postcard#national dress#early 20th century#european culture#1910s
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
"palestine was never a country in the first place!"
really?
explain my dad's PALESTINIAN birth certificate.
explain my dad and his parents PALESTINIAN passports.
explain why my grandparents still have PALESTINIAN currency, issued in the 1920s and 30s.
explain our name on the maps. explain our textile fame. explain our influence on european and middle eastern fashion for centuries.
explain our customs, our nations dress, fabrics, foods, dances, beliefs.
explain our caananite ancestry, how the land of caanan was called palestina by the ancient romans, that caanan, palestine, and judea were the names of the same country, just by other people.
#palestine#falasteeni#falasteen#free palestine#free gaza#free west bank#isntreal#israhell#jerusalem#bethlehem#tel aviv#'tel aviv'#you mean:#yaffa#?#fuck israel#anti zionisim
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
https://www.tumblr.com/thebaconsandwichofregret/189924928150/comepraisetheinfanta-thebaconsandwichofregret
whenever i see people rbing the op without the additions i die a little inside so i thought you should have a go at debunking it 🫠
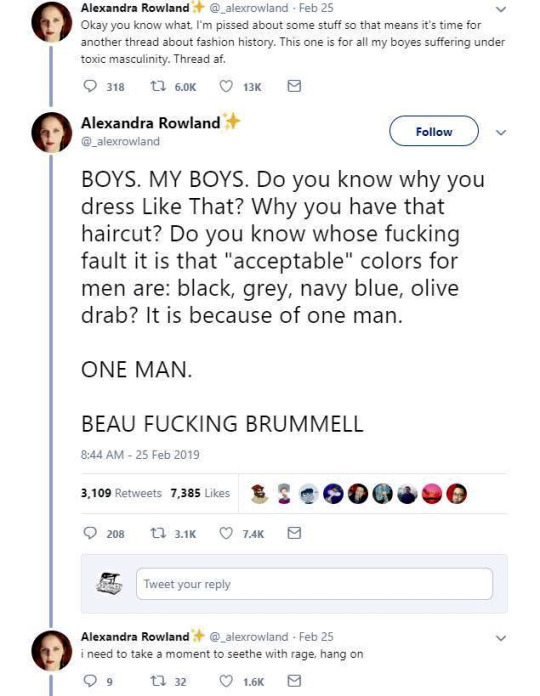


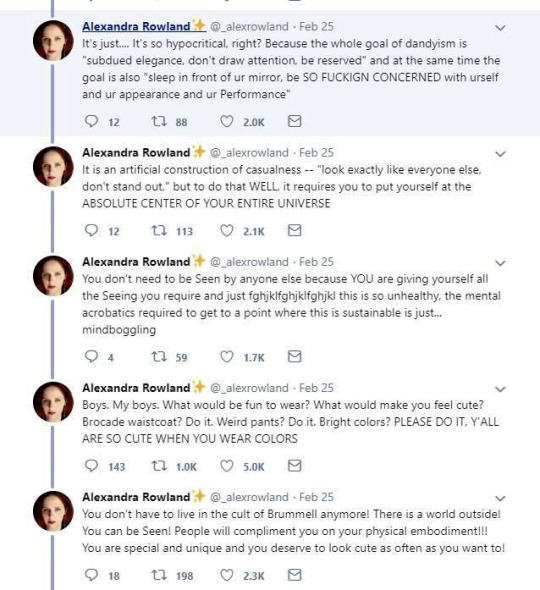
So these are the tweets from the post. I had blissfully not come across it before. This is one of the weirdest takes I have ever seen. It's amazing to see these fashion history takes that are so boldly and confidently wrong and inaccurate.
It's honestly hilariously ignorant to think that a massive cultural and societal shift that took couple of centuries was all because of one guy. It's so reductive and even goes to the great man territory to pick one person to blame for something like this that really had much more broad and complex reasons than "a guy did it". It's stressed in this tread that Beau Brummell was not noble or gentry and "just some guy", so how would he single-handedly change the fashions and concept of masculinity of the whole western world? He was a London socialite, it's not like most of his contemporaries in continental Europe knew about him. Like maybe the French, but does anyone really believe people in Eastern-Europe or Nordic countries or the Mediterranean knew about? Not to mention places like US. Yet everyone dressed like that in his lifetime, so how could his influence reach so far so quickly? Not even kings and queens could so directly and massively shift the fashions. So in the face of it the whole claim is ridiculous, but it's also full of inaccuracies.
The shift from Rococo fashion to regency fashion was extremely stark and quick in both men and women's fashion, but it happened during 1780s and 1790s, before Beau Brummell became a well known figure in the London society (he was born in 1778 and became well-known in the society after his military career, during which he befriended the Prince of Wales, around the end of 1790s). Here's first an example from 1780s and then from 1793-94 and 1797.



The one from 1780s still has some Rococo elements like the wig, but it's already much more toned down and the coat is already turning from frock coat to a tail coat. It's an example of the more casual men's countryside dress from the period. The court dress was still quite elaborate, though also toned down from the 1770s. But there's a big shift when it comes to the examples from 1790s. They are unmistakably Regency fashion. All of these example are French too. I'm sure these people had no idea and gained no influence from an unknown middle class English officer. So what did actually happen? Well, I'm pretty sure the French Revolution in 1789 had a little bigger impact on the European society and fashion than Beau Brummell.
I'm not going to go too deep into this, since I'm working on an in depth post about the masculinity and fashion in the modern era and I go into detail about how the French Revolution had a massive part in shaping them. But the short version is that the French revolutionaries rejected the elaborate fashions of the Rococo French nobility (in both men and women's fashion) as those over the top fashions stood as symbols of the excess wealth of the nobility and the extreme wealth gap. This is also why the high fashion was getting toned down thorough the 1780s before the Revolution. The anger towards the ruling class was mounting at the time and it encouraged the nobility to try to act a little more palatable in their aesthetics to maybe appease the angry people without doing any actual change to address the wealth gap and the centralization of power.
The revolutionaries looked for ideal masculinity and femininity elsewhere then. To contrast themselves against the ruling class, they looked to the antiquity and it's simplicity as well as the peasantry and the country gentleman fashion. Romanticism was the driving force behind the artistic expression of the Revolution. It weaved nationalism to the class struggle that was at the core of the revolutionary movement. So the Revolution was not just the working class and peasantry against the ruling class, but the French People against the nobility. That's how the bourgeois was able to align themselves with the working class and peasants. This is when physical labour, militarism, dominance and leadership really became intrinsically attached to masculinity, as the ideal man of the revolutionaries was a working peasant, who with military might took the the power back to the people from the nobility. The democracy would not last long, but it's not a mistake that only men could vote under the new democracy after the Revolution was won. It's also not a mistake that even when the post-Revolution France eventually abolished slavery (but not without some push-back first and a couple of slave revolts to force their hands) they didn't give most people of color rights to vote. Since colonialism whiteness had become intrinsic part of masculinity and femininity to dehumanize everyone else, and the new form of masculinity and femininity born out of the Revolution did not contest that. In fact the Enlightenment philosophy that had laid the ground work for the Revolution and the Romantic movement and it's nationalism that were driving force in it, in no way contested colonialism or it's white supremacy. In fact Enlightenment aimed to rationalize those things. Which is why the power in the new democracy went to the (mostly) white men.
These elements were in the new men's fashion too. Nationalism, the idealization of militarism, romanticization of peasantry and antiquity were basis of the fashion. Because antiquity was seen as the origins of democracy and the so called Western Civilization, that made it, and especially Antique Rome with it's militaristic connotations, perfect inspiration for the Revolutionary France. The short hairstyle was inspired from the Roman fashion seen in statues. The fashionable tail coat was influenced by military uniforms and the short jackets of the working class. The long trousers also came from working class dress. Here's examples of the revolutionary fashion of commoners, first from 1792 and then around 1790.
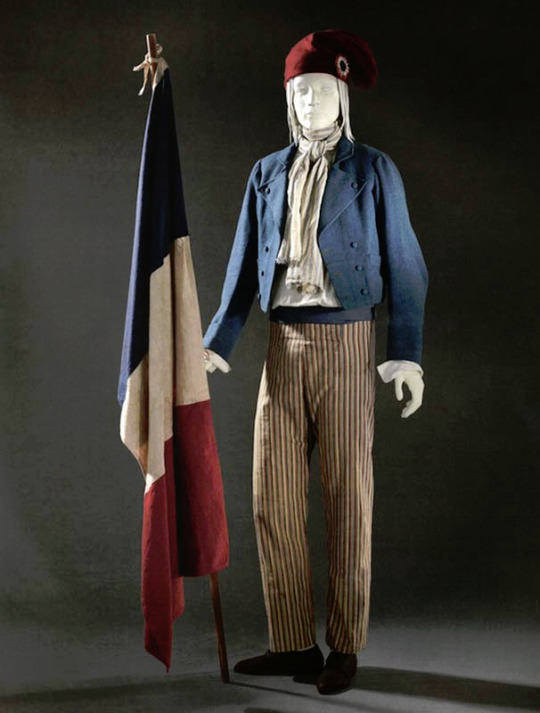


To be very clear, the revolutionaries were not a single entity with single ideology. They were collection of movements, who were united in their shared desire to overthrow the ruling class and establish some sort of democracy. But inside the movement were much more radical factions than what eventually ended in power after the French nobility. Socialists, abolitionists, feminists, slaves and others also fought for the Revolution and there was a lot of internal struggle too. Romantic movement was also very varied and contained extremely nationalistic elements as well as outright socialist elements.
It's important to note that the 18th century Rococo fashion was never as extreme elsewhere in the world as it was in France, so the change from Rococo to Regency style wasn't as stark elsewhere. If you put the most elaborate French court fashions of mid 1700s and Beau Brummell's style next to each other the difference is certainly massive, but fashion for men as well as women was through 18th century much more restrained and somber in England. Here's an English example from 1755-65 and for comparison a French example from 1755.
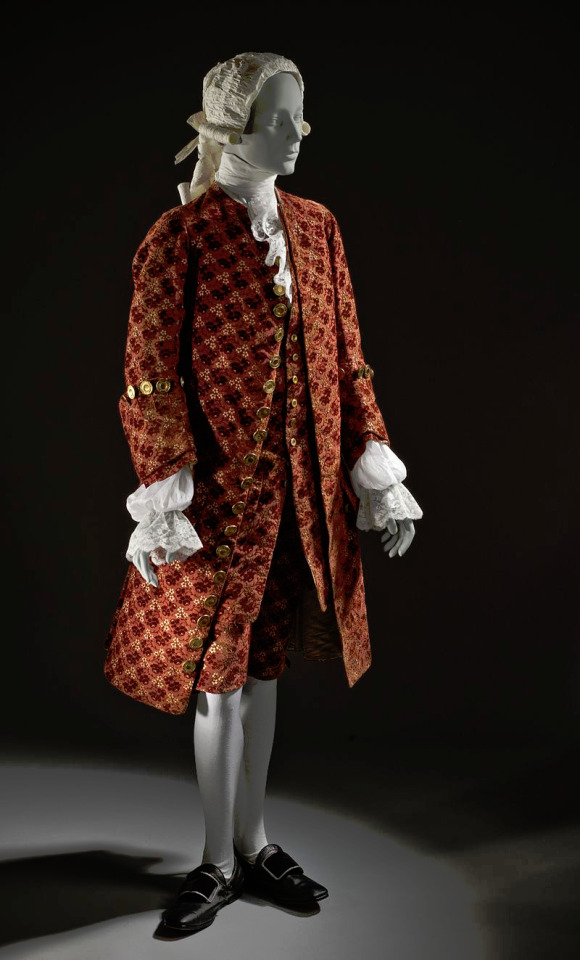


