#darwinian evolution
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

(via Animals in the World - A Study of Aristotelian Biology by Pierre Pellegrin)
"While all his previous classic Greek biologists were either purely mechanists or formalists, he understood the true diversity of the animal world and formulated his theories with a more realistic outlook..." (Read more on Booksperience site)
#books#reading#non-fiction#animals#biology#history#aristotelian biology#aristotle#animals in the world#pierre pellegrin#anthony preus#translation#biologists#galileo#the church#darwin#cuvier#genetics#evolution#darwinian evolution#essays#scientific study#scientific#hypothesis#the greek
1 note
·
View note
Text
True spirit animal, Brachycephalus coloratus
MEAN TO HIM!!!
#Brachycephalus#for clarity: attitude refers to the orientation of an object in flight#it’s not that they’ve all developed a short temper#nature#evolution is wild#darwinian evolution
32K notes
·
View notes
Text
Genesis 1-11: Authentic History from an Awesome God
The world sees God and the Lord Jesus Christ as enemies whom they believe need to be eradicated from the mind of humanity By Donald Whitchard Genesis 1:1,John 1:1-4,Hebrews 1:1-4,Psalm 19:1,Colossians 1:16-18,Psalm 47:7 Summary: This is the introduction to a series on the historical foundations of the first eleven chapters of the book of Genesis. These chapters present authentic events and…

View On WordPress
#Darwinian evolution#Eugenics#Genesis#God#history in Genesis#Jesus#master race#Salvation#useless eaters
0 notes
Text









Redid my old Fakemon starters :)
#pokemon#fakemon#the starter theme here is forms of growth and change!#the grass starter is based on plant growth (bud to full tree)#the fire starter is based on personal growth (restraining yourself to embracing yourself)#the water starter is based on darwinian evolution (the reverse of dolphin evolution specifically; pinniped to semi-aquatic mammal)#oh and global warming. it is also based on global warming.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text


By: Paula Wright
Published: Feb 19, 2023
If any man could draw up a comprehensive, infallible guide to navigating this treacherous territory, we would certainly erect a statue to his everlasting memory. There is a Twitter account dedicated to exploring and enumerating precisely the distinctions and differences between the acceptably erotic and the intolerably sexist. It’s called @SexyIsntSexist. It is, of course, under the control of a woman.” Neil Lyndon. Do men really understand what sexism is? The Telegraph 20/5/14
I created Darwinian Gender Studies (DGS) in 2008 as a cross-disciplinary area of study and research which utilises insights across the evolutionary behavioural sciences, including but not limited to, evolutionary psychology, biology, anthropology, ethology, palaeoanthropology and cultural evolution. It represents the consilience of the natural and social sciences, as envisioned by E. O. Wilson.
Back then, my planned PhD thesis was to be in developing an evolutionary, bio-cultural model of ‘patriarchy’ which challenged the premises of the feminist conception of patriarchy. Even in 2008, the project foresaw that political correctness, social justice and toxic feminism were taking us deep down the postmodern rabbit hole. My goal was to build bridges of understanding between the sexes not walls of fear and mistrust, which is what feminism does today. To learn about humans and humanity; what we are, and what we are not.
Two things we are, which we cannot cease to be and remain human, are a sexually reproducing, moderately sexually dimorphic, pair-bonded species. These are basic facts of our human nature which cannot be erased by social engineering.
Within DGS, I interrogate orthodox feminist concepts, such as patriarchy theory, objectification theory, gender, power, mating strategies, and sex differences and similarities, using humour and evolutionary explanatory models such as natural and sexual selection, parental investment theory, female choice, signalling theory, life history theory, intersexual competition and intrasexual competition.
History has demonstrated many times, that whenever our species attempts to take control of biology and bend it out of shape to ideological goals, human tragedy always follows. It’s a lesson we still don’t seem to have learned, as in spite of overwhelming evidence, many people still hold fast to the idea of an endlessly flexible human nature, and indeed, human nature is flexible, but a blank slate it is not. Neither however is it a crude caricature of immutable deterministic drives and instincts as often painted within the straw man of biological determinism. Human nature is very much mutable, but not infinitely or arbitrarily so, and here lies the nub: Within what may seem like infinite variations of human action and reaction to what life throws at us, our predispositions on an average scale are actually predictable. There are enough constants within this calculus to recognise the existence of an unmistakably human nature. This nature will vary and recalibrate between individuals and ecologies (variation is one of the engines of evolution) but these variations dance around a constant, evolutionary fire.
