#copernicus crater
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
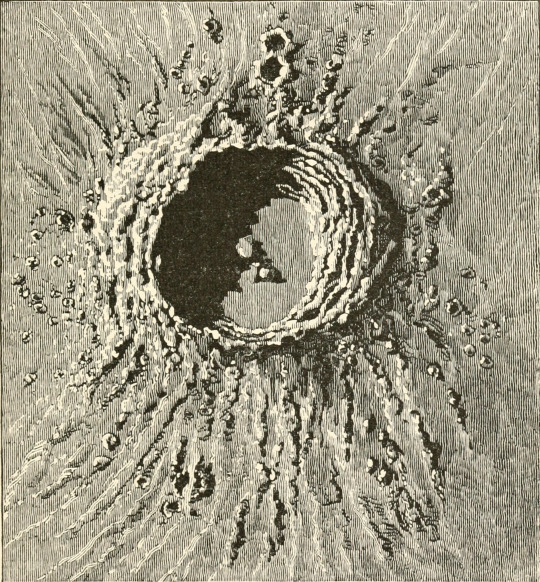
The moon's Copernicus crater. Through magic glasses. 1890.
Internet Archive
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
DUSTER WALL?!?!?!??!

it ain’t done yet though
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

11:48 AM EST February 8, 2023:
Duster - "Copernicus Crater" From the album Duster (December 13, 2019)
Last song scrobbled from iTunes at Last.fm
--

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shoemaker's first geological map of part of the Moon established the impact that created the crater Copernicus as one such epoch-defining event.
"The Moon: A History for the Future" - Oliver Morton
#book quote#the moon#oliver morton#nonfiction#gene shoemaker#geology#map#cartography#moon#impact#crater#copernicus#epoch
0 notes
Text
Indeed, the astronomer Ewen Whitaker, whose work on the history of lunar mapping is invaluable, suggests that the prominence given to Kepler, Copernicus and, most notably, Aristarchus – the ancient Greek who first suggested that the Earth circled the Sun – in Riccioli's scheme reflects a closet Copernicanism, one that he could not avow in the text but could at least hint at in his map.*
* What of Galileo? Riccioli gave him a prominent feature, too, but later observers found that the feature named for him was not, in fact, a crater, but a ray-like patch of peculiar brightness: it is now called Reiner Gamma, in accordance with later rules of nomenclature. By the time this had been realized, all the big craters were named; the crater now called Galilei is anomalously, even embarrassingly, small. In recompense, though, the four largest moons of Jupiter, which Galileo discovered and named after the Medici family to gain patronage, are now known as the Galilean moons.
"The Moon: A History for the Future" - Oliver Morton
#book quotes#the moon#oliver morton#nonfiction#astronomy#ewen whitaker#mapping#cartography#moon#johannes kepler#nicolaus copernicus#aristarchus#giovanni riccioli#nomenclature#namesake#galileo galilei#reiner gamma#crater#jupiter#medici family#io#europa#ganymede#callisto
0 notes
Video
Apollo 12 View from Lunar Orbit by NASA on The Commons Via Flickr: An Apollo 12 high-oblique view of the lunar nearside looking northeast toward the crater Copernicus (in center near horizon), as photographed from lunar orbit. The shaded crater in the foreground is Reinhold. Reinhold B is the crater next to Reinhold which as the small crater in the center of it. Also, visible is the keyhole-shaped crater Fauth near the crater Copernicus. NASA Media Usage Guidelines Credit: NASA Image Number: AS12-47-6876 Date: November 19, 1969
0 notes
Text
come to me like a ghost, whispering i dont knoooooooooooooooooww
1 note
·
View note
Text

The Barren Moon - October 31st, 1996.
"The above photo, taken as the Apollo 17 astronauts orbited the Moon in 1972, depicts the stark lunar surface around the Eratosthenes and Copernicus craters. Many similar images of a Moon devoid of life are familiar to denizens of the space age. Contrary to this modern perception, life on the Moon was reported in August of 1835 in a series of sensational stories first published by the New York Sun - apparently intended to improve the paper's circulation. These descriptions of lunar life received broad credence and became one of the most spectacular hoaxes in history. Supposedly based on telescopic observations, the stories featured full, lavish accounts of a Moon with oceans and beaches, teeming with plant and animal life and climaxing with the report of sightings of groups of winged, furry, human-like creatures resembling bats! Within a month the hoax had been revealed but the newspaper continued to enjoy an increased readership. Though barren, the Moon remains a popular setting for science fiction stories and extra-terrestrial adventures."
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
The original Moon landing sites