In fact as the tensions were rising in France the upper class begun to adopt the more toned down English styles. After the Revolution the new Republican styles would spread to Britain too. In Britain though Romanticism had a more pronounced effect as it stayed firmly monarchist. Therefore the English fashion was especially influenced by the styles worn by country side gentlemen.
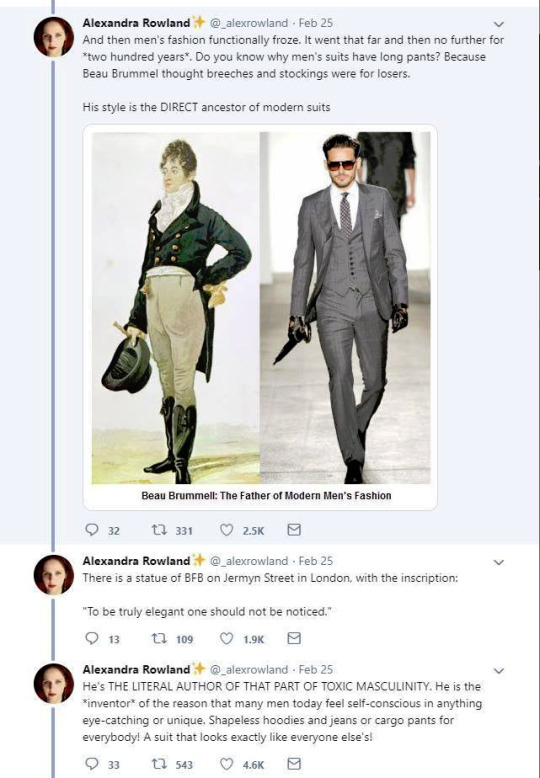
There's another claim in the thread that fully fails to understand the broad implications of fashion and societal gender and how these things change and evolve. It's the claim that Beau Brummell created the modern men's suit and he's the reason the suit has long trousers. We already went through how long trousers initially got into men's fashion and it was not him. But the writer is not wrong in saying that Beau Brummell's outfit in this picture is a direct ancestor of modern men's suit. It is.

But you know what else is a direct ancestor of men's suit? This.
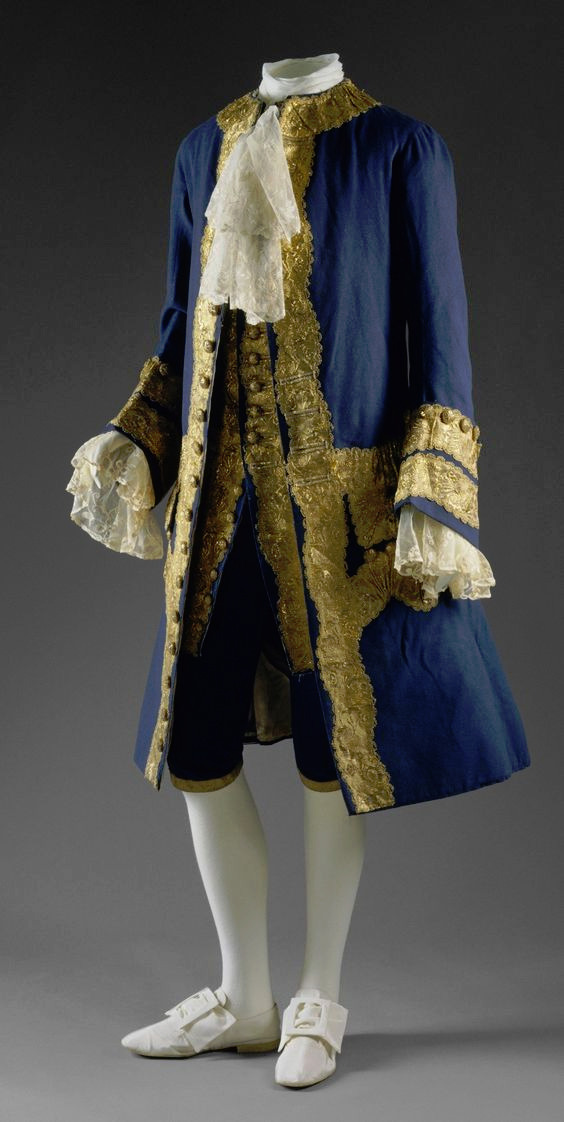

The modern three piece suit has it roots as far as in late 17th century. Before suit men wore doublets, hose and jerkins, where the sleeveless piece, jerkin, was on top of doublet. Aside from hose, these were also items women used and the fashions for men and women resembled in style and construction each other much closer than after the suit took over (as seen in these examples from 1630s). However the distinction between men and women's fashion had started to grow much earlier. A big shift that happened during the 16th century was that men stopped wearing skirts. Men and women wore the same garments for centuries before that. The styles and silhouettes for men and women had some differences (the skirts were often shorter for men for example) but they were parallel to each other. I wrote a whole very long post about how skirts stopped being acceptable for men. In it I write about how the shift in men's fashion was part of the large shift from feudalism to colonialism and capitalism, that needed a new hierarchy to justify the new system after the previous divinely justified feudal hierarchy was no longer an option. The new hierarchy was white supremacist patriarchy and therefore needed a clearer distinction between white men and white woman, that would also help distinct white people from the racialized people.


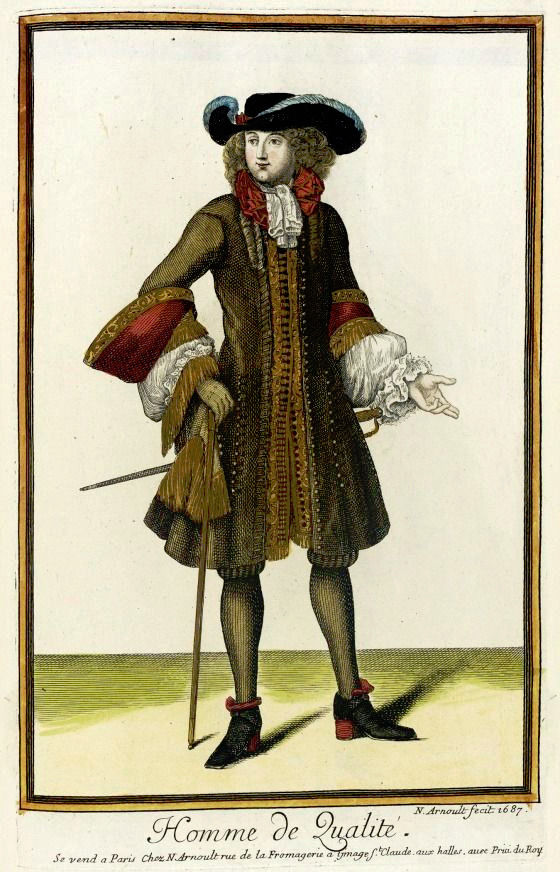
But such fundamental changes in the societal structure and culture are long processes. The process was continuing in the latter half of the 17th century, when Orientalism first became very popular. Orientalism is the dehumanization and fetishization of Asia and North-Africa, and it was born as the European colonial project was properly getting going in Asia. Colonialism in Asia and North-Africa took a little different form. I suspect it was because it was not that long ago, when Europeans had felt inferior to many of the peoples and empires in Asia and North-Africa, which they had always had much closer relationships with than the rest of Africa and certainly the Americas. I think that's why Orientalism is such a mix of coveting Asian and North-African cultures and bodies in a very fetishistic ways, while also demeaning and diminishing them. Nevertheless, Orientalism had a huge impact on European fashion in late 17th century. Both the way men and women's clothing was made after that to this day was strongly impacted by Orientalism. The coat and waistcoat combination was an adaptation of Turkish fashion. The three piece suit became popular in 1670s and fully took over men's fashion in 1680s (an example from 1687). The cravat was also adopted around the same time to men's wear from a light cavalry mercenary army in the Habsburgian Empire known as the Croats or Cravats. They were mainly Croatian, which to Western European was almost "Oriental" due to their proximity to Asia and Turkey in particular, and therefore the popularization of cravats as a fashion item was also influenced by Orientalism. Orientalist fashion encompasses the paradoxical nature of Orientalism itself; the Europeans coveted "the Orient" so they bastardized their fashions to construct a gender binary that left out the people who originated those fashions.

