#corporate lobbying
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
May 10th is the anniversary of the Santa Clara County v. Southern Pacific Railroad Company Supreme Court decision of 1886. The case first established under the 14th Amendment that corporations are considered “persons.” The 14th Amendment granted citizenship to all persons born or naturalized in the U.S, included former enslaved human beings, and provided all citizens with “equal protection” and other rights under the law. It was not intended to apply to corporations.
The Supreme Court granted corporations other constitutional rights since then, including the 4th Amendment search and seizure rights, 5th Amendment takings rights and 1st Amendment free speech rights to spend money corrupting politics. The 2010 Citizens United decision expanded corporate 1st Amendment free speech rights.
It’s a common belief that the corporations first acquired corporate constitutional rights (“corporate personhood”) in the Citizen United decision. They did not. Corporate power to hijack democracy precedes Citizens United and corporate spending money in elections by nearly a century.
Armed with constitutional rights, corporations have “railroaded” people, communities and elected officials – overturning democratically-passed laws ensuring safe food and products, protecting workers and workplaces, and ensuring a livable world – in ways that have nothing to do with Citizens United or corporate “free speech” rights.
Ending ALL corporate constitutional rights – not just overturning Citizens United and corporate “free speech” rights – is what makes Move to Amend unique. It is why we call for enactment of the We the People Amendment. And it is why May 10 is such a very important date.
#us politics#citizens united#Santa Clara County v Southern Pacific Railroad Company#14th amendment#corporate lobbying#corporate greed#Corporate personhood#may 10th
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Penn police violently manhandled the suspect who allegedly murdered the health insurance company CEO. This was done in front of the media. Hidden corporate taskmasters of local police departments contrary to American democracy?
#CEO#murder#police brutality#health insurance companies#capitalism#capitalism and democracy#accountability#violence#political violence#unitedhealthcare#union busting#luigi mangione#campaign contributions#corporate lobbying#corporate influence#regulatory capture#anti trust#competition
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Been digging into things on Canadian/British, United States/British and South American/Spanish history recently and the notable thing that has come up on both - in all three cases, the European settlers were the ones actively engaging in genocide of the indigenous population. It was not the active policy of the European government.
In all three cases the European government actually passed protective legislation for the rights of indigenous subjects at the request of either indigenous people themselves travelling to Europe to make these representations, or not-entirely-awful Europeans passing on what was happening to them. They weren’t *incredible* protections in any of the three cases, but they at least recognised that indigenous people were *people* with actual basic rights. Like “not being automatically murdered or enslaved”.
But then European settlers went *batshit* at this legislation. The entire idea of “No Genocide” policies provoked enormous settler backlashes in all three cases. It was even a material, if not enormous, factor in why the US declared independence.
And the European governments in question just…rolled over. Made no real attempt to enforce this protective legislation. And it *certainly* was *not* why Britain sent in troops when the US declared independence. The Founding Fathers just viewed even the fact they had been *asked* to not murder indigenous people as an outrage.
None of this is to excuse European colonial states today of our responsibility to pay reparations and lobby for protections for indigenous people (and BIPOC in general) in our ex-colonial states. We’ve benefitted so much, especially on mass resource plundering, that reparations are a responsibility we cannot shirk.
(I just finished a biography of Charles Hapsburg and how he frittered away *massive* silver imports stolen from South America on European wars. That huge resource injection was pretty vital to the beginning of European international capitalism in the 16th-17th centuries. Before that, states just kept coming up against insufficient metals for currency, especially ones with the intermediate value of silver that let a critical mass of lower-level transactions happen.)
What it is, however, is an examination of the different ways states can be responsible for genocide, eugenics, and other crimes.
It does not need to be active policy for a state to be responsible. Even passing protective legislation doesn’t prevent a state’s responsibility if they don’t take measures to enforce that legislation, and, particularly, *if they give in to loud backlash from privileged parties who see it as an infringement of their privilege for people they are oppressing to be given some basic rights.*
I am not a proponent of “history repeats itself”. Context *always* matters, and every different situation has a different context. However, history itself provides an incredibly important and *necessary* context for situations we face now. And these facts are *incredibly* relevant to *many* situations we are currently facing.