“Those who journey from political correctness to truth often risk public disapprobation, but it is notable that most never lose their tolerance or humanity. They may question the politics of race, but not that racism is bad; they may question campaigns about women’s pay, but not that women and men deserve equality of treatment.” Browne, A. (2006) The Retreat of Reason: Political correctness and the corruption of political debate in modern Britain. Civitas
I was, and am, standing on the shoulders of many female evolutionary scientists and philosophers who came before me such as Barbara Smuts, Sarah Blaffer Hrdy, Anne Campbell, Helena Cronin, Griet Vandermassen, Catherine Salmon, Maryanne Fisher, Bobby Low, Helen Fisher, and many more. Over the last 50 years, their scholarship has revealed that, far from feminist fears to the contrary, evolved sex differences do not equate to inferiority. Via evolution, we in fact see true equality expressed in discrete and fascinating ways.
These women (and many men) have illuminated the role females play as potent agents of evolution via the phenomenon of female choice. This is sadly still an unsung revolution – unsung by feminism, not evolutionists – as it shattered the male perspective biases that once dominated biology and Darwinism. These women did this, not with rhetorical declarations of war against ‘patriarchy’ but with logic and critical thinking.
When it comes to the principles of natural selection – the struggle to survive – men and women differ very little. Rather, it is in the principles of sexual selection – the struggle not just to survive but thrive enough to have offspring and allow them to thrive also – that the main differences start to become manifest. It is a categorical fact that none of these differences equates to any moral inferiority. No genuine evolutionary scholar would ever make such a claim.
Feminists have long claimed that logic is an exclusively male trait. So much so that to counter the “male” scientific method they felt the need to create “female” method – social constructionism - which ironically invokes every negative female stereotype they claim to want to refute. They did this not because social constructivism was a better tool – it is untested – but because it was the binary opposite of the scientific method.
Women, in fact, have nothing to fear from logic. Yet feminists do fear it, as philosopher Janet Radciffe Richards notes in her book The Sceptical Feminist,
“…in spite of girls doing better at school than boys, feminists are still woeful at rationality…feminism has some tendency to get stuck in the quagmire of unreason from time to time [but] it cannot be denied that adopting an anti-rational stance has its uses; it can be turned into an all-purpose escape route from tricky corners”
They also fear it because it falsifies the very premises feminism rests on – especially female inferiority.
This is a description of all feminisms today: radical, intersectional and all other tribes battling for dominance in the victim narrative – including ideological men’s rights, MGTOW and “red pill” groups. All feminisms eschew logic and reason for dogma and ideology and all are in thrall to the flying patriarchal spaghetti monster in the sky. Ask a question about female oppression, you already know the answer: it’s the patriarchy, stupid. And ideological men’s groups have their own version of patriarchy, known as gynocentrism. Both concepts are intellectually myopic.
I created DGS all those years ago because I wanted the opportunity to have a role, however small, in helping us better understand ourselves as a species.
It is true that as a woman I am perhaps more interested in the unique selection pressures women face due directly to their sex. As an evolutionist and a realist, however, this bias does not make me blind to the fact that men face their own unique selection pressures due explicitly to their sex.
The truth is, one sex cannot be understood except in the light of the other. Men and women have co-evolved, each shaping the other both physically and psychologically via sexual selection. Men desire power and resources because women desire men who have power and resources. And female conflict, well that doesn’t look like male conflict, and so often goes unseen, especially by feminists.
From an evolutionary perspective, feminism can be categorised as the study of the conflict between the sexes – intersexual conflict – aka the “battle of the sexes” with a particular interest in proximate, conscious mechanisms of how men can oppress women and how this oppression can be countered. But this is only half the story. Evolutionists posit that to really understand intersexual conflict one must also analyse intrasexual conflict. We do this because we observe across species that competition within a sex is always far more intense than between the sexes. An evolutionary lens also broadens the enquiry to include an analysis of ultimate, unconscious mechanisms of not just how, but why, men pursue the goal of power and resource control. What do men want to do with power? To create strong alliances, subdue rivals, protect against enemies and attract mates.
