#carbon composites
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Anakin Waits on the Balcony

STAR WARS EPISODE II: Attack of the Clones 00:11:59
#Star Wars#Episode II#Attack of the Clones#Coruscant#Galactic City#Federal District#Senate Apartment Complex#Senator Padmé Amidala’s apartment#Anakin Skywalker#unidentified transport#unidentified building#Anakin Skywalker's lightsaber#alloy metal#carbon composites#29 BBY#the Gathering#Crystal Cave#Ilum#Nicandra Counterrevolutionary Signalmen's Memorial Building
1 note
·
View note
Text

Unlocking The Power of Carbon Composite: Better Products and More Facility To End-Users
Unlocking the power of carbon composites
Design flexibility, lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and several such features make carbon composites a boon to modern manufacturing.
Application in aerospace
The lightweight and design flexibility of carbon composites make aircraft and space shuttle more fuel-efficient and more enduring to extremely high air friction. Advanced composites have several applications from the cockpit to the tail of an aircraft.
Applications in automotive
Strong and durable advanced composites enhance vehicle safety, make the vehicles more stylish, and offer better fuel economy. Advanced composites are used in making several components and parts for EVs.
Medical devices
Carbon composites offer lightweight and biocompatible solutions for prosthetics and different types of biomedical devices.
Maritime applications
Advanced composites make boats and yachts lightweight and smooth sailing. Design flexibility enables advanced aerodynamical structures.
Other applications
There is no end to the applications of carbon composites. Ships building, submarine building, railway, renewable energy sectors, and sports equipment sectors use carbon composites for better quality products.
For more information visit: https://rockman.com
0 notes
Text
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs) are used in the aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment industries. However, their recycling remains a major problem. In a recent study, researchers from Waseda University demonstrated a novel direct discharge electrical pulse method for the efficient, effective, and environmentally friendly separation of CFRPs to recover high-quality carbon fibers. This work is expected to pave the way for a more sustainable world. The world is hurtling rapidly towards a developed future, and carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs) play a key role in enabling technological and industrial progress. These composite materials are lightweight and highly strong, making them desirable for applications in various fields, including aviation, aerospace, automotive, wind power generation, and sports equipment.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Fibers#Composites#Polymers#Fiber reinforcement#Carbon fibers#REcycling#Materials processing#Waseda University
11 notes
·
View notes
Text







f-150
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Genius idea-
So I’ve always envisioned Pearl potentially having an incident where she’s split into the two major halves of her personality.
The more reserved, albeit competitive gymnast side and her upfront, temperamental side that stems from her tenacity.

Carbonara.

Calcshey
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Well, in the absence of anything specific that I can throw together in one day for Halloween, I might just wear all my most fantasy-adventurer wardrobe items tomorrow, braid my hair, and be the most generic DnD ranger ever.
Which, if I'm being entirely honest, is not that far off from my usual look. But on the bright side, I have a handy animal companion ready to go, so that's something.
#if i wanted to really sell it I'd bring one of my bows and some arrows#but my (carbon composite) arrows were fletched for function not period-correctness so the fletches are fluorescent yellow lmao#but i have 2 very elfy recurves and a beautiful leather back quiver#also this is a good excuse to trim the fringe on my orange handwoven scarf#so that's something#Halloween
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mars’ missing atmosphere could be hiding in plain sight
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/mars-missing-atmosphere-could-be-hiding-in-plain-sight/
Mars’ missing atmosphere could be hiding in plain sight