#early modern history#colonialism#colonialist legacy#canadian history#us history#south american history#capitalist history#indigenous rights#indigenous people#spanish history#british history#nonenforcement of legislation makes it worse than useless#genocide#canadian genocide#south american genocide#american genocide#eugenics#corporate lobbying#privilege#settler colonialism#settler states#european history#european reparations#reparations
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
I have a sneaking suspicion that the people—a term I use loosely— who will lead the movement against the incoming administration are going to be corporate lobbyists. The fossil fuel industry has invested billions in renewables and they are not going to abandon that work because the administration wants them to (one company has already said so). Do we really think Frito-Lay is going to bend the knee to RFK Jr? Do they think big pharma is about to stop selling vaccines, a consistent revenue stream? Do they think that the insurance industry is about to let one of its biggest boons (Obamacare) just be obliterated into smithereens?
I don’t think so.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
More than 600 communities across the U.S. have decided to build their own broadband networks after decades of predatory behavior, slow speeds, and high prices by regional telecom monopolies.
That includes the city of Bountiful, Utah, which earlier this year voted to build a $48 million fiber network to deliver affordable, gigabit broadband to every business and residence in the city. The network is to be open access, meaning that multiple competitors can come in and compete on shared central infrastructure, driving down prices for locals (see our recent Copia study on this concept).
As you might expect, regional telecom monopolies hate this sort of thing. But because these networks are so popular among consumers, they’re generally afraid to speak out against them directly. So they usually employ the help of dodgy proxy lobbying and policy middlemen, who’ll then set upon any town or city contemplating such a network using a bunch of scary, misleading rhetoric.
Like in Bountiful, where the “Utah Taxpayers Association” (which has direct financial and even obvious managerial tethers to regional telecom giants CenturyLink (now Lumen) and Comcast) launched a petition trying to force a public vote on the $48 million in revenue bonds authorized for the project under the pretense that such a project would be an unmitigated disaster for the town. (Their effort didn’t work).
Big ISPs like to pretend they’re suddenly concerned about taxpayers and force entirely new votes on these kinds of projects because they know that with unlimited marketing budgets, they can usually flood less well funded towns or cities with misleading PR to sour the public on the idea.
But after the experience most Americans had with their existing broadband options during the peak COVID home education boom, it’s been much harder for telecom giants to bullshit the public. And the stone cold fact remains: these locally owned networks that wouldn’t even be considered if locals were happy with existing options.
You’ll notice these “taxpayer groups” exploited by big ISPs never criticize the untold billions federal and local governments throw at giant telecom monopolies for half-completed networks. Or the routine taxpayer fraud companies like AT&T, Frontier, CenturyLink (now Lumen) and others routinely engage in.
And it’s because such taxpayer protection groups are effectively industry-funded performance art; perhaps well intentioned at one point, but routinely hijacked, paid, and used as a prop by telecom monopolies looking to protect market dominance.
Gigi Sohn (who you’ll recall just had her nomination to the FCC scuttled by a sleazy telecom monopoly smear campaign) has shifted her focus heavily toward advocating for locally-owned, creative alternatives to telecom monopoly power. And in an op-ed to local Utah residents in the Salt Lake Tribune, she notes how telecom giants want to have their cake and eat it too.
They don’t want to provide affordable, evenly available next-generation broadband. But they don’t want long-neglected locals to, either:
Two huge cable and broadband companies, Comcast and CenturyLink/Lumen, have been members of UTA and have sponsored the UTA annual conference. They have been vocally opposed to community-owned broadband for decades and are well-known for providing organizations like the UTA with significant financial support in exchange for pushing policies that help maintain their market dominance. Yet when given the opportunity in 2020, before anyone else, to provide Bountiful City with affordable and robust broadband, the companies balked. So the dominant cable companies not only don’t want to provide the service Bountiful City needs, they also want to block others from doing so.