Much is known about male intrasexual competition. We have had 2000 years to work it out – its role in shaping cultures and empires – for better or worse. Far less is known about conflict - and conflict resolution - between women; female intrasexual competition (FIC). It is the pink elephant in the feminist room. Do we have the same amount of time to understand female intrasexual competition? For better or worse? I don’t think we do. The epidemic of female-on-female bullying in nursing has long been acknowledged in academia, yet nothing is done about it. In the UK it costs the NHS billions of pounds in workplace attrition, sick leave and low efficiency. It can also cost lives, as a “culture of bullying” was highlighted in the official reports on two scandals in UK maternity wards where both infants and mothers lost their lives.
In another example observe the rise of intragender conflict in the West. Third-gender people exist in many cultures, but only in the West are males who identify with the female gender trying to use it as leverage to get access to sex-based rights and privileges. Then we have feminism itself a battleground fraught with female intrasexual competition, which is often mistakenly called “internalised misogyny”. Women too, it seems, want to create alliances, subdue rivals and attract the best mates.
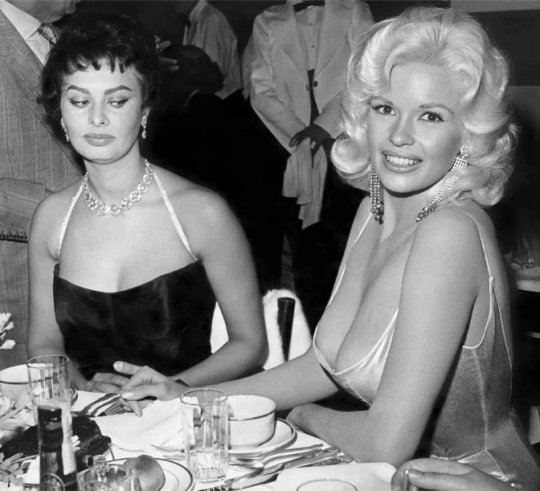

Using FIC as a lens to look anew at hot feminist topics such as the beauty industry, cosmetic surgery, anorexia, and the endless wars of attrition between the many tribes of feminisms brings fascinating new insights, as all these phenomena seem to be expressions of female competition not male oppression.
Nonetheless, there is still a comfortable consensus among all feminists that the beauty ‘ideal’ is a tyranny perpetrated upon women by the patriarchy. “Feminists down the ages have argued that the oppression of women is played out on their bodies, their clothes, their style of adornment. To politicise dress has been one of the enduring projects of the women’s movement.” (Walter, N. 1999) Naomi Wolf tackled this concept in her seminal book The Beauty Myth: How Images of Beauty Are Used Against Women. It suggested that this patriarchal strategy is one of ‘divide and rule’ as it “creates a climate of competitiveness among women that divides them from each other.”
Competitiveness is the keyword here. Perhaps the idea of sanctioning the idea, nay the fact, of female intrasexual competition seems frightening for feminists because on the surface of it, it threatens the very notion of a ‘sisterhood’. Yet we know that men are murderously competitive with one another, as homicide rates attest, and this does not seem to threaten their notion of ‘the patriarchy’.
The evidence actually shows that the beauty myth may not be a tyranny perpetuated on women by men, but on one other - if it is a tyranny at all! And it reveals a much more complex and fascinating picture of female agency which goes far to liberate women from the doctrine of passive femininity.
The fact is, women are fiercely competitive with one another, but as the existence of feminism attests, this does not stop women at least trying to cooperate to face challenges, though, as feminism also shows, its own willful ignorance of human nature means feminists cannot agree on anything for long. This explains the many tribes within feminism, and the fiercely defended hierarchies that exist within feminism itself.
I do not deny that these revelations are tricky for feminists to negotiate, but that is no reason for not taking them on. That female intrasexual competition exists is not in doubt. The degree of it however will vary from culture to culture. We know dominance hierarchies exist in many species and all apes. Humans add to the mix competence hierarchies which allow for the utilisation of innate talents and the division of labour which has allowed our species to become far more than the sum of its biologically determined parts.
We also know females have a large role in the construction and maintenance of such hierarchies, for better and worse. Women are individuals and as such are often not united in their interests. An individual’s environment is crucial to how they calibrate their own needs. Yet, ironically, the collective structure of feminism, suppresses the evolutionary mechanism of individual female choice. The epithet “choice feminism” is regarded with contempt by most feminists today.
“If we do not know what we are capable of…then we do not know what to watch out for, which human propensities to encourage, and which to guard against.” Shadows of Forgotten Ancestors.