"NASA contracted to have 15 flight-worthy Saturn V rockets produced. Apollo 11 achieved the first landing with the sixth Saturn V, leaving nine for follow-on landings. The following landing sites were chosen for these missions, planned to occur at intervals of approximately four months through July 1972."
Note: I've updated this list with the original tentative planned launch dates.
G-type Mission
Apollo 11: (G) Mare Tranquillitatis, July 1969
H-type missions
Apollo 12: (H1) Ocean of Storms (Surveyor 3 site), November 1969
Apollo 13: (H2) Fra Mauro Highlands, March 1970
Apollo 14: (H3) Littrow Crater, July 1970
Apollo 15: (H4) Censorinus Crater, November 1970
J-type missions, the extended stay missions
Apollo 16: (J1) Descartes Highlands or Tycho Crater (Surveyor 7 site), April 1971
Apollo 17: (J2) Marius Hills or Marius Hills volcanic domes, September 1971
Apollo 18: (J3) Copernicus crater or Schröter's Valley or Gassendi crater, February 1972, later July 1973
Apollo 19: (J4) Hadley Rille, July 1972, later December 1973
Apollo 20: (J5) Tycho Crater or Copernicus Crater or Marius Hills, December 1972, later July 1974
As we all know, plans were changed and missions were cancelled. But it's nice to see what was initially planned.

To compare with the actual landing sites and dates:
Apollo 12: (H1) Ocean of Storms (Surveyor 3 site), November 1969
Apollo 13: (H2) never landed, April 1970
Apollo 14: (H3) Fra Mauro, January-February 1971
Apollo 15: (J1) Hadley���Apennine, July-August 1971
Apollo 16: (J2) Descartes Highlands, April 1972
Apollo 17: (J3) Taurus–Littrow, December 1972
NASA ID: link, link
Information from Astronautix: link
Information from Wikipedia: link
#Apollo 11#Apollo 12#Apollo 13#Apollo 14#Apollo 15#Apollo 16#Apollo 17#Apollo 18#Apollo 19#Apollo 20#NASA#Apollo Program#Moon#Moon landing#Lunar Module#cancelled#G-type Mission#H-type mission#J-type mission#Cancelled Mission#my post
468 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Crater Copernicus
Credits: Apollo 17 Crew, NASA
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Central Peaks of Copernicus Crater and other lunar spots, just look at those mountain peaks! Our Moon is such a mysterious moon!







#moon photography#moon craters#moon landing#moon phases#full moon#man on the moon#moonlight#astronomy#nasa#astronomers#universe#nasa photos#astrophotography#outer space#astrophysics#nasawebb#hubble space telescope#earth and lunar show#lunar#space exploration#space#science#sky#space science#space photography#planetary science#our universe#the universe#nasa astronauts#nasa jpl
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

Copernicus crater on the Moon // Gonzalo
Copernicus crater is named after none other than Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus (1473 - 1543), the man who came up with a model of the universe that placed the Sun at the center rather than the Earth. (Just ignore Aristarchus of Samos who did that eighteen centuries earlier!)
#astronomy#astrophotography#solar system#moon#the moon#luna#lunar surface#crater#lunar crater#copernicus#nicolaus copernicus#history
28 notes
·
View notes
Text







Strawberry Moon and Select Features:
Moon
Tycho, crater
Mare Tranquillitatis, Sea of Tranquility
Copernicus (center) and Kepler (left), craters
Mare Imbrium, Sea of Showers
Mare Crisium, Sea of Crises
Oceanus Procellarum, Ocean of Storms
Los Angeles, California, USA June, 2024
29 notes
·
View notes
Photo