The Regency three piece suit also has all the same elements as the suit 150 years earlier, the individual pieces had just evolved into different cuts and silhouettes. The construction and the basic elements have stayed pretty similar to this day.
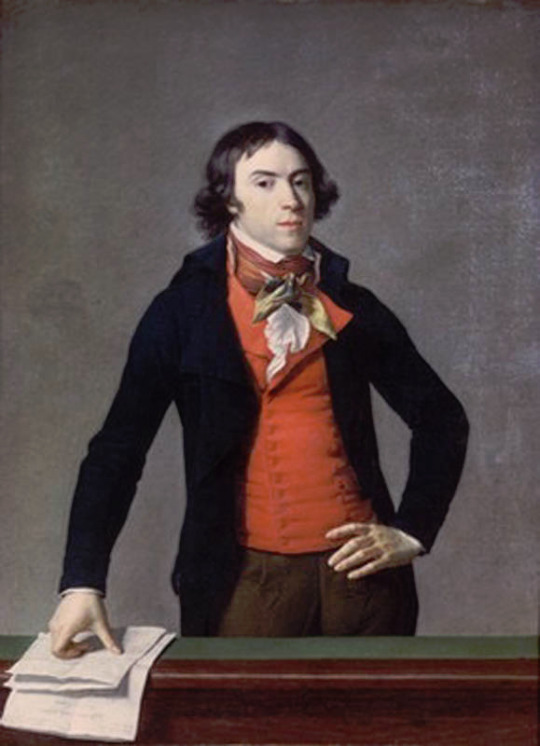
My point is not to in any way deny Beau Brummell's influence on Regency fashion. He was the most influential fashion icon for men in his era after all. I hope this just made it very clear that these bigger changes are not about individual people but much larger shifts and movements in society and culture. His actual influence was popularizing some of the English countryside styles, that were already part of casual fashion, as more formal fashion in the London high society, making extremely elaborate cravats into the fashionable items of the day and becoming the image of the English dandy.
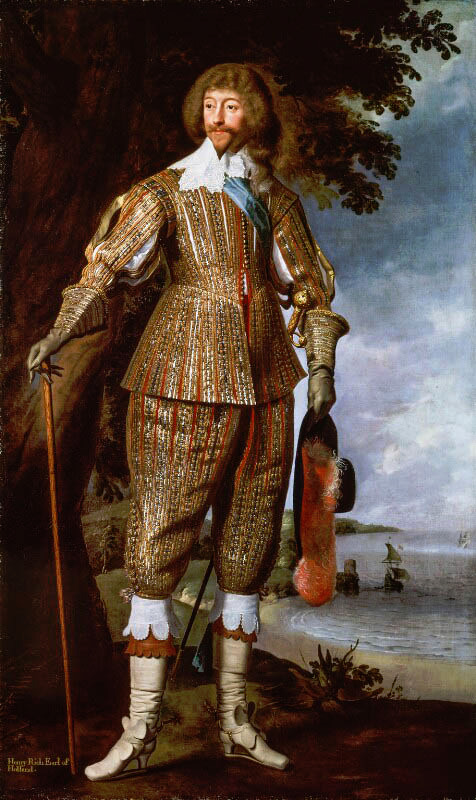
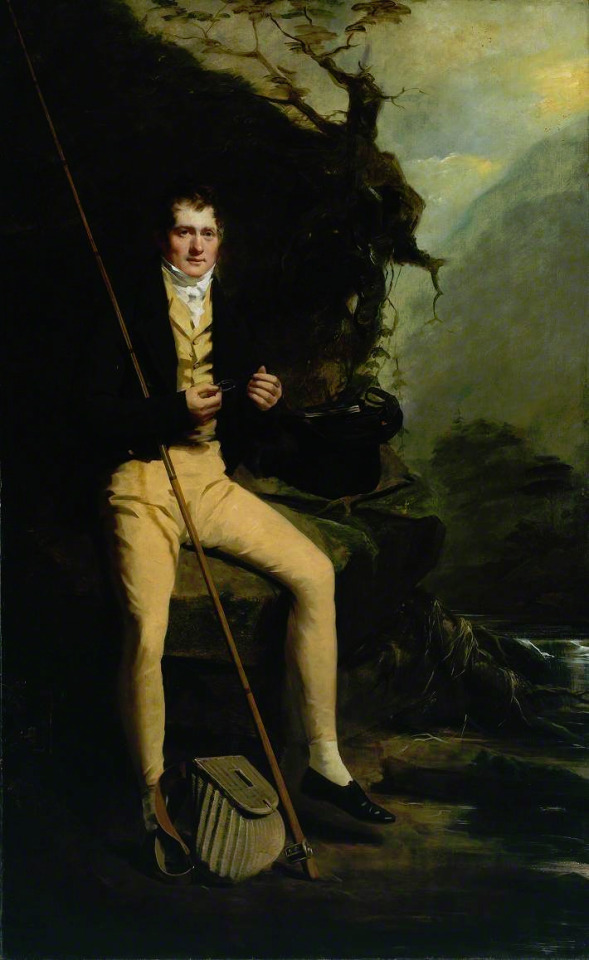
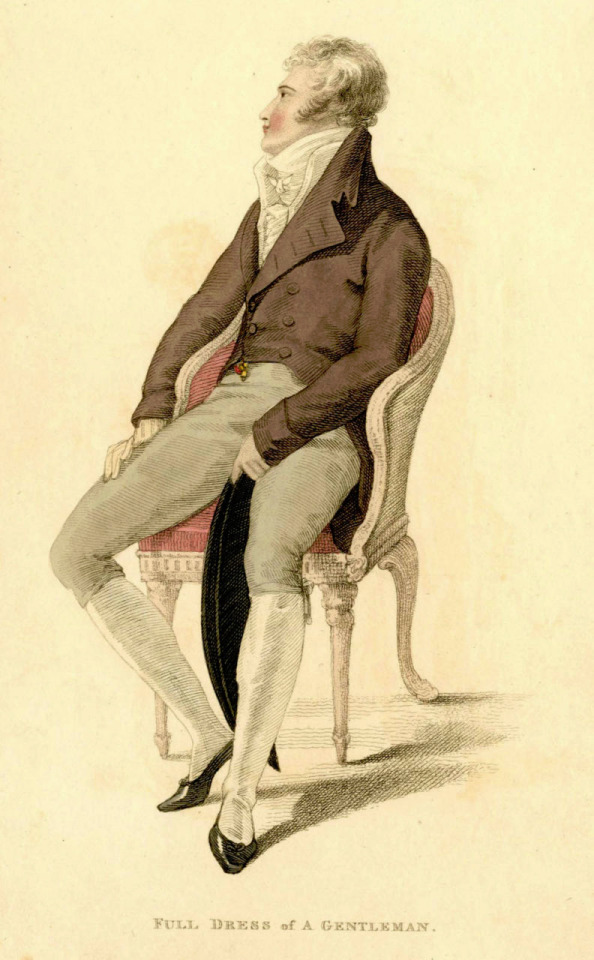
The picture of him above shows him the typical English countryside suit with dark blue tail coat, white cravat and light pantaloons with polished hessian boots. He helped to make the outfit and pantaloons in general fashionable. Breeches would stay as the formal leg wear for some a decade still, till young fashionable men would start to use black or gray pantaloons in formal events too. Pantaloons, which originated from military wear, were very fitted, basically similarly constructed as breaches but long. The trousers, which were looser than pantaloons, had their moment in France during the Revolution, but because of their Revolutionary and working class association, they didn't at first pick up in the high society, especially in Britain, until 1810s. They stayed as casual fashion through the Regency Era and only started gaining formal status in 1820s and 1830s. Beau Brummell is credited for inventing or at least popularizing trousers that have strap to go under the foot in order to keep them straight. Here's first a painting from of a gentleman in a very country style emphasized by the setting. Then a illustration from 1810 of a full formal dress with breeches and a fashion plate from 1817 of day wear with trousers.



The thread also misses what dandy really was. Dandy was the embodiment of the middle class social mobility of the modern era. He was the "self-made man", the fashionable middle class and the new celebrity of a post-feudal era. He dressed in refined fashionable countryside middle class clothing and was celebrated for his style and refinement, not for his birth. Ironically though, there was a distinct reactionary quality to the Regency dandy. After all dandy did not embody social equality, but mobility. He was the ideal man of the capitalist hierarchy. A bit of dilemma for the dandy was that being extremely fashionable was central to the dandy, but after the French revolution being too fashionable and too concerned about looks had been associated with the aristocracy and was now therefore unmanly. Which is why dandy quickly came to be seen as effeminate. There is a lot of satiric cartoons from the time period that make fun of dandies and their preoccupation with fashion and looks. Here's couple from around 1810s.
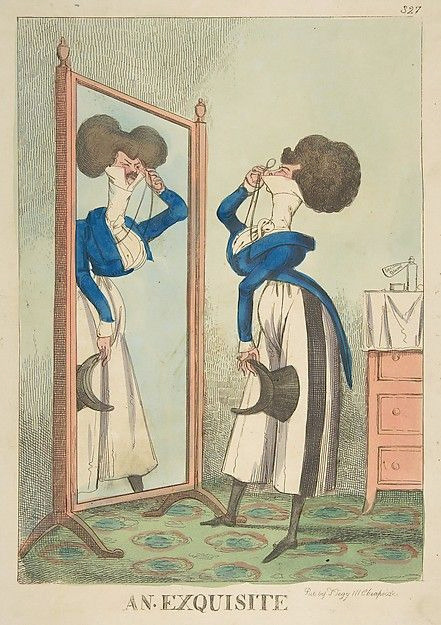



In conclusion it's pretty ridiculous to say modern men's fashion was all created by one guy. The real reason why men's formal suit (and to be clear more colorful and elaborate styles have come and gone from men's informal fashion during that time) has been what it is for more than hundred years is because much bigger changes, like capitalism, colonialism, Orientalism and white supremacist patriarchy.
#fashion history#dress history#history#regency fashion#historical fashion#men's historical fashion#18th century fashion#answers#anon
613 notes
·
View notes
Text