Further reading: Griet Vandermassen Sexual Selection: A Tale of Male Bias and Feminist Denial ; Griet Vandermassen: Who’s Afraid of Charles Darwin: Debating Feminism and Evolutionary Theory; Anne Campbell: A Mind of Her Own: The Evolutionary Psychology of Women ; Sarah Blaffer Hrdy: Mothers and Others: The Evolutionary Origins of Mutual Understanding ; Sarah Blaffer Hrdy: Mothernature ; Susan Pinker: The Sexual Paradox: Men, Women and the Real Gender Gap ; Christina Hoff Sommers: Who Stole Feminism? ; Cindy Metson & David Buss: Why Women Have Sex; Women reveal the truth about their sex lives, from adventure to revenge (and everything in between) ; E.O. Wilson: Consilience: The Unity of Knowledge ; Jerome H.Barklow (ed): Missing the Revolution: Darwinism for Social Scientists
==
We recognize that the evolution of peafowl, bees, seahorses, angler fishes and marsupial mice has resulted in males and females whose physiology and behavior development has influenced and responded to each other. Yet somehow, that female and male humans behave as they do as a result of the other is somehow unreasonable or even "sexist." Like creationist Xians, this is a denial of evolution and of humans as members of the animal kingdom.
It seems like the "god did it" dragon of "tHe PaTrIaRcHy," then, was conjured to fill the gap in the combination of denial of biological sex-based differences (directly responsible for the formulation of gender ideology; and itself a denial of evolution), and denial of intrasexual competition between women ("On Twitter, women are more misogynistic than men") in order to obscure female agency.
If "gender studies" had been based on science instead of Marxian psychosis and postmodern fantasy, it might well have been harder for the Queer Theorists to find a solid ideological foothold and enthusiastic collaborators.
#Paula Wright#evolutionary psychology#intrasexual competition#Darwinian gender studies#gender studies#feminism#patriarchy theory#biological dimorphism#dimorphism#sex based differences#western feminism#human evolution#science#religion is a mental illness
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
The fact is that two-spiritedness, homosexuality, bisexuality, and transgender are at the forefront of some of the most significant scientific re-visionings of our time – in which the gap between indigenous and Western perspectives is finally being bridged – yet their contribution is rarely, if ever, acknowledged by Western scientists. When prominent chaos theoreticians, biodiversity experts, and post-Darwinian evolutionists invoke the teachings of tribal peoples, they are usually unaware of the pivotal role played by homosexuality and transgender in these indigenous belief systems, or in the lives of the writers, storytellers, and visionaries who give poetic voice to their scientific concepts.
"Biological Exuberance: Animal Homosexuality and Natural Diversity" - Bruce Bagemihl
#book quote#biological exuberance#bruce bagemihl#nonfiction#two spirit#homosexuality#gay#lesbian#bisexual#transgender#forefront#indigenous knowledge#traditional knowledge#western science#chaos theory#biodiversity#post darwinian evolution#acknowledgment
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
It is important that scientists working in chaos theory, biodiversity/Gaia studies, and post-Darwinian evolution acknowledge their genuine affinities with indigenous perspectives.
"Biological Exuberance: Animal Homosexuality and Natural Diversity" - Bruce Bagemihl
#book quote#biological exuberance#bruce bagemihl#nonfiction#scientists#chaos theory#biodiversity#gaia theory#gaia hypothesis#post darwinian evolution#indigenous knowledge#traditional knowledge
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
You are not doomed to be stuck into a single interpretation of yourself. You are allowed to shift your identity and take on new thoughts, new actions and new beliefs. Just as nature restores herself each season, so can you. Just as she evolves and each species iterates - so can you.
#identity#self transformation#transformation#transcendence#meditations#meditation#philosophy#personal growth#high minded#high spirit#growth#growth mind#evolution#evolve#Darwinian#will to power
0 notes
Text

TSRNOSS, page 87.
#Tibet#orientals#hairlessness#altitude#radiation resistance#glutathione#cobalamin#cyanide#ataxia#earthquake#human height#darwinian selection#radon#background radiation#enzyme kinetics#lysosomal enzymes#limit dextran#leg length#evolution#nitric oxide#creativity
0 notes
Text
youtube
MIND-BLOWING New Grand Canyon Info Confirms Noah’s Flood
This MIND-BLOWING new Grand Canyon info confirms Noah’s Flood and debunks the evolutionary timeline… In this presentation, Dr. Andrew Snelling shares new research that points to the layers in the Grand Canyon being formed during the biblical flood.