Mars wasn’t always the cold desert we see today. There’s increasing evidence that water once flowed on the Red Planet’s surface, billions of years ago. And if there was water, there must also have been a thick atmosphere to keep that water from freezing. But sometime around 3.5 billion years ago, the water dried up, and the air, once heavy with carbon dioxide, dramatically thinned, leaving only the wisp of an atmosphere that clings to the planet today.
Where exactly did Mars’ atmosphere go? This question has been a central mystery of Mars’ 4.6-billion-year history.
For two MIT geologists, the answer may lie in the planet’s clay. In a paper appearing today in Science Advances, they propose that much of Mars’ missing atmosphere could be locked up in the planet’s clay-covered crust.
The team makes the case that, while water was present on Mars, the liquid could have trickled through certain rock types and set off a slow chain of reactions that progressively drew carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and converted it into methane — a form of carbon that could be stored for eons in the planet’s clay surface.
Similar processes occur in some regions on Earth. The researchers used their knowledge of interactions between rocks and gases on Earth and applied that to how similar processes could play out on Mars. They found that, given how much clay is estimated to cover Mars’ surface, the planet’s clay could hold up to 1.7 bar of carbon dioxide, which would be equivalent to around 80 percent of the planet’s initial, early atmosphere.
It’s possible that this sequestered Martian carbon could one day be recovered and converted into propellant to fuel future missions between Mars and Earth, the researchers propose.
“Based on our findings on Earth, we show that similar processes likely operated on Mars, and that copious amounts of atmospheric CO2 could have transformed to methane and been sequestered in clays,” says study author Oliver Jagoutz, professor of geology in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS). “This methane could still be present and maybe even used as an energy source on Mars in the future.”
The study’s lead author is recent EAPS graduate Joshua Murray PhD ’24.
In the folds
Jagoutz’ group at MIT seeks to identify the geologic processes and interactions that drive the evolution of Earth’s lithosphere — the hard and brittle outer layer that includes the crust and upper mantle, where tectonic plates lie.
In 2023, he and Murray focused on a type of surface clay mineral called smectite, which is known to be a highly effective trap for carbon. Within a single grain of smectite are a multitude of folds, within which carbon can sit undisturbed for billions of years. They showed that smectite on Earth was likely a product of tectonic activity, and that, once exposed at the surface, the clay minerals acted to draw down and store enough carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to cool the planet over millions of years.
Soon after the team reported their results, Jagoutz happened to look at a map of the surface of Mars and realized that much of that planet’s surface was covered in the same smectite clays. Could the clays have had a similar carbon-trapping effect on Mars, and if so, how much carbon could the clays hold?
“We know this process happens, and it is well-documented on Earth. And these rocks and clays exist on Mars,” Jagoutz says. “So, we wanted to try and connect the dots.”
“Every nook and cranny”
Unlike on Earth, where smectite is a consequence of continental plates shifting and uplifting to bring rocks from the mantle to the surface, there is no such tectonic activity on Mars. The team looked for ways in which the clays could have formed on Mars, based on what scientists know of the planet’s history and composition.
For instance, some remote measurements of Mars’ surface suggest that at least part of the planet’s crust contains ultramafic igneous rocks, similar to those that produce smectites through weathering on Earth. Other observations reveal geologic patterns similar to terrestrial rivers and tributaries, where water could have flowed and reacted with the underlying rock.
Jagoutz and Murray wondered whether water could have reacted with Mars’ deep ultramafic rocks in a way that would produce the clays that cover the surface today. They developed a simple model of rock chemistry, based on what is known of how igneous rocks interact with their environment on Earth.