Happy Pride Month and (very belated) Solarpunk Aesthetic Week! I wanted to redesign my longtime OCs, so I decided to give them a thematic twist!
Self-indulgent details about their designs under the cut:
⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻
From left to right:
Mia Based on the romantic/cottagecore style, and incorporating aspects of Eastern/Central European folk dresses, such as the Czech kroj. Her vest is made from recycled overalls and excess fabric from her apron. Her natural motif is fungi -- her bow and earrings are amanita mushrooms (if you squint, her skirt looks like one too), and the frills on her collar + sleeves are chanterelles!
Clyde He's a bohemian kinda guy, so I kept his silhouette relaxed and unstructured + harem pants + accessories. The exception is his jacket, a union of 3 different garments made to loosely resemble traditional Indian clothing like the achkan. His natural motif is the sun - hence the warm tones, which is contrasted with splashes of teal, the colour of his aura (its a fictional superpower thing).
Glace His style is more preppy/academia - turtlenecks and sweaters are his type, so I gave him 3! Sewn together in a visible mending-esque style (inspired by tumblr solarpunks and their fashion projects)! His palette is taken from the mlm flag, and there's subtle elements of a Korean hanbok - his collar, sleeve shape, sash and tassel. Rips in his pants are covered by cloud patches (his motif), all dyed to match the aesthetic!
Simmer Her thing is streetwear with a cultural twist - her top combines a bomber jacket and a Chinese qipao/cheongsam. Her detachable sleeves are extended via sewn-on zippers (useful as her powers generate a lot of heat)! Her motif is the phoenix, with patterns on her shirt and collar, hand-decorated using the batik method. Her hair streaks are inspired by stripes on a tiger - Malaysia's national animal.
Axis She's all about the y2k aesthetic, with translucent tights and a hoodie stylishly revamped to form a super crop top + a figure-hugging bodysuit. Her design is inspired by indigenous Andean fashion, such as the Ecuadorian pollera, which her skirt might be repurposed from. Her motif is butterflies, as seen in her earrings, the shape of her bodysuit, and the wing-like curves of her skirt.
Piper Initially wanted a punk-ish vibe for him but he might be a bit too cute now oops! His jacket is a mashup of 3 different pieces, and his jeans are a patchwork of denim. He's got iconic looks from French fashion (beret and scarf), as well as some African designs (the vertical pattern I referenced looked like plant cells, but also like binary code? I thought it was so on theme)! His motif is obviously plants of all types!
⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻
Thank you for checking this out (especially if you got this far)!!! ♡♡♡
#art#artists on tumblr#character design#pride#solarpunk#fashion#culture#oc#wish i couldve finished this in time for solarpunk aesthetic week but. drawing is hard ;;#maybe i'll render it in the future#also! im not an expert on cultural clothing so please correct me if i got anything wrong! still learning!#roobiedoodle#the leftoverse#tl mia#tl clyde#tl glace#tl simmer#tl axis#tl piper
119 notes
·
View notes
Text
In February 1994, in the grand ballroom of the town hall in Hamburg, Germany, the president of Estonia gave a remarkable speech. Standing before an audience in evening dress, Lennart Meri praised the values of the democratic world that Estonia then aspired to join. “The freedom of every individual, the freedom of the economy and trade, as well as the freedom of the mind, of culture and science, are inseparably interconnected,” he told the burghers of Hamburg. “They form the prerequisite of a viable democracy.” His country, having regained its independence from the Soviet Union three years earlier, believed in these values: “The Estonian people never abandoned their faith in this freedom during the decades of totalitarian oppression.”
But Meri had also come to deliver a warning: Freedom in Estonia, and in Europe, could soon be under threat. Russian President Boris Yeltsin and the circles around him were returning to the language of imperialism, speaking of Russia as primus inter pares—the first among equals—in the former Soviet empire. In 1994, Moscow was already seething with the language of resentment, aggression, and imperial nostalgia; the Russian state was developing an illiberal vision of the world, and even then was preparing to enforce it. Meri called on the democratic world to push back: The West should “make it emphatically clear to the Russian leadership that another imperialist expansion will not stand a chance.”
At that, the deputy mayor of St. Petersburg, Vladimir Putin, got up and walked out of the hall.
Meri’s fears were at that time shared in all of the formerly captive nations of Central and Eastern Europe, and they were strong enough to persuade governments in Estonia, Poland, and elsewhere to campaign for admission to NATO. They succeeded because nobody in Washington, London, or Berlin believed that the new members mattered. The Soviet Union was gone, the deputy mayor of St. Petersburg was not an important person, and Estonia would never need to be defended. That was why neither Bill Clinton nor George W. Bush made much attempt to arm or reinforce the new NATO members. Only in 2014 did the Obama administration finally place a small number of American troops in the region, largely in an effort to reassure allies after the first Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Nobody else anywhere in the Western world felt any threat at all. For 30 years, Western oil and gas companies piled into Russia, partnering with Russian oligarchs who had openly stolen the assets they controlled. Western financial institutions did lucrative business in Russia too, setting up systems to allow those same Russian kleptocrats to export their stolen money and keep it parked, anonymously, in Western property and banks. We convinced ourselves that there was no harm in enriching dictators and their cronies. Trade, we imagined, would transform our trading partners. Wealth would bring liberalism. Capitalism would bring democracy—and democracy would bring peace.
After all, it had happened before. Following the cataclysm of 1939–45, Europeans had indeed collectively abandoned wars of imperial, territorial conquest. They stopped dreaming of eliminating one another. Instead, the continent that had been the source of the two worst wars the world had ever known created the European Union, an organization designed to find negotiated solutions to conflicts and promote cooperation, commerce, and trade. Because of Europe’s metamorphosis—and especially because of the extraordinary transformation of Germany from a Nazi dictatorship into the engine of the continent’s integration and prosperity—Europeans and Americans alike believed that they had created a set of rules that would preserve peace not only on their own continents, but eventually in the whole world.
This liberal world order relied on the mantra of “Never again.” Never again would there be genocide. Never again would large nations erase smaller nations from the map. Never again would we be taken in by dictators who used the language of mass murder. At least in Europe, we would know how to react when we heard it.
But while we were happily living under the illusion that “Never again” meant something real, the leaders of Russia, owners of the world’s largest nuclear arsenal, were reconstructing an army and a propaganda machine designed to facilitate mass murder, as well as a mafia state controlled by a tiny number of men and bearing no resemblance to Western capitalism. For a long time—too long—the custodians of the liberal world order refused to understand these changes. They looked away when Russia “pacified” Chechnya by murdering tens of thousands of people. When Russia bombed schools and hospitals in Syria, Western leaders decided that that wasn’t their problem. When Russia invaded Ukraine the first time, they found reasons not to worry. Surely Putin would be satisfied by the annexation of Crimea. When Russia invaded Ukraine the second time, occupying part of the Donbas, they were sure he would be sensible enough to stop.
Even when the Russians, having grown rich on the kleptocracy we facilitated, bought Western politicians, funded far-right extremist movements, and ran disinformation campaigns during American and European democratic elections, the leaders of America and Europe still refused to take them seriously. It was just some posts on Facebook; so what? We didn’t believe that we were at war with Russia. We believed, instead, that we were safe and free, protected by treaties, by border guarantees, and by the norms and rules of the liberal world order.
With the third, more brutal invasion of Ukraine, the vacuity of those beliefs was revealed. The Russian president openly denied the existence of a legitimate Ukrainian state: “Russians and Ukrainians,” he said, “were one people—a single whole.” His army targeted civilians, hospitals, and schools. His policies aimed to create refugees so as to destabilize Western Europe. “Never again” was exposed as an empty slogan while a genocidal plan took shape in front of our eyes, right along the European Union’s eastern border. Other autocracies watched to see what we would do about it, for Russia is not the only nation in the world that covets its neighbors’ territory, that seeks to destroy entire populations, that has no qualms about the use of mass violence. North Korea can attack South Korea at any time, and has nuclear weapons that can hit Japan. China seeks to eliminate the Uyghurs as a distinct ethnic group, and has imperial designs on Taiwan.
We can’t turn the clock back to 1994, to see what would have happened had we heeded Lennart Meri’s warning. But we can face the future with honesty. We can name the challenges and prepare to meet them.
There is no natural liberal world order, and there are no rules without someone to enforce them. Unless democracies defend themselves together, the forces of autocracy will destroy them. I am using the word forces, in the plural, deliberately. Many American politicians would understandably prefer to focus on the long-term competition with China. But as long as Russia is ruled by Putin, then Russia is at war with us too. So are Belarus, North Korea, Venezuela, Iran, Nicaragua, Hungary, and potentially many others. We might not want to compete with them, or even care very much about them. But they care about us. They understand that the language of democracy, anti-corruption, and justice is dangerous to their form of autocratic power—and they know that that language originates in the democratic world, our world.
This fight is not theoretical. It requires armies, strategies, weapons, and long-term plans. It requires much closer allied cooperation, not only in Europe but in the Pacific, Africa, and Latin America. NATO can no longer operate as if it might someday be required to defend itself; it needs to start operating as it did during the Cold War, on the assumption that an invasion could happen at any time. Germany’s decision to raise defense spending by 100 billion euros is a good start; so is Denmark’s declaration that it too will boost defense spending. But deeper military and intelligence coordination might require new institutions—perhaps a voluntary European Legion, connected to the European Union, or a Baltic alliance that includes Sweden and Finland—and different thinking about where and how we invest in European and Pacific defense.
If we don’t have any means to deliver our messages to the autocratic world, then no one will hear them. Much as we assembled the Department of Homeland Security out of disparate agencies after 9/11, we now need to pull together the disparate parts of the U.S. government that think about communication, not to do propaganda but to reach more people around the world with better information and to stop autocracies from distorting that knowledge. Why haven’t we built a Russian-language television station to compete with Putin’s propaganda? Why can’t we produce more programming in Mandarin—or Uyghur? Our foreign-language broadcasters—Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty, Radio Free Asia, Radio Martí in Cuba—need not only money for programming but a major investment in research. We know very little about Russian audiences—what they read, what they might be eager to learn.
Funding for education and culture needs rethinking too. Shouldn’t there be a Russian-language university, in Vilnius or Warsaw, to house all the intellectuals and thinkers who have just left Moscow? Don’t we need to spend more on education in Arabic, Hindi, Persian? So much of what passes for cultural diplomacy runs on autopilot. Programs should be recast for a different era, one in which, though the world is more knowable than ever before, dictatorships seek to hide that knowledge from their citizens.
Trading with autocrats promotes autocracy, not democracy. Congress has made some progress in recent months in the fight against global kleptocracy, and the Biden administration was right to put the fight against corruption at the heart of its political strategy. But we can go much further, because there is no reason for any company, property, or trust ever to be held anonymously. Every U.S. state, and every democratic country, should immediately make all ownership transparent. Tax havens should be illegal. The only people who need to keep their houses, businesses, and income secret are crooks and tax cheats.
We need a dramatic and profound shift in our energy consumption, and not only because of climate change. The billions of dollars we have sent to Russia, Iran, Venezuela, and Saudi Arabia have promoted some of the worst and most corrupt dictators in the world. The transition from oil and gas to other energy sources needs to happen with far greater speed and decisiveness. Every dollar spent on Russian oil helps fund the artillery that fires on Ukrainian civilians.
Take democracy seriously. Teach it, debate it, improve it, defend it. Maybe there is no natural liberal world order, but there are liberal societies, open and free countries that offer a better chance for people to live useful lives than closed dictatorships do. They are hardly perfect; our own has deep flaws, profound divisions, terrible historical scars. But that’s all the more reason to defend and protect them. Few of them have existed across human history; many have existed for a time and then failed. They can be destroyed from the outside, but from the inside, too, by divisions and demagogues.