0 notes
Text
Top scientists at MIT have announced that they've located a 500-cubic-meter region of space where Lamarckism is true. "Now to be clear, Darwinian Evolution is true and correct everywhere else, but in here? All Lamarck, all the time," they clarified. "We're not telling anyone where, because you'd all come and do stuff even worse than what we've been doing, like with athletes and soldiers and shit. Whereas we've mostly stuck to Giraffes. Boy, have we stuck to some fucking Giraffes. You would not believe the necks that we've managed so far, I mean cut these thing's heads off at the shoulder and you're most of the way to a Titanoboa. Anyway."
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
top edits I'd retroactively make to whatever that version of the bible is that my country has such a big boner for (sorry I don't know what the different versions are actually called)
Drop the damnation/salvation system in favor of the kind where seriously only really really cruel selfish people go to hell but they can get out if they're actually nice deep down and are SUPER sorry for real
Take out any kind of sin that's stupid and doesn't make sense, replace with more sensible things like "don't drain wetlands" and "don't have slaves" and "if you find black goop in the ground just leave it there, trust us"
Throw in some handy instructions on what electricity is and how to build a solar panel. I wanna see what this does to the state of technology when I get back.
Explain what germs are and to wash your hands with soap please
Make the apostles more fun, like one of them should definitely be a skeleton guy and one should have plant powers.
Add a B-plot that canonizes the complete events of Adam Sandler's "Little Nicky"
Have God apologize for the existence of suffering but unfortunately all his power got used up to get Darwinian Evolution up and running
Sprinkle details about God's physical appearance all throughout until it's impossible to ignore that this is a description of a little dapper toad
I already ditched the garden of eden obviously because it's stupid but to make doubly sure western society likes snakes let's make jesus a big snake all along, and a venomous one. Biting becomes Jesus's main way of dealing with problems.
Ruin the modern protestant perception of absolute good and evil by having Jesus befriend a cool bad boy demon, which God is only a little concerned by like "(grumpy toad noises) I'm not so sure about this friend of yours young lady"
he will however slowly come around to meeting the demon's parents at a very funny dinner where everything goes TERRIBLY wrong but in the end they can all share a laugh about it
The apocalypse is a cool concept so I'd keep that but change it around so it's heaven, hell and earth uniting against a common foe: the god of the alternate, darker timeline I just erased. Nobody would know what that means but I think that would be compelling in itself. I'd like to see those philosophical debates.
551 notes
·
View notes
Text
Antisemitism and the Nazi Worldview: a Guide for the Perplexed
While most people know the Nazis hated Jews, few people understand just how integral Jew-hate was to the Nazi philosophy. This leads into many of the misconceptions about Nazis and the holocaust that regularly pop up, so it bears discussing what Nazis believed about racism and the Jews.
The Nazi conception of "race" was much narrower and "scientific" than we think of it today. The Nazi conception of race was that humans were split into subgroups with distinct traits, that set them apart from each other and gave them advantages in a great and bloody contest of the races. These races pattern on better to ethnicities, nationalities, or even language groups, than race as we think of it today, which is why it would make sense in a Nazi framework to talk about an Irish race, or a Polish race, for example. And of course in the Nazi mind, these races were a real biological reality, and not a social and cultural construct, and the strength and purity of a fit race might be lost through race mixing.
And of course races were differently fit or unfit, superior or inferior, and through the races warring against each other in a battle of the fittest, the superior race would rise above the rest, and subjugate the earth. Hitler came of age in a time of scarcity, war, and famine, and he believed there was no way to feed the entirety of the human race, so eliminating the lesser races through this perpetual struggle of races against each other was the only way for humanity to survive. It was all very Darwinian except that it completely misunderstood how the Darwinian model of evolution actually works, since the unit of selection was the nonexistent race, not the individual.
This struggle of the races was in Hitler and the Nazis' conception not only natural and necessary, but good. Conquest and the slaughter of inferior races was good. The state of the world with nation states and silly notions like laws, and morals, this was bad and unnatural. Humanity, or the strongest race, needed to do away with this system, or humans would all perish of starvation in a degenerate race-mixed scrum. The Nazis were heros, looking to save humanity from this foul unnatural state it had been tricked into adopting.
Tricked by the machinations of one race. One race had broken away from the others, and learned how to hack the system, to survive over and over under the rule of other races, when it should have been destroyed as a weaker lesser race. This race figured out how to lie and cheat, and live off other races as a parasite, while controlling them from within with fake, unnatural, vile concepts of laws, ethics, notions of justice and compassion, human rights, and international cooperation. And also with money. That race was the Jews.