Big telecom giants like AT&T and Comcast (and all the consultants, think tankers, and academics they hire to defend their monopoly power) love to claim that community owned broadband networks are some kind of inherent boondoggle. But they’re just another business plan, dependent on the quality of the proposal and the individuals involved.
Even then, data consistently shows that community-owned broadband networks (whether municipal, cooperative, or built on the back of the city-owned utility) provide better, faster, cheaper service than regional monopolies. Such networks routinely not only provide the fastest service in the country, they do so while being immensely popular among consumers. They’re locally-owned and staffed, so they’re more accountable to locals. And they’re just looking to break even, not make a killing.
If I was a lumbering, apathetic, telecom monopoly solely fixated on cutting corners and raising rates to please myopic Wall Street investors, I’d be worried too.
#article#telecommunications#AT&T#comcast#monopoly#internet#municipal governments#municipal internet#CenturyLink#corporate lobbying#wall street
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
and this children is why you don't fuck with big Christmas
tumblr the app u can't just swallow my posts about Santa commiting adultery on Mrs Claus this is censorship
#santa claus#mrs claus#big santa#big north pole#corporate lobbying#censorship#did you seriously think an omniscient demigod who still believes in a moral binary would not just put in some calls to have you silenced?
16K notes
·
View notes
Text
#Apple#Big Tech#Campaign Financing#Consumer Exploitation#Corporate Control#Corporate Lobbying#facts#Government Influence#Grassroots Movements#life#Media Manipulation#New World Order (NWO)#Planned Obsolescence#Podcast#Product Life Expectancy#serious#straight forward#Transparency Laws#truth#upfront#website
0 notes
Text
100,000 dollars is not a lot of money.
it is also a lot more money than i will ever have. my student loans make up half of that - they're coming back, i'm told, like we all bounced back recently. the other day while paying for gas to go to work, i overdrew my account without knowing it.
i sat in the car and looked at the charge and tried to do the math. where the fuck is the money even going? i don't live extravagantly. i live in a hole in the ground, in an apartment the size of a sneeze; covered in ants. yes, i wanted to live close to a population center. maybe that's my fault. i've downloaded the apps and i've spoken to the experts and i've cut back on excess. i can't help the pharmacy bills or the medical debt.
i have a good, well-paying job. when i googled it to see if i was getting a fair salary, i found out i'd be making "upper middle class" money. which doesn't make sense - is "upper middle class" now just "able to afford a one-bedroom without a roommate". when i was younger, upper-middle meant a nice big house and a backyard and vacations and not flinching about eating at a resturant.
i was talking to my friend who is a realtor. he said 100,000 dollars is extremely cheap for housing. he's not wrong. 100,000 dollars would change my life. 100,000 dollars also won't really buy you anything. it could get you out of debt, potentially, if you were lucky and had a certain amount of scholarships to tack onto your degree. you could pay off the car and then have enough left over for "spending" money. how fucking amazing. one vacation, maybe two if you're thrifty. and then - like magic - the money would evaporate into nothing. people would sigh and tell you see, you should have put it into savings! like "upper middle class" people can't afford to value "actually living" over squirrelling wealth. you should spend your life only in scarcity. like that is what made the rich people all their real "actually a lot of money".
100,000 dollars would literally set me free. it also would just set me back to "earning normally" instead of paying down debt into infinity. god, do you know how many of us just want that? that our first thought is we could stop scrambling and just be free of debt if we won the lottery? that we don't even necessarily need to stop working - we just wouldn't have to worry about failing or falling?
and. at the same time. 100,000 dollars is next to fucking nothing.