Perhaps, in the aftermath of this crisis, we can learn something from the Ukrainians. For decades now, we’ve been fighting a culture war between liberal values on the one hand and muscular forms of patriotism on the other. The Ukrainians are showing us a way to have both. As soon as the attacks began, they overcame their many political divisions, which are no less bitter than ours, and they picked up weapons to fight for their sovereignty and their democracy. They demonstrated that it is possible to be a patriot and a believer in an open society, that a democracy can be stronger and fiercer than its opponents. Precisely because there is no liberal world order, no norms and no rules, we must fight ferociously for the values and the hopes of liberalism if we want our open societies to continue to exist.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
People often say that LGBTQIA+ people doesn't exists in Muslim/Islamic World. Nowdays many muslims argued that LGBTQI+ rights are contrary to their traditional beliefs, homosexuality shouldn't be decriminalized in their native countries,because it goes against their moral values,cultural norms & social mores,[...].
But previous Islamic history & muslim traditions had wide range of acceptance of sexual & gender diversity.In those days Muslim communities weren't so bigotted, heterosexist,homophobic/transphobic, heteropatriarchal.Colonialism,communism,dictatorship,islamist regime justified the prejudices against queer folks in Muslim world, not Islam itself.
In 1854, Ottoman empire legalised consensual homosexuality in parts of Middle East,North Africa,Eastern Europe & West Asia.Notably Mughal,Mamluk,Khilji,Sayyid, Pathan,Lodi,Abbasid,Safavid,Qajar,Ottoman empire gave privileges to gender variants and eunuchs.Even it is also said that Aghawas (a designation for trans feminine, effeminate,agender/eunuch & intersex) were served as guardian of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH)'s mosque & tomb.There had been numerous homoerotic paintings & same sex romantic poetries in medieval islamic era.In pre-modern muslim societies ghazals (sufi spiritual song) has direct references with queerness.In some sufi traditions cross-dressing, gender fluidity was considered as sacred.
Since 18th & 19th century almost all muslim countries were colonized or being influenced by European Orthodox Christians.Europeans pushed their moral codes,heteropatriarchal system & gender roles upon muslim communities.But western colonialism was unable to erase queerness & love from asia.In Pakistan,Bangladesh,India & some parts of Afghanistan, Hijras (designation term for trans feminine,trans woman,gender diverse,intersex) are still exists.Hijras has recognition of third gender in Pakistan,India & Bangladesh.They have some civil rights in those countries mentioned.But Transgender people's livelihood in Afghanistan is very worst.Some Afghan trans people's lifestyles are very similar to Hijra/Khawaja Sara subculture. In central-asian muslim cultures gender vice-versa or variance are not uncommon.Bacha bazi or Bacha-bozi is practice where adult men get sexual services from young crossdressers and effeminates.
Waria, another transgender muslim community can be found in Indonesia.Waria transgenders has very limited rights comparing to Hijras.In South Sulawesi, Indonesia Bugis (a muslim tribe) recognized 5 genders: Oroané(masculine men), makkunrai (feminine women), Calalai (trans-masculine or masculine women), Calabai (trans-feminine or feminine male), Bissu (androgynous or non-binary).The classification of the calabai,calalai, & bissu as third genders is disputed.These roles can also be seen as fundamental occupational and spiritual callings, which are not as directly involved in designations such as male and female.In pre-Islamic culture, Bissu were seen as intermediaries between the people and the gods.The Bissu are closely associated with the female yet androgynous moon goddess, as her spiritual offspring.Up until the 1940s, the Bissu were still central to keeping ancient palace rites alive, including coronations of kings & queens. Historically, Bissu have played an important role in other ceremonies as well,particularly in weddings and childbirth events.However today Bissu & Waria faces marginalization in their homeland due to rise of Political Islamism & Islamic Extremism .
Here is a list of Muslim/Islamic nations where homosexuality is not a criminal offense (technically):
Albania - Legal since Ottoman period.
Bosnia & Herzegovina - Legal since Ottoman period.
Kosovo - Legal since Ottoman period.
Azerbaijan - Legal since 1918 or 2000 (not sure).But state often arrests LGBTQ community members.
Northern Cyprus - Legal since Ottoman period,legal in modern northern cyprus since 2015.
Turkey - Legal since Ottoman period, legal in modern turkey since 1923.
Jordan - Legal since Ottoman period,legal in hashemite kingdom of jordan since 1951.
Bahrain - Legal since Ottoman period.
West Bank (Palestine) - Female homosexuality always been legal,male homosexuality is legal since 1951.
Gaza (Palestine) -Female homosexuality always been legal.
Lebanon - Legal since Ottoman period, legal in modern lebanon since 2018 (however the legal status of homosexuality is vogue)
Kazakhstan - Legal since 1997 (de facto),nationwide legal since 1998 (de jure).
Kyrgyzstan - Legal since 1998.
Egypt - Legal since Ottoman period.Although private consensual homosexuality is not criminalized by domestic laws.Commercial & adult consensual homosexuality is de-facto illegal since 1961.
Kuwait -Female homosexuality always been legal.
UAE - There's no explicit federal law against homosexuality.But commercial & non-commercial homosexuality is de-facto illegal.
Burkina Faso - always legal
Djibouti - always legal
Mali - legal since 1961
Mayotte - always legal
Niger - always legal
Guinea Bissau - legal since 1993.
Sierra Leone -Female homosexuality always been legal.
Uzbekistan - Female homosexuality always been legal in federal law.
Turkmenistan - Female homosexuality always been legal in federal law.
Tajikistan - legal since 1998.
Indonesia - Homosexuality never been a criminal offense until 2022.LGBTQI+ people often faced persecution by state & harassment.In 2022, Indonesian parliament passed a bill that outlaws all types of sexual relationships outside the traditional marriage.
Here is a list of Muslim/Islamic nations,where transgender & gender diverse people has rights:
Iran - Transgender individuals were officially recognized by the government, under condition of undergoing sex reassignment surgery, with some financial assistance being provided by the govt. for the costs of surgery, and with a change of sex marker on birth certificates available post-surgery since early 1980s. However, substantial legal and societal barriers still exist in Iran. Trans individuals who do not undergo surgery have no legal recognition and those that do are first submitted to a long and invasive process (including virginity tests, parental approval, psychological counseling that reinforces feelings of shame & inspection by the Family Court).
Bosnia and Herzegovina - Trans people may change their legal gender in Bosnia & Herzegovina after a sex reassignment surgery & other medical treatments.
Pakistan - Pakistan recognized Hijras as third gender in 2009. In 2018 Pakistan's parliament passed “The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act” which provides fundamental rights in health, education, government and security.
Lebanon - In late 1990s Lebanon allow sex reassignment surgery.In 2016 Lebanon court legally recognized a trans man as man.
Turkey - Transgender individuals were allowed to change their gender since 1988.However later Turkey adopted harsh policies for transgenders,required many pre–requisutes in order to be able to receive gender-affirming surgery. Transgender persons had to ask & be granted permission for the surgery,be at least 18 years of age,unmarried, & sterilized in order to receive gender-affirming surgery.
Jordan - Since 2014 jordan allow trans people to change their gender after a sex change operation.
Bahrain -Since 2008 Bahrain allow trans people to change their gender after a sex change operation.
Bangladesh - since 2013 Bangladesh recognized hijras & eunuchs as third gender.In 1975 Dr. Hosne Ara Begum became the first transsexual woman to be recognised as woman in Bangladesh.
Indonesia - Indonesia allows sex change operation for Warias & give limited rights for transgenders.
Kazakhstan - Since 2003, trans people allowed to change legal gender following sex change surgery,medical examinations, & sterilisation.
Kyrgyzstan -Transgender people allowed to change legal gender following sex reassigment surgery, medical treatments,sterilisation since 2014.
Tajikistan -Under Tajik law, trans people may change their legal gender on their passport if they provide a medical statement that they have undergone sex reassignment surgery. There has been 2 sex-change operations performed – the first one in 2001 and the second one in 2014.
UAE- allows intersex persons to undergoes a sex change surgery & change their gender.
Egypt - In 1988, a sunni Islamic Fatwa by Muhammad Sayyid Tantawy grants legal permission to perform gender affirming surgery. In Egypt, those who want to undergo the surgery must seek an approval from a gender reassignment review committee at the Medical Syndicate of Al-Azhar. But the committee has not convened since 2013, when Al-Azhar withdrew its member from the ccommission. Now, Egypt only perform sex reassignment surgery for intersex individuals with court approval.
Iraq - An Iraqi transsexual undergone a sex change surgery in 2018. The Iraqi Ministry of Interior supported country's first sex change operation. However, Iraq has harsh policies for trans individuals, required pre–requisites in order to be able to receive sex reassignment surgery. Since 2023 Iraq has prohibited sex change operations based on mere personal choices, one must have court approval and have to give medical reason for it.
#lgbtqi muslims#lgbtqia+ muslim#lgbtqia#queer#religious queer#queer rights#trans rights#trending#allah loves all#loveislove#muslim
56 notes
·
View notes
Note
do you have hcs of percabeth and fam doing things that are culturally greek but arent part of tHe aMeRcIcAn pErCePtIoN Of gReEkNeSs like food music dress social norms etc? or of things they do when they visit the old country?
anon i'm so sorry about the can of worms you've just opened but this is literally the backdrop of my dissertation so
the "american perception" (/western/european perception) of greece is (currently, anyway) closely associated with what we think of ancient greece (largely ancient athens, sometimes ancient sparta, occasionally ancient crete), but the Greek cultural perception of greece is, on the whole, extremely orthodox christian, specifically in opposition to both a) catholicism and b) islam, specifically in the ottoman empire. in the nineteenth century there was a MASSIVE political and cultural debate in the new nation state of modern greece over what they would present as their national mythology, split down the middle between ancient pagan greece and medieval christian byzantium, and also the years of ottoman occupation up until the revolution. there were some writers like constantine paparrigopolous who tried to bridge the gap between the two (he claimed that alexander's military campaigns were done in part to "prepare" the territory for the coming of christ lmao), but even this was partly in response to western european ideas about What Greece Even Is, specifically jakob phillip fallmerayer who wrote a very poorly-received (in greece) treatise about how the Great and Noble Ancients shared no dna with the current inhabitants of greece, who were all "tainted" by the slavs. because european racism
so, all that aside, what is culturally greek? in general, being christian. modern greek life is built around the church, and a lot of the things that aren't Ancient Greece that we think of as being Authentically Greek have their roots in orthodox christianity: icons, byzantine churches, lamb as a central foodstuff, etc. of course, much as they are loath to admit it, a lot of greek culture today also comes from ottoman occupation: national costume (fezzes, silk brocade), music (~oriental~ tonality, distinctly eastern instruments), and, again, food (coffee, baklava [with apologies to my ancestors]). and then there's just a bunch of stuff in modern 20th century greek culture that's just a big mishmash of the population reshuffle in the 1920s, as greece and turkey had a big population exchange (that occasionally dipped into ethnic cleansing). in athens specifically, you would have greek refugees from ALL OVER asia minor, but also the islands, the levant, northern greece, and other places in the balkans, all with their own distinct cultural traditions, and historical explanations for those traditions, especially with things like dance and folk song. AND THEN ALSO the traditions of the greek diaspora, esp in america
in the 1930s, as part of the metaxas dictatorship, greek cultural policy was in the process of hammering out what it meant to be "authentically greek," in a familiar combination of ancient pagan and orthodox christian, before metaxas' death, the entry of greece into wwii, and then the greek civil war and the dictatorship of the colonels, but they never quite... finished the process
to bring this all back to your question, i dont' know. it depends. i will often hc percy/thalia/nico as being more greek-looking than other demigods bc of the big three, and sometimes i dabble with sally being greek, but whether or not they are Actually Greek is something else (in canon, anyway; in aus this is an entirely different situation). THAT SAID, the two greek traditions i know for certain that percy participates in are making great food and loving his mother. which isn't even a strictly greek thing anyway. i can't even joke about him having the traditional greek breakfast of coffee and a cigarette bc i hc him hating coffee 😂
#anon#asks#anon i'm so sorry. anyway feel free to send me more questionsi f you want clarification on this
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fashion in Uroboros
A brief overview of the different styles of fashion within the IF's setting! It was going to be much longer than it is now, since I initially explained the reasoning I chose these... but I'll resist!
Note that the fashion is not aiming to be authentic. In fact, I've highlighted some of the different ways I've attempted to make these extremely different styles take influence from one another, and even modified them to make more sense thematically for the story.
The fashion is merely inspired, not necessarily accurate to the fashion they're inspired from. Realism isn't the goal, but I still want them to be somewhat convincing, and also cool-looking! I'll also add more thoughts towards the end on this note.
༺═──────────────
Southwestern Galaio - Takes inspiration from Rococo fashion, in part because its climate is similar to western Europe (oceanic climate). Extravagant and blindingly opulent, though I envision it as incorporating more naturalistic elements, such as birds and flowers into their design. However, their design also tend to be asymmetrical and large-scaled.