They applied this model to Mars, where scientists believe the crust is mostly made up of igneous rock that is rich in the mineral olivine. The team used the model to estimate the changes that olivine-rich rock might undergo, assuming that water existed on the surface for at least a billion years, and the atmosphere was thick with carbon dioxide.
“At this time in Mars’ history, we think CO2 is everywhere, in every nook and cranny, and water percolating through the rocks is full of CO2 too,” Murray says.
Over about a billion years, water trickling through the crust would have slowly reacted with olivine — a mineral that is rich in a reduced form of iron. Oxygen molecules in water would have bound to the iron, releasing hydrogen as a result and forming the red oxidized iron which gives the planet its iconic color. This free hydrogen would then have combined with carbon dioxide in the water, to form methane. As this reaction progressed over time, olivine would have slowly transformed into another type of iron-rich rock known as serpentine, which then continued to react with water to form smectite.
“These smectite clays have so much capacity to store carbon,” Murray says. “So then we used existing knowledge of how these minerals are stored in clays on Earth, and extrapolate to say, if the Martian surface has this much clay in it, how much methane can you store in those clays?”
He and Jagoutz found that if Mars is covered in a layer of smectite that is 1,100 meters deep, this amount of clay could store a huge amount of methane, equivalent to most of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that is thought to have disappeared since the planet dried up.
“We find that estimates of global clay volumes on Mars are consistent with a significant fraction of Mars’ initial CO2 being sequestered as organic compounds within the clay-rich crust,” Murray says. “In some ways, Mars’ missing atmosphere could be hiding in plain sight.”
“Where the CO2 went from an early, thicker atmosphere is a fundamental question in the history of the Mars atmosphere, its climate, and the habitability by microbes,” says Bruce Jakosky, professor emeritus of geology at the University of Colorado and principal investigator on the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission, which has been orbiting and studying Mars’ upper atmosphere since 2014. Jakosky was not involved with the current study. “Murray and Jagoutz examine the chemical interaction of rocks with the atmosphere as a means of removing CO2. At the high end of our estimates of how much weathering has occurred, this could be a major process in removing CO2 from Mars’ early atmosphere.”
This work was supported, in part, by the National Science Foundation.
#2023#air#atmosphere#author#billion#carbon#Carbon dioxide#chemical#chemistry#climate#CO2#Color#Composition#crust#EAPS#earth#energy#Environment#Evolution#form#Foundation#Fraction#fuel#Full#Fundamental#Future#Geology#Global#highly effective#History
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
mm ok for necromancy to work a planet must be dead. john killed the planets and when he 'resurrected' that scrap of humankind, he sent them to 'live' on those dead planets, he set them up to perform death magics by the dozen so that he could learn from their mistakes. and then he made of them an army, sent that army across the galaxy to kill more planets so that there could be more places for the necros to 'live'. he has control over the river. he can summon it. more and more evidence points, in fact, to his tampering with it -- choking it with souls until they decay, fall like whales into stoma mouths, never crossing which seems to have been some original intention. christian theology amiright? and boe calls necros zombies and are they wrong? really, are they? my point being: were they ever really alive? when harrow goes to hell she lies waiting inside the tomb of alecto's body. we already doubt every aspect of the story that john presents us with. doesnt it seem likely that rather than all that resurrection, he instead found a way to blur the physical and metaphysical realities? the houses are/in hell.
#just thinking abt ecocritical suppositions of like.#'we have lived past the end of the world bc of the carbon makeup changing / the unalterable chemicals that have remade earth's composition'#and: 'we are already in hell'#plus ive been thinking a lot since tug abt what dulcie experienced -- dying again and going to the next shore#largely bc i do not like heaven and hell as concepts and im guessing/dreading their presence in atn. finding a way to get over that dislike#would make sense -- alecto the fury who belongs in the underworld but all worlds are under once a lyctor flips them etc etc
16 notes
·
View notes
Text