#writeblr#me paying my taxes this year:#haha good to know im literally doing more for my community out of my tiny apartment#than most corporations will do in their entire scope! :) these motherfuckers will NEVER pay taxes!!!#bc they lobby others to be sure we CHOKE :) !!!#i hope this is clear like. this isn't someone being like ''haha if i got 100k it wouldn't be a big deal''#it's more like. the gap between corporations and the ppl WORKING in those corporations#has become HORRIFIC. 100k to the company i work for is like. pocket change to them.#and it is LIFE CHANGING for me.#they could cut me a check for 100k tomorrow and not even budge their margin of error
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
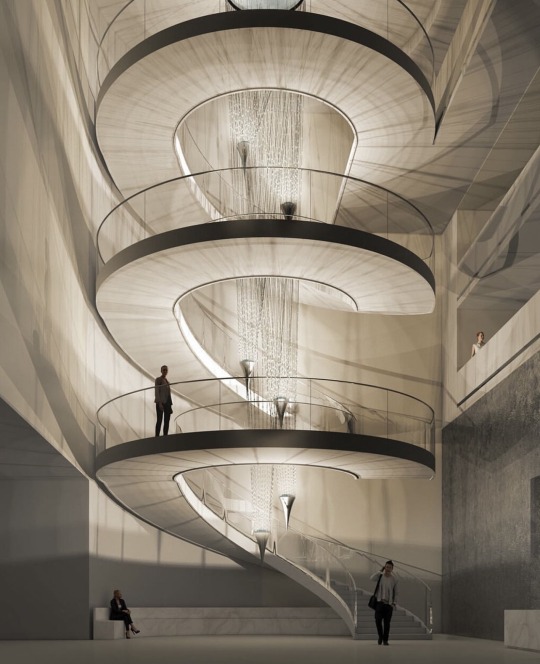

Eva Menz: Inception, Corporate Lobby (2017) Located: Geneva, Switzerland
#Eva Menz#Inception#Corporate Lobby#sculpture#stairs#interior design#interiors#Geneva#switzerland#2017
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

congrats to whatever the fuck these things are
#ttcc#toontown corporate clash#firestarter#flint bonpyre#pacesetter#graham ness payser#cant wait to actually beat them to death (im not strong enough yet)#i cant get over how those things look#let us eat bees‚ together#theyre perfect#shoutout to the wiki for calling that fountain a shower#toons wont stop bathing in the fast asleep lobby fountains it smells like wet dog in here
358 notes
·
View notes
Text

It's been a long day at work...
(Hi Chip enjoyers come get your food.)
#toontown#corporate clash#ttcc#chainsaw consultant#chip revvington#fanart#art tag#toonblr#toon tag#i imagine the context for this is everyone else has gone home from work#chip's just hanging in the lobby. contemplating his life choices
378 notes
·
View notes
Text
A beef industry group is running a campaign to influence science teachers and other educators in the US. Over the past eight years, the American Farm Bureau Foundation for Agriculture (AFBFA) has produced industry-backed lesson plans, learning resources, in-person events, and webinars as part of a program to boost the cattle industry’s reputation.
Beef has one of the highest carbon footprints of any food, but AFBFA funding documents reveal that the industry fears that science teachers are exposed to “misinformation,” “propaganda,” and “one-sided or inaccurate” information. The campaign from the AFBFA—a farming-industry-backed group that "educates" Americans about agriculture—is an attempt to fight back and leave school teachers with a “more positive perception” of the beef industry, the funding documents reveal.
According to survey data included in these documents, educators who attended at least one of the AFBFA’s programs were 8 percent more likely to trust positive statements about the beef industry. Some 82 percent of educators who participated in a program had a positive perception of how cattle are raised, and 85 percent believed that the beef industry is “very important” to society.
The beef industry “knows it has a trust issue,” says Jennifer Jacquet, a professor of environmental science and policy at the University of Miami. The industry is attempting to influence public opinion by starting with children, says Jan Dutkiewicz at the Pratt Institute’s Department of Social Science and Cultural Studies. Dutkiewicz points out that one of the AFBFA’s objectives outlined in its most recent funding document is to run events that “engage educators and students … to increase their understanding and positive perceptions of the beef industry.”
...