Portrait of Anastasia Ushakova by Ivan Kusjmitsch Makarov; painting by Lucius Rossi; and "The proposition" by Arturo Ricci
Western Galaio - Takes inspiration from Song Dynasty China, as it also has a humid subtropical climate. A time of prosperity as well, but I chose it over the Tang Dynasty because the designs are more simplistic. I wanted this region to be more muted, but still elegant in fashion compared to other regions. Not as flashy, and much less concerned about extravagant wealth. Though it's in Song style, I enlisted the help of an article to help me incorporate some western elements to it, such as lace and fans.

Lexie from Hanfu Story; Bleu from Hanfu Story; and Butterfly Dream from NewMoonDance!
Central Galaio (Part 1) - Humid continental climate. Closer to the southwest, their fashion reflects much of Rococo style as well, but with some modifications (no train for dresses, etc.). This is in reference to Catherine the Great's time, in which Russia had oriented itself towards European fashion (specifically, the Rococo style), but Catherine the Great dictated the fashion to be more Russian and instill national pride.

Catherine the Great by Fedor Rokotov, 1763
Central Galaio (Part 2) - Farther from the southwest and more towards the north, their fashion is much closer to Western Galaio. They still have elements of the southwest, but they have a strong emphasis on functionality and practicality, which the southwest appears to be fundamentally against.

hanfu by 瞳莞汉服 (left and center); photography by 松果sir and model @白川鹅 (right)
Central Galaio (Part 3) - There's a distinct region that is a cold desert. Here is inspired by Mongolian deel. It's thicker and has several layers to withstand the cold, compared to Western Galaio's clothing, which in contrast have lighter fabrics.

13th century Mongolian deel from Mongulai, founded by Telmen Luvsandorj
Eastern Galaio - Also a wealthy coastal region of Galaio. Mediterranean climate. They take inspiration from the extravagance of the southwest, but fashion is looser, free, and light. The colors are also more natural, like white, brown, blue, etc. rather than the entire spectrum of colors that the southwest and west enjoy.
Deities - Inspired by Edo period Japan, another period of flourishing economic growth. The fashion of the deities likely came from the fashion of a past time, rather than a reflection of current human fashion. Western and Central Galaio's clothing look similar to the kosode gods wear, perhaps because these regions are more rooted in tradition compared to Southwestern and Eastern Galaio. The major modification I made for the fashion of deities, however, is making it more unisex and more relaxed.

From Philadelphia Museum of Art; the Mary Griggs Burke Collection; and from asianhistory.tumblr.com
Additional Notes
I had tormented myself a lot over authenticity, but I realized the fashion can remain merely inspired, not directly referenced. I'm not actually trying to make a Walmart version of France or any of these cultures. However, I do hope that the admiration I have for these cultures shine through!
A lot of these come from periods of prosperity, the "golden ages". Galaio is beautiful and prosperous, but it obscures a deep ugliness within.
These may be subject to change, and won't be super prominent in the story itself. They merely gave me a general idea or silhouette of the kind of clothes people may wear. I think the most reference I'll give them within the IF is a general aesthetic of the clothes rather than specific details. Hence why they're merely inspired.
Thanks for reading thus far! :)
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Siam on the left, Czechoslovakia on the right.

(Operating in three different armies, the Czechoslovak Legion had three different uniforms, of which I had to exclude two to remain fair to Siam. I eventually settled on the one of the Russian army, which welcomed about 4x more Czechoslovak soldiers than the Italian and French armies).
The Kingdom of Siam was small and of few means, but the colonial pretenses of the European powers pushed it to affirm its authority. After declaring war in 1916, it sent out a Siamese Expeditionary Force of about 1,300 men which arrived in 1918. Dressed in a curious mix of Mills equipment and French helmets, their participation allowed Siam to have a say in the writing of the Treaty of Versailles and to no longer have to worry about the Allies' claims to its territory.
Czechoslovakia did not yet exist as a country when the Great War started, but its national identity was strong and alive within the Czechs and Slovaks who founded the Czechoslovak Legions which deserted Austria-Hungary's conscripted armies to fight with the Russian, Italian and French forces. Though they were too few to make a difference on the Western and Alpine fronts, their presence on the Eastern front forged their legend. Here they are wearing a standard Russian uniform, though, like the Siamese, they sport an Adrian helmet with personalised insignia which sets them apart.


Art on the right by Osprey Publishing.
46 notes
·
View notes
Text


Bulgarian woman from Smilevo (1931), Macedonian Bulgarian Woman (also known as Bulgarian woman from Smilevo) (1931)
Ivan Mrkvička
#and now for something completely different#bulgaria#bulgarian national dress#eastern europe#early 20th century#ivan mrkvička#jan vaclav mrkvicka#eastern european national dress#the two paintings are confusingly called by the same name sometimes#so they belong together#I'll do a slightly longer piece on mr mrkvicka at some point#he was a very interesting man who lived in very interesting times#macedonia#macedonian national dress
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Flag of the Cherokee Confederacy