In the Nazi mind, other races might be lesser, weaker, worthy only of a slow starvation under Nazi rule, but Jews, Jews were unique, special. Weak but cunning, only the Jews had figured out how to subvert and pervert the noble struggle of the races. The Jews were not only especially hated in the Nazi mind but they also served an explanatory purpose. The Jews were the reason humans were not in what the Nazis viewed as a state of nature, and the reason that the Aryans hadn't eliminated all the other races and taken over the world already. And anything that went wrong for the Nazis was of course caused by Jewish manipulation. The Jews had to be stripped of their unnatural power and control, and eliminated quickly, to keep them from continuing to undermine the strongest race, the Aryan Germans.
Early on, there was some discussion about how this was to be done. The mass slaughter of Jews under this philosophy might have been inevitable but it wasn't obviously inevitable to all Nazis. The important thing was to reduce the Jews to a state of nature, to take away their unnatural control, and leave them in the position of any other lesser race. This is where ideas, like sending all the Jews to Madagascar, to "build their own state" but really to inevidably die in the wilderness, came from. If Jews were separated from their stronger hosts, the logic went, they would just be one more weaker race and they would die just the same. This was also why so many Nazis took a special delight in simply denying captive Jews the means of survival, leaving them to starve, freeze, and die of disease in a state of nature, without the resources they had parasitically leached out of their host races.
But that process took too long. There were simply too many Jews, and too many (to the Nazi mind) Jewish controlled enemies. As Germany and the Axis' began to lose the war, and then as that loss became increasingly only a matter of time, the Nazis ramped up their efforts to kill Jews, by bullet and by gas, because if they could kill enough Jews, surely that Jewish control over their enemies would break and the Aryans among those enemies what recognize their racial interest, and join with the Germans, giving them victory. Instead the resources poured into the wholesale murder of Jews were resources stripped from the Nazi war machine, hastening the Allied victory.
Antisemitism wasn't simply one more bigotry for the Nazis to tack onto their general racism. It was foundational to the Nazi conception of how the world functioned. It was the explanitory mechanism in the Nazis' conspiratorial framework. And with this philosophy at the core of Nazism, the Holocaust became not only inevitable, but the highest calling of the Nazis, their sacrifice for humanity, or at least what was left of humanity after the strongest race had triumphed over all the others. Very little about Nazism is unique. Their militarism, their glorification of violence and struggle, their racial pseudo-Darwinianism, certainly their conspiratorial antisemitism, all had plenty of precident long before they came on the scene. It was their particularly potent combination of these existing elements that made them Nazis. And in this combination, it was the Jew-hate which held everything together and which provided the energizing force.
#nazism#antisemitism#nazis cw#holocaust cw#look we don't focus on the nazis' hatred of jews because the jews are super privilaged#or because the jews want us to#we do it because jew hatred was the bedrock of nazism#and claiming its because the jews are so powerful is the same kind of conspiratorial jew hate the nazis went in for#but what do I know I'm a jew#jewish#a s fischer original#The title comes with apologies to Maimonides#I read Mein Kampf in high school#which means I have this shit in my head
344 notes
·
View notes
Text
so… the seventh house is cultivating chronic illness in their ruling class to make powerful necromancers and the sixth is systematically enforcing principles of Darwinian evolution on their population to maximize genetic variation and health. the juxtaposition. no wonder dulcinea said no re: the pal-posal
#continued discussion from tiktok#I can elaborate if this is too vague#can you tell I work in genomics#the locked tomb#tlt#gideon the ninth#dulcinea septimus#seventh house#sixth house#palamedes sextus
129 notes
·
View notes
Text
you understand that the concept of cultural development and cultures being more developed than others is part of the spencerian misunderstanding of darwinian evolution into progressivism which is a flawed mentality of evolution is always building toward a more refined end product that will be the best version of that creature. spencer's misunderstanding that there is a final point of human evolution that is built to and we are currently in is fundamentally untrue, but it was applied to theories of cultural evolution to be used as justification for othered cultures to be seen as less developed than (primarily white, imperial core) western cultures. there is no culture that is more developed than another, all cultures by nature of existing in the same time period are as developed as they can be. there is no end point we are building towards in biological evolution or in cultural evolution. you have to deconstruct ideas of development in order to assess cultural concepts and differences in accordance with your own biases. when someone postulates a culture as 1. being developed 2. the only development they can develop into is capitalism, you should question it.
135 notes
·
View notes