6:31 PM EDT April 13, 2024:
Duster - "Copernicus Crater" From the album Duster (December 13, 2019)
Last song scrobbled from iTunes at Last.fm
It always takes a while for this kind of shit to line up for me, but by now, it's become crystal clear to me that this was the best album of 2019
File under: Slowcore
--

0 notes
Text
Despite favouring Tycho, Riccioli still gave Copernicus a splendid crater of his own.
"The Moon: A History for the Future" - Oliver Morton
#book quote#the moon#oliver morton#nonfiction#favor#tycho brahe#nicolaus copernicus#giovanni riccioli#crater#mapping#cartography#nomenclature#geography
0 notes
Text
gally as galileo galilei
𝖒𝖆𝖘𝖙𝖊𝖗𝖑𝖎𝖘𝖙
summary: an analysis of james dashner’s choice to name gally after galileo galilei, and the similarities gally and galileo galilei have.
word count: 560
warnings: talk of trauma, triggers, death, and abuse/manipulation by religious groups
a/n: happy birthday will poulter! this is the first part of my wave of stuff for will's birthday. just a lil observation i made, and ofc, a lot of love for my sweet precious baby, gally.
𝗘𝗩𝗘𝗥𝗬 𝗖𝗛𝗔𝗥𝗔𝗖𝗧𝗘𝗥 in The Maze Runner is named after an important historical figure. Thomas is Thomas Edison, Newt is Isaac Newton, etc…
Everyone acts like these characters got their names randomly, but it's so obvious to me that their names directly correlate to their purpose in the story.
Thomas Edison was an inventor who created unique solutions to problems that had stumped other scientists for ages…Thomas was able to creatively solve the Maze after the Gladers struggled on it for three years. Isaac Newton was smart as hell, and he made discoveries that laid the foundation for many other scientific discoveries. Sound familiar? Newt laid the foundation for the Glade by holding a massive amount of info and ideas. Winston Churchill spent his life trying to gain world peace…much like how Winston tried to make both sides happy and bridge the gap when Gally took over.
With this information in mind, let's take a look at Gally and his namesake, Galileo Galilei. Often called the father of modern science, Galileo made over fifty revolutionary discoveries about science, influencing tons of scientists, namely Isaac Newton and Albert Einstein. Galileo discovered the moons of Jupiter, the rings of Saturn, the phases of Venus, and the craters and mountains on the moon. He also proved the earlier theory of Nicolaus Copernicus that the Earth was revolving around the sun. He invented an early microscope. He developed the mathematical ideas on the motion of objects on an inclined plane, the acceleration of free-falling bodies, and the movement of a pendulum. Basically, he was a really cool dude.
Gally was one of the most knowledgeable and foundational people of the Glade, made clear by his position as a Keeper and his obvious love for stability. He wasn't afraid to share his opinion (much like Galileo) and consistently contributed important information and solutions to the Glade. Also, to be a Builder, you have to have at least a basic understanding of physics. Gally obviously understood basic physics concepts, because all of the buildings in the Glade are sturdy and standing. Similarly, math is very important to be a Builder, so as Keeper of the Builders, he obviously had an understanding of mathematics. Basically, Gally is smart. Like his namesake.
But the similarities don't end there. When Galileo tried to bring forth his evidence of the Copernician doctrine that the Earth revolves around the sun, he was labeled a heretic by the church and ex-communicated, and placed under house arrest for the rest of his life. Yeah, for stating his opinions, he was forced out of what should have been a safe place, ostracized, and had to die alone. Similar to Gally, don't you think? Sure, he shouldn't have antagonized Thomas without explaining why, but the truth still remains that he had trauma and Thomas was a trigger. He thought he was helping by pointing out Thomas's role in his memories, and then instead of at least listening, his friends of the past three years immediately sided with the boy they'd known for three days, ostracizing him from the only safe place and family he'd ever known. He was also left to die alone by these friends, much like Galileo.
Yeah, as much as I hate to say it, James Dashner knew what he was doing here, and Gally and Galileo both need to find better friends.
#gally#gally tmr#tmr gally#the maze runner#gally the maze runner#analysis#character study#galileo galilei#gally character study#will poulter#will poulter's birthday#happy birthday will poulter
41 notes
·
View notes