This is the flag of the Cherokee Confederacy. It comes from a world where the Spanish Armada successfully conquered England in 1588. While England did eventually regain its independence, the Spanish conquest severely stunted England’s growth as a world power, and lead to greater political instability. As a result, England never became a demographic juggernaut during the colonization of North America. The lands that would have become the Thirteen Colonies are a patchwork of nations and colonies founded by numerous European nations. There are also several independent indigenous nations, such as the Cherokee Confederacy.
The Cherokee Confederacy also includes the Muskogee, Chickasaw, and Choctaw tribes. The Cherokee, as reflected by the name, were the founding tribe of the confederacy. The Cherokee Confederacy was one of the first indigenous nations of North America to implement westernization and industrialization programs. Today, most Cherokee dress in European-style clothing, but do wear traditional clothing on special occasions. Like most southern nations in eastern North America, the Cherokee historically practiced slavery. Slavery was formally abolished in 1885 as part of the modernization efforts. Racial divides and tensions still remain, but the Cherokee government has, in recent years, implement programs to help blacks integrate into Cherokee society.
The Cherokee legislature, known as the Tribal Council, is organized into a semi-parliamentary democracy, with a prime minister as the Head of Government, and a president as Head of State. The Cherokee Tribal Council is closer in style to the French National Assmbly, rather than to the English Parliament. The Cherokee Confederacy is centered around what would be western North Carolina, Tennessee, and the northern bits of Alabama, Mississippi, and Georgia. The indigenous republics of North America, being sovereign nations, did not suffer an equivalent of the Indian Removal Act.
Historically, the Cherokee Confederacy has been rivals with the Haudenosaunee Federation. However, in recent times the two nations have been putting their rivalries behind them. In terms of good relations, the Cherokee Confederacy has historically been an ally of New Neatherlands, which in located in Virginia. The various nations of North America have formed a European Union-style economic union, and there are hopes that this will eventually leads to a federation. There is a general spirit of good will and optimism. That said, North America still has a ways to go before its nation states become united.
The flag contains seven gold stars in the shape of the Big Dipper, or Ursa Major, on an orange field with a green border. Ursa Major is an important constellation to several tribes within the Cherokee Confederacy. It also symbolizes how the same night sky shine over the entire Cherokee Confederacy. Blue would seem a natural color choice, but the Cherokee picked orange instead. There is some debate about why this is. Popular belief says that it symbolizes the Cherokee Confederacy’s ties to New Netherlands. However, the Cherokee actually picked orange to contrast with the blue flags several other North American nations use. The green border is to offset the orange.
Link to the original flag on my blog: https://drakoniandgriffalco.blogspot.com/2022/05/flag-of-cherokee-confederacy.html?m=1
#alternate history#alternate history flag#alternate history flags#flag#flags#vexillology#Cherokee#Cherokee Confederacy#Creek#muskogee#chickasaw#Five Civilized Tribes#Choctaw#indigenous people#Native Americans#Native American#indigenous#north america#United States#America#USA#United States of America#alt history
37 notes
·
View notes
Note
The thing that a lot of people miss behind the (similar) problematic behaviors of AW and Ale is that the main differences lie in the intentions behind these actions. And in that case, it actually looks worse on AW for a multitude of reasons.
Ale is just foolish and bratty (I’m using these as adjectives, not insults!). This is NOT an attempt to excuse her behavior. There was plenty she did that warrants heavy side-eying and dislike, but at her core, Ale is just a spoiled party girl. Other than some questionable baiting, I don’t believe her behavior was malicious, I think it was careless. It’s also worth noting that the majority of the fans coming at her for things like CA are based in the US and don’t realize that in terms of race relations and political correctness, not every country is where the US is. I have cousins from Italy and Spain who don’t understand why we frown upon CA in the US. To them, a “Mexican party” is an okay way to theme an event. I don’t agree with it, I don’t like it, but I understand that they aren’t being malicious because they weren’t taught it was wrong in the first place. And I guarantee you that Sebastian, having spent his first decade of life in Europe and still having family there, understood this very well.
Annabelle, on the other hand, absolutely knows that what she does is wrong and she doesn’t care. And you want to know how I know that? She’s real quick to play the angel and pretend nothing ever happened. It doesn’t take a team of people to say, “maybe this isn’t the greatest look,” for her like it did for Ale. Ale didn’t rebrand herself, her team rebranded her. AW knows what is considered right and wrong in Western/North American culture and still tries to sneak in inappropriate, sexually charged, culturally insensitive, or fat shaming content wherever she can because she just can’t help herself. She is a creepy, elitist person who operates from a place of immense narcissism and entitlement. And on top of it all, she’s about 10 years older than Ale, and is a whopping 12 years older than Ale was when she was with Sebastian. So yeah, she should and does absolutely know better, she probably just has a lot of malice in her heart. She finds it amusing to make cruel, unfunny jokes. She finds it amusing to stalk people who are 10+ years younger and multiple tax brackets beneath her to see what they’re saying about her. She is so thirsty for validation that she’ll latch onto a man who treats her poorly and drain every ounce of attention she can get from being connected to his name. Healthy, sane, good-natured people just don’t do this. Even if you believe Ale was PR, you have to remember that she was young and trying to make a name for herself in the US. It doesn’t make an arrangement like that any less grimy, but I get it because she was new to the industry. AW is 40 and has been around for a hot minute. She has been handed more than enough chances to create her own success and has fumbled every one. If people can’t look at her for all that she is, all that she does, and all that we know about her and see that something is clearly wrong, then I can’t help.
To sum this up: Ale has a giant list of flaws, but people only seeing hers and refusing to see Annabelle’s are simply not living in reality.
Gosh, you said it so well.
I was born and raised in Europe, in Romania and we looove to share our culture. If someone came here, we'd totally dress them up in our national costumes and party with them and show them around + share out traditional food.
We also have a different humor in Europe comoared to the US (at least eastern Europe). We are taught not to have an issue with certain topics or Idk... if people call us refering to our hair color (again, at least in Romania)
We were not taught to see many things as problematic. I had no idea about half of the slurs till I started to search on it because we do not have this history that US has. I never understood what CA meant because in many European countries (and other continents as well), it's seen as a cultural exchange/connection. We share culture, we do not try to disrespect it or the people. We try to get closer and to understand.
I had no idea it's disrespectful in the USA till I saw people talking about CA because I was so used to our culture here.
Basically many people here still do not understand what CA is because we are/were not taught to see it this way. We are taught to share and connect with people. So we need to educate ourselves on the topic.
Spanish people are very fun, and love to feel good, and have parties, and enjoy time with their friends.
No one excuses problematic behaviour, but as you said, there is a context.
They hate Ale for speaking Spanish as a first language, for being from Spain. They were upset that she is younger because they are also young, closer to her age than Annabelle and the fact "she had a change" and they don't... gosh, I can't even continue, I find it concerning and disturbing. They bodyshamed her so much for having a bigger bum. They made fun of her cheeks, of her thighs.
I am roetty sure Sebastian knew who she was when they got together and did pap walks together (he did them with Margarita as well... it's called couple pr which ≠ pr couple. People who are together for real and use opportunities to gain attention together).
Ale was in a popular show on Netflix called Alta Mar at the time + she is a known model in Spain. Here in Romania Alta Mar was super popular so I was not surprised to see Sebastian with her (because in my head she was pretty popular too and Romania is also a warm, welcoming country just like Spain. There are many and big Romanian communities there)
And yes, she was young. And the threats she got for just being with him? Gosh!
Some even said this year that they were actually jealous.
The way they tried to say bad things about their videos and pics they posted, acting as if he didn't post and comment in a similar way when he was with Margarita. When she posted Monday they were so pissed, but when Annabelle baits him it's all good.
Ale gained more hate than anything else. So if we use their logic and this was just PR, she literally left with more haters than fans... what was in for her?
They treated Ale in a way they would never treat Annabelle even though Annabelle is really problematic in many ways (which is why I never liked her + her acting was never good in my pov)
It shows it's actually about jealousy. They objectify her, talk about her like she is a doll they can project their fantasies onto. I don't mean everyone, obviously, but many.
Annabelle is a grown up woman, a nepo baby who did not have her big moment even after PB. She posted fake news about Palestine, poses as someone she is not amd her screentime was cut in one of the biggest projects she's even been a part of.
Her problematic behaviour is excused or ignored, and that bothers me as a person who gets called names for calling that out.
People need to understand you don't have to step on your values for anyone, let alone a random person you do not even know, and that we can have different opinions without fighting or sending death threats. My first thought when someone doesn't like x celebrity I like isn't that: what a hater, what an awful person, let me stalk them forever and send death threats. We have to accept we are different as long as we are respectful.
Anyway, you pointed out the double standards very well! Hugs
1 note
·
View note
Text
Empires make us believe that we have to operate only with reconstructed clothes when making a historically accurate outfit, which is found only locally. Well, that is a very narrow way of thinking. By such way, you'll never gonna understand how people actually dressed. How can we think wider?
We should take into account with whom people traded. For example: we know that Baltic tribes sold amber to ancient Italy and France. If they sold something, they must have bought something too. This is how nations work. Take any ancient Italian/French item which you like, imagine how it would look like in Baltic weather/religious/etc conditions - voila. You unlocked a new ancient Baltic look! Of course, for this, you must be fluent in Baltics history and culture, this is the hardest part.
Btw, this is exactly how empires operate. They just take a random piece of clothes/jewelry which they bought/colonized, add some cultural details - voila. Instead of a clearly Finnish female corset, you have a proud ancient Novgorod corset; instead of a suspiciously Turkic looking hat, you have a Polish/Ukrainian hat. It's all about the economics. The nation, which has more audacity to call something purely their own wins. Why can't we, Eastern Europeans, do this as well? Maybe we must get rid of our inferiority complex?
8 notes
·
View notes
Text


15. downtown.
the evil eye doesn't always work, and there's millions between me and you! so just sing to me about eggplants or anything, except for how tired we are...
sketched some familiar (and unfamiliar) faces of the Black Organisation (in civilian clothes)
click below to find out some more details about them! minor warning for mild spoilers up to chapter 15 :)
point of interest: they're all somehow from former east bloc or once-soviet countries
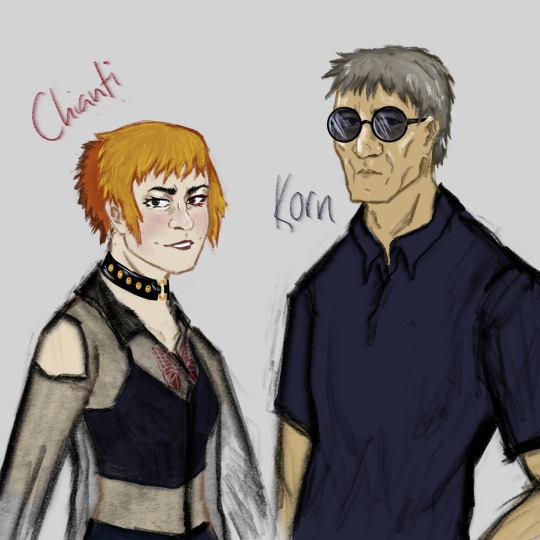
Chianti, Sniper
chinese (?), under 30 years old
VERY short, has a complex about this
she's got the nickname 'Key' but if you call her that without her consent she will throw you
her tattoos are butterfly-and-eye themed (you might see that she's got two tattoos in the drawing, teehee). also, you cannot tell me that the reason for her canon tattoo ISNT a bullet with butterfly wings reference
says "lol" and "lmfao" in casual conversation
might have gotten corrective laser eye surgery (or something similar) - the tattoo on her eyelid might indicate a slightly more long-lasting problem
“Try me again, asshole!” she shrieks, “I’ll stab your dick, too!”
has a girlfriend(?) who gifts italian designer products
vague sibling relationship with Cognac; they're either bickering or they're besties or they're teaming up to gossip about others
“She’s a gamer.”
Korn, Sniper
has a very hoarse voice, possibly resulting from some chronic problem? possible that he doesnt talk much because of this issue
around 45-50 y.o & mongolian
i gave him a wife because i think he deserves someone normal and sane to return home to. according to Vodka's 'accidental' namedrop, she's called Sarnai (the name means Rose in Mongolian <3). also, he's implied to become a father soon
Chianti called him Eeyore in this chapter and it might be one of the funniest things i've ever written. i actually love their dynamic in canon so much that it's a big part of my inspiration for this fic; they just feel so much like they have a life outside of their mandated Black Organisation Cameo Appearance
he and Vodka practice ARB
i sent my friend that picture and he said "this man looks like he's never put any real effort into how he dresses and, in fact, never will" - and honestly? yep.
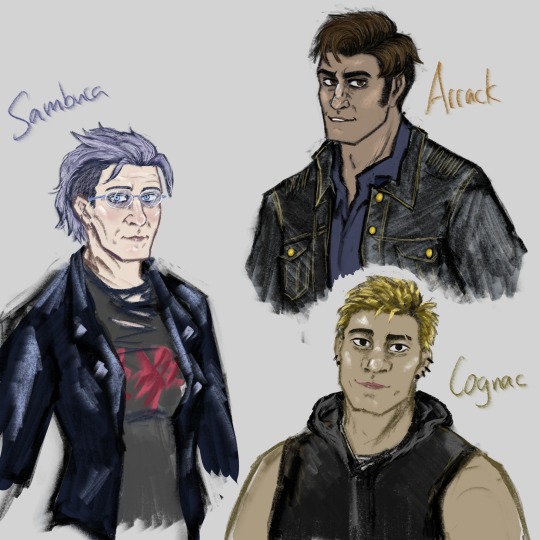
Arrack, Assassin (?)
arab, though exact national origin is relatively hard to clock (Jenever only figured it out because she remembered Shiraz indirectly referencing him)
was mentioned in Akai's notes from 29/7/2010 >:3c
has a very polished appearance, sculpted muscles type beat
mean slut, "mad dog", self-described bastard. VERY flashy fighter, but also "doesn't care if he loses so long as you're hurt worse"
has some pretty normal Star Wars opinions tbh
"resident fuckboy" / "fuckboy-in-chief" -- context clues indicate he might be a honeypot assassin (like Akai speculates in his notes)
generally easy-going despite being unsettlingly intense, but has a very short temper when Shiraz is brought up. (his degree of Shiraz-obsession probably outshines Jenever's tbh)
he's a one-off B.O. member who shows up in a spin-off comic or something, but you literally cannot introduce a character like that and expect me not to sink my evil little claws into them
Sambuca, "Audiovisual manipulation, back-up IT expert"
slavic & eastern european (exact national origin not yet divulged); around 50 y.o woman
wore a metalcore t-shirt to PT
Gin's previous main IT crow. was part of Tequila's Tokyo office at the time of Teq's death; planted there mostly to train
perfectly faked all of Jenever's and Red's credentials to get them into the japanese police institutions. also seems to be in charge of editing Crows out of CCTV footage. overall, really important behind-the-scenes security/cleanup job
her arms are covered in disparate stick-and-poke tattoos. motifs are not unified. a lot of the words/letters are in cyrillic (not visible in the art bc of leather jacket, sorry hehe)
seems to have a phobia of guns/firearms
Cognac, Hardware & Demolitions
south-east asian (exact national origin not yet divulged)
around 30ish years old. not THAT short (like idk 169cm?), but has major gremlin energy
HORRIBLE frosted tips hairstyle situation
vegetarian
wideset body, physically quite strong but has a vaguely soft appearance
remembers Rye sparring with their team a few times. seems p keen to gossip about him (and anyone, for that matter)
"I am literally a whole bisexual!"
gave his denim jacket to Red Label back in Afghanistan (Arrack was soooo mad about this, probably bc they have matching jackets or smth)
#dc-crows#original character#detco fanart#crows 1: soldiers#supplementary material#detco oc#black organisation#detco fanfiction#detective conan oc
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Galley Gala No. 4 - Saudia
Okay, so Saudia's livery isn't fantastic. But their cabin crew uniforms? Top notch.
I feel like the first thing that pops into a Westerner's mind when considering what a Saudia stewardess might look like is "aren't women in Muslim-majority countries legally required to wear a hair covering?" And the answer for airline cabin crew is not only 'no', but actually a fairly emphatic one. Emirates and Qatar Airways actually both ban the hijab (the hair covering). This means that, if you're hijabi and hoping to be a flight attendant, British Airways or WestJet would be a better choice than the national airlines of countries where the majority of women are hijabi. That's bizarre to me, personally.
(It should be clarified that the majority of these countries actually employ primarily foreign cabin crew; while certainly many Saudia flight attendants would have always been Muslim, they only began hiring Saudi women in 2020. Before this, they were all foreigners. The majority were Filipino, Thai, or Eastern European. This is true of many fields in many countries in the Persian Gulf. The UAE and Qatar also have never required head coverings by law, and from what I've heard non-Muslim foreigners generally just don't wear them.)