Pagani Utopia
#Pagani Utopia#italian supercars#automotive photography#Mercedes AMG V12#composite chassis#carbon fiber
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Types of Fillers in Construction
Introduction Fillers play a pivotal role in construction, providing stability, strength, and insulation. Their selection is critical, affecting the cost, durability, and environmental impact of a project. This article delves into the various types of fillers utilized in the construction industry. 1. Natural Fillers Natural fillers like sand, gravel, and stone are ubiquitous in construction due to…

View On WordPress
#aerogel insulation in construction#carbon fiber for structural reinforcement#composite fillers in construction#construction aggregate materials#construction filler selection guide#construction fillers#construction industry standards for fillers#construction material innovation#cost-effective fillers for construction#durable fillers for construction#eco-friendly construction fillers#EPS beads in construction#fiber-reinforced concrete#fiberglass in concrete#fly ash concrete filler#graphene in building materials#insulation panels in construction#lightweight construction fillers#mineral fillers in concrete#natural fillers in construction#organic fillers for construction#silica fume in construction#specialty construction fillers#sustainable building materials#synthetic fillers for building#thermal insulation fillers#types of construction fillers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anakin's Lightsaber Lost


STAR WARS EPISODE II: Attack of the Clones 00:20:17 - 00:20:19
#Star Wars#Episode II#Attack of the Clones#Coruscant#Galactic City#Warehouse Zone#Senator Simon Greyshade’s custom XJ-6 luxury airspeeder#Obi-Wan Kenobi#the POTU#unidentified cargo ship#handgrip#unidentified transport#power cell housing#electrostatic damper#blade length adjust#Anakin Skywalker's lightsaber#alloy metal#carbon composite#blade emitter shroud#unidentified speeder truck#crane#girder
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Current trends in advanced composite solutions Composite parts offer various benefits over traditional materials like metal, glass, and plastic. They are more durable, stronger, lightweight, less expensive, more sustainable, and easily convertible to different shapes. For more information please visit our page https://rockmanac.com/about/and get in touch with us at https://www.linkedin.com/company/rockmanac
#Composite parts#rockman advanced composites#composite manufacturing companies#advance composite#carbon composites#carbon fiber parts
0 notes
Text
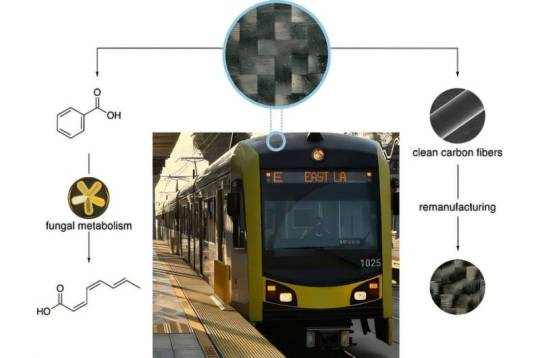
New method successfully recycles carbon fiber composite into reusable materials
USC researchers have developed a new process to upcycle the composite materials appearing in automobile panels and light rail vehicles, addressing a current environmental challenge in the transportation and energy sectors. The study recently appeared in the Journal of the American Chemical Society. "I wasn't sure if it was possible to fully recycle composite materials," said Travis Williams, professor of chemistry at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences. "As wonderful as these materials are for making energy-efficient vehicles, the problem with composites is we don't have a practical route to recycle them, so the materials end up in landfills." The chemistry demonstrated in the study, a partnership among Williams and professors Steven Nutt of the M.C. Gill Composites Center at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering, Clay C.C. Wang of the USC Alfred E. Mann School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences and Berl Oakley of the University of Kansas, is a new approach that shows that composite materials can be recovered and recycled in a manner that preserves the integrity of the materials.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Carbon fiber#Fibers#Composites#Carbon#Recycling#Waste#Fungi#Polymers#University of Southern California
17 notes
·
View notes
Photo
I just looked up the law, and it seems to define "weather modification" so loosely—
any activity performed with the intention of producing artificial changes in the composition, behaviour, or dynamics of the atmosphere
—that it covers intentionally creating a systematic pattern of pressure waves in the air around you, also known as "speaking," which most assuredly is an artificial change in the dynamics of the atmosphere.



Mulder. Please tell me what part of the american legal code covers this.
#and let's not even get into the way you just changed its composition by replacing oxygen with carbon dioxide#last time you took a breath#better write a letter to the Secretary of Commerce pronto
19K notes
·
View notes
Text

High-Performance Carbon Composite Manufacturers | Rockman Industries
Explore top-notch carbon composite products by Rockman Industries. We offer advanced materials designed for superior performance and efficiency.
https://www.rockman.in/auto-chain-division/
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Uses for Carbon Fiber Unidirectional Fabric inModern Engineering
Carbon fiber unidirectional fabric is a cutting-edge material that has transformed the engineering world.Known for its exceptional strength, lightweight properties, and corrosion resistance, it has become cornerstone for various high-performance applications. Engineers and designers across industries are leveraging this material to innovate and improve their products, from aerospace components to sports equipment.

0 notes