The AFBFA is a contractor to Beef Checkoff, a US-wide program in which beef producers and importers pay a per-animal fee that funds programs to boost beef demand in the US and abroad. In 2024, Beef Checkoff has approximately $42 million to disperse across its initiatives, and a funding request reveals that the AFBFA’s campaign for 2024 is projected to cost $800,000. The allocation of Beef Checkoff funding to programs like this is approved by members of the Cattlemen’s Beef Board and the Federation of State Beef Councils, two groups that represent the cattle industry in the US.
One lesson plan provided as part of the program directs students to beef industry resources to help devise a school menu. In another lesson plan students are directed to create a presentation for a conservation agency regarding the introduction of cattle into their ecological preserve. A worksheet aimed at younger students has them practice their sums by adding up the acreage of cow pastures. Another worksheet based around a bingo game aimed at 8- to 11-year-olds asks teachers to “remind students that lean beef is a nutritions source of protein that can be incorporated in daily meals.”
Science teachers in many states are currently updating their lessons to incorporate the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)—a set of teaching guidelines that encourage educators to place more emphasis on how science is used in the real world. AFBFA funding documents show that the foundation intends to use the adoption of the NGSS as an opportunity to provide teachers with learning materials that relate to the beef industry.
“Furthermore, NGSS requires teachers to approach challenging topics such as climate change and sustainability,” reads an AFBFA funding authorization request for its education program. It continues: “Teachers and students are receiving information from educationally trusted sources that do not represent agriculture accurately or in a balanced way, and beef production is often the target of "misinformation". To achieve balance and to ensure the accuracy of information, a concerted effort must be made to engage teachers in the conversation around these topics.”
Dutkiewicz says that food production should be taught in US schools but that industry-funded material is unlikely to provide objective information about the impact of beef production. “I worry that clearly partial resources that are strategically designed to achieve a corporate messaging are being provided by a Checkoff program,” he says.
#enviromentalism#ecology#Beef industry#cattle#livestock industry#meat industry#livestock#lobbyists#corporate lobbying#American farm Bureau Foundation for agriculture#AFBFA#Cattle industry#Cattlemen Beef Board#Beef lobby
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The tech industrial complex was unusually visible at the inauguration, sitting between Cabinet secretary-nominees and Trump's business family. Dorothy: Pay no attention to the men mingling behind the curtain. https://thewordenreport-governmentandmarkets.blogspot.com/2025/01/the-tech-industrial-complex-plus.html
#trump#inauguration#corruption#business and government#lobbying#corporate lobbying#social media#titans#tech industrial complex#military industrial complex#business and public policy#Apple#Facebook#Microsoft#X#human rights#Gaza#Israel#arms sales#collusion
0 notes
Text



Merry Christmas TTCC nerds!! 🎄✨️💕
#i know this is late... i posted these on Christmas on twitter tho!#whats a good silly holiday pic without POG?#the secretary bird cog is and OC of mine named Ter Byrd#hes a secretary for a paper + office supply company#he and Benjamin are friends and met when Benjamin was accidentally trapped in a meeting of office men in a hotel lobby#ttcc#toontown corporate clash#toontown#toontown: corporate clash#oc#au#ttcc au#pacesetter#graham ness payser#benjamin biggs#bellringer#kilo kidd#scapegoat
90 notes
·
View notes
Text

#hallway#corridor#corporate#hotel#hotel lobby#the backrooms#backrooms#liminal spaces#liminal space#liminality#liminal#open space#unsettling#oddcore#surrealism#oddly familiar#midjourney#mid journey#ai generated#ai photography#ai art#ai aesthetics#ai image#unreality#multiverse#dereality#au#weirdcore#after hours#mine
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
I knew High Roller was capable of a lot of unexplainable stuff.. but this is a new one.
- 🦝
#toontown#toontown corporate clash#ttcc#toonblr#corporate clash#cogs#toontastic toons#sparrowatheartoc#sparrowatheartgames#High Roller#jj trickyfluff#Into the Void apparently?#Just tried to sit on the couch in the lobby
42 notes
·
View notes