Saudia's cabin crew, until 2020, dressed in a very smart blue pantsuit with gold hardware and a crisp white shirt underneath. From the neck down, it is literally just a very nice-looking flight attendant uniform which doesn't come with a skirt option in order to preserve hijab (the concept).

Underneath the jackets, there are these lovely light-looking shirts and matching blue vests. I would, in a heartbeat, wear exactly identical clothing to a pre-2020 Saudia flight attendant, except with different shoes. It's stylish! And it comes with these headpieces which have headscarves attached to them, in order to actually cover the wearer's hair. It's a pretty stylish and clever way to approach the task. The scarf blends really well into the vest without constricting the neck, so if it catches on something in an evacuation the wearer won't be horribly strangled. I fully approve.
In 2020, they released an updated version. In addition to incorporating cabin crew's feedback on comfort and practicality, it updates the appearance to something I think is very chic.
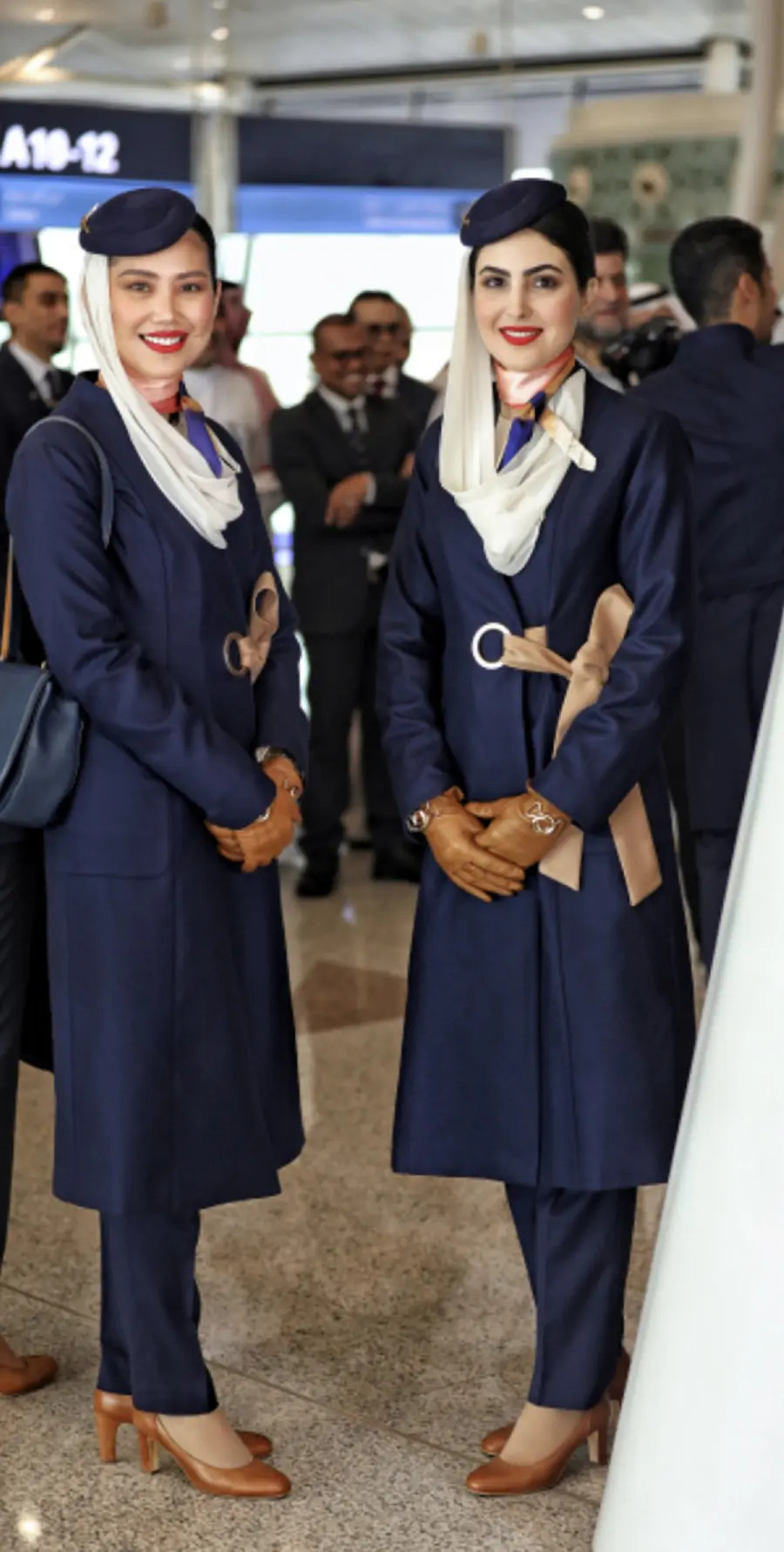

These coats, with the brown gloves and shoes, are gorgeous, and I just adore the new darker blue. These are just downright nice outfits. If you asked me what job these women have, I would not guess that they're flight attendants - I would think they're working in some glamorous, high-profile job. Being a flight attendant in Saudi Arabia is not considered glamorous in the least, but you wouldn't be able to tell it from this updated look.

In addition to the darker blue, the female cabin crew are now given the choice to wear skirts, and their suits are given a belted waist for a very 40s look. I like it a lot. I think these are some of the best looking 'traditional' flight attendant uniforms out there. This has all the features Saudia's livery should have, but doesn't.
Here's something a bit weird, though. I think Saudia may have just banned the hijab*?
*The literal headscarf. The rest of their uniform is still quite hijab-compliant as far as I, a non-Muslim man, can tell.

So, there's this drapey bit. It's pretty similar to Emirates's uniforms (which I will discuss some day). Emirates bans the hijab. Emirates flight attendants are all required to remove their hijab for work, if they wear one. Saudi Arabia, until 2018, required all women, including non-Muslims and foreigners, to wear abaya. Since 2018, there is no legal requirement to wear a hair covering, and now their flag carrier seems to have banned hijabs for flight attendants.
The absence of a hair covering inbuilt in the uniform isn't equivalent to it being banned, of course. The reason I think it might be is that it's been three years now and I haven't seen anything to indicate that it isn't, despite other people asking the same question. When this is partnered with the habits of other carriers it begins to feel like it implies something. I don't know. I can't find Saudia saying anything on the topic. This particular headgear really looks almost identical to Emirates's in particular. I wouldn't be surprised if there's a bit of active imitation going on, since Emirates is absolutely massive and Saudia is probably kicking themselves for not getting into imitating them earlier and buying A380s while they still could. Imagine the efficiency of all-economy A380 hajj flights. On the other hand, Saudia's low-cost subsidiary, Flyadeal, doesn't require head coverings but does allow them, so I ultimately just don't know what's happening and am sort of curious. If anyone reading this knows more than I do, I would love to hear from you.

Anyway, all that aside, Saudia cabin crew look absolutely fantastic. These uniforms are elegant in their wide strokes and immaculate in their details, and are up there as one of my favorite uniforms that could be described in structure and vibe as "a suit".
18 notes
·
View notes